Salient Object Detection via Feature Permutation and Space Activation
-
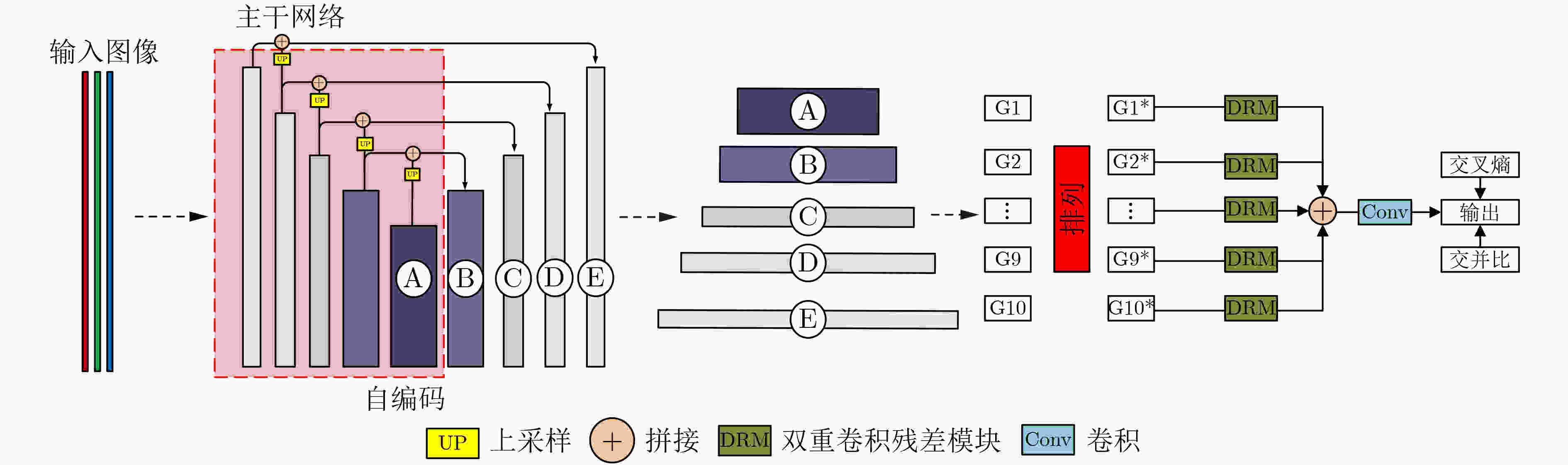
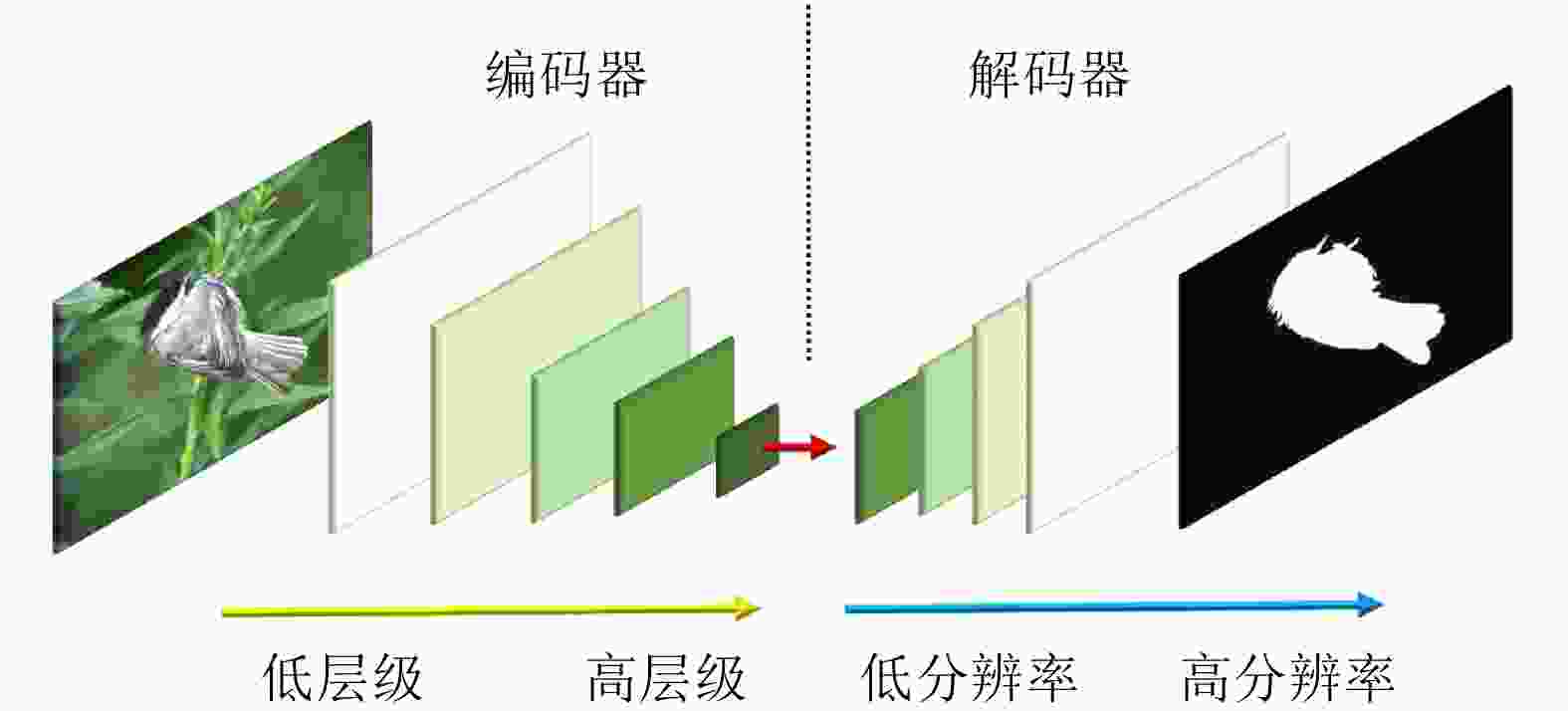
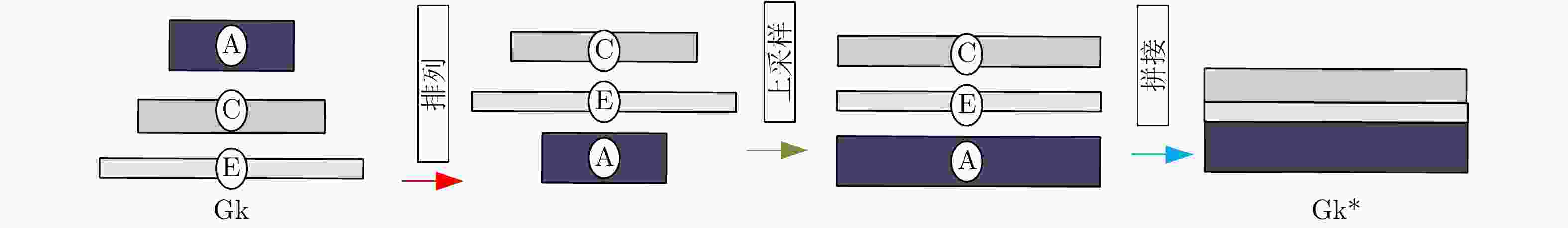
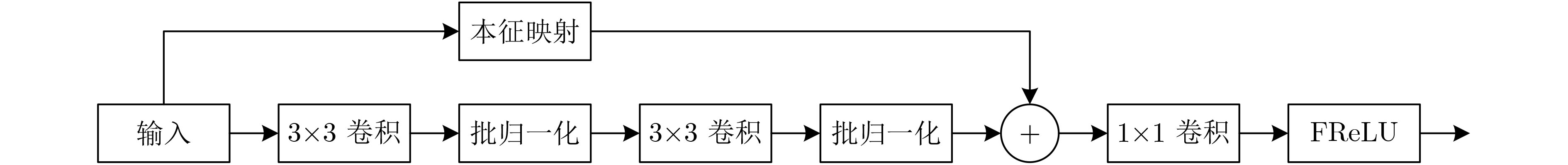
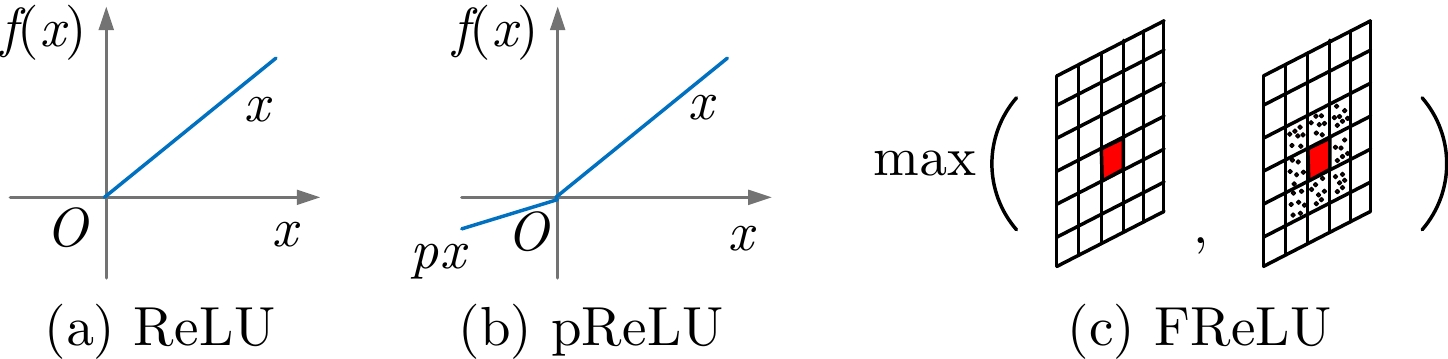
摘要: 显著物体检测目前在计算机视觉领域中非常重要,如何处理不同尺度的特征信息成为能否获得优秀预测结果的关键。该文有两个主要贡献,一是提出一种用于显著目标检测的特征排列方法,基于自编码结构的卷积神经网络模型,利用尺度表征的概念将特征图进行分组和重排列,以获得一个更加泛化的显著目标检测模型和更加准确的显著目标预测结果;二是在输出部分利用了双重卷积残差和FReLU激活函数,抓取更全面的像素信息,完成空间信息上的激活。利用两种算法的特点融合作用于模型的学习训练。实验结果表明,将该文算法与主流的显著目标检测算法进行比较,在所有评测指标上都达到了最优的效果。Abstract: Salient object detection occupies an important position in the field of computer vision. How to deal with feature information on different scales becomes the key to obtain excellent prediction results. Two contributions are made in this article. On the one hand, a feature permutation method for salient object detection is proposed. The proposed method is a convolutional neural network based on the self-encoding network structure. It uses the concept of scale representation proposed in this paper to group and permute the multiscale feature maps of different layers in the neural network. So the proposed method obtains a more generalized salient object detection model and a more accurate prediction results about salient object detection. On the other hand, the proposed method adopts the double-conv residual and FReLU activation for the output of the model, so that more complete pixel information could be obtained, and the spatial information is also activated as well. The characteristics of the two algorithms are fused to act on the learning and training of the model. Finally, the proposed algorithm is compared with the mainstream salient object detection algorithms, and the experimental results show that the proposed algorithm obtains the best results from all.
-
Key words:
- Salient object detection /
- Multi-scale /
- Feature permutation /
- Space activation
-
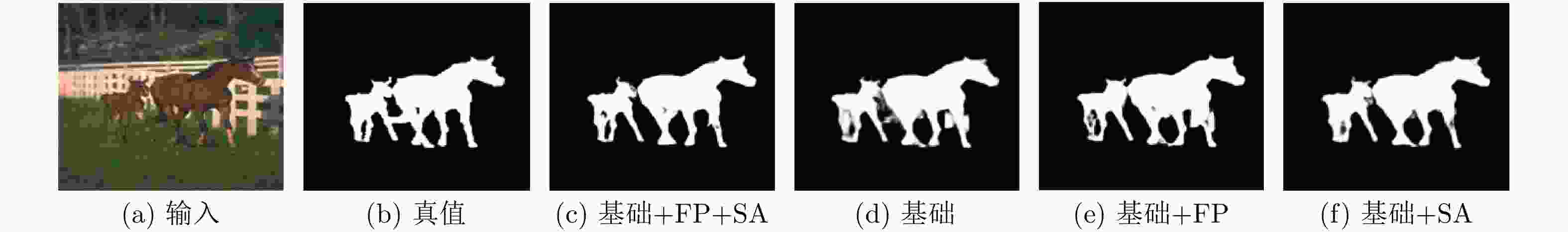
表 1 特征排列和空间激活对模型的影响对比研究
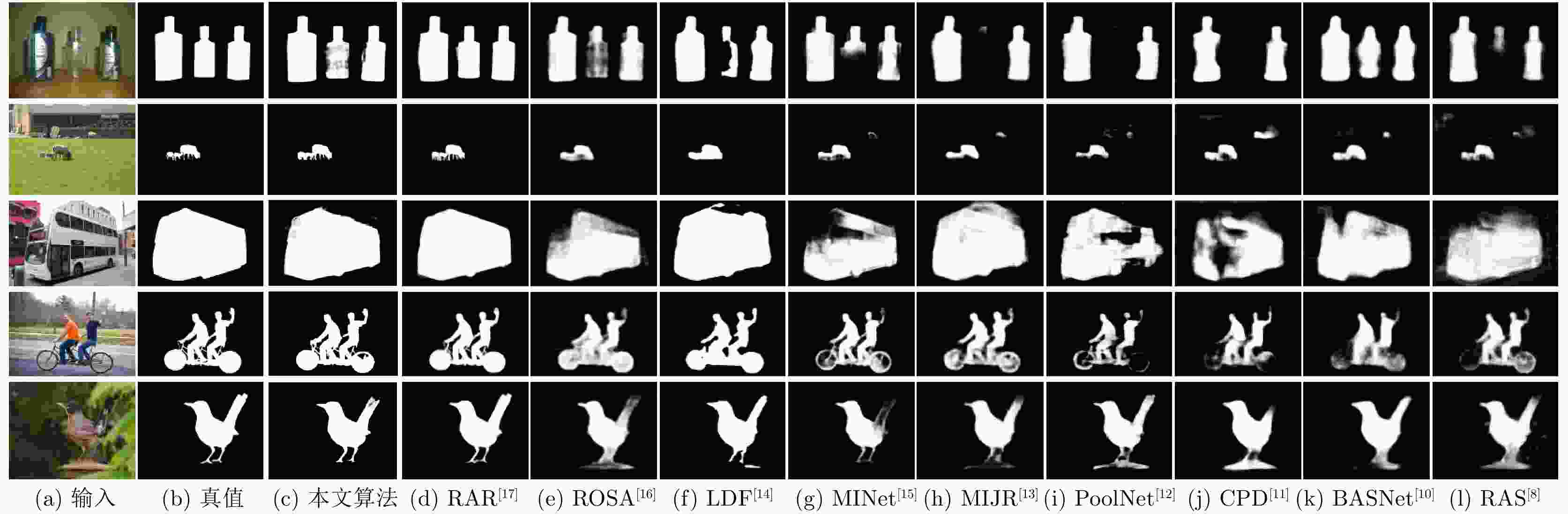
基础 特征排列 空间激活 BCE loss IOU loss maxF↑ S-Measure↑ MAE↓ √ √ √ 0.859 0.833 0.078 √ √ √ √ 0.874 0.852 0.061 √ √ √ √ 0.869 0.846 0.072 √ √ √ √ 0.889 0.871 0.049 √ √ √ √ 0.884 0.873 0.050 √ √ √ √ √ 0.892 0.877 0.044 表 2 本文算法和其他主流显著物体检测算法在不同数据集上数据指标对比研究
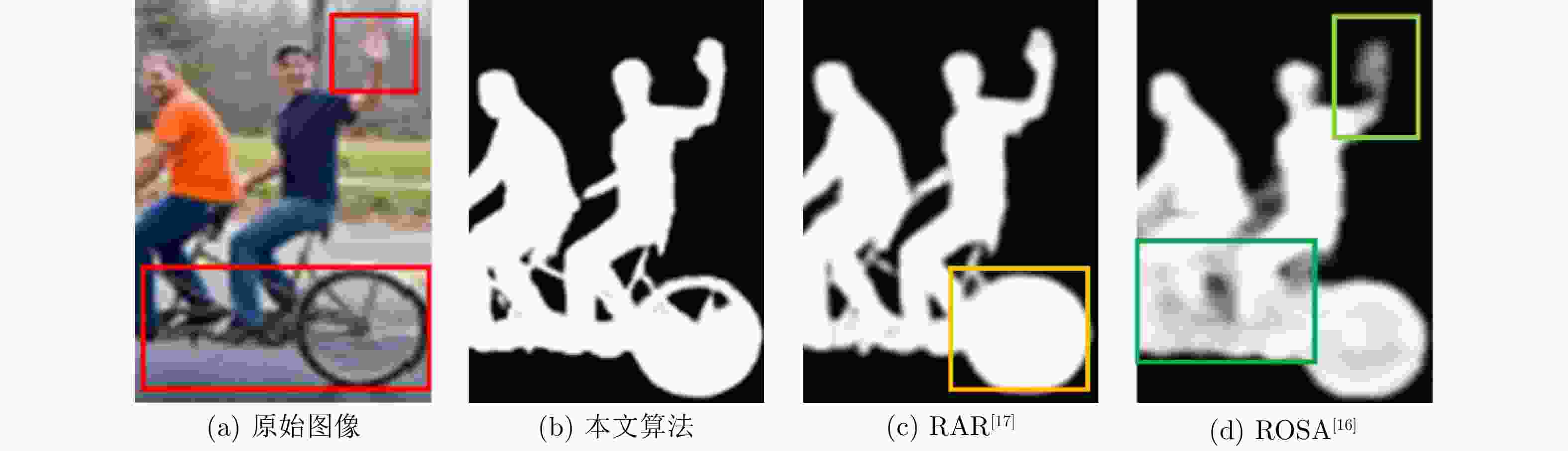
HKU-IS DUTS-Test SOD maxF↑ S-measure↑ MAE↓ maxF↑ S-measure↑ MAE↓ maxF↑ S-measure↑ MAE↓ RAS[8] 0.901 0.887 0.045 0.807 0.839 0.059 0.810 0.764 0.124 BASNet[10] 0.919 0.909 0.032 0.838 0.866 0.048 0.805 0.769 0.114 CPD[11] 0.911 0.905 0.034 0.840 0.869 0.043 0.814 0.767 0.112 PoolNet[12] 0.923 0.919 0.030 0.865 0.886 0.037 0.831 0.788 0.106 MIJR[13] 0.901 0.887 0.045 0.807 0.839 0.059 0.810 0.764 0.124 MINet[15] 0.913 0.905 0.031 0.840 0.863 0.037 0.814 0.776 0.126 LDF[14] 0.919 0.916 0.037 0.850 0.874 0.035 0.843 0.777 0.113 ROSA[16] 0.897 0.887 0.041 0.865 0.886 0.040 0.803 0.763 0.110 RAR[17] 0.917 0.919 0.026 0.854 0.871 0.042 0.856 0.780 0.104 本文 0.943 0.934 0.022 0.885 0.893 0.030 0.878 0.794 0.092 -
[1] GIBSON K B, VO D T, and NGUYEN T Q. An investigation of dehazing effects on image and video coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(2): 662–673. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2166968 [2] SULLIVAN G J, OHM J R, HAN W J, et al. Overview of the high efficiency video coding (HEVC) standard[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2012, 22(12): 1649–1668. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2012.2221191 [3] OHM J R, SULLIVAN G J, SCHWARZ H, et al. Comparison of the coding efficiency of video coding standards—including high efficiency video coding (HEVC)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2012, 22(12): 1669–1684. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2012.2221192 [4] TREISMAN A M and GELADE G. A feature-integration theory of attention[J]. Cognitive Psychology, 1980, 12(1): 97–136. doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(80)90005-5 [5] KOCH C and ULLMAN S. Shifts in selective visual attention: Towards the underlying neural circuitry[J]. Human Neurobiology, 1985, 4(4): 219–227. [6] ITTI L, KOCH C, and NIEBUR E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254–1259. doi: 10.1109/34.730558 [7] LIU Nian, HAN Junwei, and YANG M H. PiCANet: Learning pixel-wise contextual attention for saliency detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3089–3098. [8] CHEN Shuhan, TAN Xiuli, WANG Ben, et al. Reverse attention for salient object detection[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, Springer, 2018: 236–252. [9] LI Xin, YANG Fan, CHENG Hong, et al. Contour knowledge transfer for salient object detection[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 370–385. [10] QIN Xuebin, ZHANG Zichen, HUANG Chenyang, et al. BASNet: Boundary-aware salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7471–7481. [11] WU Zhe, SU Li, and HUANG Qingming. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3902–3911. [12] LIU Jiangjiang, HOU Qibin, CHENG Mingming, et al. A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3912–3921. [13] MA Guangxiao, CHEN Chenglizhao, LI Shuai, et al. Salient object detection via multiple instance joint re-learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 22(2): 324–336. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2019.2929943 [14] WEI Jun, WANG Shuhui, WU Zhe, et al. Label decoupling framework for salient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 13025–13034. [15] PANG Youwei, ZHAO Xiaoqi, ZHANG Lihe, et al. Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 9413–9422. [16] LI Haofeng, LI Guanbin, and YU Yizhou. ROSA: Robust salient object detection against adversarial attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(11): 4835–4847. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2914099 [17] CHEN Shuhan, TAN Xiuli, WANG Ben, et al. Reverse attention-based residual network for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 3763–3776. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2965989 [18] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [19] ZHANG Xianyu, ZHOU Xinyu, LIN Mengxiao, et al. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6848–6856. [20] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. [21] MA Ningning, ZHANG Xiangyu, and SUN Jian. Funnel activation for visual recognition[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 1–17. [22] RAHMAN M A and WANG Yang. Optimizing intersection-over-union in deep neural networks for image segmentation[C]. The 12th International Symposium on Visual Computing, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 234–244. [23] MARGOLIN R, ZELNIK-MANOR L, and TAL A. How to evaluate foreground maps[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 248–255. [24] FAN Dengping, CHENG Mingming, LIU Yun, et al. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4558–4567. [25] PERAZZI F, KRÄHENBÜHL P, PRITCH Y, et al. Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 733–740. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
