The Uncertainty Similarity Measure of Cloud Model Based on the Fusion of Distribution Contour and Local Feature
-
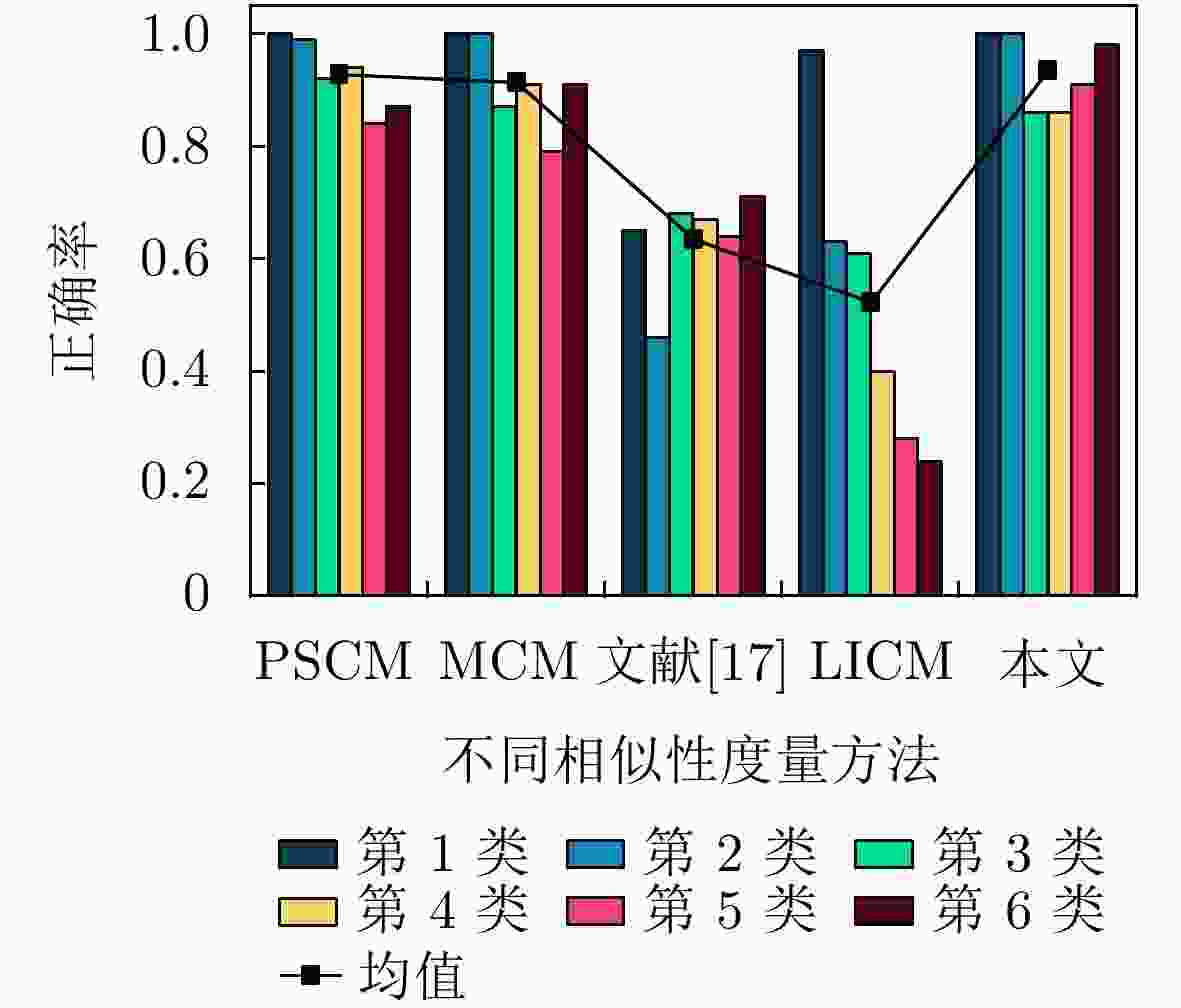
摘要: 针对当前基于云模型的不确定性相似度量或为精确局部数据的量化计算,或单纯通过其整体几何特征进行度量,导致结果具有较大的片面性问题,综合考虑云模型整体几何特征与微观云滴分布贡献,该文提出了一种分布轮廓与局部特征融合的不确定性相似度量方法,即基于包络带及其云滴贡献度的云模型不确定性相似度量方法(EACCM)。该方法将体现云模型几何特征的包络带(内包络曲线和外包络曲线之间区域)作为相似度量基础,结合其重叠部分包含云滴的贡献度大小建立综合度量模型。仿真结果显示,该方法度量结果更为科学合理,并且有效避免了同一数字特征相差较大或者非常接近时导致的相似性异常问题。Abstract: In view of the fact that the current uncertainty similarity measurement based on cloud model is either the quantitative calculation of accurate local data, or the measurement only through its overall geometric features, which leads to the result with great one sidedness. In this paper, considering the overall geometric features of cloud model and the contribution of micro cloud droplets distribution, an uncertainty similarity measurement method based on the fusion of distribution contour and local features is proposed, i.e. the Envelope Area of the Contribution based on Cloud Model (EACCM). In this method, the envelope (the area between the inner envelope curve and the outer envelope curve) which reflects the geometric characteristics of the cloud model is used as the basis of similarity measurement, and a comprehensive measurement model is established based on the contribution of cloud droplets contained in the overlapped part. The simulation results show that the method is more scientific and reasonable, and can effectively avoid the problem of abnormally similarity caused by the large difference or very close of the same digital features.
-
Key words:
- Cloud model /
- Similarity measurement /
- Normal distribution /
- Envelope /
- Contribution
-
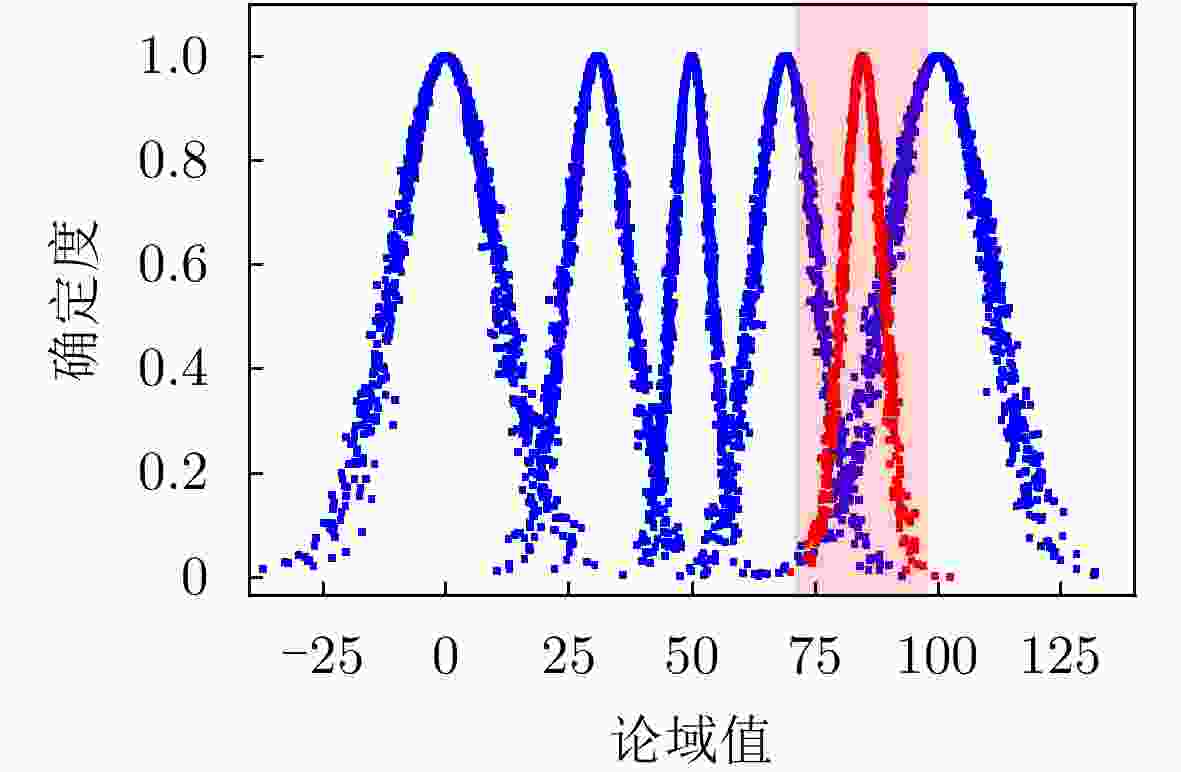
表 1 能力等级划分对应的子区间及评估标尺
等级描述 区间 云模型 优 [68.8, 100.0] C5(100.0, 10.3, 1.04) 良 [49.9, 88.3] C4(69.1, 6.37, 0.64) 中 [38.0, 62.0] C3(50.0, 3.93, 0.39) 差 [11.7, 50.1] C2(30.9, 6.37, 0.64) 极差 [0, 31.2] C1(0, 10.3, 1.04) -
[1] NAVON D. Forest before trees: The precedence of global features in visual perception[J]. Cognitive Psychology, 1977, 9(3): 353–383. doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(77)90012-3 [2] ZHANG Haoyuan and MARSH D W R. Multi-state deterioration prediction for infrastructure asset: Learning from uncertain data, knowledge and similar groups[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 529: 197–213. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.11.017 [3] LIU Huchen, LUAN Xue, LIN Wanlong, et al. Grey reasoning petri nets for large group knowledge representation and reasoning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(12): 3315–3329. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2949770 [4] LUSH G J. Probability theory[J]. Nature, 1978, 272(5648): 107. doi: 10.1038/272107b0 [5] ZADEH L A. Fuzzy sets[J]. Information and Control, 1965, 8(3): 338–353. doi: 10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X [6] PAWLAK Z. Rough sets[J]. International Journal of Computer & Information Sciences, 1982, 11(5): 341–356. doi: 10.1007/BF01001956 [7] 杨洁, 王国胤, 张清华, 等. 多粒度云模型的相似性度量[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2018, 31(8): 677–692. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201808001YANG Jie, WANG Guoyin, ZHANG Qinghua, et al. Similarity measure of multi-granularity cloud model[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 31(8): 677–692. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201808001 [8] 李德毅, 孟海军, 史雪梅. 隶属云和隶属云发生器[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 1995, 32(6): 15–20.LI Deyi, MENG Haijun, and SHI Xuemei. Membership clouds and membership cloud generators[J]. Computer R &D, 1995, 32(6): 15–20. [9] 尹荣荣, 张文元, 杨绸绸, 等. 基于简化云与K/N投票的选择性转发攻击检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 2841–2848. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190274YIN Rongrong, ZHANG Wenyuan, YANG Chouchou, et al. A selective forwarding attack detection method based on simplified cloud and K/N voting model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 2841–2848. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190274 [10] 王佩, 张婧, 张威威. 基于云模型和多层权重求解的多粒度语言大群体决策方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(9): 2257–2266. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.0102WANG Pei, ZHANG Jing, and ZHANG Weiwei. Multi-granularity linguistic large group decision-making based on cloud model and multi-layer weight determination[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(9): 2257–2266. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.0102 [11] 刘敦楠, 张潜, 李霄彤, 等. 基于云模型与模糊Petri网的电力市场潜在危害行为识别[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43(2): 25–33. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180405004LIU Dunnan, ZHANG Qian, LI Xiaotong, et al. Identification of potential harmful behaviors in electricity market based on cloud model and fuzzy Petri net[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(2): 25–33. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180405004 [12] 王琪, 秦伟伟, 沈强, 等. 基于Weibull云模型的陀螺输出可靠性分析[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2020, 28(3): 415–420. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2020.03.021WANG Qi, QIN Weiwei, SHEN Qiang, et al. Reliability analysis of gyro based on Weibull cloud model[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2020, 28(3): 415–420. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2020.03.021 [13] PENG Honggang, ZHANG Hongyu, WANG Jianqiang, et al. An uncertain Z-number multicriteria group decision-making method with cloud models[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 501: 136–154. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.05.090 [14] 张光卫, 李德毅, 李鹏, 等. 基于云模型的协同过滤推荐算法[J]. 软件学报, 2007, 18(10): 2403–2411. doi: 10.1360/jos182403ZHANG Guangwei, LI Deyi, LI Peng, et al. A collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on cloud model[J]. Journal of Software, 2007, 18(10): 2403–2411. doi: 10.1360/jos182403 [15] CHEN Lin. Topological structure in visual perception[J]. Science, 1982, 218(4573): 699–700. doi: 10.1126/science.7134969 [16] 张勇, 赵东宁, 李德毅. 相似云及其度量分析方法[J]. 信息与控制, 2004, 33(2): 129–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0411.2004.02.001ZHANG Yong, ZHAO Dongning, and LI Deyi. The similar cloud and the measurement method[J]. Information and Control, 2004, 33(2): 129–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0411.2004.02.001 [17] WANG Pei, XU Xuanhua, HUANG Shuai, et al. A linguistic large group decision making method based on the cloud model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(6): 3314–3326. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2822242 [18] 徐聪, 潘小东. 基于正态云相似度的语言型多属性群决策方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(6): 218–223. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.06.033XU Cong and PAN Xiaodong. Linguistic multi-attribute group decision making method based on normal cloud similarity[J]. Computer Science, 2019, 46(6): 218–223. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.06.033 [19] 李海林, 郭崇慧, 邱望仁. 正态云模型相似度计算方法[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(11): 2561–2567.LI Hailin, GUO Chonghui, and QIU Wangren. Similarity measurement between normal cloud models[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(11): 2561–2567. [20] 查翔, 倪世宏, 谢川, 等. 云相似度的概念跃升间接计算方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(7): 1676–1682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.07.32ZHA Xiang, NI Shihong, XIE Chuan, et al. Indirect computation approach of cloud model similarity based on conception skipping[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(7): 1676–1682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.07.32 [21] 李德毅. 知识表示中的不确定性[J]. 中国工程科学, 2000, 2(10): 73–79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2000.10.018LI Deyi. Uncertainty in knowledge representation[J]. Engineering Science, 2000, 2(10): 73–79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2000.10.018 [22] 李德毅, 刘常昱, 淦文燕. 正态云模型的重尾性质证明[J]. 中国工程科学, 2011, 13(4): 20–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2011.04.004LI Deyi, LIU Changyu, and GAN Wenyan. Proof of the heavy-tailed property of normal cloud model[J]. Engineering Science, 2011, 13(4): 20–23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2011.04.004 [23] 付凯, 夏靖波, 韦泽鲲, 等. 基于相互隶属度的云模型相似性度量方法[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(4): 405–411. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.04.013FU Kai, XIA Jingbo, WEI Zekun, et al. Similarity measurement between cloud models based on mutual membership degree[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(4): 405–411. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.04.013 [24] 杨宏伟, 岳勇, 杨学强. 一种新的一维正态云概念隶属度判定算法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2012, 18(9): 2117–2123. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2012.09.217.yanghw.024YANG Hongwei, YUE Yong, and YANG Xueqiang. New determining algorithm for conception membership of one-dimensional normal cloud[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2012, 18(9): 2117–2123. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2012.09.217.yanghw.024 [25] 许昌林, 王国胤. 实现稳定双向认知映射的逆向云变换算法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2013, 26(7): 634–642. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2013.07.005XU Changlin and WANG Guoyin. Backward cloud transformation algorithm for realizing stability bidirectional cognitive mapping[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 26(7): 634–642. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2013.07.005 -





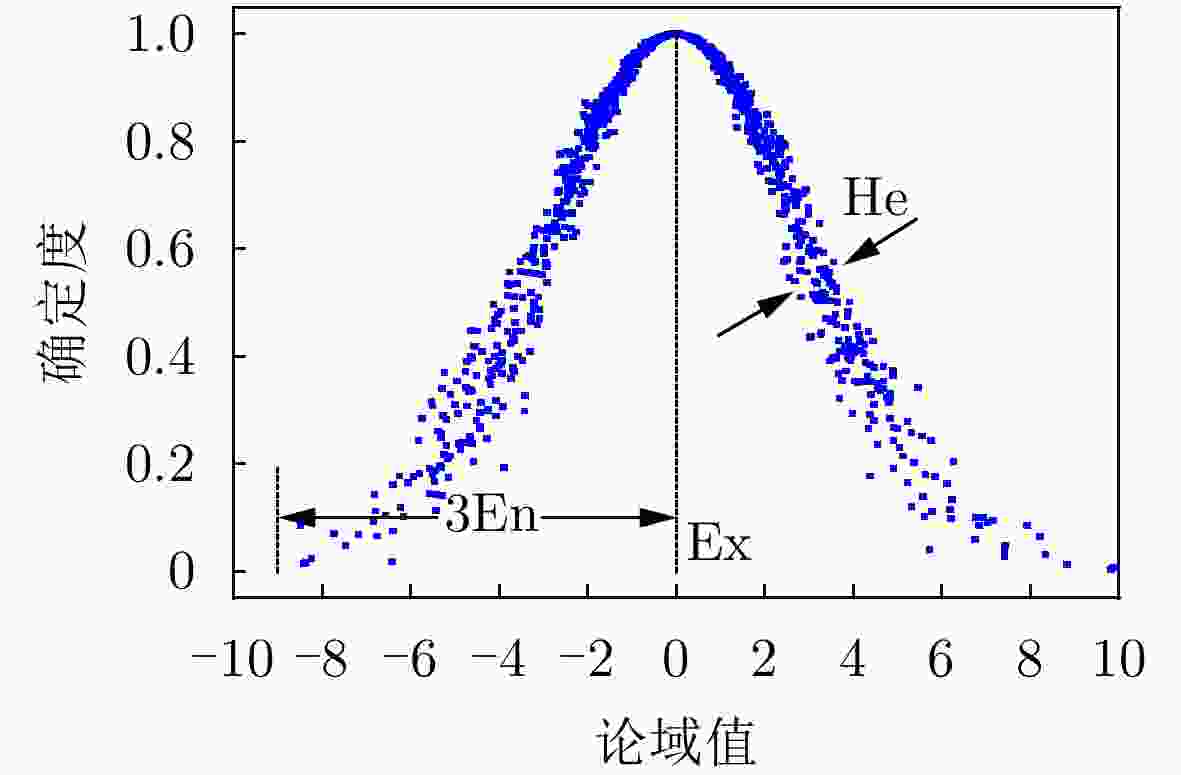
 下载:
下载:
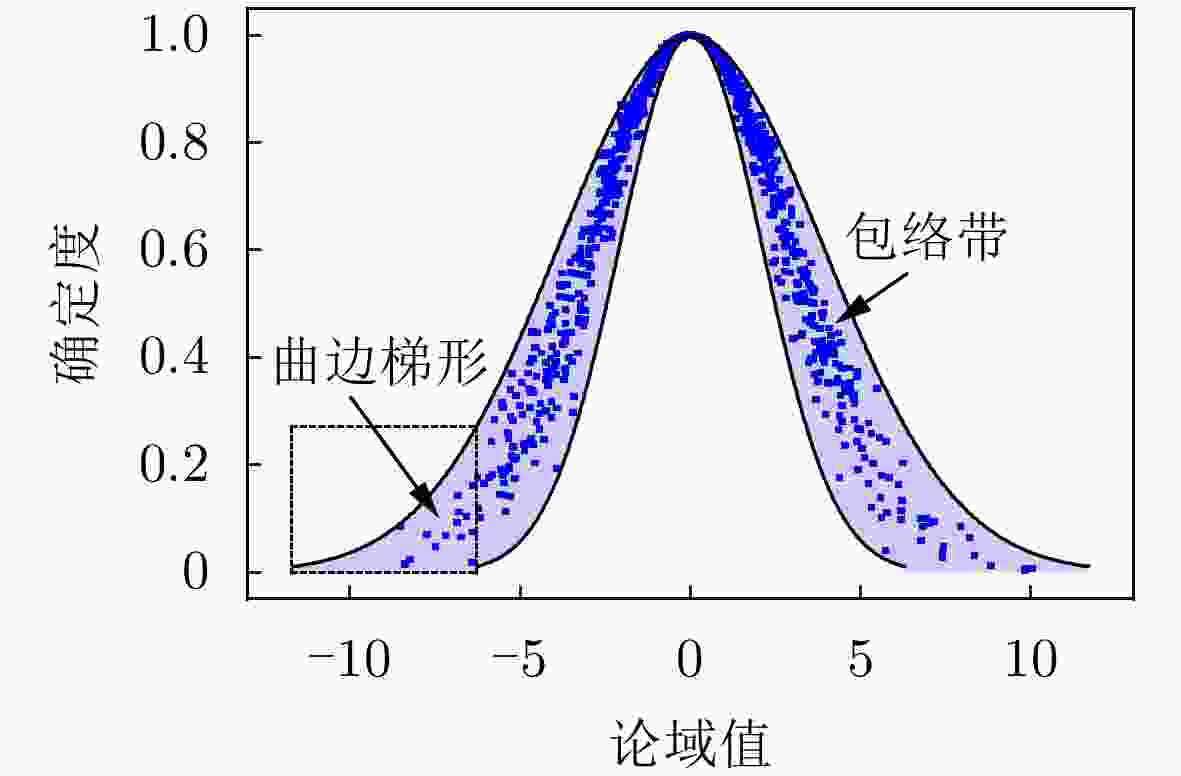
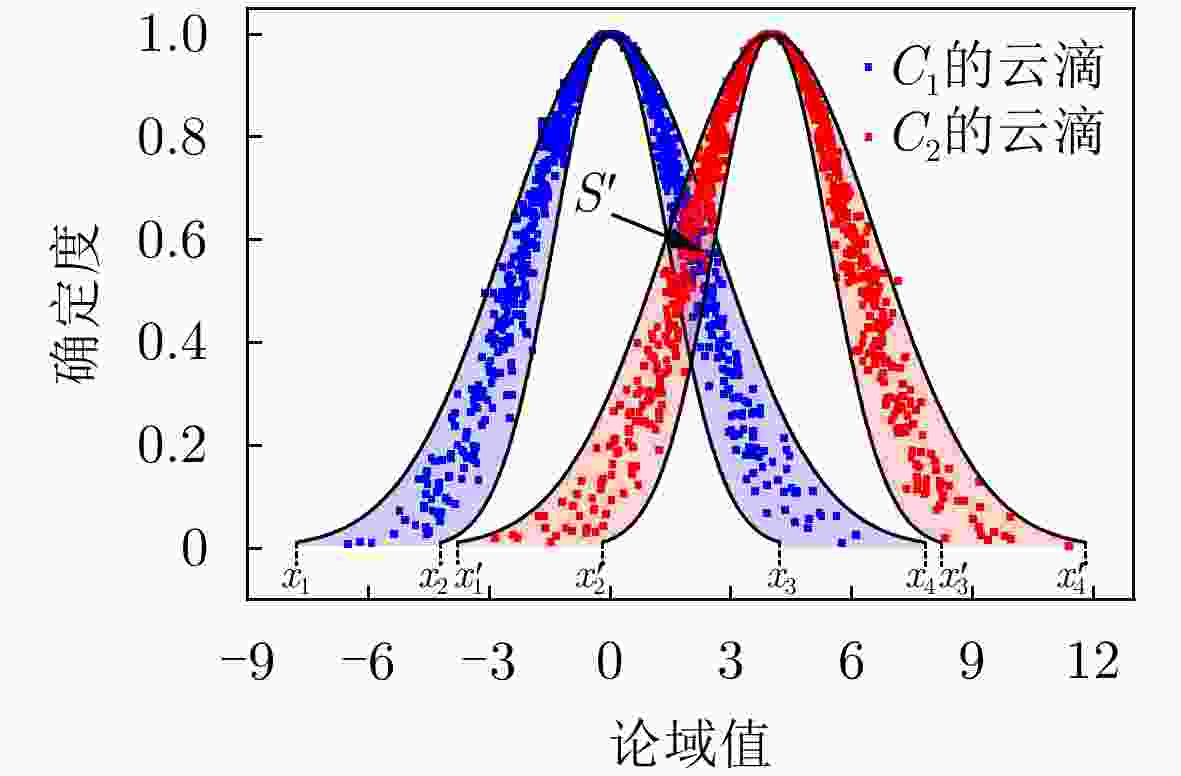


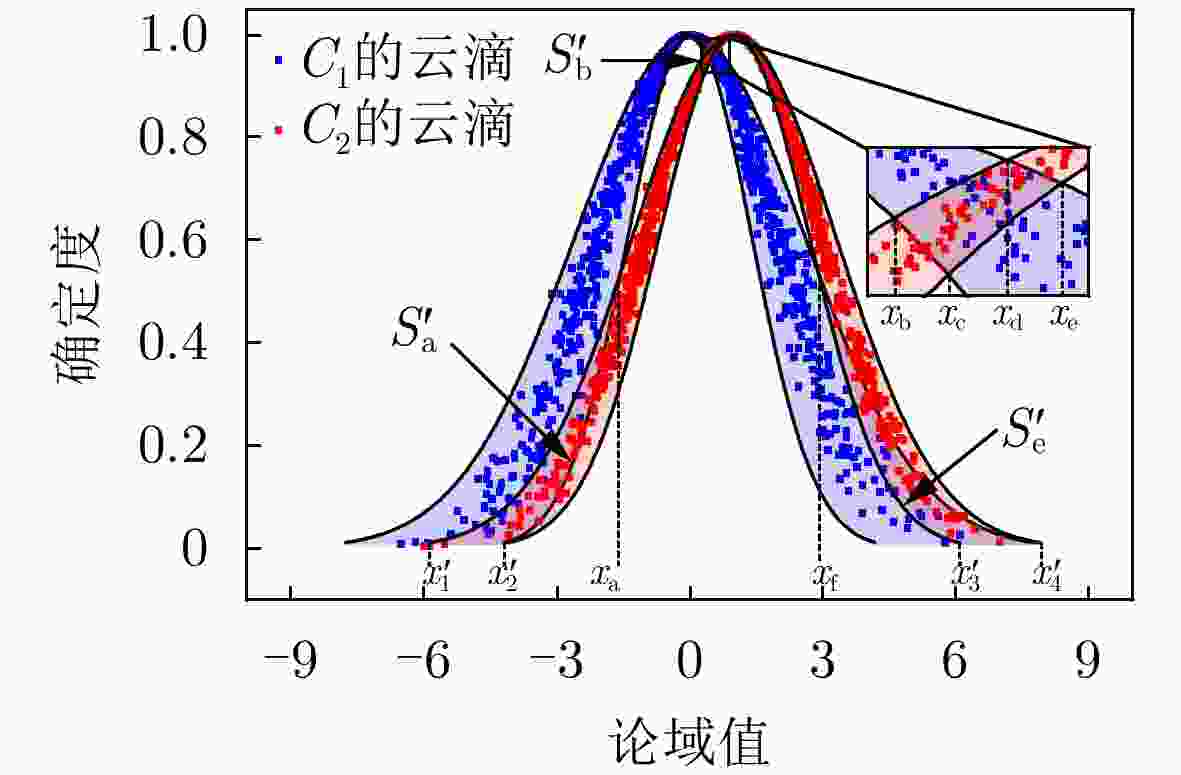


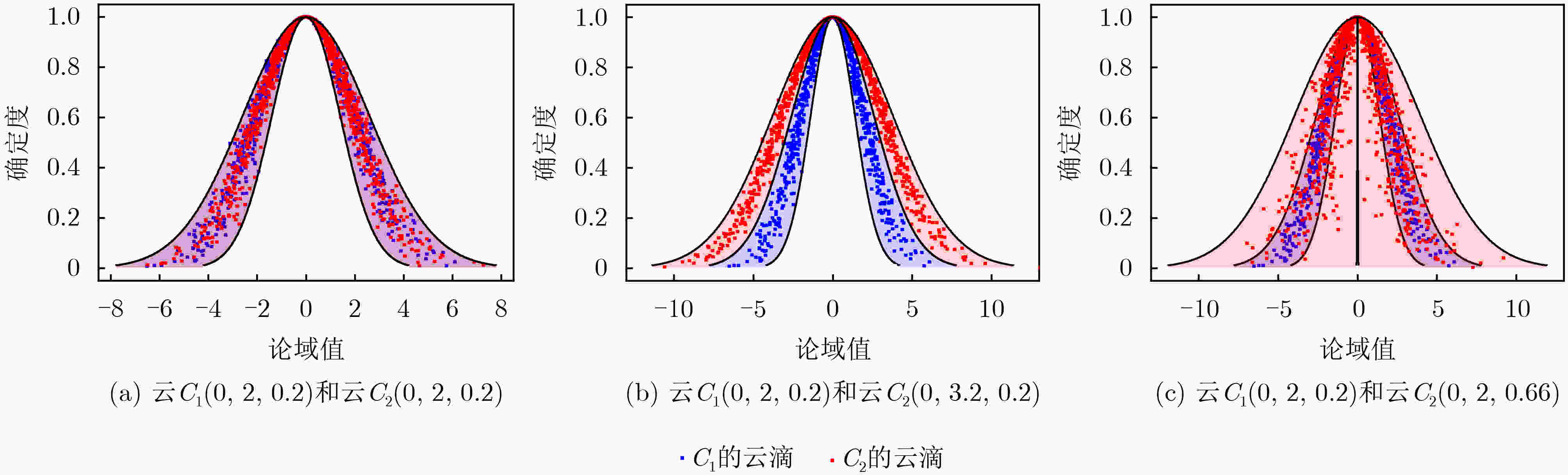




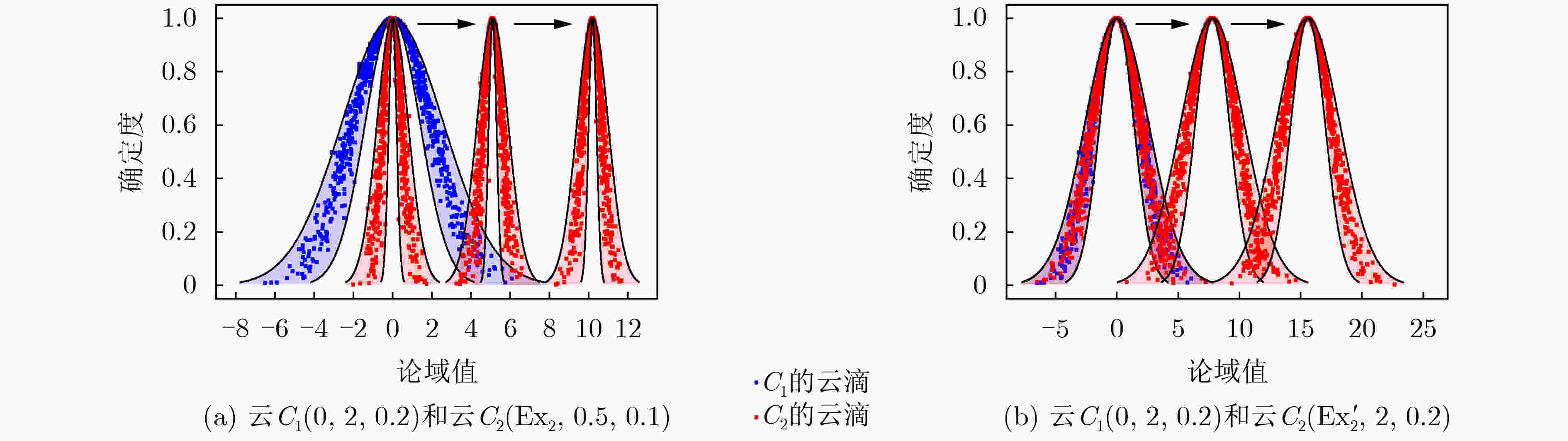




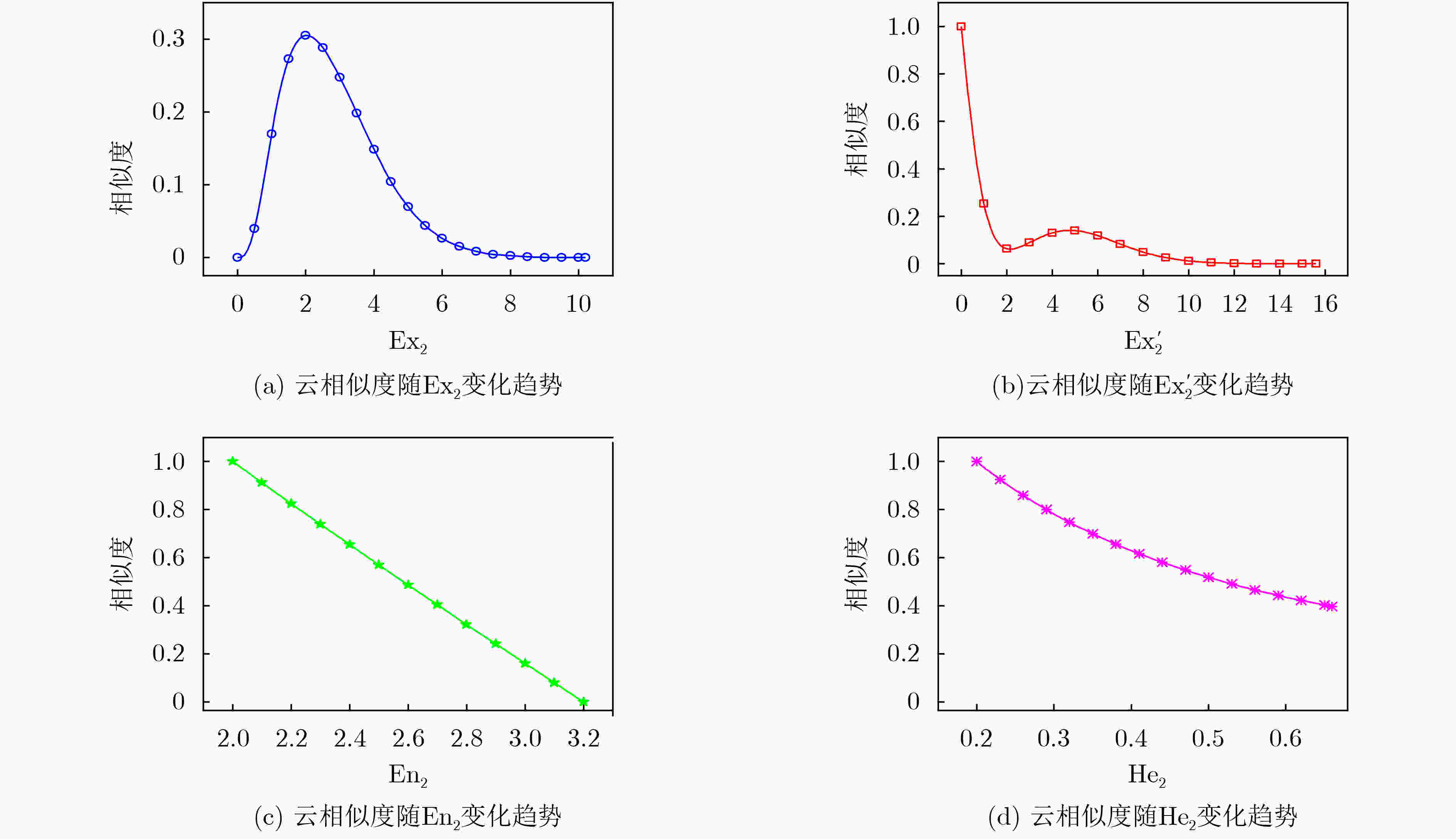






 下载:
下载:
