Research on Low Frequency Communication Technology Based on Rotating Permanent Magnet
-
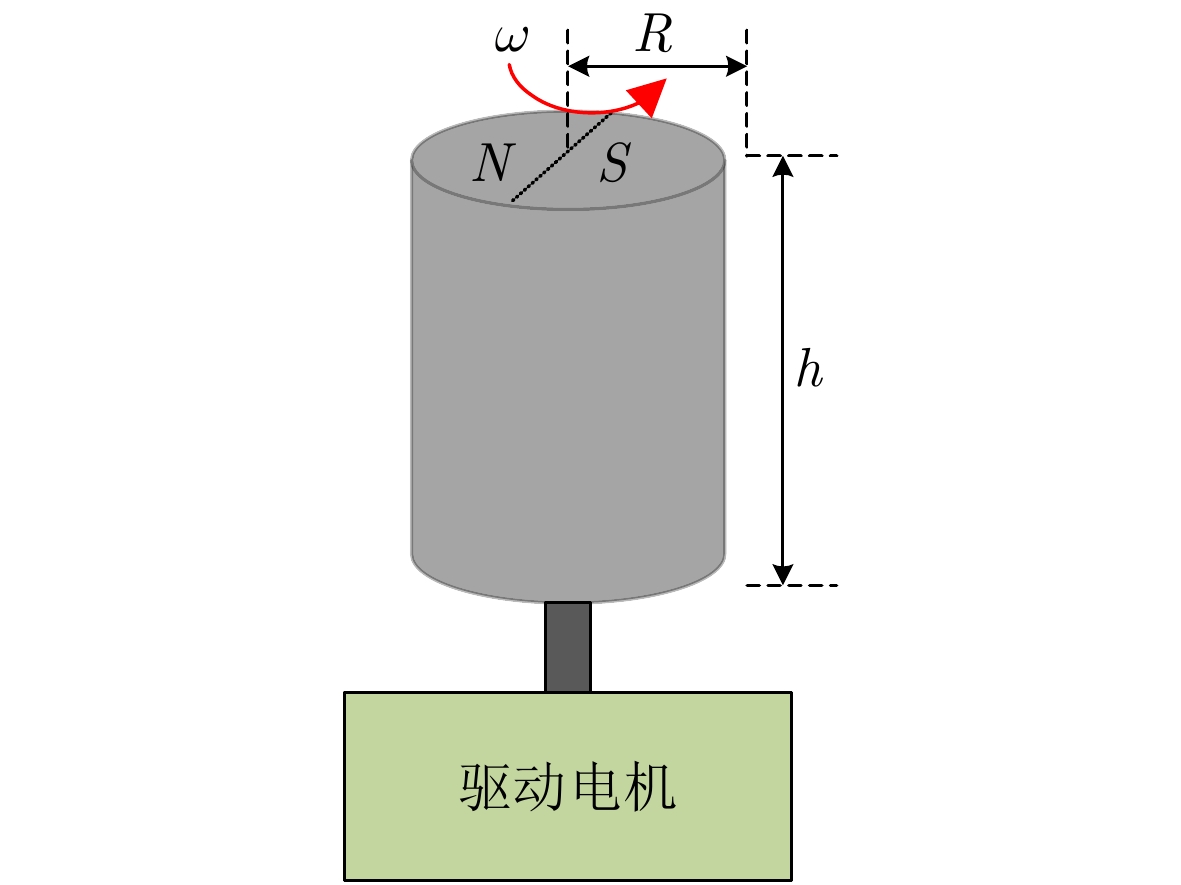
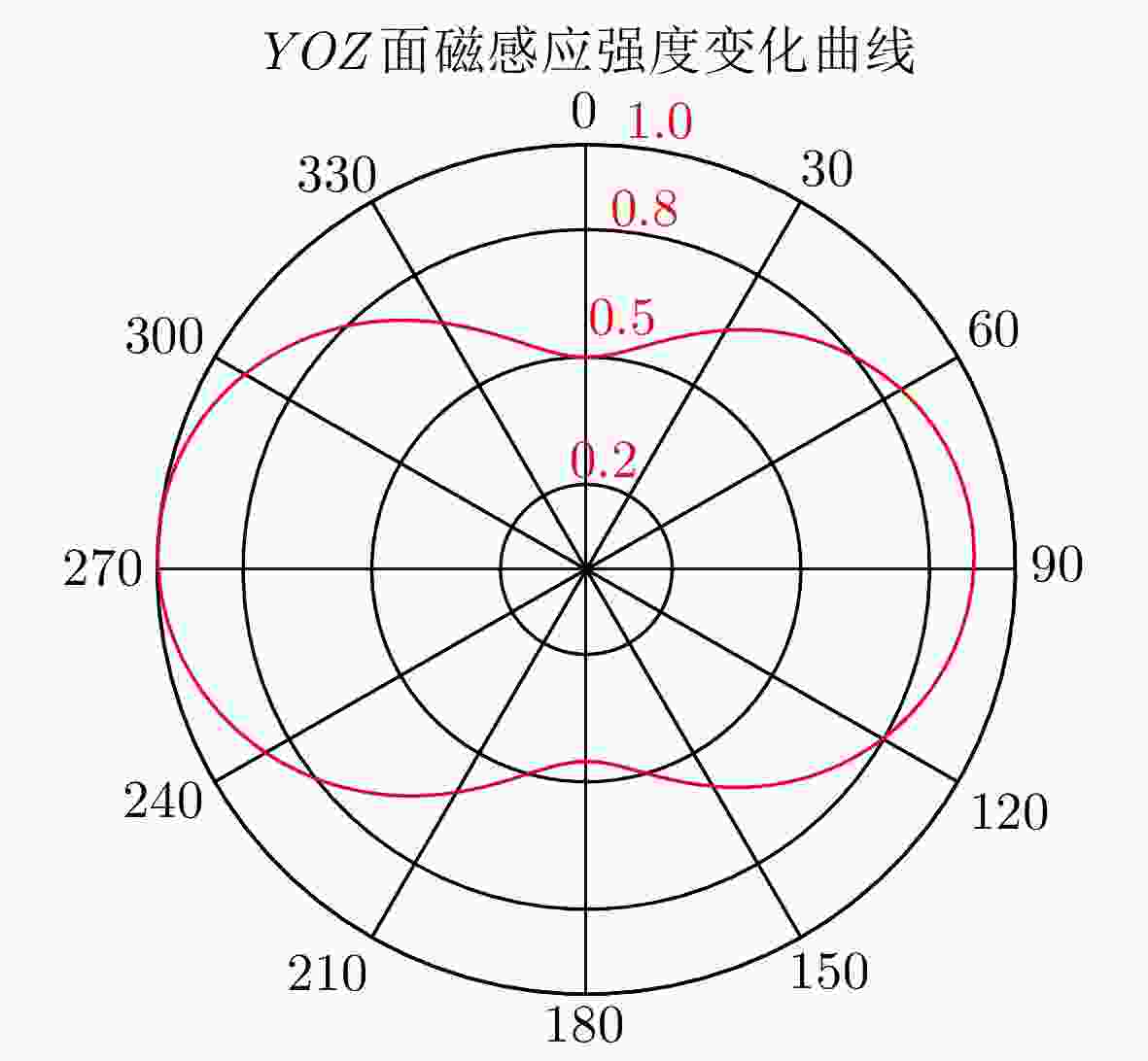
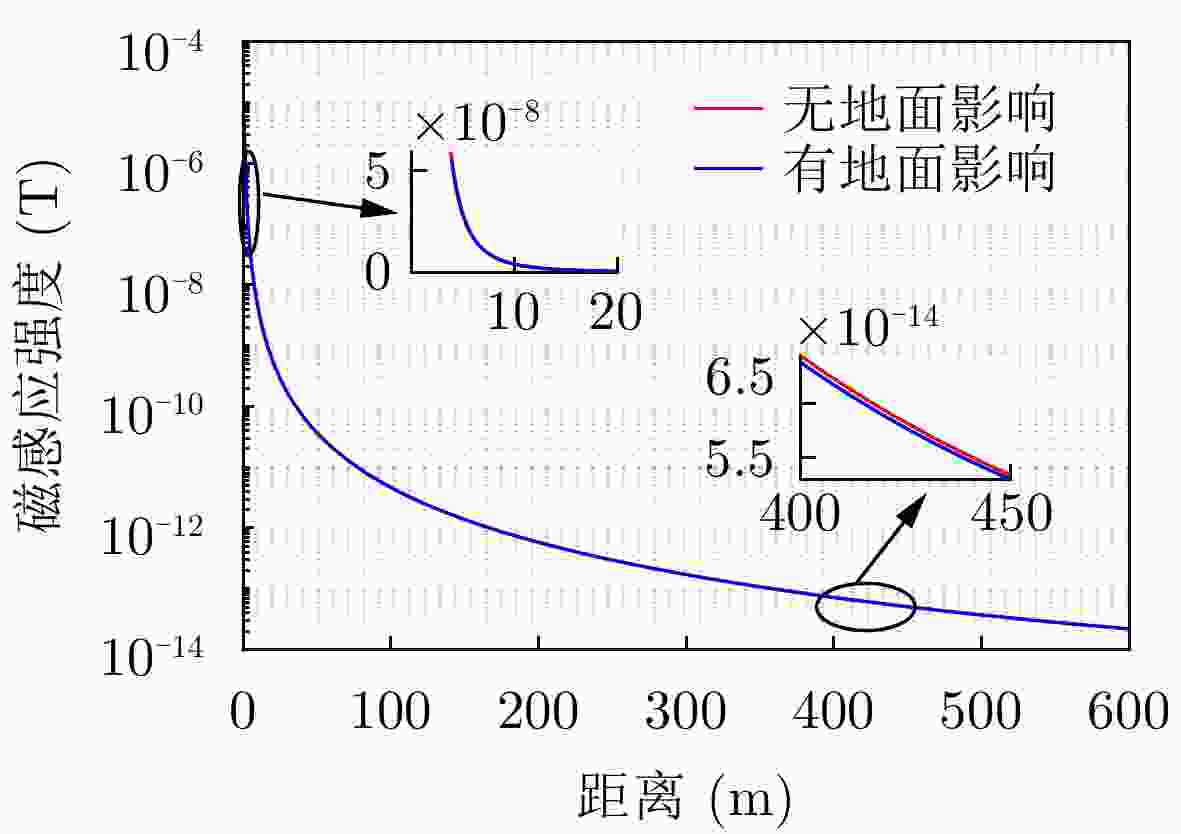
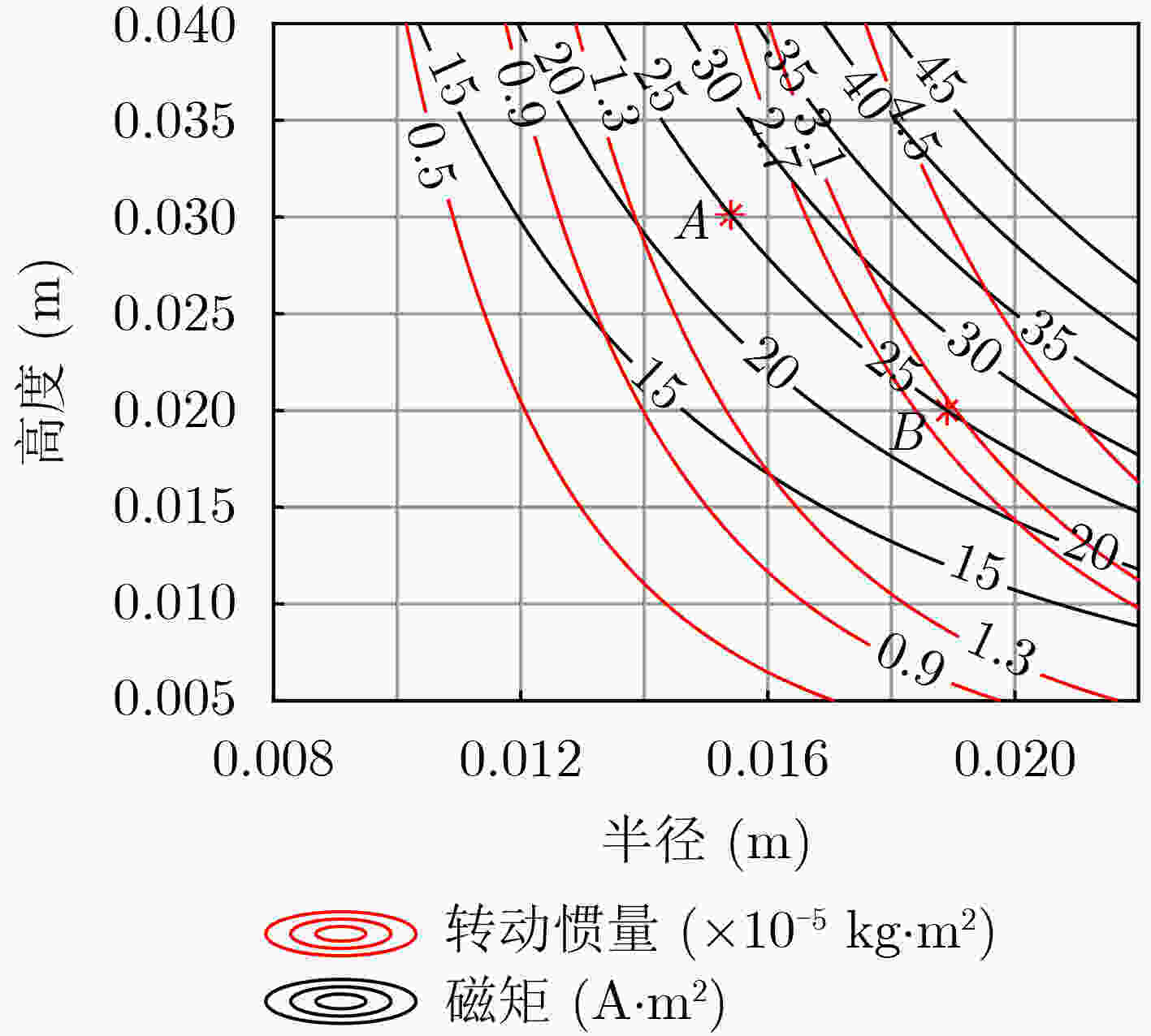
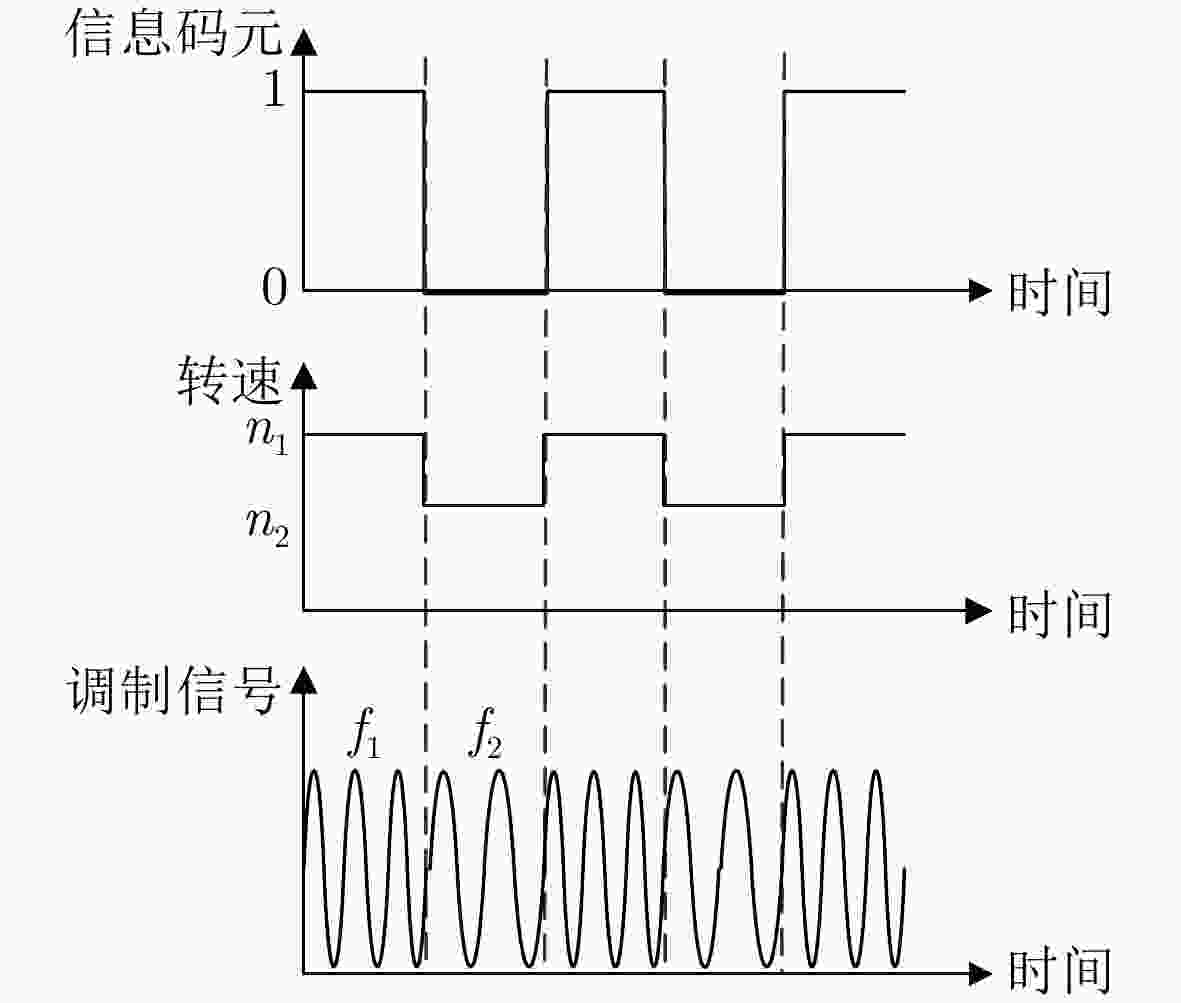
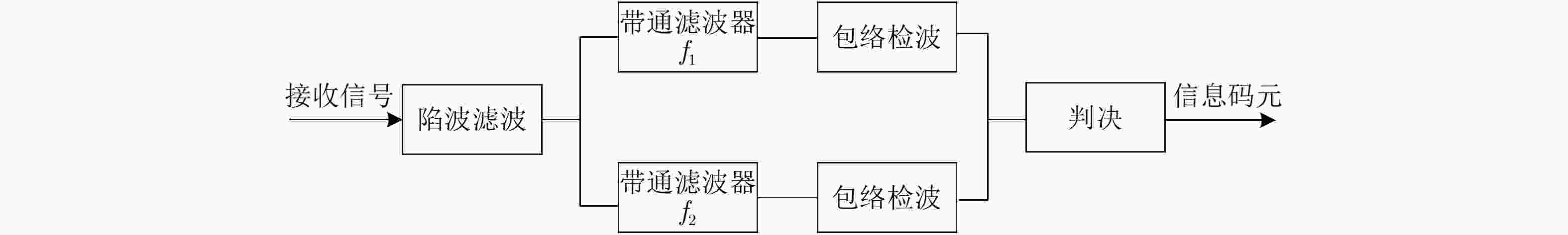
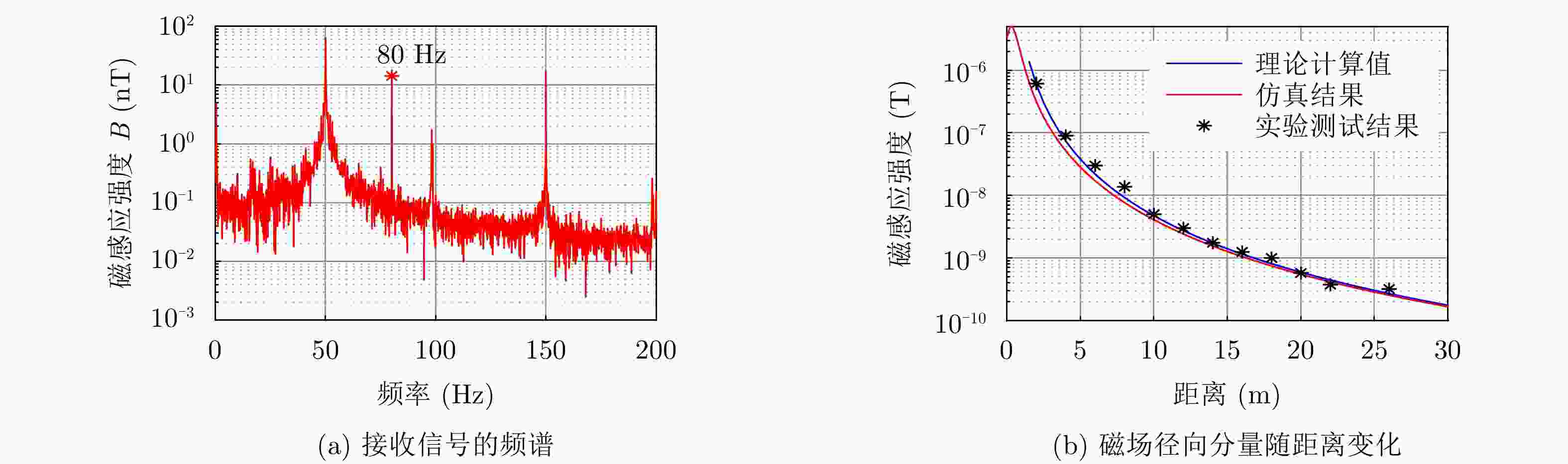
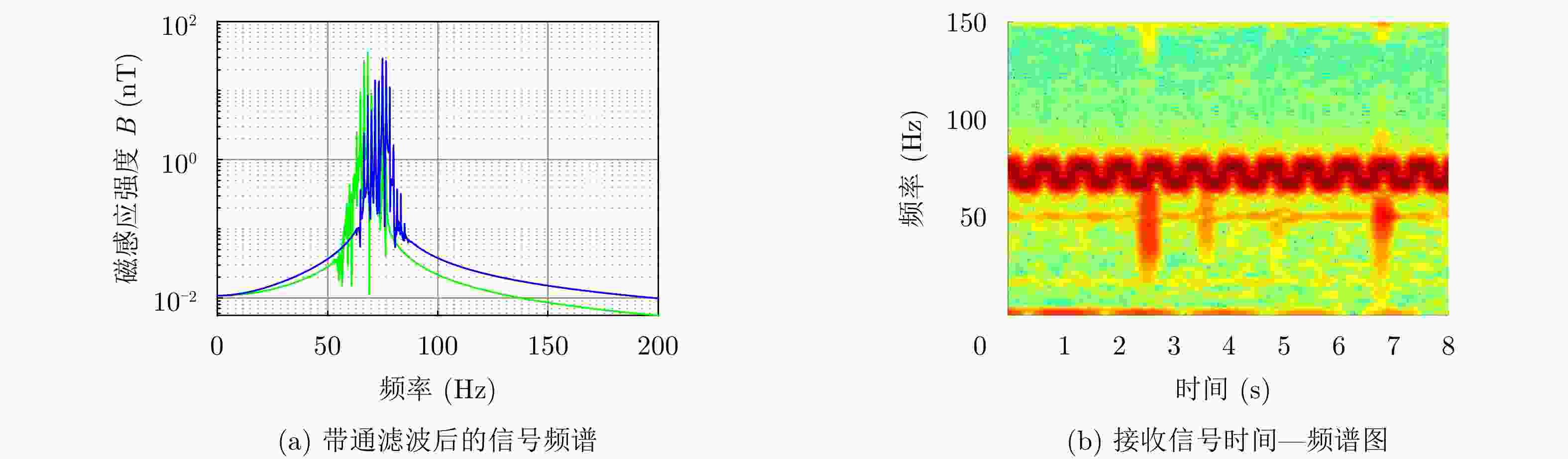
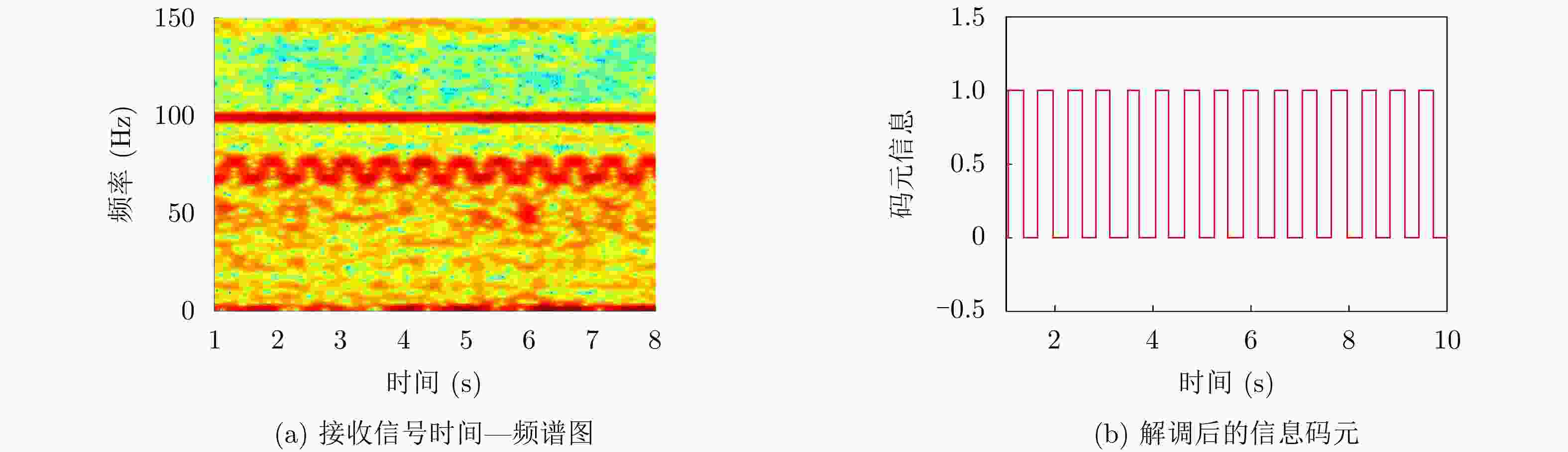
摘要: 旋转永磁体天线作为一种新型低频磁天线,克服了传统低频线圈体积大、功耗高、效率低的缺点,主要应用于近场低频磁通信中。该文利用FEKO分析了天线近区磁场随方向的变化规律,探究了近场范围内无限大地面对天线近区磁场分布的影响,结果表明:天线在其径向辐射强度最大,在其轴向辐射强度最小。并且在较近的通信距离范围内,地面对磁场信号的影响较小。分析了转动惯量和磁矩之间的关系,对永磁体结构参数进行了优化,研制了两款样机,并对优化前后的旋转永磁体天线功耗进行测试,实验结果表明:在质量大30 g的情况下,优化后的永磁体天线比优化前的天线平均功耗低5.5 W左右。利用直接天线调制方式磁场的2FSK调制,通过非相干解调恢复码元信息,测试结果表明:复杂电磁环境下,优化后的永磁体天线可以在20 m范围内实现码元速率为3.5 bps的超低频通信。Abstract: As a new type of low-frequency magnetic antenna, the rotating magnet antenna overcomes the shortcomings including large size, high power consumption, and low radiation efficiency of traditional low-frequency antenna and is mainly used in near-field low-frequency magnetic communication. FEKO is used to analyze the change of the magnetic field in the near area of the antenna with the direction, and explore the influence of the infinite ground on the magnetic field distribution in the near area of the antenna. The result shows that the antenna has the largest radiation intensity in its radial direction and the smallest radiation intensity in its axial direction. And the earth’s surface has less influence on the magnetic field signal in the short communication distance range. The relationship between magnetic and moment of inertia is analyzed, and the dimension parameters are optimized. An optimized prototype antenna and an original antenna are manufactured, and the power consumption of the two antennas during operating are measured. The experimental results demonstrate that the optimized antenna, which weighs 30 g more than the original antenna, reduces power consumption of about 5.5 W. The direct antenna modulation method is used to 2FSK modulation of the near-zone magnetic field, and the original symbol information is recovered using non-coherent demodulation. The measured results show that the optimized antenna can achieve ultra-low frequency communication with a symbol rate of 3.5 bps within a 20 m range in harsh electromagnetic environment.
-
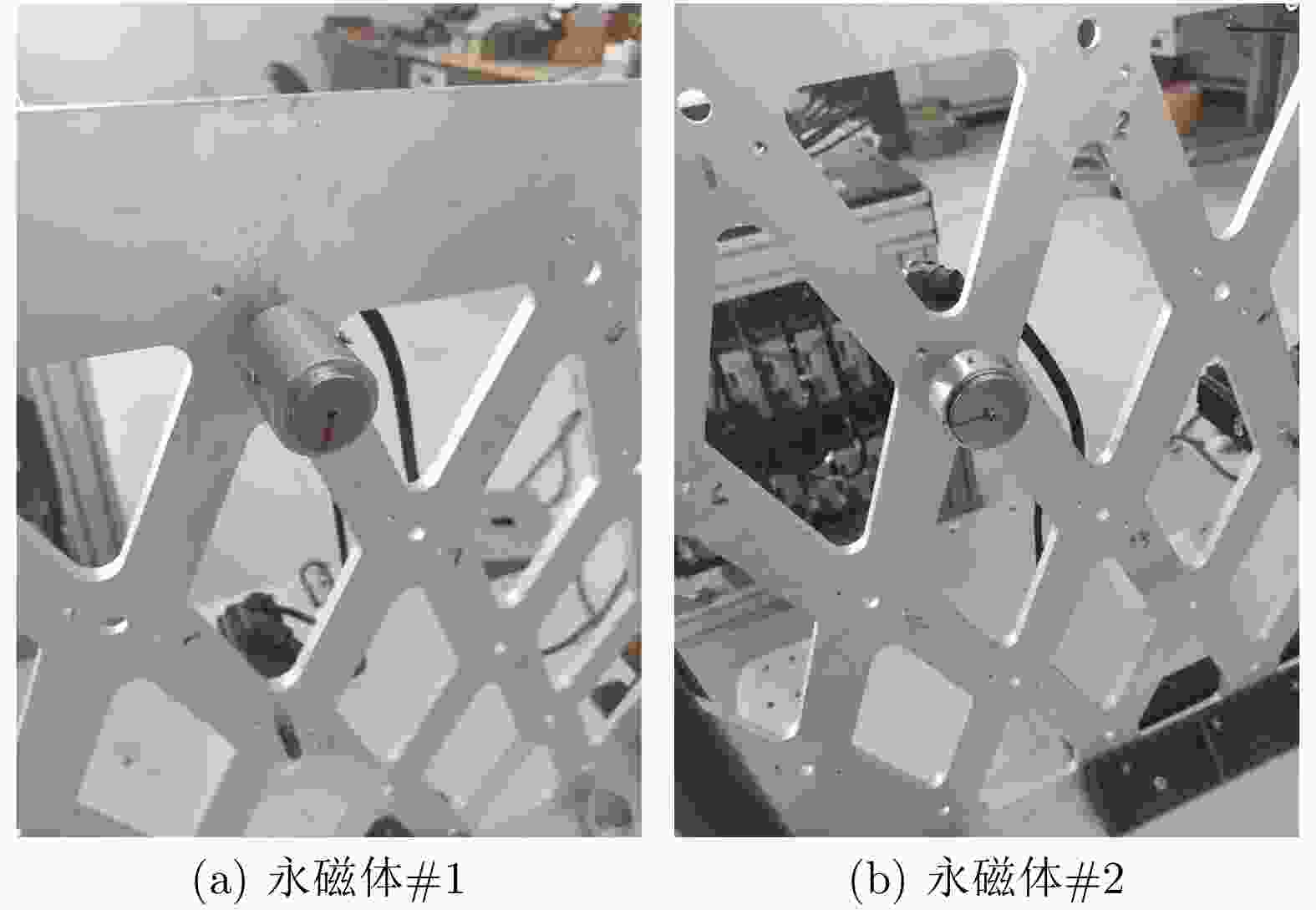
表 1 两个永磁体的相关规格
永磁体编号 直径(mm) 高度(mm) 发射磁矩(Am2) 质量(g) 永磁体#1 26 40 23.66 210 永磁体#2 36 20 19.44 180 -
[1] 罗卓颖, 刘翠海, 黄玉成, 等. 超低频传播特性分析[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2009, 29(2): 148–150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2009.02.044LUO Zhuoying, LIU Cuihai, HUANG Yucheng, et al. Analysis of the characteristic of super low frequency propagation[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2009, 29(2): 148–150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2009.02.044 [2] DARPA. A MEchanically based antenna (AMEBA)[P]. US, HR001117S0007, 2016. [3] 丁宏. DARPA机械天线项目或掀起军事通信革命[J]. 现代军事, 2017(4): 71–73.DING Hong. DARPA’s mechanical antenna program could revolutionize military communication[J]. Conmilit, 2017(4): 71–73. [4] BURCH H C, GARRAUD A, MITCHELL M F, et al. Experimental generation of ELF radio signals using a rotating magnet[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(11): 6265–6272. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2869205 [5] FAWOLE O C and TABIB-AZAR M. An electromechanically modulated permanent magnet antenna for wireless communication in harsh electromagnetic environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(12): 6927–6936. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2761555 [6] SELVIN S, PRASAD M N S, HUANG Yikun, et al. Spinning magnet antenna for VLF transmitting[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, San Diego, USA, 2017: 1477–1478. [7] GOLKOWSKI M, PARK J, BITTLE J, et al. Novel mechanical magnetic shutter antenna for ELF/VLF radiation[C]. 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Boston, USA, 2018: 65–66. [8] PRASAD M N S, TOK R U, FEREIDOONY F, et al. Magnetic pendulum arrays for efficient ULF transmission[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 13220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49341-4 [9] STRACHEN N, BOOSKE J, BEHDAD N, et al. A mechanically based magneto-inductive transmitter with electrically modulated reluctance[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(6): e0199934. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199934 [10] 周强, 姚富强, 施伟, 等. 机械式低频天线机理及其关键技术研究[J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2020, 50(1): 69–84. doi: 10.1360/SST-2019-0118ZHOU Qiang, YAO Fuqiang, SHI Wei, et al. Research on mechanism and key technology of mechanical antenna for a low-frequency transmission[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Technologica, 2020, 50(1): 69–84. doi: 10.1360/SST-2019-0118 [11] 周强, 施伟, 刘斌, 等. 旋转永磁式机械天线的研究与实现[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2020, 42(3): 128–136. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202003017ZHOU Qiang, SHI Wei, LIU Bin, et al. Research and practice of the mechanical antennas based on rotating permanent magnet[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2020, 42(3): 128–136. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202003017 [12] 崔勇, 吴明, 宋晓, 等. 小型低频发射天线的研究进展[J]. 物理学报, 2020, 69(20): 208401. doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20200792CUI Yong, WU Ming, SONG Xiao, et al. Research progress of small low-frequency transmitting antenna[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2020, 69(20): 208401. doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20200792 [13] BICKFORD J A, DUWEL A E, WEINBERG M S, et al. Performance of electrically small conventional and mechanical antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(4): 2209–2223. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2893329 [14] 钟顺时. 天线理论与技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2015: 19–25.ZHONG Shunshi. Antenna Theory and Techniques[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2015: 19–25. [15] 施伟, 周强, 刘斌. 基于旋转永磁体的超低频机械天线电磁特性分析[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68(18): 188401. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20190339SHI Wei, ZHOU Qiang, and LIU Bin. Performance analysis of spinning magnet as mechanical antenna[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(18): 188401. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20190339 [16] YAO Weijun and WANG Yuanxun. Direct antenna modulation-a promise for ultra-wideband (UWB) transmitting[C]. 2004 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37535), Fort Worth, USA, 2004: 1273–1276. doi: 10.1109/MWSYM.2004.1339221. [17] WEICKHMANN M. Nd-Fe-B Magnets, Properties and Applications[Z]. Hanau: Vacuumschmelze GmbH and Co, 2009. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
