Ultra-Reliable and Robust Channel Estimation Using Basis Expansion Model-Based UKF-RTSS Scheme for V2V Systems
-
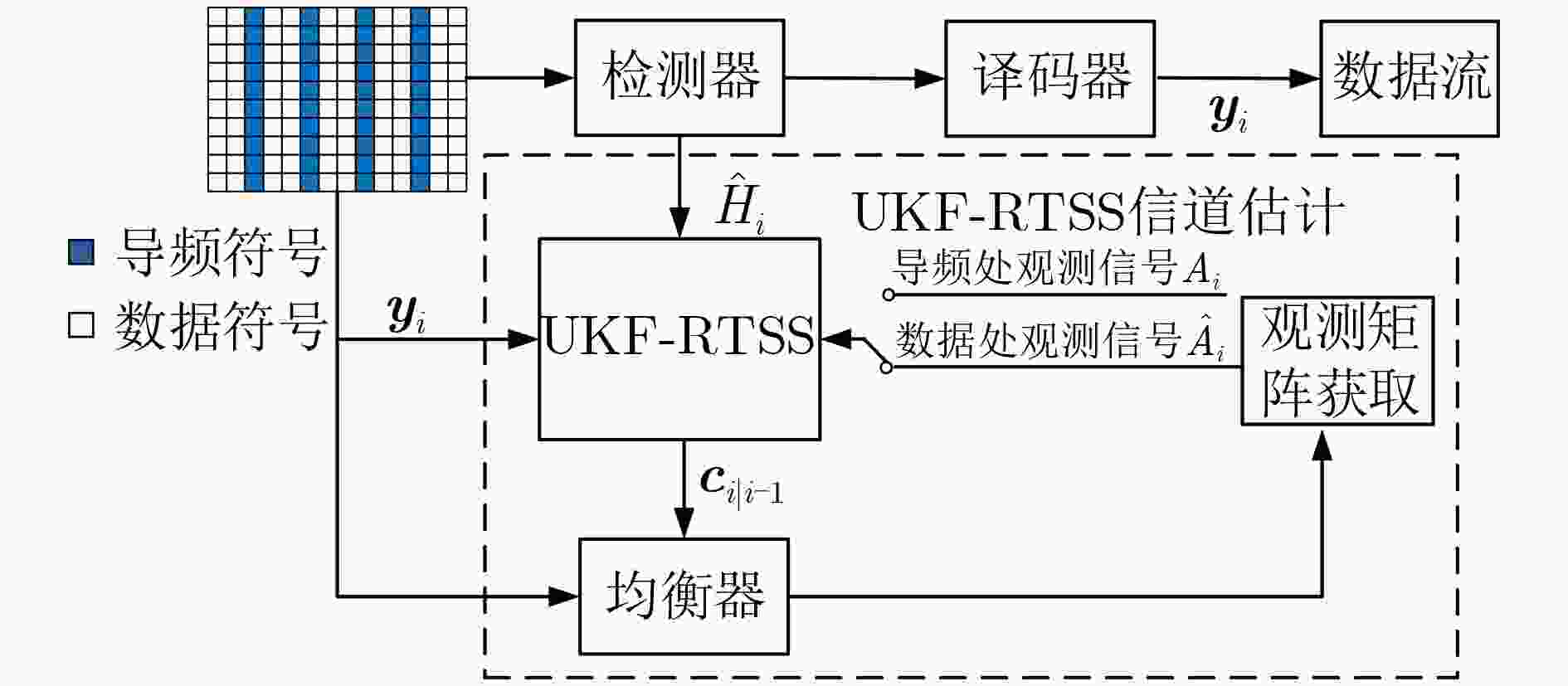
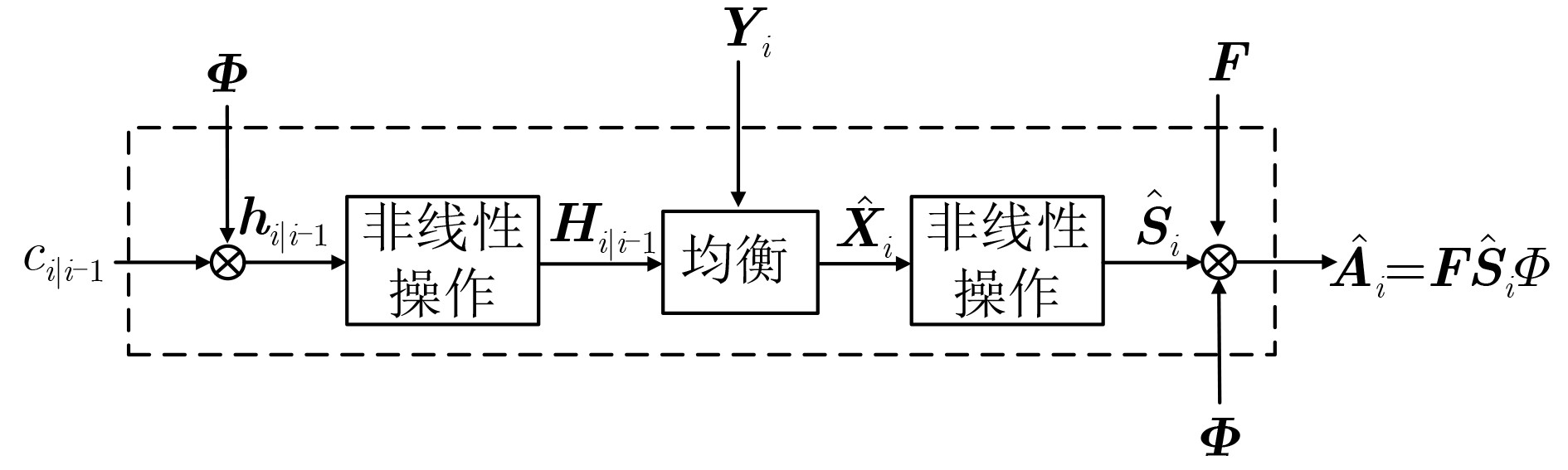
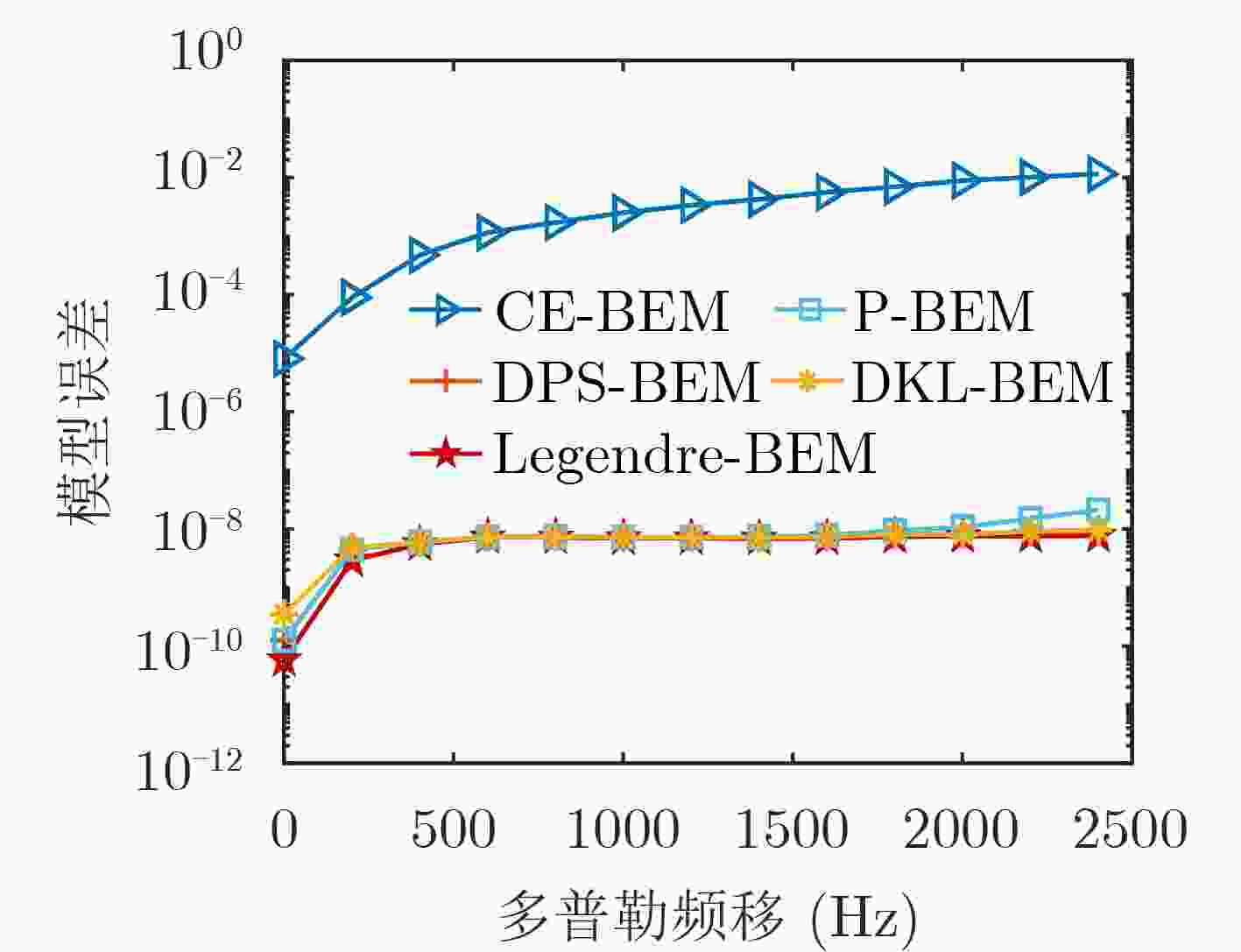
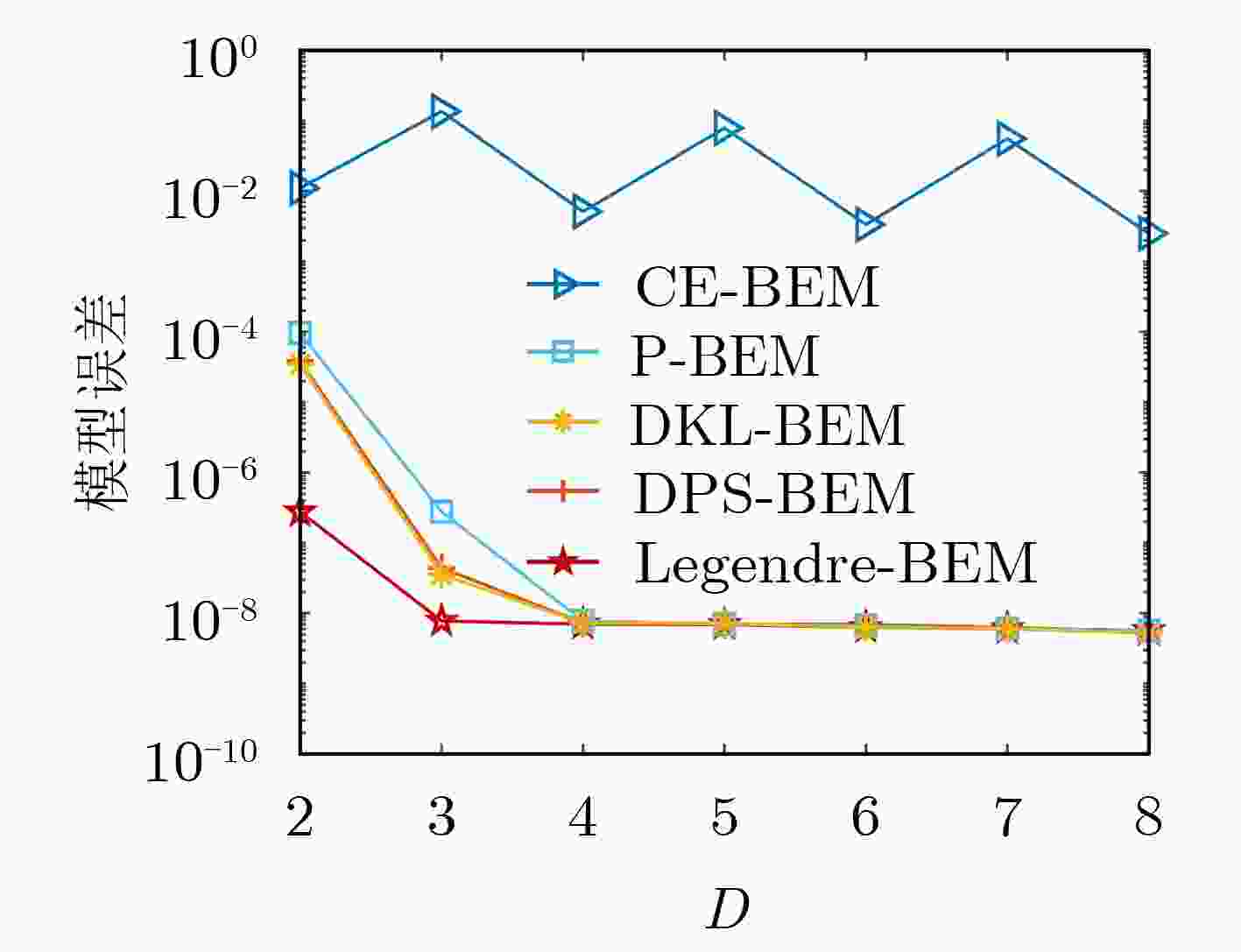
摘要: 车联网应用场景对无线通信在带宽、时延、可靠性方面提出了更高的需求,特别是车辆对车辆(Vehicle to Vehicle, V2V)场景。针对V2V高速移动场景,时/频域选择性衰落(双选衰落)和非平稳特性给信道估计带来的技术挑战,该文提出了一种基于基扩展模型(Basis Expansion Model, BEM)的UKF-RTSS (Unscented Kalman Filter- Rauch-Tung-Striebel Smoother)信道估计方法。该方法采用BEM拟合快时变信道,将信道参数的估计转化为基函数系数的估计;通过无迹卡尔曼滤波(UKF),联合估计数据处信道冲激响应与时域自相关系数,用于追踪快时变的信道响应。为了进一步提升信道估计的精度,引入RTSS对后向信道状态信息进行信道估计和插值,与UKF构成了“滤波和平滑”结构的UKF-RTSS联合估计器。系统仿真分析表明,在不同速度的快时变条件下,所提方法相比其他经典方法具有更高的信道估计精度和鲁棒性,特别适用于车联网下的无线通信场景。Abstract: The Internet of vehicles application scenarios put forward higher requirements for wireless communication in terms of bandwidth, delay, and reliability, especially in the Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V) communication scenario. For the technical challenges of channel estimation caused by time/frequency domain selective fading (dual selection fading) and non-stationary characteristics in the V2V high-speed mobile scenario, this paper proposes a channel estimation method of BEM (Basis Expansion Model)-based UKF-RTSS (Unscented Kalman Filter-Rauch-Tung-Striebel Smoother). The BEM model is used to fit the time-varying channel, and the estimation of the channel parameters is converted into the estimation of the basis function coefficients; The unscented Kalman filter (UKF) algorithm is used to estimate jointly the channel impulse response and the time-varying time-domain autocorrelation coefficient at the data, tracking the fast time-varying channel response. In order to improve further the accuracy of channel estimation, RTSS is introduced to perform channel estimation and interpolation on the backward channel state information, and it forms a joint estimator with a "filtering and smoothing" structure with UKF. System simulation analysis shows that under different speed and time-varying conditions, the BEM-based UKF-RTSS channel estimation method has higher channel estimation accuracy and robustness than other classic methods, and is especially suitable for wireless communication in the Internet of vehicles scenarios.
-
表 1 各种估计算法的复杂度对比
估计算法 时间复杂度 LS $ O\left( N \right) $ BEM-LS $ O\left( {{{\left( {DL} \right)}^2}N} \right) $ BEM-iROMP[14] $ O\left( {{{\left( {DL} \right)}^2}N\lg S} \right) $ BEM-LMMSE $ O\left( {{N^2}\left( {DL} \right)} \right) $ BEM-LS-UKF $ O\left( {{N^2}\left( {DL} \right)} \right) $ BEM-LMMSE-UKF $ O\left( {{N^2}\left( {DL} \right)} \right) $ BEM-LS-UKF-RTSS $ O\left( {{N^2}\left( {DL} \right)} \right) $ BEM-LMMSE-UKF-RTSS $ O\left( {{N^2}\left( {DL} \right)} \right) $ 表 2 仿真系统参数
参数 数值 载波频率 5.9 GHz 系统带宽 10 MHz 子载波数 600 子载波间隔
FFT长度1024
15 kHz基向量维数D 4 调制方式 16QAM 信道模型 EVA 多径抽头延迟(ns) [0 50 120 200 230 500 1600 2300 5000] 相对功率时延(dB) [–1.0 –1.0 –1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 –3.0 –5.0 –7.0] -
[1] ABBOUD K, OMAR H A, and ZHUANG Weihua. Interworking of DSRC and cellular network technologies for V2X communications: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(12): 9457–9470. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2591558 [2] ANWAR W, FRANCHI N, and FETTWEIS G. Physical layer evaluation of V2X communications technologies: 5G NR-V2X, LTE-V2X, IEEE 802.11bd, and IEEE 802.11p[C]. 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, USA, 2019: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/VTCFall.2019.8891313. [3] CHEN Shanzhi, HU Jinling, SHI Yan, et al. LTE-V: A TD-LTE-based V2X solution for future vehicular network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(6): 997–1005. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2611605 [4] CHEN Shanzhi, HU Jinling, SHI Yan, et al. A Vision of C-V2X: Technologies, field testing, and challenges with Chinese development[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(5): 3872–3881. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2974823 [5] CHEN Shanzhi, HU Jinling, SHI Yan, et al. Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) services supported by LTE-based systems and 5G[J]. IEEE Communications Standards Magazine, 2017, 1(2): 70–76. doi: 10.1109/MCOMSTD.2017.1700015 [6] 陈维, 李源, 刘玮. 车联网产业进展及关键技术分析[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2020, 26(1): 5–11. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202001003CHEN Wei, LI Yuan, and LIU Wei. Industrial progress and key technologies of internet of vehicles[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2020, 26(1): 5–11. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202001003 [7] FARZAMNIA A, HLAING N W, HALDAR M K, et al. Channel estimation for sparse channel OFDM systems using least square and minimum mean square error techniques[C]. 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, USA, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICEngTechnol.2017.8308193. [8] ZARRINKOUB H. Understanding LTE with MATLAB: From Mathematical Modeling to Simulation and Prototyping[M]. Chichester: Wiley Publishing, 2014. [9] HRYCAK T, DAS S, MATZ G, et al. Practical estimation of rapidly varying channels for OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2011, 59(11): 3040–3048. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2011.082111.110075 [10] ZAFARANI E, OMIDI M J, HEYDARYAN F, et al. Oversampled Legendre basis expansion model for doubly-selective channels[C]. 2011 19th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, Tehran, Iran, 2011: 1–5. [11] BORAH D K and HART B T. Frequency-selective fading channel estimation with a polynomial time-varying channel model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1999, 47(6): 862–873. doi: 10.1109/26.771343 [12] TEO K A D and OHNO S. Optimal MMSE finite parameter model for doubly-selective channels[C]. GLOBECOM '05. IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, 2005, St. Louis, USA, 2005: 3507. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2005.1578424. [13] QU Huiyang, LIU Guanghui, WANG Yanyan, et al. A time-domain approach to channel estimation and equalization for the SC-FDM system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2019, 65(4): 713–726. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2019.2904849 [14] 廖勇, 蔡志镕. 基于基扩展模型的改进正则化正交匹配追踪V2X快时变SC-FDMA信道估计[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(4): 177–184.LIAO Yong and CAI Zhirong. Basis expansion model-based improved regularized orthogonal matching pursuit channel estimation for V2X fast time-varying SC-FDMA[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(4): 177–184. [15] LIAO Yong, SHEN Xuanfan, DAI Xuewu, et al. EKF-based joint channel estimation and decoding design for non-stationary OFDM channel[C]. GLOBECOM 2017 - 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2017.8254544. [16] PEDROSA P, CASTANHEIRA D, SILVA A, et al. Efficient joint channel equalization and tracking for V2X communications using SC-FDE schemes[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 55158–55169. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2981717 [17] BADDOUR K E and BEAULIEU N C. Autoregressive modeling for fading channel simulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2005, 4(4): 1650–1662. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2005.850327 [18] SARKKA S. Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013. -





 下载:
下载:

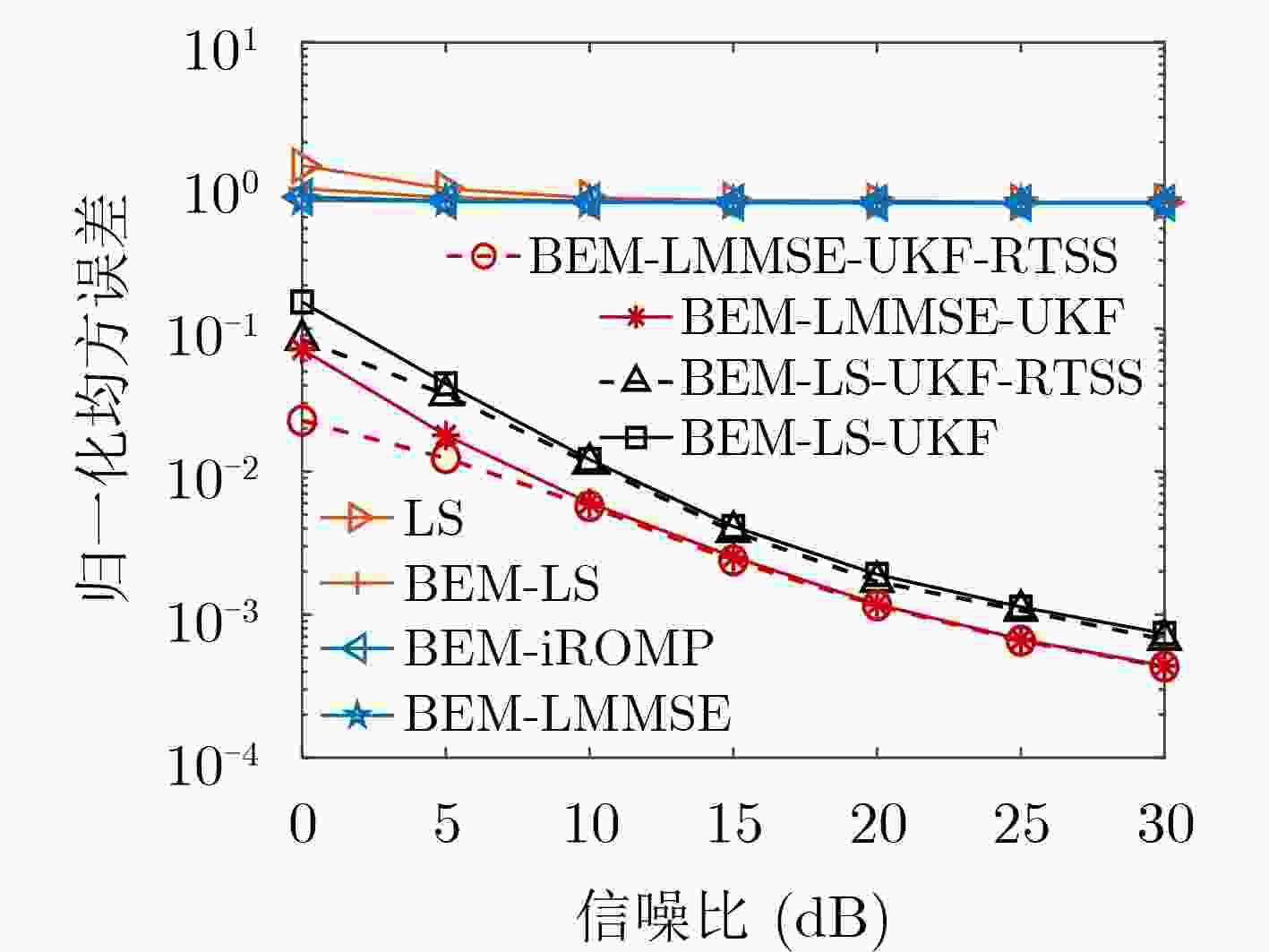
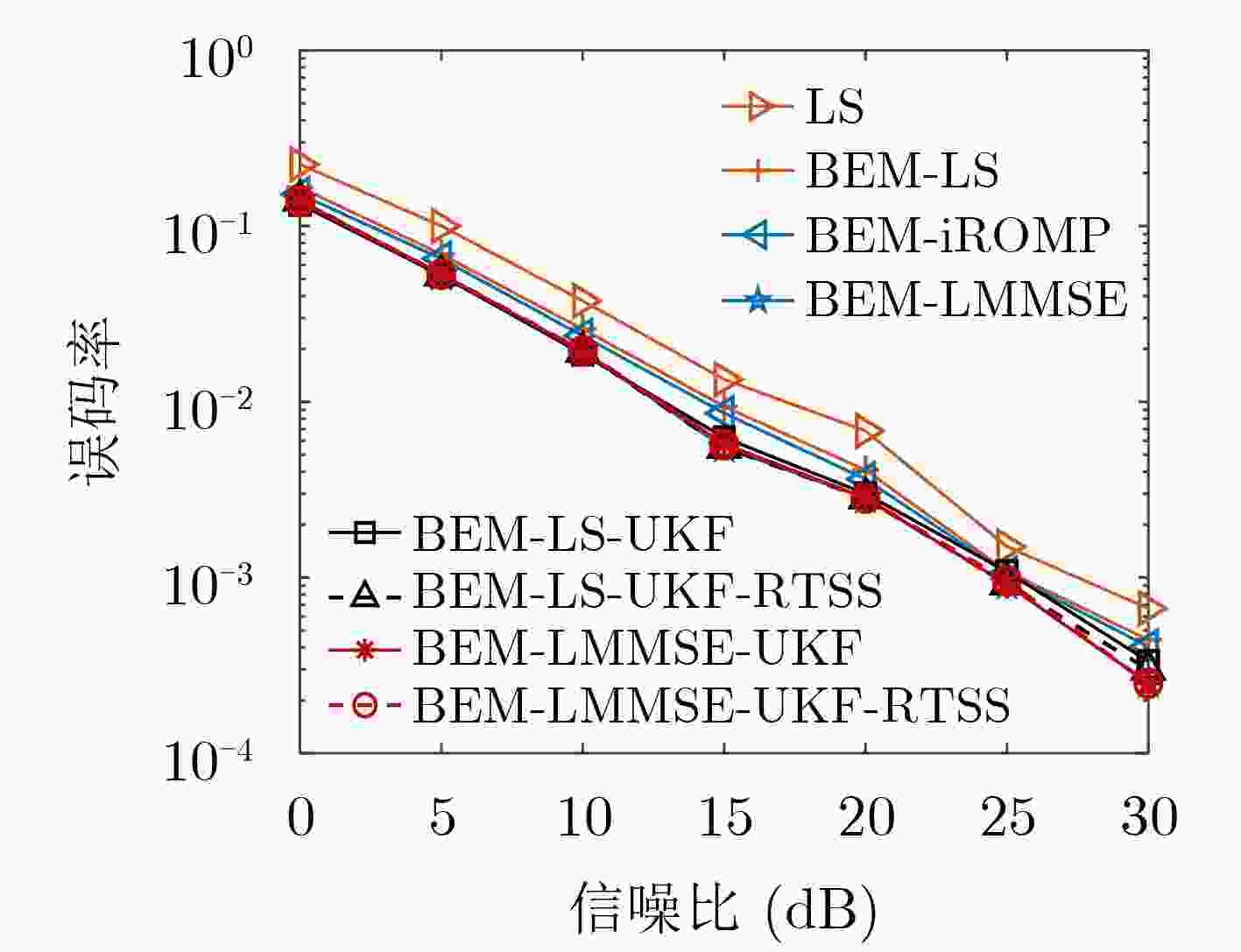
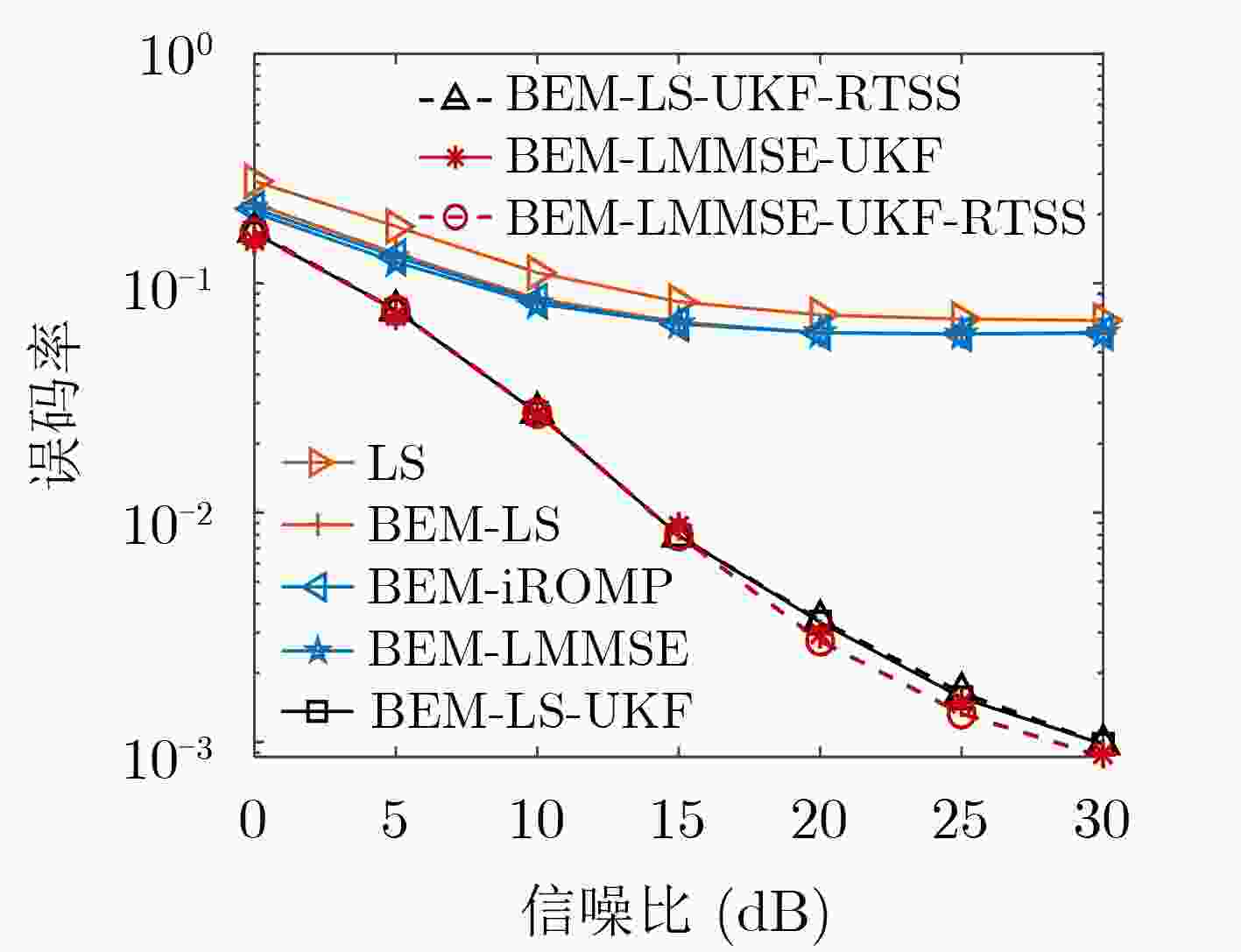


 下载:
下载:
