High-Robust Sub-threshold Standard Cells Using Schmitt Trigger
-
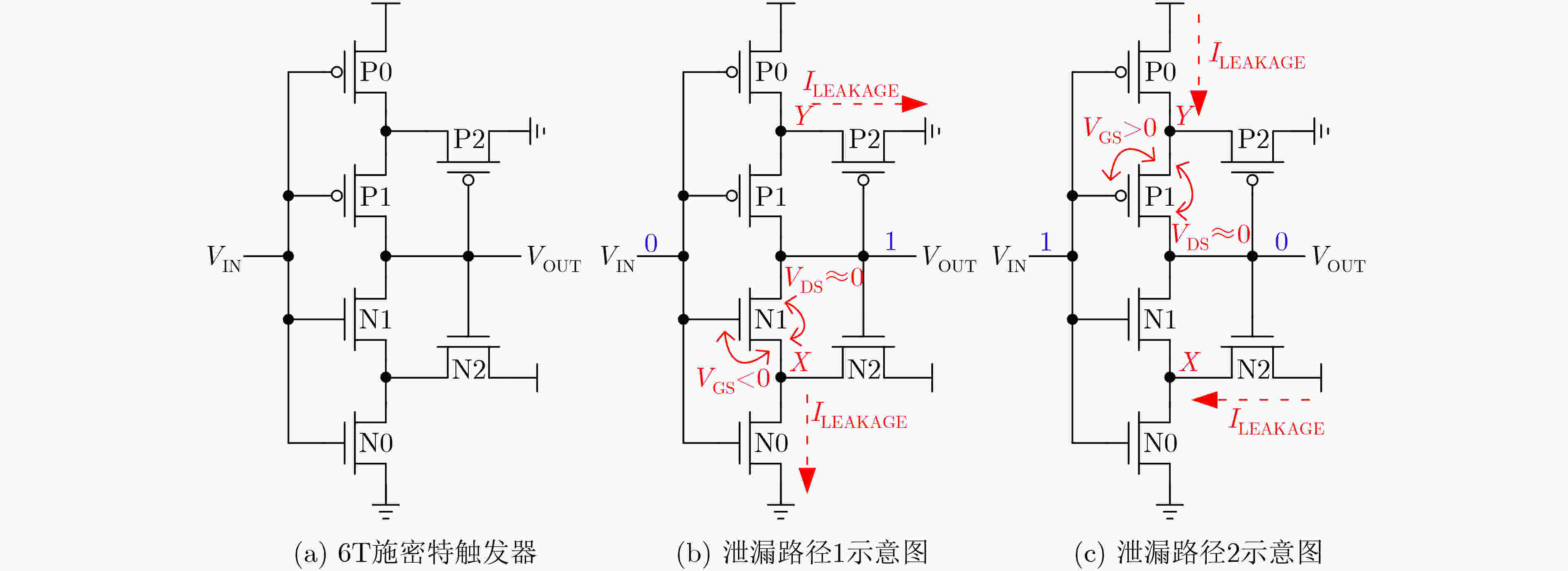
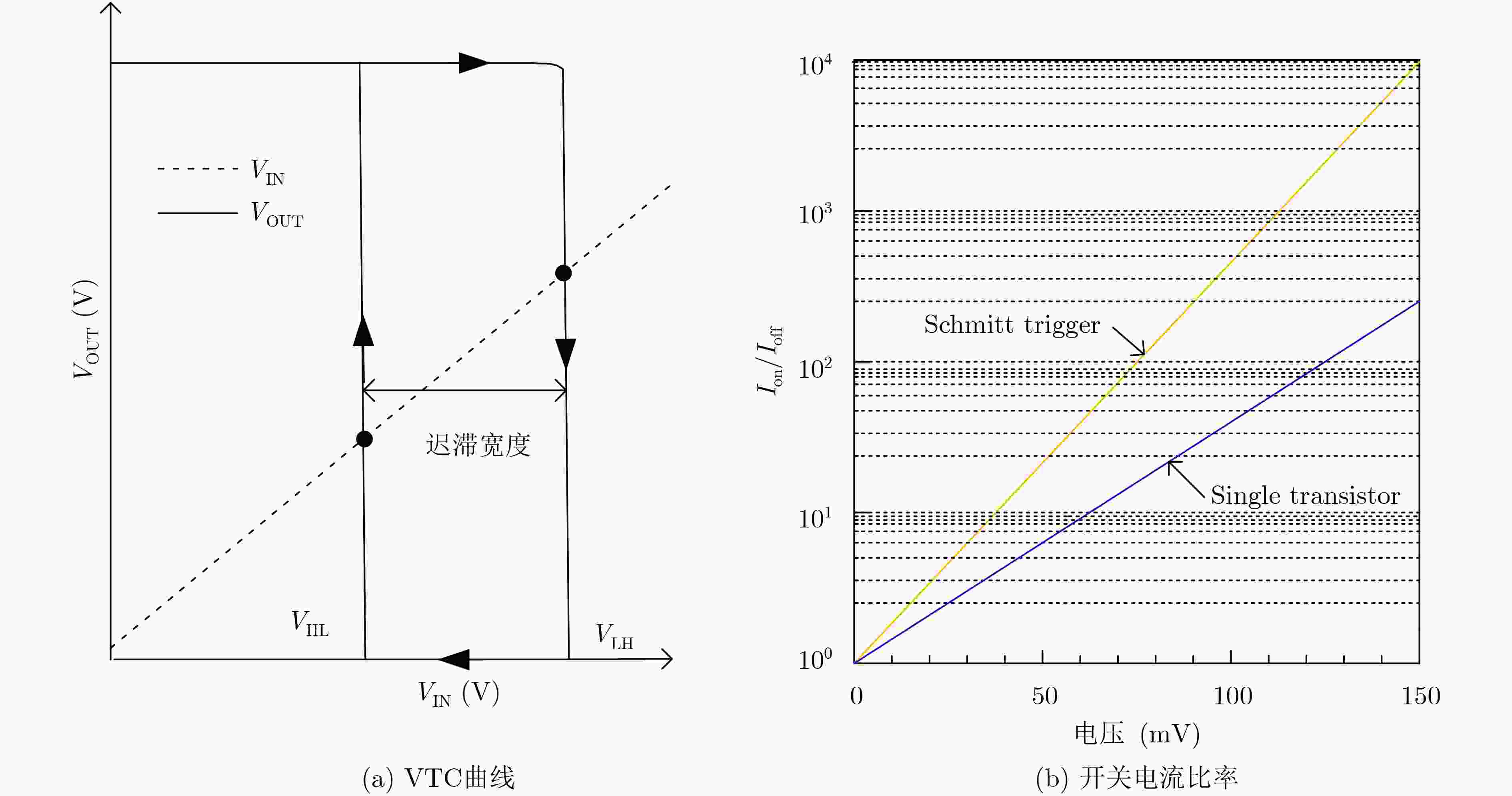
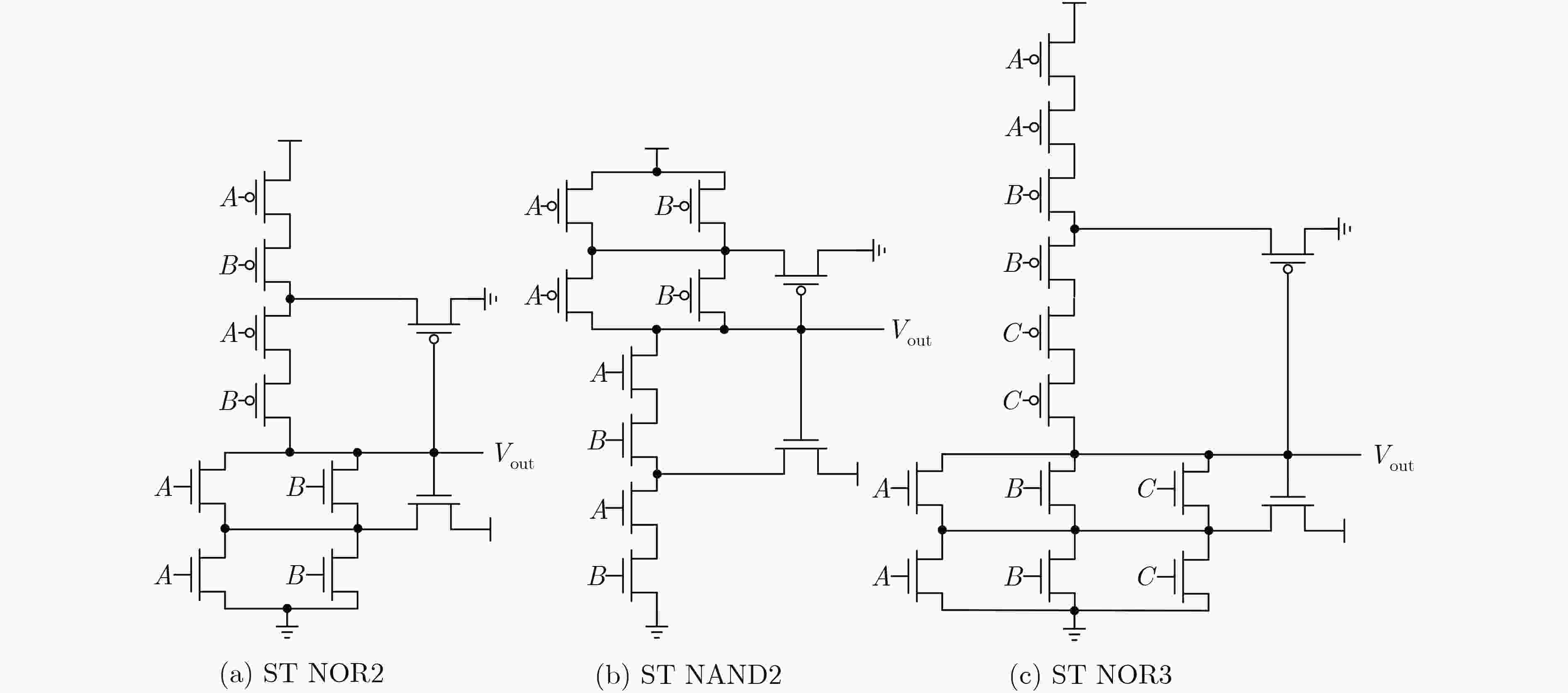
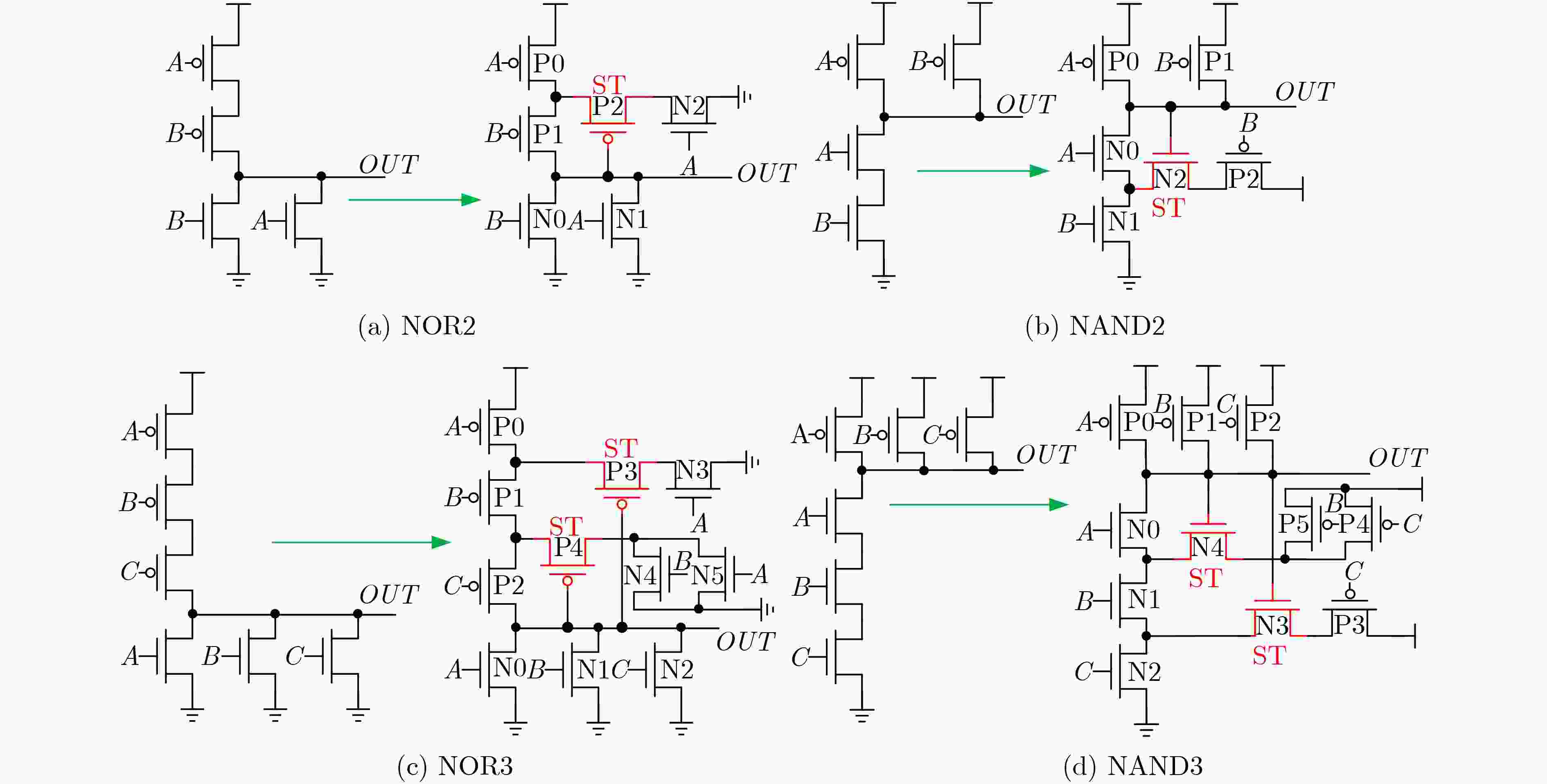
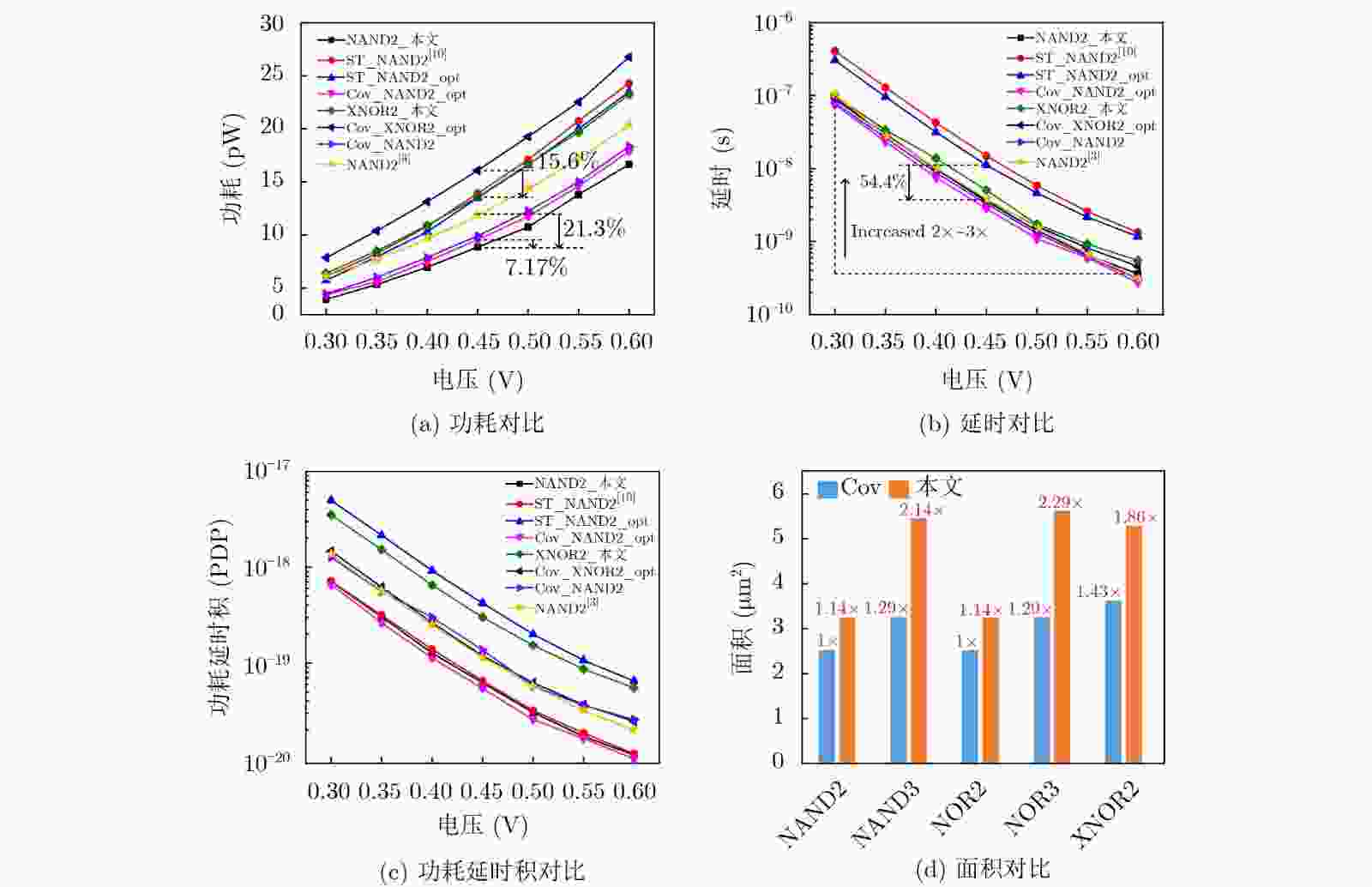
摘要: 亚阈值电路是低功耗重要发展方向之一。随着电源电压降低,晶圆代工厂提供的标准单元电路性能容易受噪声和工艺偏差的影响,已经成为制约亚阈值芯片的瓶颈。该文提出一种基于施密特触发(ST)与反向窄宽度效应(INWE)的亚阈值标准单元设计方案。该方案首先利用ST的迟滞效应与反馈机制,在电路堆叠结点处添加施密特反馈管以优化逻辑门、减少漏电流、增强鲁棒性;然后,采用INWE最小宽度尺寸与分指版图设计方法,提高电路的开关阈值与MOS管的驱动电流;最后,在TSMC 65 nm工艺下构建标准单元的物理库、逻辑库和时序库,完成测试验证。实验结果表明,所设计的亚阈值标准单元与文献相比,功耗降低7.2%~15.6%,噪声容限提升11.5%~15.3%,ISCAS测试电路的平均功耗降低15.8%。Abstract: Sub-threshold circuit is an important development direction of low power consumption. With the reduction of power supply voltage, the performance of standard cell circuits provided by foundries is susceptible to noise and process deviations, which has become a bottleneck restricting sub-threshold chips. The high-robust sub-threshold standard cells are proposed in this work. The Schmitt Trigger (ST) and Inverse Narrow Width Effect (INWE) are used to improve the performance, leakage, robust of the logic gates. Then, the INWE minimum width size and finger layout methods are used to increase the switching threshold of the circuit and the drive current of transistor. Finally, the standard cell library is designed and verified with TSMC 65 nm process. The experimental results show that the power of designed standard cells is reduced about 7.2%~15.6%, the noise margin is improved about 11.5%~15.3%, and the average power of ISCAS test circuit is reduced about 15.8%.
-
Key words:
- Standard cell /
- Low power /
- Sub-threshold /
- Schmitt Trigger (ST)
-
表 1 基准测试电路验证与对比
基准测试电路 面积(µm2) 单元数量 功耗(mW) 延时(nS) Cov_lib 本文 Cov_lib 本文 Cov_lib 本文 Cov_lib 本文 c432 301 447 139 148 1.20E-02 1.01E-02 28.20 27.18 c499 571 742 193 180 3.48E-02 3.20E-02 23.01 21.53 c880 623 869 240 259 2.24E-02 1.86E-02 25.07 22.40 c3540 1942 2641 768 795 7.21E-02 6.10E-02 37.23 32.40 c7552 3193 3726 1246 1161 1.65E-01 1.26E-01 38.81 37.01 -
[1] WANG A and CHANDRAKASAN A. A 180-mV subthreshold FFT processor using a minimum energy design methodology[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(1): 310–319. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.837945 [2] SHI Weiwei, PENG Panfeng, and CHOY C S. A 90nm passive RFID tag’s custom baseband processor for subthreshold operation below 0.3V[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2017, 26(4): 720–724. doi: 10.1049/cje.2017.04.006 [3] WEN Liang, NAN Longmei, ZHANG Jing, et al. 65 nm sub-threshold logic standard cell library using quasi-schmitt-trigger design scheme and inverse narrow width effect aware sizing[J]. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 2020, 14(3): 303–310. doi: 10.1049/iet-cds.2019.0028 [4] ZHOU Jun, JAYAPAL S, BUSZE B, et al. A 40 nm dual-width standard cell library for near/sub-threshold operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2012, 59(11): 2569–2577. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2190674 [5] 金威. 面向超低功耗的抗PVT波动电路设计技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 上海交通大学, 2017.JIN Wei. Research on ultra-low power PVT tolerant circuits design techniques[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2017. [6] MORRIS J. A novel deep submicron bulk planar sizing strategy for low energy subthreshold standard cell libraries[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Newcastle University, 2018. [7] MIYAMOTO M, OHTA H, KUMAGAI Y, et al. Impact of reducing STI-induced stress on layout dependence of MOSFET characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2004, 51(3): 440–443. doi: 10.1109/TED.2003.822877 [8] ALAM N, ANAND B, and DASGUPTA S. The impact of process-induced mechanical stress in narrow width devices and circuit design issues[C]. 2012 International Symposium on Electronic System Design, Kolkata, India, 2012: 213–215. doi: 10.1109/ISED.2012.42. [9] REYNDERS N and DEHAENE W. Variation-resilient building blocks for ultra-low-energy sub-threshold design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2012, 59(12): 898–902. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2012.2231022 [10] LOTZE N and MANOLI Y. A 62mV 0.13μm CMOS standard-cell-based design technique using schmitt-trigger logic[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco USA, 2011: 340–342. doi: 10.1109/ISSCC.2011.5746345. [11] SHARMA P, JAIN P, and DAS B P. An optimal device sizing for a performance-driven and area-efficient subthreshold cell library for IoT applications[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2019, 92: 104613. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2019.104613 [12] NISHIZAWA S, ISHIHARA T, and ONODERA H. A flexible structure of standard cell and its optimization method for near-threshold voltage operation[C]. The 2012 IEEE 30th International Conference on Computer Design, Montreal, Canada, 2012: 235–240. doi: 10.1109/ICCD.2012.6378646. [13] GEMMEKE T, ASHOUEI M, LIU Bo, et al. Cell libraries for robust low-voltage operation in nanometer technologies[J]. Solid-State Electronics, 2013, 84: 132–141. doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2013.02.006 [14] AYERS J E. Digital Integrated Circuits: Analysis and Design[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2010: 256–257. [15] HSIAO S F, TSAI M Y, and WEN C S. Low area/power synthesis using hybrid pass transistor/CMOS logic cells in standard cell-based design environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2010, 57(1): 21–25. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2009.2034198 [16] JUN J, SONG J, and KIM C. A near-threshold voltage oriented digital cell library for high-energy efficiency and optimized performance in 65nm CMOS process[J] IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2018, 65(5): 1567–1580. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2017.2758793. [17] BORTOLON F T, MOREIRA M T, MORAES F G, et al. Estimation methods for static noise margins in CMOS subthreshold logic circuits[C]. The 30th Symposium on Integrated Circuits and Systems Design, Fortaleza, Brazil, 2017: 90–95. doi: 10.1145/3109984.3109998. [18] 丁杰. 0.6V 40nm低电压标准单元库设计[D]. [硕士论文], 东南大学, 2016.DING Jie. Design of 40nm standard cell library for 0.6V low voltage[D]. [Master dissertation], Southeast University, 2016. -





 下载:
下载:
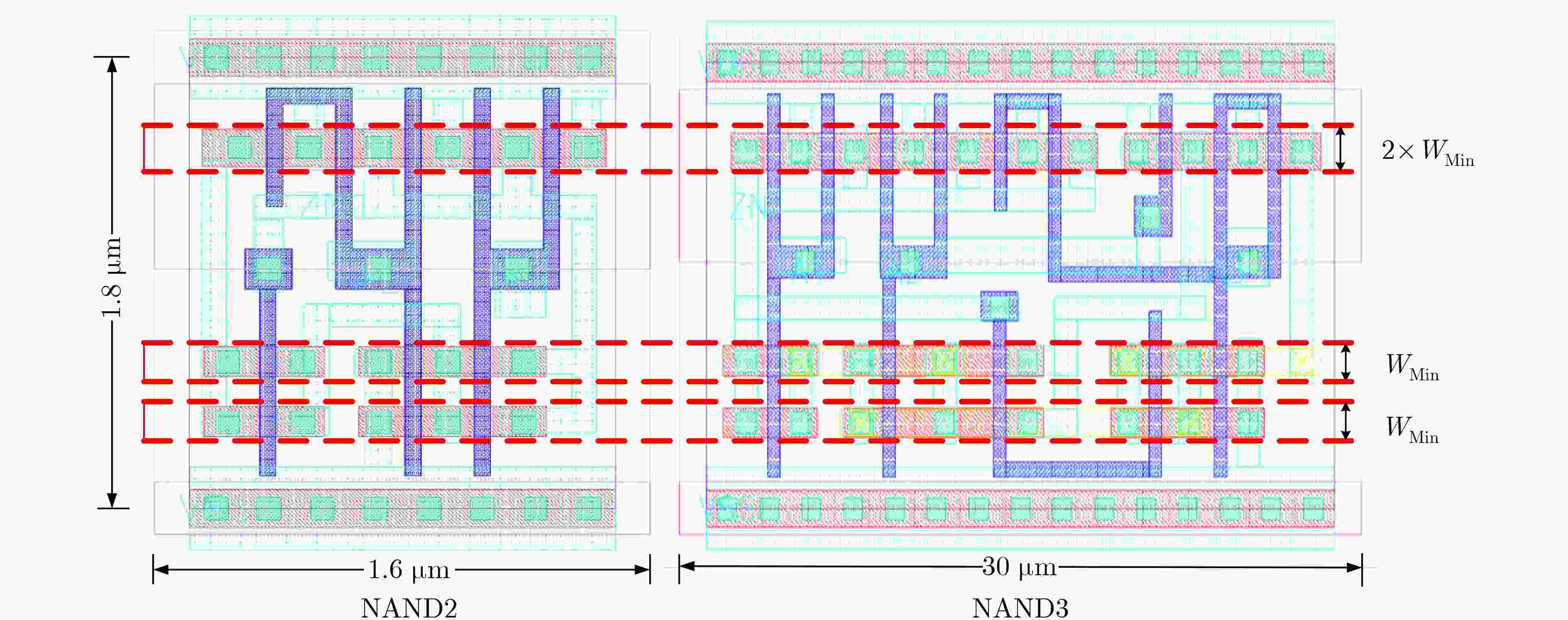
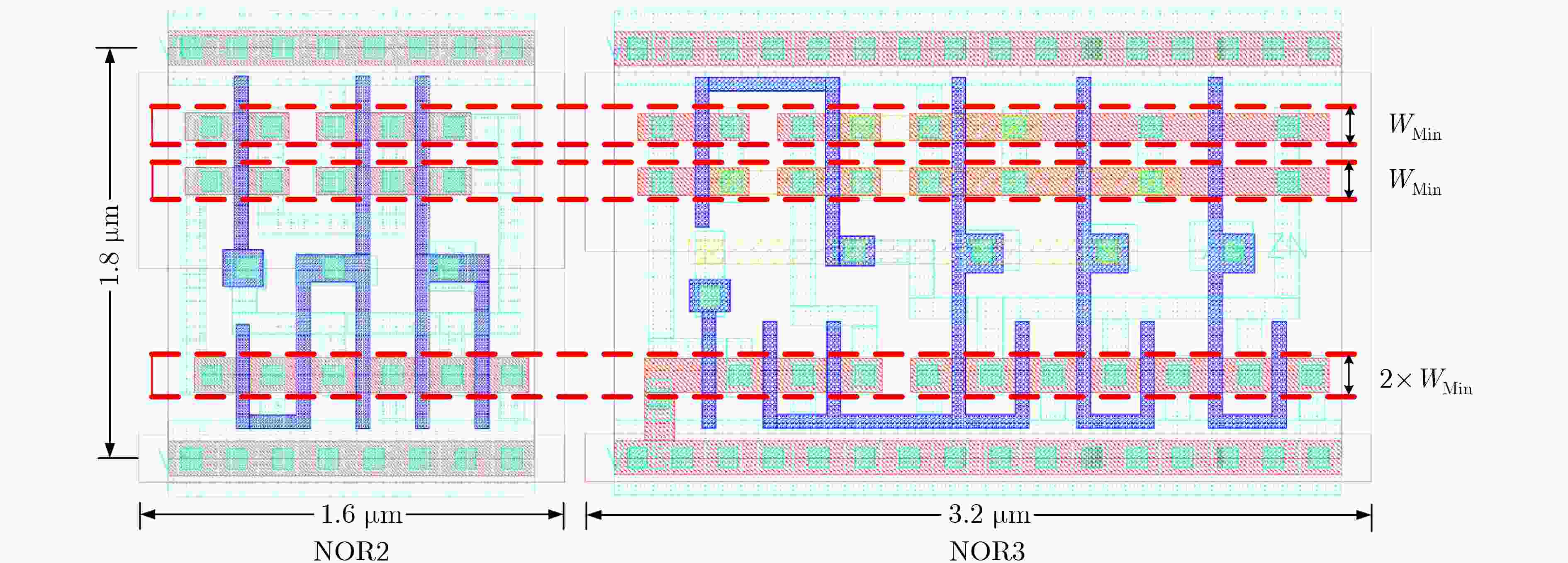
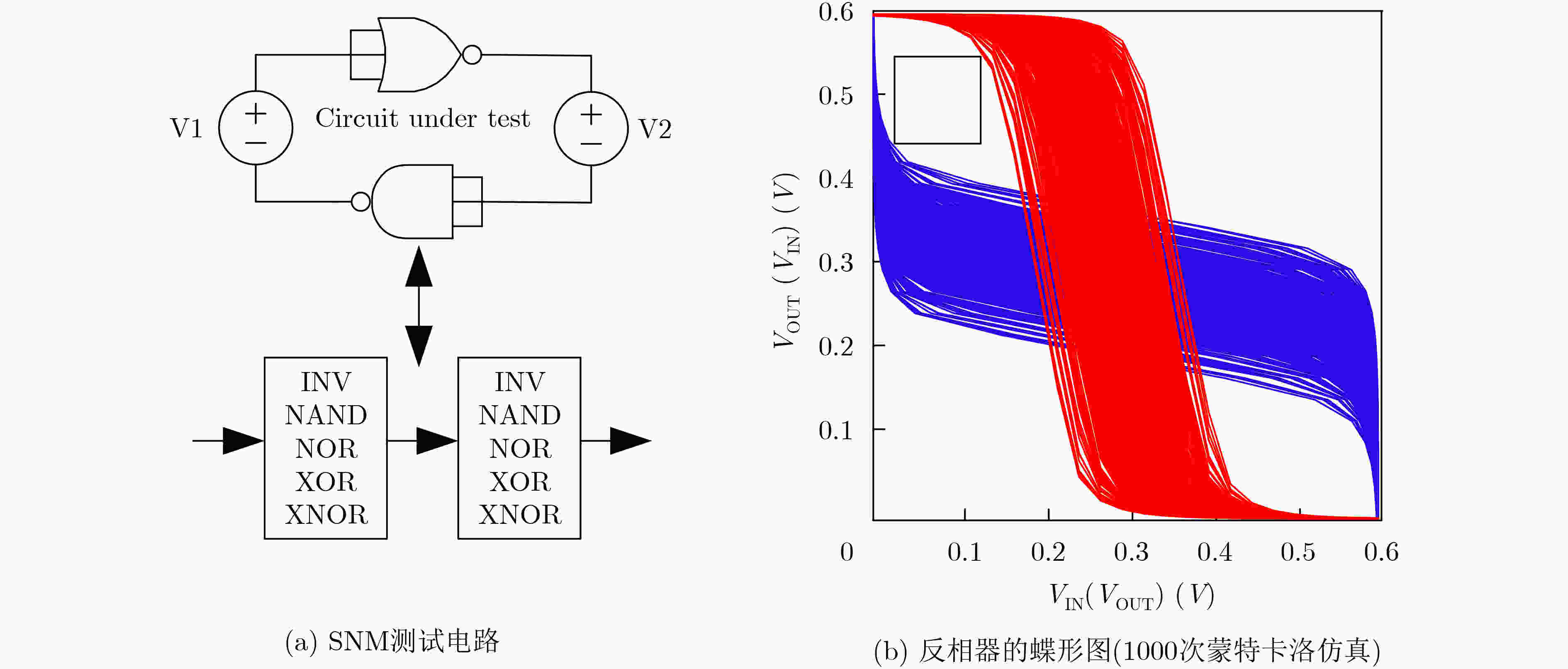
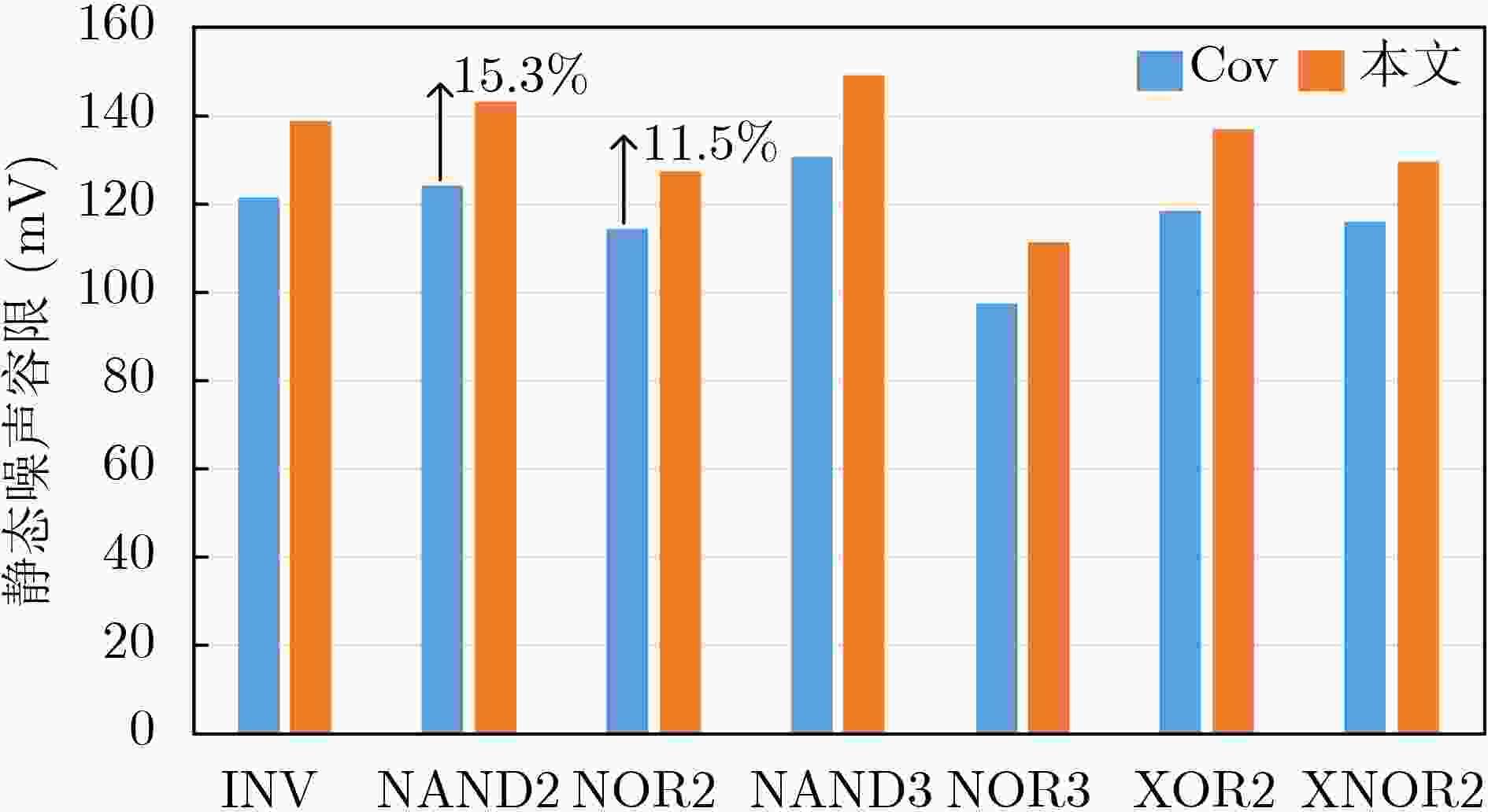


 下载:
下载:
