Image Harmonization via Multi-scale Feature Calibration
-
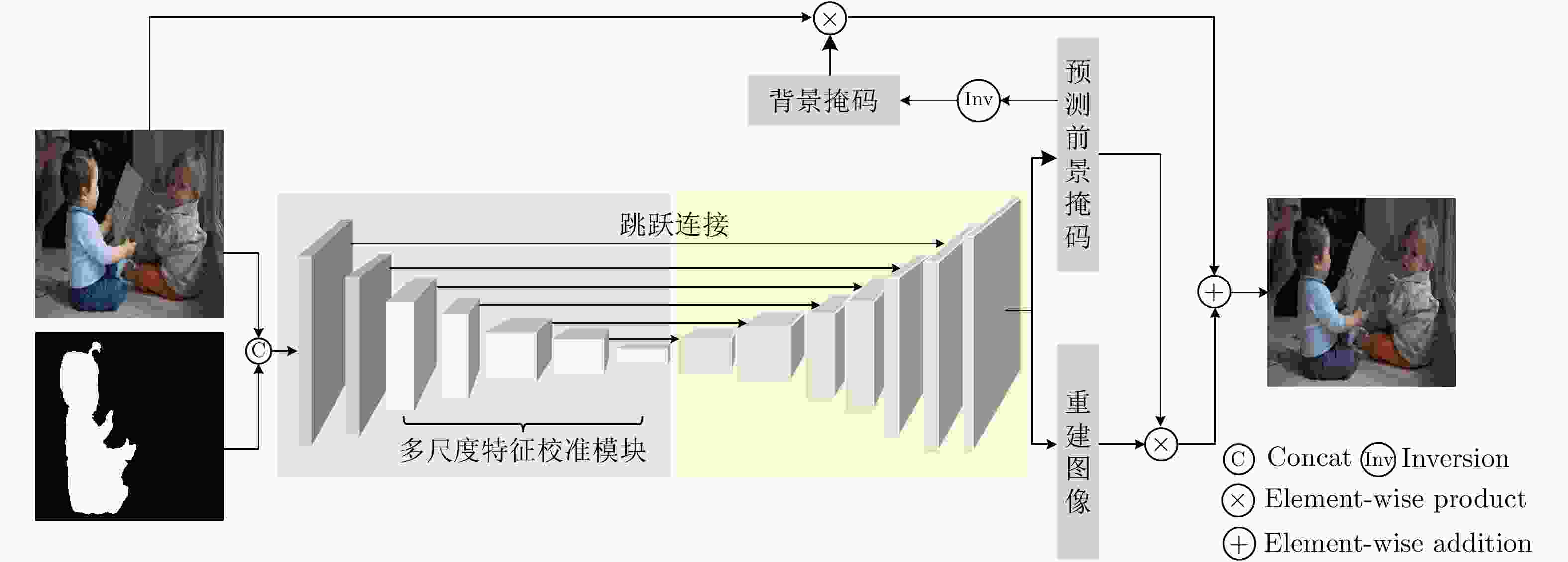
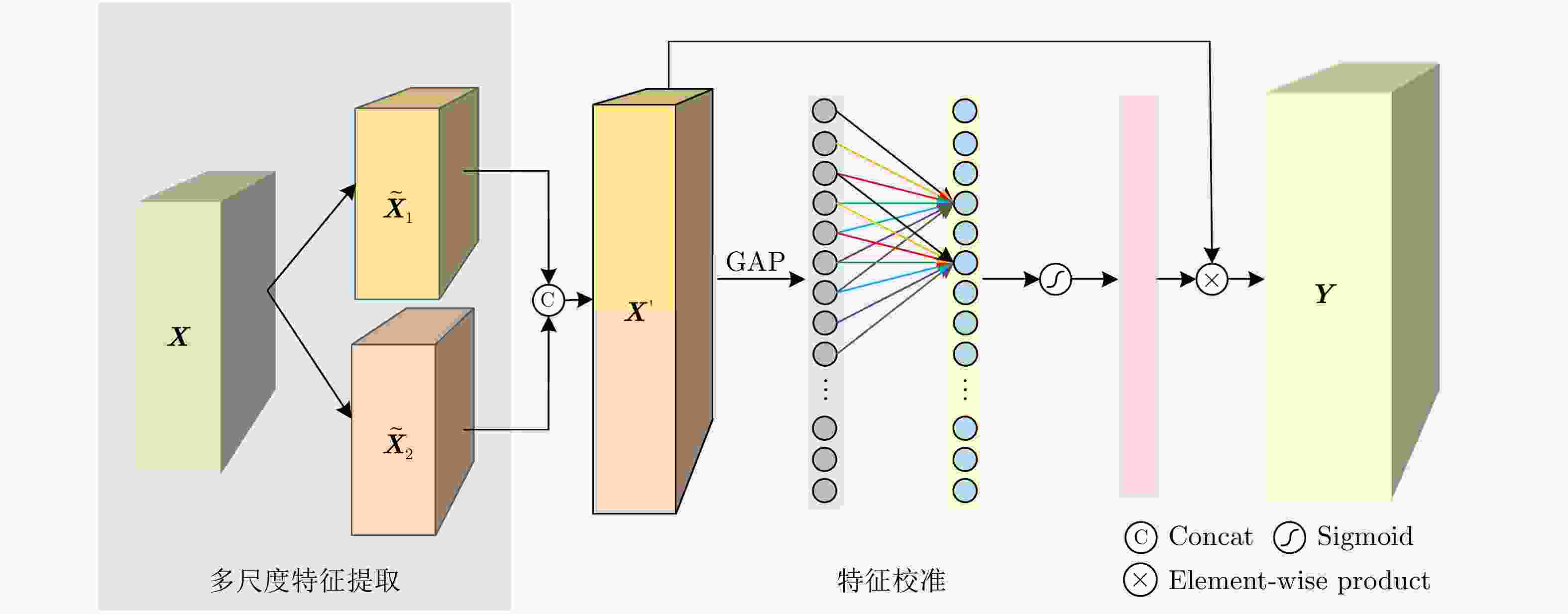
摘要: 图像组合是图像处理中一个重要操作,然而组合图像中前景区域与背景区域的外观不协调使得组合图像看起来不真实。图像协调化是图像组合中极其重要的一个环节,其目的是调整组合图像前景区域的外观使其与背景区域一致,从而让组合图像在视觉上看起来真实。然而,现有方法只考虑了组合图像前景与背景之间的外观差异,忽略了图像局部的亮度变化差异,这使得图像整体的光照不协调。为此,该文提出一个新的多尺度特征校准模块(MFCM)学习不同尺度的感受野之间细微的特征差异。基于所提模块,该文进一步设计了一个新的编码器学习组合图像中前景与背景的外观差异和局部亮度变化,然后利用解码器重构出图像,并通过一个对前景区域归一化的回归损失指导网络学习调整前景区域的外观。在广泛使用的iHarmony4数据集上进行实验验证,结果表明该方法的效果超过了目前最优的方法,验证了该方法的有效性。Abstract: Image composition is an important operation in image processing, but the inharmonious appearance between the foreground region and background makes the composite image look unrealistic. Image harmonization is a very important step in image compositing, and targets at adjusting the appearances of foreground to make it consistent with background, improving the visual quality of output image. However, previous approaches only consider the appearance difference between the foreground and the background of the composite image, and neglect the local brightness change of the image, making the illumination of the whole image inharmonious. In order to solve the problem, in this work, a novel module named Multi-scale Feature Calibration Module (MFCM) is proposed to learn the subtle feature differences between multiple scales of receptive field. Based on the proposed MFCM, a novel encoder is designed further to learn the illumination and brightness change in composite image, followed by a decoder is used to reconstruct image. The foreground normalized regression loss is utilized to instruct the network to learn and adjust the appearances of the foreground. The proposed method is validated on a widely used iHarmony4 dataset. The results show that the proposed method achieves the state of the art and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
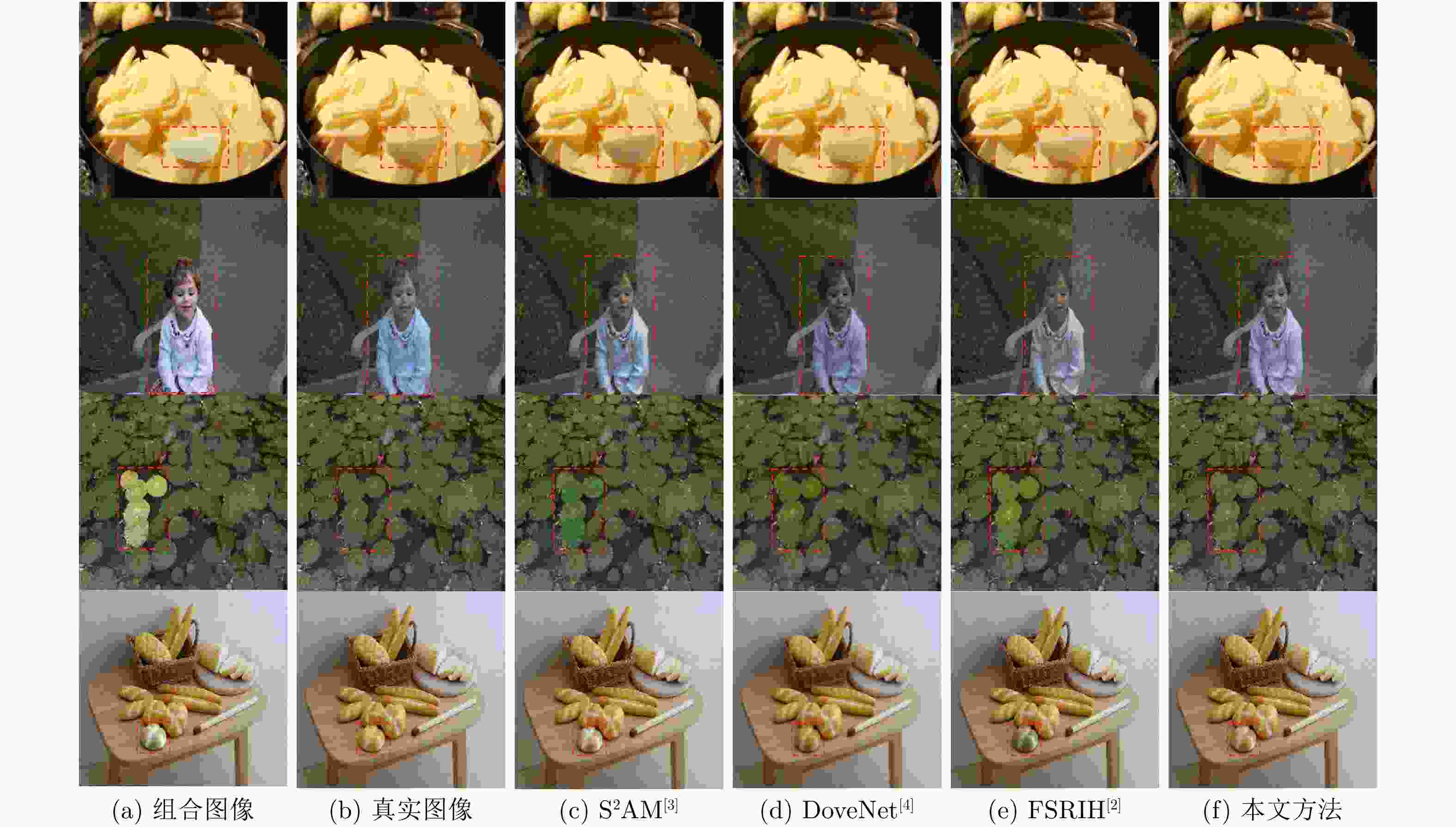
表 1 不同方法在iHarmony4测试集上的性能对比
方法 HFlickr Hday2night HCOCO HAdobe5k iHarmony4 MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR DIH [1] 163.38 29.55 82.34 34.62 51.85 34.69 92.65 32.28 76.77 33.41 S2AM [3] 143.45 30.03 76.61 34.50 41.07 35.47 63.40 33.77 59.67 34.35 DoveNet [4] 133.14 30.21 54.05 35.18 36.72 35.83 52.32 34.34 52.36 34.75 FSRIH [2] 86.20 32.55 47.18 37.12 19.30 38.43 31.33 36.01 30.79 37.05 本文方法 72.05 33.11 46.67 36.92 17.62 38.80 27.55 37.31 27.13 37.69 表 2 不同方法在iHarmony4测试集上不同前景区域比例的MSE和fMSE指标对比
方法 0~5% 5%~15% 15%~100% 0~100% MSE fMSE MSE fMSE MSE fMSE MSE fMSE DIH [1] 18.92 799.17 64.23 725.86 228.86 768.89 76.77 773.18 S2AM [3] 15.09 623.11 48.33 540.54 177.62 592.83 59.67 594.67 DoveNet [4] 14.03 591.88 44.90 504.42 152.07 505.82 52.36 549.96 FSRIH [2] 8.48 371.47 25.85 294.64 89.68 296.80 30.79 334.89 本文方法 7.68 341.13 23.15 264.23 78.06 256.03 27.13 302.25 表 3 多尺度特征校准模块不同组件的消融实验结果
HFlickr Hday2night HCOCO HAdobe5k iHarmony4 MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR RF=3 83.39 32.54 56.48 36.60 20.63 38.26 32.36 36.66 31.71 37.12 RF=5 89.33 32.29 64.55 36.34 22.21 38.05 35.95 36.37 34.49 36.89 MFE 76.52 32.85 55.73 36.69 19.02 38.49 29.13 37.06 29.06 37.41 MFE+FC 72.05 33.11 46.67 36.92 17.62 38.80 27.55 37.31 27.13 37.69 表 4 以不同的方式进行特征校准的实验结果
特征校准方式 HFlickr Hday2night HCOCO HAdobe5k iHarmony4 MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR 独立特征校准 72.55 32.99 49.55 37.20 17.70 38.75 28.69 37.23 27.61 37.63 邻域特征交互 72.05 33.11 46.67 36.92 17.62 38.80 27.55 37.31 27.13 37.69 全局特征交互 75.33 32.93 52.82 36.66 18.37 38.65 27.51 37.07 28.02 37.51 表 5 以不同的跨通道范围进行特征校准的实验结果
跨通道范围$ k $ HFlickr Hday2night HCOCO HAdobe5k iHarmony4 MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR MSE PSNR 3 75.59 33.08 48.29 37.10 18.24 38.68 27.69 37.15 27.95 37.58 5 71.64 32.94 54.55 36.89 17.94 38.68 30.78 37.17 28.35 37.57 7 72.05 33.11 46.67 36.92 17.62 38.80 27.55 37.31 27.13 37.69 9 74.66 32.85 52.14 36.82 18.16 38.58 30.54 36.68 28.70 37.35 -
[1] TSAI Y H, SHEN Xiaohui, LIN Zhe, et al. Deep image harmonization[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2799–2807. [2] SOFIIUK K, POPENOVA P, and KONUSHIN A. Foreground-aware semantic representations for image harmonization[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.00809, 2020. [3] CUN Xiaodong and PUN C M. Improving the harmony of the composite image by spatial-separated attention module[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4759–4771. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2975979 [4] CONG Wenyan, ZHANG Jianfu, NIU Li, et al. DoveNet: Deep image harmonization via domain verification[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 8391–8400. [5] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. [6] LI Xiang, WANG Wenhai, HU Xiaolin, et al. Selective kernel networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 510–519. [7] SUNKAVALLI K, JOHNSON M K, MATUSIK W, et al. Multi-scale image harmonization[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2010, 29(4): 1–10. doi: 10.1145/1778765.1778862 [8] ZHU Junyan, KR?HENB?HL P, SHECHTMAN E, et al. Learning a discriminative model for the perception of realism in composite images[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3943–3951. [9] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967–5976. [10] 尹梦晓, 林振峰, 杨锋. 基于动态感受野的自适应多尺度信息融合的图像转换[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2386–2394. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200675YIN Mengxiao, LIN Zhenfeng, and YANG Feng. Adaptive multi-scale information fusion based on dynamic receptive field for image-to-image translation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2386–2394. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200675 [11] LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZ?R F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 105–114. [12] WANG Xintao, YU Ke, WU Shixiang, et al. ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 63–79. [13] XIONG Wei, YU Jiahui, LIN Zhe, et al. Foreground-aware image inpainting[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5833–5841. [14] 易诗, 吴志娟, 朱竞铭, 等. 基于多尺度生成对抗网络的运动散焦红外图像复原[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1766–1773. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190495YI Shi, WU Zhijuan, ZHU Jingming, et al. Motion defocus infrared image restoration based on multi scale generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1766–1773. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190495 [15] KOTOVENKO D, SANAKOYEU A, MA Pingchuan, et al. A content transformation block for image style transfer[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 10024–10033. [16] 张惊雷, 厚雅伟. 基于改进循环生成式对抗网络的图像风格迁移[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1216–1222. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190407ZHANG Jinglei and HOU Yawei. Image-to-image translation based on improved cycle-consistent generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1216–1222. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190407 [17] ANOKHIN I, SOLOVEV P, KORZHENKOV D, et al. High-resolution daytime translation without domain labels[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 7485–7494. [18] HE Mingming, LIAO Jing, CHEN Dongdong, et al. Progressive color transfer with dense semantic correspondences[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(2): 1–18. doi: 10.1145/3292482 [19] ULYANOV D, VEDALDI A, and LEMPITSKY V. Instance normalization: The missing ingredient for fast stylization[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.08022, 2017. [20] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. The 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning - Volume 37, Lille, France, 2015: 448–456. [21] HU Jie, SHEN Li, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011–2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [22] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. [23] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. The 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. [24] BYCHKOVSKY V, PARIS S, CHAN E, et al. Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs[C]. The CVPR 2011, Colorado, USA, 2011: 97–104. [25] ZHOU Hao, SATTLER T, and JACOBS D W. Evaluating local features for day-night matching[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Holland, 2016: 724–736. [26] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
