Research on Energy Efficiency Probability Model and Architecture of RISCV Cryptographic Processor
-
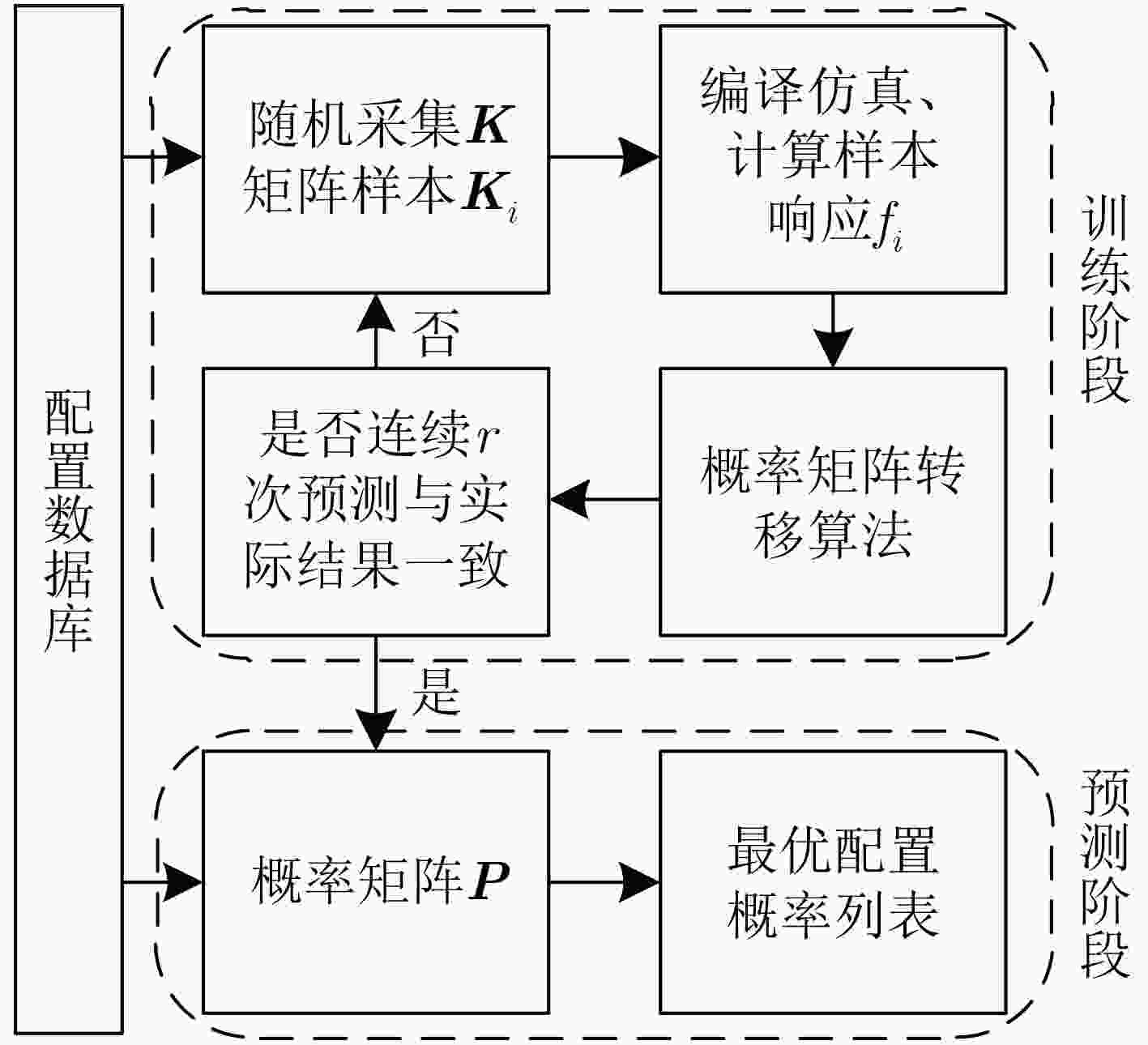
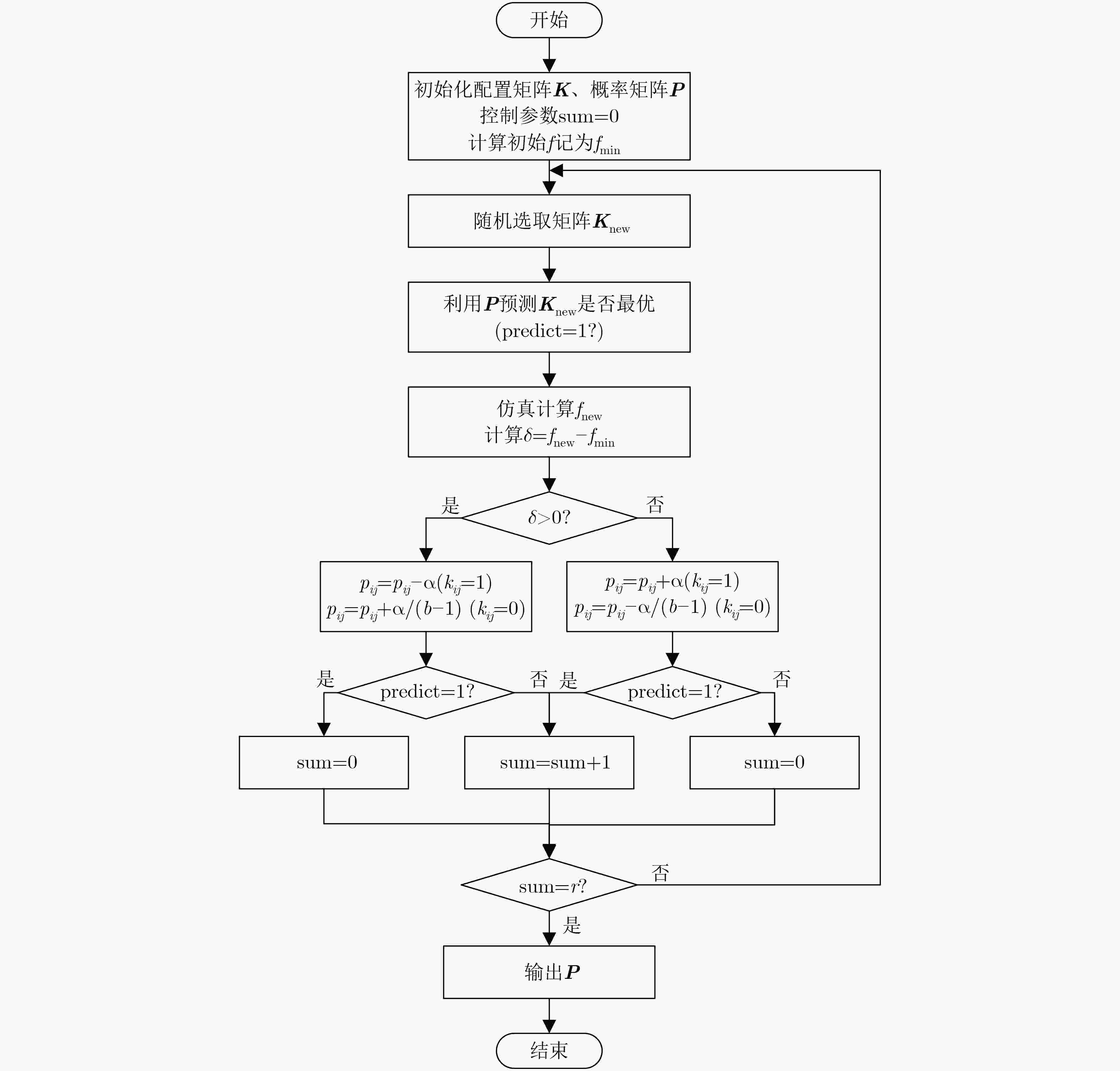
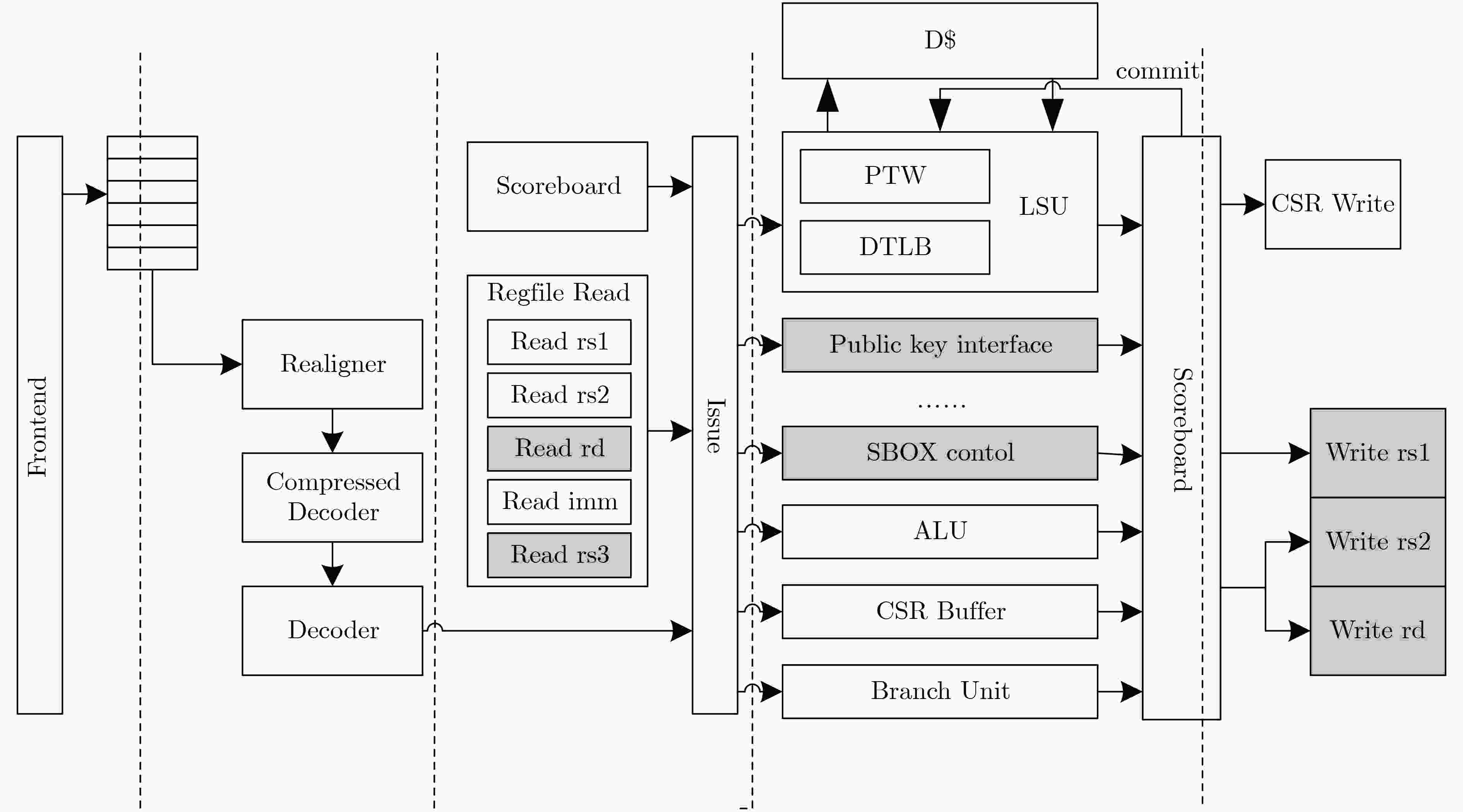
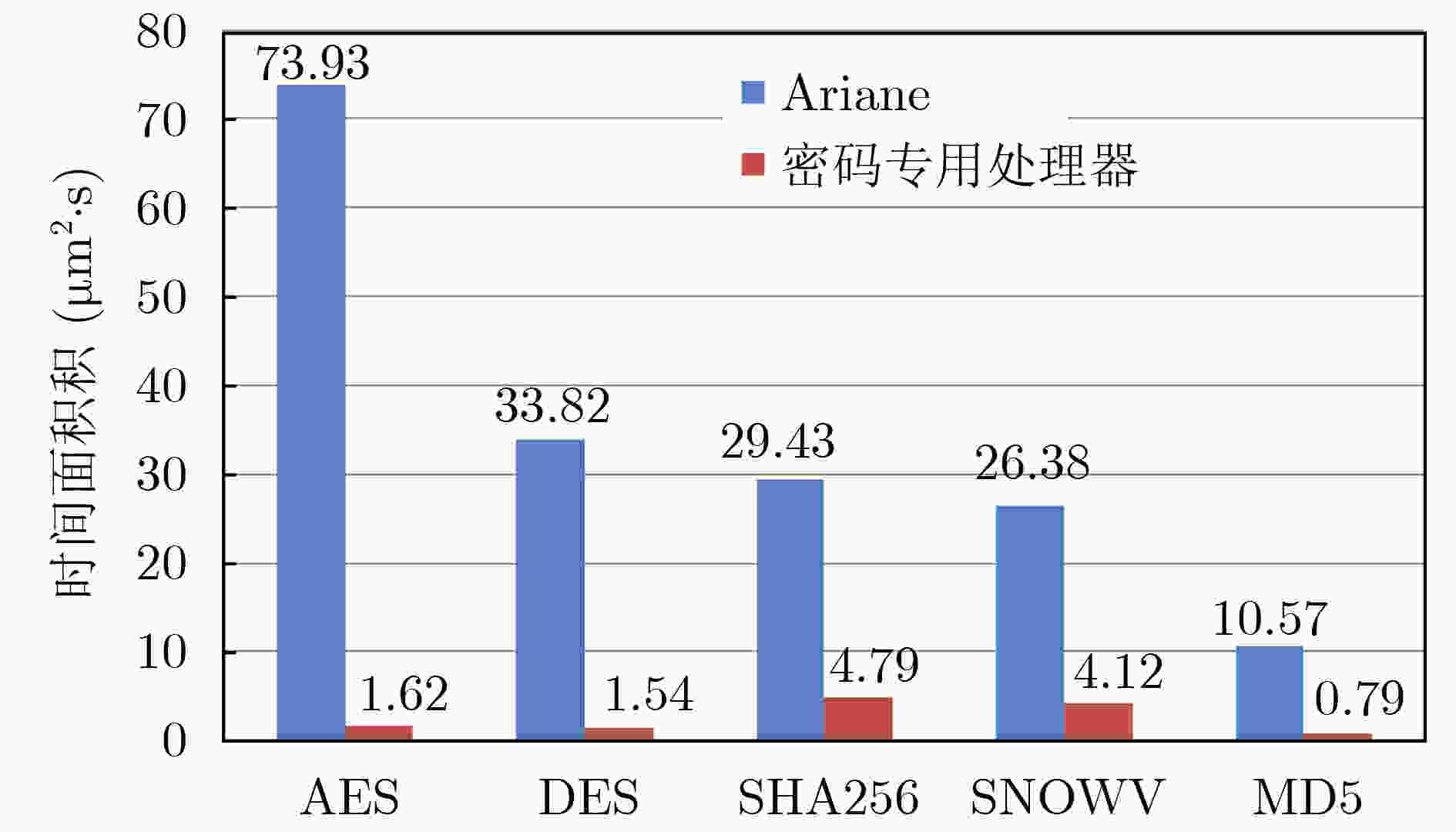
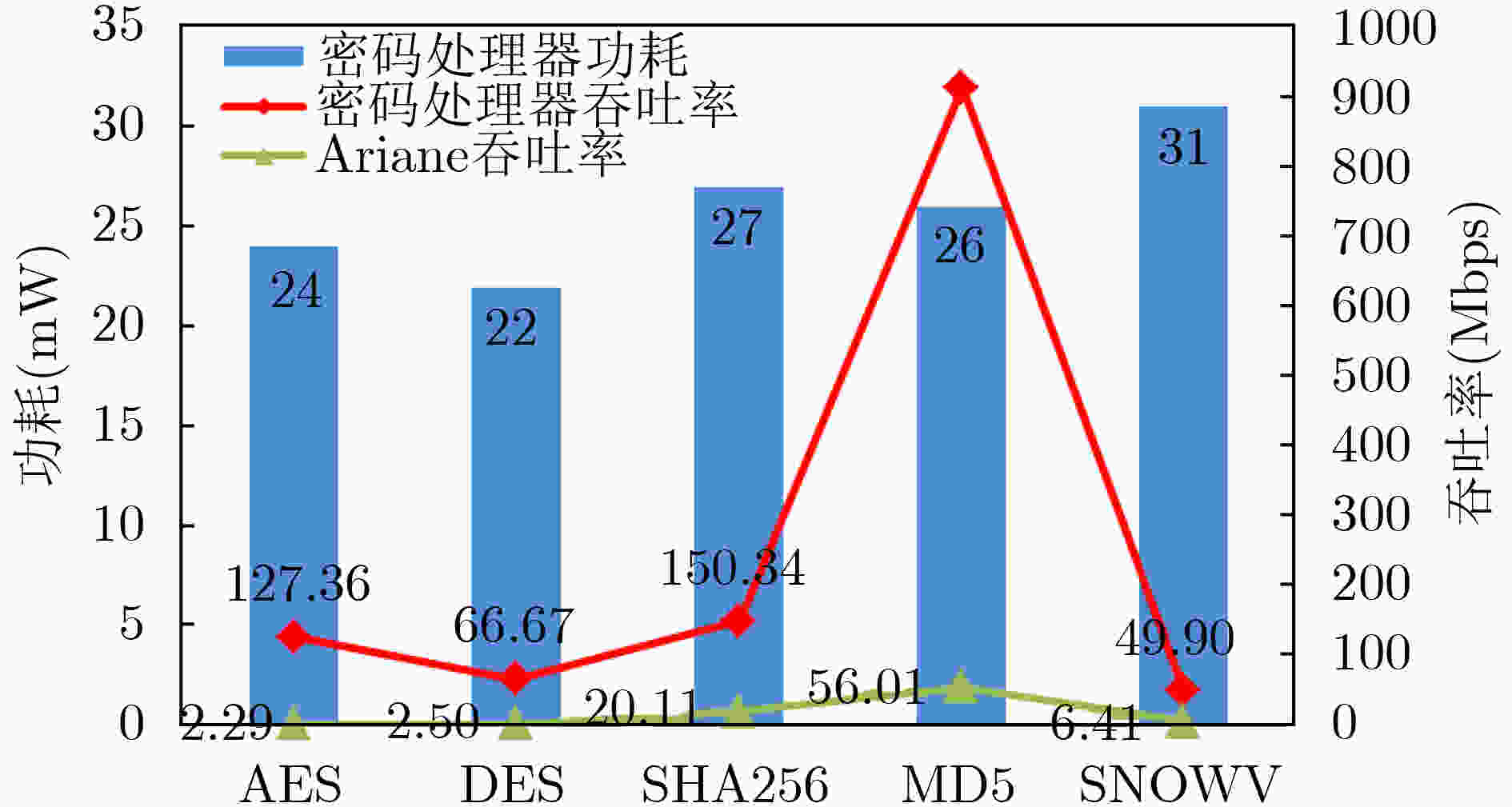
摘要: 该文以高能效为目标,建立了密码专用处理器能效概率模型,并指导高能效密码专用处理器体系结构设计。该文将面向密码领域的专用指令处理器设计空间探索问题描述为“1”值在配置矩阵中的定位问题,通过引入概率矩阵进一步将定位问题转化为最优配置的概率问题,并基于机器学习思想提出了密码专用处理器最高能效概率模型。实验证明,该文提出的能效概率模型平均经过2300次迭代输出最终结果,且预测准确率达到92.7%。根据最高能效概率模型,对密码专用处理器设计空间进行探索,获取满足高能效需求的密码专用处理器运算单元集合,以扩展指令的方式将其集成到开源通用64位RISCV处理器核心Araine中,提出高能效密码专用处理器体系结构。将该处理器在CMOS 55 nm工艺下进行逻辑综合,结果表明,该文提出的RISCV密码专用处理器与扩展前相比面积增大了426874 μm2,关键延迟增加了0.51 ns,完成密码算法总时间面积积增幅之和为0.46,执行常见密码算法能效比在1.61~35.16 Mbps/mW范围内。Abstract: This paper establishes an energy efficiency probability model for a dedicated cryptographic processor, and guides the design of the cryptographic processor. The design space exploration problem of a processor is designed as the positioning problem of "1" values in the configuration matrix. The probability matrix is introduced to transform the positioning problem into an optimal configuration probability problem. Based on the idea of machine learning, a probability model for the highest energy efficiency of a dedicated cryptographic processor is proposed. Experiments prove that the energy efficiency probability model in this paper outputs the final result after 2300 iterations on average, and the prediction accuracy rate reaches 92.7%. According to the highest energy efficiency probability model, a collection of computing units that meet high energy efficiency requirements can be obtained, and they are integrated into the open source general-purpose 64 bit RISCV processor core named Ariane. A dedicated processor for energy-efficient cryptography is built. The processor is synthesized under the CMOS 55 nm process, and the results show that compared with Ariane, the area of the proposed cryptographic processor increases by 426874 μm2, the key delay increases by 0.51 ns, and the sum of the increasing total time area of the cryptographic algorithm is 0.46, the energy efficiency ratio of common cryptographic algorithms is within the range of 1.6~35.16 Mbps/mW.
-
表 1 参数列表
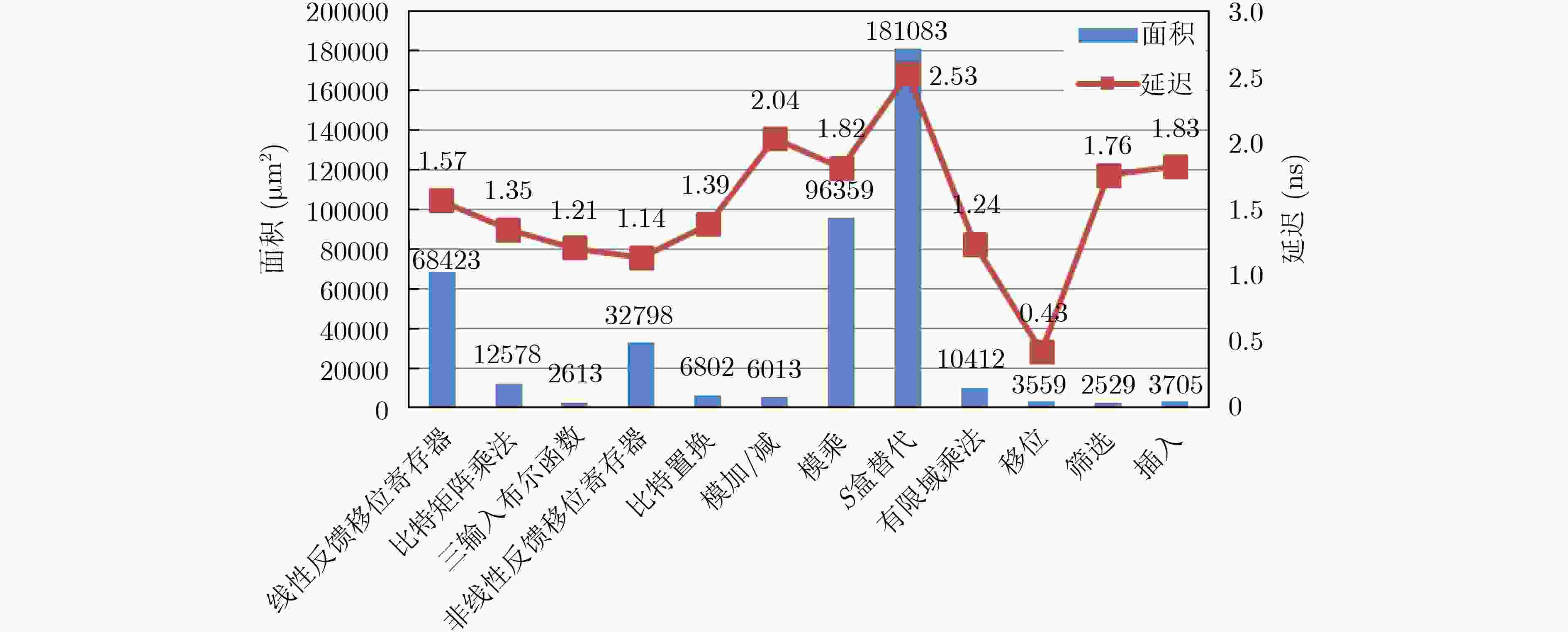
参数 约束 含义 ${x_i}$ $1 \le i \le n$ 可集成到处理器中的密码加速单元 ${y_i}$ $1 \le l \le m$ 算法集合中某目标密码算法 ${t_i}$ $1 \le i \le n$ 密码加速单元${x_i}$对应的关键延迟 ${s_i}$ $1 \le i \le n$ 密码加速单元${x_i}$对应的面积 ${k_i}$ ${k_i} \in \left[ {0,1} \right]$ 表示单元${x_i}$是否为处理器扩展单元(1表示扩展) ${t_0}$ 表示未扩展密码运算单元时处理器关键延迟 ${s_0}$ 表示为扩展密码运算单元时处理器面积 ${C_l}$ 一种密码运算单元扩展配置下完成${y_l}$算法所需时钟周期数 ${C_{l0}}$ 未扩展密码运算单元时完成${y_l}$算法所需时钟周期数 表 2 指令模板
[31:26] [25] [24:20] [1915] [14:12] [11:7] [6:0] RL Funt7 Rsd2 Rsd1 Funt3 Funt5 opcode SRI Imm[5:0] Funt1 Rsd2 Rsd1 Funt3 Rds opcode C Funt7 Rs2 Rs1 Imm[7:0] opcode 表 3 RISCV密码专用处理器性能
Ariane 密码专用处理器 关键延迟(ns) 1.9 2.3 面积(μm2) 1321154 1748028 表 4 RISCV密码专用处理器实现算法所需指令周期数
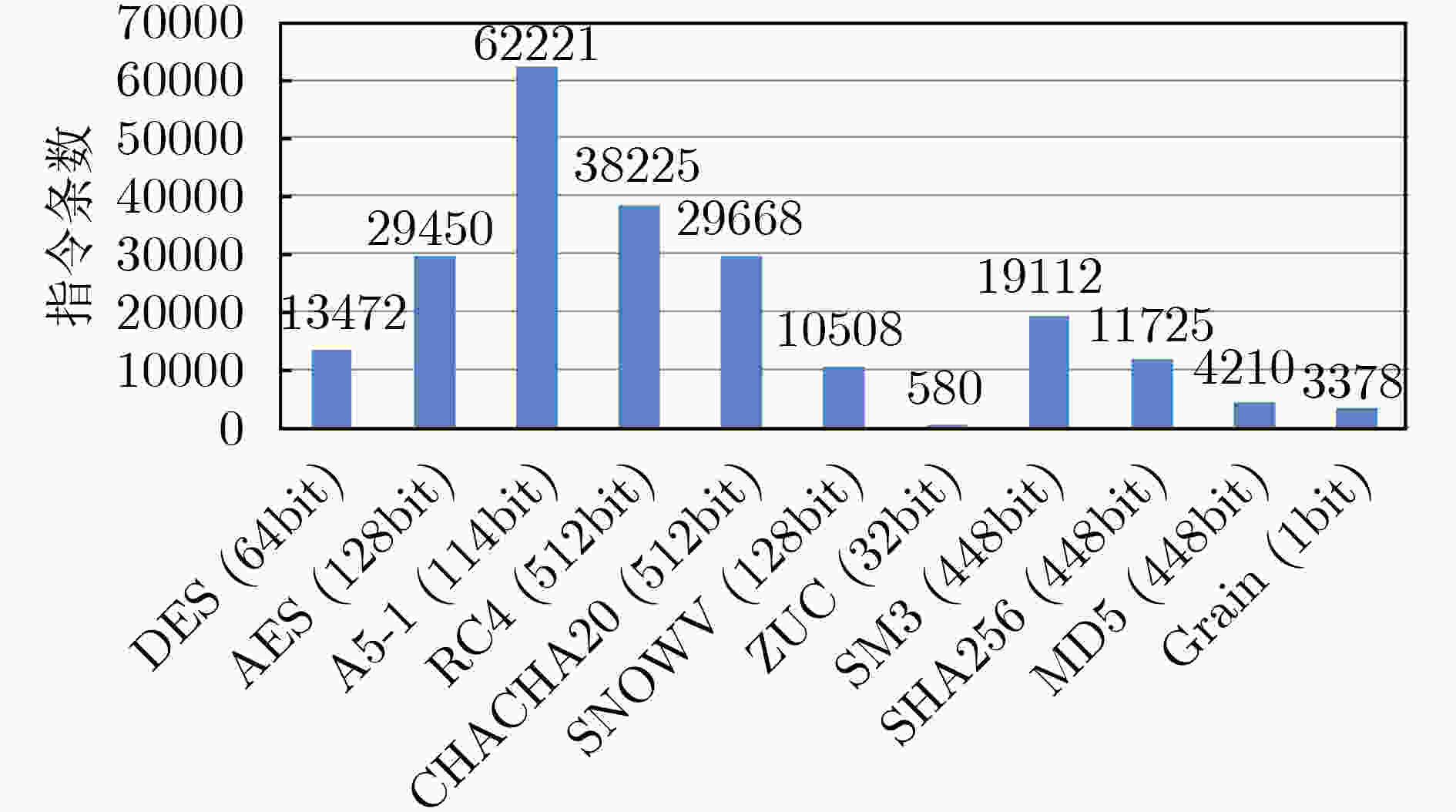
Ariane 密码专用处理器 AES 29450 402 DES 13472 384 SHA256 11725 1192 SNOWV 10508 1026 MD5 4210 196 -
[1] AZIZI O, MAHESRI A, LEE B C, et al. Energy-performance tradeoffs in processor architecture and circuit design: A marginal cost analysis[J]. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 2010, 38(3): 26–36. doi: 10.1145/1816038.1815967 [2] DUBACH C, JONES T M, and O’BOYLE M F P. Exploring and predicting the architecture/optimising compiler Co-design Space[C]. The 2008 International Conference on Compilers, Architecture, and Synthesis for Embedded Systems, Atlanta, USA, 2008: 31–40. [3] LEE B C and BROOKS D M. Accurate and efficient regression modeling for microarchitectural performance and power prediction[C]. The 12th International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, San Jose, USA, 2006: 185–194. [4] LEE B C and BROOKS D M. Illustrative design space studies with microarchitectural regression models[C]. The 13th IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture, Scottsdale, USA, 2007: 340–351. [5] LEE B C and BROOKS D. Applied inference: Case studies in microarchitectural design[J]. ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization, 2010, 7(2): 1–37. [6] PALERMO G, SILVANO C, and ZACCARIA V. ReSPIR: A response surface-based pareto iterative refinement for application-specific design space exploration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2009, 28(12): 1816–1829. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2009.2028681 [7] CHEN Tianshi, GUO Qi, TANG Ke, et al. ArchRanker: A ranking approach to design space exploration[C]. The 41st ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Minneapolis, USA, 2014: 85–96. [8] CHEN Tianshi, CHEN Yunji, GUO Qi, et al. Effective and efficient microprocessor design space exploration using unlabeled design configurations[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2014, 5(1): 20. [9] LI W, ZENG Xiaoyang, NAN Longmei, et al. A reconfigurable block cryptographic processor based on VLIW architecture[J]. China Communications, 2016, 13(1): 91–99. doi: 10.1109/CC.2016.7405707 [10] 孟沫舒. CISC处理器复杂指令的实现方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学院研究生院, 2012. [11] SHAN Weiwei, ZHANG Shuai, XU Jiaming, et al. Machine learning assisted side-channel-attack countermeasure and its application on a 28-nm AES circuit[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(3): 794–804. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2953855 [12] LI Wei, CHANG Zhongxiang, FENG Xiao, et al. Fast parallel extract-shift and parallel deposit-shift in general-purpose processors[C]. The 12th IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing, Beijing, China, 2015: 764–771. [13] 马超, 李伟, 戴紫彬, 等. 新型可重构移位-置换单元研究与设计[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(5): 1025–1034. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.05.001MA Chao, LI Wei, DAI Zibin, et al. A novel reconfigurable rotation-permutation unit research and implementation[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(5): 1025–1034. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.05.001 [14] 马超, 戴紫彬, 李伟, 等. RPRU: 一种面向处理器的比特抽取与移位统一架构[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2018, 55(2): 426–437. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20160775MA Chao, DAI Zibin, LI Wei, et al. RPRU: A unified architecture for rotation and bit-extraction operations in general-propose processor[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(2): 426–437. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20160775 [15] 徐光明, 徐金甫, 常忠祥, 等. 序列密码非线性反馈移存器的可重构研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2015, 32(9): 2823–2826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2015.09.062XU Guangming, XU Jinfu, CHANG Zhongxiang, et al. Reconfigurability study on nonlinear feedback shift registers in stream cipher[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2015, 32(9): 2823–2826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2015.09.062 [16] LIU Bin and BAAS B M. Parallel AES encryption engines for many-core processor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2013, 62(3): 536–547. doi: 10.1109/TC.2011.251 [17] LI Wei, ZENG Xiaoyang, DAI Zibin, et al. A high energy-efficient reconfigurable VLIW symmetric cryptographic processor with loop buffer structure and chain processing mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2017, 26(6): 1161–1167. doi: 10.1049/cje.2017.06.010 [18] SAYILAR G and CHIOU D. Cryptoraptor: High throughput reconfigurable cryptographic processor[C]. 2014 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Jose, USA, 2014: 155–161. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
