Scheduling Method for Multi-channel Wireless Networks Based on Optimization of Age of Information
-
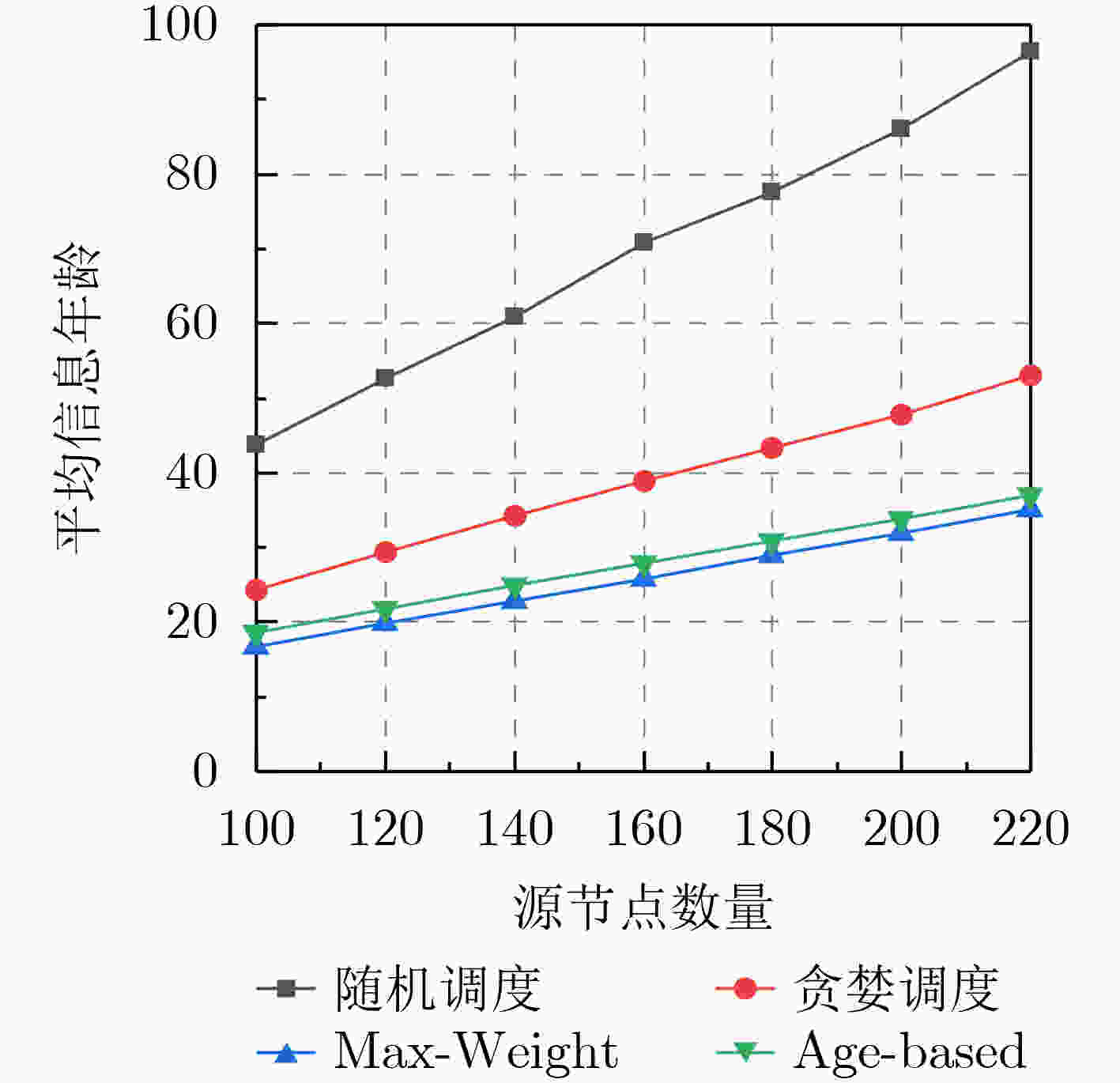
摘要: 信息年龄(AoI)是近年来针对时间敏感类应用所提出的一种描述数据交付及时性的度量标准,它是从网络中目标节点的角度出发,衡量其最新收到的数据包的新鲜程度。在信道资源受限的多信道无线网络场景中,基于信息年龄的链路调度问题需要考虑信道资源和链路冲突的约束。针对上述问题,该文提出一种逐时隙调度链路进行数据传输的调度方法,以最小化网络的平均信息年龄。该文首先将信息年龄的优化问题转化为李雅普诺夫优化问题,然后将冲突约束下的多信道分配问题转换为二分图匹配问题并采用Kuhn-Munkres(KM)算法进行求解,进而得到约束条件下的链路调度方法。仿真结果表明,所提方法有效地优化了网络中的平均信息年龄,提升了网络数据的新鲜度。Abstract: Age of Information (AoI) is a novel metric that describes the timeliness of data delivery for time-sensitive applications, which measures the freshness of the most recently received packet from the perspective of destination node. In the multi-channel wireless network scenario with limited channel resources, the constraints of channel resources and link conflicts should be considered in the link scheduling with respect to AoI. To address this issue, in this paper, a time slot based scheduling method for data transmission to minimize the average AoI in the network is proposed. In this method, the optimization problem of AoI is first formulated into a Lyapunov optimization problem. Then the multi-channel conflict problem is converted to find the maximum matching policy of bipartite graph, which is solved by Kuhn-Munkres (KM) algorithm. Thus, a scheduling policy under constraints is obtained. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method optimizes effectively the average AoI and improves the freshness of data in the network.
-
表 1 KM匹配算法执行过程
KM匹配算法求解带权二分图的最大权匹配 步骤 1 构建二分图$G$的点集为信道的点集$\{ {x_1},\;{x_2},\;\cdots,\;{x_M}\} $,目标节点的点集$\{ {y_1},\;{y_2},\;\cdots,\;{y_a}\} $。定义信道${x_j}$和目标节点${y_b}$的边权为
$w({x_j},\;{y_b}) = \max \;\{ - {W_{i,j} }|i \in ({y_{b - 1} } + 1,\;{y_{b - 1} } + 2,\;\cdots,\;{y_b})\}$。步骤 2 定义信道点集和目标节点的点集的顶标值,对于信道${x_j}$的顶标值为$L({x_j}) = \max \;\{ w({x_j},\;{y_b})|b \in (1,\;2,\;\cdots,\;a)\} $,即为信道${x_j}$在所
有目标节点下最大的边权值;初始化信道点集的顶标值,对于信道${y_b}$的顶标值$L({y_b}) = 0$。步骤 3 构建相等子图${G_e}$,用来保留二分图$G$中所有的点集和顶标值。 步骤 4 ${\rm{for}} \;j = 1,\;2,\;\cdots,\;M$ 在相等子图${G_e}$中添加满足匹配条件$L({x_j}) + L({y_b}) = w({x_j},{y_b})$的边,使用匈牙利算法在${G_e}$中寻找其最优匹配[19]。若未找到其最优匹配,
则根据匈牙利算法中形成的交错树,该交错树为匈牙利算法中所访问的目标节点与信道间形成的点集,取相等子图点集中所有信道节点
$x_j^{'}$被访问到而目标节点$y_b^{'}$没被访问到的边,求解交错树中的各松弛量$L(x_j^{'}) + L(y_b^{'}) - w(x_j^{'},y_b^{'})$的最小值$q$,将交错树中所有信道顶标减
小$q$,目标节点顶标增加$q$,再重新匹配该信道。end for 表 2 Max-Weight方法的平均执行时间(ms)
节点数量 20 40 60 80 100 平均运行时间 0.354 0.457 0.557 0.743 0.939 -
[1] CHEN Maohong, XIAO Yong, LI Qiang, et al. Minimizing age-of-information for fog computing-supported vehicular networks with deep Q-learning[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. [2] LI Jie, ZHOU Yong, and CHEN He. Age of information for multicast transmission with fixed and random deadlines in IoT systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(9): 8178–8191. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2981144 [3] KAUL S, YATES R, and GRUTESER M. Real-time status: How often should one update?[C]. 2012 Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, Orlando, USA, 2012: 2731–2735. [4] KAM C, KOMPELLA S, NGUYEN G D, et al. On the age of information with packet deadlines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2018, 64(9): 6419–6428. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2018.2818739 [5] KUANG Qiaobin, GONG Jie, CHEN Xiang, et al. Age-of-information for computation-intensive messages in mobile edge computing[C]. 2019 11th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Xi’an, China, 2019: 1–6. [6] KUANG Qiaobin, GONG Jie, CHEN Xiang, et al. Analysis on computation-intensive status update in mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(4): 4353–4366. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2974816 [7] KADOTA I, SINHA A, UYSAL-BIYIKOGLU E, et al. Scheduling policies for minimizing age of information in broadcast wireless networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2018, 26(6): 2637–2650. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2018.2873606 [8] HSU Y P, MODIANO E, and DUAN Lingjie. Age of information: Design and analysis of optimal scheduling algorithms[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Aachen, German, 2017: 561–565. [9] KADOTA I, SINHA A, and MODIANO E. Scheduling algorithms for optimizing age of information in wireless networks with throughput constraints[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2019, 27(4): 1359–1372. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2019.2918736 [10] TANG Haoyue, WANG Jintao, SONG Linqi, et al. Minimizing age of information with power constraints: multi-user opportunistic scheduling in multi-state time-varying channels[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(5): 854–868. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.2980911 [11] 路新华, MANCHÓN C N, 王忠勇, 等. 大规模MIMO系统上行链路时间-空间结构信道估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 519–525. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180676LU Xinhua, MANCHÓN C N, WANG Zhongyong, et al. Channel estimation algorithm using temporal-spatial structure for up-link of massive MIMO systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 519–525. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180676 [12] 赵悦超, 杨涛, 胡波. 无线传感器网络中基于信息年龄的状态更新策略[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2020, 37(11): 29–34.ZHAO Yuechao, YANG Tao, and HU Bo. A status updating policy based on age of information in wireless sensor network[J]. Microelectronics &Computer, 2020, 37(11): 29–34. [13] SOMBABU B and MOHARIR S. Age-of-information based scheduling for multi-channel systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(7): 4439–4448. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2983670 [14] TALAK R, KARAMAN S, and MODIANO E. Improving age of information in wireless networks with perfect channel state information[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2020, 28(4): 1765–1778. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2020.2996237 [15] TALAK R, KARAMAN S, and MODIANO E. Minimizing age-of-information in multi-hop wireless networks[C]. 2017 55th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, USA, 2017: 486–493. [16] TALAK R, KADOTA I, KARAMAN S, et al. Scheduling policies for age minimization in wireless networks with unknown channel state[C]. 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Vail, USA, 2018: 2564–2568. [17] ZHOU Bo and SAAD W. Minimum age of information in the internet of things with non-uniform status packet sizes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(3): 1933–1947. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2891598 [18] LIU Chenfeng and BENNIS M. Taming the tail of maximal information age in wireless industrial networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(12): 2442–2446. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2940965 [19] XIAO Qinkun, LUO Yichuang, and LÜ Zhongkai. Motion retrieval based on graph matching and revised Kuhn-Munkres algorithm[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication and Computing, Kunming, China, 2013: 1–4. [20] 吕敬祥, 罗文浪. 无线传感网络量化及能量优化策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1118–1124. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190185LÜ Jingxiang and LUO Wenlang. Quantization and energy optimization strategy of wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1118–1124. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190185 -





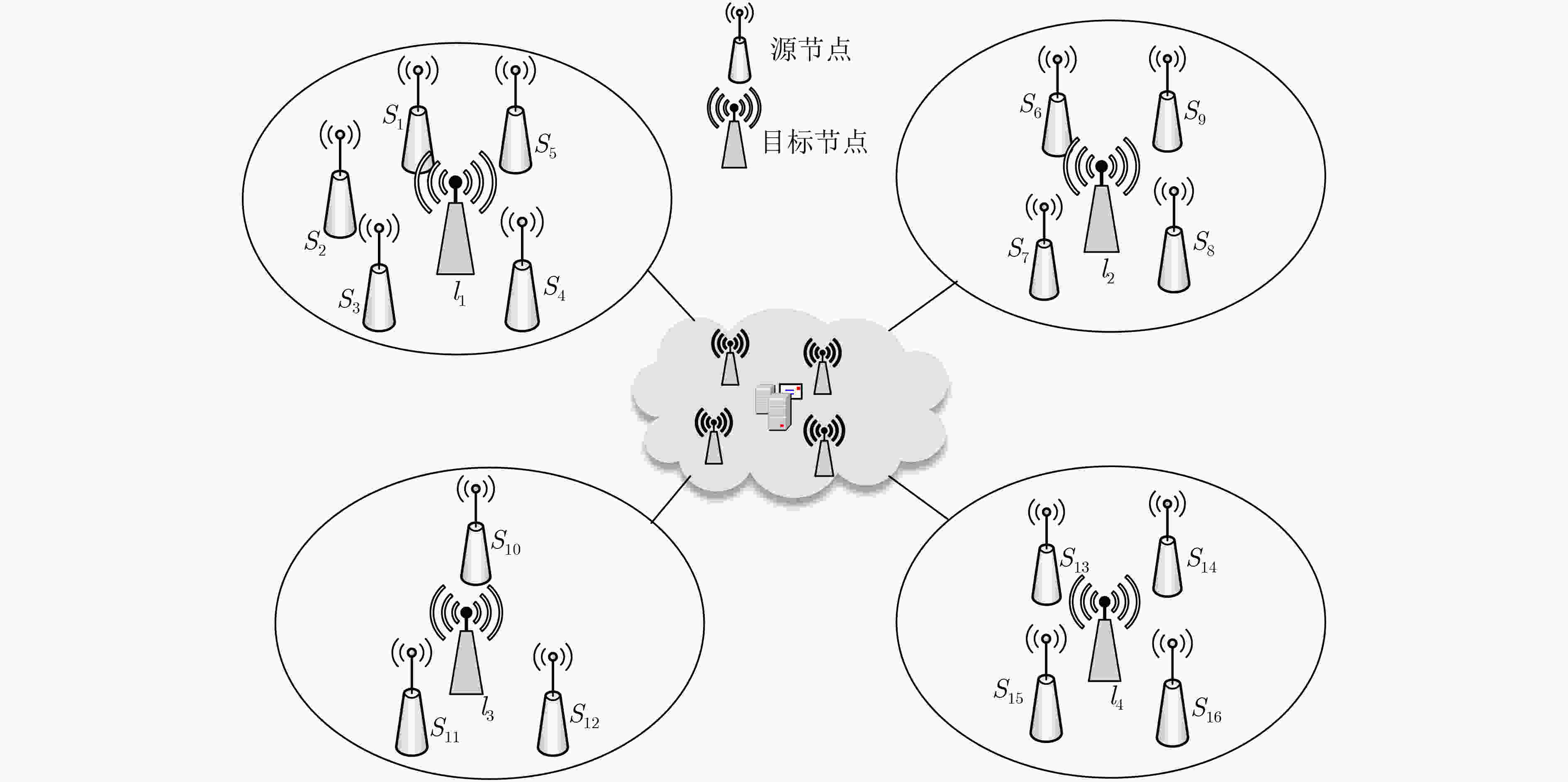
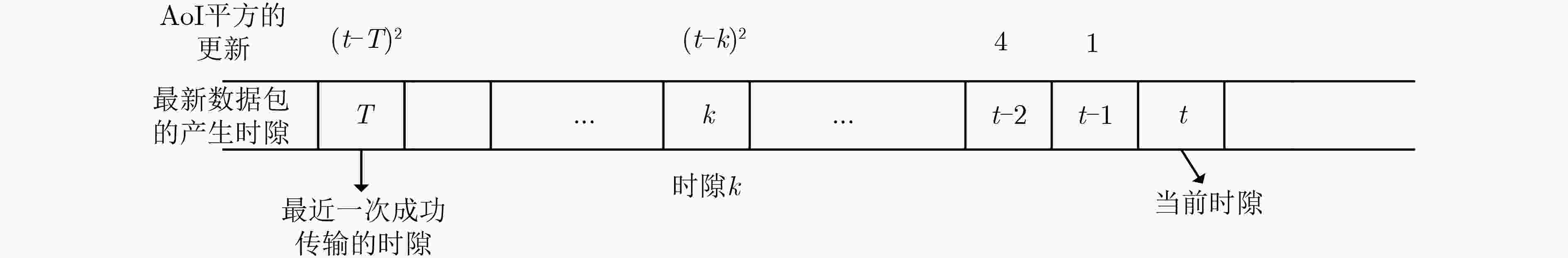
 下载:
下载:
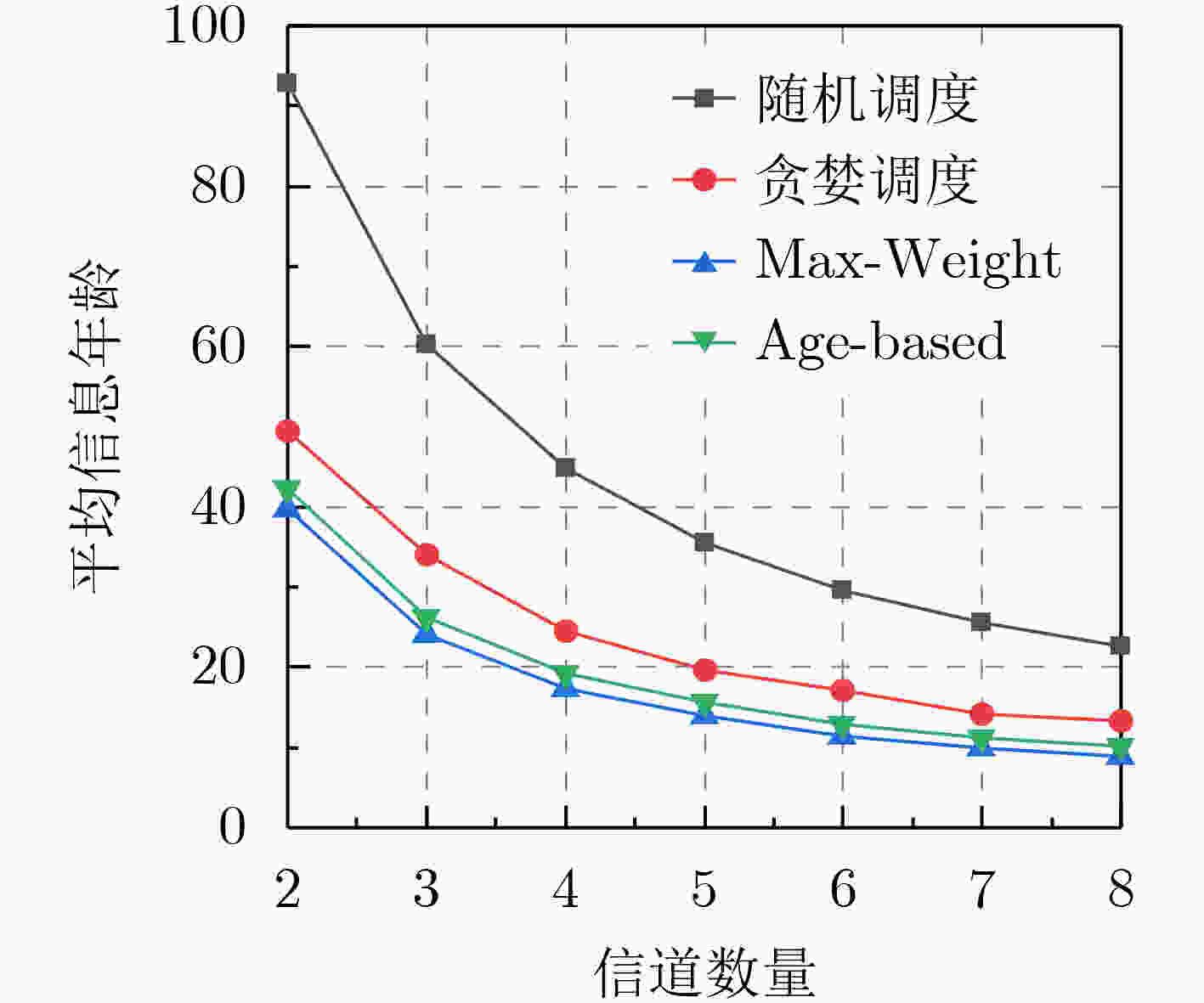
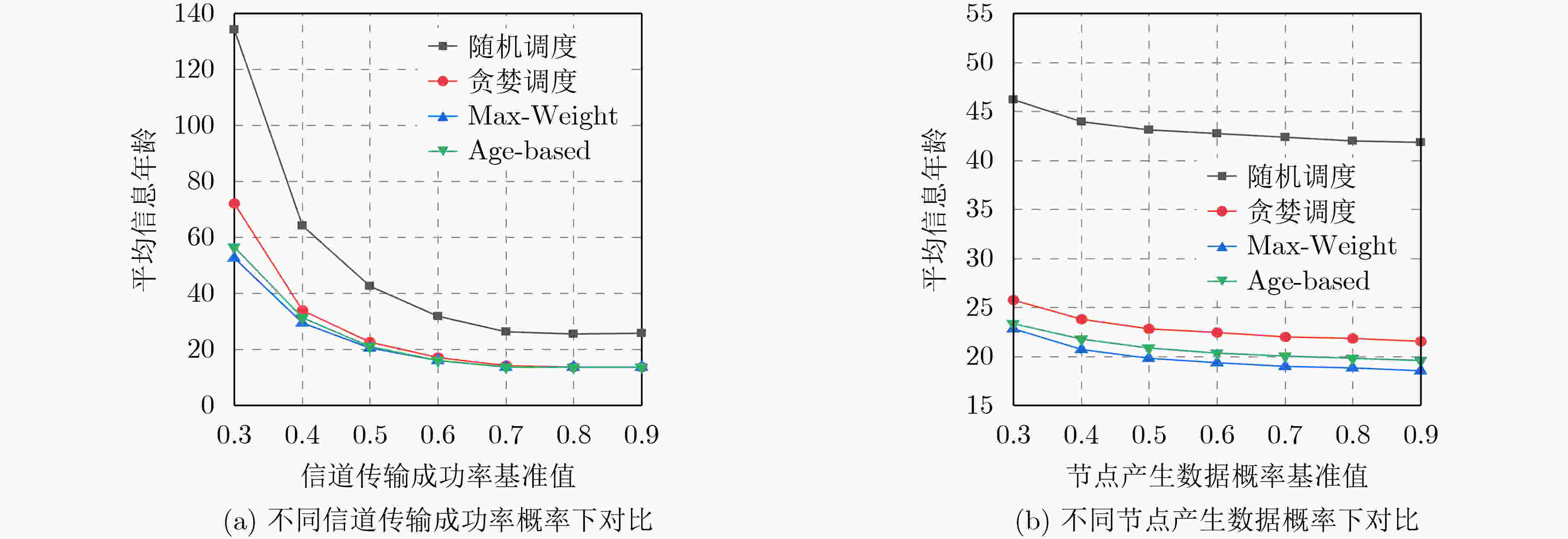


 下载:
下载:
