Hardware Trojan Detection Based on Multiple Structural Features
-
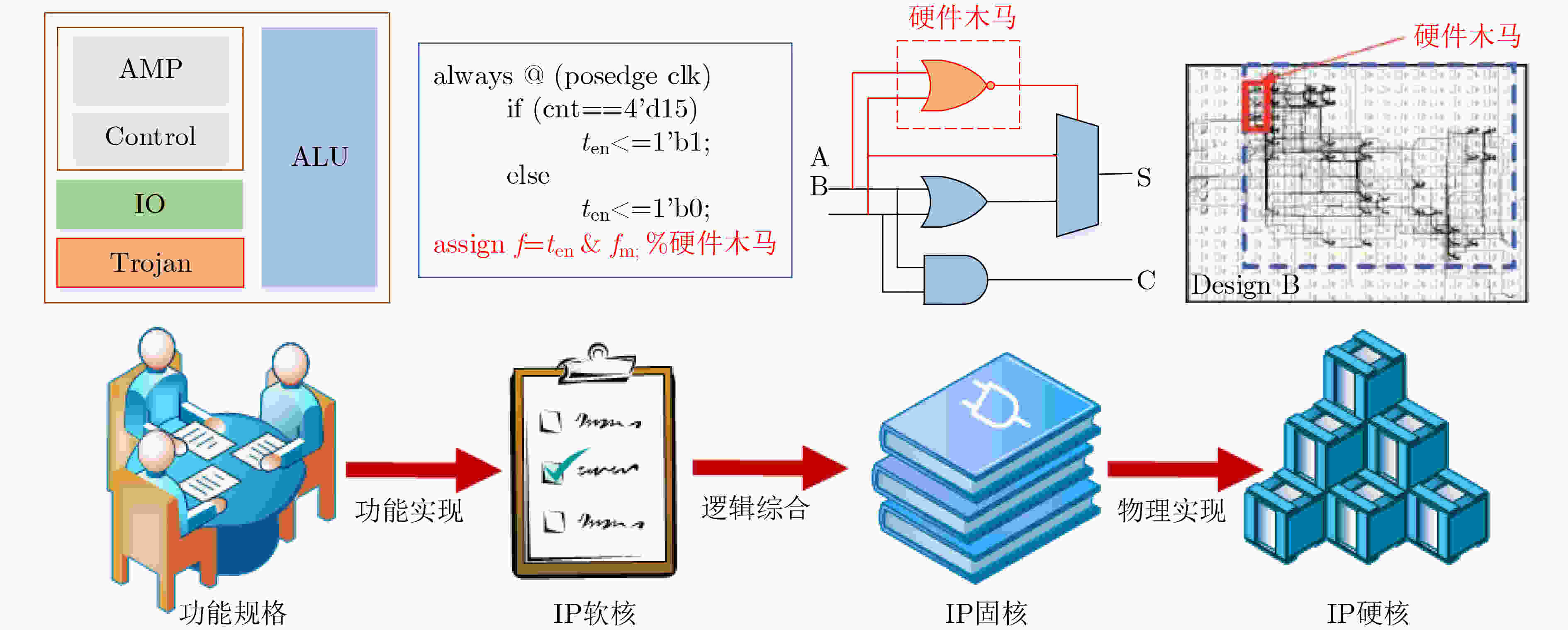
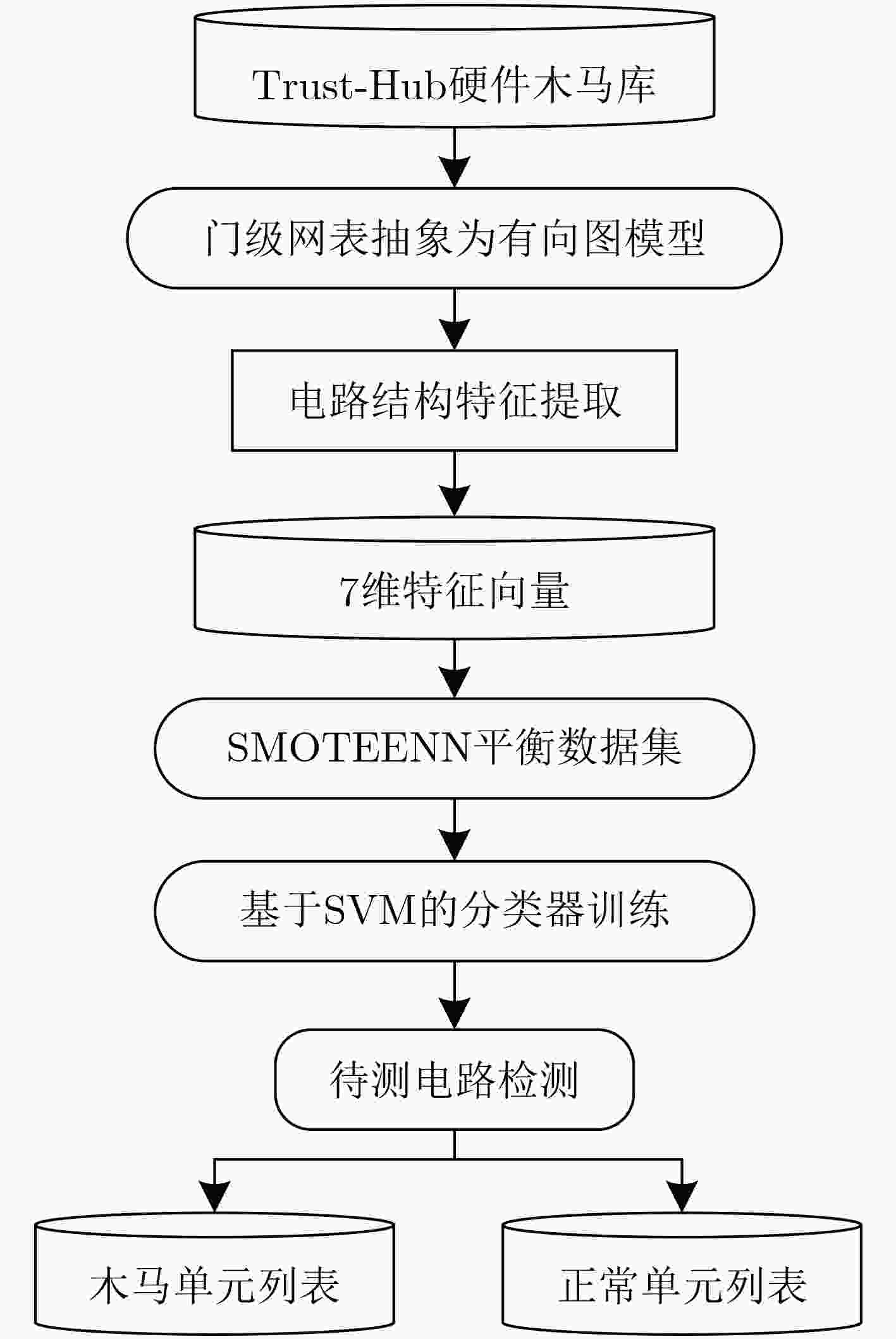
摘要: 硬件木马是第三方知识产权(IP)核的主要安全威胁,现有的安全性分析方法提取的特征过于单一,导致特征分布不够均衡,极易出现较高的误识别率。该文提出了基于有向图的门级网表抽象化建模算法,建立了门级网表的有向图模型,简化了电路分析流程;分析了硬件木马共性特征,基于有向图建立了涵盖扇入单元数、扇入触发器数、扇出触发器数、输入拓扑深度、输出拓扑深度、多路选择器和反相器数量等多维度硬件木马结构特征;提出了基于最近邻不平衡数据分类(SMOTEENN)算法的硬件木马特征扩展算法,有效解决了样本特征集较少的问题,利用支持向量机建立硬件木马检测模型并识别出硬件木马的特征。该文基于Trust_Hub硬件木马库开展方法验证实验,准确率高达97.02%,与现有文献相比真正类率(TPR)提高了13.80%,真负类率(TNR)和分类准确率(ACC)分别提高了0.92%和2.48%,在保证低假阳性率的基础上有效识别硬件木马。Abstract: Hardware Trojans are the main security threats of the third-party Intellectual Property (IP) cores. The existing pre-silicon hardware Trojan detection methods are difficult to be used in a large amount of hardware Trojans detection and the detection accuracy is hard to be enhanced. A gate-level netlist abstract modeling algorithm is proposed to reduce the cost of trustworthiness analysis method, which establishes a directed graph of the gate-level netlist and stores the graph data into the crosslinked list. Furthermore, the characteristics of hardware Trojans are analyzed in the view of the attacker view and a 7-dimensional feature vector based on the directed graph is proposed. Moreover, a hardware Trojan feature extraction algorithm is proposed to extract the 7-dimensional feature of the gate-level netlist, and a Trojan feature expansion algorithm based on the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique and Edited Nearest Neighbor (SMOTEENN) is introduced to expand the number of Trojan samples and the Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm is utilized to identify the existence of hardware Trojan. 15 benchmark circuits from the Trust-hub are used to validate the efficacy of the proposed approach and the accuracy rate we achieved is 97.02%. True Positive Rate (TPR) is increased by 13.80%, True Negative Rate (TNR) and ACCuracy (ACC) is increased by 0.92% and 2.48% respectively compared with the existing reference.
-
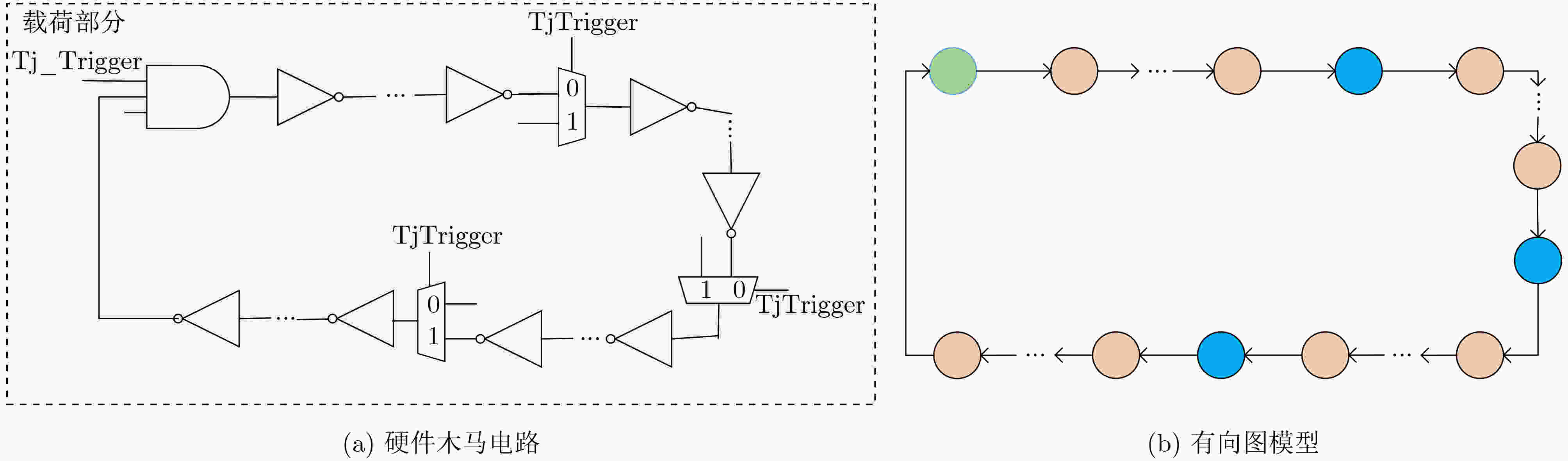
表 1 硬件木马结构特征描述
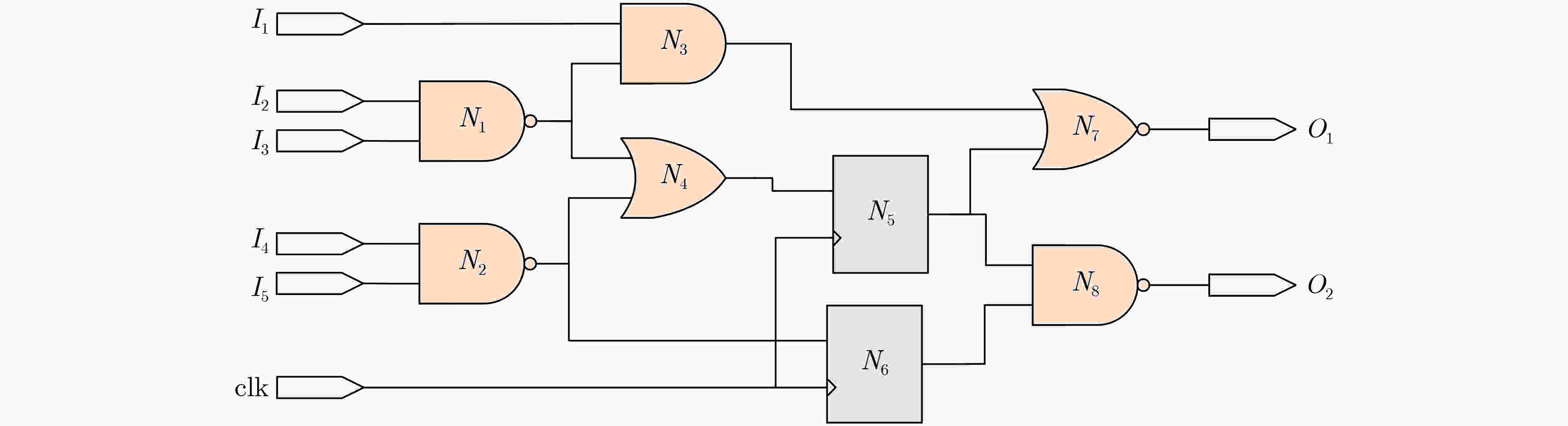
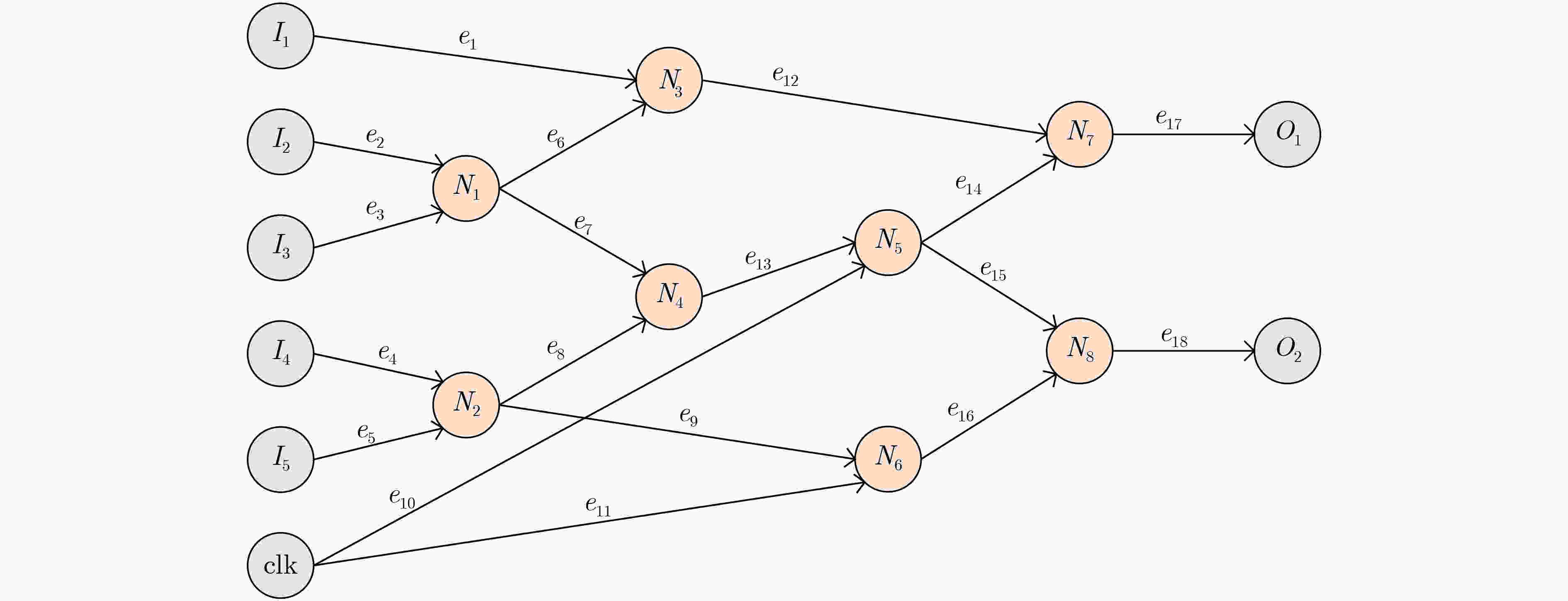
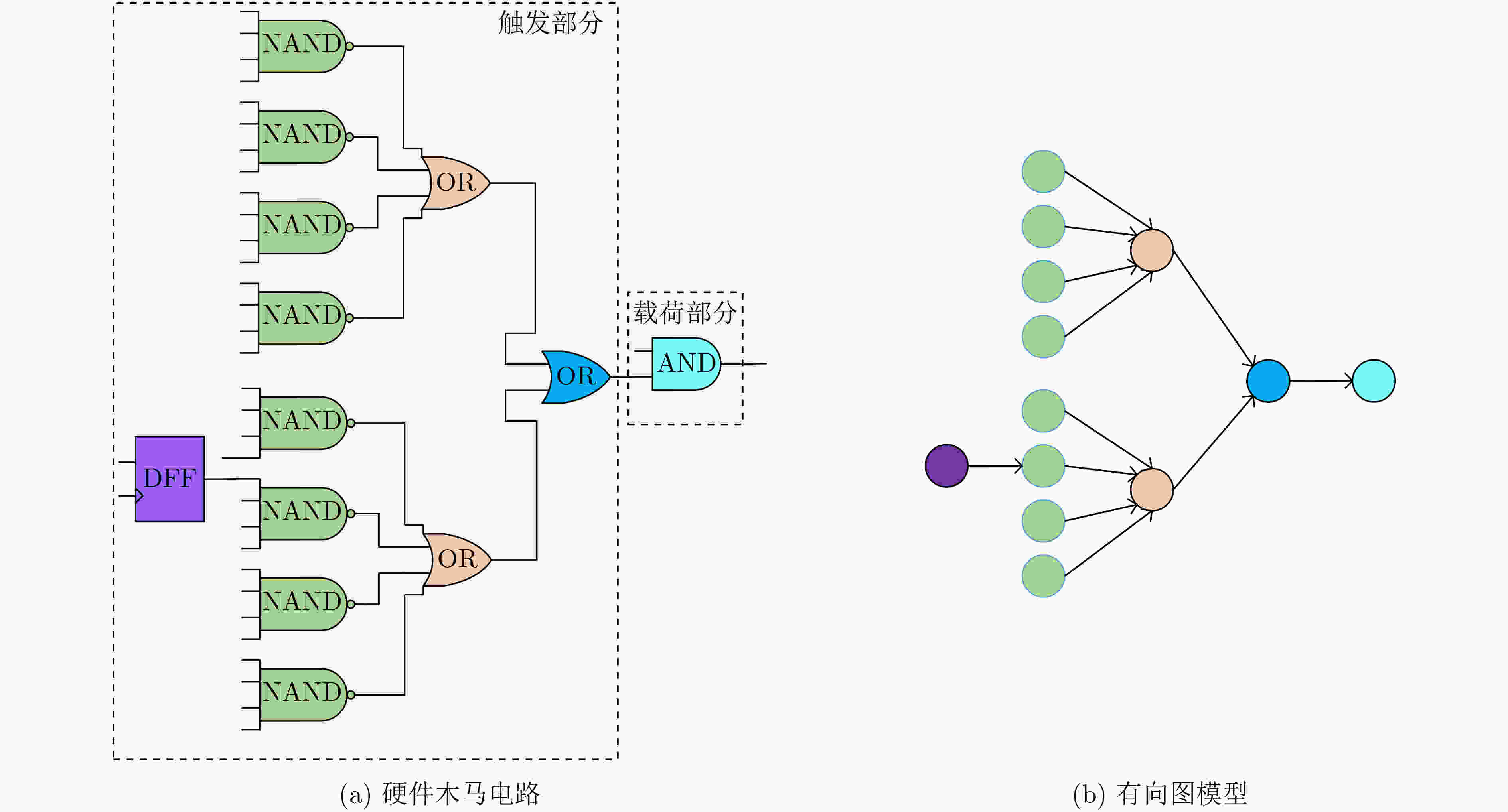
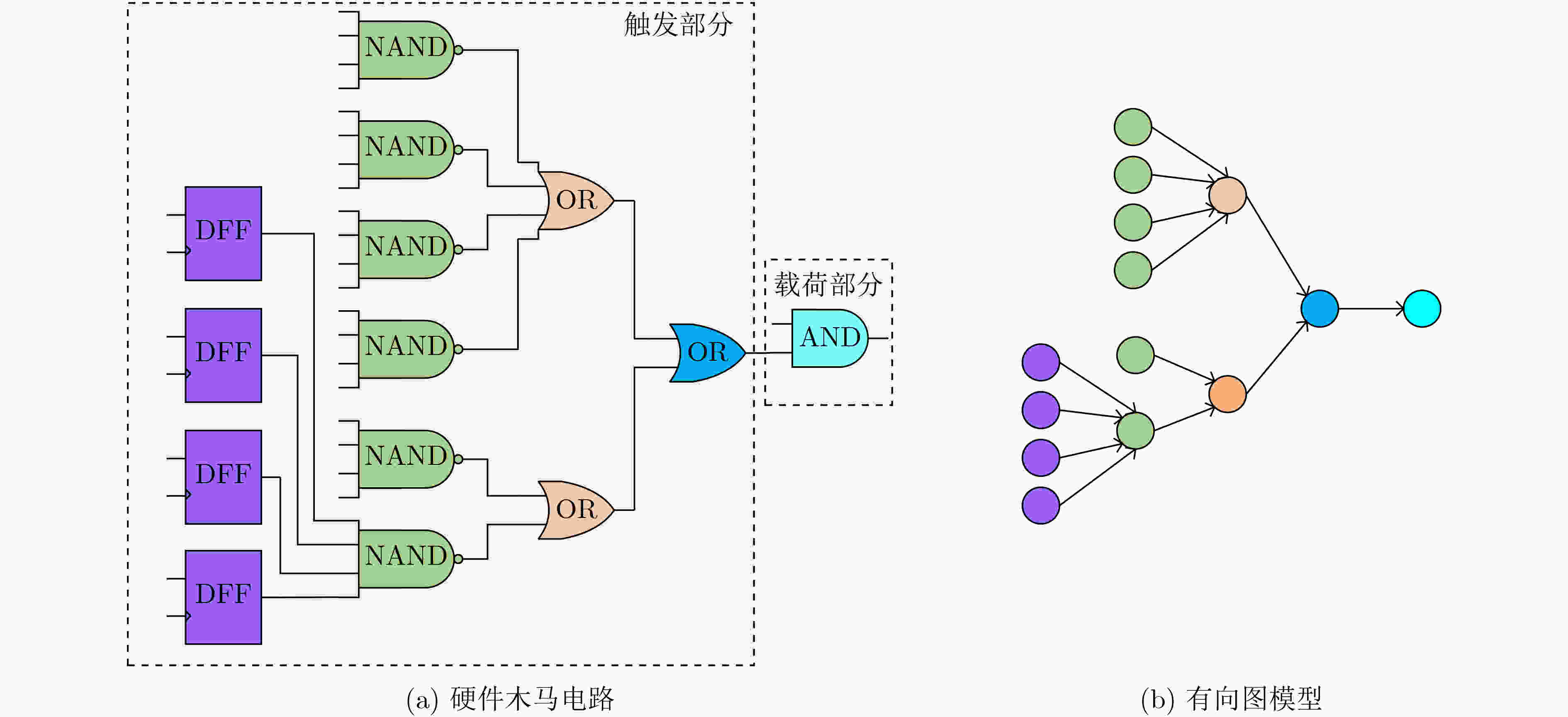
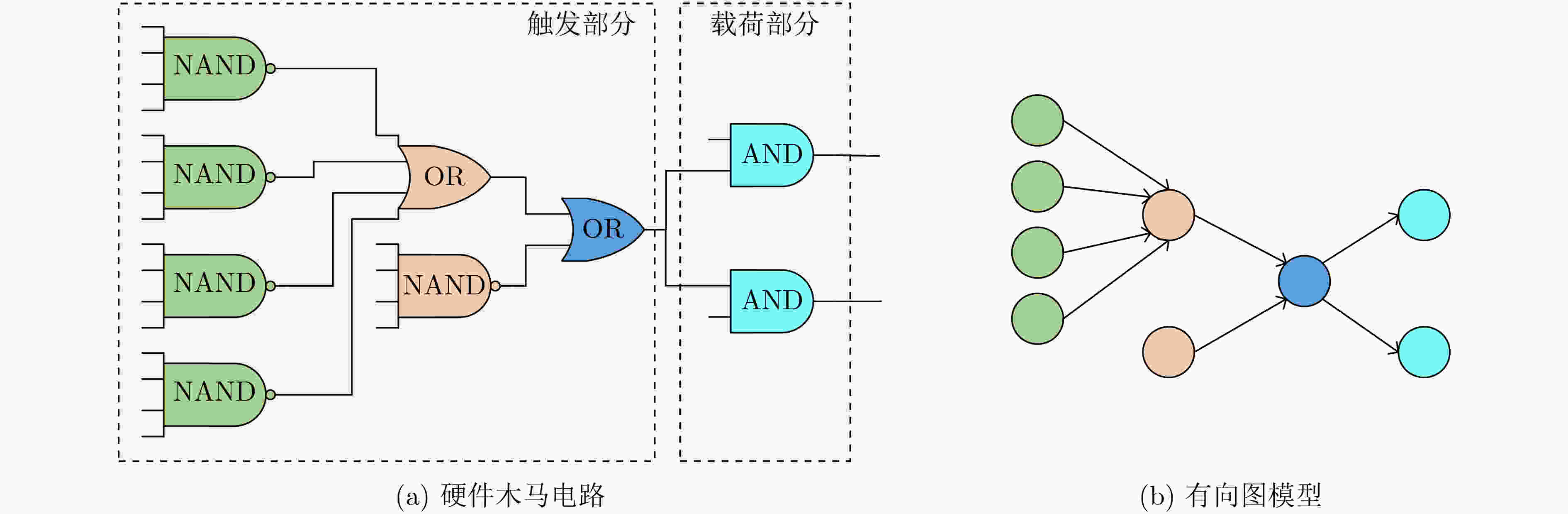
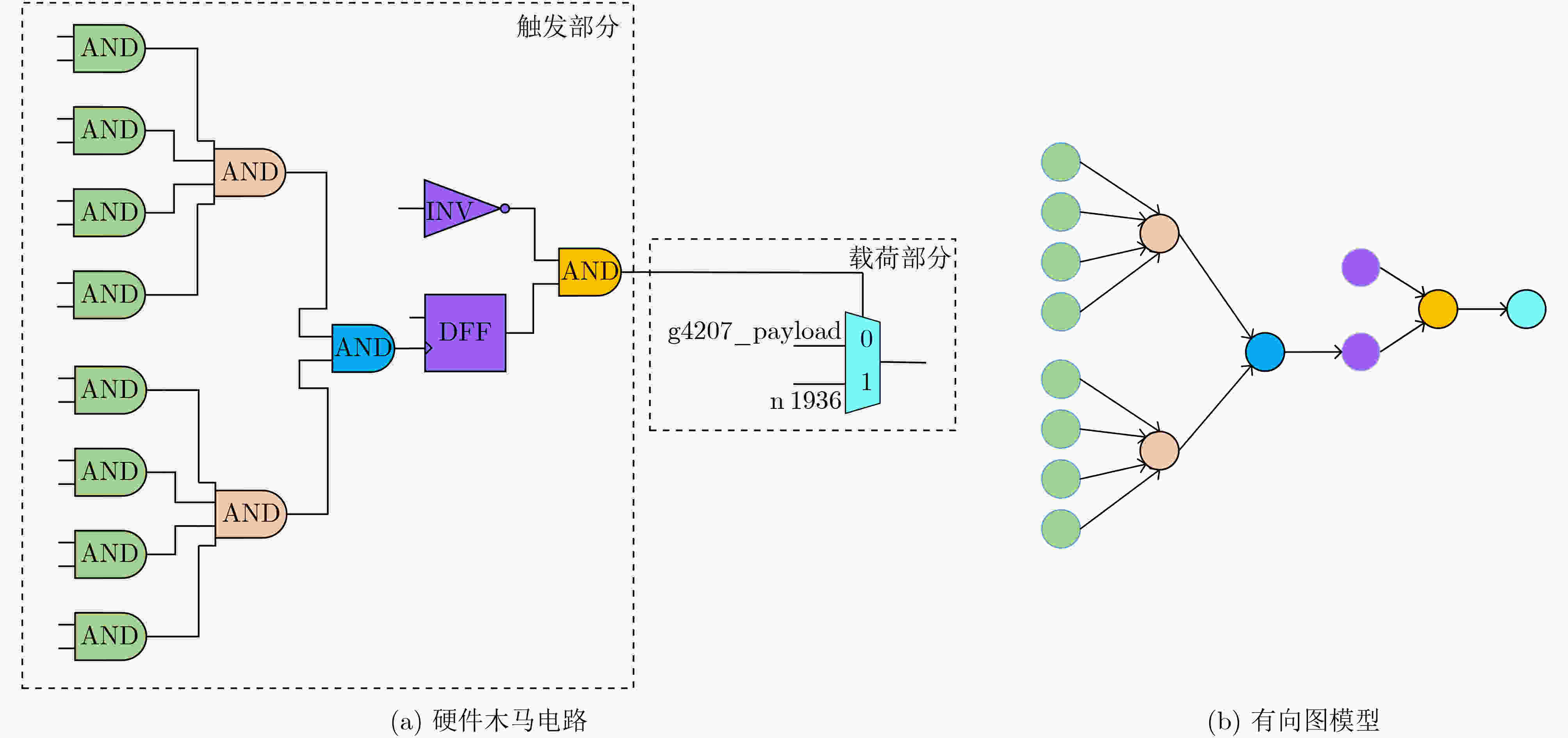
结构特征 具体描述 FAN_IN 距离单元n 4级逻辑门的扇入单元总数 FF_IN 从输入方向距离单元n 4级逻辑门的触发器单元数目 FF_OUT 从输出方向距离单元n 4级逻辑门的触发器单元数目 DPI 单元n距最近的基本输入的距离 DPO 单元n距最近的基本输出的距离 MUX 单元n前后4级包含的多路选择器数量 INV 单元n前后4级包含的反相器数量 表 2 基于广度优先搜索的硬件木马特征扩展算法
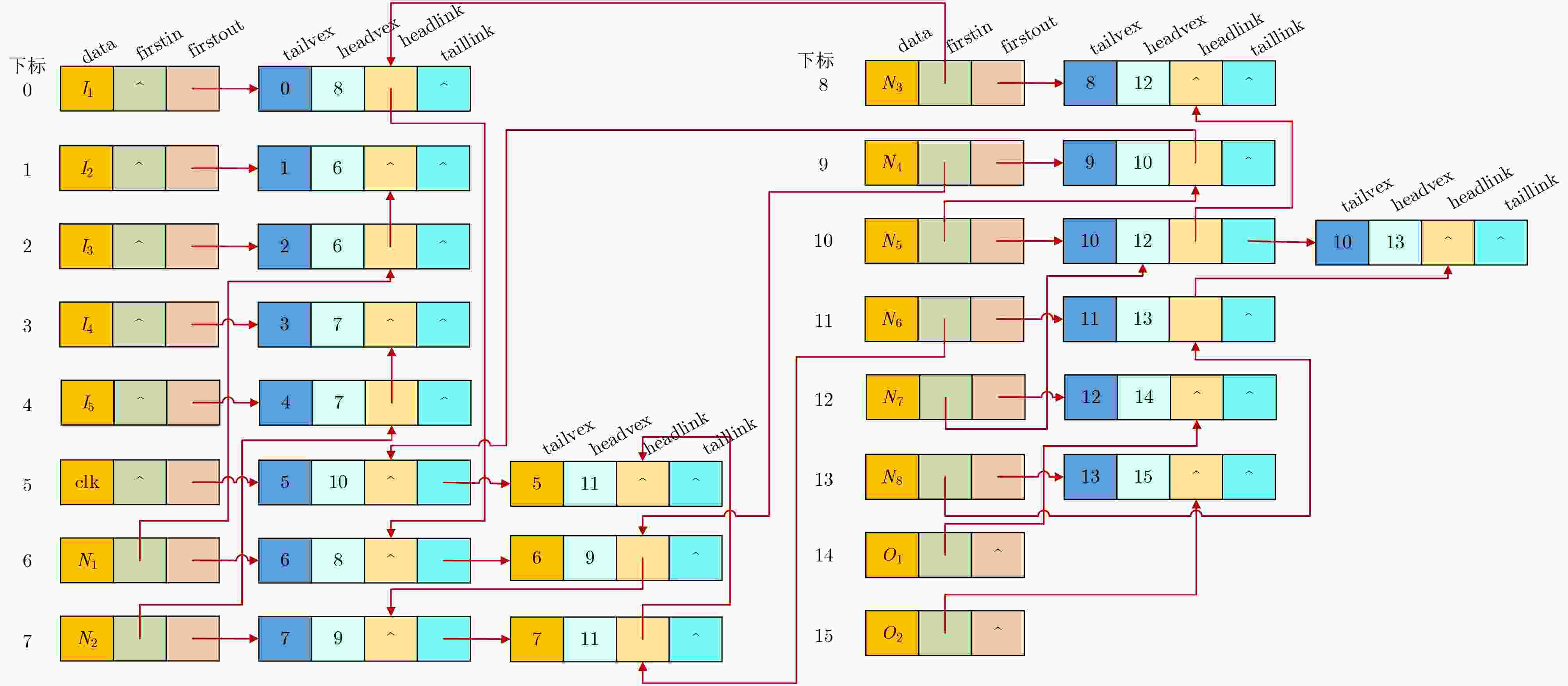
输入:${\boldsymbol{G}},n,m$ 输出:${\boldsymbol{\psi}} $ (1) for $i \le n$ do (2) for $j \le 7$ do (3) ${\boldsymbol{Q}}$←intialize(); (4) ${\boldsymbol{Q}}$←enqueue(vi); (5) while ${\boldsymbol{Q} } = \varnothing$ and $f < m$ (6) $v$←dequeue(${\boldsymbol{Q}}$); (7) ${\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} $←adjacentEdges(G, $v$); (8) for $w \in {\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} $ do (9) ${\boldsymbol{Q}}$← enqueue($w$); (10) Endfor (11) Endwhile (12) ${\boldsymbol{\psi}} (i,j) \leftarrow {F_j}({v_i})$; (13) Endfor (14) Endfor 表 3 木马电路的具体描述
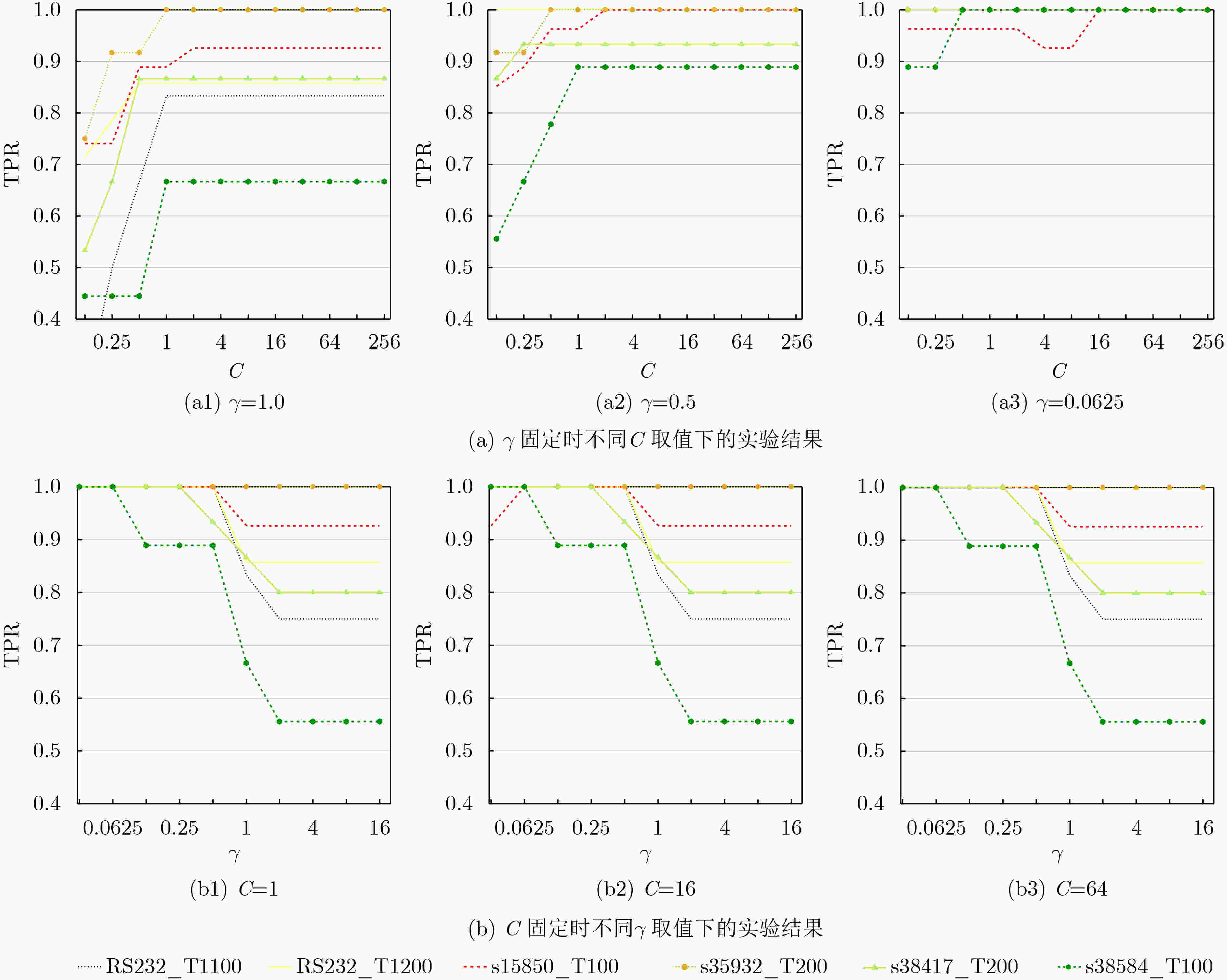
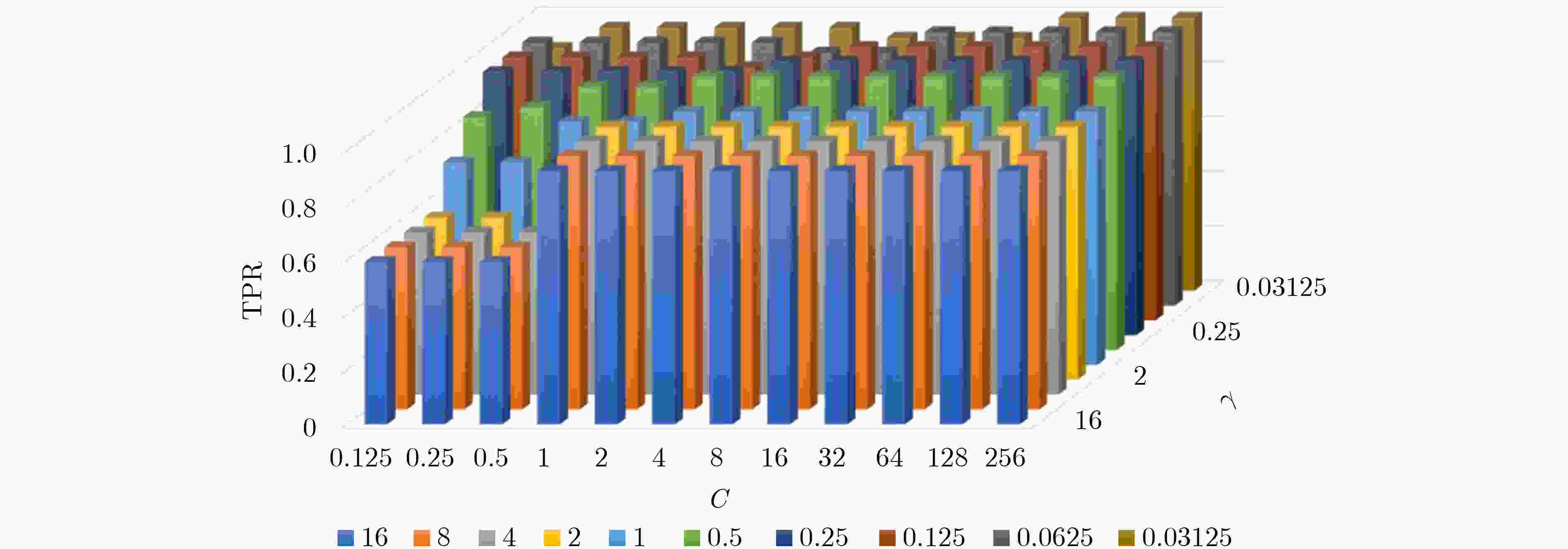
测试电路 电路规模 木马单元数量 正常单元数量 触发电路类型 触发概率 木马功能 RS232-T1000 242 13 229 组合型 3.55×10–13 改变功能 RS232-T1100 244 12 232 时序型 3.55×10–13 改变功能 RS232-T1200 243 14 229 时序型 5.00×10–11 改变功能 RS232-T1300 240 9 231 时序型 8.00×10–10 改变功能 RS232-T1400 242 13 230 时序型 5.20×10–15 改变功能 RS232-T1500 243 14 229 时序型 3.55×10–13 改变功能 RS232-T1600 241 12 229 时序型 5.77×10–9 改变功能 s15850-T100 2432 28 2404 混合型 – 拒绝服务,改变功能 s35932-T100 5999 16 5983 混合型 – 改变功能,泄露信息 s35932-T200 5999 12 5987 组合型 – 拒绝服务 s35932-T300 6019 36 5983 组合型 – 拒绝服务,降低性能 s38417-T100 5677 12 5665 组合型 1.42×10–7 改变功能,拒绝服务 s38417-T200 5680 15 5665 组合型 1.66×10–44 改变功能,拒绝服务 s38417-T300 5711 46 5665 混合型 1.66×10–44 改变功能,拒绝服务 s38584-T100 7026 9 7017 组合型 – 改变功能,拒绝服务 表 4 本文方法实验结果及与现有方法的比较(%)
测试电路 文献[16] 文献[17] 本文 TPR TNR ACC TPR TNR ACC TPR TNR ACC RS232_T1000 100.00 98.90 99.06 100.00 96.77 97.08 100.00 99.50 99.59 RS232_T1100 50.00 98.20 92.81 100.00 97.58 97.78 100.00 99.02 99.18 RS232_T1200 88.20 100.00 98.76 100.00 96.67 96.92 64.29 100.00 97.94 RS232_T1300 100.00 100.00 100.00 88.89 97.64 97.06 100.00 99.02 98.75 RS232_T1400 97.80 99.60 99.69 91.67 97.52 96.99 92.31 98.51 98.35 RS232_T1500 94.90 99.00 99.07 92.31 96.88 96.45 100.00 99.50 99.59 RS232_T1600 93.10 100.00 98.44 90.00 96.24 95.80 83.33 100.00 99.17 s15850_T100 77.80 100.00 99.71 95.83 95.05 95.06 74.07 94.18 93.96 s35932_T100 73.30 100.00 99.94 91.67 100.00 95.06 100.00 98.88 98.98 s35932_T200 8.30 100.00 99.83 100.00 99.46 99.50 8.33 99.41 99.28 s35932_T300 81.10 100.00 99.88 37.50 100.00 83.74 97.22 99.23 99.29 s38417_T100 33.30 100.00 99.86 91.67 97.30 97.22 33.33 99.74 99.59 s38417_T200 46.70 100.00 99.86 86.67 95.64 95.50 46.67 89.99 89.88 s38417_T300 75.00 100.00 99.81 30.00 91.89 89.22 100.00 99.16 99.21 s38584_T100 5.30 100.00 99.73 87.50 86.74 86.74 66.67 82.60 82.58 平均值 68.32 99.71 99.10 85.58 96.36 94.67 77.75 97.25 97.02 -
[1] LIU Yanjiang, HE Jiaji, MA Haocheng, et al. Golden chip free Trojan detection leveraging probabilistic neural network with genetic algorithm applied in the training phase[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(2): 129401. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-9803-8 [2] 张伟, 冯建华. IP保护方法研究进展[J]. 微纳电子与智能制造, 2020, 2(1): 95–101. doi: 10.19816/j.cnki.10-1594/tn.2020.01.095ZHANG Wei and FENG Jianhua. Research progress on IP protection techniques[J]. Micro/Nano Electronics and Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020, 2(1): 95–101. doi: 10.19816/j.cnki.10-1594/tn.2020.01.095 [3] OYA M, SHI Youhua, YANAGISAWA M, et al. A score-based classification method for identifying hardware-Trojans at gate-level netlists[C]. 2015 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, Grenoble, France, 2015: 465–470. doi: 10.7873/DATE.2015.0352. [4] YAO Song, CHEN Xiaoming, ZHANG Jie, et al. FASTrust: Feature analysis for third-party IP trust verification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Test Conference, Anaheim, USA, 2015: 1–10. doi: 10.1109/TEST.2015.7342417. [5] HASEGAWA K, OYA M, YANAGISAWA M, et al. Hardware Trojans classification for gate-level netlists based on machine learning[C]. The 22nd IEEE International Symposium on On-Line Testing and Robust System Design, Sant Feliu de Guixols, Spain, 2016: 203–206. doi: 10.1109/IOLTS.2016.7604700. [6] CHEN Fuqiang and LIU Qiang. Single-triggered hardware Trojan identification based on gate-level circuit structural characteristics[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2017.8050673. [7] LI Chensheng, QIN Xiaowei, XU Xiaodong, et al. Scalable graph convolutional networks with fast localized spectral filter for directed graphs[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 105634–105644. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2999520 [8] SAADATNIAKI F, XIN Ran, and KHAN U A. Decentralized optimization over time-varying directed graphs with row and column-stochastic matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(11): 4769–4780. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.2969721 [9] 薛春艳. 基于邻接表结构的拓扑排序的全序列算法研究[J]. 现代计算机, 2016(19): 74–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2016.19.018XUE Chunyan. Research on the algorithm for all topology sorting based on adjacency list structure[J]. Modern Computer, 2016(19): 74–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2016.19.018 [10] Trust-HUB. Chip-level Trojan benchmarks[EB/OL]. https://www.trust-hub.org/benchmarks/chip-level-trojan.2020.09. [11] MANJU B R and NAIR A R. Classification of cardiac arrhythmia of 12 lead ECG using combination of SMOTEENN, XGBoost and machine learning algorithms[C]. The 9th International Symposium on Embedded Computing and System Design, Kollam, India, 2019: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ISED48680.2019.9096244. [12] 刘东启. 基于支持向量机的不平衡数据分类算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 浙江大学, 2017.LIU Dongqi. Support vector machine based classification algorithms research for imbalanced data[D]. [Master dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2017. [13] 张剑飞, 王真, 崔文升, 等. 一种基于SVM的不平衡数据分类方法研究[J]. 东北师大学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 52(3): 96–104. doi: 10.16163/j.cnki.22-1123/n.2020.03.014ZHANG Jianfei, WANG Zhen, CUI Wensheng, et al. Research on an unbalanced data classification method based on SVM[J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 52(3): 96–104. doi: 10.16163/j.cnki.22-1123/n.2020.03.014 [14] KOK C H, OOI C Y, MOGHBEL M, et al. Classification of Trojan nets based on SCOAP values using supervised learning[C]. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Sapporo, Japan, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2019.8702462. [15] 魏建安, 黄海松, 康佩栋. 针对不平衡数据的PSO-DEC-IFSVM分类算法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2019, 34(4): 723–735. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2019.04.018WEI Jian’an, HUANG Haisong, and KANG Peidong. PSO-DEC-IFSVM classification algorithm for unbalanced data[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition &Processing, 2019, 34(4): 723–735. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2019.04.018 [16] HASEGAWA K, YANAGISAWA M, and TOGAWA N. Trojan-feature extraction at gate-level netlists and its application to hardware-Trojan detection using random forest classifier[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2017.8050827. [17] 高良俊, 于金星, 陈鑫, 等. 基于特征提取和SVM的硬件木马检测方法[J]. 微电子学, 2020, 50(6): 914–919. doi: 10.13911/j.cnki.1004-3365.200034GAO Liangjun, YU Jinxing, CHEN Xin, et al. Hardware Trojan detection method based on feature extraction and SVM[J]. Microelectronics, 2020, 50(6): 914–919. doi: 10.13911/j.cnki.1004-3365.200034 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
