Design of Low-jitter, Multi-phase Clock Generation Circuit for Geiger-mode Avalanche Focal Plane Array Applications
-
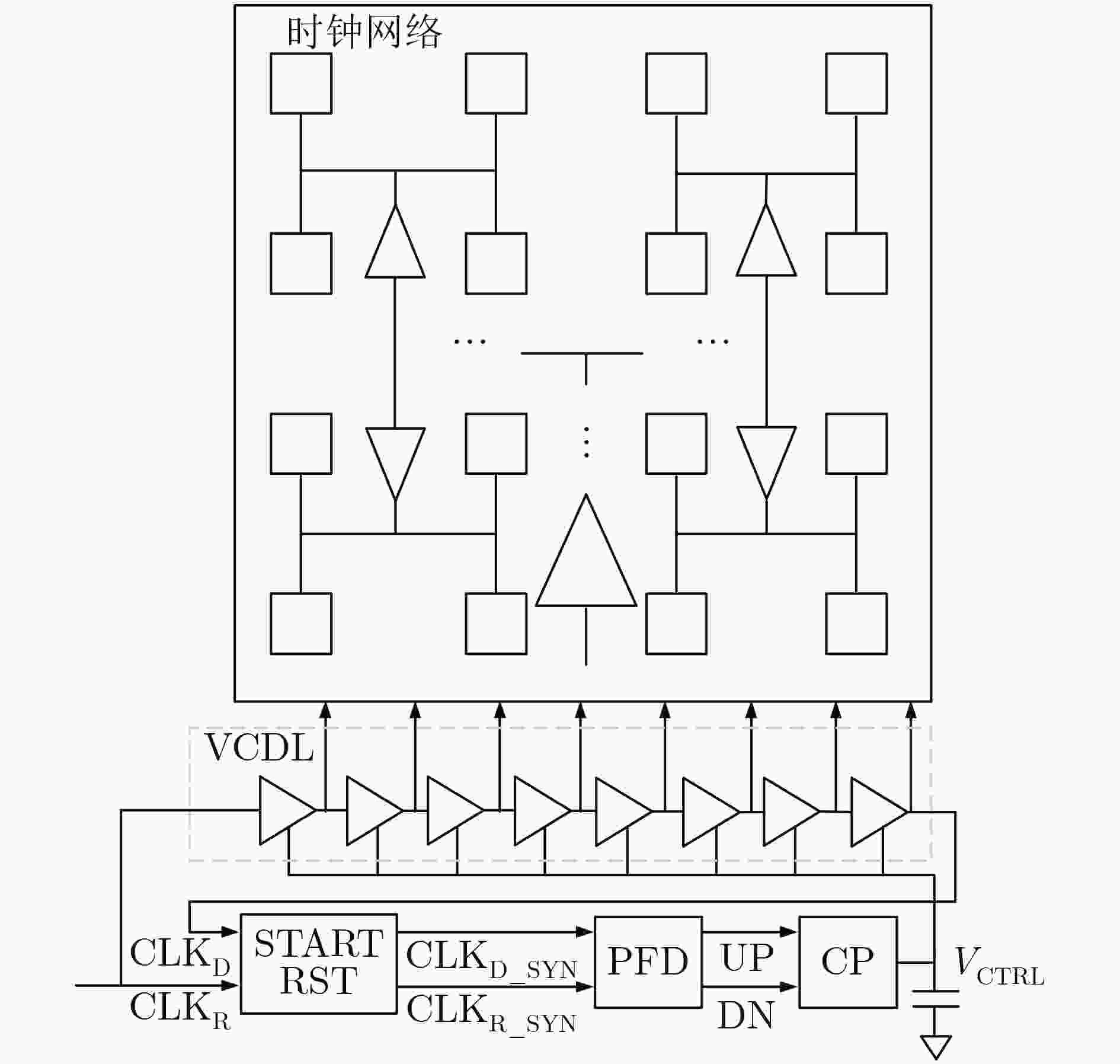
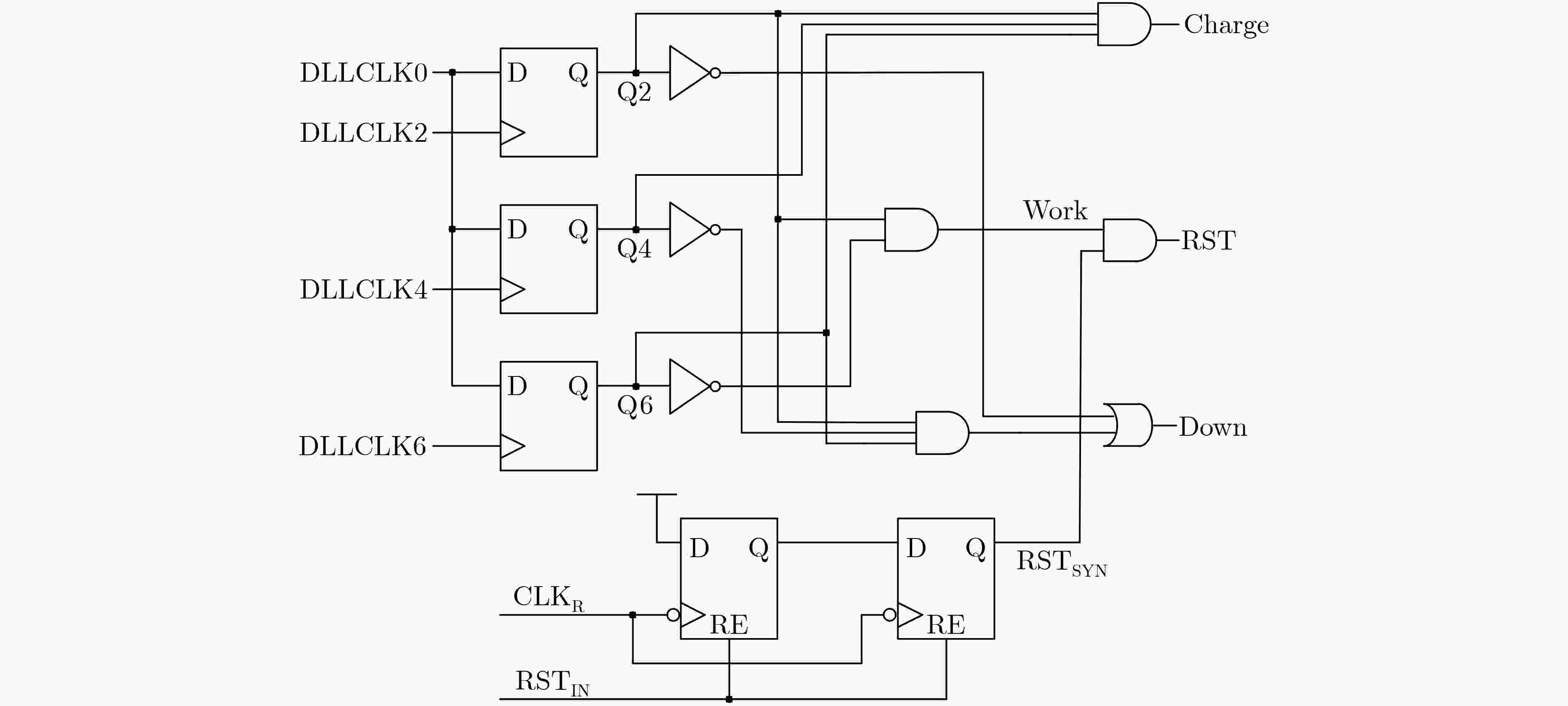
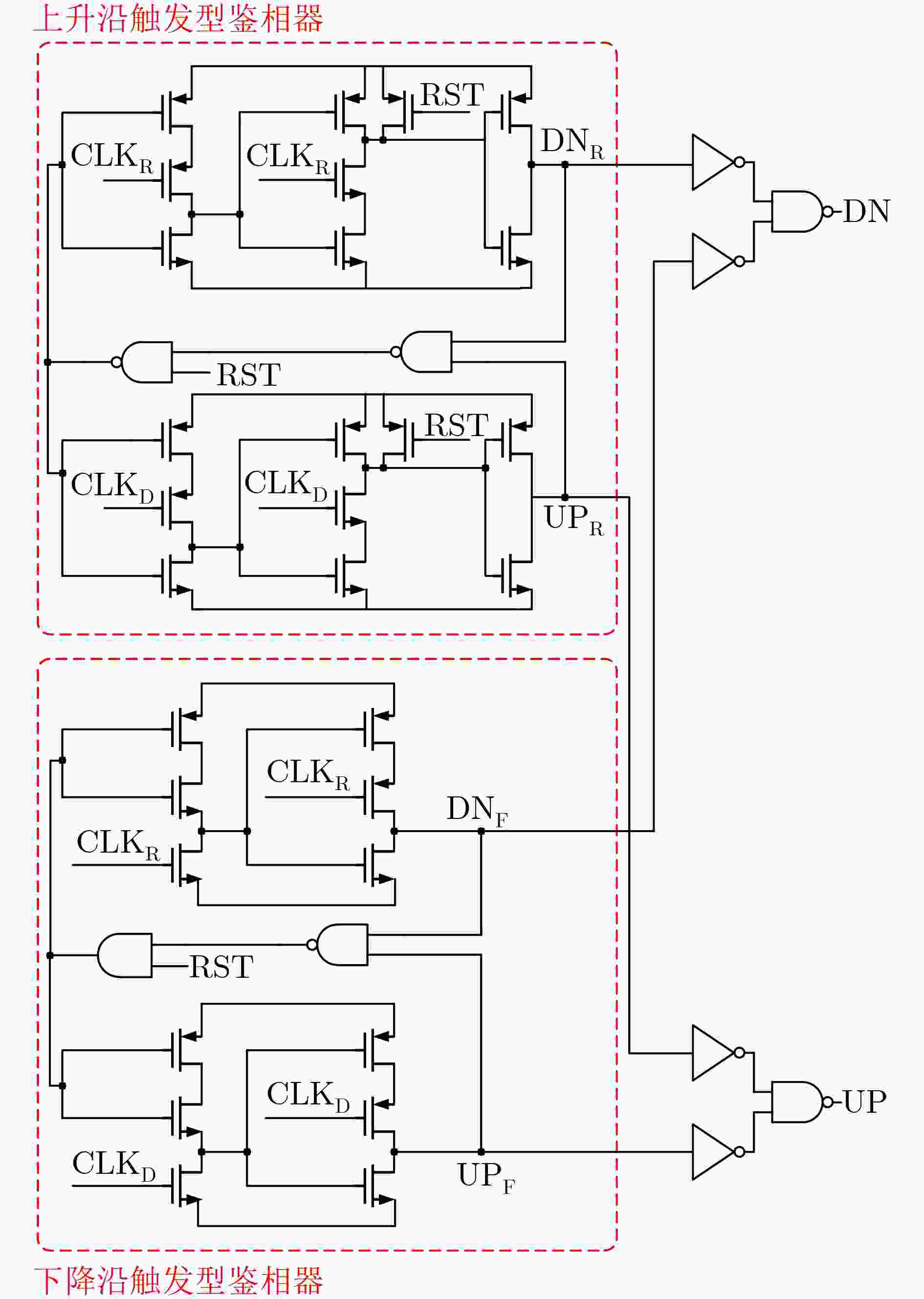
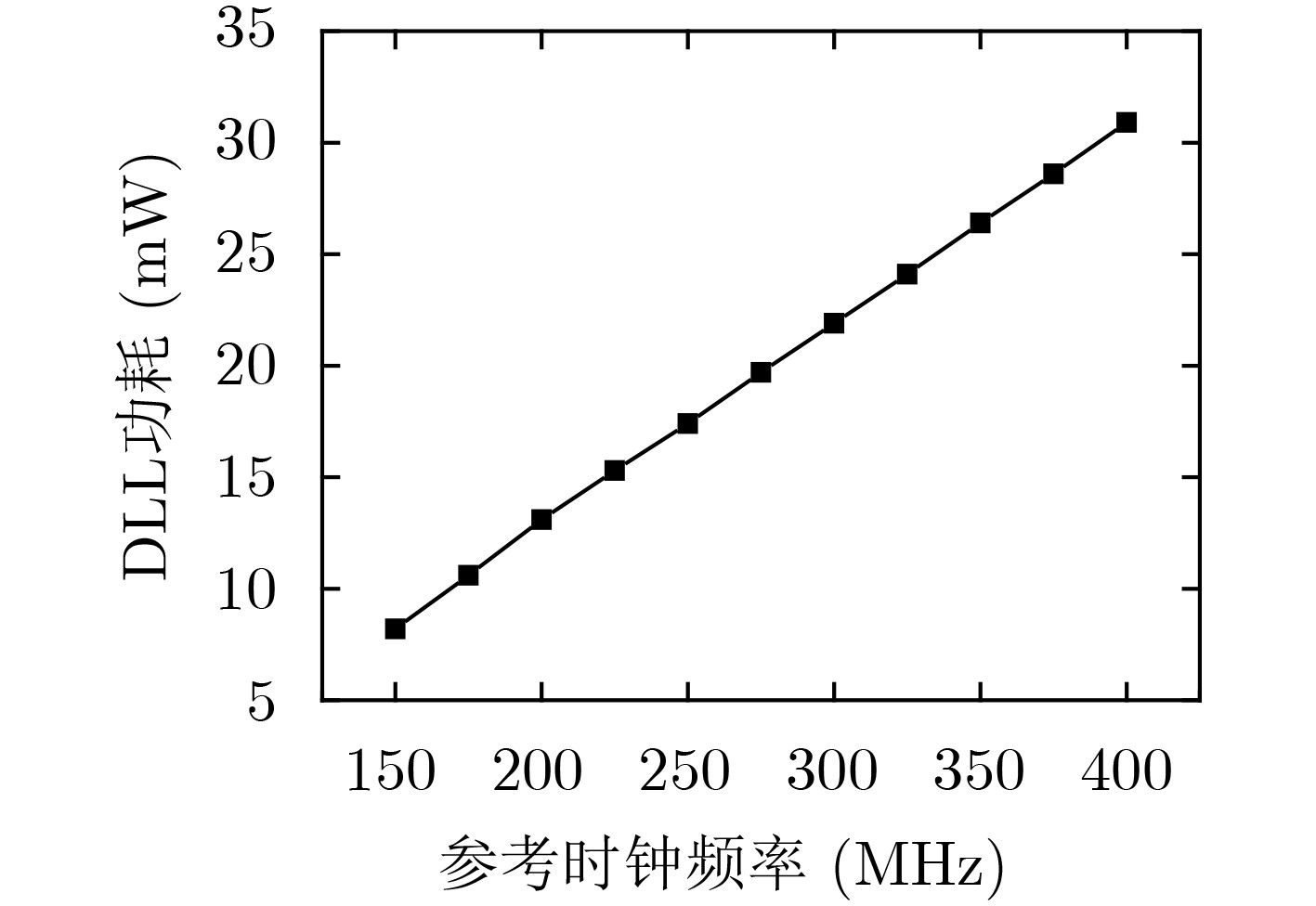
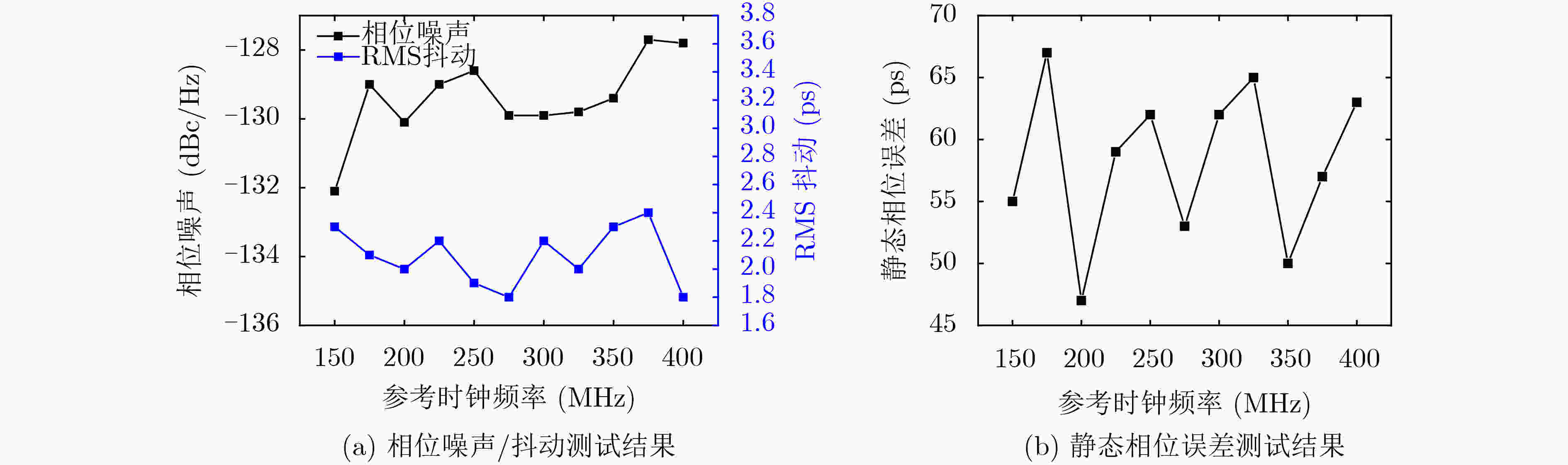
摘要: 针对单光子探测盖革雪崩焦平面读出电路应用,基于全局共享延迟锁相环和2维H型时钟树网络,该文设计一款低抖动多相位时钟电路。延迟锁相环采用8相位压控延迟链、双边沿触发型鉴相器和启动-复位模块,引入差分电荷泵结构,减小充放电流失配,降低时钟抖动。采用H时钟树结构,减小大规模电路芯片传输路径不对称引起的相位差异,确保多路分相时钟等延迟到达像素单元。采用0.18 µm CMOS工艺流片,测试结果表明,延迟锁相环锁定频率范围150~400 MHz。锁定范围内,相位噪声低于–127 dBc/Hz@1 MHz,时钟RMS抖动低于2.5 ps,静态相位误差低于65 ps。Abstract: A low-jitter multi-phase clock generation circuit is designed based on a global shared Delay Locked Loop (DLL) and a two-dimensional H-shaped clock tree network for Geiger-mode avalanche focal plane array applications. The DLL adopts an eight-phase voltage-controlled delay chain, a double-edge trigger phase detector and a start reset module. A differential charge pump structure is introduced to reduce the current mismatch between charging and discharging and lower the clock timing jitter. H clock tree structure is involved to diminish the phase variation induced by the asymmetry of the transmission route for large scale integrated circuit, ensuring an equal delay of the multi-channel split-phase clock signal to the pixel unit. The locking frequency range of 150~400 MHz, phase noises below -127 dBc/Hz at 1 MHz offset, RMS timing jitter of below 2.5 ps and static phase error below 65 ps are achieved based on a 0.18 µm digital-analog hybrid CMOS technology.
-
表 1 DLL各模块噪声特性
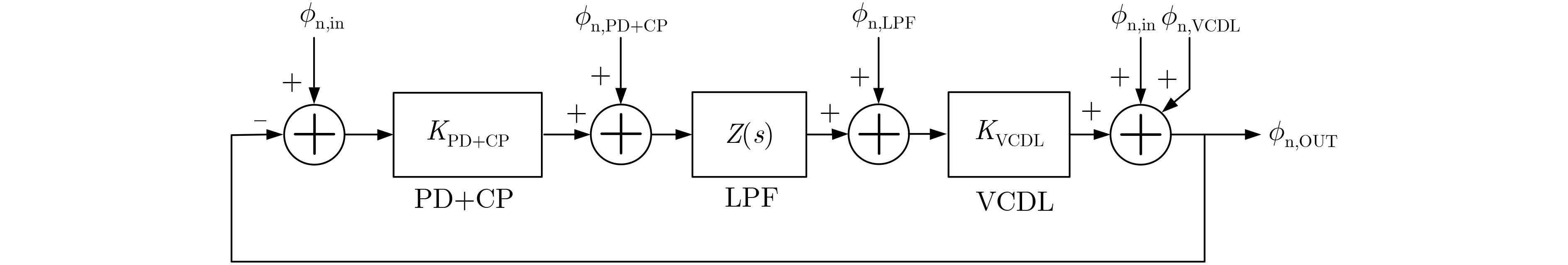
噪声模块 传递函数 噪声特性 输入参考时钟 $\scriptsize{\varphi _{{\rm{n ,out}}}^2 = \varphi _{{\rm{n ,in}}}^2}$ 全通 鉴相器+电荷泵 $\scriptsize{\varphi _{{\rm{n ,out}}}^2 = {\left| {\dfrac{{{H_{\rm{O}}}(s)}}{{1 + {H_{\rm{O}}}(s)}}} \right|^2}\varphi _{{\rm{n,PD + CP}}}^2}$ 低通,带内平坦,带外衰减 环路滤波器 $\scriptsize{\varphi _{{\rm{n ,out}}}^2 = {\left| {\dfrac{{{K_{{\rm{VCDL}}}}}}{{1 + {H_{\rm{O}}}(s)}}} \right|^2}\varphi _{{\rm{n,LPF}}}^2}$ 高通,带内衰减,带外平坦 压控延迟链 $\scriptsize{\varphi _{{\rm{n ,out}}}^2 = {\left| {\dfrac{1}{{1 + {H_{\rm{O}}}(s)}}} \right|^2}\varphi _{{\rm{n,VCDL}}}^2}$ 高通,带内衰减,带外平坦 表 2 64×64规模时钟网络后仿真延迟时间(ns)
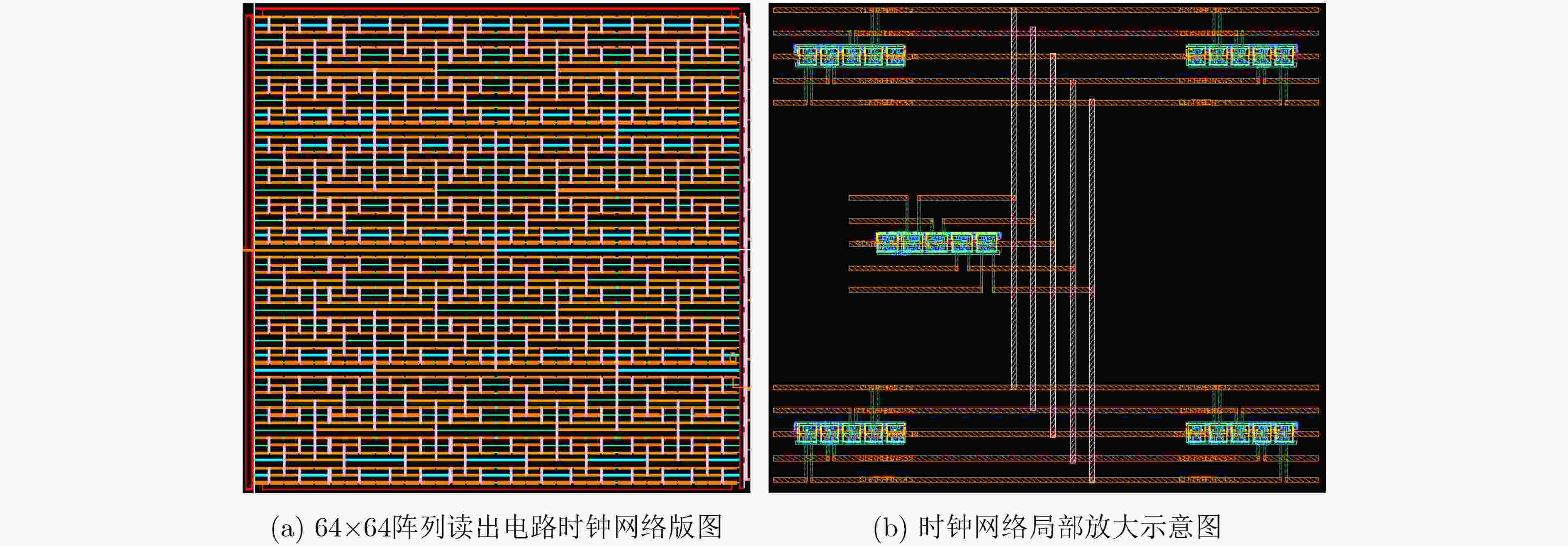
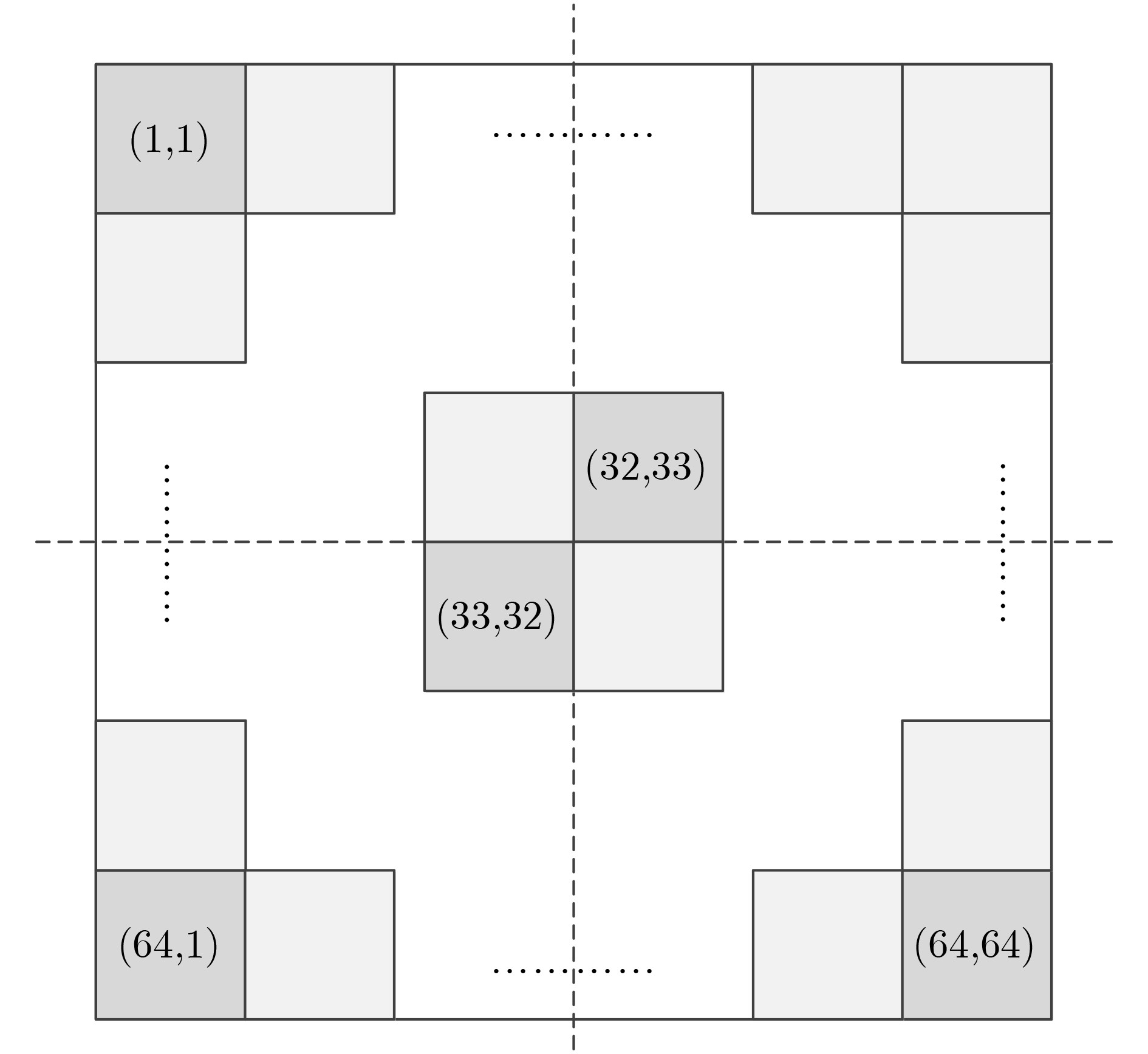
叶节点编号 tt corner ss corner ff corner snfp corner fnsp corner 叶节点1 1.266 1.524 1.017 1.234 1.239 叶节点2 1.268 1.527 1.019 1.232 1.237 叶节点3 1.264 1.526 1.016 1.236 1.241 叶节点4 1.263 1.523 1.017 1.235 1.240 叶节点5 1.265 1.526 1.015 1.232 1.238 表 3 64×64规模时钟网络功耗
工艺角 功耗(mW) tt 147.6 ss 143.4 ff 153.0 snfp 147.6 fnsp 147.6 表 4 测试与后仿真总结
性能参数 测试/后仿真结果 工艺(μm) 0.18 电源电压(V) 1.8 DLL锁定范围(MHz) 150~400 DLL功耗(mW) 8.2~30.9 锁定范围内RMS Jitter(ps) 1.8~2.4 锁定范围内相位噪声(dBc/Hz)@1 MHz –127.8~–132.1 锁定范围内静态相位误差(ps) 47~65 时钟树各节点后仿真延迟(ps) 1247~1253 -
[1] 舒嵘, 黄庚华, 孔伟. 空间激光测高技术发展及展望[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(11): 9–18.SHU Rong, HUANG Genghua, and KONG Wei. Development and review of space-based laser altimetry technology[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(11): 9–18. [2] 陈兆东. 高距离精度条纹探测和单光子计数复合激光三维成像研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.CHEN Zhaodong. Research on high range accuracy hybrid three dimensional laser imaging based on streak array detecting and single-photon counting[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. [3] HENDERSON R K, JOHNSTON N, ROCCA F M D, et al. A 192×128 time correlated SPAD image sensor in 40-nm CMOS technology[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54(7): 1907–1916. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2905163 [4] JIANG Xudong, ITZLER M, O’DONNELL K, et al. InP-based single-photon detectors and Geiger-mode APD arrays for quantum communications applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2015, 21(3): 3800112. [5] DENG Shijie, GORDON D, and MORRISON A P. A Geiger-mode APD photon counting system with adjustable dead-time and interchangeable detector[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2016, 28(1): 99–102. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2015.2487342 [6] 刘俊良, 李永富, 张春芳, 等. 基于APD-PIN结电容平衡电路的门控单光子探测器[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(11): 3181–3185.LIU Junliang, LI Yongfu, ZHANG Chunfang, et al. Single-photon detector based on GPQC with balanced APD-PIN junction capacitance[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(11): 3181–3185. [7] 王燕, 王鹏辉. 激光主动成像技术综述[J]. 电子质量, 2019(7): 1–3.WANG Yan and WANG Penghui. Overview of laser active imaging technology[J]. Electronics Quality, 2019(7): 1–3. [8] 吴金, 俞向荣, 史书芳, 等. 采用APD单光子阵列读出集成电路的红外测距技术[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2017, 46(6): 69–74.WU Jin, YU Xiangrong, SHI Shufang, et al. Infrared ranging technology by using single photon APD array readout integrated circuit[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(6): 69–74. [9] JAHROMI S, JANSSON J P, KERÄNEN P, et al. A 32 × 128 SPAD-257 TDC receiver IC for pulsed TOF solid-State 3-D imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(7): 1960–1970. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.2970704 [10] NICLASS C, SOGA M, MATSUBARA H, et al. A 100-m range 10-frame/s 340 ×96-pixel time-of-flight depth sensor in 0.18-µm CMOS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(2): 559–572. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2227607 [11] VERGHESE S, DONNELLY J P, DUERR E K, et al. Arrays of InP-based avalanche photodiodes for photon counting[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2007, 13(4): 870–886. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2007.904464 [12] REZAEIAN A, ARDESHIR G, and GHOLAMI M. A low-power and high-frequency phase frequency detector for a 3.33-GHz delay locked loop[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2020, 39(4): 1735–1750. doi: 10.1007/s00034-019-01232-9 [13] ZHU Shijia, WANG Yu, YE Fan, et al. A clock interpolation structure using DLL for clock distribution in ADC[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on ASIC, Guiyang, China, 2017: 769–772. [14] CHITHRA and KRISHNAPURA N. A flexible 18-channel multi-hit time-to-digital converter for trigger-based data acquisition systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2020, 67(6): 1892–1901. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.2969977 [15] CHITHRA and KRISHNAPURA N. Static phase offset reduction technique for delay locked loops[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Sapporo, Japan, 2019: 1–5. [16] CHENG S, TONG H, SILVA-MARTINEZ J, et al. Design and analysis of an ultrahigh-speed glitch-free fully differential charge pump with minimum output current variation and accurate matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2006, 53(9): 843–847. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2006.879100 -





 下载:
下载:

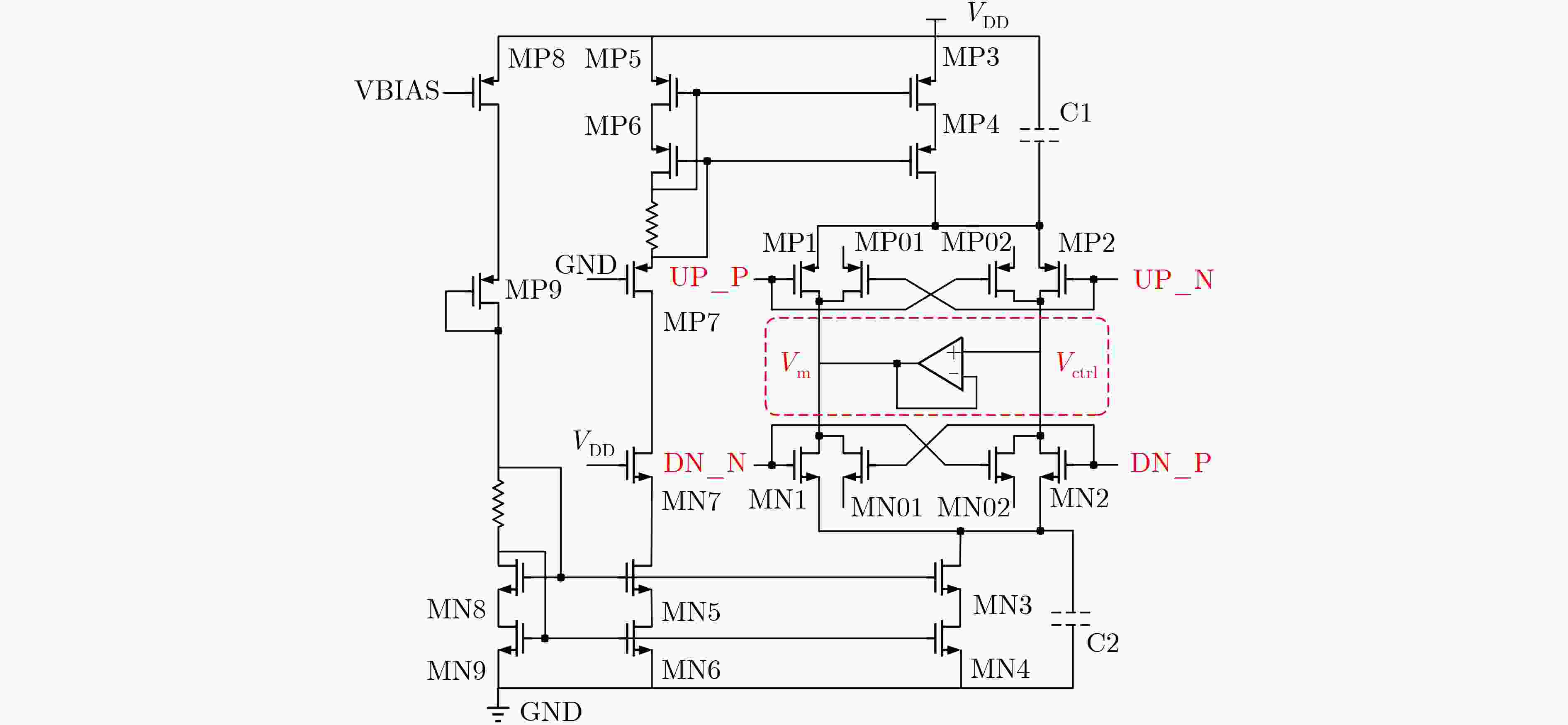
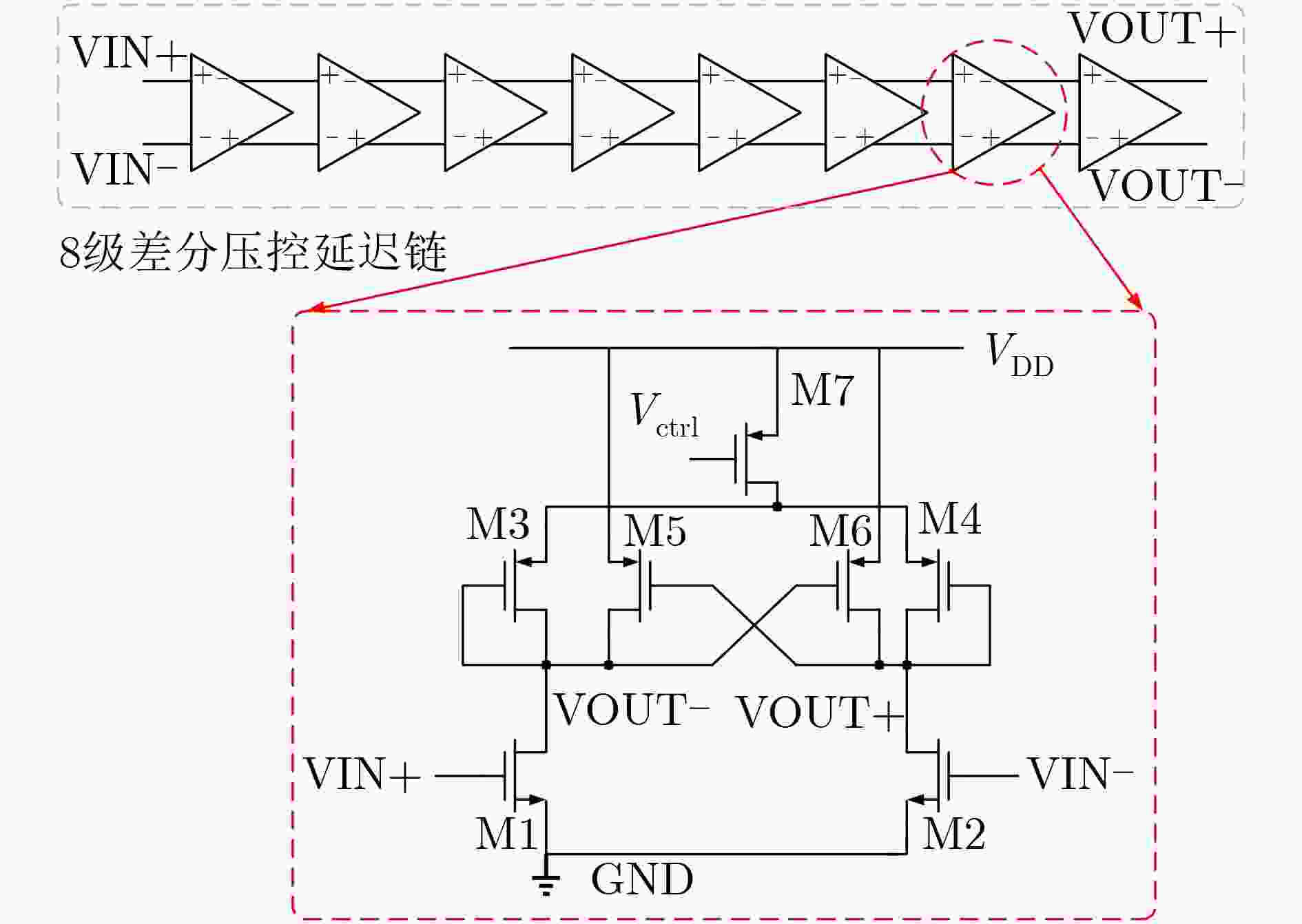
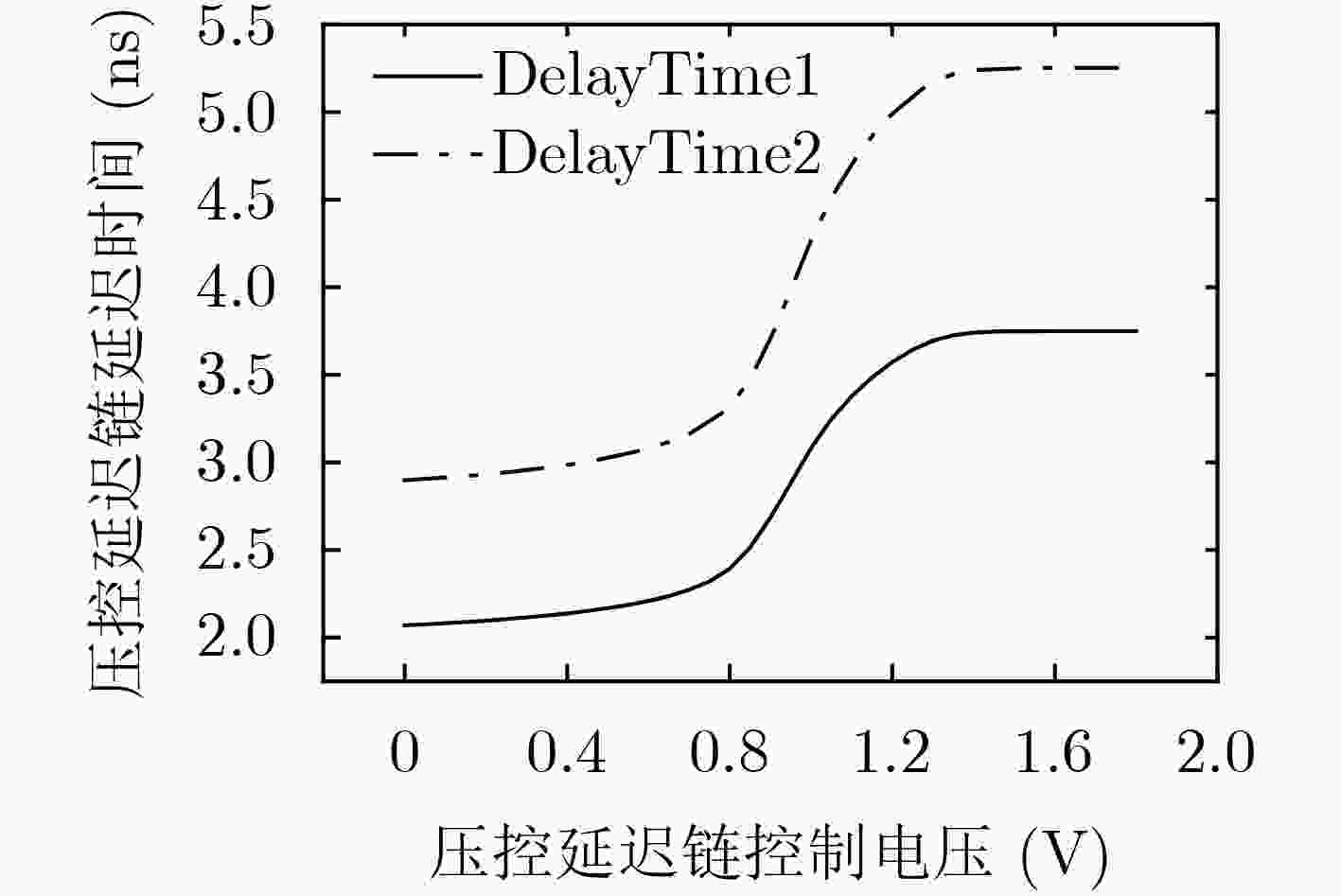
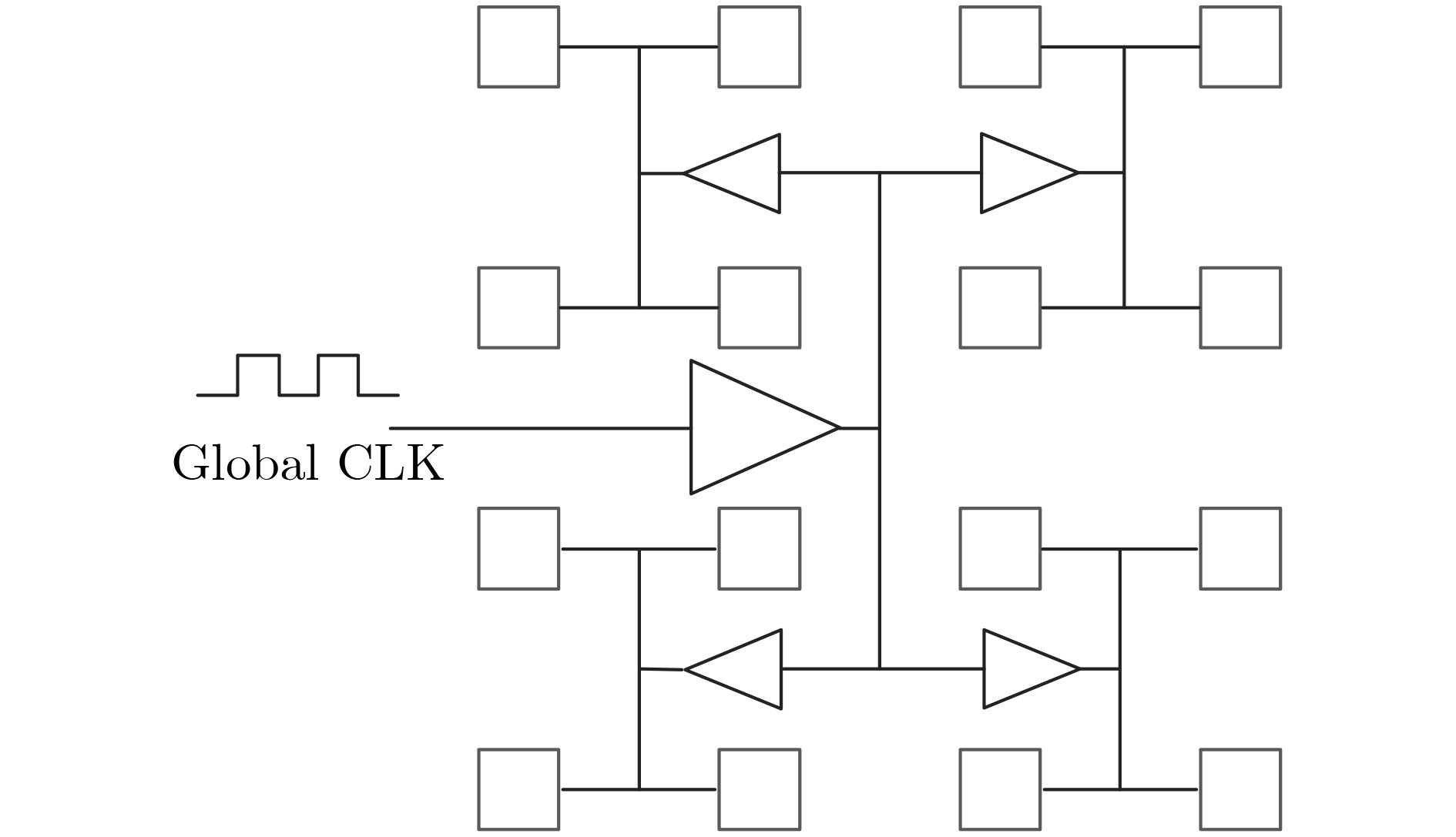



 下载:
下载:
