Low Complexity Two-Dimensional Direction Of Arrival Estimation Using Wideband Uniform Concentric Spherical Arrays
-
摘要: 该文提出一种基于宽带均匀同心球阵列(UCSA)的2维波达方向(2D-DOA)低复杂度估计算法。该方法将宽带UCSA输出信号转换为相位模式,并对其进行频率补偿,实现近似频率不变(FI)特性,从而降低宽带信号处理的计算复杂度。为了进一步降低2D-DOA估计的计算复杂度,该文提出基于FI-UCSA的降维多重信号分类(MUSIC)算法。该方法将相位模式导向向量分解为方位角和仰角相关的两个矩阵,从而把2维搜索问题简化为1维(1D)搜索,实现降维优化并降低计算复杂度。仿真结果表明,该算法计算复杂度相较于2维MUSIC算法得到了极大的降低,并且在估计精度和分辨率上均稍有改善。
-
关键词:
- 二维波达方向估计 /
- 频率不变 /
- 均匀同心球阵列 /
- 降维多重信号分类算法
Abstract: A low complexity Two-Dimensional Direction Of Arrival (2D-DOA) estimation algorithm using wideband Uniform Concentric Spherical Arrays (UCSA) is proposed in this paper. The output signals of the wideband UCSA are firstly converted to phase mode signals, which are then compensated by filters to achieve Frequency Invariant (FI) characteristic. The FI characteristic of the array can reduce the computational complexity of the wideband signal processing. To reduce further the complexity of 2D-DOA estimation, a reduced-dimension MUltiple SIgnal Classification (MUSIC) algorithm using FI-UCSA is proposed. The equivalent steering vector of the phase mode signal is decomposed into two matrices, which are related to azimuth and elevation angles, respectively. The 2D MUSIC is then simplified to One-Dimensional (1D) search, which optimizes DOA estimation in reduced dimension and substantially lower the computation complexity. Simulation results show that the computational complexity of the proposed algorithm is greatly reduced compared with the 2D MUSIC algorithm. In addition, the estimation accuracy and the resolution are slightly improved. -
表 1 计算复杂度随相位模式总个数
$b$ 的变化$b$ 25 49 81 121 RD MUSIC 2.26×107 1.24×108 4.38×108 1.19×109 2D MUSIC 7.29×109 2.95×1010 8.24×1010 1.86×1011 表 2 ISM与FIB计算复杂度对比
$b$ 25 49 81 FIB 2.26×107 1.24×108 4.38×108 ISM 4.52×109 2.48×1010 8.74×1010 RSS 1.29×108 5.79×108 1.85×109 基于阵列接收数据的修正算法 1.14×108 5.14×108 1.61×109 -
[1] 张家成, 邱天爽, 栾声扬, 等. 脉冲噪声下基于循环相关熵和稀疏重构的宽带信号DOA估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(11): 2587–2591. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190521ZHANG Jiacheng, QIU Tianshuang, LUAN Shengyang, et al. Wideband DOA estimation via cyclic correntropy and sparse reconstruction in the presence of impulsive noise[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(11): 2587–2591. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190521 [2] STOICA P and NEHORAI A. MUSIC, maximum likelihood, and Cramer-Rao bound[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(5): 720–741. doi: 10.1109/29.17564 [3] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 [4] ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276 [5] 王旭东, 仲倩, 闫贺, 等. 一种二维信号波达方向估计的改进多重信号分类算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2137–2142. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181090WANG Xudong, ZHONG Qian, YAN He, et al. An improved MUSIC algorithm for two dimensional direction of arrival estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2137–2142. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181090 [6] XU Haiyun, WANG Daming, BA Bin, et al. Direction-of-arrival estimation for both uncorrelated and coherent signals in coprime array[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 18590–18600. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2896979 [7] SAMAL S K and SUBUDHI B. New signal subspace approach to estimate the inter-area oscillatory modes in power system using TLS-ESPRIT algorithm[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2019, 13(18): 4123–4140. [8] SHAH S M, SAMAR R, KHAN N M, et al. Fractional-order adaptive signal processing strategies for active noise control systems[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 85(3): 1363–1376. doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-2765-6 [9] ZHANG Xiaofei, CHEN Weiyang, ZHENG Wang, et al. Localization of near-field sources: A reduced-dimension MUSIC algorithm[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(7): 1422–1425. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2837049 [10] 张铁峰, 吉波. 基于降维处理的MUSIC二维DOA估计算法[J]. 现代导航, 2018, 9(3): 196–199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7976.2018.03.007ZHANG Tiefeng and JI Bo. Two dimensional DOA estimation based on reduced-dimension MUSIC[J]. Modern Navigation, 2018, 9(3): 196–199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7976.2018.03.007 [11] 徐乐, 吴日恒, 张小飞. L阵基于降维MUSIC的二维DOA与频率估计[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(1): 1–8.XU Le, WU Riheng, and ZHANG Xiaofei. 2D-DOA and frequency estimation for L-shaped array via reduced-dimensional MUSIC[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(1): 1–8. [12] 徐正勤, 伍世虔, 刘清宇. 一种准确鲁棒的宽带信号DOA估计算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(11A): 376–380, 398.XU Zhengqin, WU Shiqian, and LIU Qingyu. Accurate and robust algorithm for broadband signal DOA estimation[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(11A): 376–380, 398. [13] WANG H and KAVEH M. Coherent signal-subspace processing for the detection and estimation of angles of arrival of multiple wide-band sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1985, 33(4): 823–831. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1985.1164667 [14] 孟子健, 王沛曌, 陈海华. 基于均匀同心圆阵列的近场宽带波束形成[J]. 压电与声光, 2020, 42(3): 428–432. doi: 10.11977/j.issn.1004-2474.2020.03.031MENG Zijian, WANG Peizhao, and CHEN Haihua. Near-field broadband beamforming based on uniform concentric circular array[J]. Piezoelectrics &Acoustooptics, 2020, 42(3): 428–432. doi: 10.11977/j.issn.1004-2474.2020.03.031 [15] WARD D B, KENNEDY R A, and WILLIAMSON R C. Theory and design of broadband sensor arrays with frequency invariant far-field beam patterns[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1995, 97(2): 1023–1034. doi: 10.1121/1.412215 [16] CHAN S C and PUN C K S. On the design of digital broadband beamformer for uniform circular array with frequency invariant characteristics[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Phoenix-Scottsdale, USA, 2002: 693–696. [17] CHEN H H and CHAN S C. Adaptive beamforming and DOA estimation using uniform concentric spherical arrays with frequency invariant characteristics[J]. The Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for Signal, Image, and Video Technology, 2007, 46(1): 15–34. doi: 10.1007/s11265-006-0005-x -





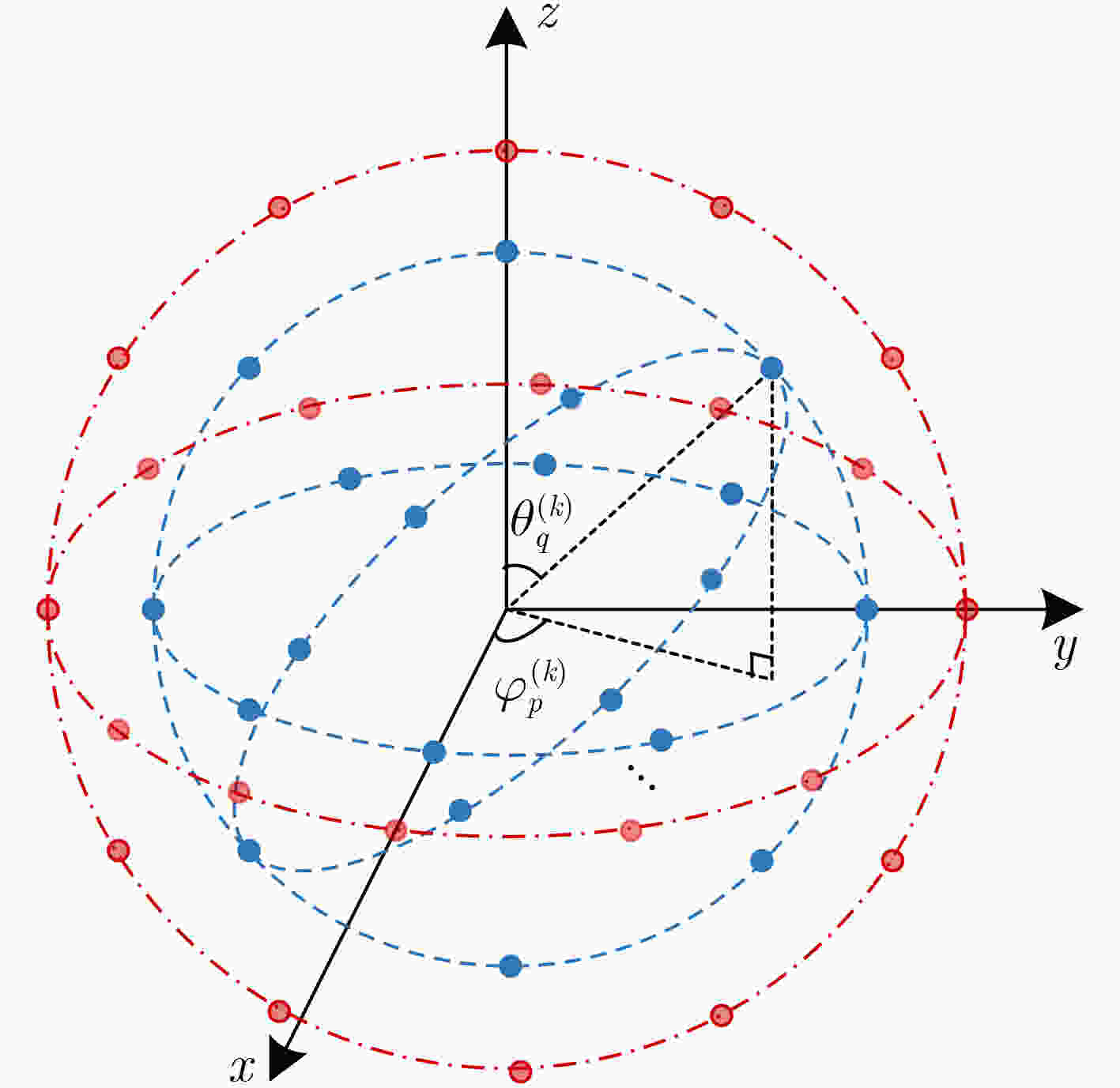
 下载:
下载:
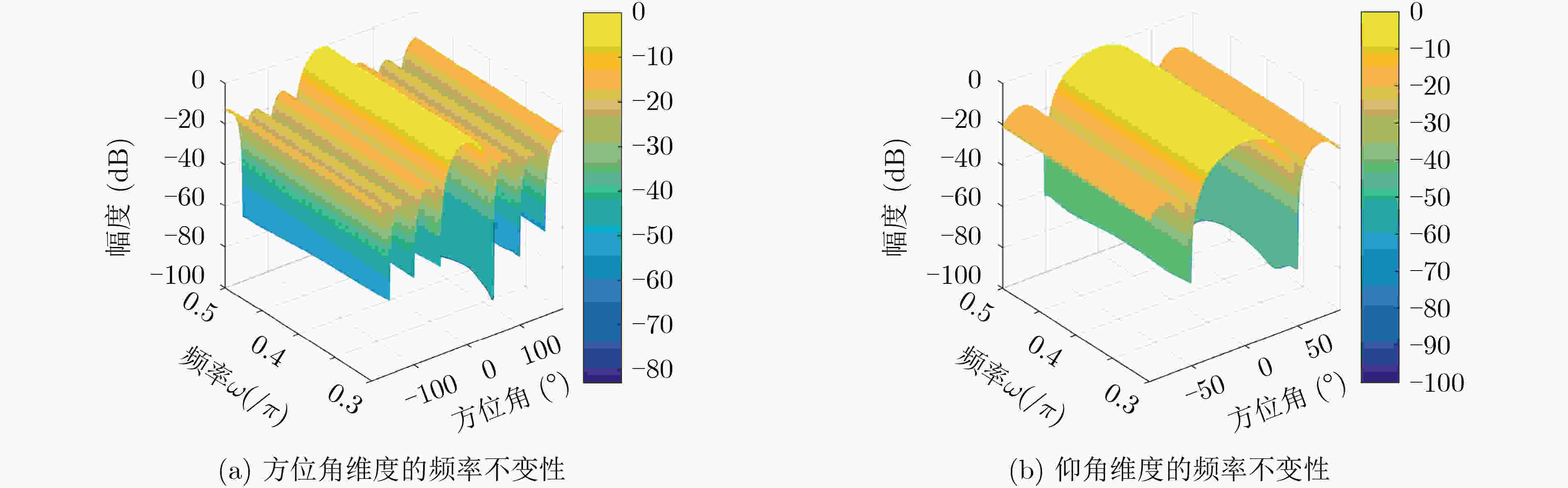
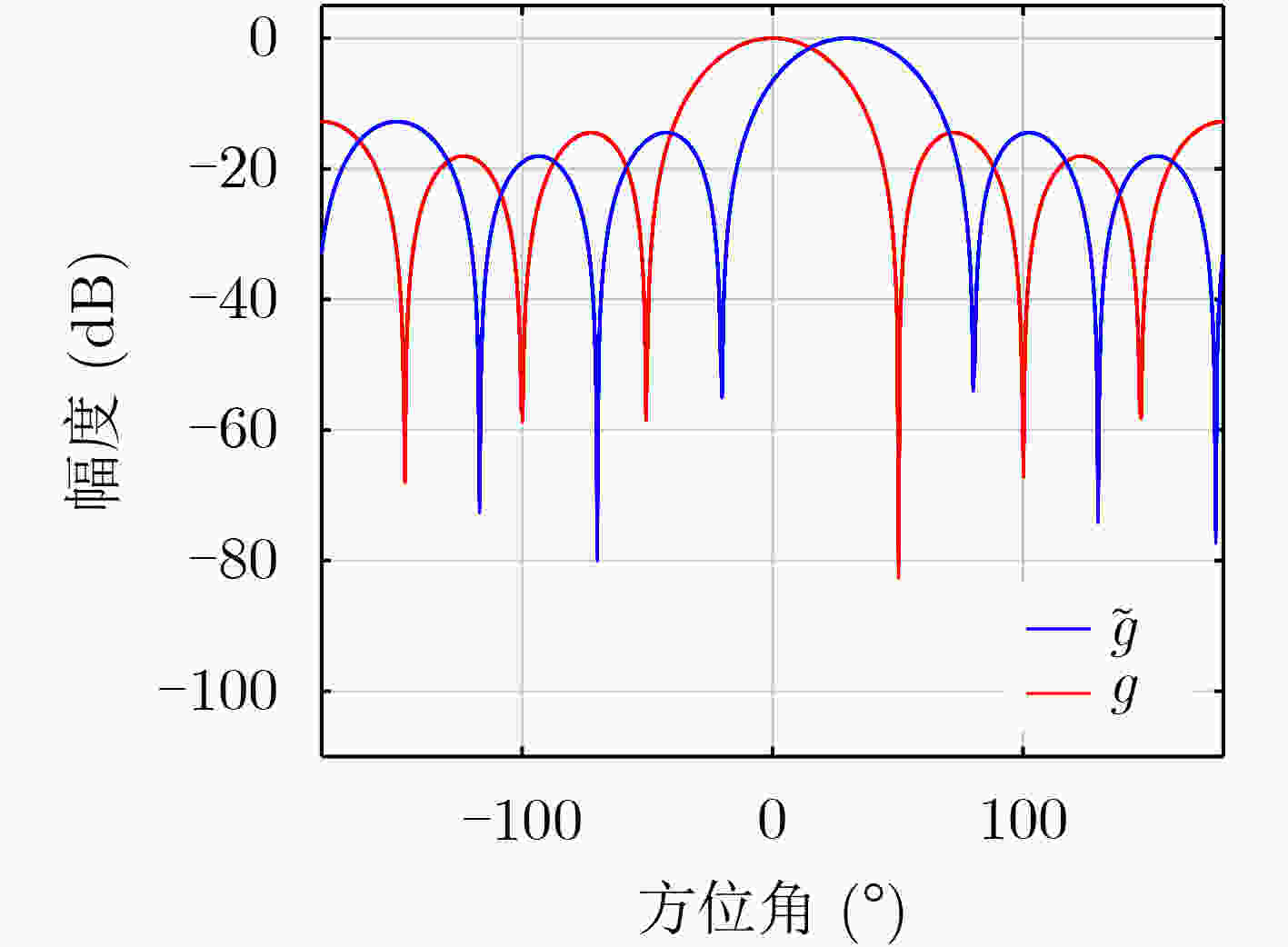
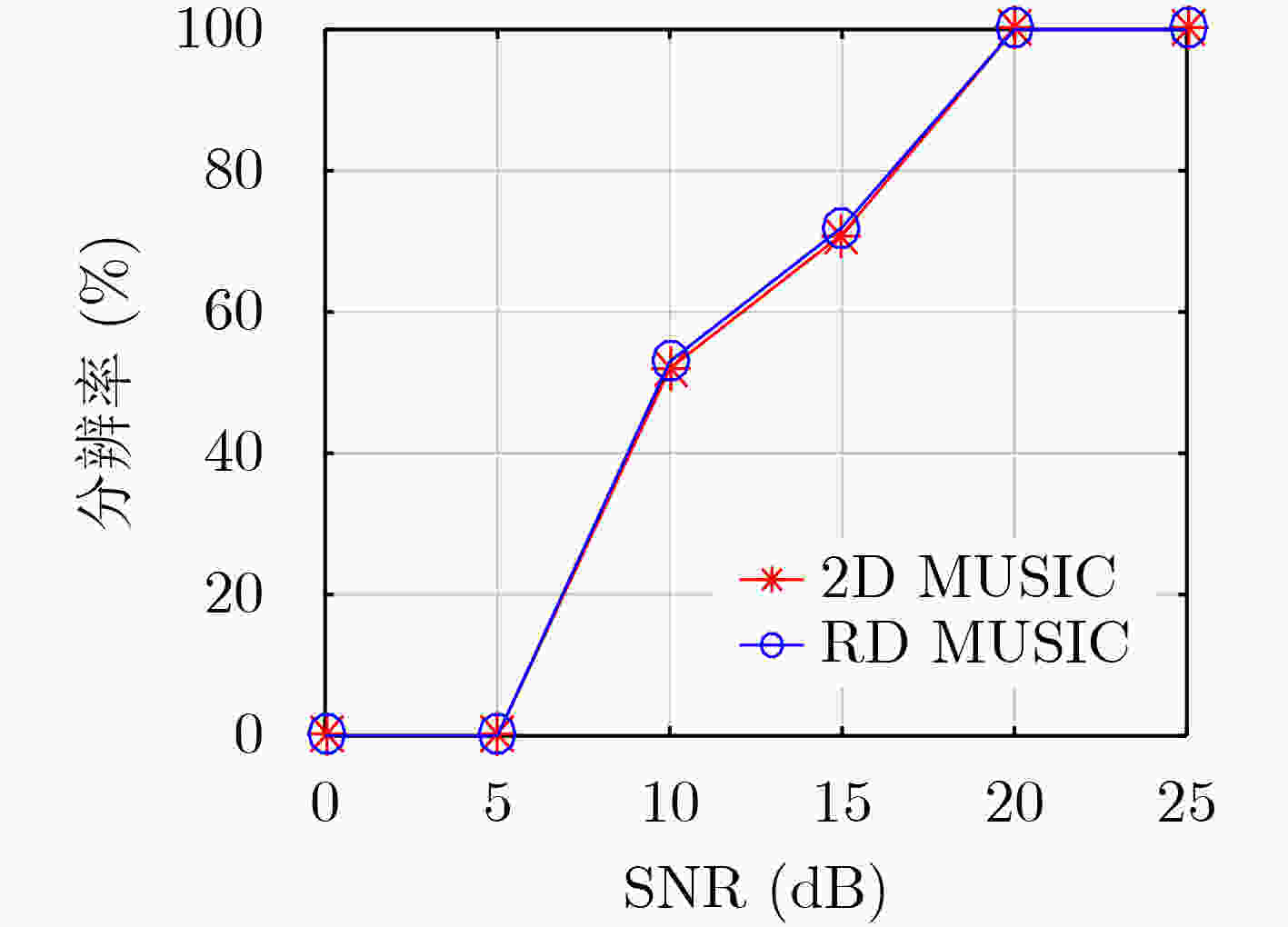

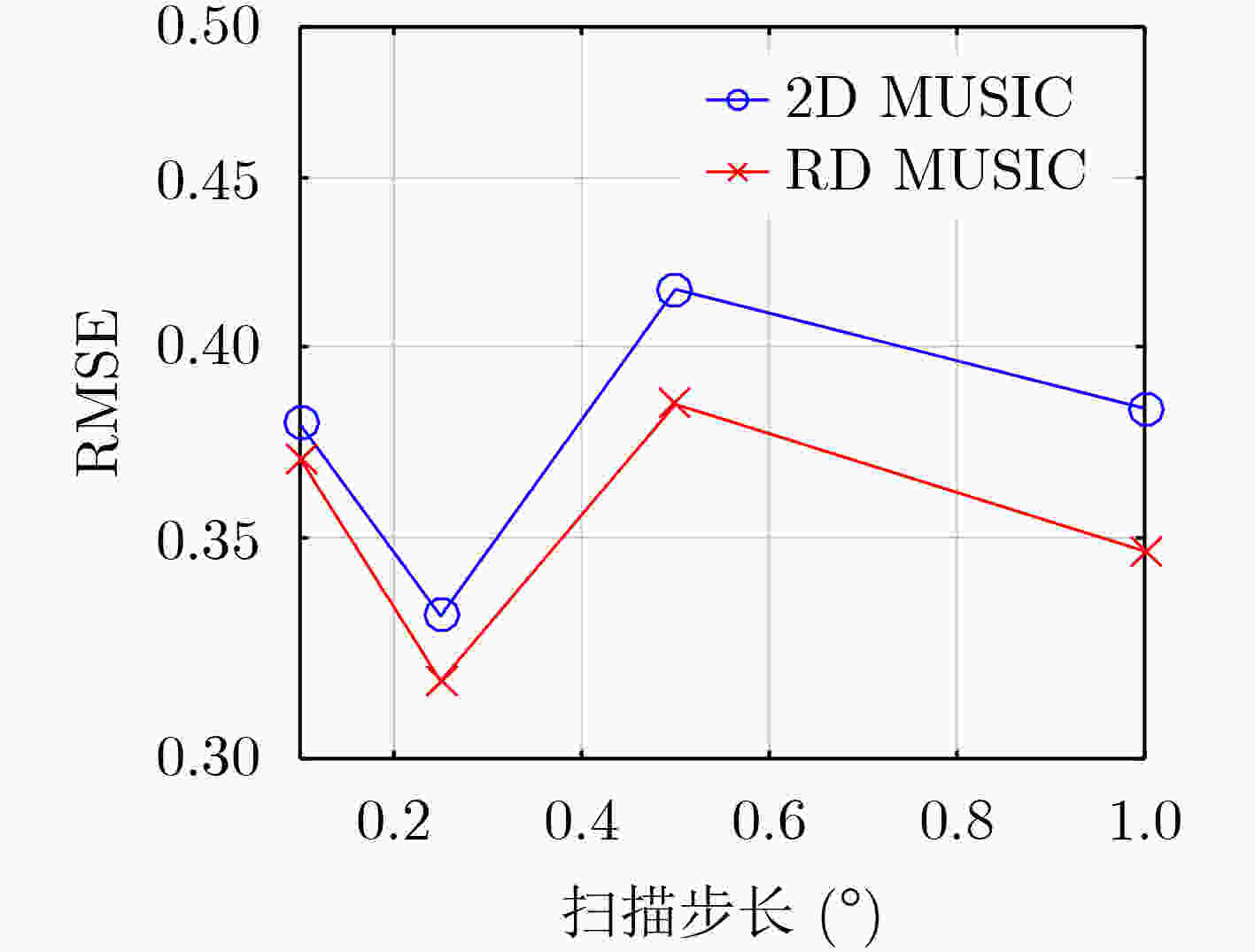
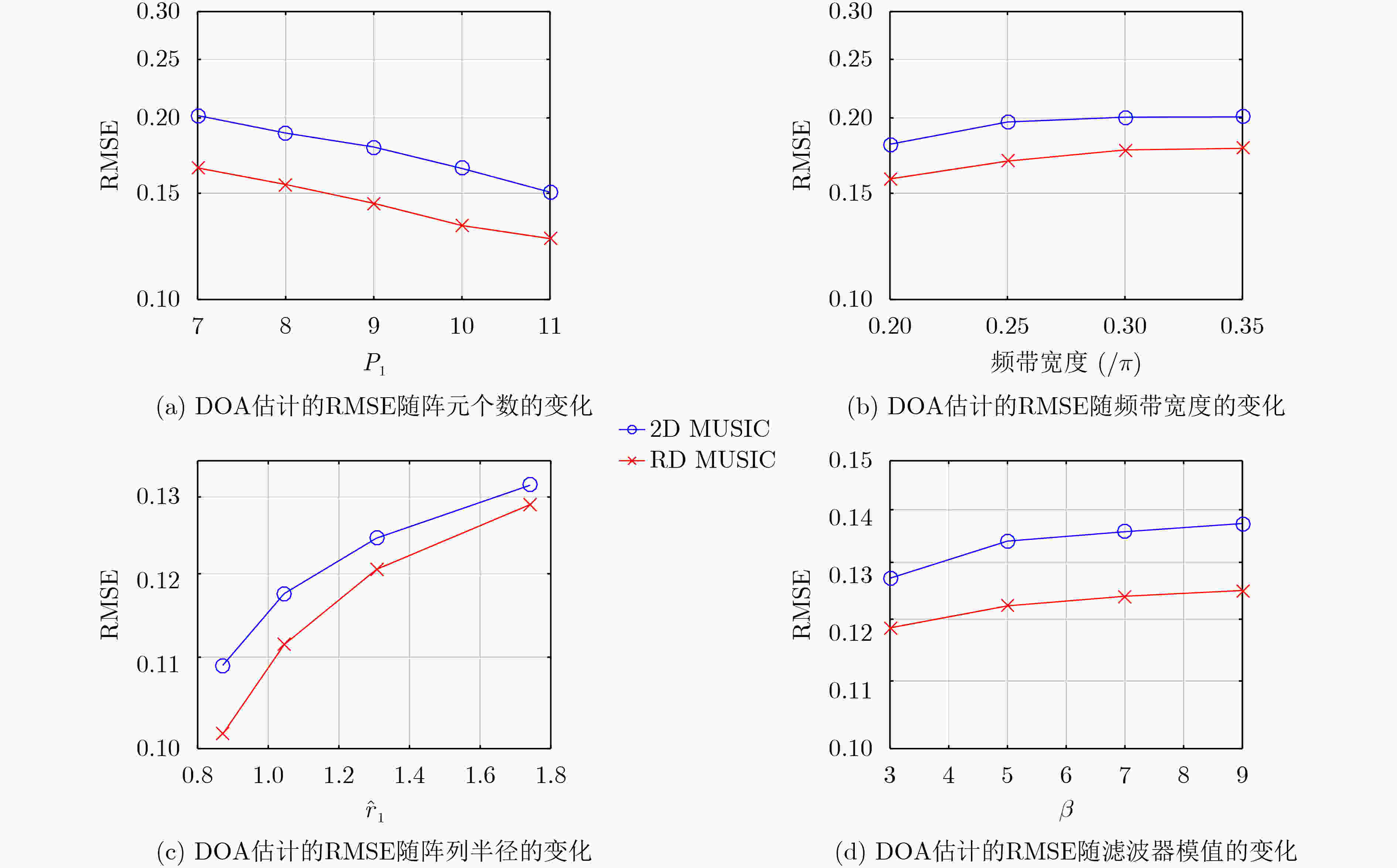



 下载:
下载:
