A Fast and Efficient FPGA-based Level Set Hardware Accelerator for Image Segmentation
-
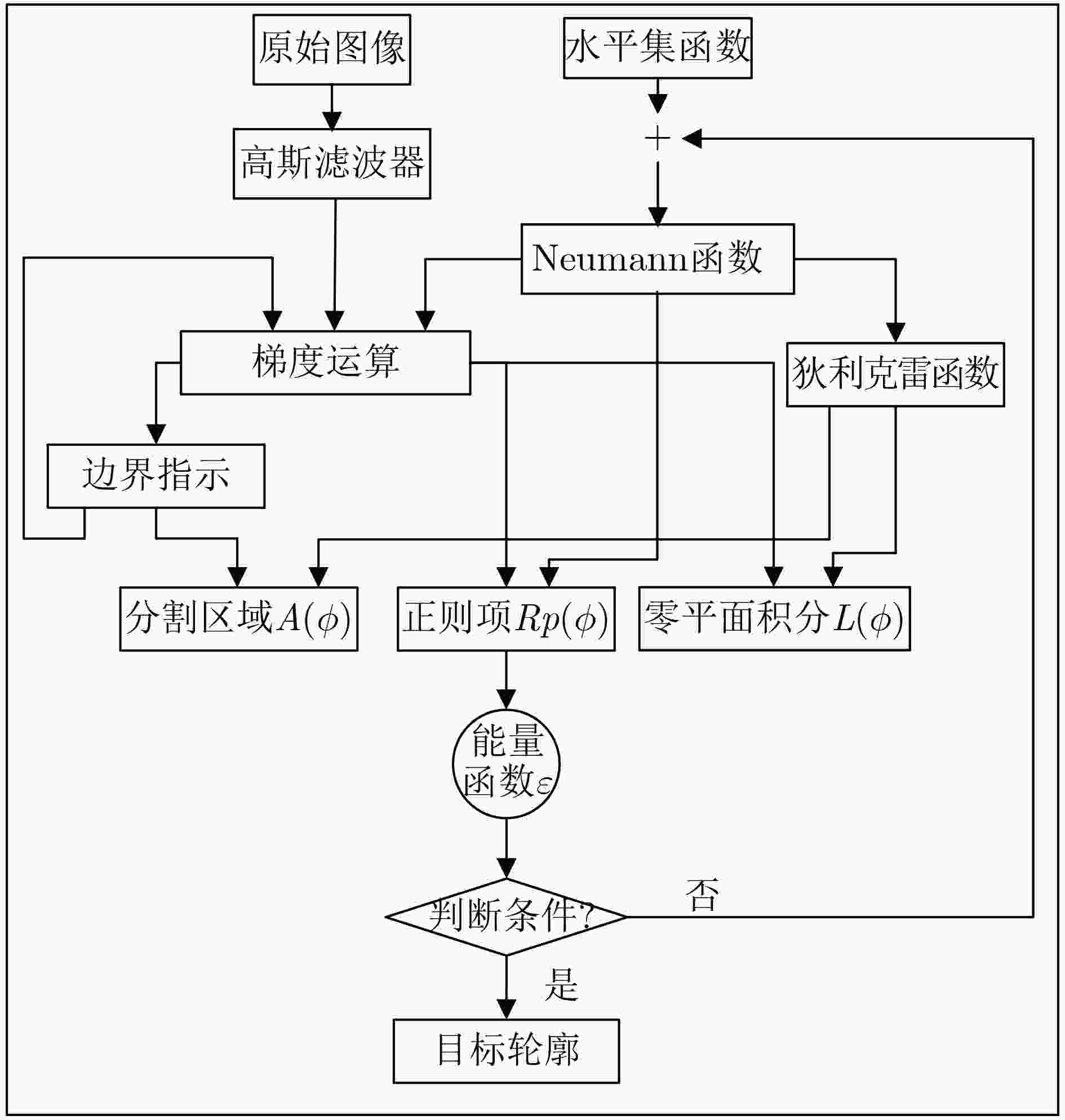
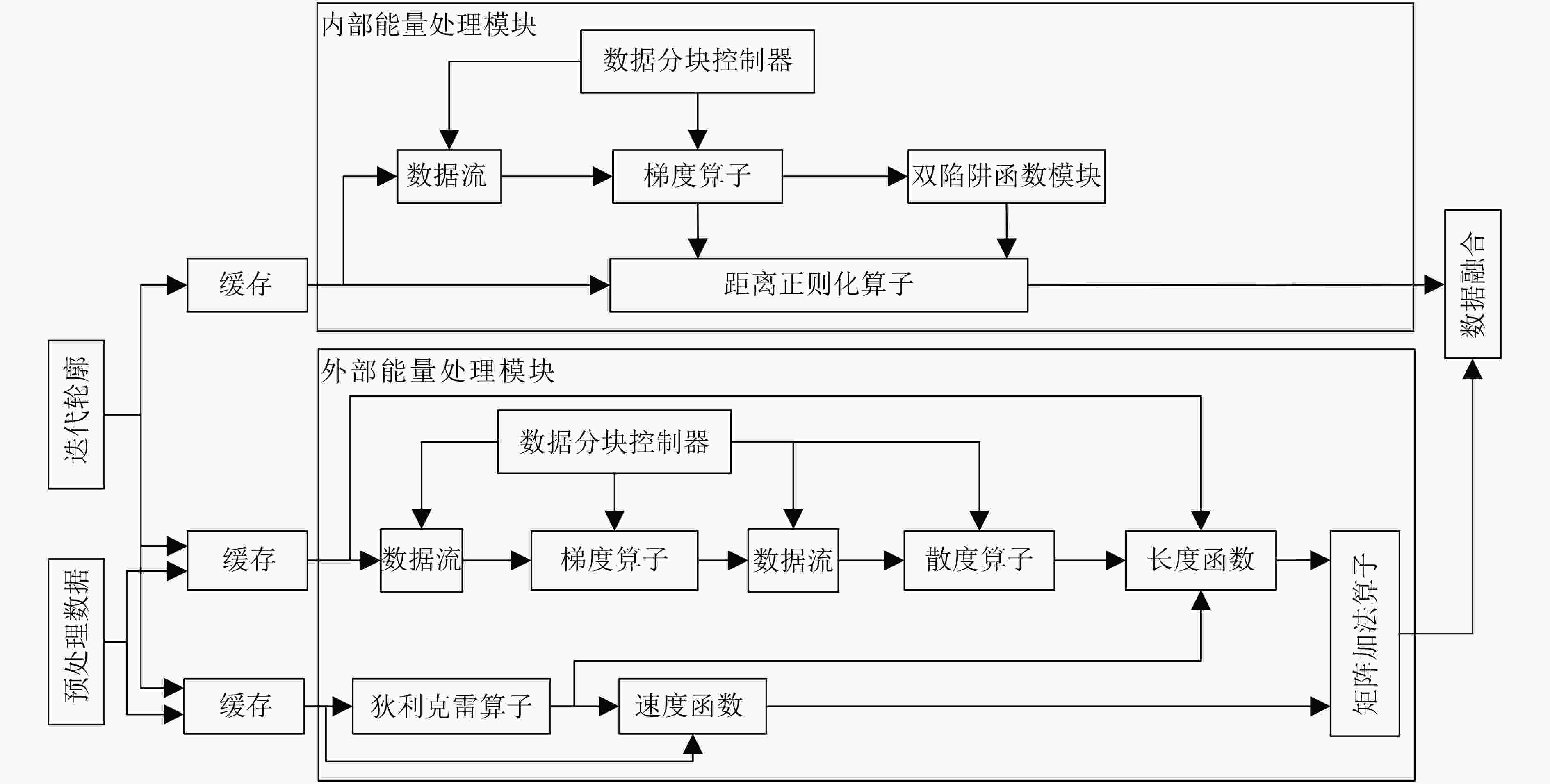
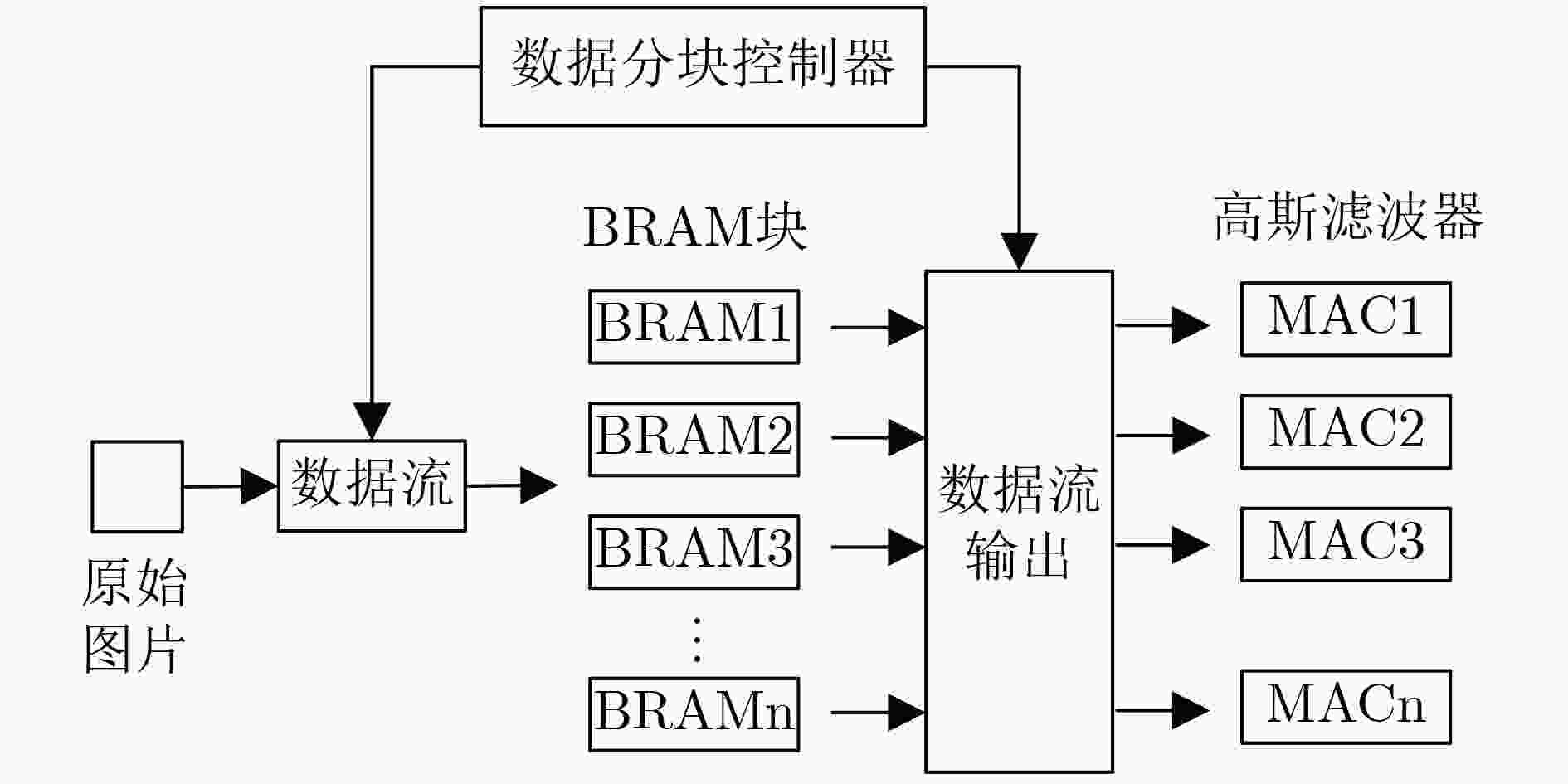
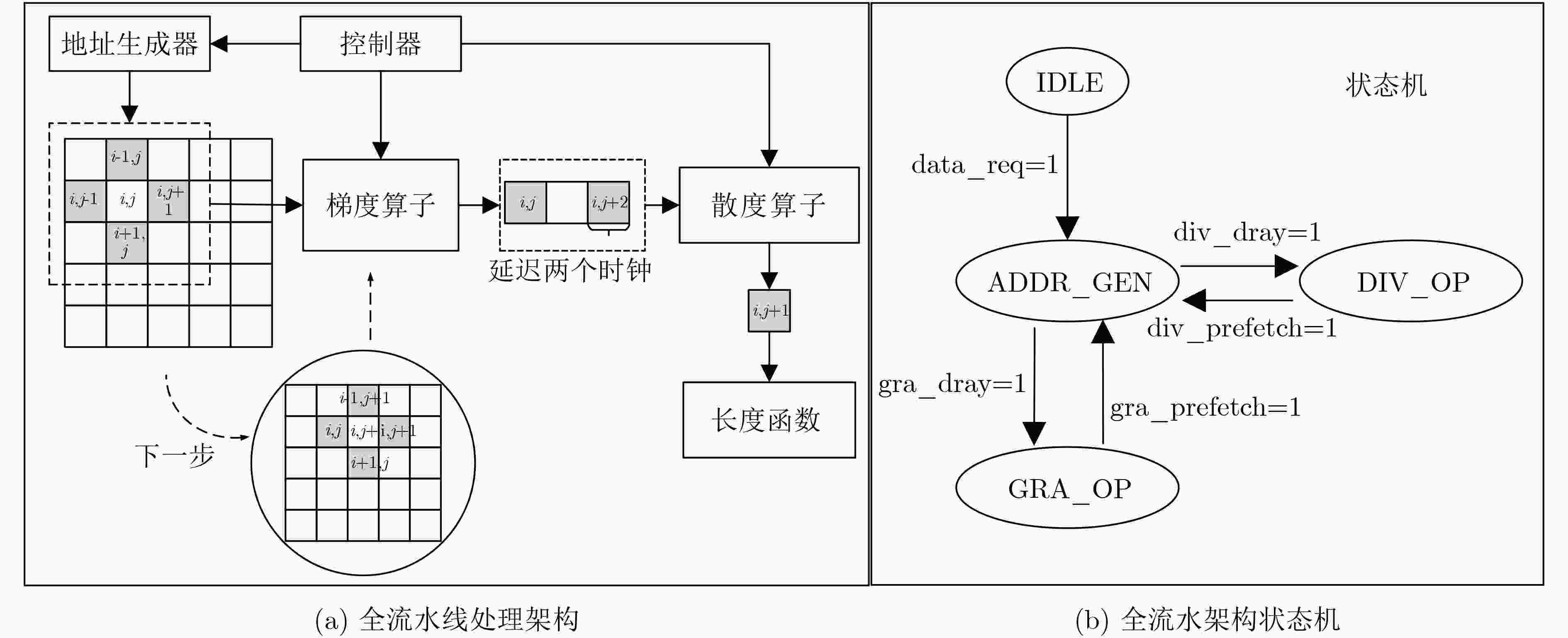
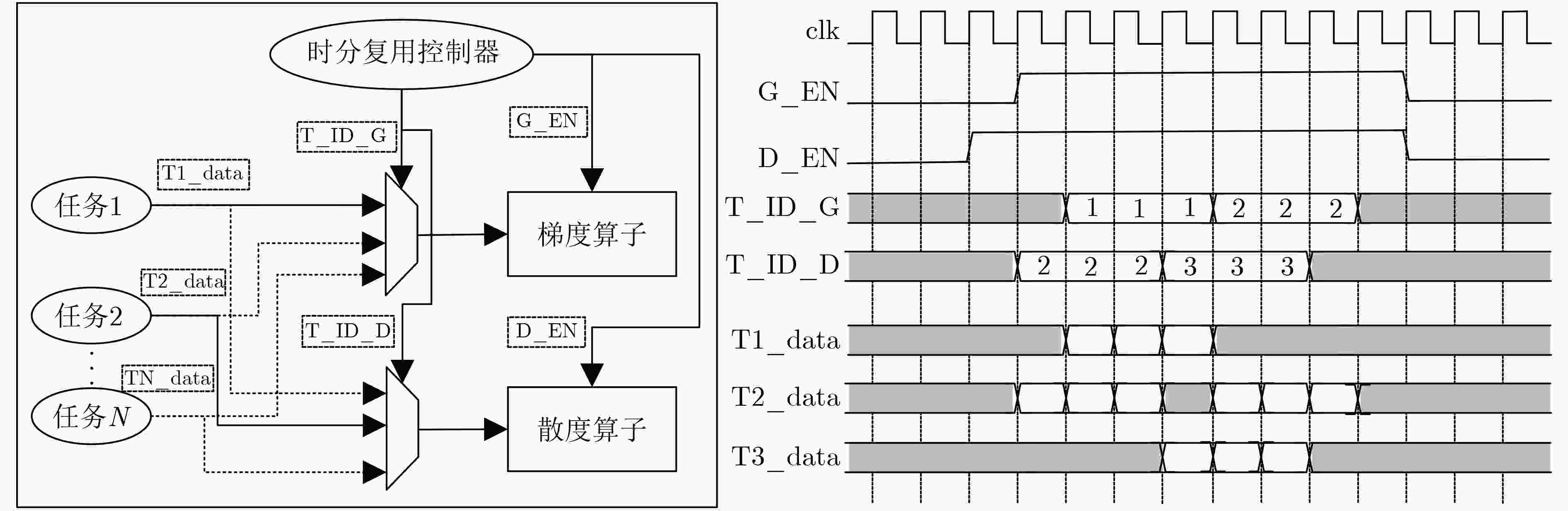
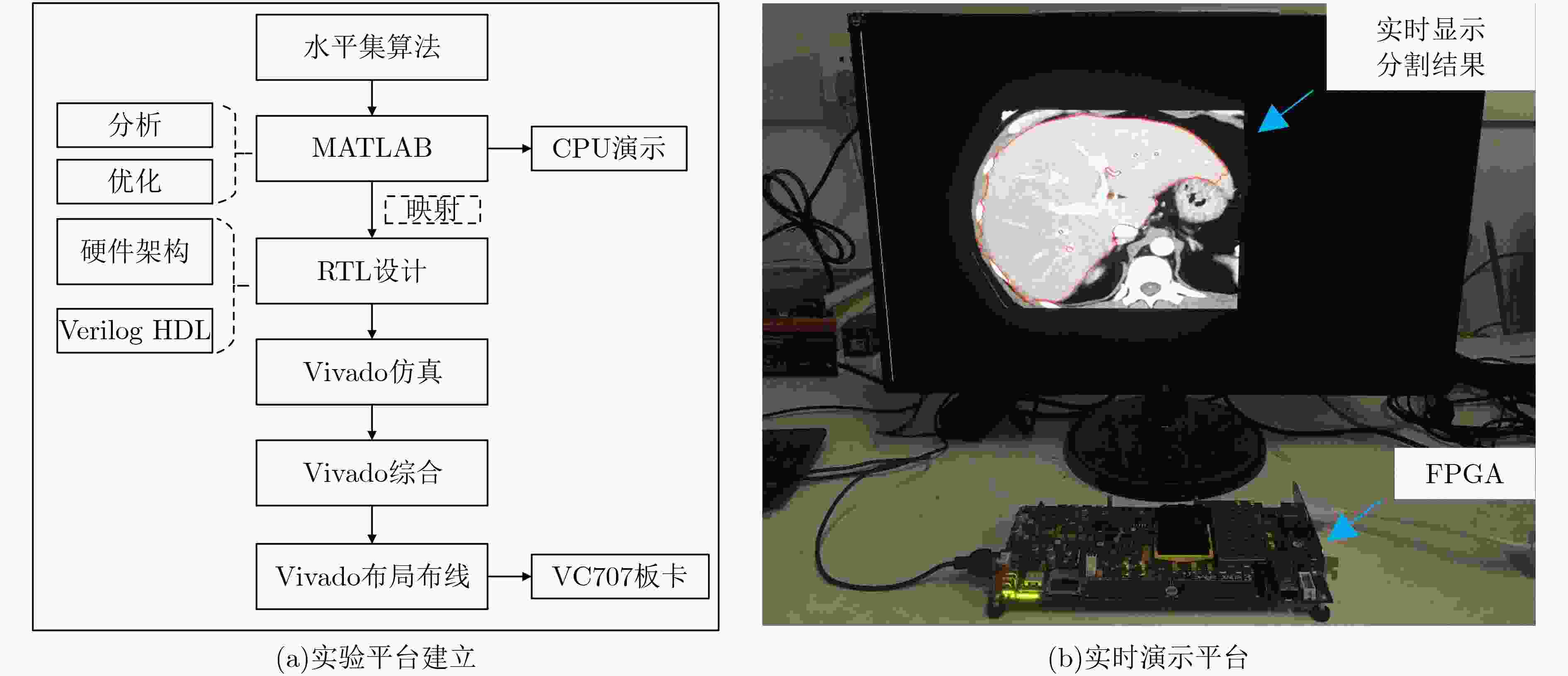
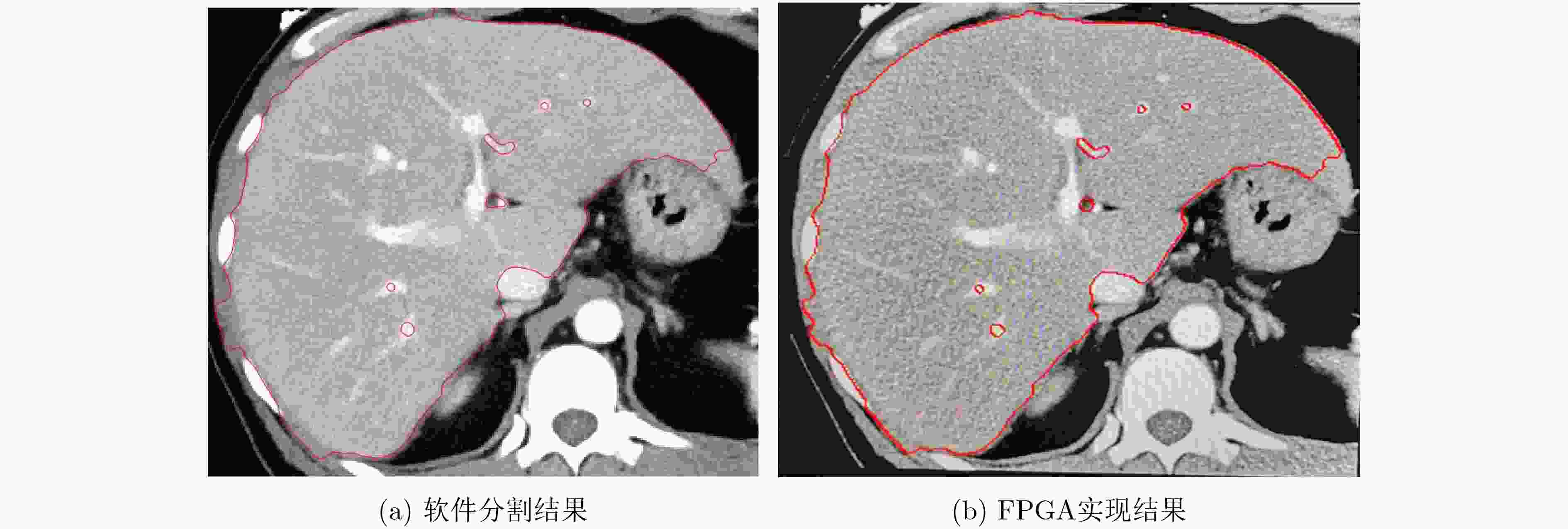
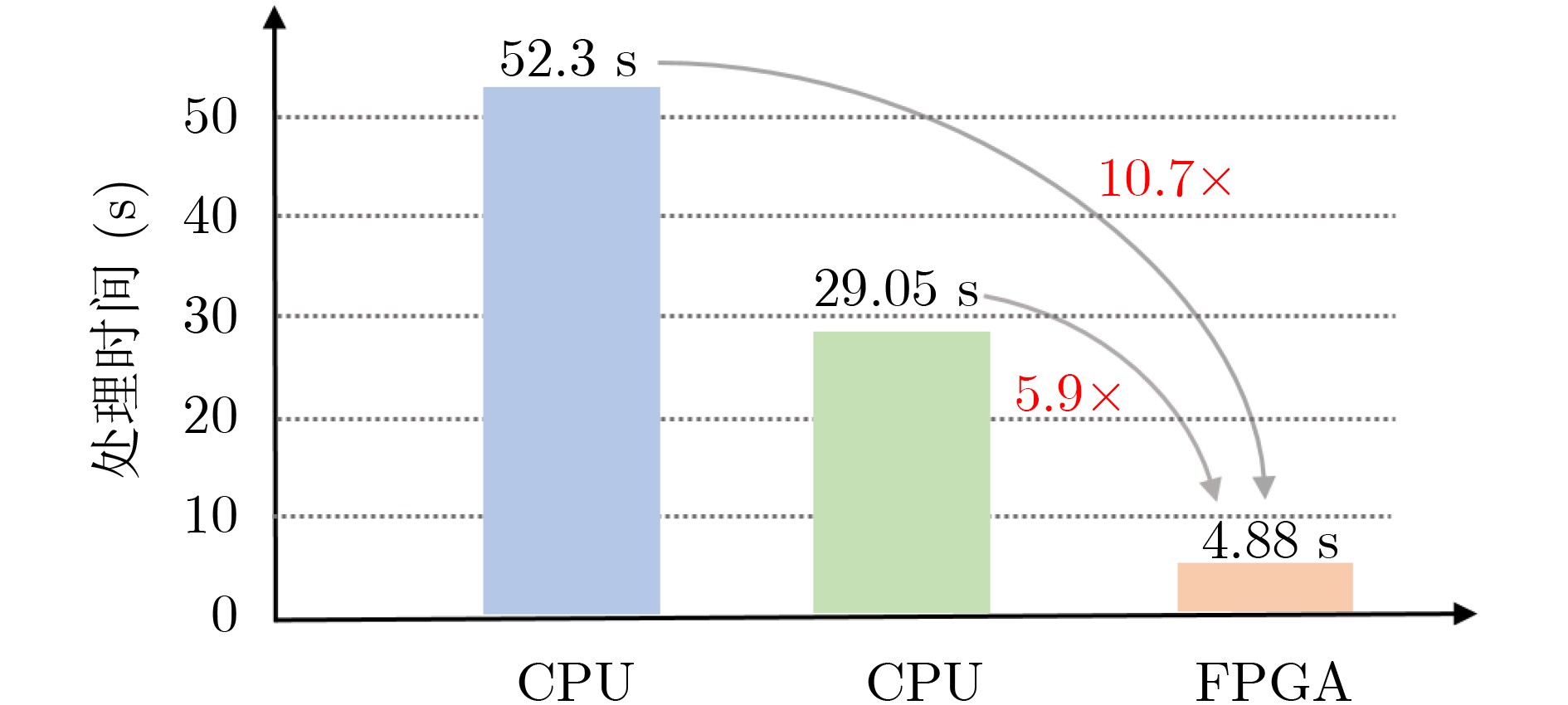
摘要: 水平集算法因其出色的性能,在图像分割领域中得到了广泛的应用。同时,与基于深度学习的图像分割算法相比,水平集算法不需要训练数据,大幅降低了数据标记带来的工作量。然而,目前水平集算法主要是基于软件开发,涉及大量复杂的计算,以及计算的多次迭代,导致较高的处理延时与功耗。为了加快水平集算法的处理速度和降低功耗,该文提出了一种基于FPGA的水平集图像分割算法加速器,其中包含4个设计创新点:任务级并行处理、图像分块像素级并行处理、全流水线处理架构、分时复用的梯度和散度算子处理。实验结果表明,与在CPU上执行的水平集算法相比,该文提出的硬件加速器处理速度提升10.7倍,功耗仅为2.2 W。Abstract: The level set algorithm is widely used for image segmentation due to its high accuracy. In addition, compared to the deep learning-based image segmentation methods, the level set algorithm can be implemented without training data, which reduces significantly the labeling efforts. However, the normal level set algorithm is still developed using software, involving complex computation with a large number of pixels and iterations andcausing long processing time and large power consumption. In this work, an FPGA-based level set hardware accelerator is proposed for image segmentation. The proposed hardware accelerator contains four design components: task-level parallel processing, image splitting processing, fully-pipelined processing architecture, and time-multiplexed gradient and divergence processing engine. Based on the experimental results, the proposed hardware accelerator achieves up to 10.7 times acceleration compared to the level set algorithm executing on the CPU, with only 2.2 W power consumption.
-
Key words:
- FPGA /
- Hardware accelerator /
- Level set /
- Image segmentation
-
表 1 资源利用率
FPGA型号 时钟频率 (MHz) Regs LUT DSP Virtex7 100 40655(6.69%) 30680(10.10%) 307(10.96%) -
[1] NIRKIN Y, MASI I, TRAN TUAN A, et al. On face segmentation, face swapping, and face perception[C]. Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi'an, China, 2018: 98–105. doi: 10.1109/FG.2018.00024. [2] WANG Guotai, LI Wenqi, ZULUAGA M A, et al. Interactive medical image segmentation using deep learning with image-specific fine tuning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(7): 1562–1573. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2791721 [3] MISHRA S, LIANG Peixian, CZAJKA A, et al. CC-NET: Image complexity guided network compression for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 2019: 57–60. doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2019.8759448. [4] HU Haigen, ZHENG Yixing, ZHOU Qianwei, et al. MC-Unet: Multi-scale convolution unet for bladder cancer cell segmentation in phase-contrast microscopy images[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), San Diego, USA, 2019: 1197–1199. doi: 10.1109/BIBM47256.2019.8983121. [5] OSHER S and SETHIAN J A. Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: Algorithms based on hamilton-jacobi formulations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1998, 79(1): 12–49. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(88)90002-2 [6] KASS M, WITKIN A, and TERZOPOULOS D. Snakes: Active contour models[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1988, 1(4): 321–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00133570 [7] XU Chenyang and PRINCE J L. Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1998, 7(3): 359–369. doi: 10.1109/83.661186 [8] CASELLES V, CATTÉ F, COLL T, et al. A geometric model for active contours in image processing[J]. Numerische Mathematik, 1993, 66(1): 1–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01385685 [9] CASELLES V, KIMMEL R, and SAPIRO G. Geodesic active contours[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1997, 22(1): 61–79. doi: 10.1023/A:1007979827043 [10] MALLADI R, SETHIAN J A, and VEMURI B C. Shape modeling with front propagation: A level set approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1995, 17(2): 158–175. doi: 10.1109/34.368173 [11] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [12] LIU Ye, WANG Yin, CHANG Liang, et al. A fast and efficient FPGA-based level set hardware accelerator for image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications (ICTA), Nanjing, China, 2020: 83–84. doi: 10.1109/ICTA50426.2020.9331957. [13] CHAN T F and VESE L A. Active contours without edges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(2): 266–277. doi: 10.1109/83.902291 [14] LI Chunming, HUANG Rui, DING Zhaohua, et al. A level set method for image segmentation in the presence of intensity inhomogeneities with application to MRI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(7): 2007–2016. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2146190 [15] LI Chunming, XU Chenyang, GUI Changfeng, et al. Level set evolution without re-initialization: A new variational formulation[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, USA, 2005: 430–436. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2005.213. [16] LI Chunming, XU Chenyang, GUI Changfeng, et al. Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(12): 3243–3254. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2069690 [17] EVANS L C. Partial Differential Equations[M]. 2nd ed. USA: American Mathematical Society, 2010. [18] JALBA A C, VAN DER LAAN W J, and ROERDINK J B T M. Fast sparse level sets on graphics hardware[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2013, 19(1): 30–44. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2012.69 [19] BALLA-ARABÉ S, GAO Xinbo, and WANG Bin. GPU accelerated edge-region based level set evolution constrained by 2d gray-scale histogram[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(7): 2688–2698. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2255304 [20] TSUYAMA H and MARUYAMA T. An FPGA acceleration of a level set segmentation method[C]. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Oslo, Norway, 2012: 414–420. doi: 10.1109/FPL.2012.6339138. -





 下载:
下载:

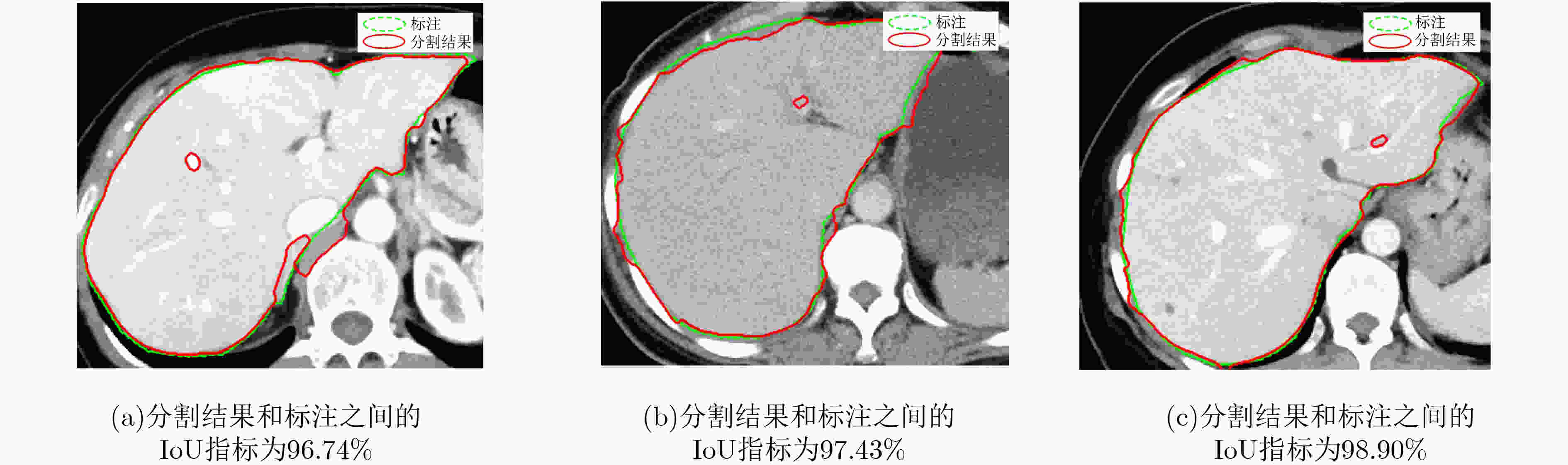
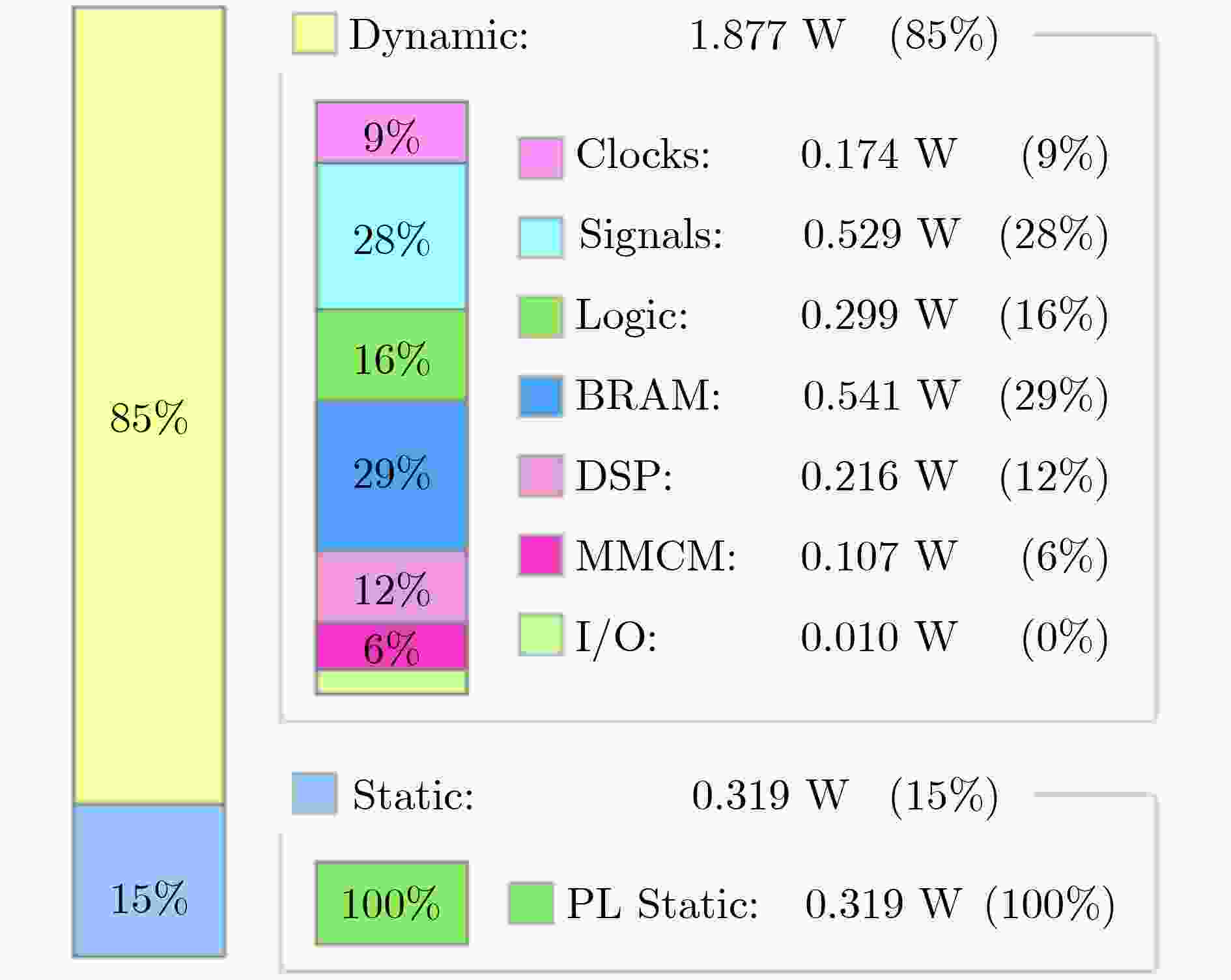


 下载:
下载:
