Probabilistic Matrix Factorization Recommendation Model Incorporating Multiple Weighting Factors
-
摘要: 针对个性化推荐精度较低、对冷启动敏感等问题,该文提出一种融合多权重因素的低秩概率矩阵分解推荐模型MWFPMF。模型利用给定的社交网络构建信任网络,借助Page rank算法和信任传递机制求取用户间信任度;基于Page rank计算用户社会地位,利用活动评分和评分时间修正用户间关系权重;引入词频-逆文本频率技术(TF-IDF)求取用户标签,通过标签相似性表征用户间同质性;将用户间信任度、用户社会地位影响力和用户同质性3因素融入低秩概率矩阵分解中,从而使用户偏好和活动特征映射到同一低秩空间,实现用户-活动评分矩阵的分解,在正则化约束下,最终完成低秩特征矩阵对用户评分缺失的有效预测。利用豆瓣同城北京和Ciao数据集确定各模块的参数设置值。通过仿真对比实验可知,本推荐模型获得了较高的推荐精度,与其他5种传统推荐算法相比,平均绝对误差至少降低了6.58%,均方差误差至少降低了6.27%,与深度学习推进算法相比,推荐精度基本接近;在冷启动用户推荐上优势明显,与其他推荐算法相比,平均绝对误差至少降低了0.89%,均方差误差至少降低了3.01%。Abstract: Considering the problems of low accuracy of personalized recommendation and sensitivity to cold start, low-rank Probabilistic Matrix Factorization recommendation model incorporating Multiple Weighting Factors (MWFPMF) is proposed; The trust network is constructed using a given social network, and the trust between users is calculated using the Page rank algorithm and trust transfer mechanism; The user’s social status is calculated based on Page rank, and the weight of the relationship between users is modified using activity scores and scoring time; Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency(TF-IDF) is introduced to take user tags, and the homogeneity between users is characterized by tag similarity; The three factors of trust among users, influence of users’ social status, and user homogeneity are integrated into the low-rank probability matrix decomposition, so that user preferences and activity characteristics are mapped to the same low-rank space, and the user-activity scoring matrix is decomposed. Under the premise of regularization as a constraint, the effective prediction of the lack of user ratings by the low-rank feature matrix is finally completed. The data sets of Douban Beijing and Ciao are used to determine the parameter settings of each module. Through simulation and comparison experiments, it can be seen that this recommendation model obtains higher recommendation model accuracy. Compared with the other five traditional recommendation algorithms, the mean absolute error is reduced by at least 6.58%, and the mean square error is reduced by at least 6.27%, compared with the deep learning advancing algorithm, the recommendation accuracy is almost the same; It has obvious advantages in cold-start user recommendation. Compared with other recommendation algorithms, the average absolute error is reduced by at least 0.89%, and the mean square error is reduced by at least 3.01%.
-
表 1 参数设置
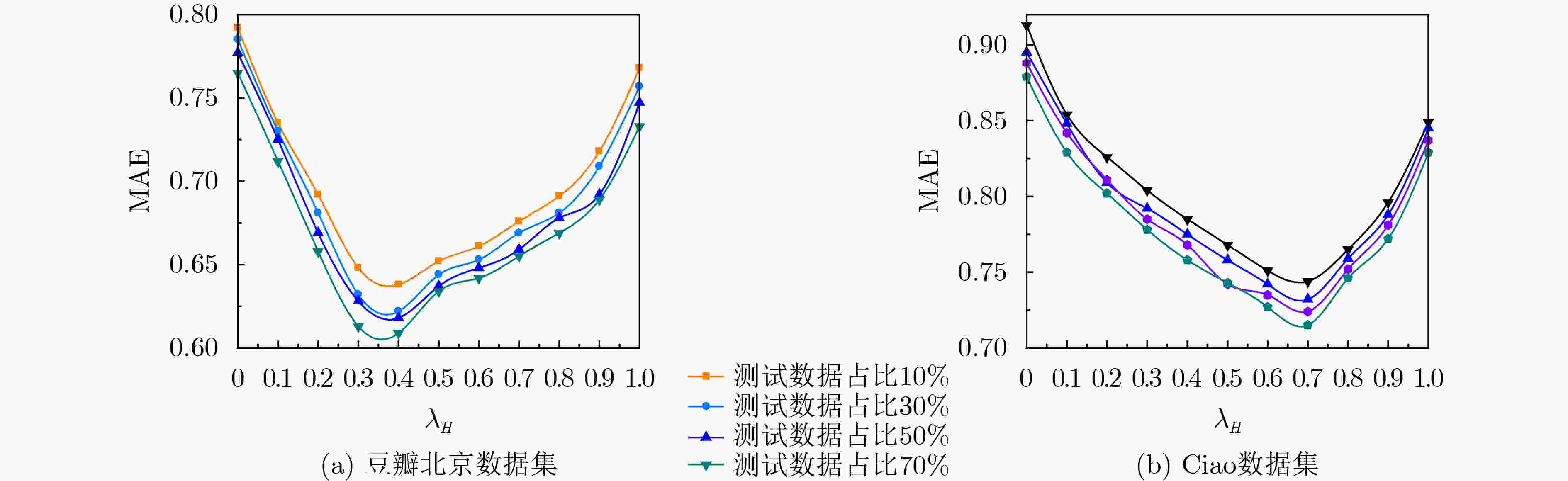
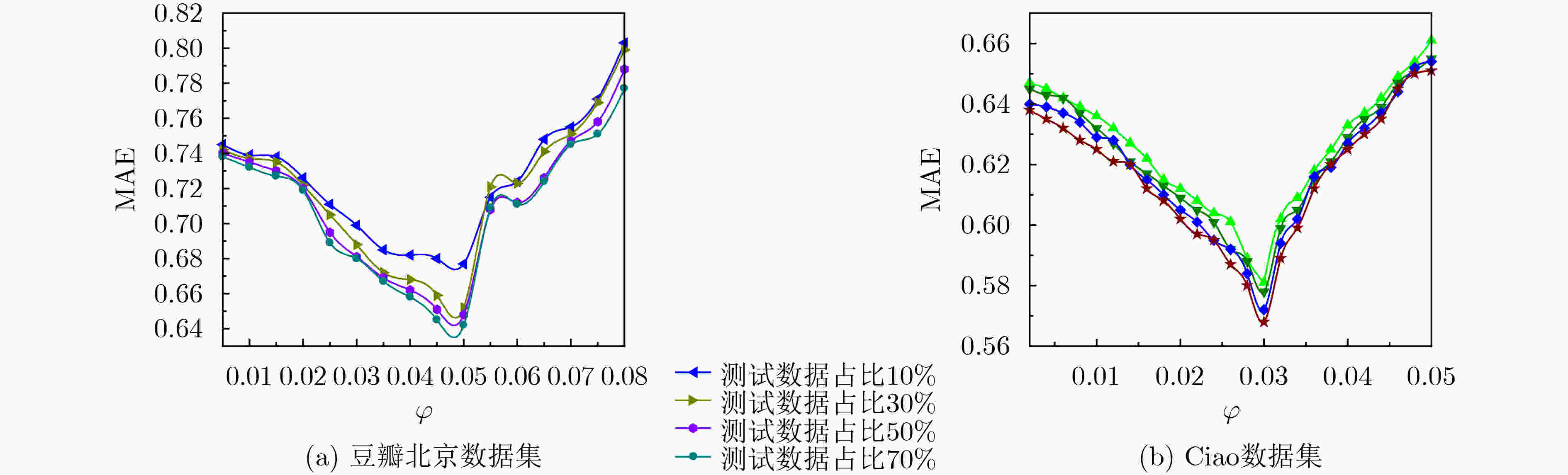
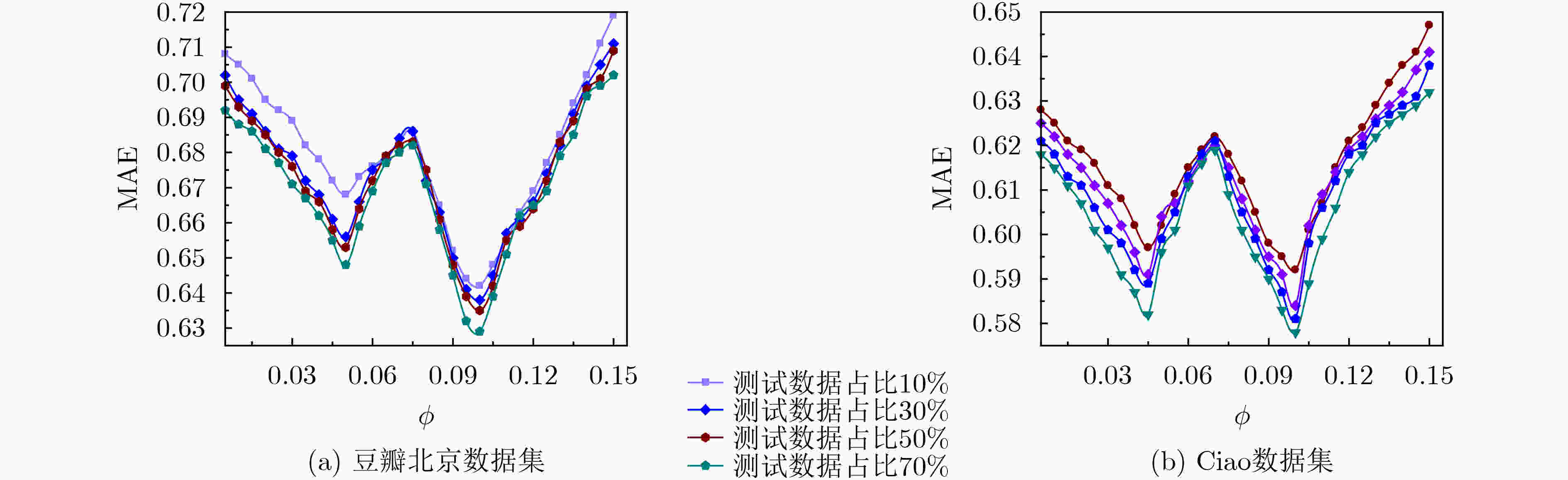
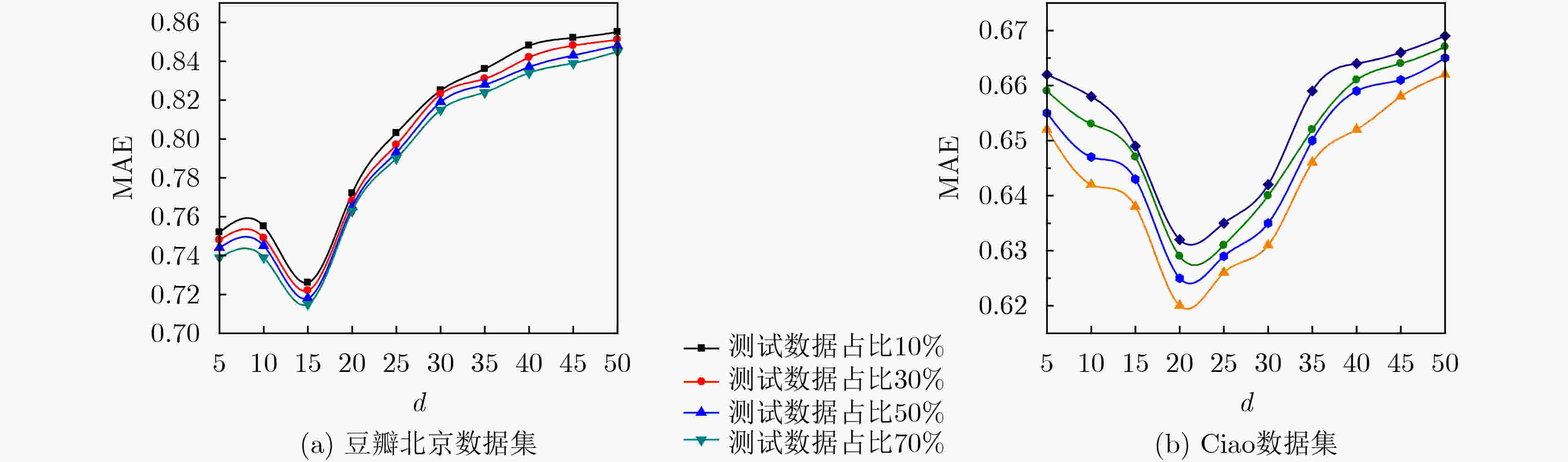
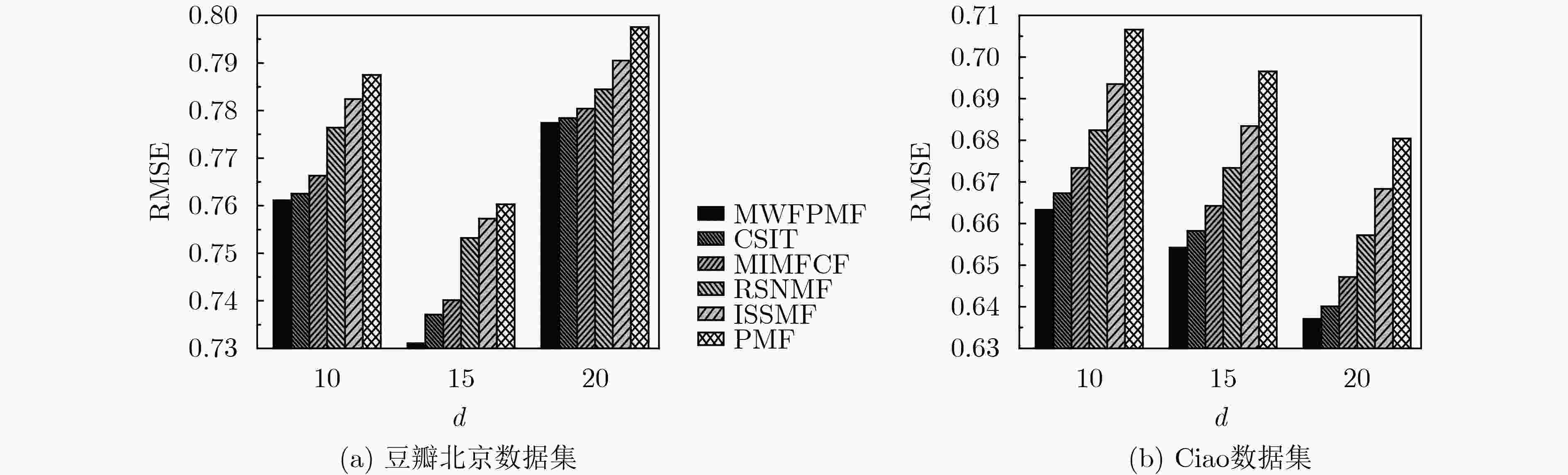
参数 值 参数 值 用户特征正则化控制参数${\lambda _{{\boldsymbol{Ut}}} }$ 0.1 用户同质性调节参数${\lambda _H}$ 0.5 活动特征正则化控制参数${\lambda _{{\boldsymbol{St}}} }$ 0.1 用户信任网络跳出率$\rho $ 0.85 用户社会影响力调节参数${\lambda _W}$ 5 隐特征矩阵维度$d$ 15 梯度学习速率$\beta $ 0.01 跳数阈值${h_\theta }$ 3 同质相似性阈值$\alpha $ 0.8 时间衰减参数$\delta$ 0.5 表 2 各算法对冷启动用户的推荐性能比较
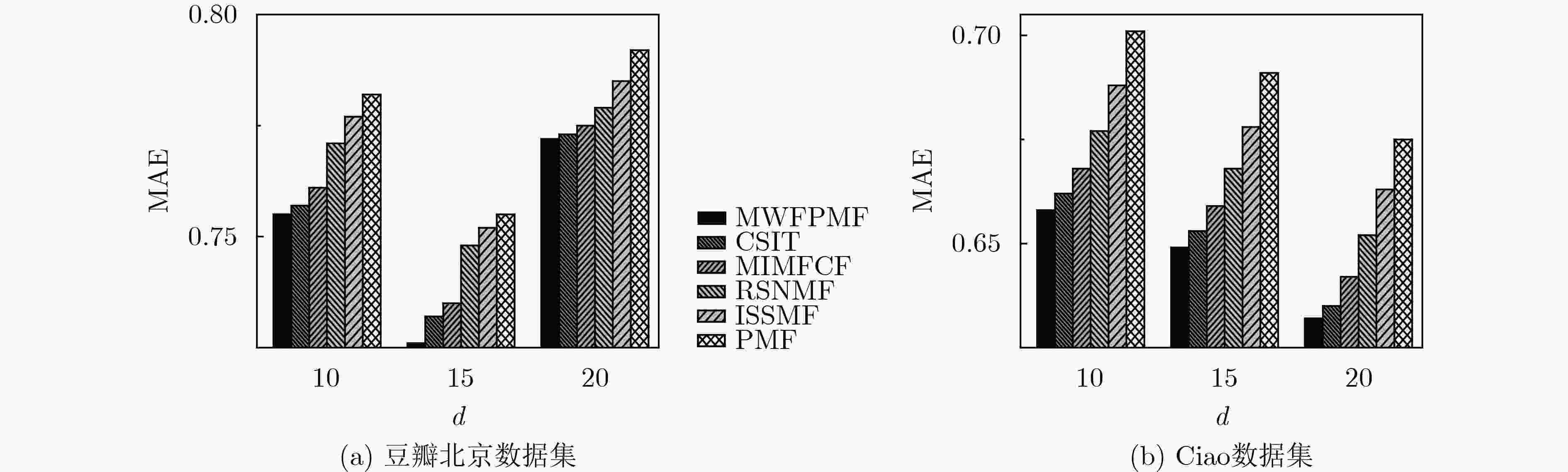
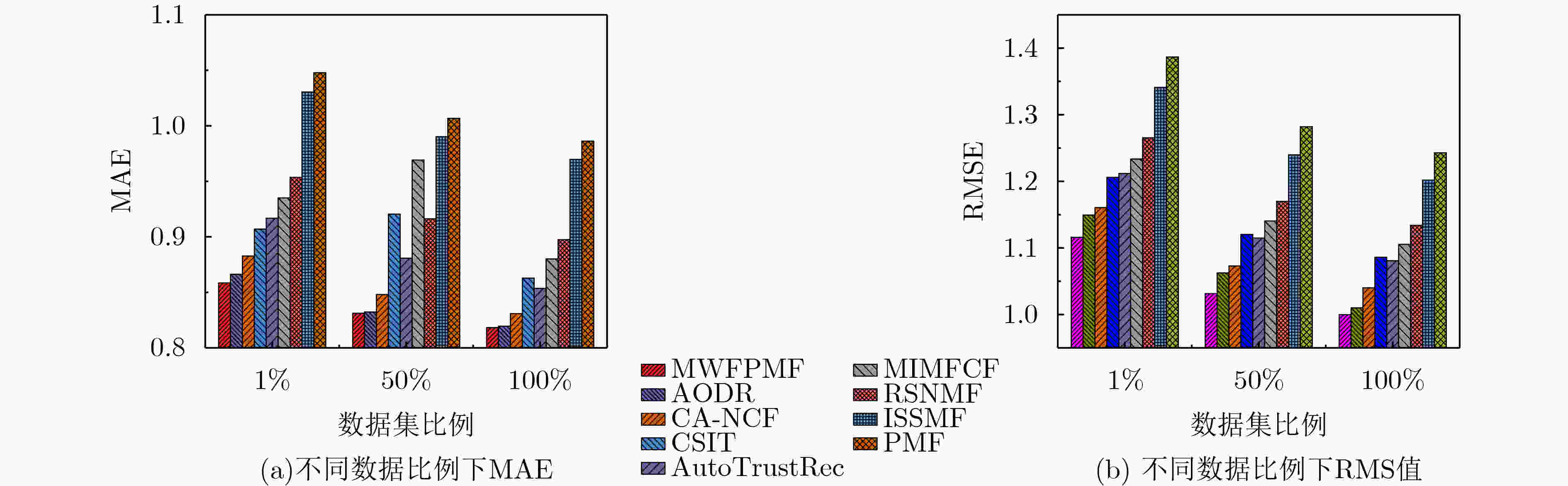
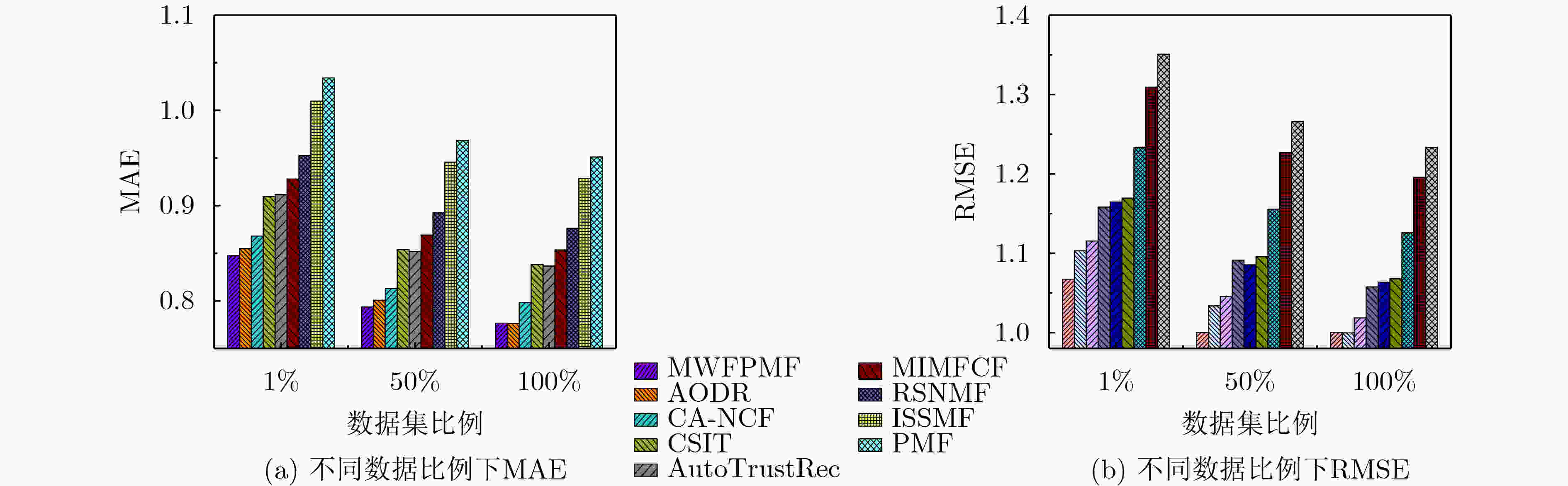
推荐算法 豆瓣北京数据集 Ciao数据集 ${\rm{MAE}}$ ${\rm{RMSE}}$ ${\rm{MAE}}$ ${\rm{RMSE}}$ MWFPMF 0.8417 1.0526 0.8333 1.0348 AODR 0.8493 1.0843 0.8407 1.0695 CA-NCF 0.8654 1.0949 0.8537 1.0814 CSIT 0.8892 1.1377 0.8945 1.1229 AutoTrustRec 0.8988 1.1432 0.8964 1.1291 MIMFCF 0.9168 1.1637 0.9125 1.1339 RSNMF 0.9349 1.1938 0.9368 1.1954 ISSMF 1.0102 1.2651 0.9929 1.2695 PMF 1.0273 1.3081 1.0169 1.3096 -
[1] CUI Zhihua, XU Xianghua, XUE Fei, et al. Personalized recommendation system based on collaborative filtering for IoT scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2020, 13(4): 685–695. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2020.2964552 [2] LI Shugang, SONG Xuewei, LU Hanyu, et al. Friend recommendation for cross marketing in online brand community based on intelligent attention allocation link prediction algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 139: 112839. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112839 [3] AHMADIAN S, AFSHARCHI M, and MEGHDADI M. A novel approach based on multi-view reliability measures to alleviate data sparsity in recommender systems[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(13): 17763–17798. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-7079-x [4] GUO Guibing, ZHANG Jie, and YORKE-SMITH N. A novel recommendation model regularized with user trust and item ratings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2016, 28(7): 1607–1620. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2016.2528249 [5] WANG Ximeng, LIU Yun, ZHANG Guangquan, et al. Diffusion-based recommendation with trust relations on tripartite graphs[J]. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, 2017, 2017(8): 083405. doi: 10.1088/1742-5468/aa8189 [6] PAPNEJA S, SHARMA K, and KHILWANI N. Context aware personalized content recommendation using ontology based spreading activation[J]. International Journal of Information Technology, 2018, 10(2): 133–138. doi: 10.1007/s41870-017-0052-5 [7] CHEN Lingjiao and GAO Jian. A trust-based recommendation method using network diffusion processes[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 506: 679–691. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.04.089 [8] GUAN Jiansheng, XU Min, and KONG Xiangsong. Learning social regularized user representation in recommender system[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 144: 306–310. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.09.015 [9] AGHDAM M H. Context-aware recommender systems using hierarchical hidden Markov model[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 518: 89–98. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.11.037 [10] YAO Weilong, HE Jing, HUANG Guangyan, et al. Modeling dual role preferences for trust-aware recommendation[C]. The 37th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval, Queensland, Australia, 2014: 975–978. [11] WANG Xin, WANG Ying, and SUN Hongbin. Exploring the combination of dempster-shafer theory and neural network for predicting trust and distrust[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2016, 2016: 5403105. [12] 余永红, 高阳, 王皓, 等. 融合用户社会地位和矩阵分解的推荐算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2018, 55(1): 113–124. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20160704YU Yonghong, GAO Yang, WANG Hao, et al. Integrating user social status and matrix factorization for item recommendation[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(1): 113–124. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20160704 [13] 王英, 王鑫, 左万利. 基于社会学理论的信任关系预测模型[J]. 软件学报, 2014, 25(12): 2893–2904.WANG Ying, WANG Xin, and ZUO Wanli. Trust prediction modeling based on social theories[J]. Journal of Software, 2014, 25(12): 2893–2904. [14] ZHENG Xiaoyao, LUO Yonglong, SUN Liping, et al. A novel social network hybrid recommender system based on hypergraph topologic structure[J]. World Wide Web, 2018, 21(4): 985–1013. doi: 10.1007/s11280-017-0494-5 [15] TANG Jiliang, GAO Huiji, and LIU Huan. mTrust: discerning multi-faceted trust in a connected world[C]. The Fifth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Washington, USA, 2012: 93–102. [16] GAO Honghao, KUANG Li, YIN Yuyu, et al. Mining consuming behaviors with temporal evolution for personalized recommendation in mobile marketing apps[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020, 25(4): 1233–1248. doi: 10.1007/s11036-020-01535-1 [17] LI Yangyang, WANG Dong, HE Haiyang, et al. Mining intrinsic information by matrix factorization-based approaches for collaborative filtering in recommender systems[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 249: 48–63. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.03.002 [18] CHEN Yan, DAI Yongfang, HAN Xiulong, et al. Dig users’ intentions via attention flow network for personalized recommendation[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 547: 1122–1135. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.09.007 [19] LI Jun, CHEN Chaochao, CHEN Huiling, et al. Towards context-aware social recommendation via individual trust[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 127: 58–66. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2017.02.032 [20] BI Jianwu, LIU Yang, FAN Zhiping. A deep neural networks based recommendation algorithm using user and item basic data[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2020, 11(4): 763–777. doi: 10.1007/s13042-019-00981-y [21] LUO Xin, ZHOU Mengchu, XIA Yunni, et al. An efficient non-negative matrix-factorization-based approach to collaborative filtering for recommender systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2014, 10(2): 1273–1284. doi: 10.1109/TII.2014.2308433 [22] SALAKHUTDINOV R and MNIH A. Probabilistic matrix factorization[C]. The 20th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, USA, 2007: 1257–1264. [23] DA’U A, SALIM N, RABIU I, et al. Weighted aspect-based opinion mining using deep learning for recommender system[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 140: 112871. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112871 [24] JAWARNEH I M A, BELLAVISTA P, CORRADI A, et al. A pre-filtering approach for incorporating contextual information into deep learning based recommender systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 40485–40498. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2975167 [25] BATHLA G, AGGARWAL H, and RANI R. AutoTrustRec: recommender system with social trust and deep learning using AutoEncoder[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(29): 20845–20860. -





 下载:
下载:
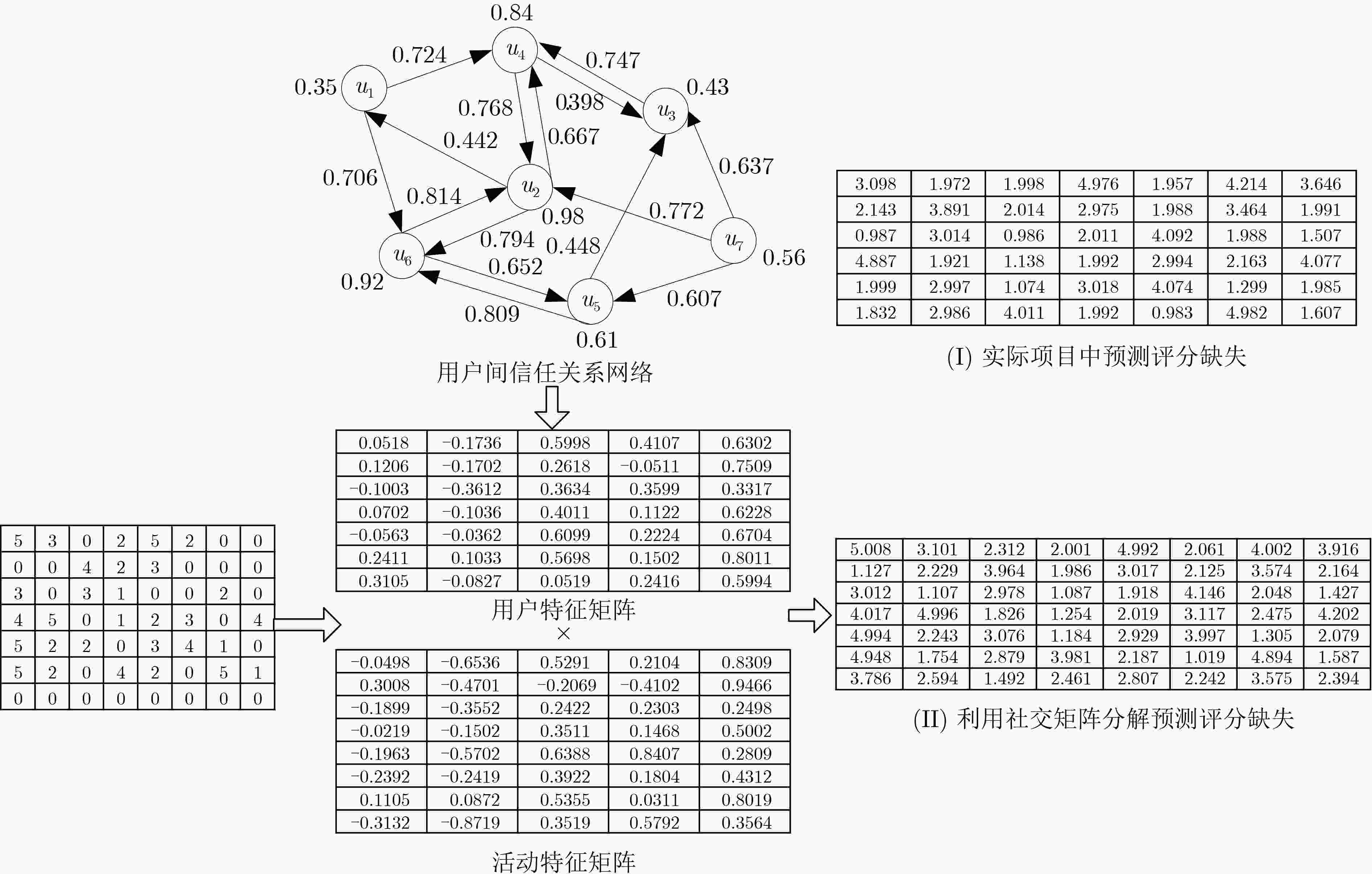

















 下载:
下载:
