Recommendation Model by Integrating Knowledge Graph and Image Features
-
摘要: 目前知识图谱研究主要面向信息检索、自然语言理解等领域,在推荐系统中融合知识图谱成为推荐领域学者广泛关注的问题。为了解决单一知识图谱忽略的丰富知识信息,该文对知识图谱进行多模态扩展,并提出一种融合知识图谱与图片特征的推荐模型(KG-I)。不同于其他基于知识图谱的推荐算法,该方法增加视觉嵌入、知识嵌入和结构嵌入去挖掘用户项目之间的隐式反馈信息。该模型利用深度游走模型(Deep Walk)捕获空间结构的方法和波纹网络模型(RippleNet)挖掘知识图谱的知识表达的思想,并且考虑图片对用户偏好的影响,有效地将信息进行融合,并在真实数据集上与其他模型实验比较,研究多种特征的影响,分析不同稀疏度数据下的表现。结果表明,融合知识图谱与图片特征的个性化推荐模型完全优于其他的对比算法并且有效缓解数据稀疏情况。Abstract: At present, the study of knowledge graph focuses mainly on information retrieval, natural language understanding and other fields. Integrating knowledge graph with recommendation system has been concerned by scholars in the field. In order to mine the rich information ignored in knowledge graph, the knowledge graph is extended to multimodal and a recommendation model that incorporates Knowledge Graph with Image (KG-I) features is proposed. Different from other recommendation algorithms, visual embedding, knowledge embedding and structure embedding are combined to capture implicit feedback between user-items. The Deep Walk is used to capture the spatial structure and the ideal of RippleNet to retain the semantic features of knowledge graph, and the effect of images on preference is considered to integrate information. Compared with other models on the real data set, the influence of various features is studied, and the performance of different sparsity data is analyzed. The results show that the personalized recommendation model based on knowledge graph and image features outperforms other algorithms and the data sparsity can be alleviated.
-
Key words:
- Image processing /
- Knowledge graph /
- Data fusion /
- Multimodality
-
表 1 实验数据
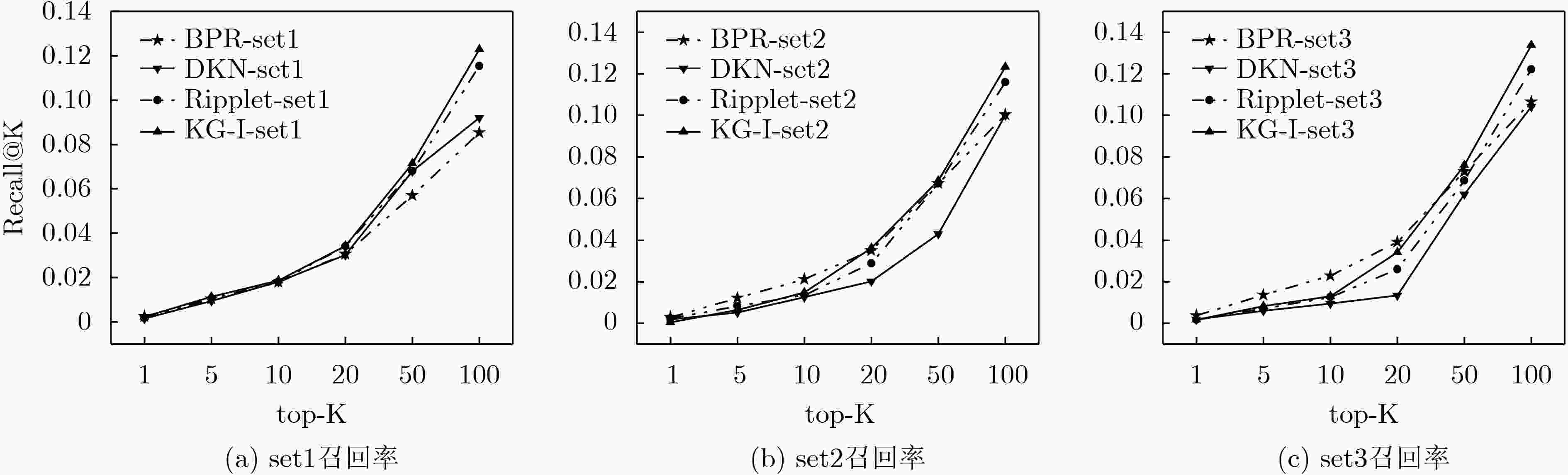
数据集 指标类型 指标值 数据集 指标类型 指标值 电影评分数据 用户数量 610 知识图谱数据 用户实体数量 610 项目数量 9742 项目实体数量 9742 评分数量 100836 演职人员关系 52904 评分级别 0.5, 1, ···, 5 电影类别关系 24226 电影海报数量 9730 项目图片数量 9730 表 2 在MovieLens集上各种算法AUC和Acc对比
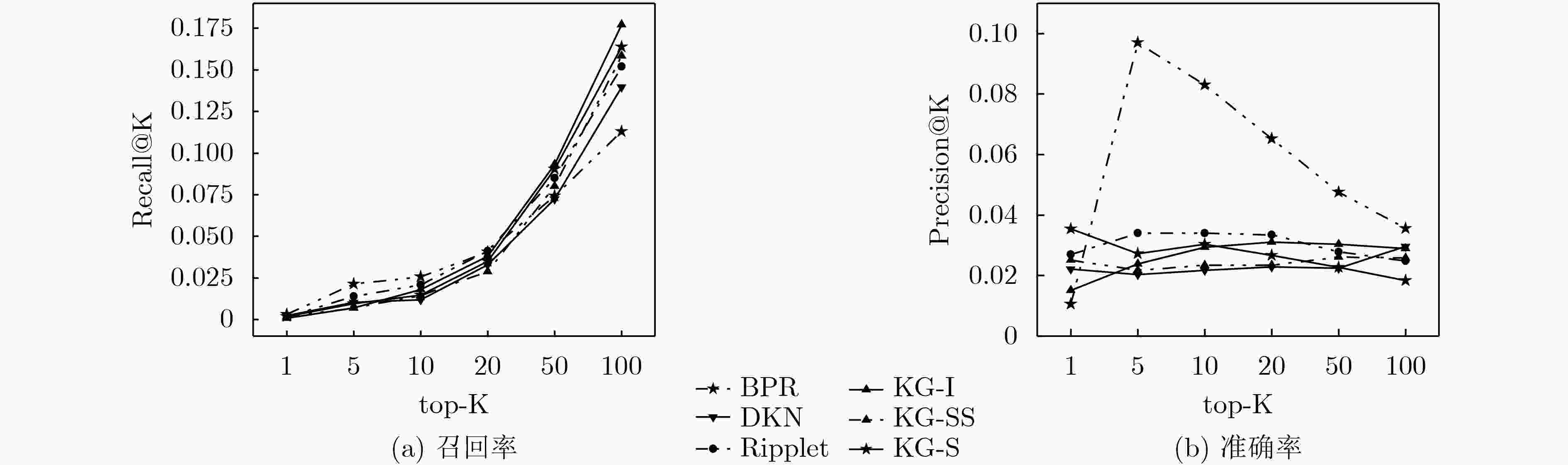
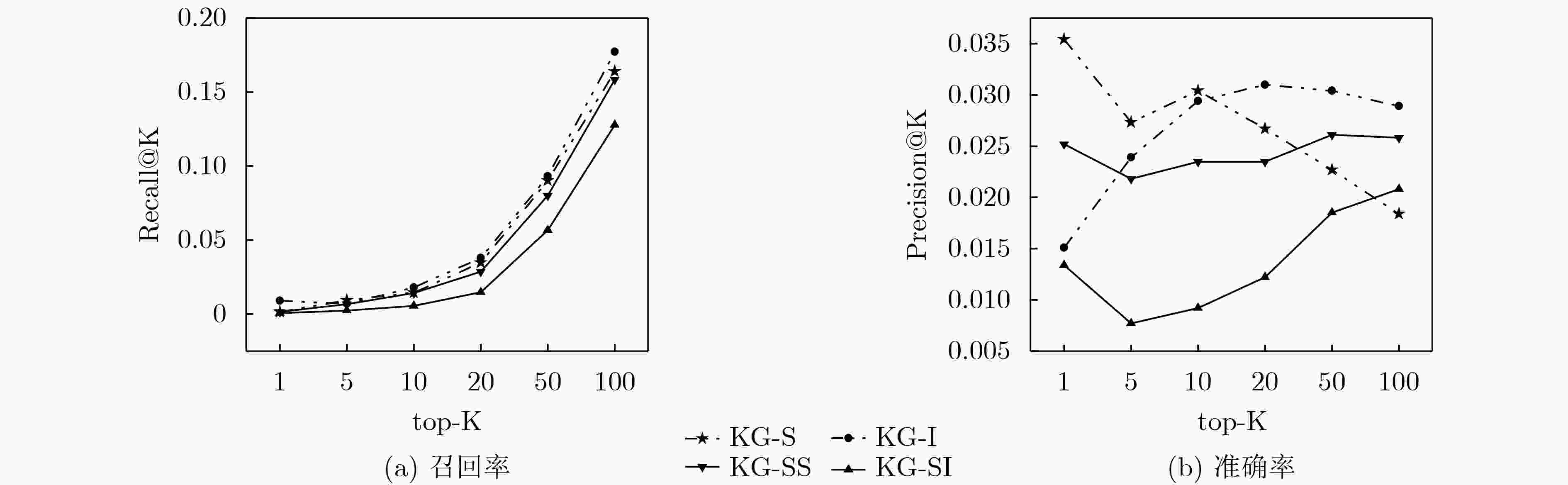
BPRMF DKN RippleNet KG-I KG-SS KG-S AUC 0.7137 0.7925 0.8353 0.8544 0.8438 0.8345 Acc 0.6396 0.7268 0.7769 0.7880 0.7756 0.7802 -
[1] TEWARI A S. Generating items recommendations by fusing content and user-item based collaborative filtering[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 167: 1934–1940. doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2020.03.215 [2] ZENG Lanying and XIE Xiaolan. Collaborative filtering recommendation based on CS-kmeans optimization clustering[C]. The 4th International Conference on Intelligent Information Processing, New York, USA, 2019: 334–340. [3] HUANG Liusheng, CHEN Huaping, WANG Xun, et al. A fast algorithm for mining association rules[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2000, 15(6): 619–624. doi: 10.1007/BF02948845 [4] 戴琳, 孟祥武, 张玉洁, 等. 融合多种数据信息的餐馆推荐模型[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(9): 2869–2885. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005540DAI Lin, MENG Xiangwu, ZHANG Yujie, et al. Restaurant recommendation model with multiple information fusion[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(9): 2869–2885. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005540 [5] CHENG H T, KOC L, HARMSEN J, et al. Wide & deep learning for recommender systems[C]. The 1st Workshop on Deep Learning for Recommender Systems, New York, USA, 2016: 7–10. [6] HE Xiangnan, LIAO Lizi, ZHANG Hanwang, et al. Neural collaborative filtering[C]. The 26th International Conference on World Wide Web, Republic and Canton of Geneva, Switzerland, 2017: 173–182. [7] ZHOU Guorui, ZHU Xiaoqiang, SONG Chengru, et al. Deep interest network for click-through rate prediction[C]. The 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 2018: 1059–1068. [8] TAN Y K, XU Xinxing, and LIU Yong. Improved recurrent neural networks for session-based recommendations[C]. The 1st Workshop on Deep Learning for Recommender Systems, New York, USA, 2016: 17–22. [9] WANG Hongwei, ZHANG Fuzheng, WANG Jialin, et al. RippleNet: Propagating user preferences on the knowledge graph for recommender systems[C]. The 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, New York, USA, 2018: 417–426. [10] WANG Hongwei, ZHANG Fuzheng, ZHAO Miao, et al. Multi-task feature learning for knowledge graph enhanced recommendation[C]. The World Wide Web Conference, New York, USA, 2019: 2000–2010. [11] ABU-EL-HAIJA S, PEROZZI B, KAPOOR A, et al. MixHop: Higher-order graph convolutional architectures via sparsified neighborhood mixing[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 21–29. [12] WANG Hongwei, ZHANG Fuzheng, XIE Xing, et al. DKN: Deep knowledge-aware network for news recommendation[C]. The 2018 World Wide Web Conference, Lyon, France, 2018: 1835–1844. [13] ZHAO Huan, YAO Quanming, LI Jianda, et al. Meta-graph based recommendation fusion over heterogeneous information networks[C]. The 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, USA, 2017: 635–644. [14] DAI Feifei, GU Xiaoyan, LI Bo, et al. Meta-graph based attention-aware recommendation over heterogeneous information networks[C]. 19th International Conference on Computational Science, Faro, Portugal, 2019: 580–594. [15] PEROZZI B, AL-RFOU R, and SKIENA S. DeepWalk: Online learning of social representations[C]. The 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, USA, 2014: 701–710. [16] 程淑玉, 黄淑桦, 印鉴. 融合知识图谱与循环神经网络的推荐模型[J]. 小型微型计算机, 2020, 41(8): 1670–1675.CHENG Shuyu, HUANG Shuhua, and YIN Jian. Recommendation model based on knowledge graph and recurrent neural network[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2020, 41(8): 1670–1675. [17] WANG Xiang, XU Yaokun, HE Xiangnan, et al. Reinforced negative sampling over knowledge graph for recommendation[C]. The Web Conference, New York, USA, 2020: 99–109. [18] ZHANG Fuzheng, YUAN N J, LIAN Defu, et al. Collaborative knowledge base embedding for recommender systems[C]. The 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, USA, 2016: 353–362. [19] YU Xiao, REN Xiang, SUN Yizhou, et al. Personalized entity recommendation: A heterogeneous information network approach[C]. The 7th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, New York, USA, 2014: 283–292. [20] MOUSSELLY-SERGIEH H, BOTSCHEN T, GUREVYCH I, et al. A multimodal translation-based approach for knowledge graph representation learning[C]. The 7th Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational New Orleans, USA, 2018: 225–234. [21] PEZESHKPOUR P, CHEN Liyan, and SINGH S. Embedding multimodal relational data for knowledge base completion[C]. The Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 2018: 3208–3218. [22] YUAN M and LIN Y. Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society:Series B (Statistical Methodology) , 2006, 68(1): 49–67. doi: 10.1111/J.1467–9868.2005.00532.X [23] JONATHON S. A tutorial on principal component analysis[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2014, 51(2): 2–12. [24] RENDLE S, FREUDENTHALER C, GANTNER Z, et al. BPR: Bayesian personalized ranking from implicit feedback[C]. The 25th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Arlington, USA, 2009: 452–461. -





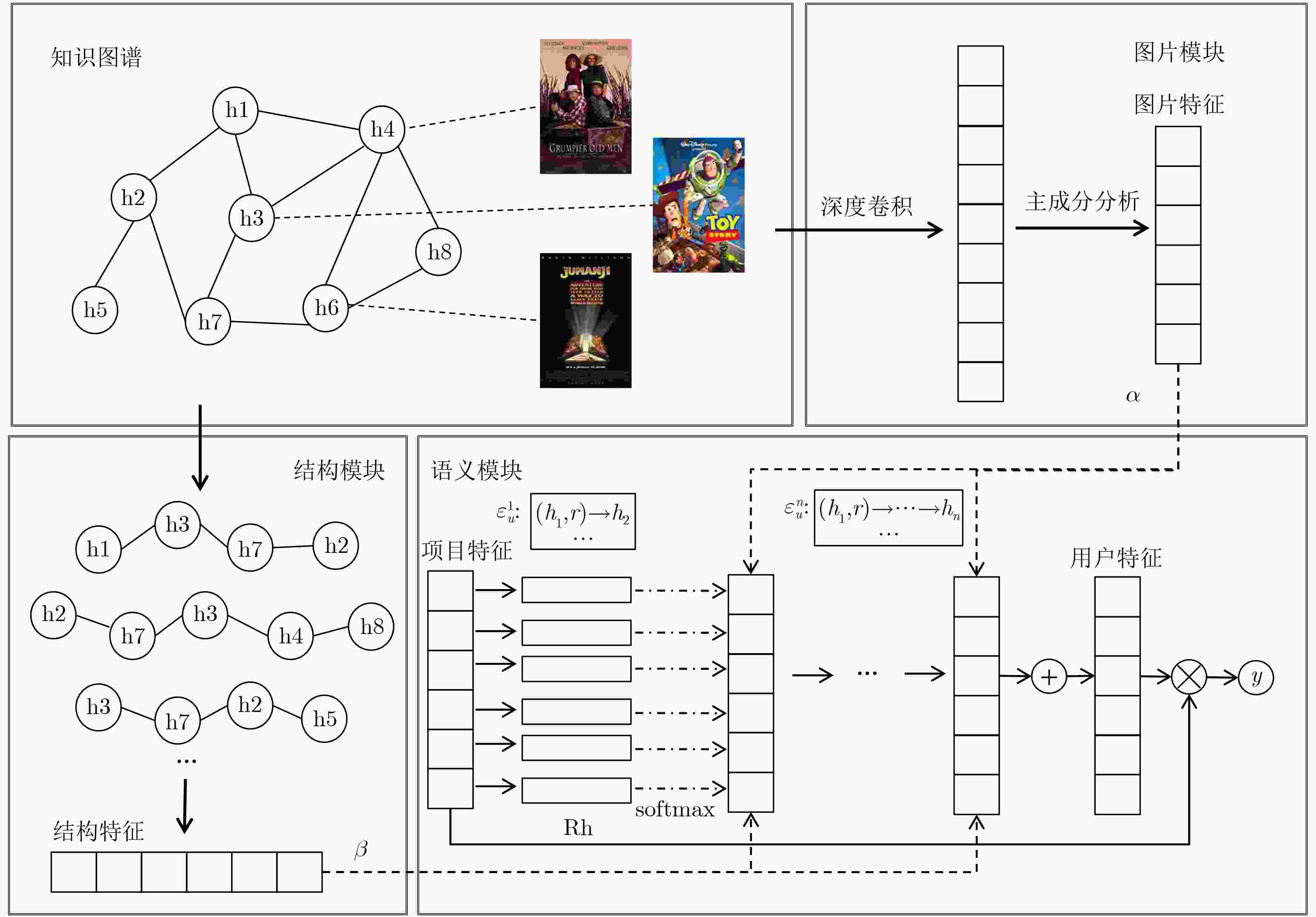
 下载:
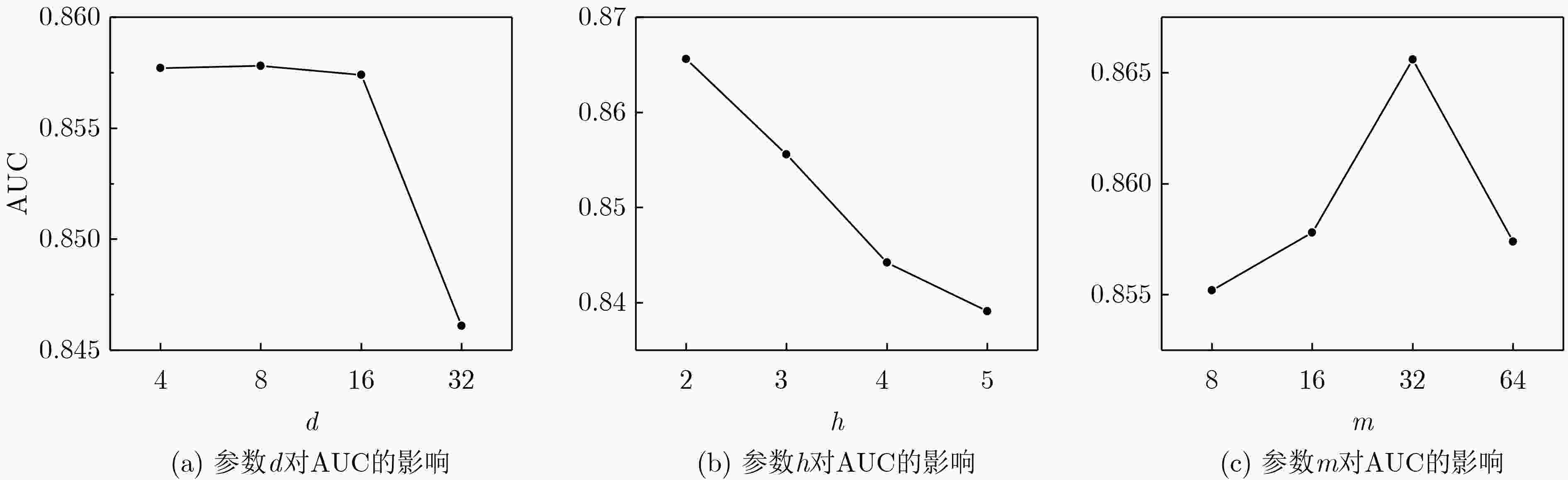
下载:

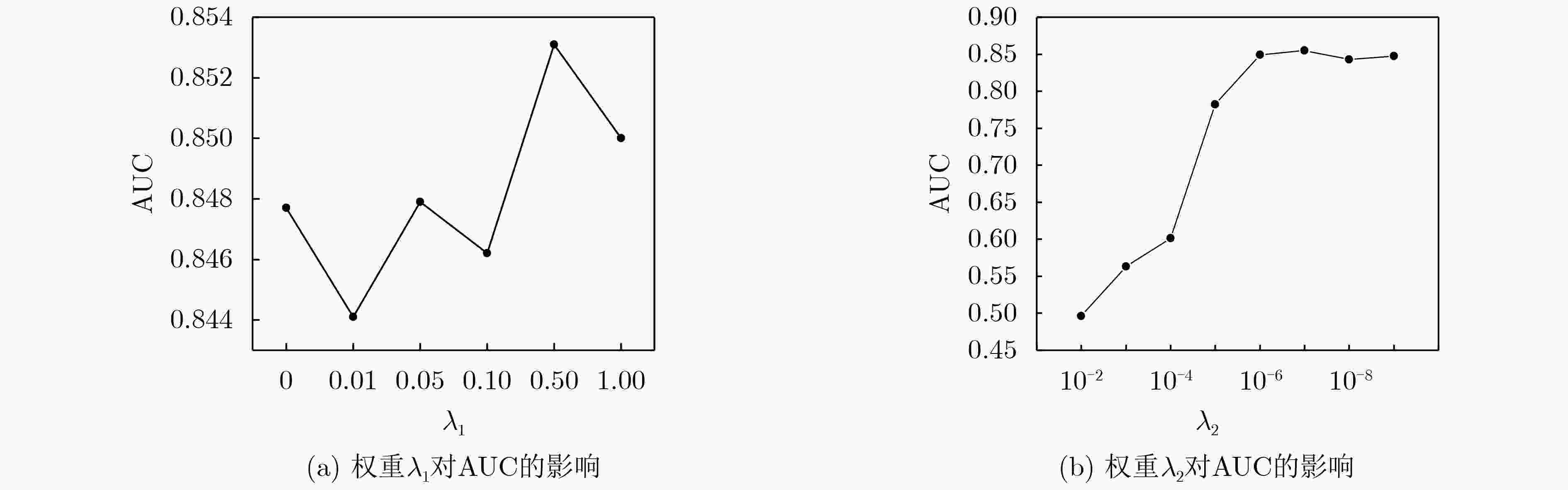


 下载:
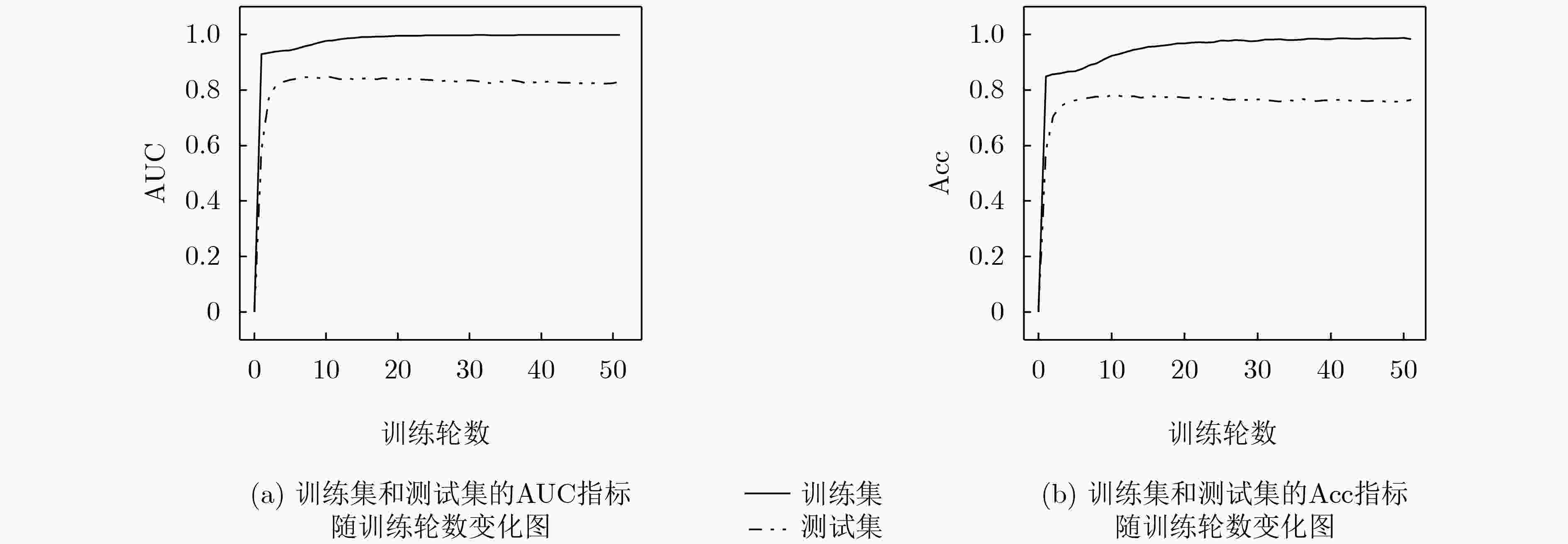
下载:
