Online Joint Optimization of Power and Modulation in Energy Harvesting Communication Systems
-
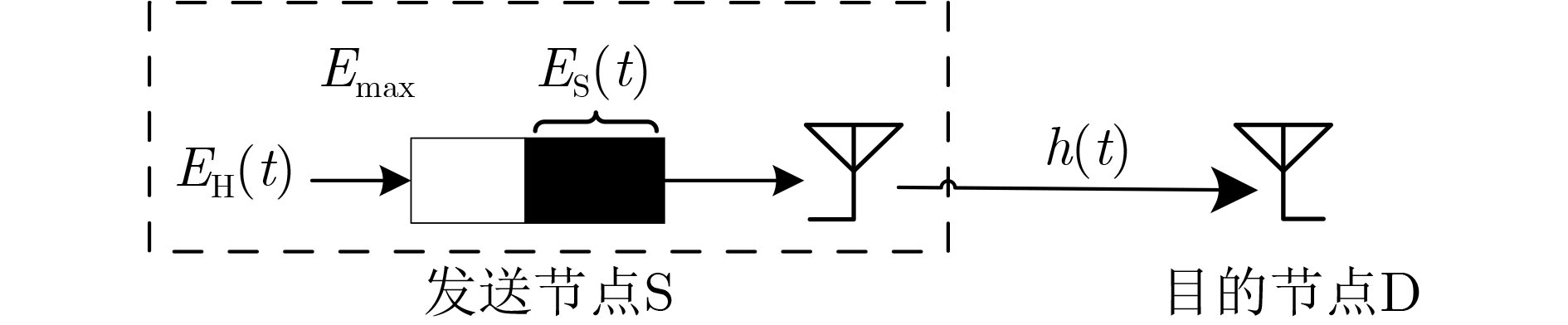
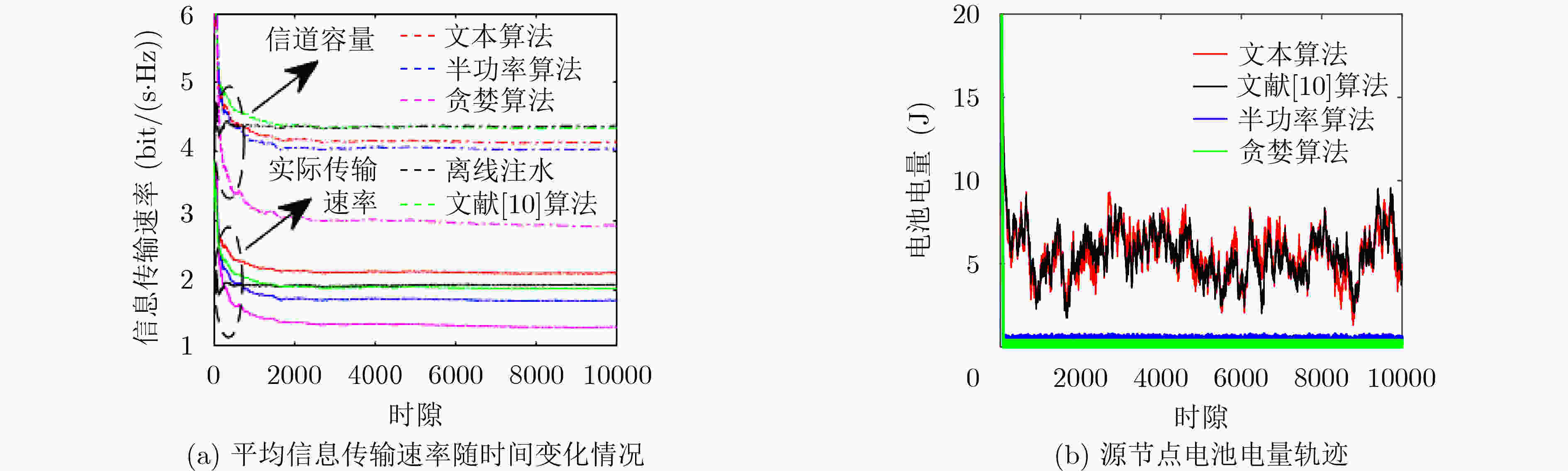
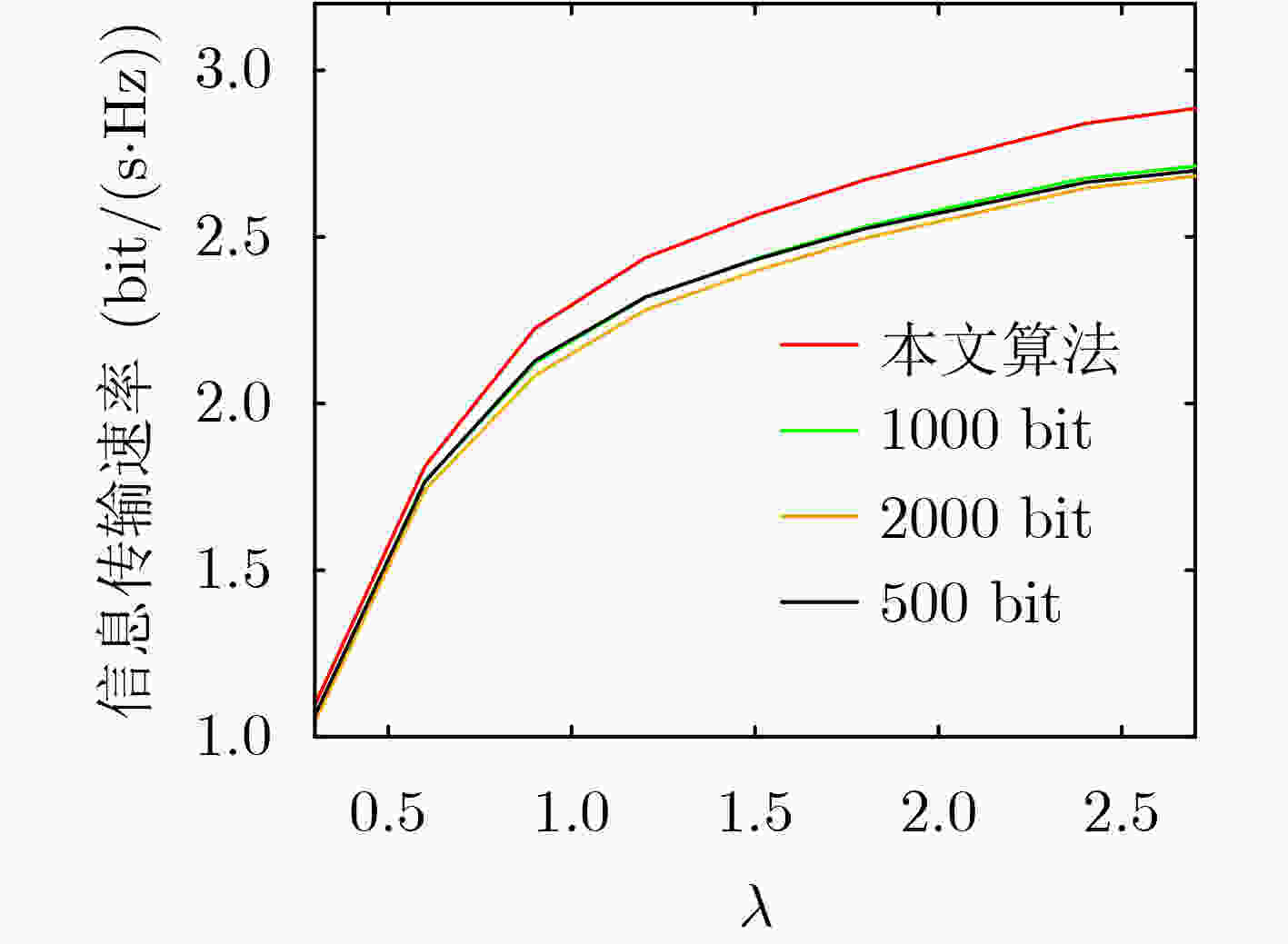
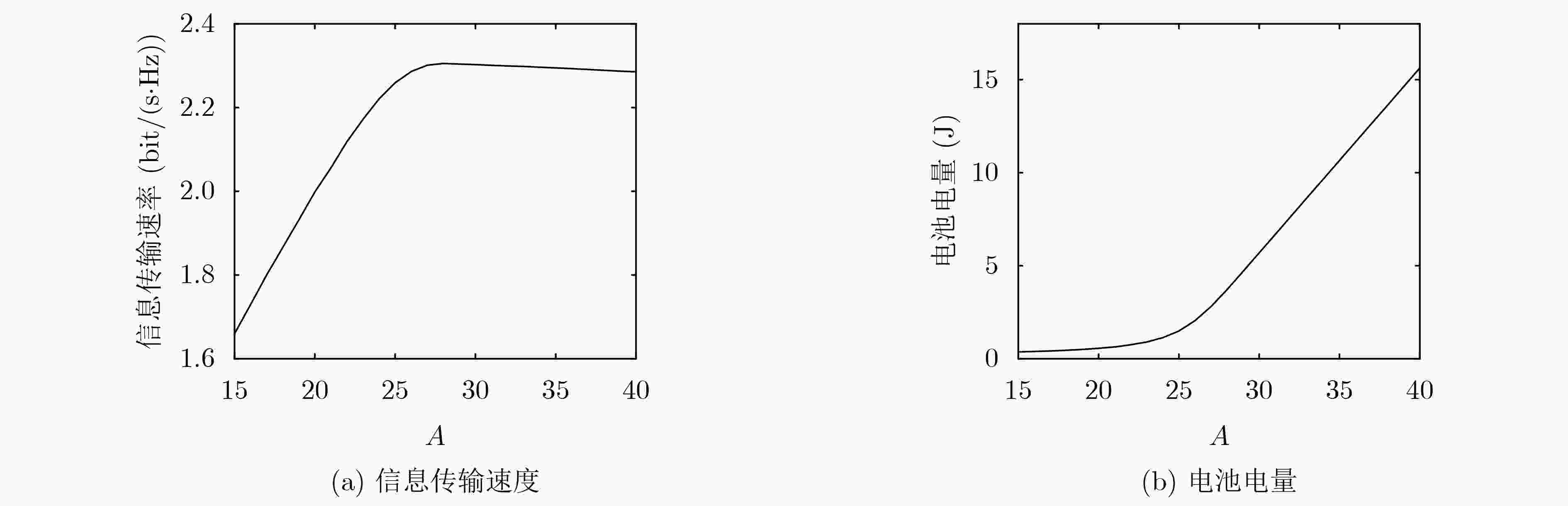
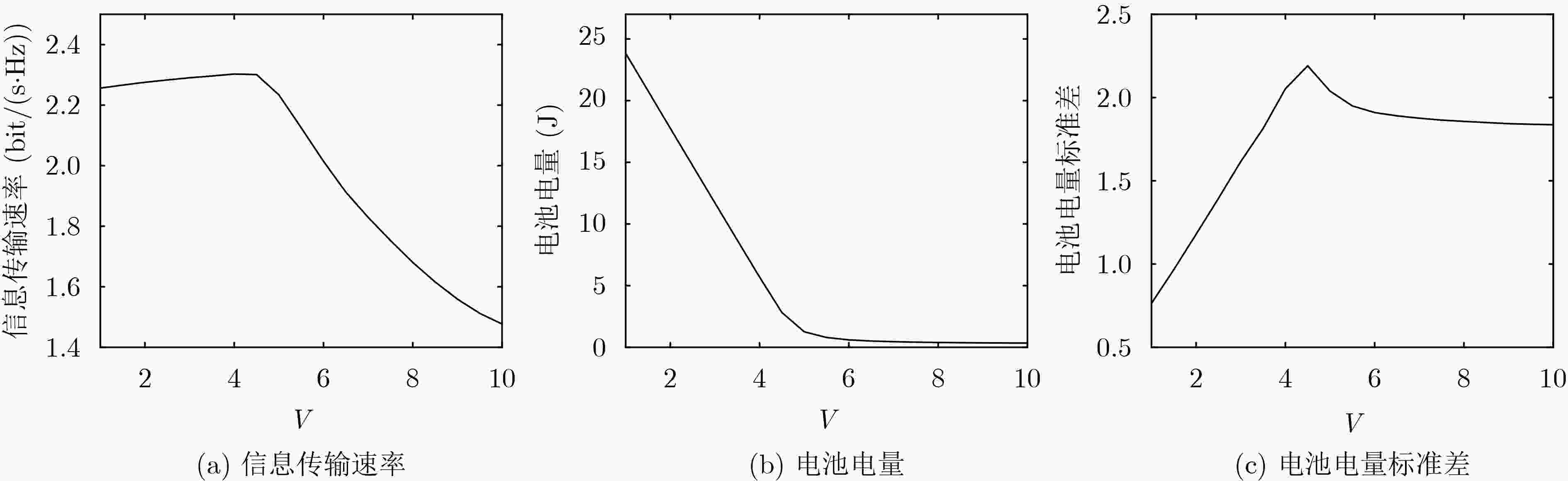
摘要: 针对源节点配备能量收集装置的点对点能量收集无线通信系统,该文以最大化长期平均传输速率为目标,提出一种基于Lyapunov优化框架的在线功率控制和自适应调制联合优化策略。由于能量到达和信道状态的随机性,优化问题是一个随机优化问题。利用Lyapunov优化框架将电池操作和可用能量约束下的长期时间优化问题转化为每时隙以虚队列“漂移加惩罚”最小化为目标的发送功率、调制方式和帧长的联合优化问题,并求解。该算法仅依赖当前的电池状态和信道状态信息做出决策,计算复杂度低,实用性强。仿真结果显示,所提算法通过联合优化发送功率、调制方式和帧长,能够高效地利用收集的能量,适应信道变化,长期平均实际可达的信息传输速率要明显优于贪婪和半功率算法,即使相比较以信道容量最大化为目标的离线注水算法和其他对比算法,在实际可达的信息传输速率上也有优势。
-
关键词:
- 能量收集 /
- 功率控制 /
- 自适应调制 /
- Lyapunov优化
Abstract: For a point-to-point energy harvesting wireless communication system equipped with energy harvesting devices at the source node, to maximize the long-term average transmission rate, an online power control and adaptive modulation joint optimization strategy based on Lyapunov optimization framework is proposed. Due to the randomness of the energy arrival and the channel state, the optimization problem is a stochastic optimization problem. By using Lyapunov optimization framework, the long-term optimization problem under the constraints of battery operation and available energy is transformed into a joint optimization problem of the transmission power, the modulation mode and the frame length to minimize the virtual queue drift-plus-penalty" per time slot. The proposed algorithm only dependes on the current channel state and the battery state. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively utilize the harvested energy and adapt to the channel changes. The long-term average actual achievable information transmission rate is significantly better than the greedy and the half-power algorithm. Compared with the offline water filling algorithm and other comparison algorithms, both which aim at maximizing the channel capacity, the proposed algorithm also can achieve a higher actual transmission rate.-
Key words:
- Energy harvesting /
- Power control /
- Adaptive modulation /
- Lyapunov optimization
-
表 1 算法实现流程
设定参数:权重V,虚队列偏移量A; 输入:可选调制方案,初始电池电量Eb(0),搜索步长$ \delta $; 输出:最优调制方式M,帧长N,发送功率P(t); 在时隙t: (1) 观察系统状态:$ h(t) $,$ X(t) $; (2) for M=1,2,3,4,5,6 do %给定M下优化$P(t), N$,目
标函数为$ J(P(t),N|M) $(3) if $ X(t) \ge 0 $ (4) $ P(t) = \min \left( {{P_{{\text{d}},\max }},{E_{\text{S}}}(t)/\Delta t} \right) $; (5) 由式(7)得到Peb; (6) 由式(30)得到N; (7) else (8) 将$ \frac{{\partial J(P(t),N|M)}}{{\partial N}} = 0 $中的Peb看成已知数,由
式(30)得到$ N(P(t)) $;(9) 将$ N(P(t)) $代入目标函数中,在[0, Pd,max]内以
$ \delta $为步长搜索使目标函数最大化的P(t);(10) 由式(7)得到Peb; (11) 由式(30)得到N; (12) end if (13) end for (14) 计算所有M下各自最优$ \{ P(t),N\} $时的目标函数
$ J(P(t),M,N) $,选择目标函数最大的M及对应的
$ \{ P(t),N\} $;(15) if $ N \le {N_{{\text{CRC}}}} $ then (16) P(t)=0,$ {R_{\text{b}}}(t) = 0 $; (17) end if (18) return P(t),M,N; -
[1] KUMAR A, SINGH K, and BHATTACHARYA D. Green communication and wireless networking[C]. Proceedings of 2013 International Conference on Green Computing, Communication and Conservation of Energy, Chennai, India, 2013: 49–52. doi: 10.1109/ICGCE.2013.6823398. [2] ZHANG Hao, GUO Yongxin, ZHONG Zheng, et al. Cooperative integration of RF energy harvesting and dedicated WPT for wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2019, 29(4): 291–293. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2019.2902047 [3] ALTINEL D and KURT G K. Modeling of hybrid energy harvesting communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2019, 3(2): 523–534. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2019.2908086 [4] REZAEE M, MIRMOHSENI M, and AREF M R. Energy harvesting systems with continuous energy and data arrivals: The optimal offline and heuristic online algorithms[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(12): 3739–3753. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2621355 [5] OZEL O, TUTUNCUOGLU K, YANG Jing, et al. Transmission with energy harvesting nodes in fading wireless channels: Optimal policies[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(8): 1732–1743. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2011.110921 [6] WANG Zhe, AGGARWAL V, and WANG Xiaodong. Iterative dynamic water-filling for fading multiple-access channels with energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2015, 33(3): 382–395. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2391571 [7] WANG Zhe, AGGARWAL V, and WANG Xiaodong. Power allocation for energy harvesting transmitter with causal information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2014, 62(11): 4080–4093. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2014.2357430 [8] BAI Qing, AMJAD R A, and NOSSEK J A. Average throughput maximization for energy harvesting transmitters with causal energy arrival information[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Shanghai, China, 2013: 4232–4237. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2013.6555257. [9] 黄晓舸, 樊伟伟, 曹春燕, 等. 小蜂窝网络中不活跃用户的最优能量效率资源分配方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 637–644. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190303HUANG Xiaoge, FAN Weiwei, CAO Chunyan, et al. Energy efficient resource allocation scheme based on inactive users in small cell networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 637–644. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190303 [10] AMIRNAVAEI F and DONG Min. Online power control optimization for wireless transmission with energy harvesting and storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(7): 4888–4901. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2548459 [11] DONG Min, LI Wen, and AMIRNAVAEI F. Online joint power control for two-hop wireless relay networks with energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(2): 463–478. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2768040 [12] 雷维嘉, 宋海娜, 谢显中. 高阶QAM调制下基于对数似然比门限的自适应解调方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(6): 1305–1312. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160821LEI Weijia, SONG Haina, and XIE Xianzhong. Adaptive demodulation scheme of high order QAM based on log-likelihood ratio threshold[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(6): 1305–1312. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160821 [13] MA Rui and ZHANG Wei. Adaptive MQAM for energy harvesting wireless communications with 1-bit channel feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(11): 6459–6470. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2455494 [14] LI Mingyu, ZHAO Xiaohui, LIANG Hui, et al. Deep reinforcement learning optimal transmission policy for communication systems with energy harvesting and adaptive MQAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5782–5793. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2911544 [15] QIU Chengrun, HU Yang, CHEN Yan, et al. Lyapunov optimization for energy harvesting wireless sensor communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(3): 1947–1956. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2817590 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
