An Adaptive Asymmetric Parallel Graphic Equalizer Correction Method without Overlapping Frequency Bands
-
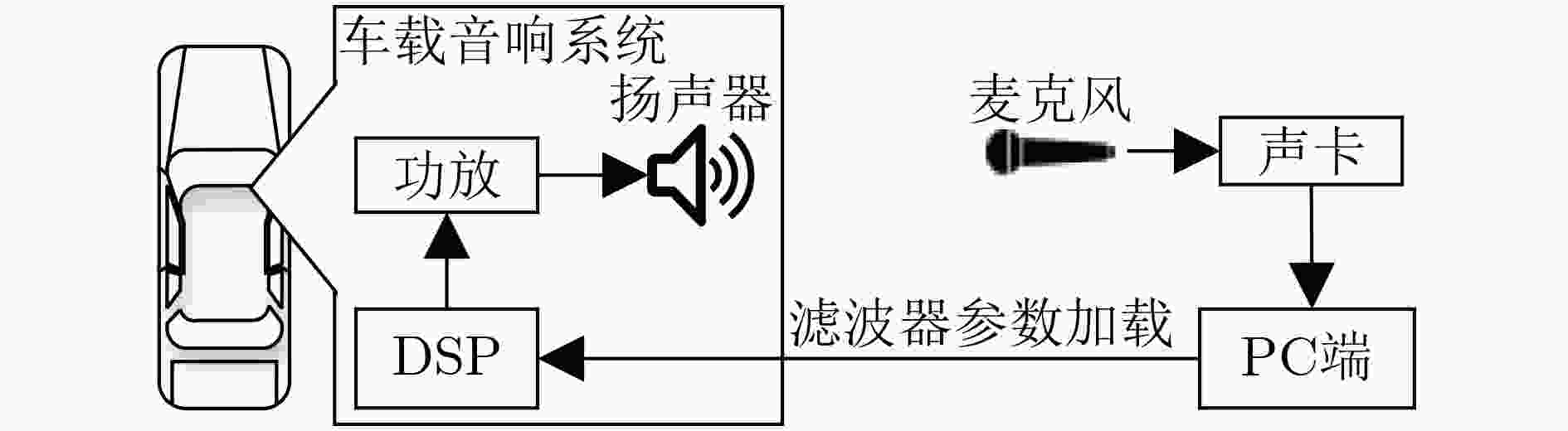
摘要: 针对车载音响的声场校正精度低、效率低的问题,该文提出一种无重叠频带的自适应非对称并联图示均衡器校正方法。在车载音响声场动态变化情况下,该方法考虑了有效均衡范围和自适应增益,而不是经典方法中的固定均衡范围和人工给定的增益。通过对实测数据进行实验分析,所提方法比经典方法所用均衡滤波器个数平均减少大约20%,拟合目标增益更准确,校正后频谱曲线更平坦。Abstract: In order to solve the problem of low accuracy and low efficiency of car loudspeakers sound field correction, a correction method of adaptive asymmetric parallel graphic equalizer without overlapping frequency bands is proposed in this paper. In the case of the dynamic change of the sound field in the car, the proposed method takes into account the effective equalization range and adaptive gains, rather than the fixed equalization range and given artificially gains in the classical methods. Through the experimental analysis of the measured data, the average number of equalization filters used by the proposed method is about 20% less than the classical methods, whose fitting target gains is more accurate, and the spectrum curve is flatter after correction.
-
表 1 车载扬声器分类及其频响范围表
车载扬声器分类 常见频率响应范围 低音 20~150 Hz 中音 150 Hz~5 kHz 高音 5~20 kHz 中低音 20 Hz~5 kHz 中高音 110 Hz~20 kHz 全频段 50 Hz~20 kHz 表 2 1/3倍频程中心频率和带宽
频带编号 $ {f_{\text{c}}} $(Hz) $ {f_{\text{B}}} $(Hz) 频带编号 $ {f_{\text{c}}} $(Hz) $ {f_{\text{B}}} $(Hz) 1 20 9.3 17 800 373 2 25 11.7 18 1000 466.2 3 31.5 14.7 19 1250 582.8 4 40 18.6 20 1600 745.9 5 50 23.3 21 2000 932.4 6 63 29.4 22 2500 1166 7 80 37.3 23 3150 1469 8 100 46.6 24 4000 1865 9 125 58.3 25 5000 2331 10 160 74.6 26 6300 2937 11 200 93.2 27 8000 3730 12 250 116.6 28 10000 4662 13 315 146.9 29 12500 5828 14 400 186.5 30 16000 7459 15 500 233.1 31 20000 9324 16 630 293.7 表 3 不同方法指标对比
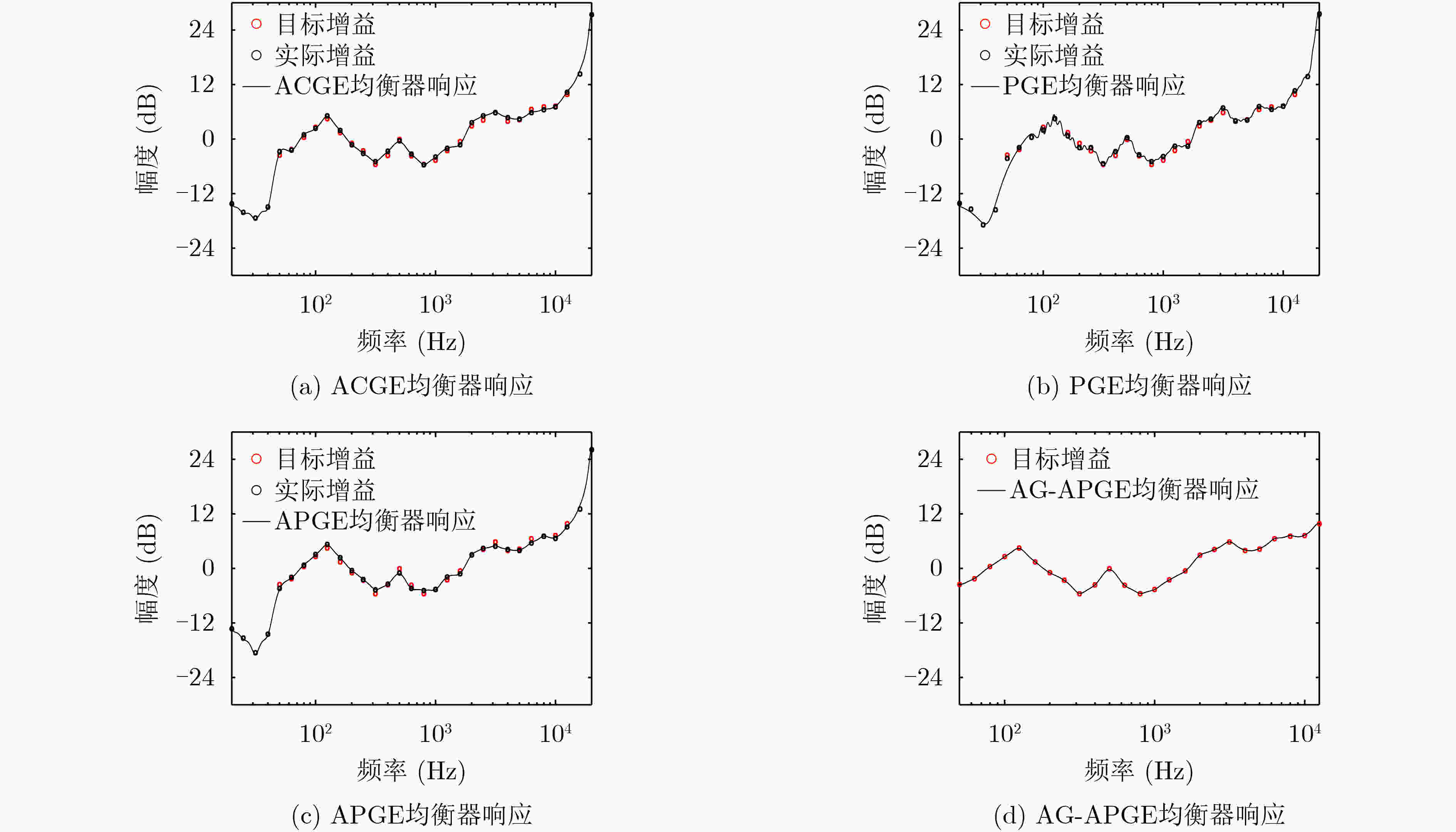
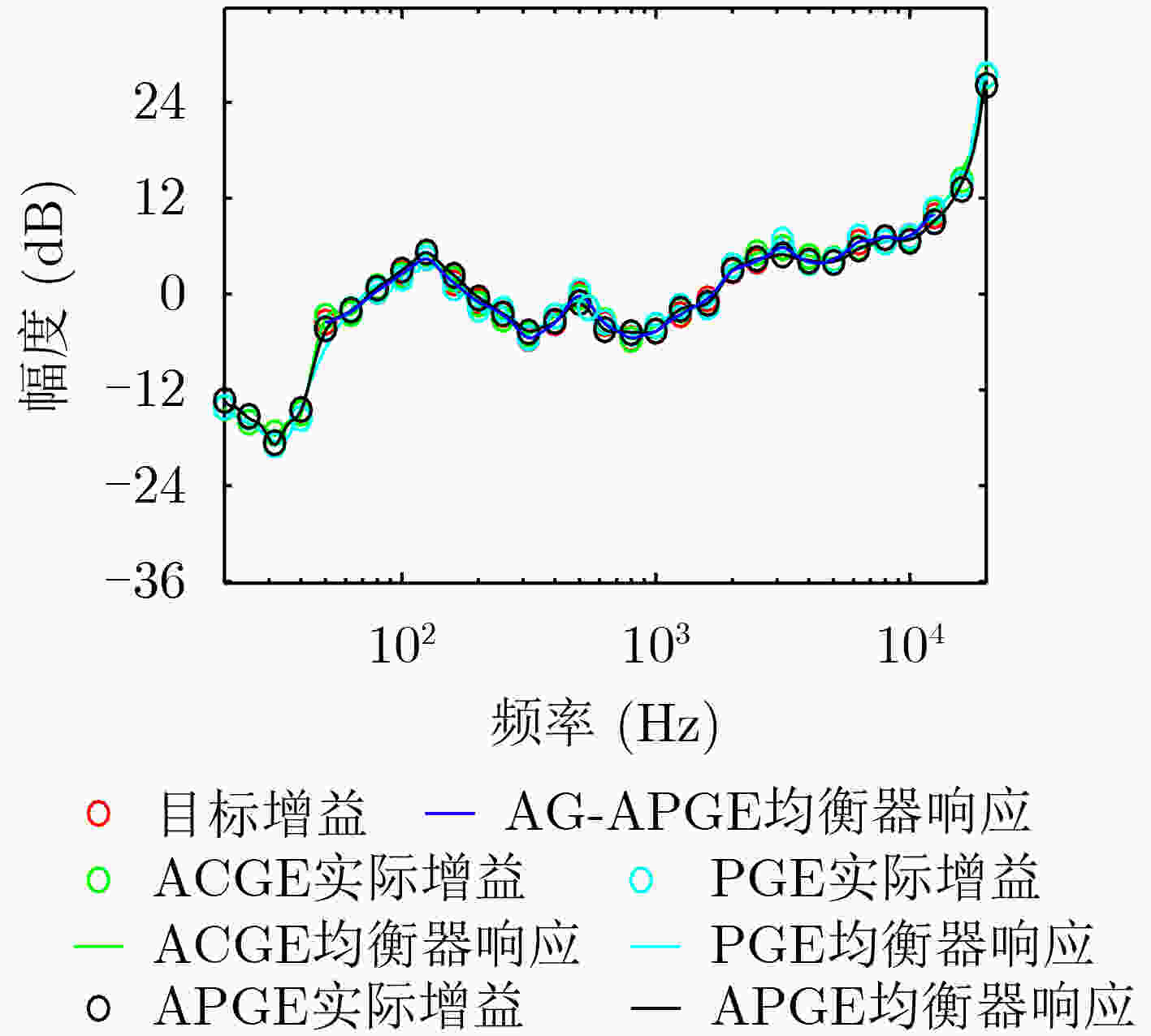
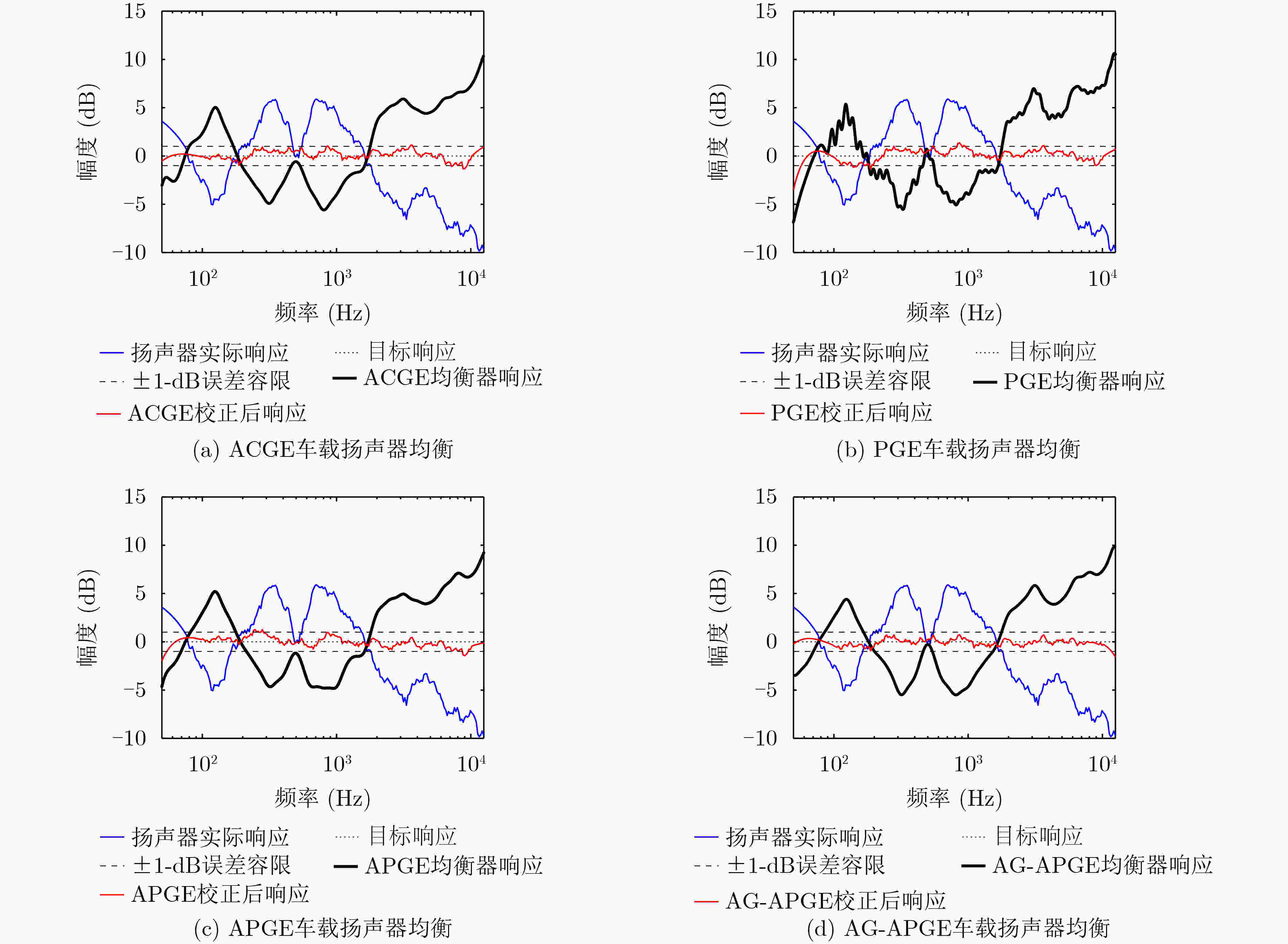
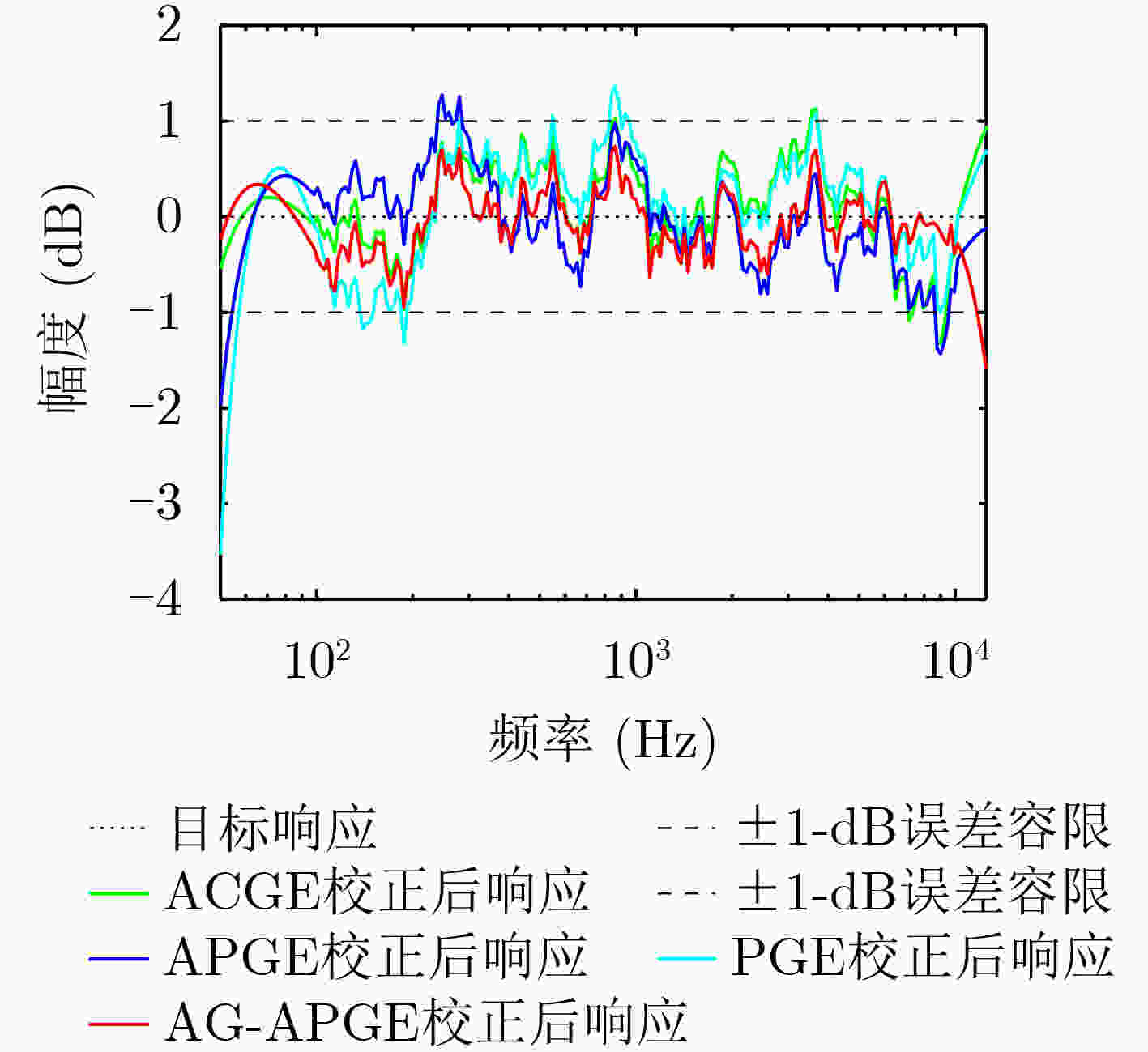
指标 ACGE PGE APGE AG-APGE 平均拟合最大误差(dB) 1.08 2.65 1.07 0.23 平均原始SFM 0.652 0.652 0.652 0.652 平均校正后SFM 0.987 0.980 0.986 0.991 平均均衡滤波器个数 31 62 31 25 平均设计所需时间 0.57 ms 1.22 s 0.70 ms 0.48 ms 平均操作数 加法 124 248 124 100 乘法 155 249 125 101 总和 279 497 249 201 -
[1] VÄLIMÄKI V and REISS J D. All about audio equalization: Solutions and frontiers[J]. Applied Sciences, 2016, 6(5): 129. doi: 10.3390/app6050129 [2] CECCHI S, CARINI A, and SPORS S. Room response equalization—a review[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(1): 16. doi: 10.3390/app8010016 [3] PEPE G, GABRIELLI L, SQUARTINI S, et al. Evolutionary tuning of filters coefficients for binaural audio equalization[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2020, 163: 107204. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2019.107204 [4] DAGAR A, NITISH S S, and HEGDE R. Joint adaptive impulse response estimation and inverse filtering for enhancing in-car audio[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, Canada, 2018: 416–420. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8462329. [5] VAIRETTI G, DE SENA E, CATRYSSE M, et al. An automatic design procedure for low-order IIR parametric equalizers[J]. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 2018, 66(11): 935–952. doi: 10.17743/jaes.2018.0049 [6] RÄMÖ J and VÄLIMÄKI V. Graphic delay equalizer[C]. ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, England, 2019: 8018–8022. doi: 10.1109/icassp.2019.8682949. [7] PRINCE S and KUMAR K R S. A novel Nth-order IIR filter-based graphic equalizer optimized through genetic algorithm for computing filter order[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(8): 2683–2691. doi: 10.1007/s00500-018-3640-9 [8] PEPE G, GABRIELLI L, SQUARTINI S, et al. Gravitational search algorithm for IIR filter-based audio equalization[C]. 2020 28th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Amsterdam, Holland, 2021: 496–500. doi: 10.23919/Eusipco47968.2020.9287421. [9] PEPE G, GABRIELLI L, SQUARTINI S, et al. Designing audio equalization filters by deep neural networks[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(7): 2483. doi: 10.3390/app10072483 [10] RÄMÖ J, LISKI J, and VÄLIMÄKI V. Third-octave and bark graphic-equalizer design with symmetric band filters[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(4): 1222. doi: 10.3390/app10041222 [11] RÄMÖ J and VÄLIMÄKI V. Neural third-octave graphic equalizer[C]. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx-19), Birmingham, UK, 2019: 2–6. [12] VÄLIMÄKI V and RÄMÖ J. Neurally controlled graphic equalizer[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2019, 27(12): 2140–2149. doi: 10.1109/taslp.2019.2935809 [13] RAMÍREZ M A M and REISS J D. End-to-end equalization with convolutional neural networks[C]. 21st International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx-18), Aveiro, Portugal, 2018: 296–303. [14] RÄMÖ J and VÄLIMÄKI V. Optimizing a high-order graphic equalizer for audio processing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(3): 301–305. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2014.2301557 [15] LISKI J, RÄMÖ J, and VÄLIMÄKI V. Graphic equalizer design with symmetric biquad filters[C]. 2019 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), New Paltz, USA, 2019: 55–59. doi: 10.1109/WASPAA.2019.8937168. [16] VÄLIMÄKI V and LISKI J. Accurate cascade graphic equalizer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(2): 176–180. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2016.2645280 [17] LISKI J and VÄLIMÄKI V. The quest for the best graphic equalizer[C]. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx-17), Edinburgh, UK, 2017: 95–102. [18] LISKI J, BANK B, SMITH J O, et al. Converting series biquad filters into delayed parallel form: Application to graphic equalizers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(14): 3785–3795. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2919419 [19] TAO Hao, FANG Yong, LIU Huaping, et al. Optimization method for a high-precision graphic equalizer with lower order filter[C]. 2018 14th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Beijing, China, 2018: 22–26. doi: 10.1109/ICSP.2018.8652302. [20] BANK B. Converting infinite impulse response filters to parallel form [tips & tricks][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2018, 35(3): 124–130. doi: 10.1109/msp.2018.2805358 [21] BANK B, BELLOCH J A, and VÄLIMÄKI V. Efficient design of a parallel graphic equalizer[J]. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 2017, 65(10): 817–825. doi: 10.17743/jaes.2017.0029 [22] RÄMÖ J, VÄLIMÄKI V, and BANK B. High-precision parallel graphic equalizer[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014, 22(12): 1894–1904. doi: 10.1109/taslp.2014.2354241 [23] CHEN Zhe, GENG Guosheng, YIN Fuliang, et al. A pre-distortion based design method for digital audio graphic equalizer[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2014, 25: 296–302. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2013.11.007 [24] ORFANIDIS S J. Introduction to Signal Processing[M]. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 1995. [25] KARJALAINEN M, PIIRILÄ E, JÄRVINEN A, et al. Comparison of loudspeaker equalization methods based on DSP techniques[J]. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 1999, 47(1/2): 14–31. -





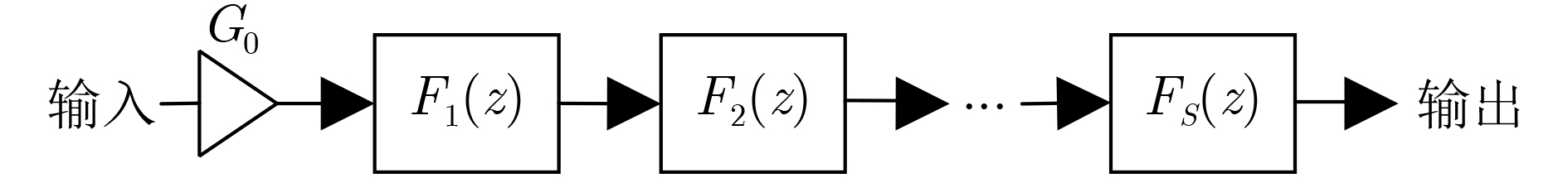
 下载:
下载:
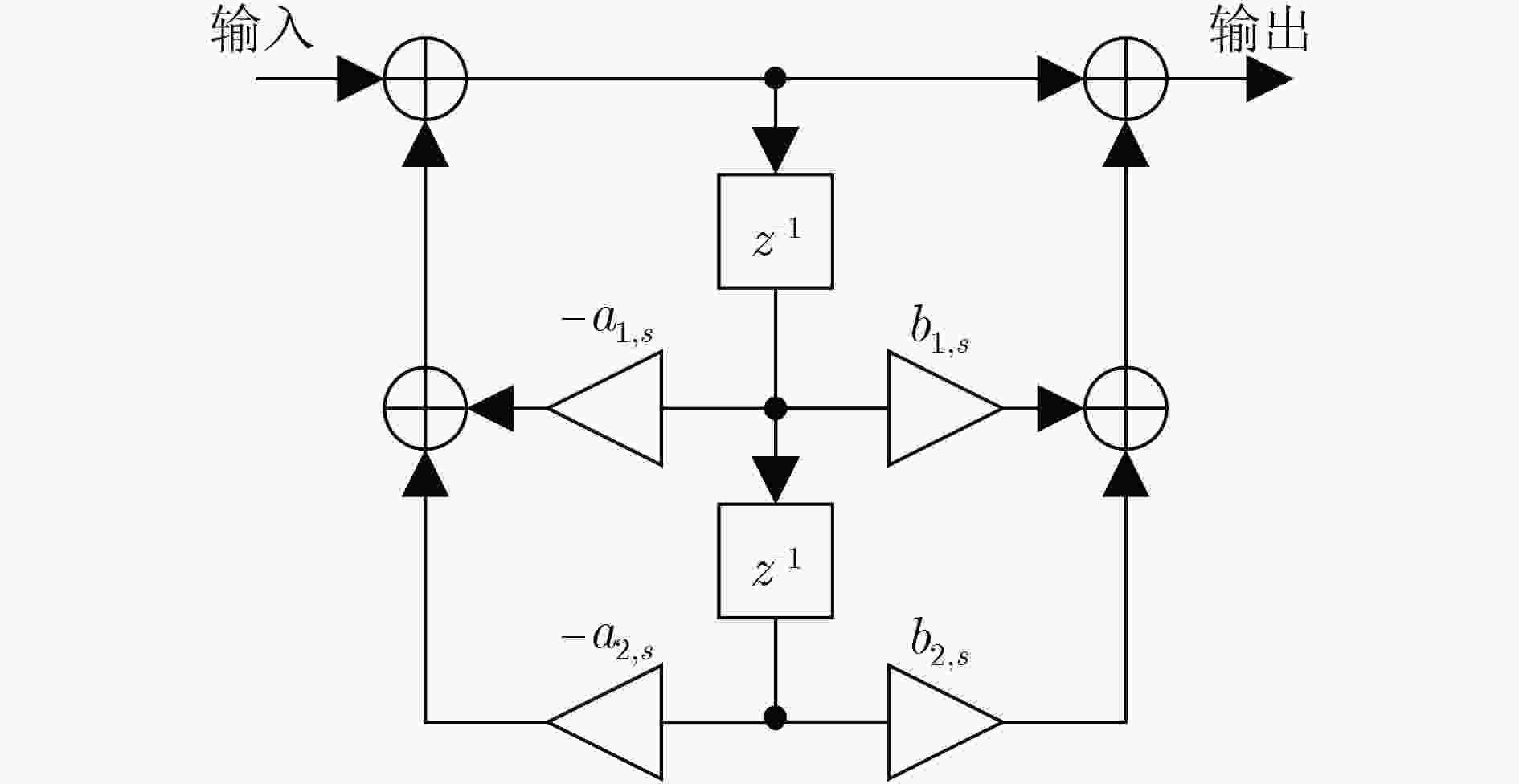
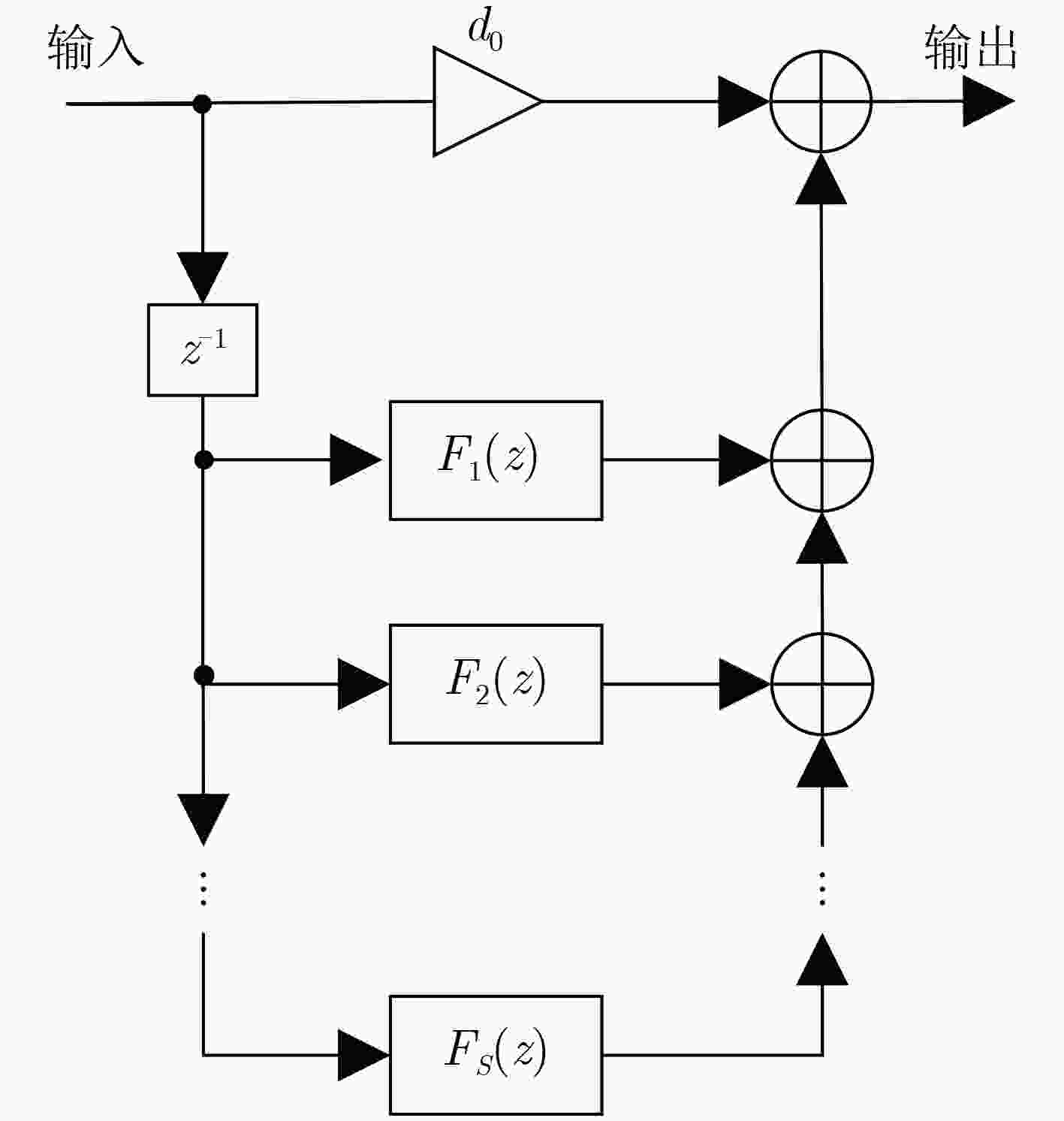
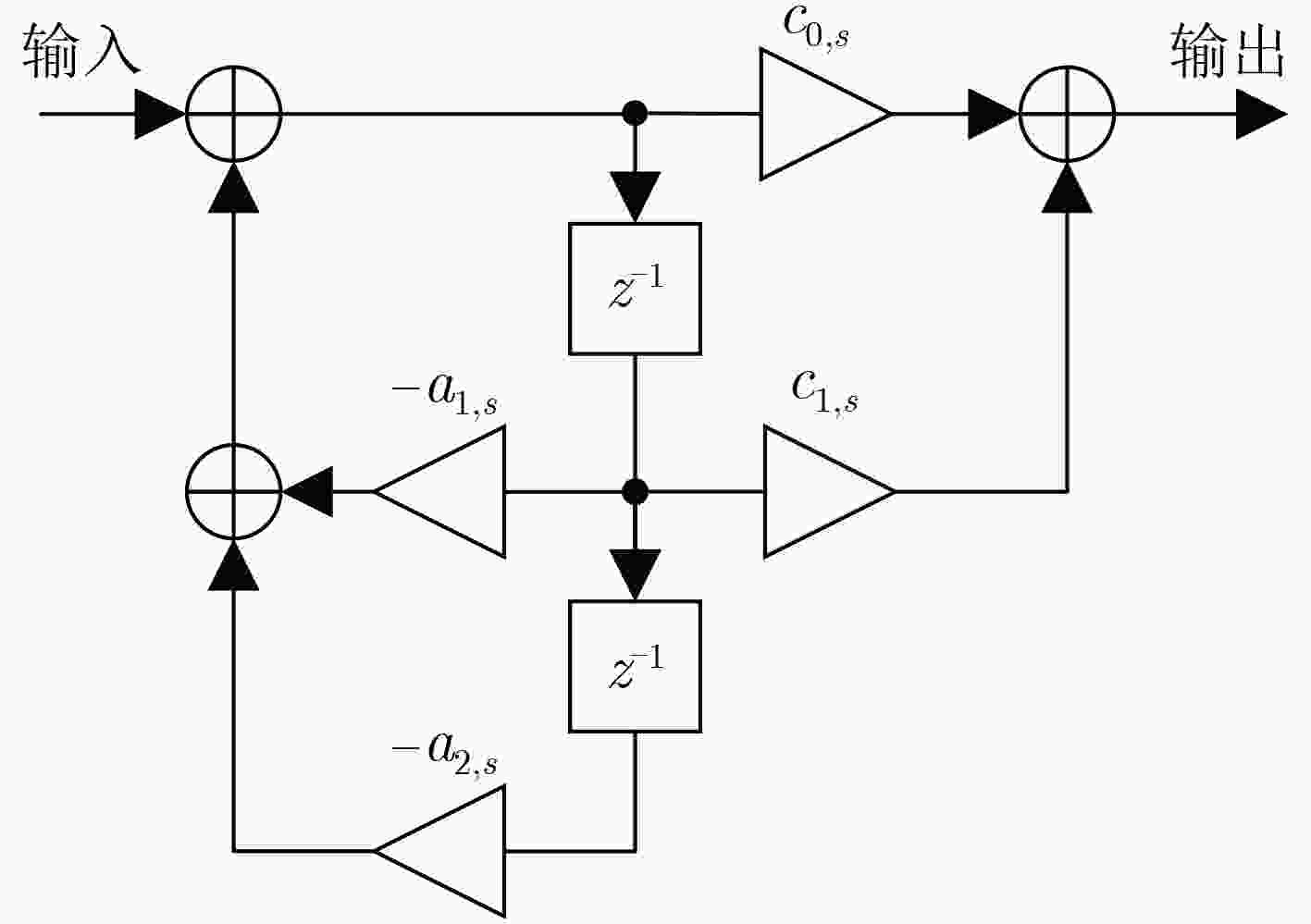


 下载:
下载:
