Few-Shot Segmentation on Mobile Phone Screen Defect Based on Co-Attention
-
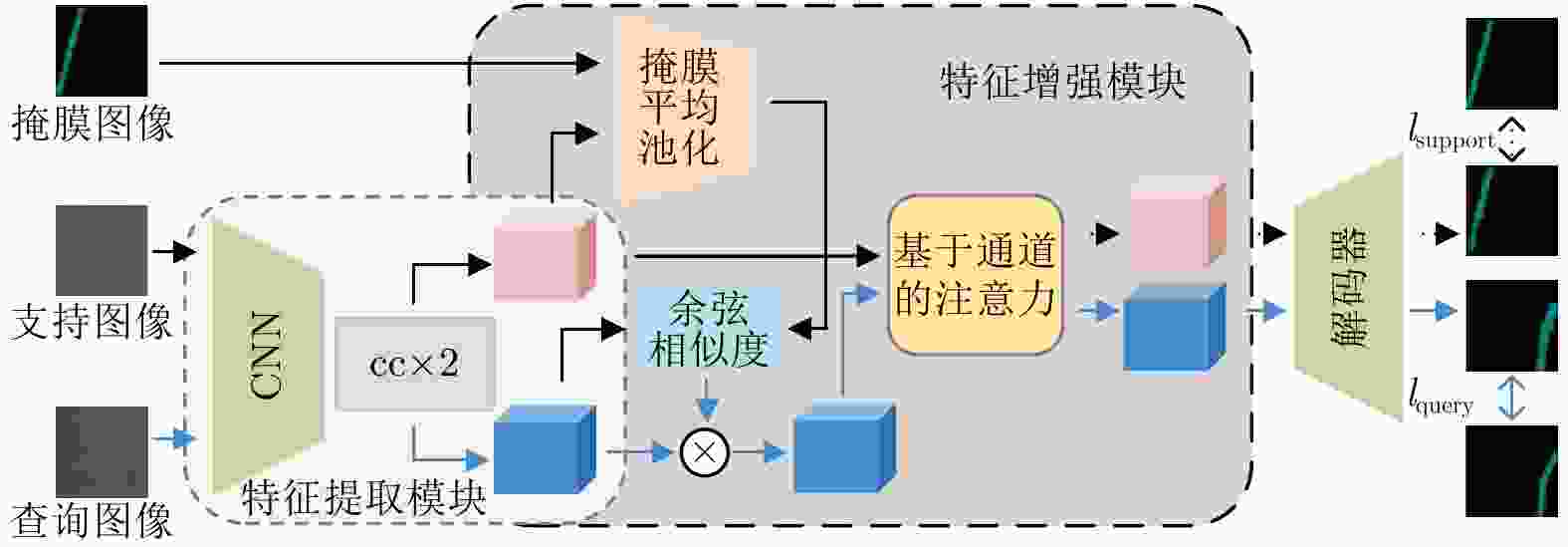
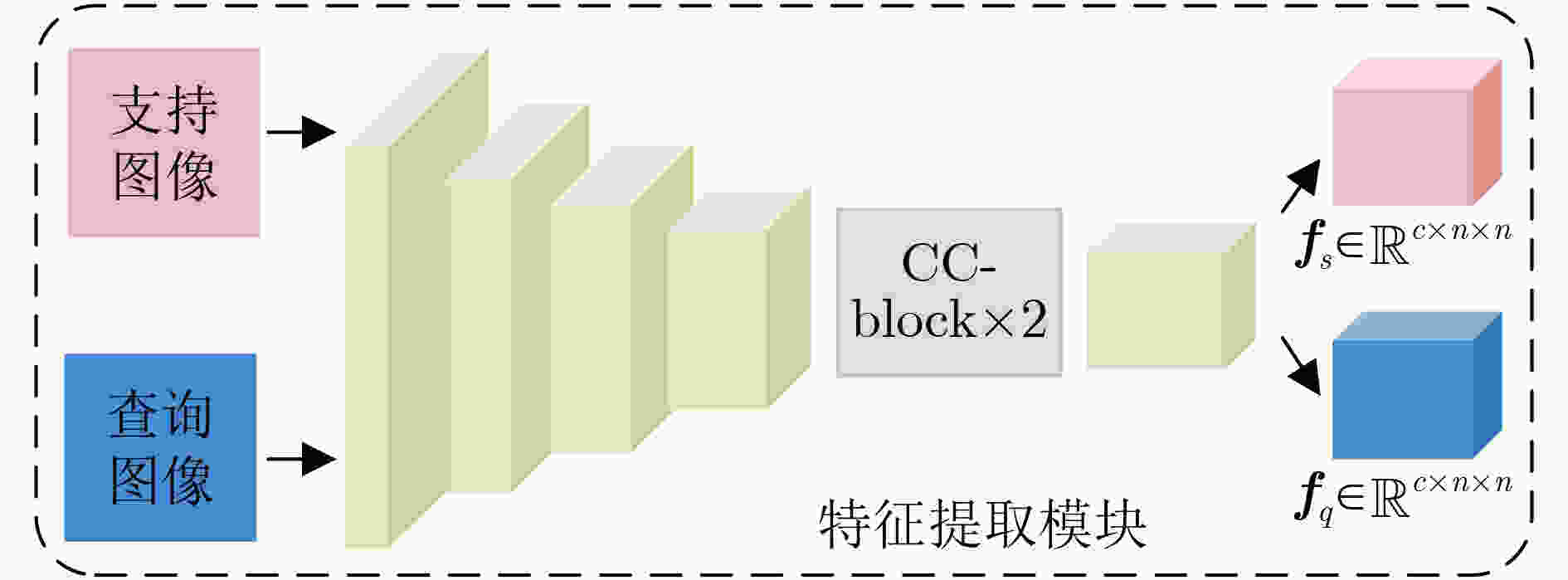
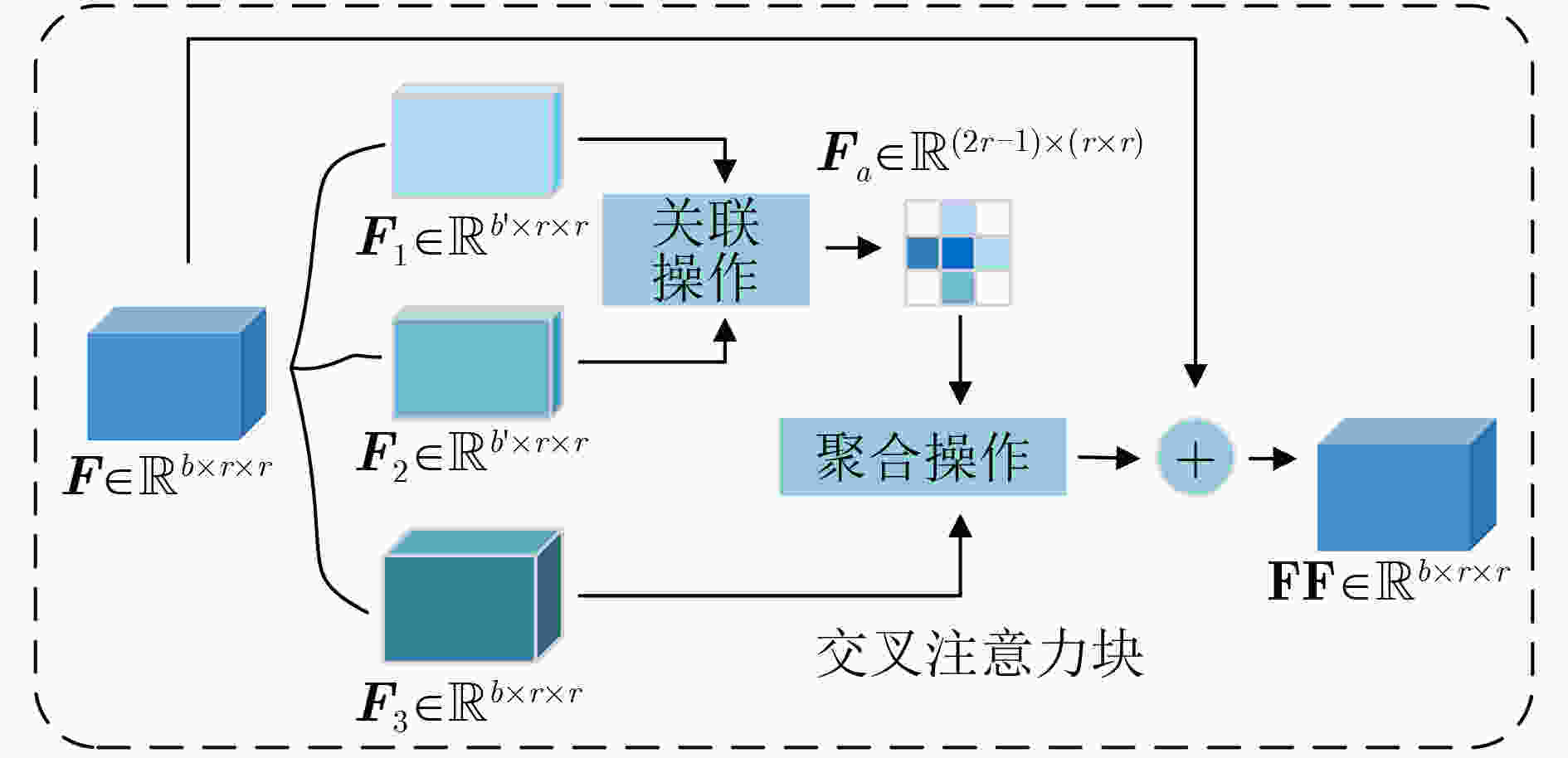
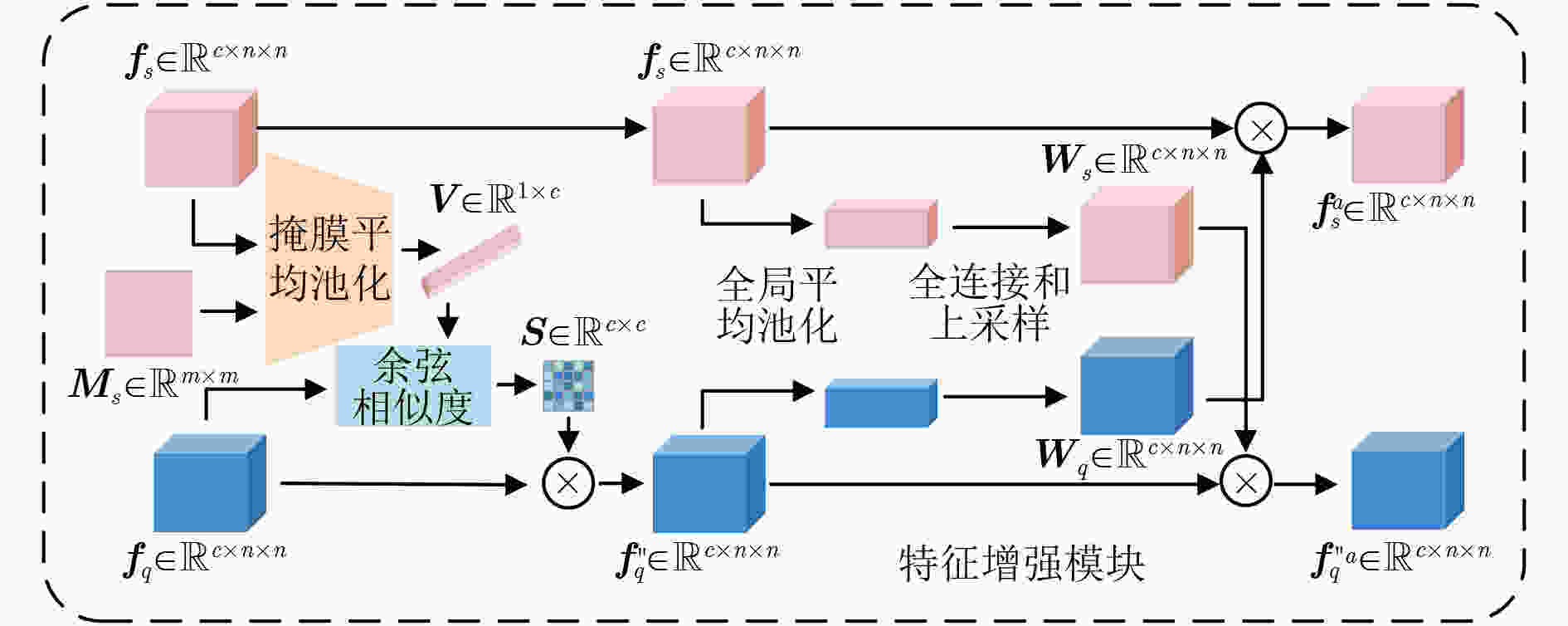
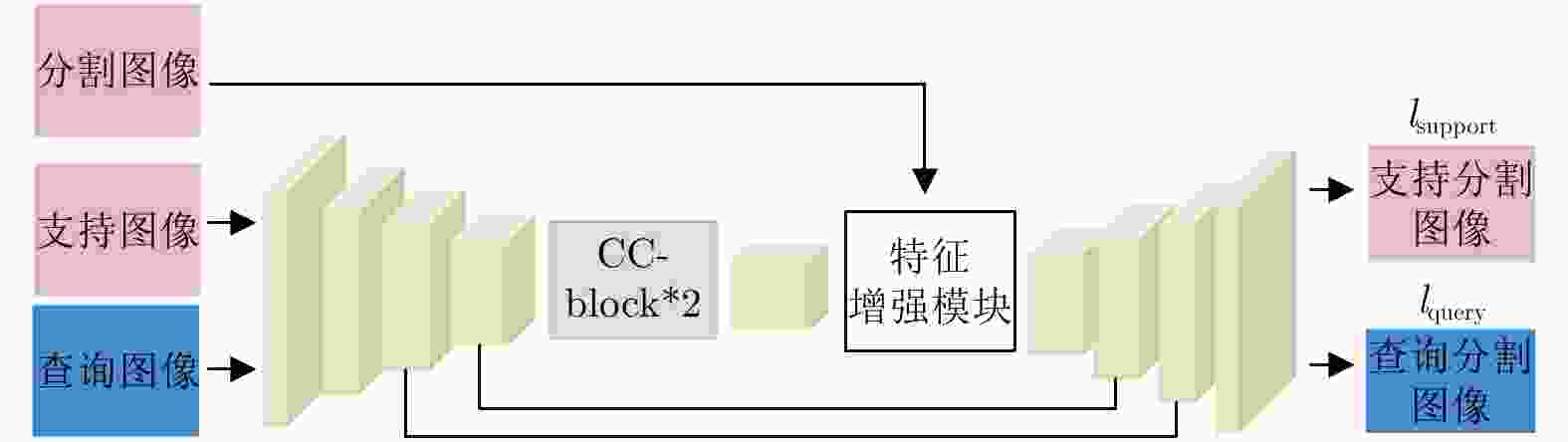
摘要: 在手机屏幕工业化生产过程中,缺陷检测的好坏直接影响手机屏幕的合格率。少量的缺陷样本不足以完成数据驱动的分割网络的训练,因此如何利用少量的缺陷图像完成缺陷分割成为关键问题。该文针对此问题提出一种基于协同注意力的小样本手机屏幕缺陷分割网络(Co-ASNet)。该网络使用交叉注意力块在特征提取时获取更加丰富的上下文缺陷特征信息,同时引入了协同注意力的方式来加强支持图像与查询图像相同缺陷目标之间的特征信息交互,增强缺陷特征表示,另外,使用了改进的联合损失函数来完成网络的训练。该文采用手机屏幕缺陷数据集进行实验,实验结果表明,Co-ASNet能够使用少量的缺陷样本完成良好的缺陷分割效果。Abstract: In the commercial process of mobile phone screens, the quality of defect detection affects directly the qualified rate of mobile phone screens. A few defect samples are not enough to complete the training of data-driven segmentation networks, so how to use a few defect samples to complete the defect segmentation is a key problem. In view of this problem, a Co-Attention Segmentation Network (Co-ASNet) is proposed. This network uses Criss-cross attention blocks to capture contextual defect feature information during feature extraction. At the same time, the Co-attention method is applied to enhance the defect feature information interaction between the same defect target in the support image and query image, and then the defect feature representation is reinforced. Also, the improved joint loss function is used to complete the network training. The experimental results show that Co-ASNet can use a few defect samples to achieve an excellent effect of defect segmentation.
-
表 1 手机屏幕缺陷图像数据集
类别 点 线 面 缺陷图像 


掩膜图像 


表 2 不同分割网络模型在手机屏幕缺陷数据集的性能比较
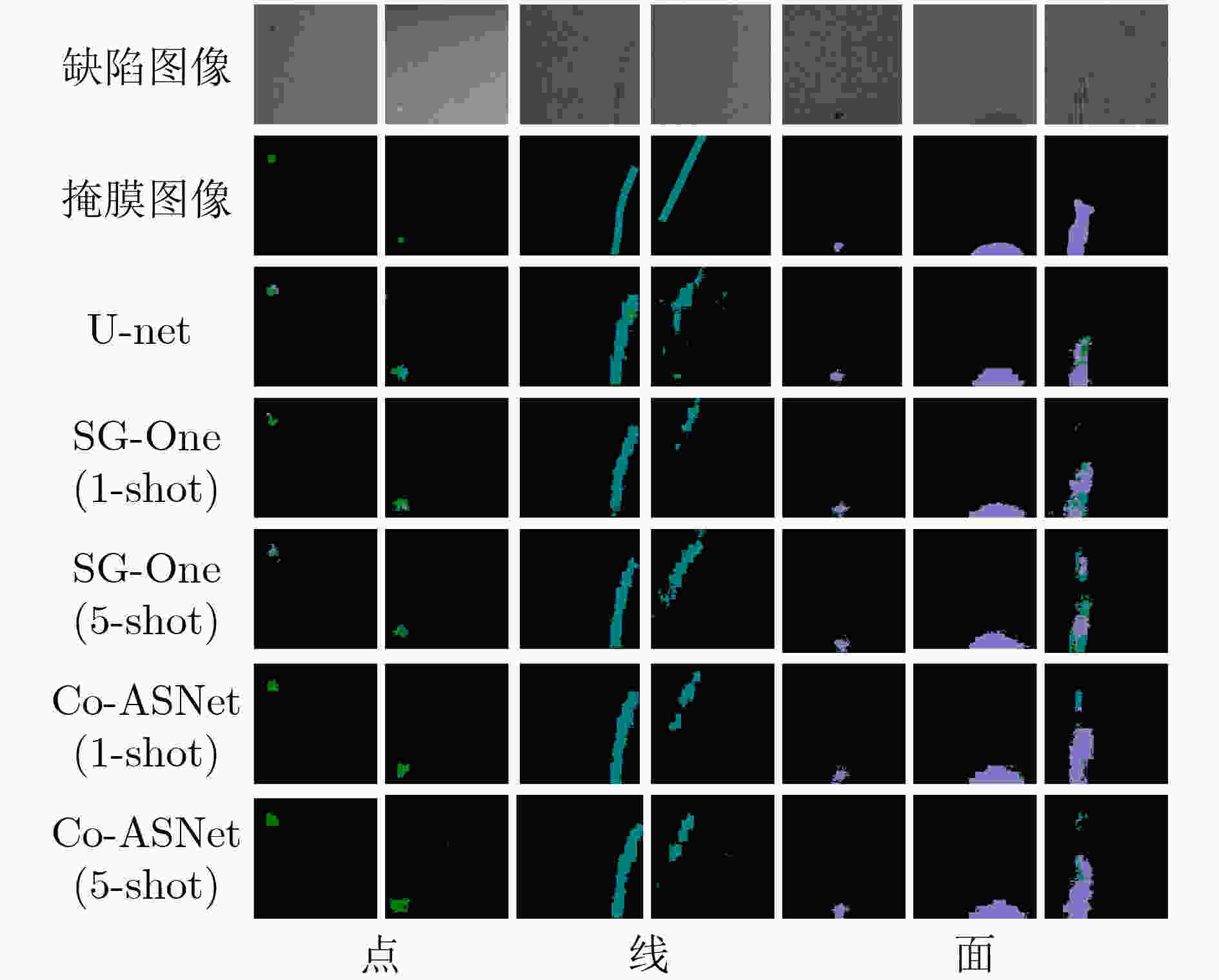
模型 PA MPA MIoU FWMIoU U-net 0.9610 0.4635 0.4074 0.9334 SG-One(1-shot) 0.9658 0.5392 0.4647 0.9412 SG-One(5-shot) 0.9669 0.5199 0.4622 0.9432 Co-ASNet(1-shot) 0.9712 0.6435 0.5588 0.9489 Co-ASNet(5-shot) 0.9709 0.6711 0.5771 0.9482 表 3 在手机屏幕缺陷图像数据集上的分割结果(MIoU)
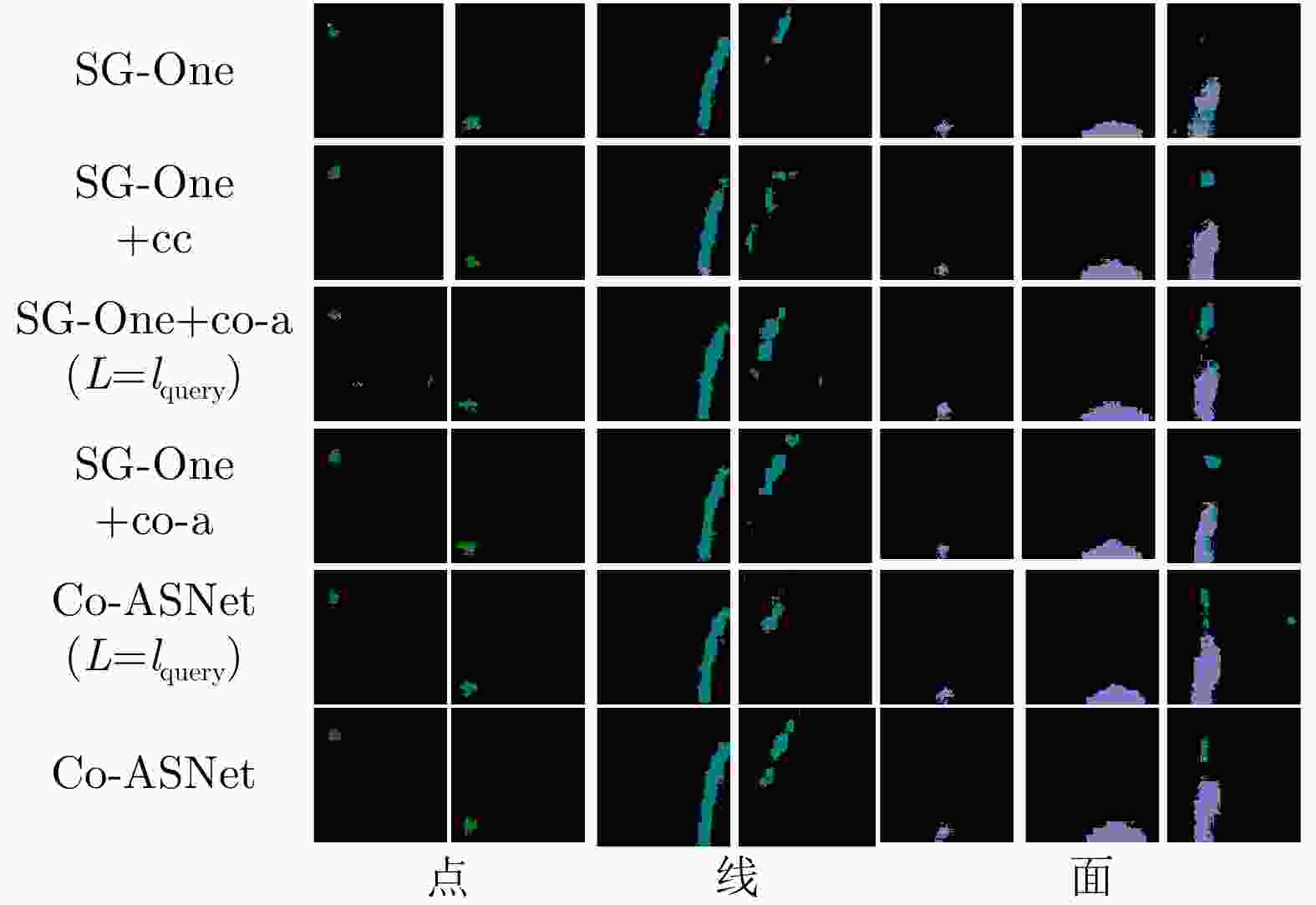
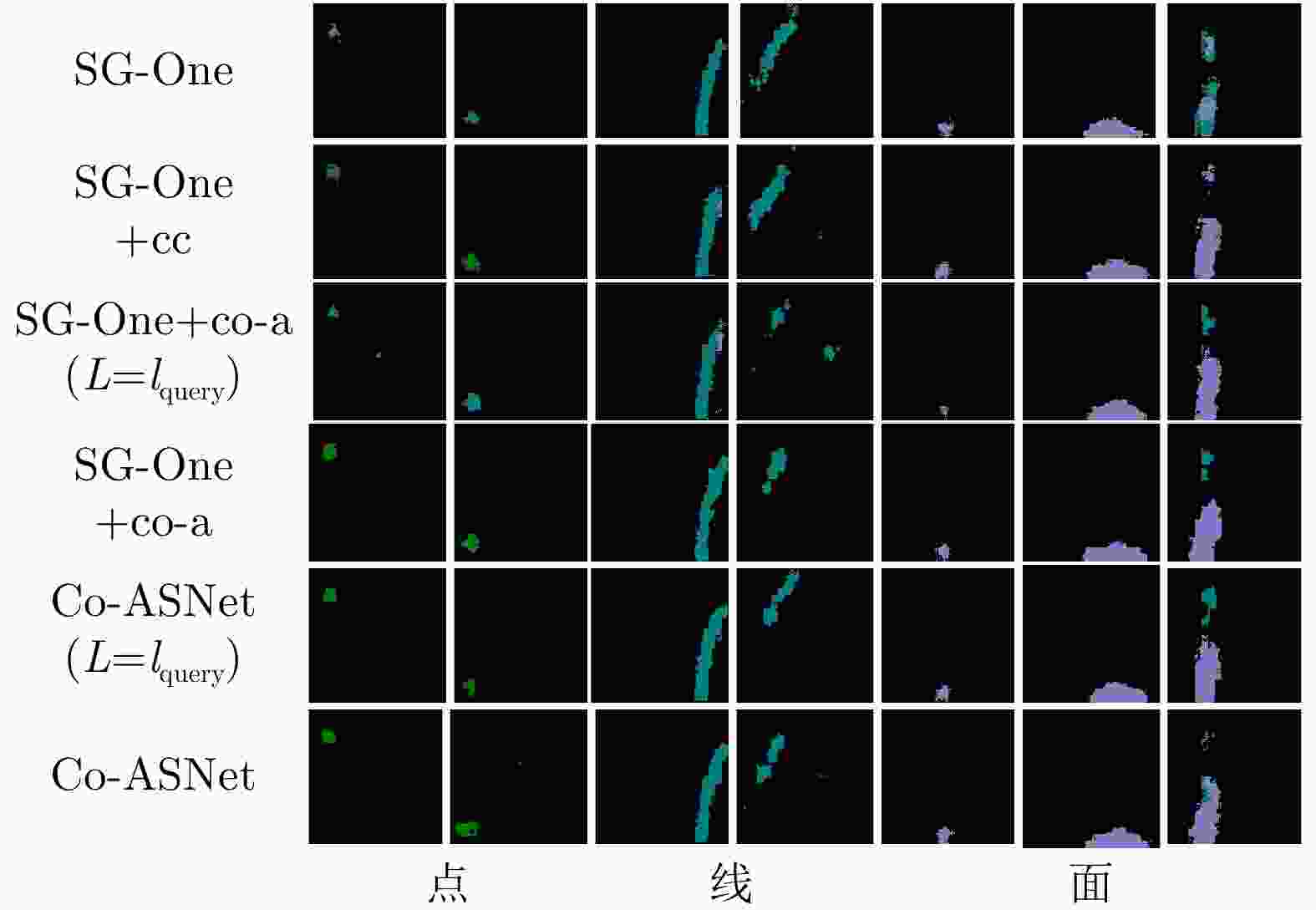
模型 1-shot 5-shot SG-One 0.4647 0.4622 SG-One + cc-block 0.5244 0.5592 SG-One + co-a ($L{\rm{ }} = {l_{{\rm{query}}}}$) 0.4563 0.4584 SG-One + co-a 0.5476 0.5701 Co-ASNet($L{\rm{ }} = {l_{{\rm{query}}}}$) 0.4988 0.5380 Co-ASNet 0.5588 0.5771 -
[1] TABERNIK D, ŠELA S, SKVARČ J, et al. Segmentation-based deep-learning approach for surface-defect detection[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020, 31(3): 759–776. doi: 10.1007/s10845-019-01476-x [2] YU Zhiyang, WU Xiaojun, and GU Xiaodong. Fully convolutional networks for surface defect inspection in industrial environment[C]. 11th International Conference on Computer Vision Systems, Shenzhen, China, 2017: 417-426. [3] QIU Lingteng, WU Xiaojun, and YU Zhiyang. A high-efficiency fully convolutional networks for pixel-wise surface defect detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 15884–15893. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2894420 [4] 张宏伟, 汤文博, 李鹏飞, 等. 基于去噪卷积自编码器的色织衬衫裁片缺陷检测[J]. 纺织高校基础科学学报, 2019, 32(2): 119–125, 132.ZHANG Hongwei, TANG Wenbo, LI Pengfei, et al. Defect detection and location of yarn-dyed shirt piece based on denoising convolutional autoencoder[J]. Basic Sciences Journal of Textile Universities, 2019, 32(2): 119–125, 132. [5] ZHAO Zhixuan, LI Bo, DONG Rong, et al. A surface defect detection method based on positive samples[C]. The 15th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Nanjing, China, 2018: 473-481. [6] YANG Hua, CHEN Yifan, SONG Kaiyou, et al. Multiscale feature-clustering-based fully convolutional autoencoder for fast accurate visual inspection of texture surface defects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(3): 1450–1467. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2018.2886031 [7] HU Guanghua, HUANG Junfeng, WANG Qinghui, et al. Unsupervised fabric defect detection based on a deep convolutional generative adversarial network[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2020, 90(3/4): 247–270. [8] 刘宇轩, 孟凡满, 李宏亮, 等. 一种结合全局和局部相似性的小样本分割方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(3): 665–674.LIU Yuxuan, MENG Fanman, LI Hongliang, et al. A few shot segmentation method combining global and local similarity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(3): 665–674. [9] 董阳, 潘海为, 崔倩娜, 等. 面向多模态磁共振脑瘤图像的小样本分割方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(4): 1049–1054.DONG Yang, PAN Haiwei, CUI Qianna, et al. Few-shot segmentation method for multi-modal magnetic resonance images of brain Tumor[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(4): 1049–1054. [10] 罗善威, 陈黎. 基于双重相似度孪生网络的小样本实例分割[J]. 武汉科技大学学报, 2020, 43(1): 59–66.LUO Shanwei and CHEN Li. Few-shot instance segmentation based on double similarity Siamese network[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2020, 43(1): 59–66. [11] SHELHAMER E, LONG J, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640–651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [12] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241. [13] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, and CIPOLLA R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481–2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [14] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.7062, 2014. [15] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, , 2017, 40(4): 834–848. [16] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706.05587, 2017. [17] CHEN L C, ZHU Yukun, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 833-851. [18] REN Mengye, TRIANTAFILLOU E, RAVI S, et al. Meta-learning for semi-supervised few-shot classification[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1803.00676, 2018. [19] FINN C, ABBEEL P, and LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1126-1135. [20] NICHOL A and SCHULMAN J. Reptile: A scalable metalearning algorithm[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1803.02999, 2018. [21] SNELL J, SWERSKY K, and ZEMEL Z. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4080-4090. [22] SUNG F, YANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li, et al. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1199-1208. [23] VINYALS O, BLUNDELL C, LILLICRAP T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]. Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 3637-3645. [24] SHABAN A, BANSAL S, LIU Zhen, et al. One-shot learning for semantic segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1709.03410, 2017. [25] RAKELLY K, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T, et al. Conditional networks for few-shot semantic segmentation[C]. Sixth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018. [26] ZHANG Xiaolin, WEI Yunchao, YANG Yi, et al. SG-One: Similarity guidance network for one-shot semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(9): 3855–3865. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2992433 [27] ZHANG Chi, LIN Guosheng, LIU Fayao, et al. CANet: Class-agnostic segmentation networks with iterative refinement and attentive few-shot learning[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5212-5221. [28] WANG Kaixin, LIEW J H, ZOU Yingtian, et al. PANet: Few-shot image semantic segmentation with prototype alignment[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 9196-9205. [29] NGUYEN K and TODOROVIC S. Feature weighting and boosting for few-shot segmentation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 622-631. [30] LIU Weide, ZHANG Chi, LIN Guosheng, et al. CRNet: Cross-reference networks for few-shot segmentation[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 4164-4172. [31] HUANG Zilong, WANG Xinggang, HUANG Lichao, et al. CCNet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 603-612. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
