Image Hiding Method Based on Two-Channel Deep Convolutional Neural Network
-
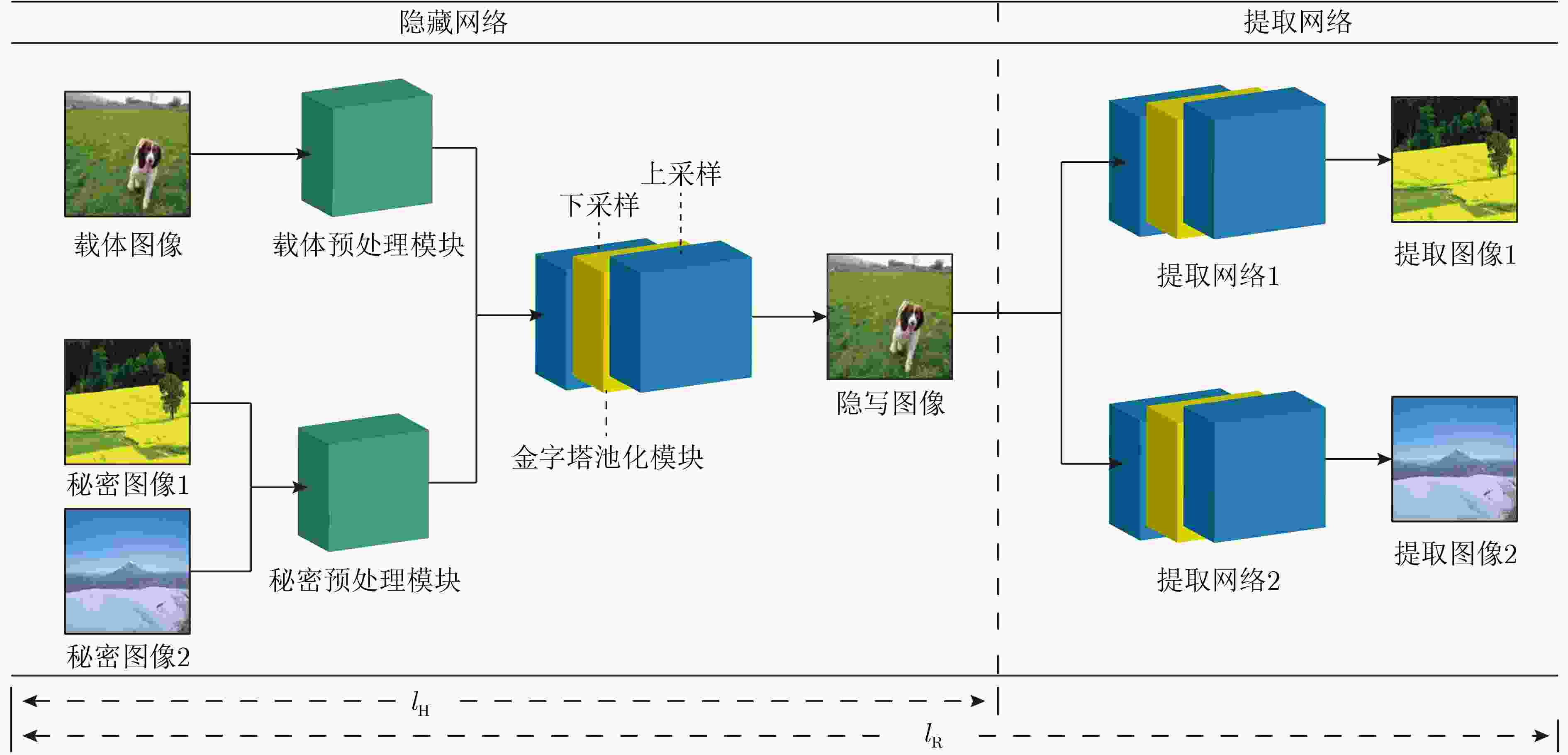
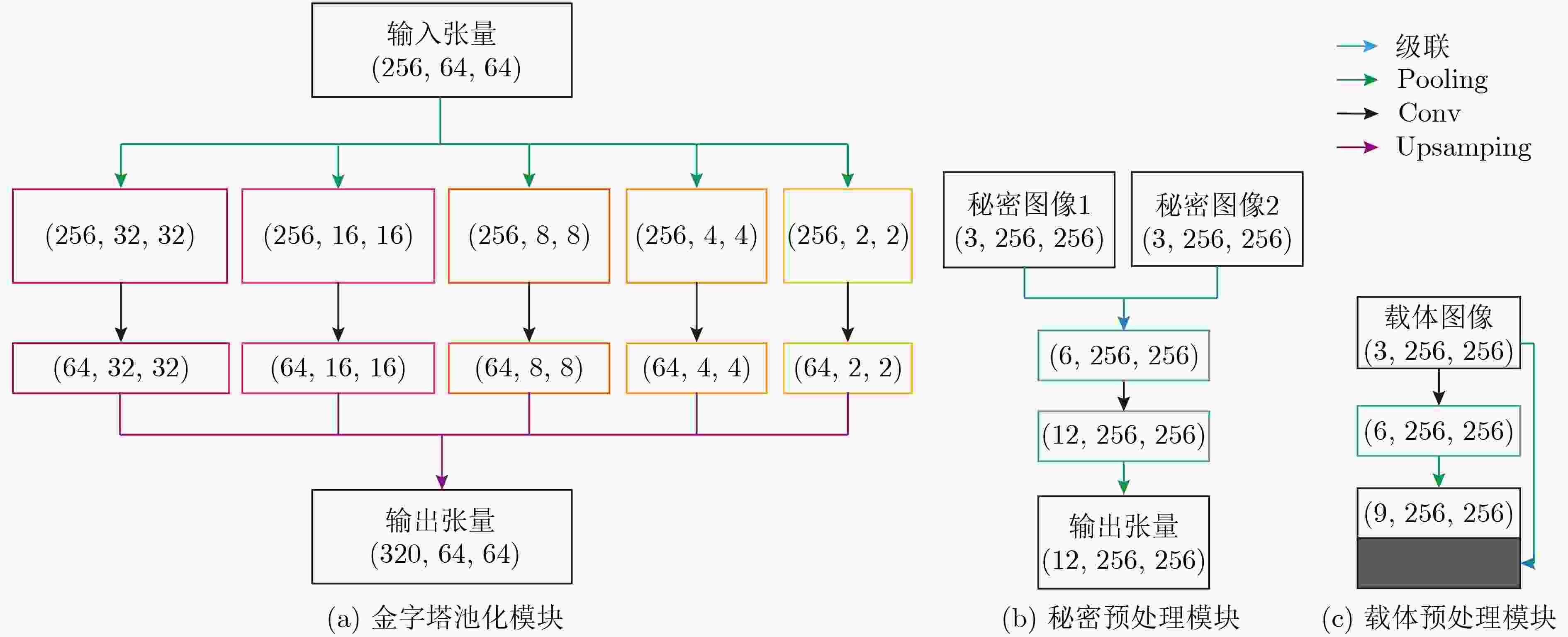
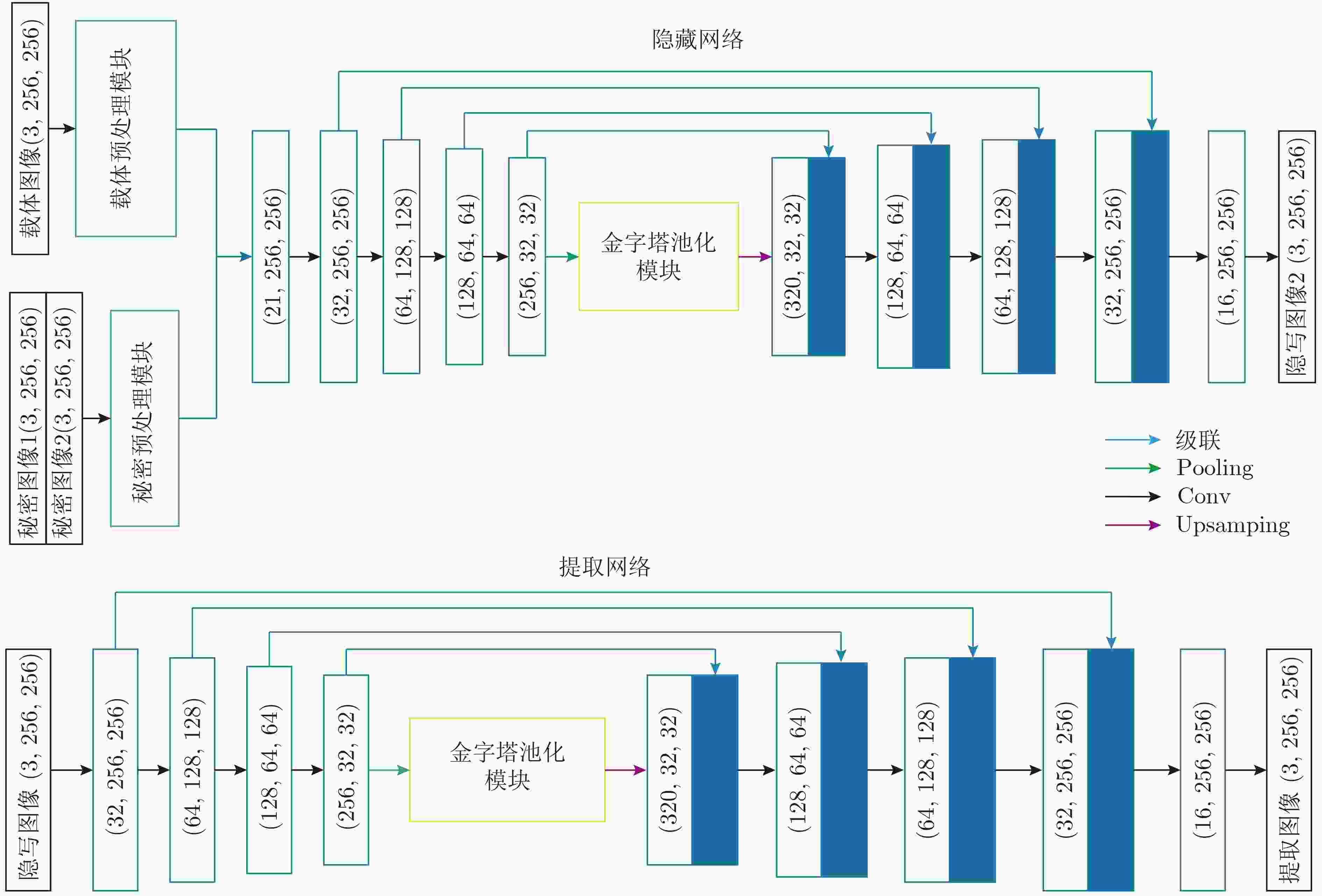
摘要: 现有的基于深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)实现的图像信息隐藏方法存在图像视觉质量差和隐藏容量低的问题。针对此类问题,该文提出一种基于两通道深度卷积神经网络的图像隐藏方法。首先,与以往的隐藏框架不同,该文提出的隐藏方法中包含1个隐藏网络和2个结构相同的提取网络,实现了在1幅载体图像上同时对2幅全尺寸秘密图像进行有效的隐藏和提取;其次,为了提高图像的视觉质量,在隐藏网络和提取网络中加入了改进的金字塔池化模块和预处理模块。在多个数据集上的测试结果表明,所提方法较现有的图像信息隐藏方法在视觉质量上有显著提升,载体图像PSNR和SSIM分别提高了3.75 dB和3.61%,实现的相对容量为2,同时具有良好的泛化能力。Abstract: The existing image information hiding methods based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNN) have the problems of poor image visual quality and low hiding capacity. Addressing such issues, an image hiding method based on a two-channel deep convolutional neural network is proposed. First, different from the previous hiding framework, the hiding method proposed in this paper includes one hiding network and two revealing networks with the same structure, and two full-size secret images can be effectively hidden and revealed at the same time is realized. Then, to improve the visual quality of the image, an improved pyramid pooling module and a preprocessing module are added to the hiding and revealing network. The test results on multiple data sets show that the proposed method has a significant improvement in visual quality compared with existing image information hiding methods. The Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) values are increased by 3.75 dB and 3.61 % respectively, a relative capacity of 2 and good generalization ability are achieved.
-
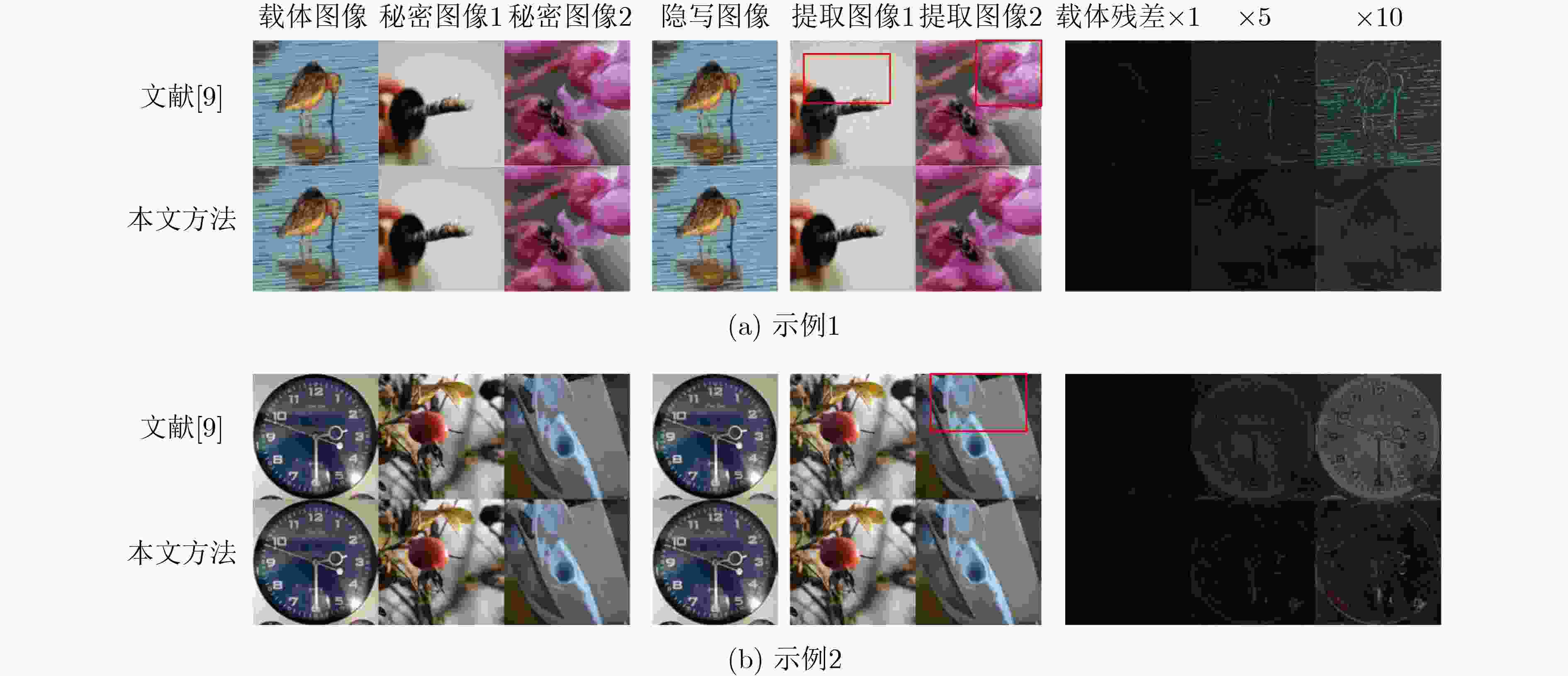
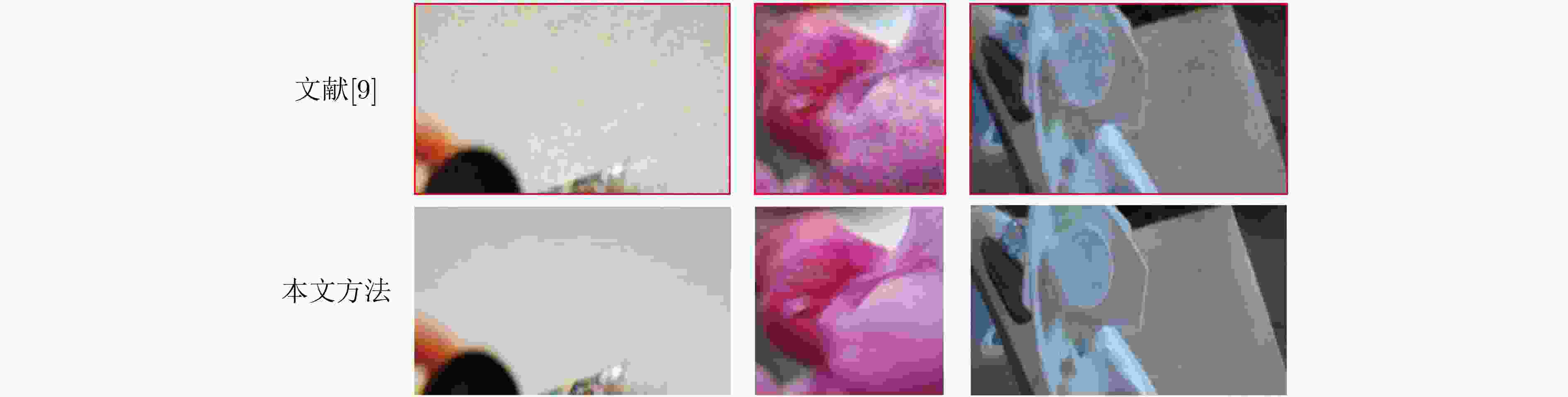
表 1 与文献[9]比较
图像 方法 载体图像-隐写图像 秘密图像1-提取图像1 秘密图像2-提取图像2 PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) 图4(a) 文献[9] 31.95 94.44 29.68 83.90 26.93 78.43 本文方法 34.48 99.28 40.13 97.91 32.60 98.22 图4(b) 文献[9] 31.08 95.19 28.72 93.01 33.22 88.67 本文方法 38.17 98.47 37.16 98.11 34.35 97.28 平均值 文献[9] 32.32 94.81 30.40 90.70 30.55 90.29 本文方法 36.07 98.42 34.97 96.56 35.11 96.48 表 2 消融实验的PSNR和SSIM比较
图像 载体图像-隐写图像 秘密图像1-提取图像1 秘密图像2-提取图像2 PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) ImageNet 36.07 98.42 34.97 96.56 35.11 96.48 *Prep 35.66 96.89 34.23 95.12 34.44 95.17 *Pyramid 34.86 95.65 33.85 94.93 34.10 96.27 表 3 隐写分析结果
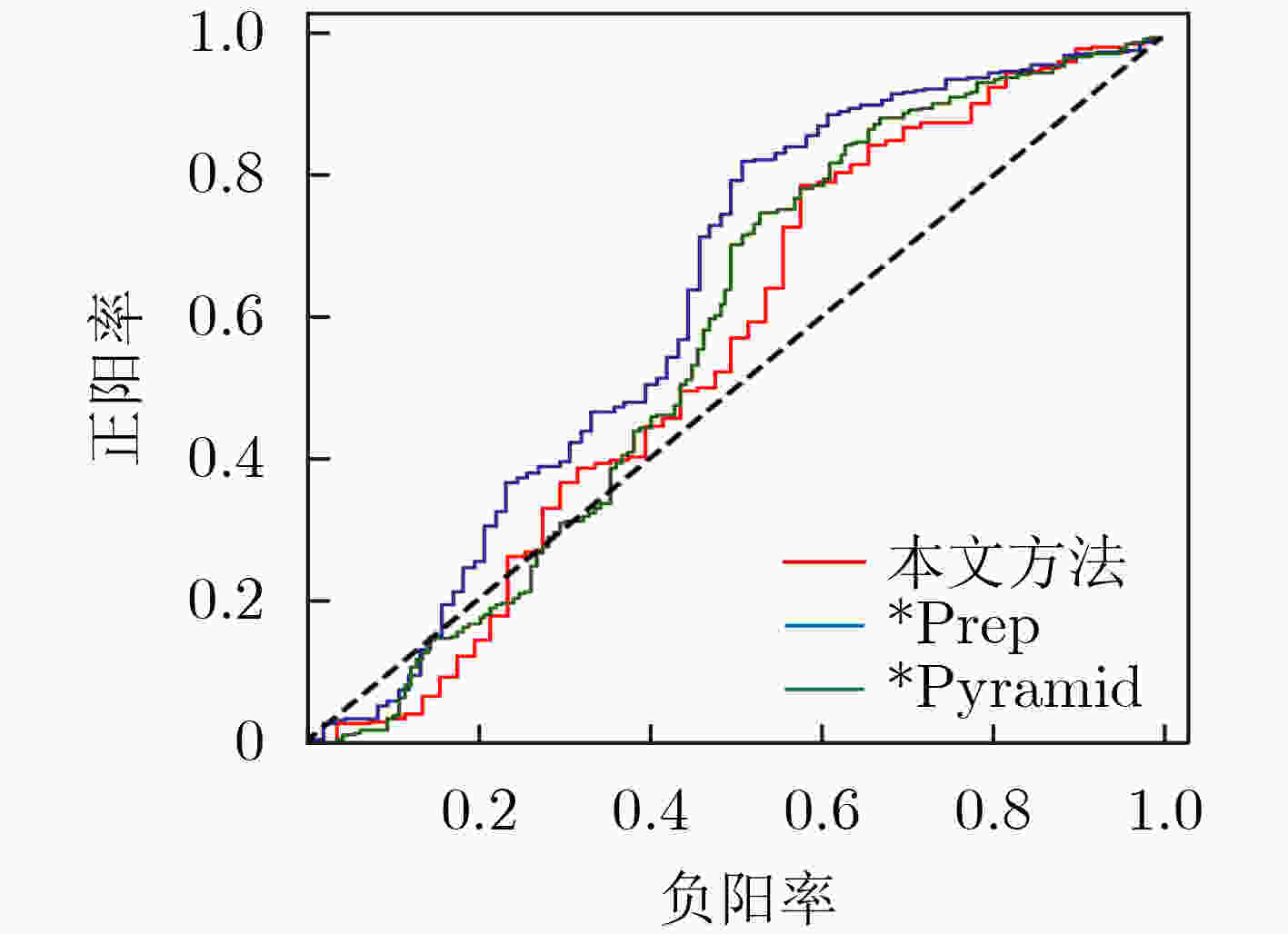
隐藏模型 StegExpose AUC SRNet
隐写分析准确率本文方法 0.5533 0.6844 文献[9] – 0.6975 *Prep 0.6223 0.7195 *Pyramid 0.5698 0.6994 表 4 嵌入容量比较
方法 绝对容量(Byte) 隐写图像大小(Byte) 相对容量 文献[21] 18.3~135.4 64$ \times $64 1.49×10–3~1.10×10–2 文献[22] 1535~4300 1024$ \times $1024 1.46×10–3~4.10×10–3 文献[23] 26214~104857 512$ \times $512 1×10–1~4×10–1 文献[10] 3$ \times $224$ \times $224 3$ \times $224$ \times $224 1 文献[12] 3$ \times $256$ \times $256~3$ \times $512$ \times $512 3$ \times $512$ \times $512 2.5×10–1~1 本文方法 6$ \times $256$ \times $256 3$ \times $256$ \times $256 2 表 5 修改率和提取率比较(%)
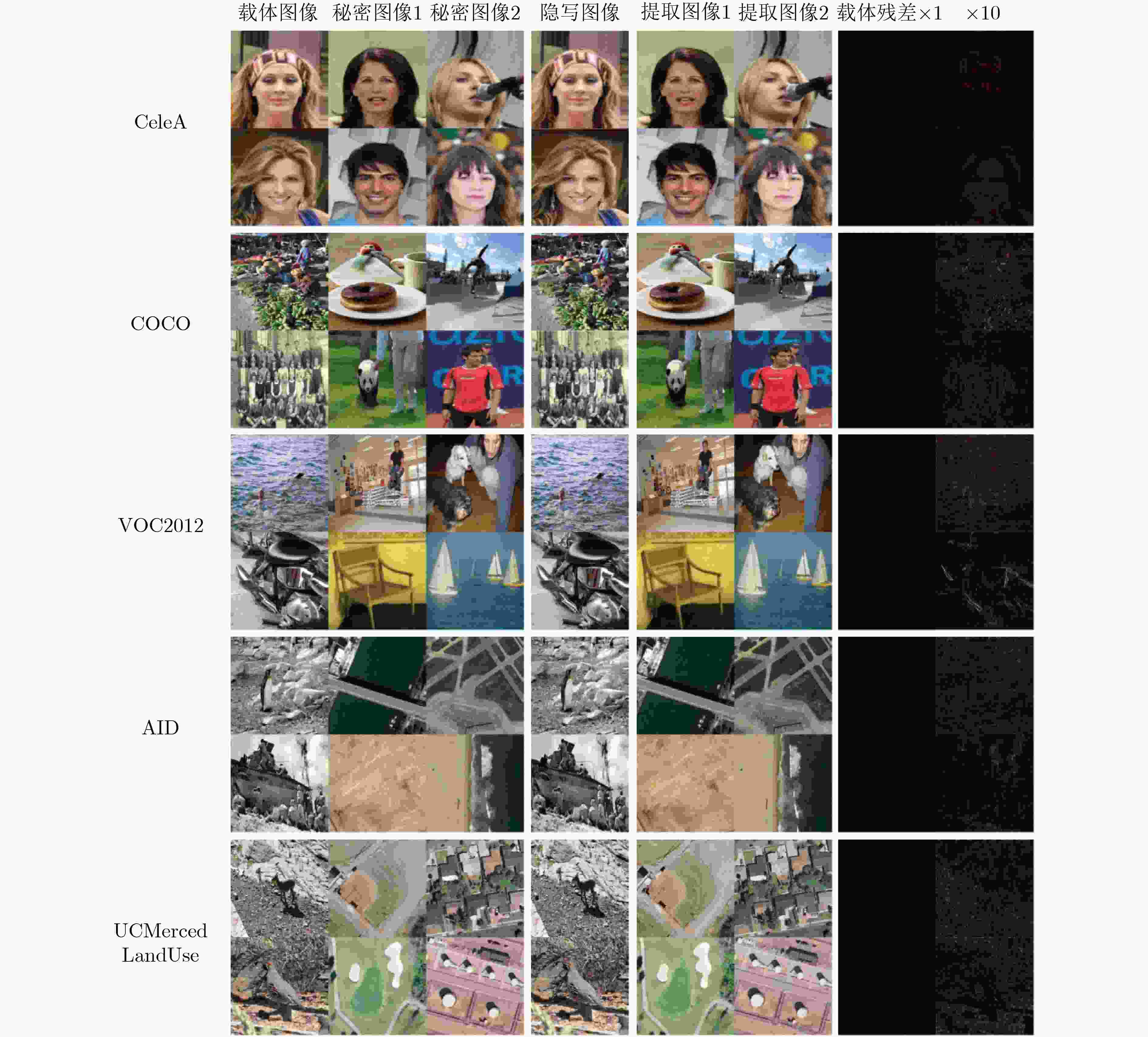
表 6 5组数据集的测试结果
数据集 载体图像-隐写图像 秘密图像1-提取图像1 秘密图像2-提取图像2 PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) 修改率(%) PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) 提取率(%) PSNR(dB) SSIM(%) 提取率(%) CeleA 35.81 96.40 1.83 36.18 96.90 98.22 36.24 97.50 98.24 COCO 34.03 96.41 2.22 33.29 93.79 97.62 33.82 94.98 97.76 VOC2012 34.06 96.48 2.23 33.45 93.54 97.66 34.10 94.80 97.80 AID 34.83 97.29 2.07 32.35 93.28 96.75 34.12 95.22 97.65 UCMerced Land Use 34.53 96.88 2.16 31.25 92.52 96.44 32.12 94.76 96.85 -
[1] ZHANG Chaoning, LIN Chenguo, BENZ P, et al. A brief survey on deep learning based data hiding, steganography and watermarking[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.01607, 2021. [2] KER A D. Improved detection of LSB steganography in grayscale images[C]. The 6th International Workshop on Information Hiding (IH), Toronto, Canada, 2004: 97–115. [3] FILLER T, JUDAS J, and FRIDRICH J. Minimizing additive distortion in steganography using Syndrome-Trellis Codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2011, 6(3): 920–935. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2011.2134094 [4] FRIDRICH J and FILLER T. Practical methods for minimizing embedding impact in steganography[C]. SPIE 6505, Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents IX, San Jose, USA, 2007: 13–27. [5] FRIDRICH J, GOLJAN M, LISONEK P, et al. Writing on wet paper[C]. SPIE 5681, Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents VII, San Jose, USA, 2005: 328–340. [6] TANG Weixuan, LI Bin, BARNI M, et al. An automatic cost learning framework for image steganography using deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 952–967. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.3025438 [7] ZHANG Chaoning, BENZ P, KARJAUV A, et al. UDH: Universal Deep Hiding for steganography, watermarking, and light field messaging[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 10223–10234. [8] LUO Xiyang, ZHAN Ruohan, CHANG Huiwen, et al. Distortion agnostic deep watermarking[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 13545–13554. [9] BALUJA S. Hiding images within images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(7): 1685–1697. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2901877 [10] CHEN Feng, XING Qinghua, and LIU Fuxian. Technology of hiding and protecting the secret image based on two-channel deep hiding network[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 21966–21979. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2969524 [11] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. [12] YU Chong. Attention based data hiding with generative adversarial networks[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, USA, 2020: 1120–1128. [13] ZHU Junyan, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2242–2251. [14] ZHOU Bolei, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA À, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2921–2929. [15] ZHOU Bolei, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA À, et al. Object detectors emerge in deep scene CNNs[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6856, 2015. [16] ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230–6239. [17] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [18] HORÉ A and ZIOU D. Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM[C]. The 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 2010: 2366–2369. [19] YE Yuanxin, SHAN Jie, BRUZZONE L, et al. Robust registration of multimodal remote sensing images based on structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(5): 2941–2958. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2656380 [20] BOEHM B. StegExpose - A tool for detecting LSB steganography[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1410.6656, 2014. [21] BOROUMAND M, CHEN Mo, and FRIDRICH J. Deep residual network for steganalysis of digital images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(5): 1181–1193. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2871749 [22] WU Kuochen and WANG C. Steganography using reversible texture synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(1): 130–139. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2371246 [23] YANG Jianhua, LIU Kai, KANG Xiangui, et al. Spatial image steganography based on generative adversarial network[OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1804.07939, 2018. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
