Remote Sensing Image Retrieval Based on Multi-scale Pooling and Norm Attention Mechanism
-
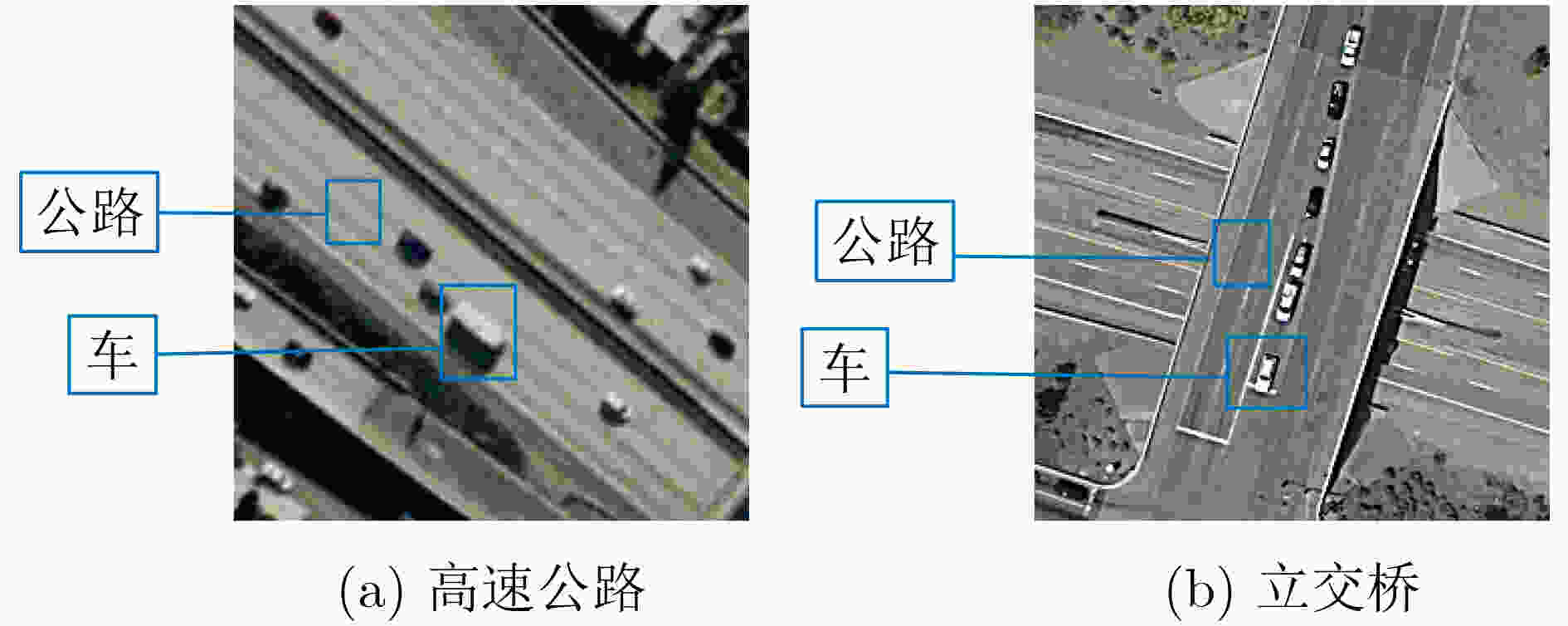
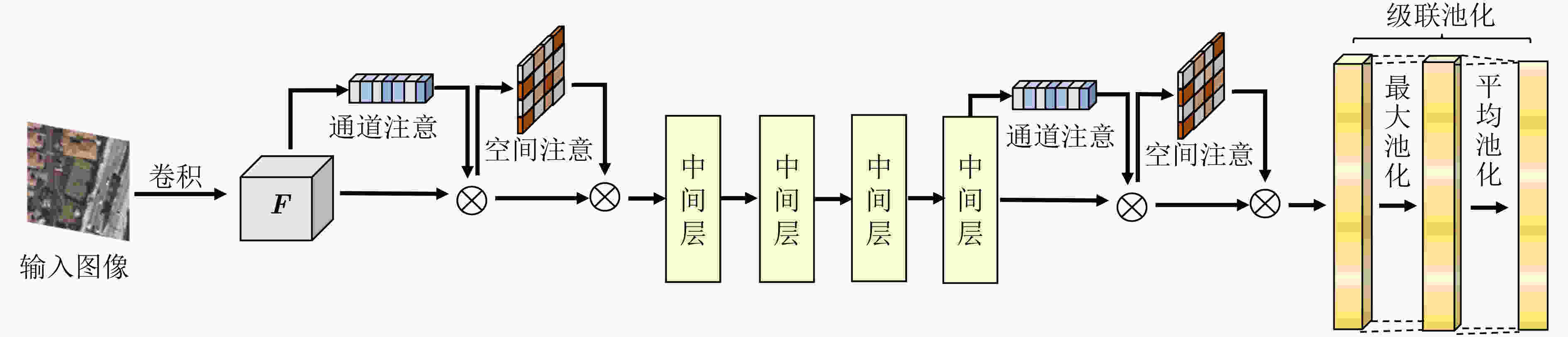
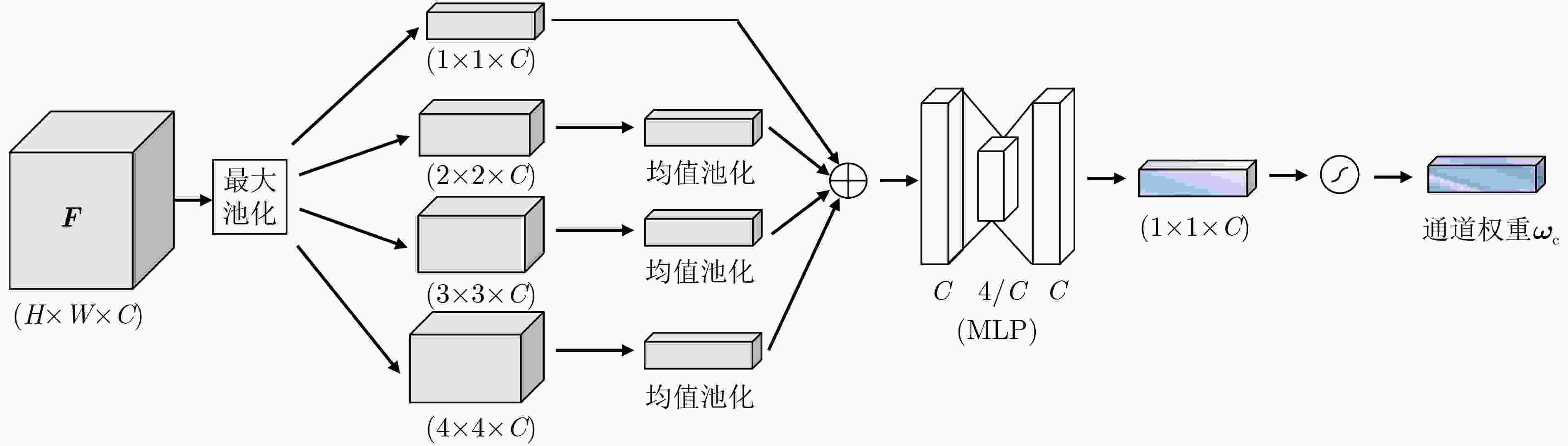
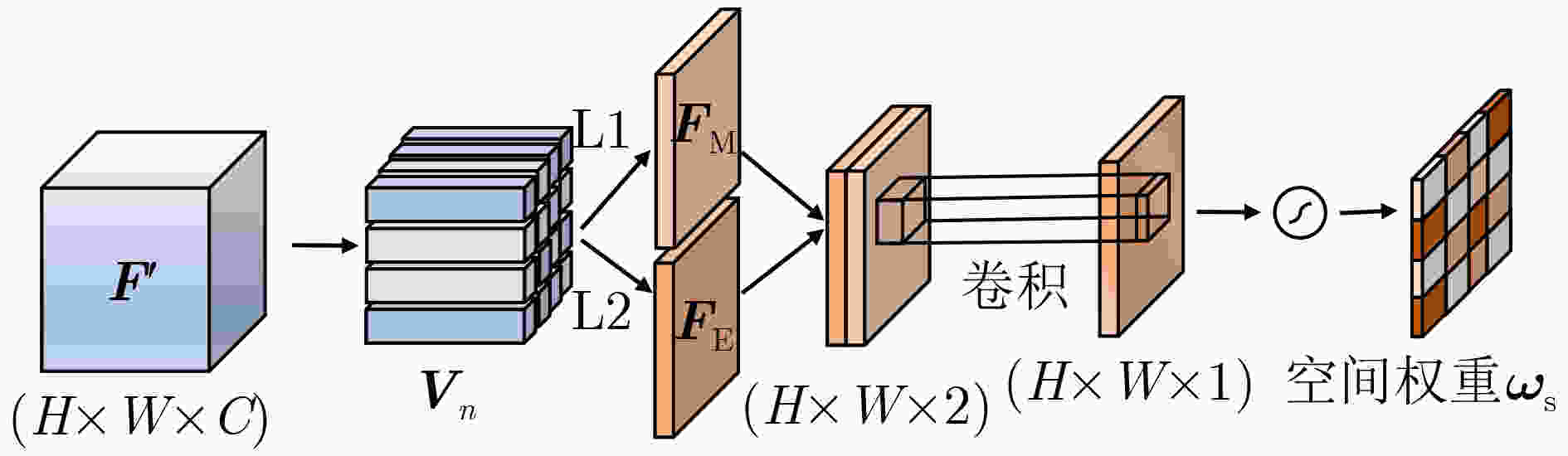
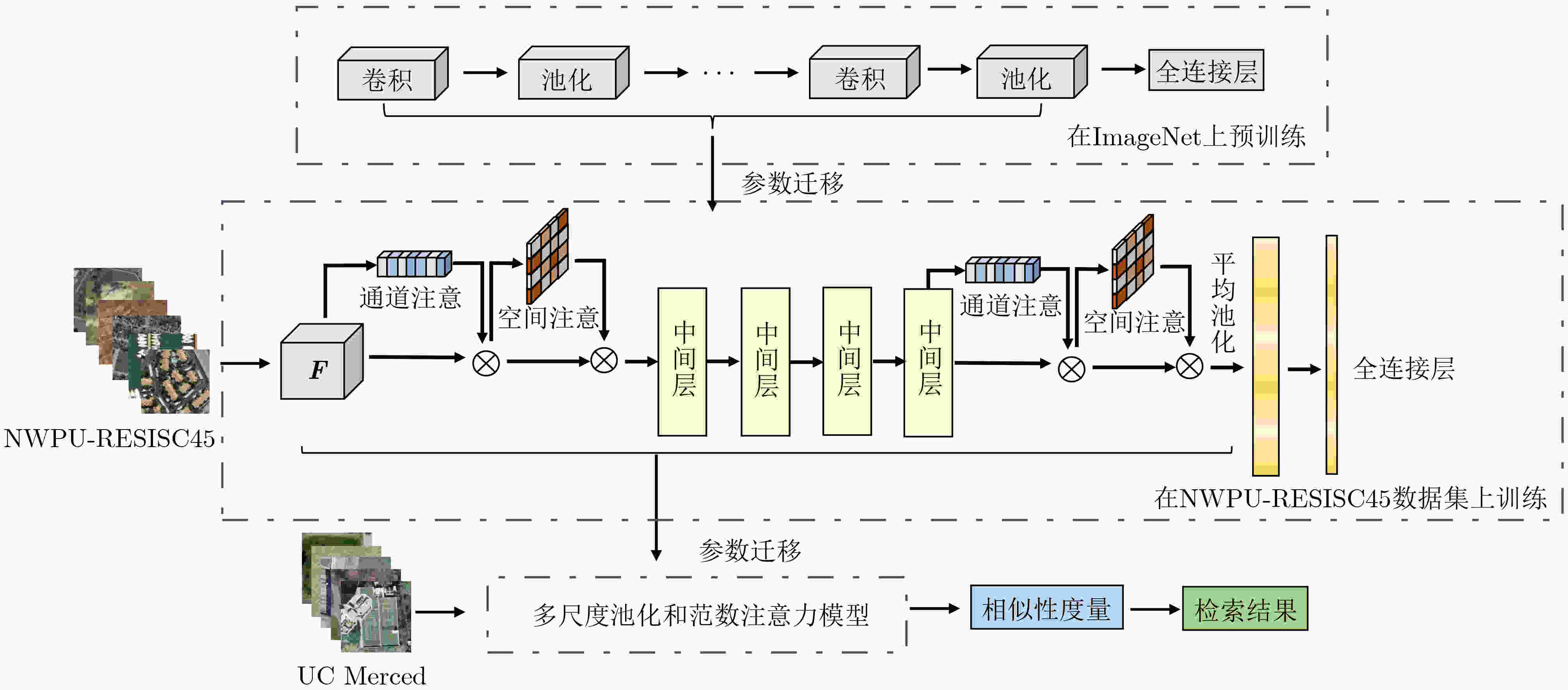
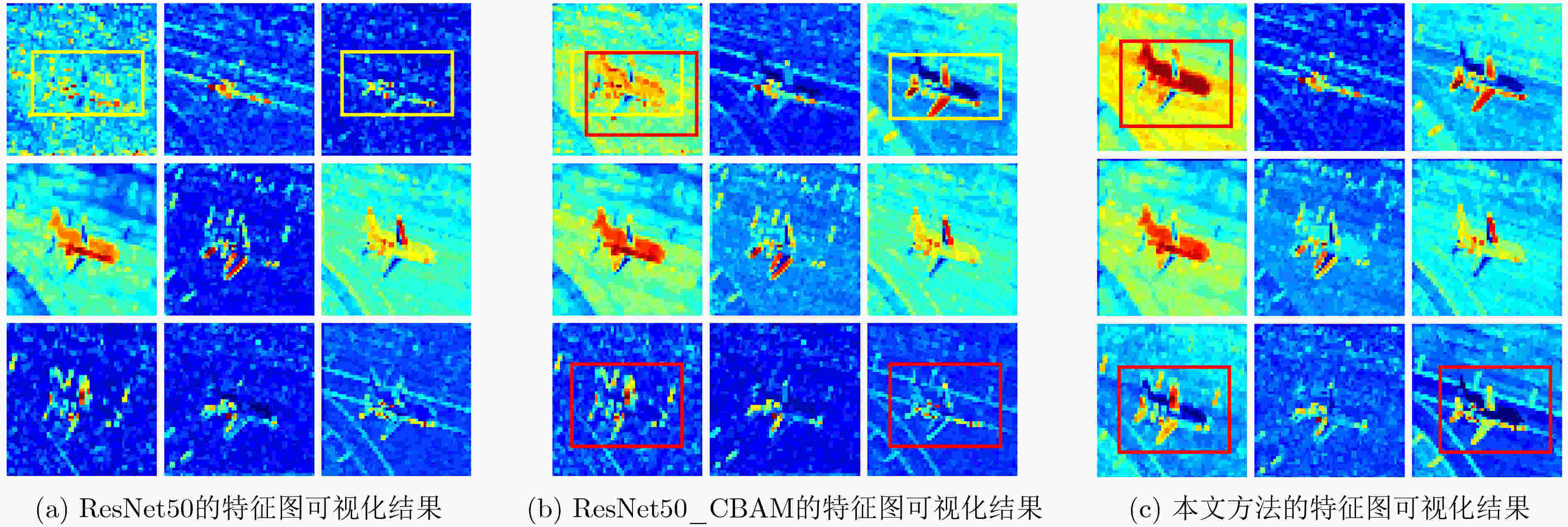
摘要: 遥感图像内容丰富,一般的深度模型提取遥感图像特征时容易受复杂背景干扰,对关键特征的提取效果不佳,并且难以表达图像的空间信息,该文提出一种基于多尺度池化和范数注意力机制的深度卷积神经网络,在通道层面与空间层面自适应地给显著特征加权。首先,在多尺度池化通道注意力模块中,结合空间金字塔池化的思想,对每个通道上的特征图进行不同尺度的最大池化。接着,采用自适应均值池化将尺寸不同的特征图转换为统一尺寸,以便通过逐像素相加的方式来关注不同尺度的显著特征。然后,在范数空间注意力模块中,将各通道对应同一空间位置的像素构成向量,通过计算向量组的L1范数和L2范数,获得具有空间信息的特征图。最后,采用级联池化的方法优化高层特征,并将该高层特征用于遥感图像检索。在UC Merced, AID与NWPU-RESISC45 3个数据集上进行实验,结果表明该文所提注意力模型,关注了不同尺度的显著特征,结合了空间信息,提高了检索性能。Abstract: Remote sensing images have rich content, and then the features extracted by the general depth model are easily interfered by the complex background. The key features can not be extracted well, and it is difficult to express the spatial information of the image. A deep convolutional neural network based on multi-scale pooling and norm attention mechanism is proposed, which weights adaptively salient features at the channel level and the spatial level. First, in the multi-scale pooling channel attention module, the max pooling of different scales is performed on the feature map of each channel based on spatial pyramid pooling. Next, the feature maps of different sizes are transformed to a uniform size by adaptive average pooling. Thus the salient features of different scales can be paid attention by element-wise addition. Then, in the norm spatial attention module, the pixels corresponding to the same spatial position of each channel are formed into vectors, and the feature map with spatial information is obtained by calculating the L1 norm and L2 norm of the vector group. Finally, the cascaded pooling method is adopted to optimize the high-level features, and the high-level features are used for remote sensing image retrieval. Experiment are conducted on UC Merced data set, AID data set and NWPU-RESISC45 data set. The results show that the proposed attention model improves the retrieval performance by concerning the salient features of different scales and combining the spatial information.
-
Key words:
- Remote sensing image retrieval /
- Spatial pyramid /
- Norm /
- Attention mechanism /
- Cascading pooling
-
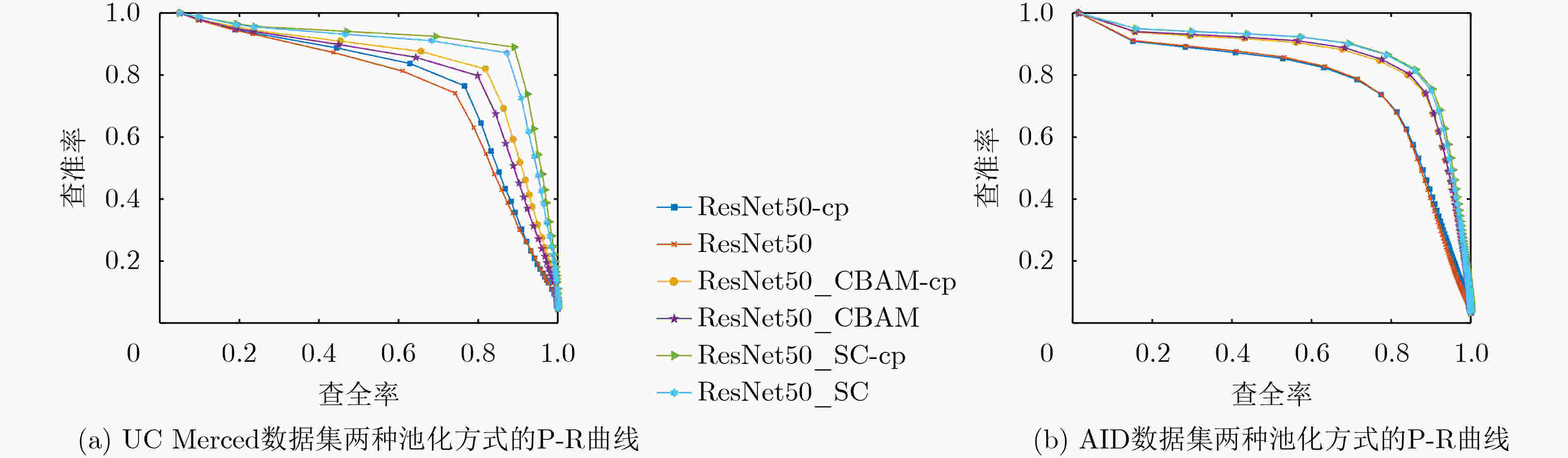
表 1 UC Merced数据集和AID数据集不同方法检索结果
方法 UC Merced数据集 AID数据集 mAP ANMRR mAP ANMRR Resnet50-cp 0.812 0.163 0.850 0.142 Resnet50_CBAM-cp 0.870 0.110 0.920 0.083 Resnet50_C-cp 0.898 0.084 0.935 0.073 Resnet50_S-cp 0.892 0.073 0.936 0.074 Resnet50_SC-cp 0.924 0.059 0.940 0.068 注:加粗字体为每列最优结果。 表 2 不同方法的平均检索时间比较(ms)
方法 平均检索时间 Resnet50 2.17 Resnet50_CBAM 2.18 Resnet50_SC 2.18 注:加粗字体为每列最优结果。 表 3 迁移特征的检索结果
方法 全局池化 级联池化 mAP ANMRR mAP ANMRR Resnet50_CBAM 0.763 0.190 0.790 0.168 Resnet50_C 0.800 0.161 0.809 0.154 Resnet50_S 0.789 0.169 0.812 0.149 Resnet50_SC 0.818 0.146 0.827 0.138 注:加粗字体为每列最优结果。 -
[1] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. Computer Science, arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [2] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. [3] HU Jie, SHEN Li, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011–2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [4] 叶发茂, 董萌, 罗威, 等. 基于卷积神经网络和重排序的农业遥感图像检索[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(15): 138–145. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.15.018YE Famao, DONG Meng, LUO Wei, et al. Agricultural remote sensing image retrieval based on convolutional neural network and reranking[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(15): 138–145. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.15.018 [5] LI Yansheng, ZHANG Yongjun, HUANG Xin, et al. Large-scale remote sensing image retrieval by deep hashing neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 950–965. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2756911 [6] ROY S, SANGINETO E, DEMIR B, et al. Metric-learning-based deep hashing network for content-based retrieval of remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(2): 226–230. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2974629 [7] 彭晏飞, 宋晓男, 武宏, 等. 结合深度学习与相关反馈的遥感图像检索[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 24(3): 420–434. doi: 10.11834/jig.180384PENG Yanfei, SONG Xiaonan, WU Hong, et al. Remote sensing image retrieval combined with deep learning and relevance feedback[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(3): 420–434. doi: 10.11834/jig.180384 [8] YE Famao, ZHAO Xuqing, LUO Wei, et al. Query-adaptive remote sensing image retrieval based on image rank similarity and image-to-query class similarity[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 116824–116839. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004360 [9] MA Chenhui, MU Xiaodong, and SHA Dexuan. Multi-layers feature fusion of convolutional neural network for scene classification of remote sensing[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 121685–121694. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2936215 [10] LIU Yishu, CHEN Conghui, HAN Zhengzhuo, et al. High-resolution remote sensing image retrieval based on classification-similarity networks and double fusion[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 1119–1133. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2981372 [11] 储珺, 朱晓阳, 冷璐, 等. 引入通道注意力和残差学习的目标检测器[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2020, 33(10): 889–897. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.202010003CHU Jun, ZHU Xiaoyang, LENG Lu, et al. Target detector with channel attention and residual learning[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 33(10): 889–897. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.202010003 [12] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. [13] 翟鹏博, 杨浩, 宋婷婷, 等. 结合注意力机制的双路径语义分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(8): 1627–1636. doi: 10.11834/jig.190533ZHAI Pengbo, YANG Hao, SONG Tingting, et al. Two-path semantic segmentation algorithm combining attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(8): 1627–1636. doi: 10.11834/jig.190533 [14] WANG Qi, LIU Shaoteng, CHANUSSOT J, et al. Scene classification with recurrent attention of VHR remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 1155–1167. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2864987 [15] GUO Yiyou, JI Jingsheng, LU Xiankai, et al. Global-local attention network for aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 67200–67212. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2918732 [16] ZHANG Shu, YUAN Qiangqiang, LI Jie, et al. Scene-adaptive remote sensing image super-resolution using a multiscale attention network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(7): 4764–4779. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2966805 [17] 徐从安, 吕亚飞, 张筱晗, 等. 基于双重注意力机制的遥感图像场景分类特征表示方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 683–691. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200568XU Congan, LÜ Yafei, ZHANG Xiaohan, et al. A Discriminative feature representation method based on dual attention mechanism for remote sensing image scene classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 683–691. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200568 [18] ZHANG Yongmei, XU Min, and LI Xiaodong. Remote sensing image retrieval based on DenseNet model and CBAM[C]. 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Computer and Communication Engineering Technology (CCET), Beijing, China, 2020: 86–90. doi: 10.1109/CCET50901.2020.9213121. [19] WANG Yameng, JI Shunping, LU Meng, et al. Attention boosted bilinear pooling for remote sensing image retrieval[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(7): 2704–2724. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1697010 [20] LIU Chao, MA Jingjing, TANG Xu, et al. Deep hash learning for remote sensing image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(4): 3420–3443. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3007533 [21] XIONG Wei, LÜ Yafei, CUI Yaqi, et al. A discriminative feature learning approach for remote sensing image retrieval[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(3): 281. doi: 10.3390/rs11030281 [22] GE Yun, TANG Yiling, JIANG Shunliang, et al. Region-based cascade pooling of convolutional features for HRRS image retrieval[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 9(10): 1002–1010. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2018.1504334 [23] CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, and LU Xiaoqiang. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(10): 1865–1883. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2675998 [24] 孙月驰, 李冠. 基于卷积神经网络嵌套模型的人群异常行为检测[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2019, 36(3): 196–201, 276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.03.036SUN Yuechi and LI Guan. Abnormal behavior detection of crowds based on nested model of convolutional neural network[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2019, 36(3): 196–201, 276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2019.03.036 [25] YANG Yi and NEWSAM S. Geographic image retrieval using local invariant features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(2): 818–832. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2205158 [26] XIA Guisong, HU Jingwen, HU Fan, et al. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3965–3981. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2685945 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
