Method of Phase Filtering for Wide-Swath Interferometric Imaging Radar Altimeter Based on Total Variation
-
摘要: 宽幅干涉成像高度计采用双天线近天底角短基线干涉测高技术,实现对海洋亚中尺度现象的高时空分辨率与高精度观测。在反演海面高度(SSH)的过程中,干涉相位滤波处理是抑制随机相位噪声,保持相位边缘细节的重要环节。该文针对成像高度计干涉相位随机噪声方差在刈幅范围内分布不均匀的特点,基于宽幅干涉成像高度计相位模型,提出一种改进的总变分正则化滤波方法,可以有效抑制去平地后成像高度计的干涉相位噪声。通过仿真数据验证,滤波相位误差的标准差(STD)由0.32 rad降低至0.023 rad,且刈幅范围内STD最大偏差小于0.001 rad。改进的总变分滤波方法实现全刈幅干涉相位误差精度的均匀分布,较好地保持了分辨率和边缘信息,为海面高程精度的一致性提供有效保障。Abstract: The wide-swath interferometric imaging radar altimeter with short baseline and at near nadir angles will satisfy the requirement of high precision, high temporal and spatial resolution Sea Surface Height (SSH) for sub-mesoscale ocean features. In the process of retrieving sea level, interferometric phase filtering is an important part of suppressing random phase noise and maintaining the details of phase edges. The varying random noise of flattened phase will be attenuated effectively with total variation regularization filtering which based on the features of noise distribution along the cross-track direction for the altimeter. Simulation results show the STandard Deviation (STD) of the filtered phase error using the proposed method is reduced from 0.32 rad to 0.023 rad, and the maximum deviation is less than 0.001 rad within the swath. The distribution of the phase error accuracy using the proposed method is more homogeneous compared to traditional phase filtering methods. Simulation results also show the proposed method can preserve the resolution and edge information, which provides an effective guarantee for the consistency of sea surface elevation accuracy.
-
表 1 SWOT卫星任务参数
参数 值 轨道高度 890.5 km 工作频率 35.75 GHz 信号带宽 200 MHz 基线长度 10 m 天线尺寸 5×0.25 m 单侧视角 0.5~3.6° 观测刈幅 10~60 km -
[1] LI Zhijin, WANG Jinbo, and FU L L. An observing system simulation experiment for ocean state estimation to assess the performance of the SWOT mission: Part 1-A twin experiment[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124(7): 4838–4855. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014869 [2] D'ADDEZIO J M, SMITH S, JACOBS G A, et al. Quantifying wavelengths constrained by simulated SWOT observations in a submesoscale resolving ocean analysis/forecasting system[J]. Ocean Modelling, 2019, 135: 40–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2019.02.001 [3] MORROW R, FU L L, ARDHUIN F, et al. Global observations of fine-scale ocean surface topography with the surface water and ocean topography (SWOT) mission[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2019, 6: 232. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00232 [4] REN Lin, YANG Jingsong, DONG Xiao, et al. Preliminary evaluation and correction of sea surface height from Chinese Tiangong-2 interferometric imaging radar altimeter[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(15): 2496. doi: 10.3390/rs12152496 [5] LI Tingting, CHEN Kunshan, and LEE J S. Enhanced interferometric phase noise filtering of the refined InSAR filter[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(9): 1528–1532. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2951635 [6] WU Nan, FENG Dazheng, and LI Junxia. A locally adaptive filter of interferometric phase images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(1): 73–77. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2005.856703 [7] CHAO C F, CHEN Kunshan, and LEE J S. Refined filtering of interferometric phase from InSAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(12): 5315–5323. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2234467 [8] SICA F, COZZOLINO D, ZHU Xiaoxiang, et al. InSAR-BM3D: A nonlocal filter for SAR interferometric phase restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3456–3467. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2800087 [9] YOU Yanan, WANG Rui, and ZHOU Wenli. An optimized filtering method of massive interferometric SAR data for urban areas by online tensor decomposition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(16): 2582. doi: 10.3390/rs12162582 [10] ZHENG Yujie, ZEBKER H, and MICHAELIDES R. A new decorrelation phase covariance model for noise reduction in unwrapped interferometric phase stacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 54(12): 10126–10135. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3050087 [11] HENSLEY S. An analytic expression for the phase noise of the Goldstein-Werner filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6499–6516. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2906549 [12] FATHI J, GHZALA K, ELKHARROUBA E, et al. Differential synthetic aperture radar interferometric phase map despeckling in discrete Riesz wavelets domain[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2020, 14(4): 044520. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.14.044520 [13] JEDLOVEC G. Advances in Geoscience and Remote Sensing[M]. Vukovar: In-Teh, 2009: 419–440. [14] LEE C O, NAM C, and PARK J. Domain decomposition methods using dual conversion for the total variation minimization with L1 fidelity term[J]. Journal of Scientific Computing, 2019, 78(2): 951–970. doi: 10.1007/s10915-018-0791-x [15] YU Meiting, DONG Ganggang, FAN Haiyan, et al. SAR target recognition via local sparse representation of multi-manifold regularized low-rank approximation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 211. doi: 10.3390/rs10020211 [16] LUO Xiaomei, WANG Xiangfeng, SUO Zhiyong, et al. Efficient InSAR phase noise reduction via total variation regularization[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(8): 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s11432-014-5244-z [17] XU Gang, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. Sparse regularization of interferometric phase and amplitude for InSAR image formation based on Bayesian representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 2123–2136. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2355592 [18] HUANG H Y H, TIAN L, ZHANG Z, et al. Path-independent phase unwrapping using phase gradient and total-variation (TV) denoising[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(13): 14075–14089. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.014075 [19] SONG Huina and SUN Yingfei. InSAR phase filtering using spatially adapted total generalized variation[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 8(4): 370–379. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2016.1268731 [20] ROSEN P A, HENSLEY S, JOUGHIN I R, et al. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2000, 88(3): 333–382. doi: 10.1109/5.838084 [21] DONG Xiao and ZHANG Yunhua. Non-uniform phase filter for Tiangong-2 interferometric imaging radar altimeter[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(19): 5610–5613. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0430 [22] ESTEBAN F D, POLLARD B V P, and ABELSON R. SWOT project mission performance and error budget[R]. JPL, NASA, 2017. [23] VANDEMARK D, CHAPRON B, SUN J, et al. Ocean wave slope observations using radar backscatter and laser altimeters[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2004, 34(12): 2825–2842. doi: 10.1175/JPO2663.1 [24] FREILICH M H and CHALLENOR P G. A new approach for determining fully empirical altimeter wind speed model functions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1994, 99(C12): 25051–25062. doi: 10.1029/94JC01996 [25] BIOUCAS-DIAS J M and FIGUEIREDO M A T. A new TwIST: Two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithms for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(12): 2992–3004. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.909319 [26] BRAS N B, BIOUCAS-DIAS J, MARTINS R C, et al. An alternating direction algorithm for total variation reconstruction of distributed parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(6): 3004–3016. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2188033 [27] ZHANG Yunhua, DONG Xiao, SHI Xiaojin, et al. Demonstration of ocean target detection by Tiangong-2 interferometric imaging radar altimeter[C]. 2018 22nd International Microwave and Radar Conference (MIKON), Poznan, Poland, 2018: 261–264. -





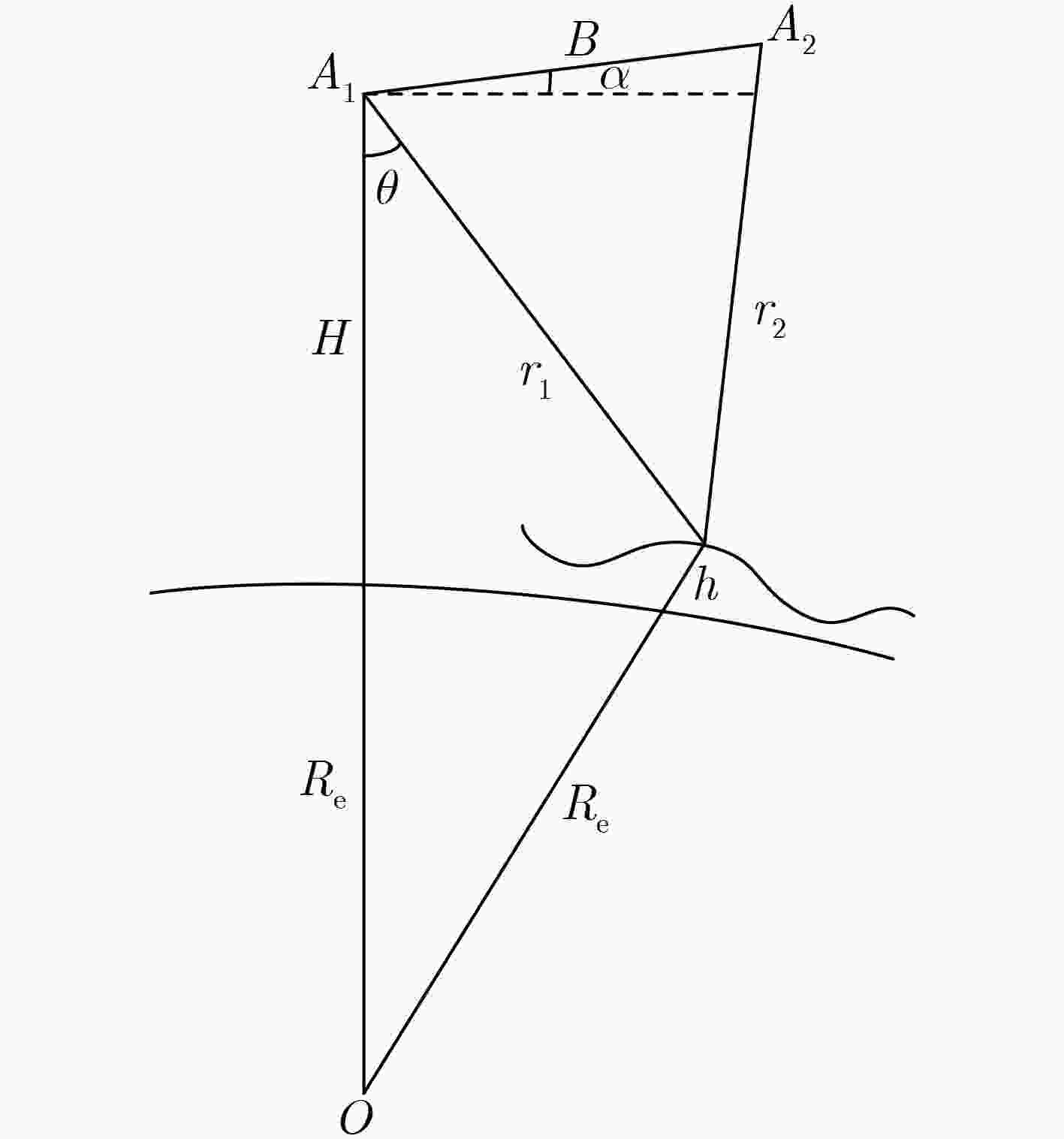
 下载:
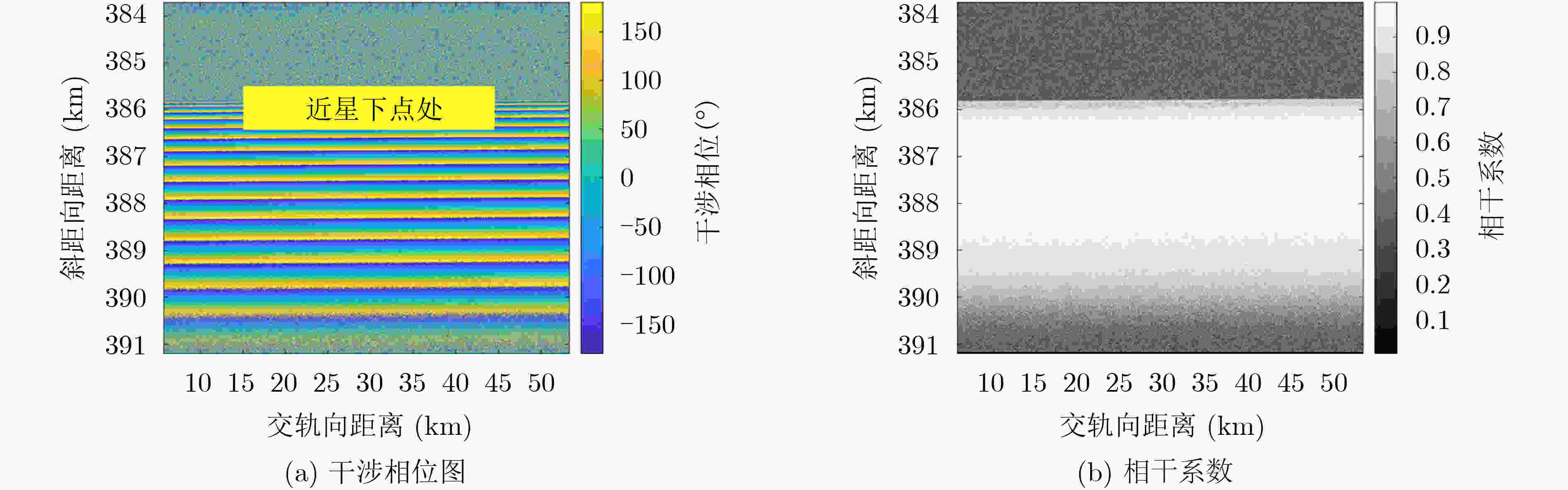
下载:
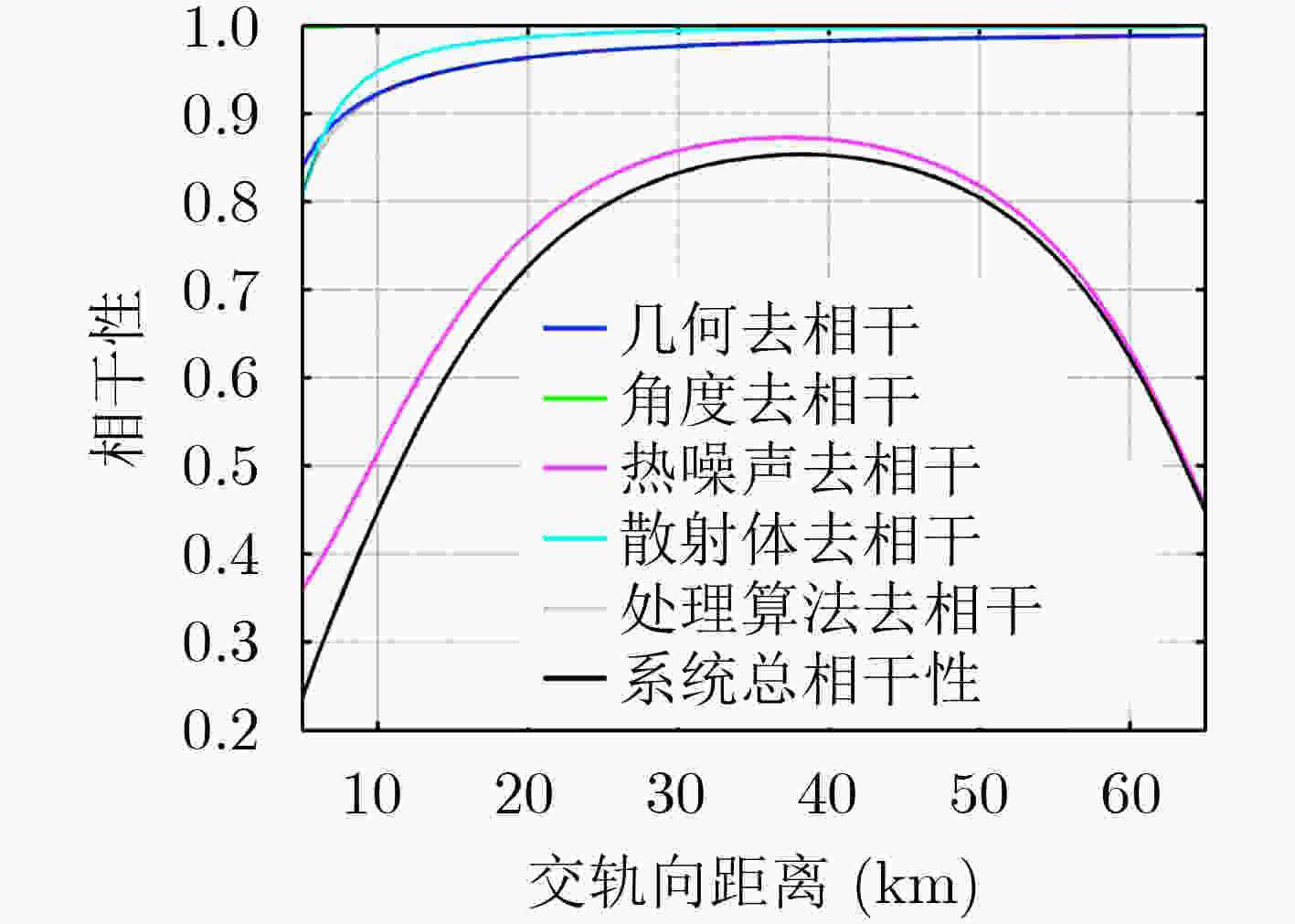
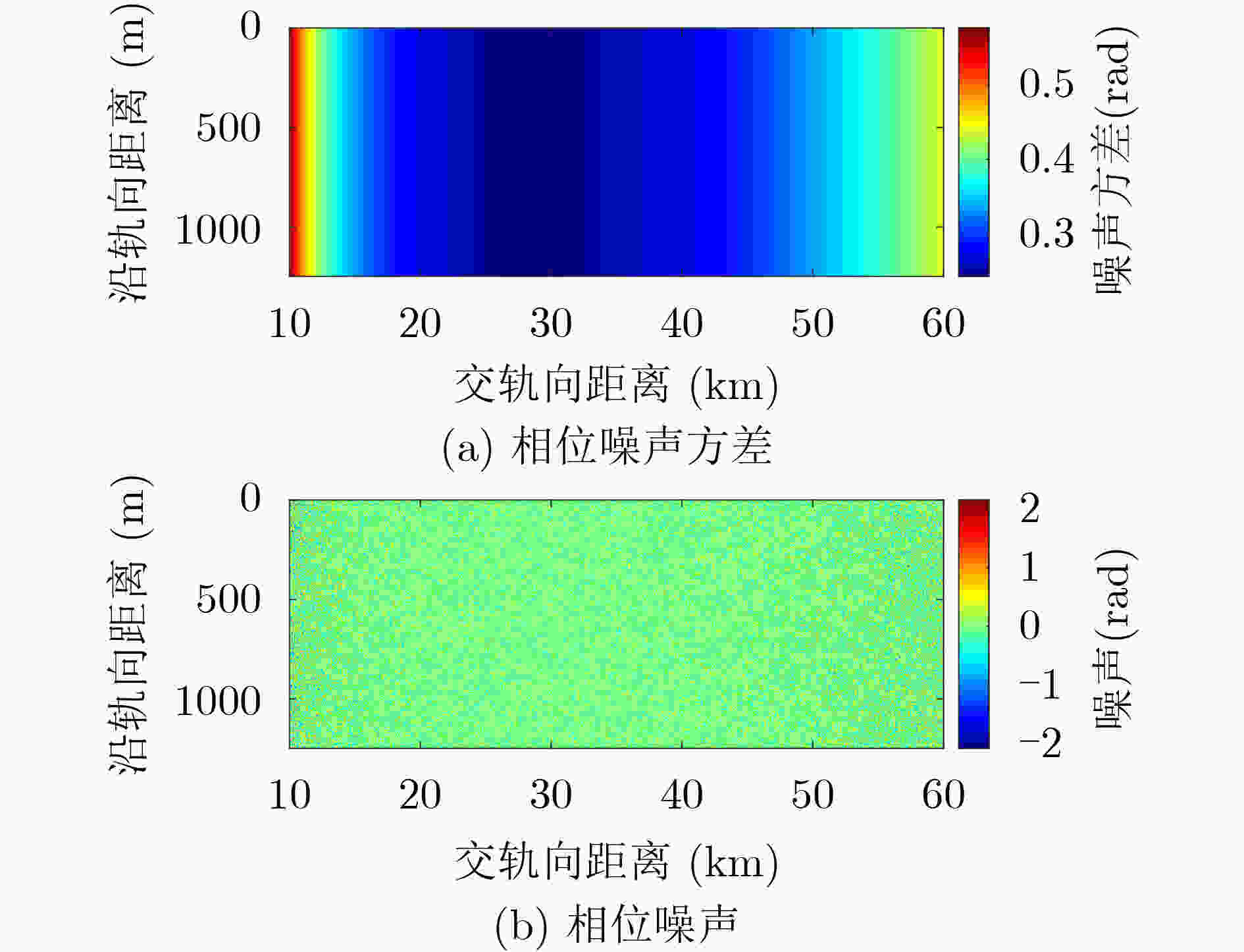
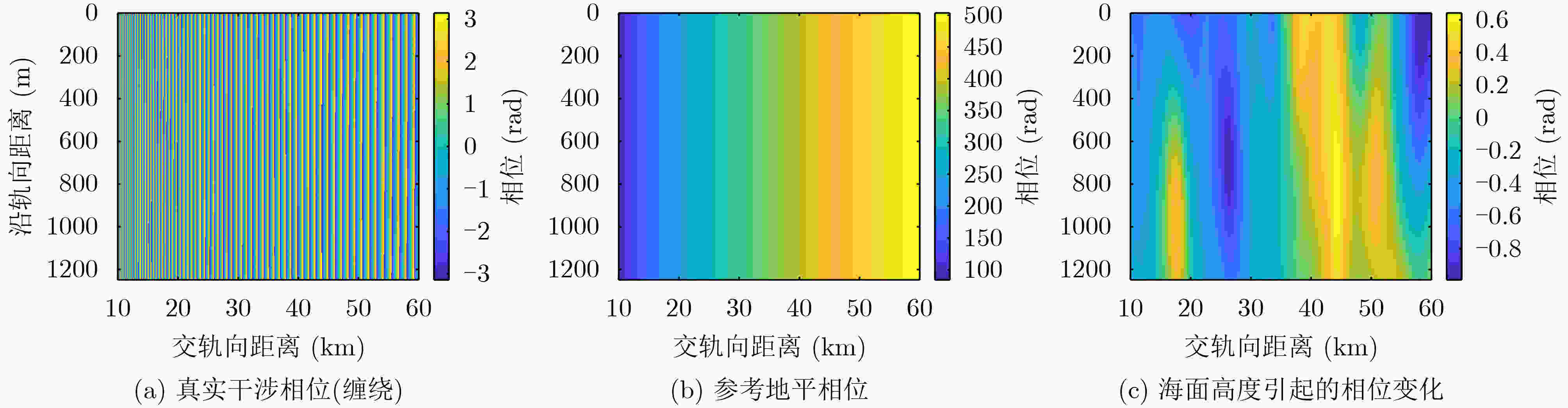
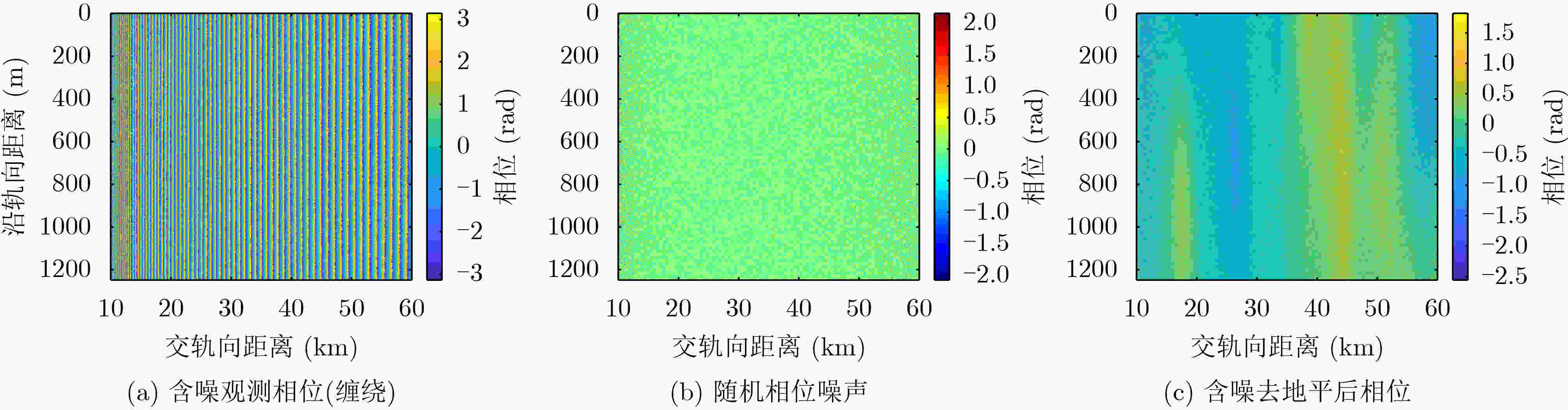

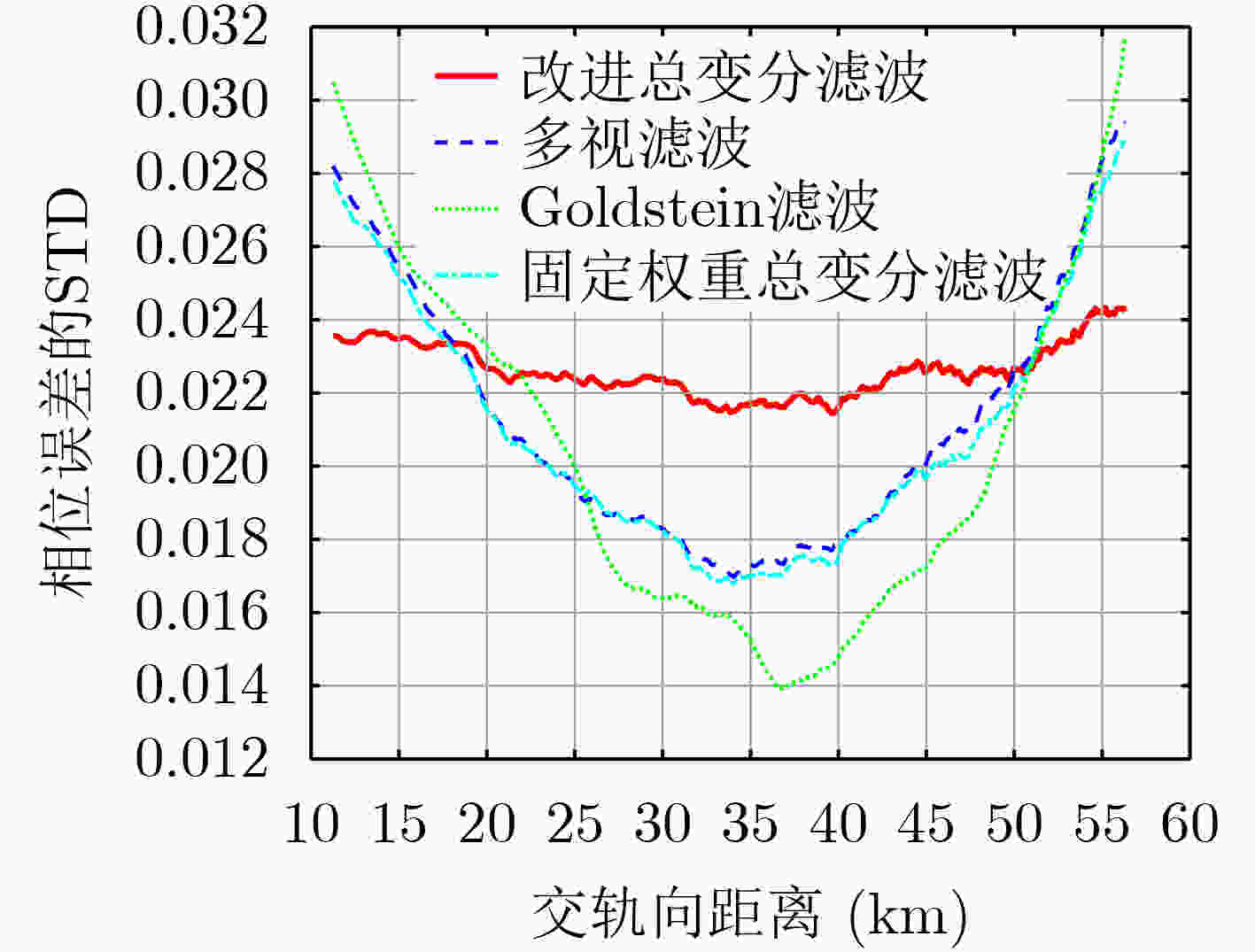

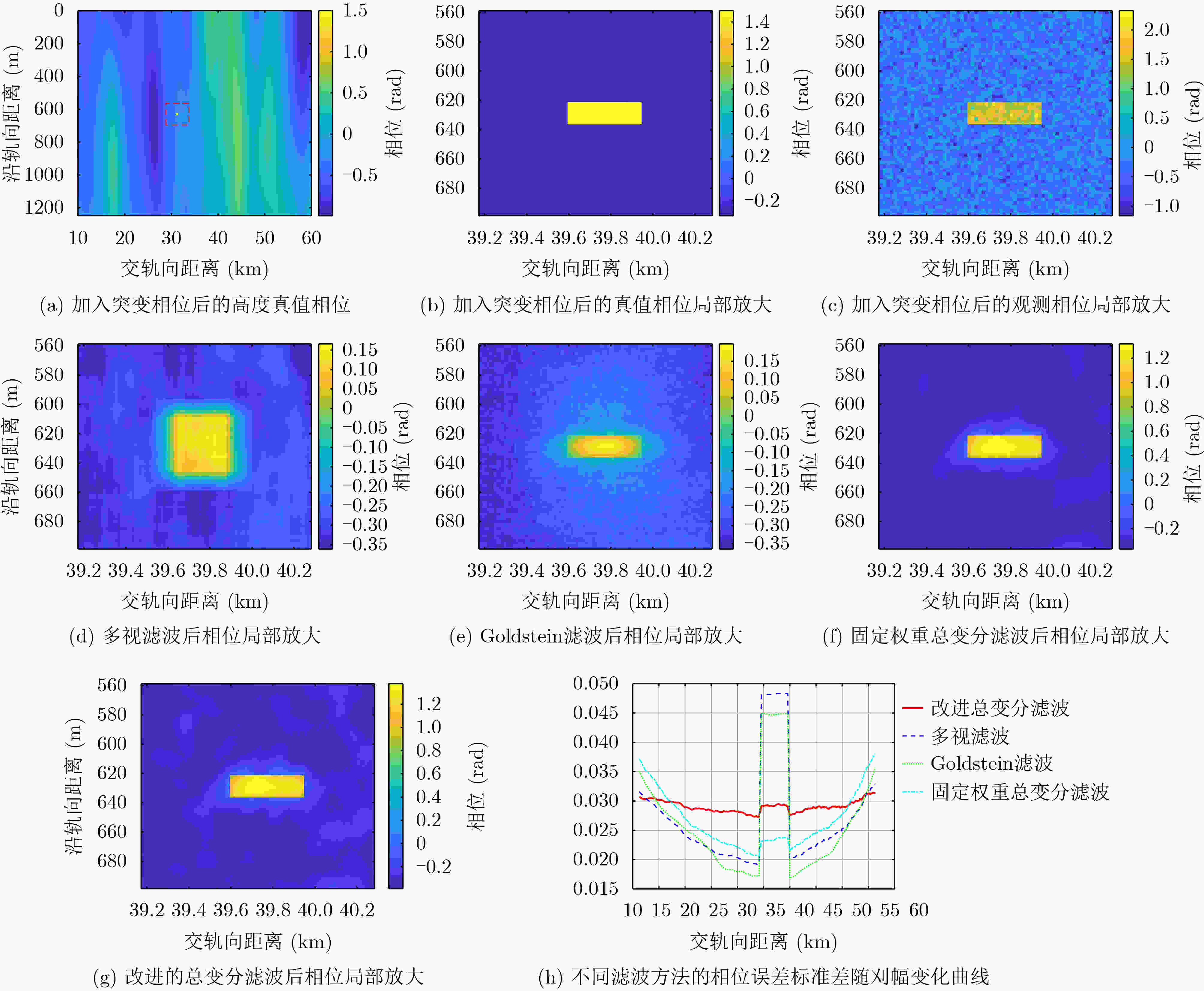


 下载:
下载:
