A Temporal Link Predict Algorithm Based on Fusion Local Structure Influence
-
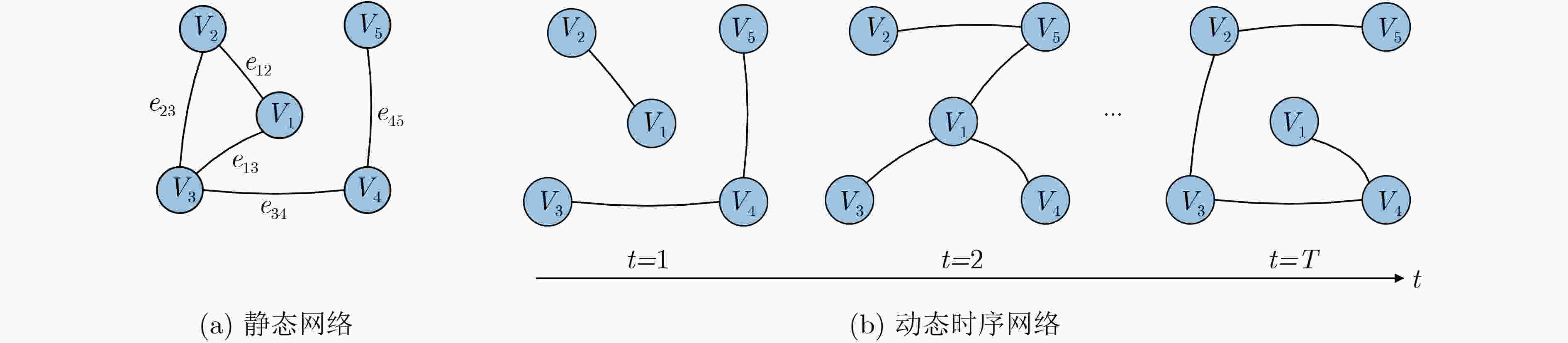
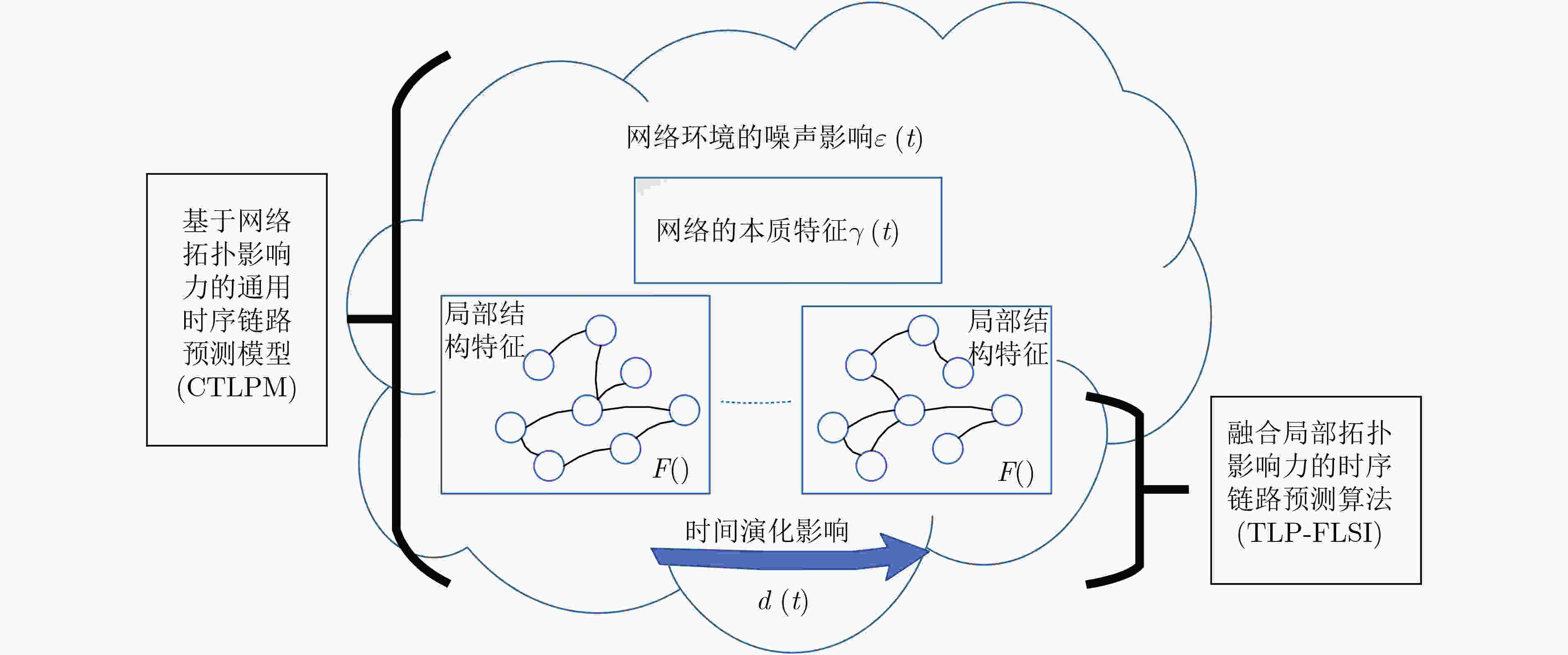
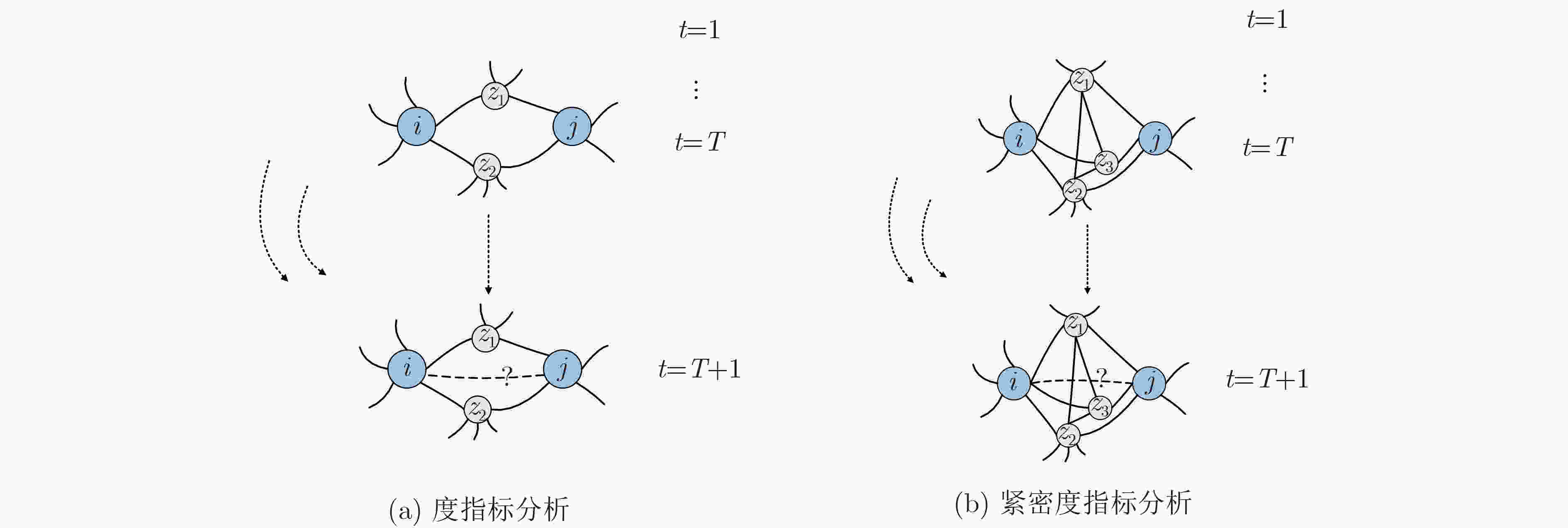
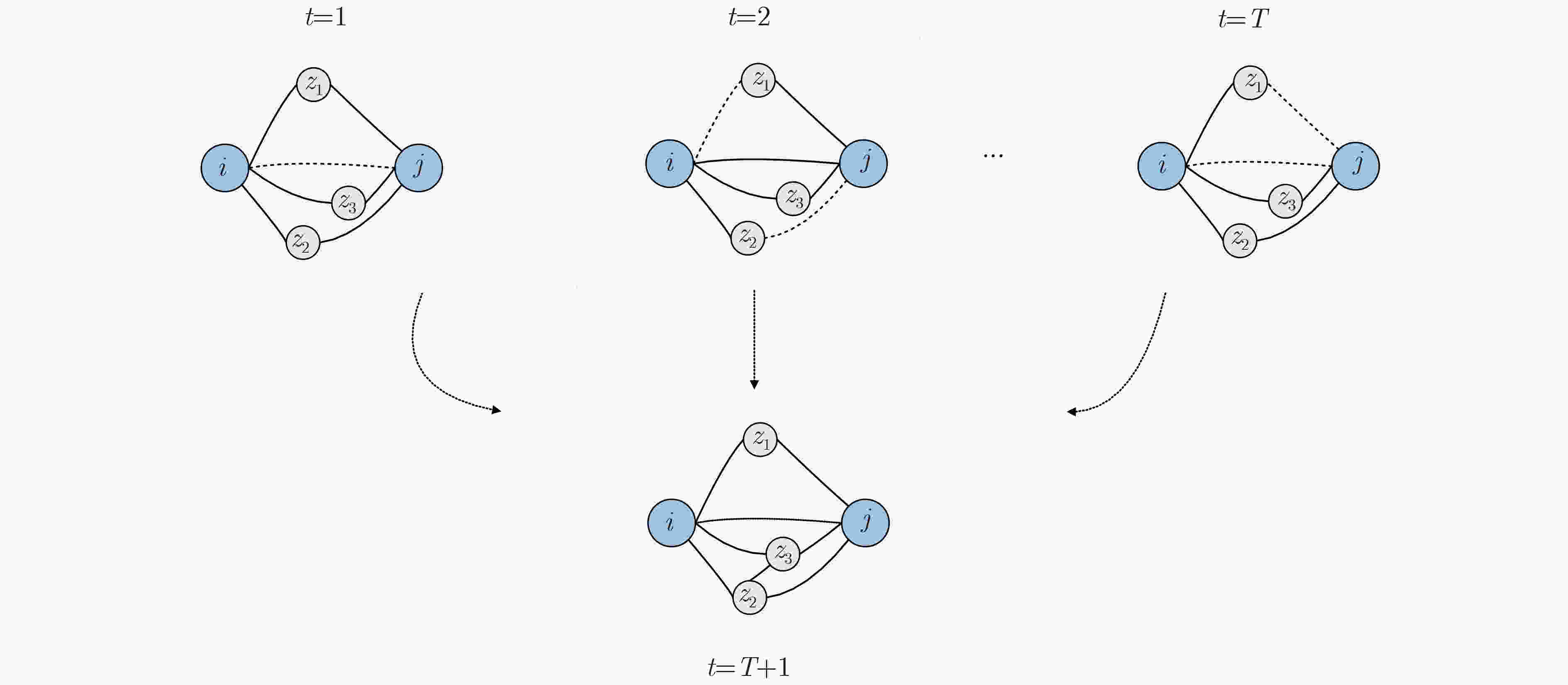
摘要: 链路预测旨在发现复杂网络中的未知连接和未来可能的连接,在推荐系统等实际应用中具有重要作用。考虑到许多真实网络的时序特性,时序链路预测逐渐成为研究热点。当前,基于时间序列分析的方法往往忽略了网络演化过程对网络本身的影响,而基于静态网络演化的方法大多仅考虑了局部连边的演化影响,对网络拓扑结构的演化特性挖掘有限。针对上述问题,该文提出一种融合局部拓扑影响力的时序链路预测算法(TLP-FLSI)。首先,基于网络拓扑结构影响力作用,提出时序链路预测的通用模型(CTLPM);其次,研究拓扑实体间相互作用在动态网络上的演化规律,分别定义了节点和连边的演化因子,以及时间序列衰减的演化因子,综合利用多个维度的特征信息,给出了融合局部节点和连边特征影响力的时序链路预测算法;最后,在7个真实数据集上分别进行实验,对比传统基于移动平均方法、误差修正、邻居扩展加权和图注意力网络等时序链路预测方法,实验结果证明该算法具有较好的准确率和排序性能。Abstract: Link prediction aims to discover missing connected edges and possible future interaction in complex networks. The evolution mechanism of temporal networks has gained the attention of researchers with its ubiquitous applications in a variety of real-world scenarios. At present, many methods based on time series analysis are proposed, but the influence of the network evolution process on the network itself is ignored, and the methods based on the static network algorithm only consider the influence of the evolution of edges, which may lead to inadequate utilization of feature information and can not achieve better prediction accuracy. In view of the above problems, a novel Temporal Link Prediction algorithm base on Fusion Local Structure Influence (TLP-FLSI) is proposed, which fuses the impact of local nodes and edges. Firstly, based on the influence of network topology structure, Common Temporal Link Prediction Model(CTLPM)is proposed. Secondly, the evolution mechanism of the interaction between topological entities on the dynamic network is studied, and the evolution factors of nodes and edges, as well as the decay evolution factors of time series are defined respectively, and considering various factors, TLP-FLSI is derivated from CTLPM. Finally, compared with traditional temporal link predict method, including moving average methods, error correction methods, extended weighted method, graph attention methods, experimental results of seven real data sets show that TLP-FLSI achieves great improvement in accuracy and ranking score.
-
Key words:
- Temporal dynamic network /
- Link prediction /
- Fusion features /
- Similarity metrics /
- Influence decay
-
表 1 数据集参数表
Email Enron Facebook DNC MAN UCI LEM 节点数 1005 87273 63891 2029 167 1899 485 连边数 332334 1048576 855542 39264 82927 59835 196364 快照图数 76 66 52 33 39 28 51 时序周期 周 周 2周 天 周 周 半年 表 2 不同方法的平均AUC性能结果
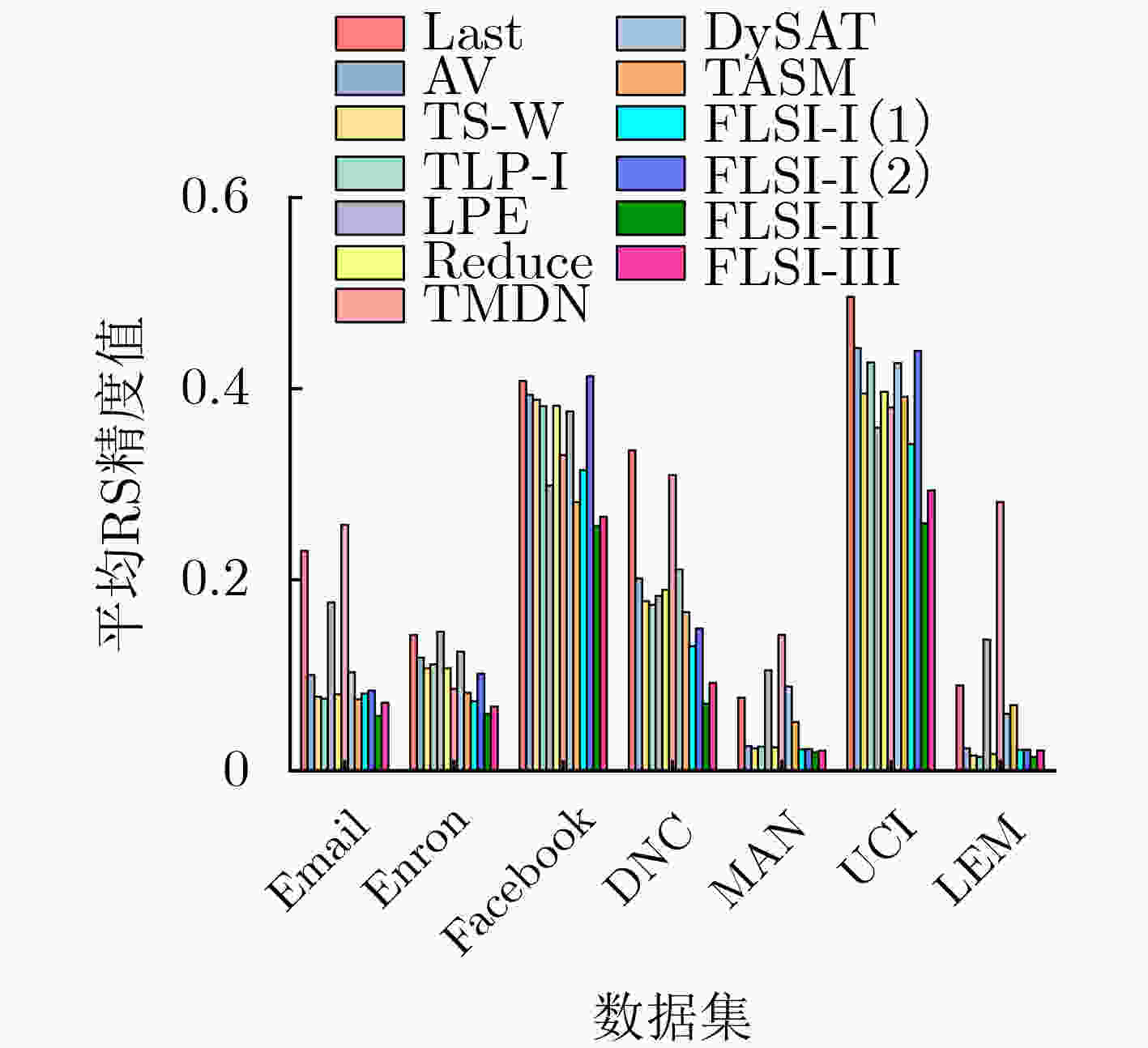
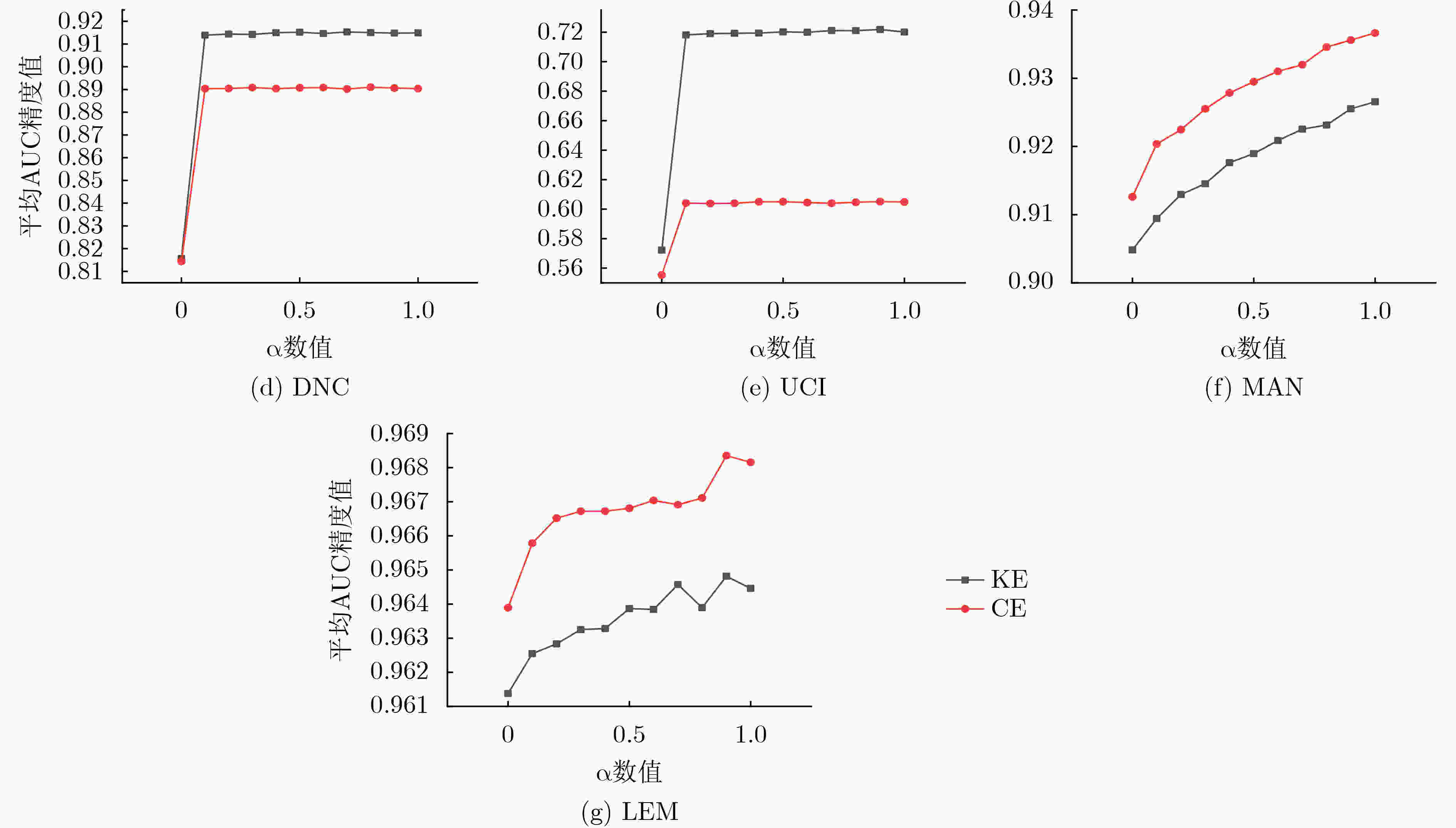
模型 Email Enron Facebook DNC MAN UCI LEM Last 0.7535 0.6056 0.5158 0.7011 0.8415 0.5152 0.9021 AV 0.8793 0.7282 0.5350 0.8156 0.9064 0.5724 0.9620 TS-W 0.8993 0.7646 0.5422 0.8357 0.9099 0.6170 0.9682 TLP-I 0.9051 0.7480 0.5526 0.8407 0.8989 0.5864 0.9692 LPE 0.8202 0.7728 0.6507 0.8264 0.8901 0.6699 0.8623 Reduce 0.8954 0.7732 0.5522 0.8252 0.8925 0.6157 0.9630 TMDN 0.8447 0.8103 0.6745 0.8561 0.8939 0.6995 0.8631 DySAT 0.8603 0.7885 0.7515 0.8376 0.9020 0.7187 0.8352 TASM 0.8501 0.7945 0.7702 0.8462 0.8975 0.7230 0.8373 FLSI-I(1) 0.9101 0.8551 0.6860 0.9148 0.9199 0.7192 0.9637 FLSI-I(2) 0.9092 0.7753 0.6193 0.8907 0.9306 0.6137 0.9669 FLSI-II 0.9246 0.8803 0.6973 0.9347 0.9264 0.7574 0.9709 FLSI-III 0.9111 0.8551 0.6860 0.9152 0.9180 0.7220 0.9650 -
[1] PORTER M A. Nonlinearity + Networks: A 2020 Vision[M]. KEVREKIDIS P G, CUEVAS-MARAVER J, and SAXENA A. Emerging Frontiers in Nonlinear Science. Cham: Springer, 2020: 131–159. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-44992-6_6. [2] WANG Yongcheng, WANG Yu, LIN Xinye, et al. The influence of network structural preference on link prediction[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2020, 2020: 6148273. doi: 10.1155/2020/6148273 [3] KERRACHE S, ALHARBI R, and BENHIDOUR H. A scalable similarity-popularity link prediction method[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 6394. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62636-1 [4] DIVAKARAN A and MOHAN A. Temporal link prediction: A survey[J]. New Generation Computing, 2020, 38(1): 213–258. doi: 10.1007/s00354-019-00065-z [5] 李治成, 吉立新, 刘树新, 等. 基于拓扑稳定性的有向网络链路预测方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2020, 37(12): 3744–3748. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2019.09.0550LI Zhicheng, JI Lixin, LIU Shuxin, et al. Link prediction method based on topological stability in directed network[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2020, 37(12): 3744–3748. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2019.09.0550 [6] 王凯, 刘树新, 陈鸿昶, 等. 一种基于节点间资源承载度的链路预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1225–1234. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180553WANG Kai, LIU Shuxin, CHEN Hongchang, et al. A new link prediction method for complex networks based on resources carrying capacity between nodes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1225–1234. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180553 [7] 刘树新, 李星, 陈鸿昶, 等. 基于资源传输匹配度的复杂网络链路预测方法[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(6): 70–79. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020124LIU Shuxin, LI Xing, CHEN Hongchang, et al. Link prediction method based on matching degree of resource transmission for complex network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(6): 70–79. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020124 [8] DA SILVA SOARES P R and PRUDÊNCIO R B C. Time series based link prediction[C]. The 2012 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Brisbane, Australia, 2012, 20: 1–7. [9] HUANG Zan and LIN D K J. The time-series link prediction problem with applications in communication surveillance[J]. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 2009, 21(2): 286–303. doi: 10.1287/ijoc.1080.0292 [10] GÜNEŞ İ, GÜNDÜZ-ÖĞÜDÜCÜ Ş, and ÇATALTEPE Z. Link prediction using time series of neighborhood-based node similarity scores[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2016, 30(1): 147–180. doi: 10.1007/s10618-015-0407-0 [11] 刘继嘉, 王童, 何兴盛, 等. 一种基于混合结构的动态网络链路预测算法[J]. 电子技术, 2018, 47(7): 53–59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0755.2018.07.015LIU Jijia, WANG Tong, HE Xingsheng, et al. A link prediction method of dynamic network based on hybrid structure[J]. Electronic Technology, 2018, 47(7): 53–59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0755.2018.07.015 [12] MUNASINGHE L and ICHISE R. Time score: A new feature for link prediction in social networks[J]. IEICE TRANSACTIONS on Information and Systems, 2012, E95-D(3): 821–828. doi: 10.1587/transinf.E95.D.821 [13] ZHANG Zhongbao, WEN Jian, SUN Li, et al. Efficient incremental dynamic link prediction algorithms in social network[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 132: 226–235. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2017.06.035 [14] 邓志宏, 老松杨, 白亮. 基于预测误差修正的时序链路预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(2): 325–331. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00657DENG Zhihong, LAO Songyang, and BAI Liang. A temporal link prediction method based on link prediction error correction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(2): 325–331. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00657 [15] BLISS C A, FRANK M R, DANFORTH C M, et al. An evolutionary algorithm approach to link prediction in dynamic social networks[J]. Journal of Computational Science, 2014, 5(5): 750–764. doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2014.01.003 [16] CASADIEGO J, NITZAN M, HALLERBERG S, et al. Model-free inference of direct network interactions from nonlinear collective dynamics[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 2192. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02288-4 [17] WANG Wenxu, LAI Yingcheng, and GREBOGI C. Data based identification and prediction of nonlinear and complex dynamical systems[J]. Physics Reports, 2016, 644: 1–76. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.06.004 [18] HAN Xiao, SHEN Zhesi, WANG Wenxu, et al. Robust reconstruction of complex networks from sparse data[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2015, 114(2): 028701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.028701 [19] 尹赢, 张建朋, 吉立新, 等. 基于霍克斯点过程的动态网络表示学习方法[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(11): 2154–2161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.11.009YIN Ying, ZHANG Jianpeng, JI Lixin, et al. Dynamic network representation learning based on Hawkes point process[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(11): 2154–2161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.11.009 [20] LÜ Linyuan and ZHOU Tao. Link prediction in complex networks: A survey[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2011, 390(6): 1150–1170. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2010.11.027 [21] LIU Shuxin, JI Xinsheng, LIU Caixia, et al. Extended resource allocation index for link prediction of complex network[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2017, 479: 174–183. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2017.02.078 [22] TANG Jian, QU Meng, WANG Mingzhe, et al. LINE: Large-scale information network embedding[C]. The 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, Florence, Italy, 2015: 1067–1077. doi: 10.1145/2736277.2741093. [23] LESKOVEC J, KLEINBERG J, and FALOUTSOS C. Graph evolution: Densification and shrinking diameters[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2007, 1(1): 2–es. doi: 10.1145/1217299.1217301 [24] LESKOVEC J, LANG K J, DASGUPTA A, et al. Community structure in large networks: Natural cluster sizes and the absence of large well-defined clusters[J]. Internet Mathematics, 2009, 6(1): 29–123. doi: 10.1080/15427951.2009.10129177 [25] VISWANATH B, MISLOVE A, CHA M, et al. On the evolution of user interaction in Facebook[J]. Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Online Social Networks, 2009, 39(4): 37–42. [26] KUNEGIS J. Konect: The Koblenz network collection[C]. Companion: The 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013: 1343–1350. [27] PANZARASA P, OPSAHL T, and CARLEY K M. Patterns and dynamics of users’ behavior and interaction: Network analysis of an online community[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 2009, 60(5): 911–932. doi: 10.1002/asi.21015 [28] LESKOVEC J and KREVL A. SNAP datasets: Stanford large network dataset collection[DB/OL]. http://snap.stanford.edu/data/, 2018. [29] IBRAHIM N M A and CHEN Ling. Link prediction in dynamic social networks by integrating different types of information[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2015, 42(4): 738–750. doi: 10.1007/s10489-014-0631-0 [30] 李聪, 季新生, 李海涛, 等. 一种基于节点匹配度的动态网络链路预测方法[J]. 网络与信息安全学报, 2020, 5(4): 325–331. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-109x.2019xxxLI Cong, JI Xinsheng, LI Haitao, et al. A link prediction method for dynamic networks based on matching degree of nodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2020, 5(4): 325–331. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-109x.2019xxx [31] SANKAR A, WU Yanhong, GOU Liang, et al. DySAT: Deep neural representation learning on dynamic graphs via self-attention networks[C]. The 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Houston, USA, 2020: 519–527. [32] LI Jinsong, PENG Jianhua, LIU Shuxin, et al. TSAM: Temporal link prediction in directed networks based on self-attention mechanism[EB/OL]. arXiv: 2008.10021, 2020. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
