Bayesian Network Structure Algorithm Based on V-structure & Log-Likelihood Orientation and Tabu Hill Climbing
-
摘要: 针对爬山算法搜索空间过大和易陷入局部最优的问题,该文提出基于V-结构&对数似然函数定向与禁忌爬山的贝叶斯网络结构算法(VTH)。该算法利用定向最大支撑树约束搜索空间,在最大支撑树定向过程中,提出V-结构与对数似然函数(VLL)结合的定向策略;在评分搜索过程中,提出禁忌爬山(VTH)评分搜索策略,该策略将禁忌表清空机制与爬山搜索的局部择优准则结合,在提高全局寻优能力的同时也能保证搜索效率。该算法与其他算法在Asia, Car, Child和Alarm 4种标准网络中进行仿真实验,对比汉明距离、F1值、平衡评分函数(BSF)值、运行时间4个指标,验证了该算法的有效性。Abstract: Hill climbing algorithm has too large search space and is easy to fall into local optimum. In this paper, a new Bayesian network structure algorithm based on V-structure & log-likelihood orientation and Tabu Hill (VTH) climbing is proposed. The algorithm limits the search space by using the oriented maximum weight spanning tree. In the process of maximum weight spanning tree orientation, the orientation strategy based on V-structure and Log-Likelihood (VLL) function is proposed. Tabu Hill Climbing (THC) scoring search strategy is established during the process of search, it combines the tabu list clearing mechanism with the local optimization criteria of hill climbing, the strategy not only ensures the search efficiency, but also improves the global optimization ability. By comparing Hamming distance, F1-value, Balanced Scoring Function(BSF) value and Time with other algorithms in Asia, Car, Child and Alarm standard networks, the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified.
-
表 1 4种网络中VLL策略和CRAE策略定向结果
网络 数据量 VLL策略 CRAE策略 T F acc(%) T F acc(%) Asia 1000 5.56 0.58 90.58 3.58 2.56 58.33 5000 6.02 0.47 92.81 3.62 2.87 55.82 10000 6.27 0.47 93.07 3.71 3.02 55.12 Car 1000 7.93 0.96 89.25 5.87 3.02 66.00 5000 8.18 0.82 90.86 6.00 2.98 66.83 10000 8.11 0.89 90.12 6.00 3.00 66.67 Child 1000 13.78 4.98 73.46 14.31 4.44 76.30 5000 13.93 5.07 73.33 14.20 4.80 74.74 10000 13.98 5.02 73.57 14.18 4.82 74.62 Alarm 1000 33.49 0.44 98.69 23.40 10.53 68.96 5000 34.02 0 100.00 22.84 11.18 67.15 10000 34.00 0 100.00 22.69 11.31 66.73 表 2 对比算法介绍
算法 描述 HC算法 经典爬山算法 Tabu算法 利用禁忌表提高爬山全局寻优能力的禁忌搜索算法 MMHC算法 依赖分析与爬山算法结合的经典混合算法 CHC算法 通过动态限制提高爬山效率的高效算法 FastCHC算法 对CHC算法的改进算法 SHC算法 标准节点序定向最大支撑树与简化爬山结合的有效算法 SaiyanH算法 新近提出的爬山算法和禁忌搜索结合的混合算法 表 4 Car网络中不同算法F1值和BSF值结果
数据量 对比项 HC MMHC Tabu SHC CHC FastCHC SaiyanH VTH 1000 F1 0.6383 0.8317 0.6962 0.7690 0.6456 0.6495 0.7852 0.8810 BSF 0.6357 0.7589 0.6742 0.7686 0.6410 0.6430 0.7380 0.8203 5000 F1 0.7133 0.9042 0.7673 0.8133 0.7161 0.7179 0.8299 0.9609 BSF 0.6989 0.8333 0.7345 0.8118 0.7006 0.7020 0.7785 0.8958 10000 F1 0.7346 0.8982 0.7844 0.8462 0.7346 0.7346 0.8443 0.9617 BSF 0.7164 0.8277 0.7485 0.8426 0.7164 0.7164 0.7911 0.8919 表 5 Child网络中不同算法F1值和BSF值结果
数据量 对比项 HC MMHC Tabu SHC CHC FastCHC SaiyanH VTH 1000 F1 0.7054 0.8367 0.7644 0.8930 0.7068 0.6999 0.8467 0.8554 BSF 0.6193 0.7250 0.6649 0.7736 0.6209 0.6152 0.7308 0.7386 5000 F1 0.7666 0.9167 0.8291 0.9698 0.7654 0.7636 0.9187 0.9715 BSF 0.7273 0.8422 0.7776 0.9014 0.7273 0.7251 0.8526 0.9061 10000 F1 0.8000 0.9267 0.8514 0.9717 0.8016 0.8021 0.9061 0.9366 BSF 0.7607 0.8569 0.8006 0.9030 0.7621 0.7626 0.8466 0.8775 表 3 Asia网络中不同算法F1值和BSF值结果
数据量 对比项 HC MMHC Tabu SHC CHC FastCHC SaiyanH VTH 1000 F1 0.6579 0.7450 0.6862 0.8369 0.6424 0.6401 0.6319 0.8788 BSF 0.4964 0.5696 0.5192 0.6730 0.4841 0.4823 0.4782 0.6950 5000 F1 0.5900 0.8549 0.6481 0.8739 0.5923 0.5923 0.7687 0.9118 BSF 0.4512 0.6812 0.4966 0.7137 0.4530 0.4530 0.5990 0.7325 10000 F1 0.6526 0.8748 0.6721 0.9046 0.6526 0.6526 0.7974 0.9335 BSF 0.5069 0.7052 0.5226 0.7468 0.5069 0.5069 0.6300 0.7605 表 6 Alarm网络中不同算法F1值和BSF值结果
数据量 对比项 HC MMHC Tabu SHC CHC FastCHC SaiyanH VTH 1000 F1 0.5128 0.7767 0.5369 0.7951 0.5068 0.5095 0.7616 0.8090 BSF 0.5680 0.7644 0.5807 0.7457 0.5642 0.5658 0.7413 0.7545 5000 F1 0.5463 0.8690 0.5589 0.8866 0.5485 0.5485 0.7891 0.9165 BSF 0.6413 0.8474 0.6485 0.8488 0.6425 0.6421 0.7955 0.8755 10000 F1 0.5313 0.8268 0.5484 0.9093 0.5308 0.5329 0.7972 0.9514 BSF 0.6402 0.8183 0.6505 0.8856 0.6399 0.6381 0.8072 0.9174 -
[1] 李硕豪, 张军. 贝叶斯网络结构学习综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2015, 32(3): 641–646. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2015.03.001LI Shuohao and ZHANG Jun. Review of Bayesian networks structure learning[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2015, 32(3): 641–646. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2015.03.001 [2] ZHAO Xuan, PENG Benhong, ELAHI E, et al. Optimization of Chinese coal-fired power plants for cleaner production using Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 273: 122837. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122837 [3] MCLACHLAN S, DUBE K, HITMAN G A, et al. Bayesian networks in healthcare: Distribution by medical condition[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2020, 107: 101912. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101912 [4] CARRIGER J F and BARRON M G. A Bayesian network approach to refining ecological risk assessments: Mercury and the Florida panther (Puma concolor coryi)[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2020, 418: 108911. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2019.108911 [5] ANDERSON B. Using Bayesian networks to perform reject inference[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 137: 349–356. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.07.011 [6] SCANAGATTA M, SALMERÓN A, and STELLA F. A survey on Bayesian network structure learning from data[J]. Progress in Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 8(4): 425–439. doi: 10.1007/s13748-019-00194-y [7] HECKERMAN D, GEIGER D, and CHICKERING D M. Learning Bayesian networks: The combination of knowledge and statistical data[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 197–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00994016 [8] 曹杰. 贝叶斯网络结构学习与应用研究[D].[博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2017.CAO Jie. Bayesian network structure learning and application[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2017. [9] TSAMARDINOS I, BROWN L E, and ALIFERIS C F. The max-min hill-climbing Bayesian network structure learning algorithm[J]. Machine Learning, 2006, 65(1): 31–78. doi: 10.1007/s10994-006-6889-7 [10] 冀俊忠, 张鸿勋, 胡仁兵, 等. 基于禁忌搜索的贝叶斯网结构学习算法[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2011, 37(8): 1274–1280.JI Junzhong, ZHANG Hongxun, HU Renbing, et al. A Tabu-search based Bayesian network structure learning algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2011, 37(8): 1274–1280. [11] GÁMEZ J A, MATEO J L, and PUERTA J M. Learning Bayesian networks by hill climbing: Efficient methods based on progressive restriction of the neighborhood[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2011, 22(1-2): 106–148. doi: 10.1007/s10618-010-0178-6 [12] GÁMEZ J A, MATEO J L, and PUERTA J M. One iteration CHC algorithm for learning Bayesian networks: An effective and efficient algorithm for high dimensional problems[J]. Progress in Artificial Intelligence, 2012, 1(4): 329–346. doi: 10.1007/s13748-012-0033-7 [13] ARIAS J, GÁMEZ J A, and PUERTA J M. Structural learning of Bayesian networks via constrained hill climbing algorithms: Adjusting trade-off between efficiency and accuracy[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2015, 30(3): 292–325. doi: 10.1002/int.21701 [14] 刘浩然, 吕晓贺, 李轩, 等. 基于Bayesian改进算法的回转窑故障诊断模型研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2015, 36(7): 1554–1561. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2015.07.014LIU Haoran, LÜ Xiaohe, LI Xuan, et al. A study on the fault diagnosis model of rotary kiln based on an improved algorithm of Bayesian[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2015, 36(7): 1554–1561. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2015.07.014 [15] 刘彬, 刘永记, 刘浩然, 等. 基于改进遗传爬山算法的篦冷机熟料换热二次风温故障诊断[J]. 计量学报, 2018, 39(5): 651–658. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2018.05.10LIU Bin, LIU Yongji, LIU Haoran, et al. Fault diagnosis of secondary air temperature of grate cooler cement clinker heat transfer based on improved genetic hill climbing algorithm[J]. Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2018, 39(5): 651–658. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1158.2018.05.10 [16] CONSTANTINOU A C. Learning Bayesian networks that enable full propagation of evidence[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 124845–124856. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3006472 [17] CHEN Guangjie and GE Zhiqiang. Robust Bayesian networks for low-quality data modeling and process monitoring applications[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2020, 97: 104344. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2020.104344 [18] YANG Jing, GUO Xiaoxue, AN Ning, et al. Streaming feature-based causal structure learning algorithm with symmetrical uncertainty[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 467: 708–724. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.04.076 [19] PRIM R C. Shortest connection networks and some generalizations[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1957, 36(6): 1389–1401. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1957.tb01515.x [20] DAI Jingguo, REN Jia, and DU Wencai. Decomposition-based Bayesian network structure learning algorithm using local topology information[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 195: 105602. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105602 [21] BEHJATI S and BEIGY H. Improved K2 algorithm for Bayesian network structure learning[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 91: 103617. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2020.103617 [22] ZHAO Jianjun and HO S S. Improving Bayesian network local structure learning via data-driven symmetry correction methods[J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2019, 107: 101–121. doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2019.02.004 [23] CONSTANTINOU A C. The importance of temporal information in Bayesian network structure learning[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 164: 113814. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113814 [24] JIANG Jinke, WANG Juyun, YU Hua, et al. Poison identification based on Bayesian network: A novel improvement on K2 algorithm via Markov Blanket[C]. The 4th International Conference on Advances in Swarm Intelligence, Harbin, China, 2013: 173–182. -





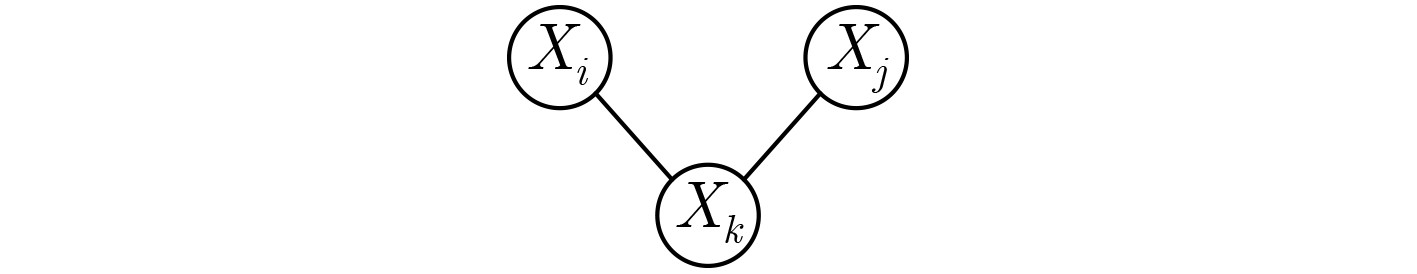
 下载:
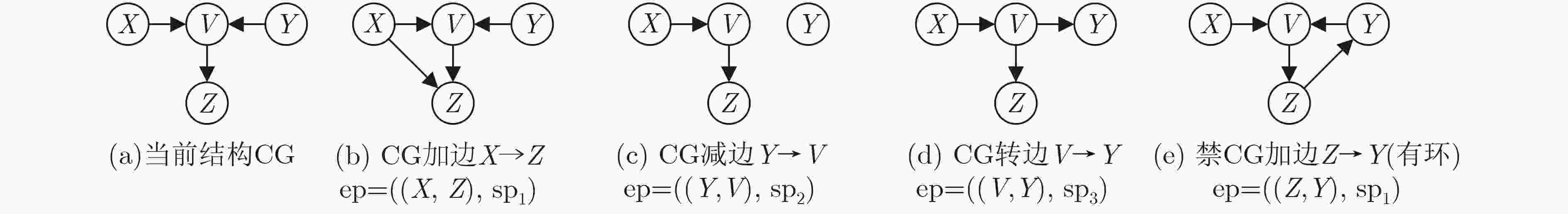
下载:
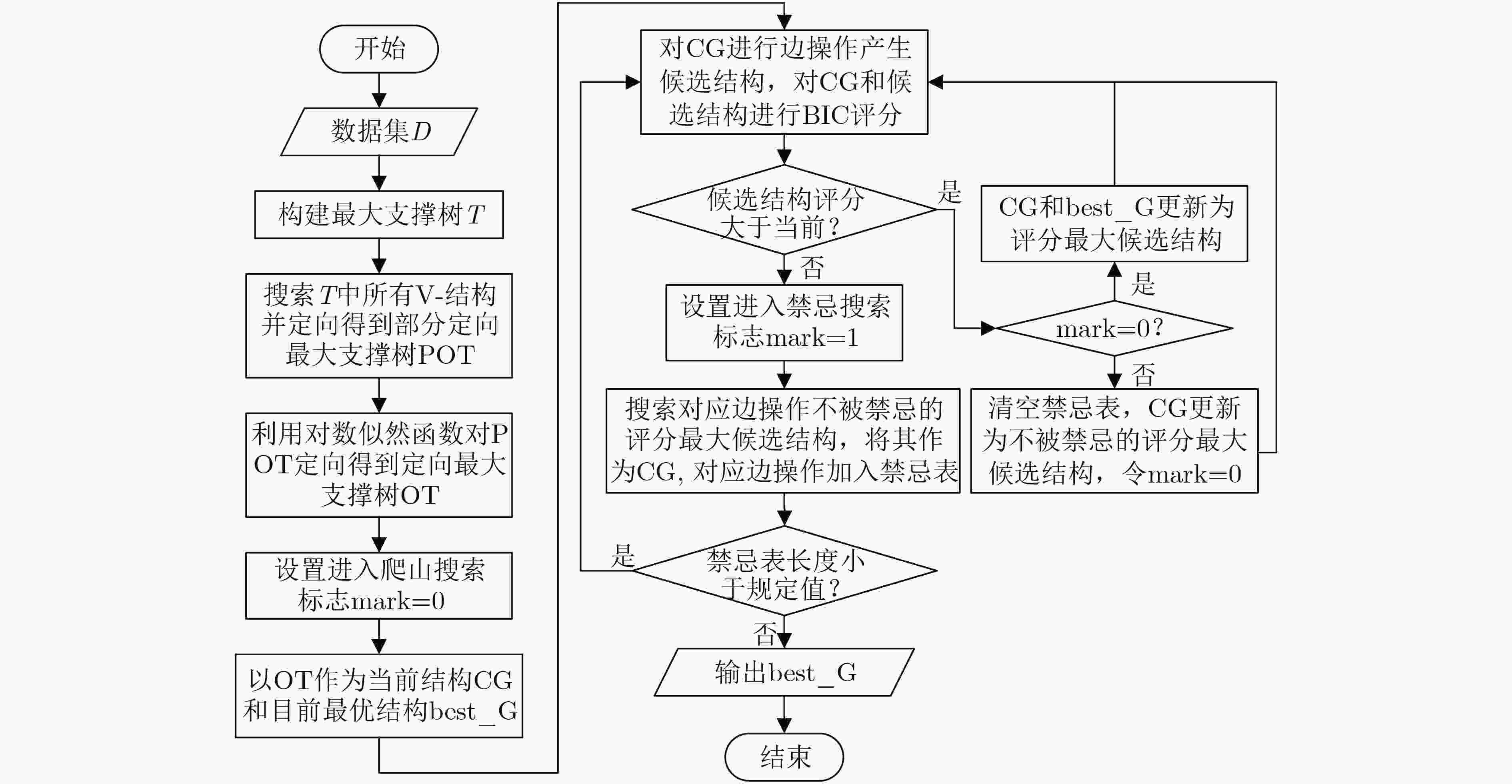
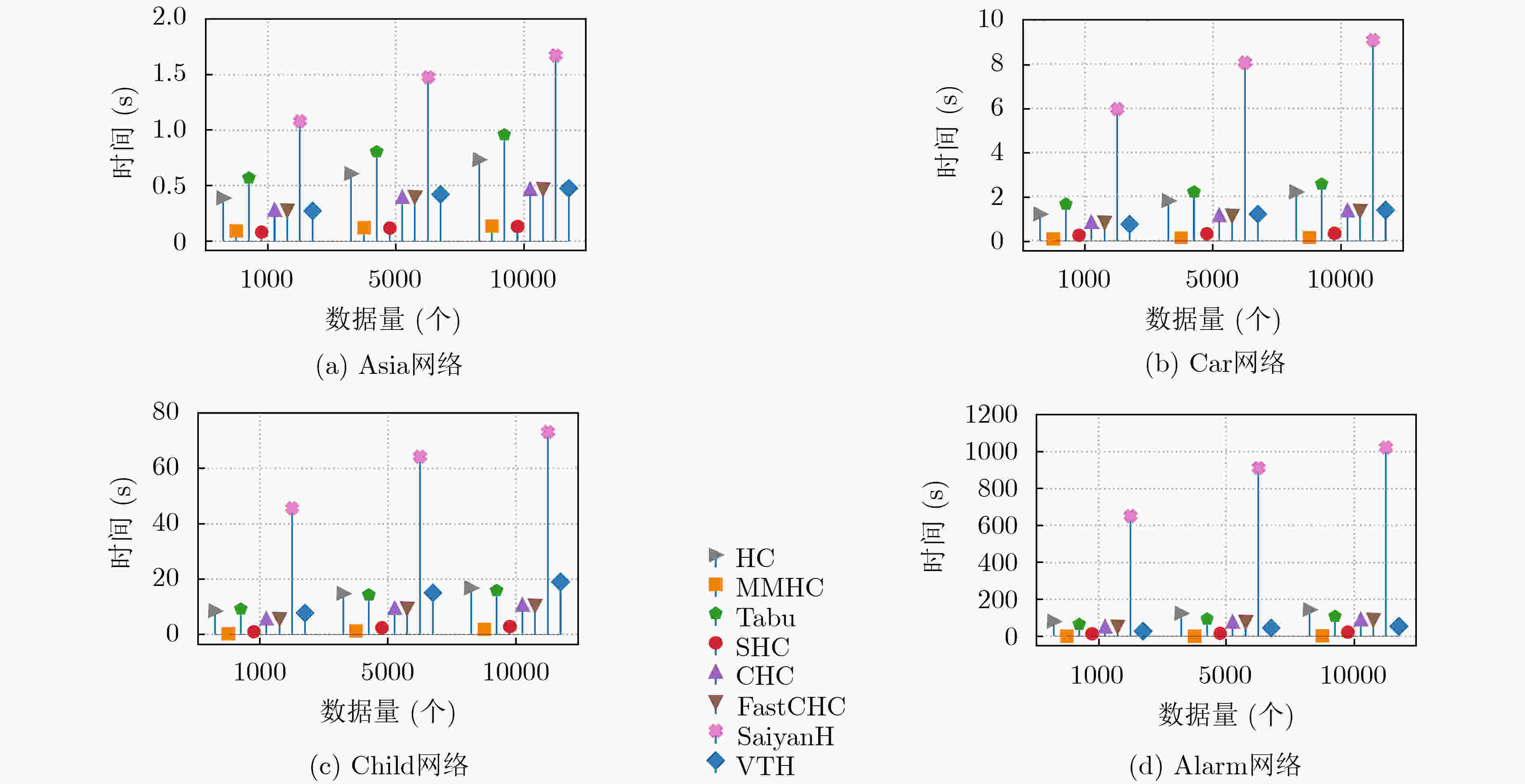
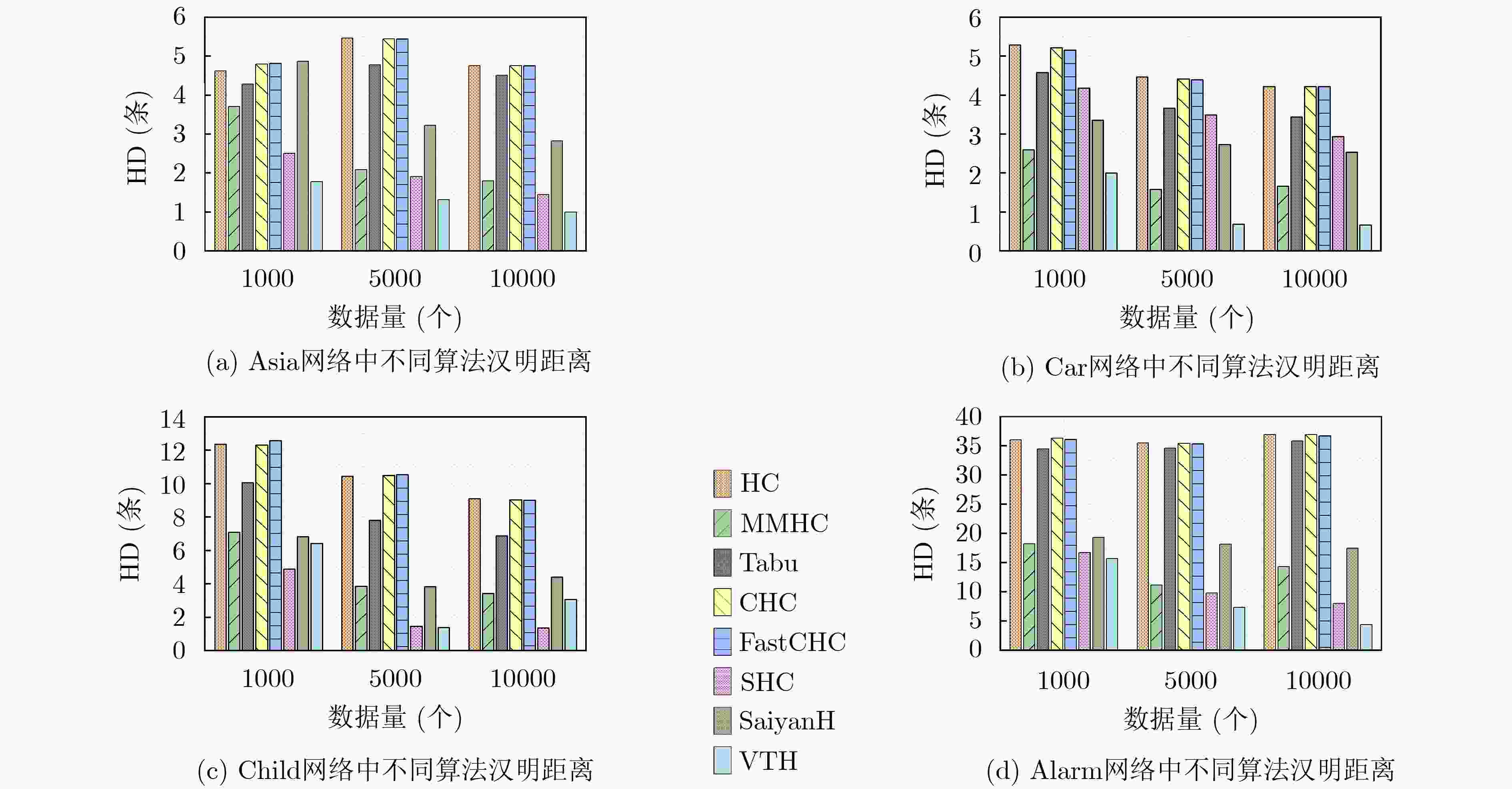


 下载:
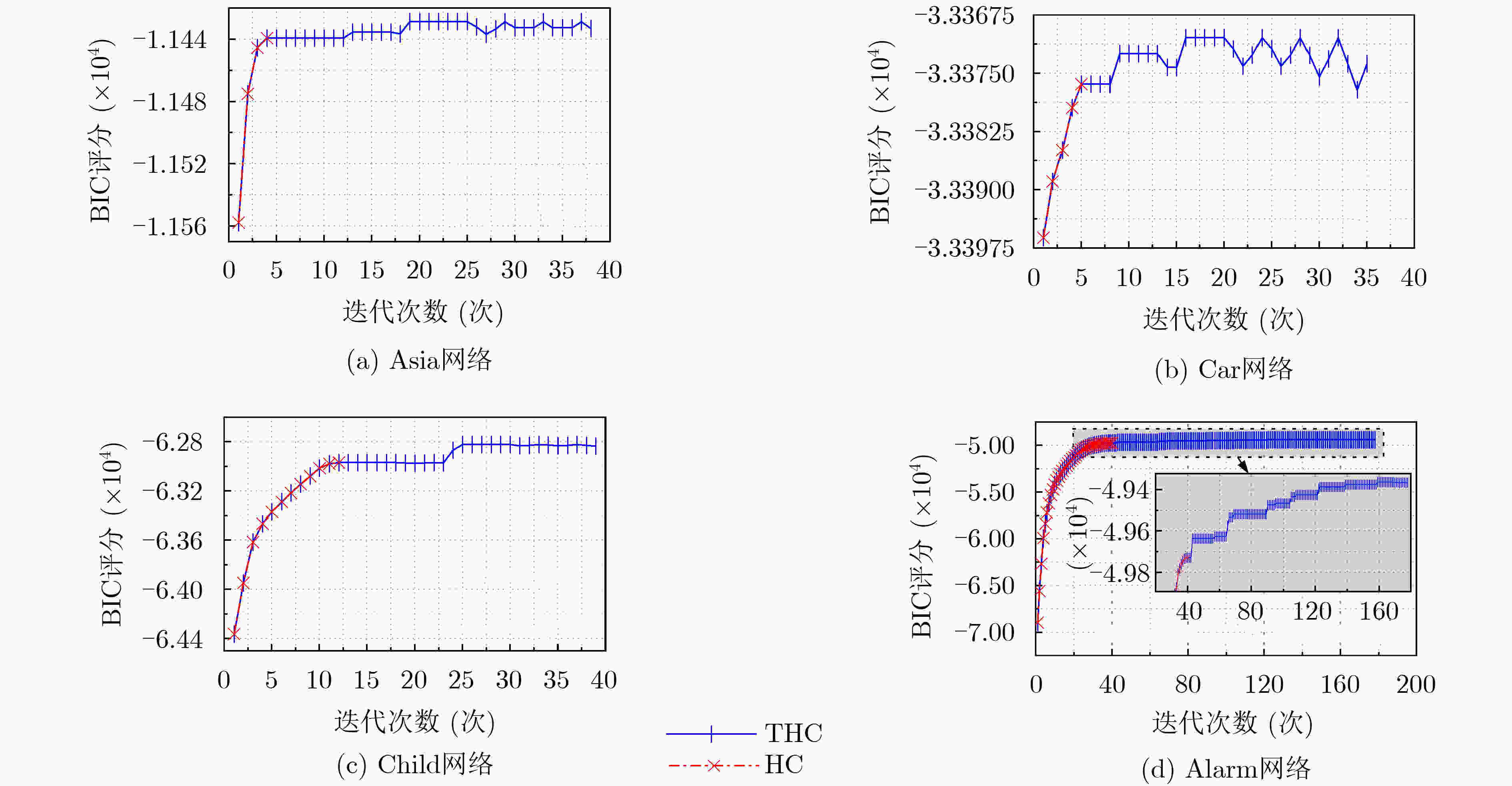
下载:
