Design of Heterogeneous Memristor Based 1T2M Multi-value Memory Crossbar Array
-
摘要: 忆阻器作为一种新型电子元件,具有尺寸小、读写速度快、非易失性和易于与CMOS电路兼容等特性,是实现非易失性存储器最具发展前景的技术之一。但是已有的多值存储交叉阵列存在电路结构复杂、漏电流和存储密度低等问题,影响了多值存储交叉阵列的实用性。该文提出一种基于异构忆阻器的多值存储交叉阵列,其中存储单元由1个MOS管和两个具有不同阈值电压和Ron阻值的异构忆阻器构成(1T2M),可实现单个电压信号完成4值读写的操作,减少电流通路的同时简化了电路结构。通过PSpice进行仿真验证,表明所提出的1T2M多值存储器交叉阵列与已有工作相比,电路结构更简单,读写速度更快,并较好地克服了漏电流问题。Abstract: As a new type of electronic component, memristor has the characteristics of small size, fast reading and writing speed, non-volatile and easy to be compatible with CMOS circuits. It is one of the most promising technologies to realize non-volatile memory. However, the existing multi-value storage cross array has problems such as complex circuit structure, sneak path problem and low storage density, which affect the practicability of the multi-value storage cross array. In this paper, a multi-value memory crossbar array based on heterogeneous memristors is proposed, in which the memory cell is composed of one Transistor and two heterogeneous Memristors (1T2M) with different threshold voltages and Ron resistance values. A single voltage signal completes the four-value read and write operation, which reduces the current path and simplifies the circuit structure. Simulation verification by PSpice shows that compared with existing work, the proposed 1T2M multi-value memory crossbar array has simpler circuit structure, higher storage density, faster reading and writing speed, and overcomes better the leakage current problem.
-
Key words:
- Memristor /
- Memory /
- Crossbar array /
- Sneak paths
-
表 1 忆阻器M1, M2的电阻值和逻辑值的关系
M2 M1 逻辑值 $ {R}_{\rm{off}} $ $ {R}_{\rm{off}} $ 00 $ {R}_{\rm{off}} $ $ {2R}_{\rm{on}} $ 01 $ {R}_{\rm{on}} $ $ {R}_{\rm{off}} $ 10 $ {R}_{\rm{on}} $ $ {2R}_{\rm{on}} $ 11 表 2 忆阻器M1, M2的电阻值与电压区间的关系
区间 电压 $ {R}_{{\rm{M}}2} $ $ {R}_{{\rm{M}}1} $ 1 $ \left(-{\infty },{V}_{2{\rm{off}}}\right) $ $ {R}_{\rm{off}} $ $ {R}_{\rm{off}} $ 2 $ \left({V}_{2{\rm{off}}},{V}_{1{\rm{off}}}\right) $ $ {R}_{{\rm{ini}}2} $ $ {R}_{\rm{off}} $ 3 $ \left({V}_{1{\rm{off}}},{V}_{1{\rm{on}}}\right) $ $ {R}_{{\rm{ini}}2} $ $ {R}_{{\rm{ini}}1} $ 4 $ \left({V}_{1{\rm{on}}},{V}_{2{\rm{on}}}\right) $ $ {R}_{{\rm{ini}}2} $ $2 {R}_{\rm{on} }$ 5 $ \left({V}_{2{\rm{on}}},+{\infty }\right) $ $ {R}_{\rm{on}} $ $2 {R}_{\rm{on} }$ 表 3 忆阻器参数设置
参数 $ {\alpha }_{\rm{off}} $ $ {\alpha }_{\rm{on}} $ $ {V}_{\rm{off}}\left({\rm{V}}\right) $ $ {V}_{\rm{on}}\left({\rm{V}}\right) $ $ {R}_{\rm{off}}\left({\Omega }\right) $ $ {R}_{\rm{on}}\left({\Omega }\right) $ $ {k}_{\rm{off}}({\rm{m}}/{\rm{s}}) $ $ {k}_{\rm{on}}({\rm{m}}/{\rm{s}}) $ M2 1 3 –0.8 0.8 2E6 1E4 2E6 –3E7 M1 1 3 –0.6 0.6 2E6 2E4 2E6 –3E7 参数 $ D\left({\rm{nm}}\right) $ $ {w}_{\rm{off}}\left({\rm{nm}}\right) $ $ {w}_{\rm{on}}\left({\rm{nm}}\right) $ $ {a}_{\rm{off}} $ $ {a}_{\rm{on}} $ $ {p}_{\rm{off}} $ $ {p}_{\rm{on}} $ M2 10 10 0 10 10 2.4 3.2 M1 10 10 0 10 12.9 2.4 4.2 -
[1] 曾晓洋, 薛晓勇, 温亮. 嵌入式存储器架构、电路与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 1–5.ZENG Xiaoyang, XUE Xiaoyong, and WEN Liang. Embedded Memory Architecture, Circuits and Applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020: 1–5. [2] 王晓媛, 金晨曦, 周鹏飞. 忆阻数字逻辑电路设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 851–861. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190864WANG Xiaoyuan, JIN Chenxi, and ZHOU Pengfei. Memristive digital logic circuit design[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 851–861. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190864 [3] 王将, 钱辉, 包伯成, 等. 一种浮地磁控忆阻模拟器设计与特性分析[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2018, 37(9): 74–78.WANG Jiang, QIAN Hui, BAO Bocheng, et al. Design and characteristic analysis for a kind of floating flux-controlled memristor emulator[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2018, 37(9): 74–78. [4] 闵富红, 王珠林, 曹弋, 等. 基于双曲函数的双忆阻器混沌电路多稳态特性分析[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(2): 486–494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.02.031MIN Fuhong, WANG Zhulin, CAO Yi, et al. Multistability analysis of a dual-memristor circuit based on hyperbolic function[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(2): 486–494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.02.031 [5] 刘威, 王光义. TiO2忆阻器的磁控模型分析及电路实现[J]. 杭州电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 35(2): 5–8.LIU Wei and WANG Guangyi. Flux-controlled model analysis and circuit implementation of TiO2 memristor[J]. Journal of Hangzhou Dianzi University:Natural Sciences, 2015, 35(2): 5–8. [6] 甘朝晖, 张士英, 吴宇鑫. 一种带有非线性漂移函数的分数阶忆阻器模型[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2018, 30(8): 2884–2891.GAN Zhaohui, ZHANG Shiying, and WU Yuxin. Fractional-order memristor model with nonlinear drift function[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2018, 30(8): 2884–2891. [7] BORGHETTI J, SNIDER G S, KUEKES P J, et al. Memristive’ switches enable ‘stateful’ logic operations via material implication[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7290): 873–876. doi: 10.1038/nature08940 [8] KVATINSKY S, WALD N, SATAT G, et al. MRL — memristor ratioed logic[C]. The 13th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and their Applications, Turin, Italy, 2012: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/CNNA.2012.6331426. [9] KVATINSKY S, BELOUSOV D, LIMAN S, et al. MAGIC—memristor-aided logic[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2014, 61(11): 895–899. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2014.2357292 [10] 王光义, 沈书航, 刘公致, 等. 基于忆阻器的乘法器电路设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 827–834. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190811WANG Guangyi, SHEN Shuhang, LIU Gongzhi, et al. Design of memristor based multiplier circuits[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 827–834. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190811 [11] WANG Chunhua, XIA Hu, and ZHOU Ling. A memristive hyperchaotic multiscroll jerk system with controllable scroll numbers[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2017, 27(6): 1750091. doi: 10.1142/S0218127417500912 [12] ZHU Minghao, WANG Chunhua, DENG Quanli, et al. Locally active memristor with three coexisting pinched hysteresis loops and its emulator circuit[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2020, 30(13): 2050184. doi: 10.1142/S0218127420501849 [13] LIN Hairong, WANG Chunhua, YAO Wei, et al. Chaotic dynamics in a neural network with different types of external stimuli[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2020, 90: 105390. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105390 [14] LIN Hairong, WANG Chunhua, HONG Qinghui, et al. A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2020, 67(12): 3472–3476. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.3000492 [15] LIN Hairong, WANG Chunhua, SUN Yichuang, et al. Firing multistability in a locally active memristive neuron model[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2020, 100(4): 3667–3683. doi: 10.1007/s11071-020-05687-3 [16] YAO Wei, WANG Chunhua, SUN Yichuang, et al. Exponential multistability of memristive Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with stochastic parameter perturbations[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2020, 386: 125483. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2020.125483 [17] HONG Qinghui, SHI Zirui, SUN Jingru, et al. Memristive self-learning logic circuit with application to encoder and decoder[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33: 4901–4913. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05281-z [18] 王春华, 蔺海荣, 孙晶如, 等. 基于忆阻器的混沌、存储器及神经网络电路研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821WANG Chunhua, LIN Hairong, SUN Jingru, et al. Research progress on chaos, memory and neural network circuits based on memristor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821 [19] KIM H, SAH M P, YANG Changju, et al. Memristor-based multilevel memory[C]. The 12th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and their Applications, Berkeley, USA, 2010: 1–6, doi: 10.1109/CNNA.2010.5430320. [20] MANEM H and ROSE G S. A read-monitored write circuit for 1T1M multi-level memristor memories[C]. 2011 IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2011: 2938–2941. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2011.5938207. [21] RABBANI P, DEHGHANI R, and SHAHPARI N. A multilevel memristor-CMOS memory cell as a ReRAM[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2015, 46(12): 1283–1290. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2015.10.006 [22] KVATINSKY S, FRIEDMAN E G, KOLODNY A, et al. TEAM: ThrEshold adaptive memristor model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2013, 60(1): 211–221. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215714 [23] KVATINSKY S, RAMADAN M, FRIEDMAN E G, et al. VTEAM: A general model for voltage-controlled memristors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2015, 62(8): 786–790. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2015.2433536 [24] SAKIB M N, HASSAN R, BISWAS S N, et al. Memristor-based high-speed memory cell with stable successive read operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(5): 1037–1049. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2729464 [25] ZANGENEH M and JOSHI A. Design and optimization of nonvolatile multibit 1T1R resistive RAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2014, 22(8): 1815–1828. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2013.2277715 [26] EMARA A, GHONEIMA M, and El-DESSOUKY M. Differential 1T2M memristor memory cell for single/multi-bit RRAM modules[C]. The 6th Computer Science and Electronic Engineering Conference, Colchester, 2014: 69–72. doi: 10.1109/CEEC.2014.6958557. [27] WANG Xiaoping, LI Shuai, LIU Hui, et al. A compact scheme of reading and writing for memristor-based multivalued memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(7): 1505–1509. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2753199 [28] BIOLEK D, DI VENTRA M, and PERSHIN Y V. Reliable SPICE Simulations of Memristors, Memcapacitors and Meminductors[J]. Radioengineering, 2013, 22(4): 945–968. [29] BIOLEK Z, BIOLEK D, and BIOLKOVÁ V. SPICE model of memristor with nonlinear dopant drift[J]. Radioengineering, 2009, 18(2): 210–214. -





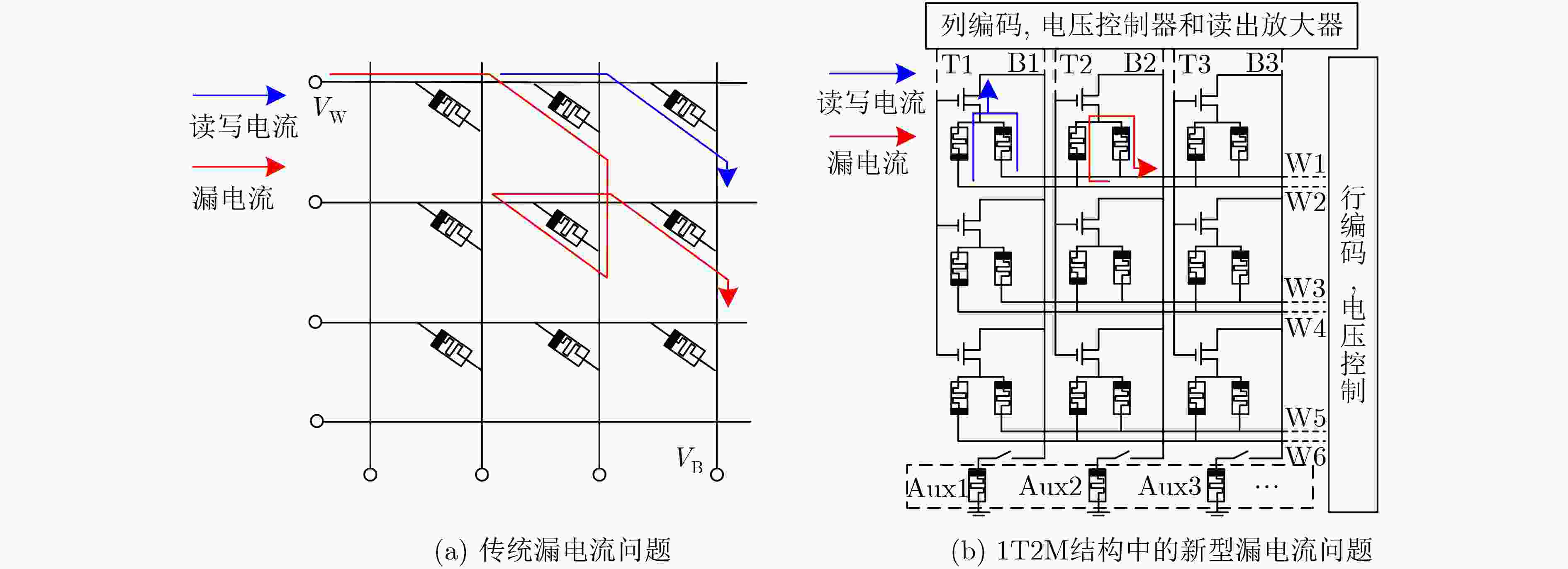
 下载:
下载:
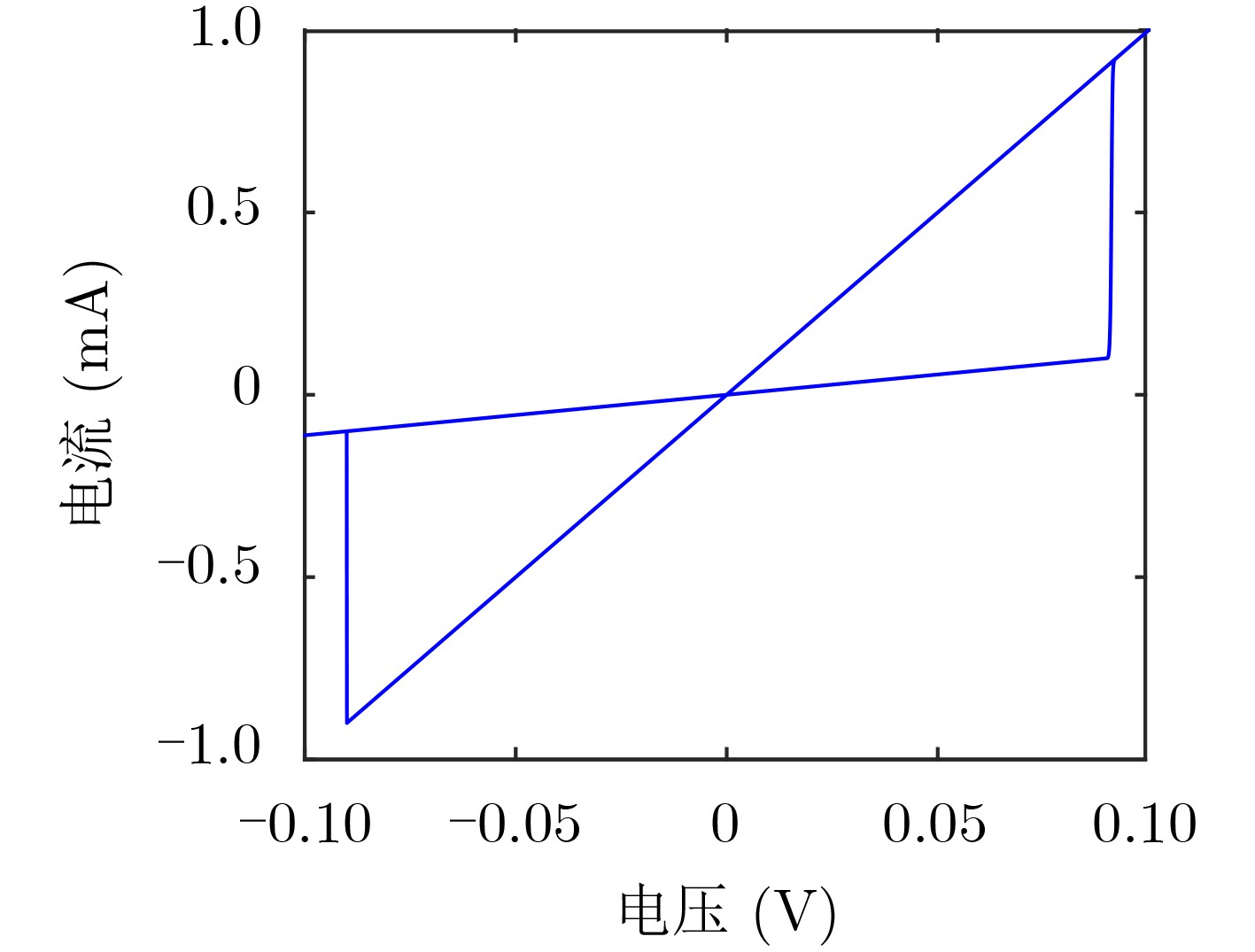
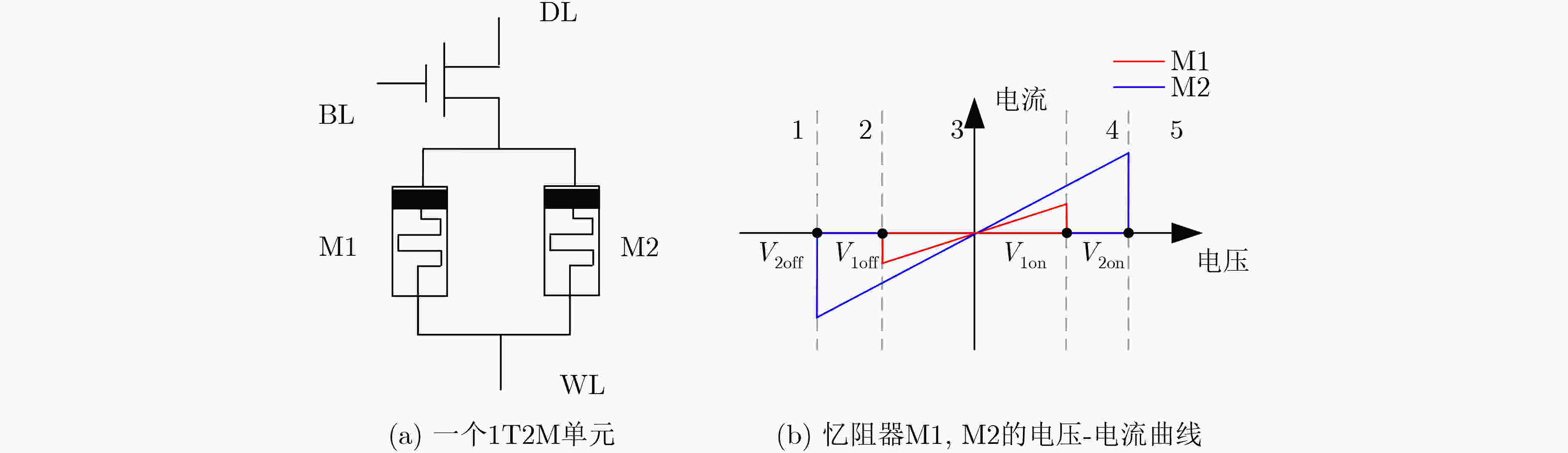
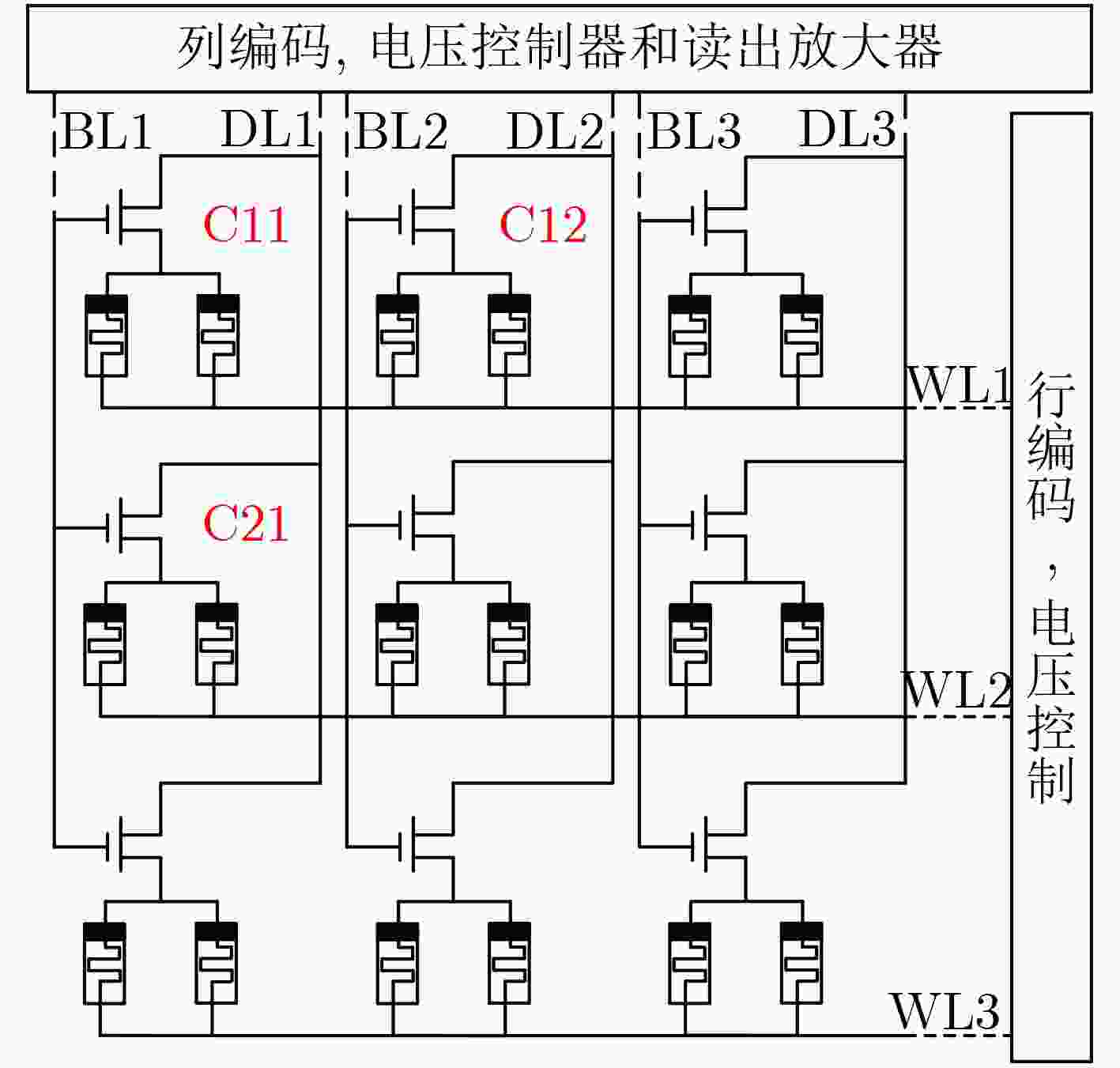
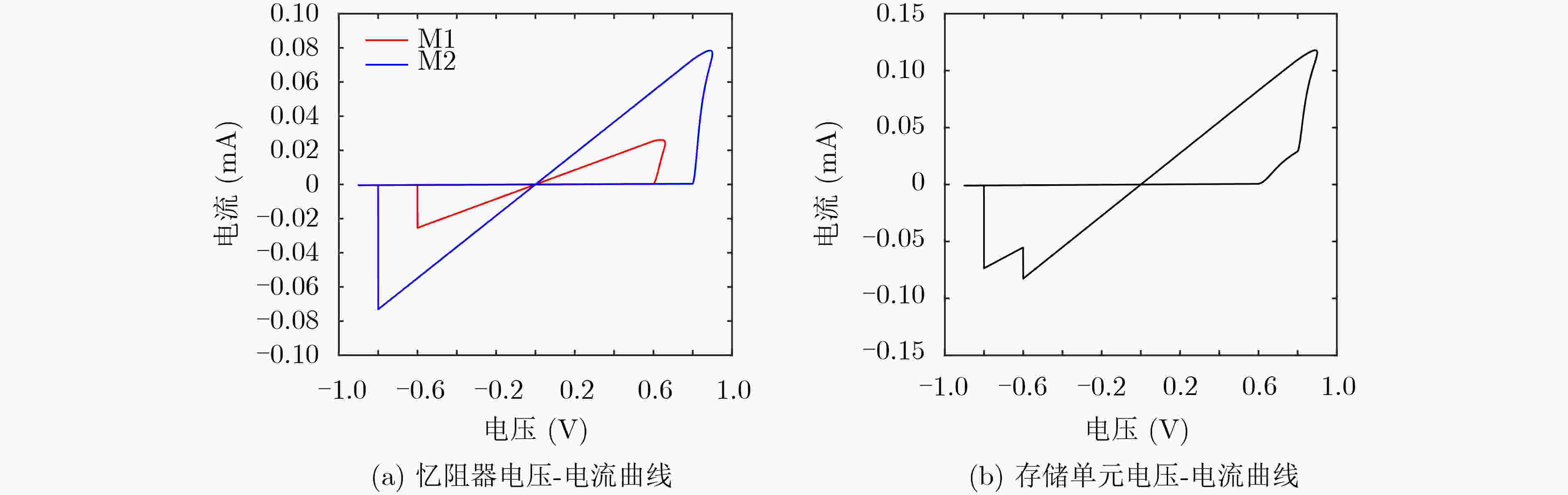
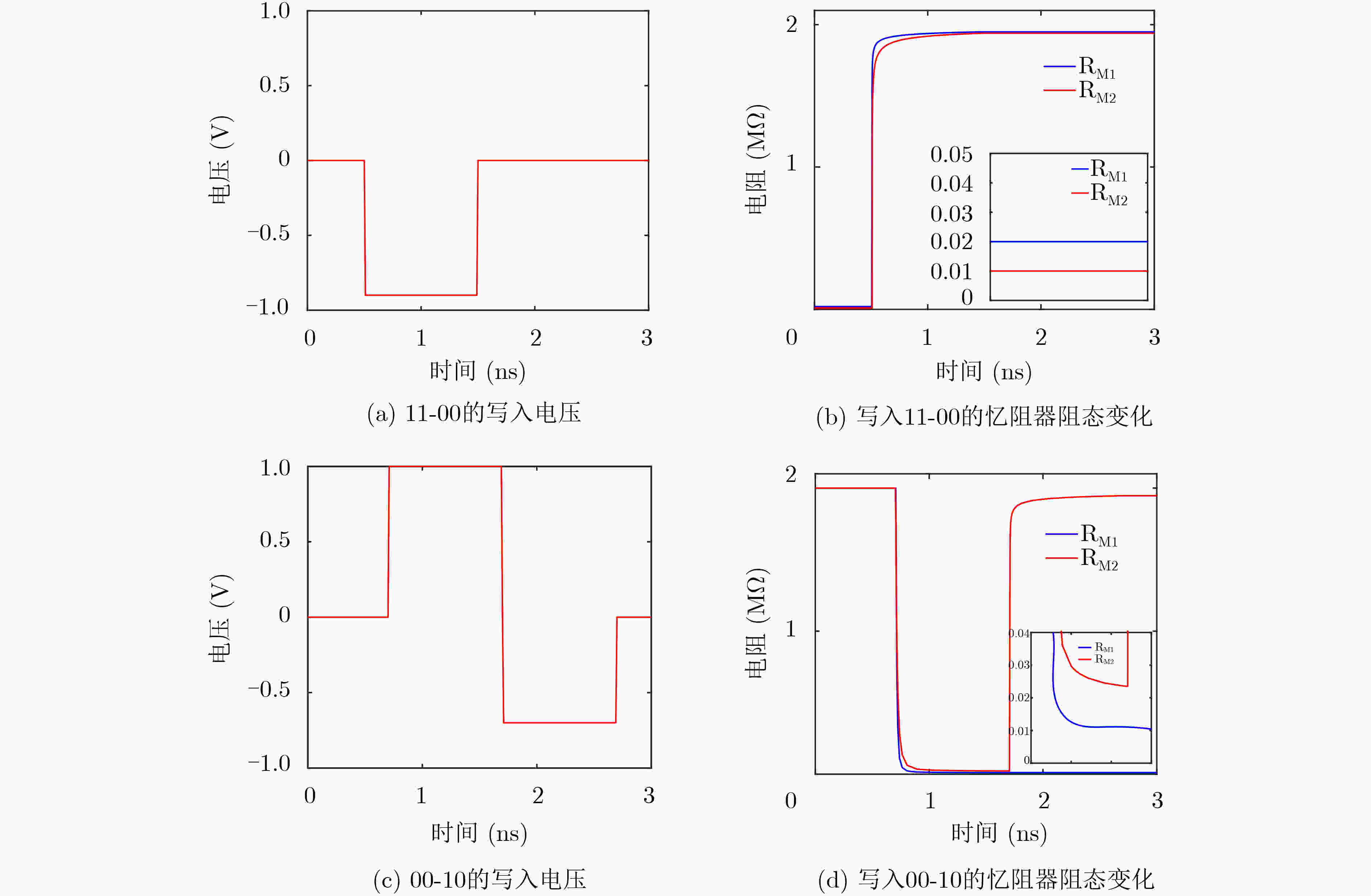
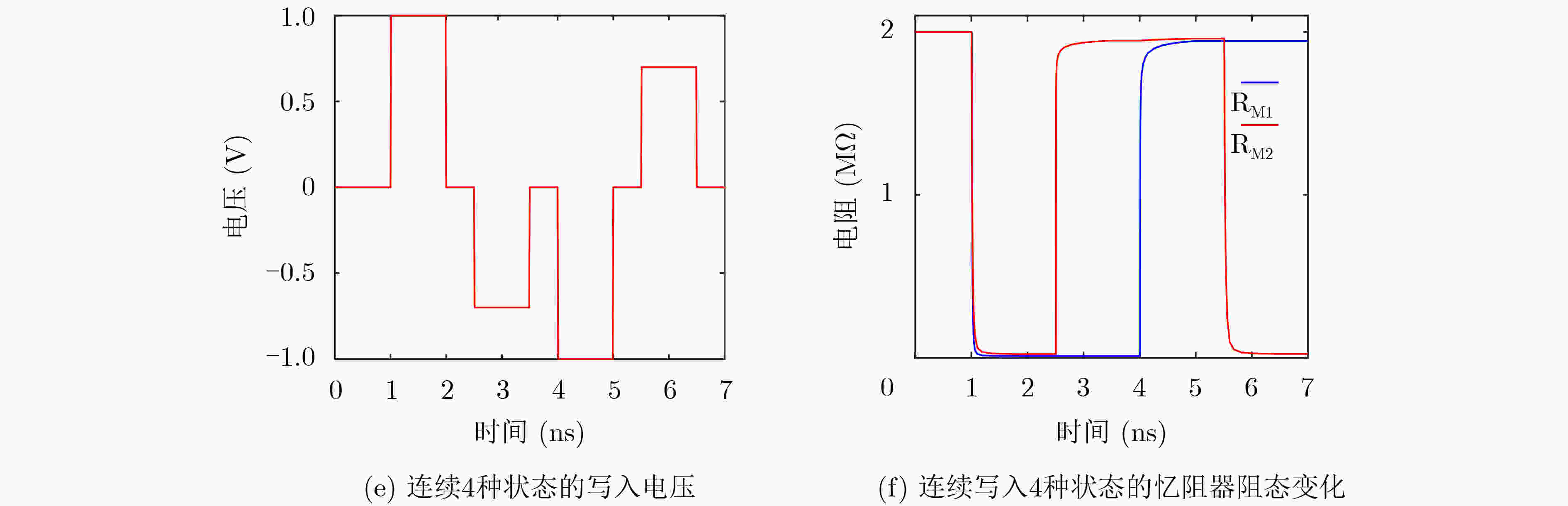
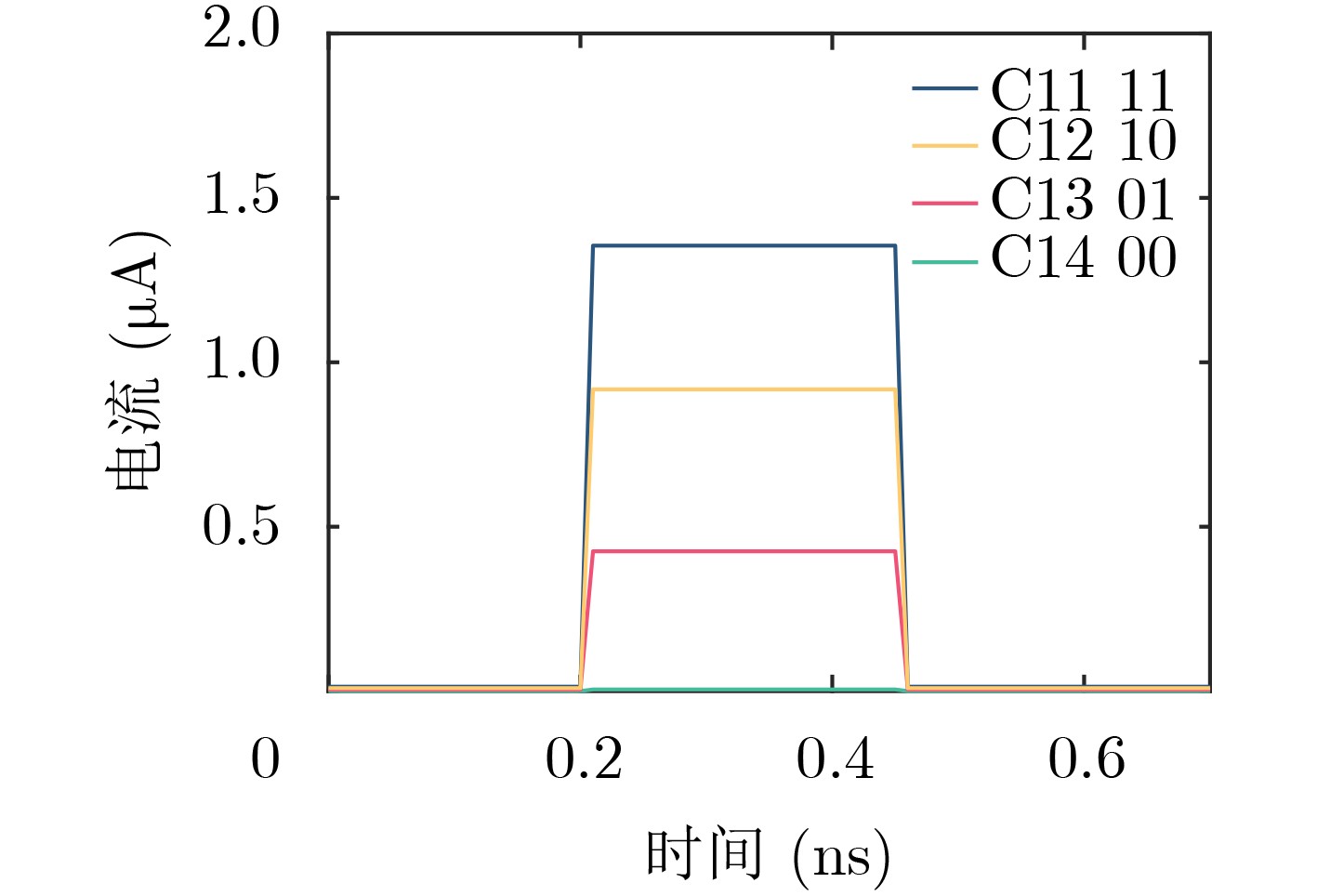
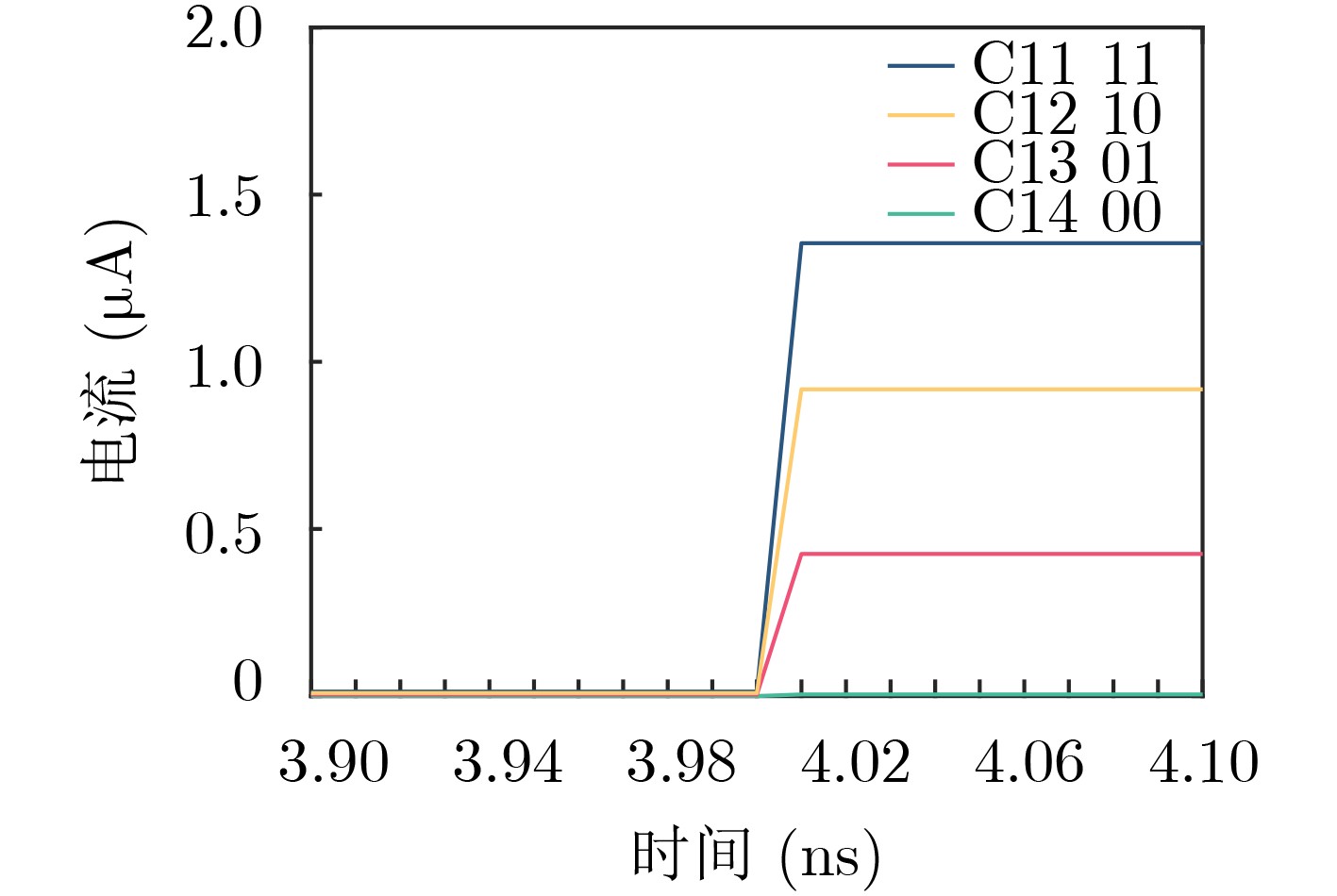
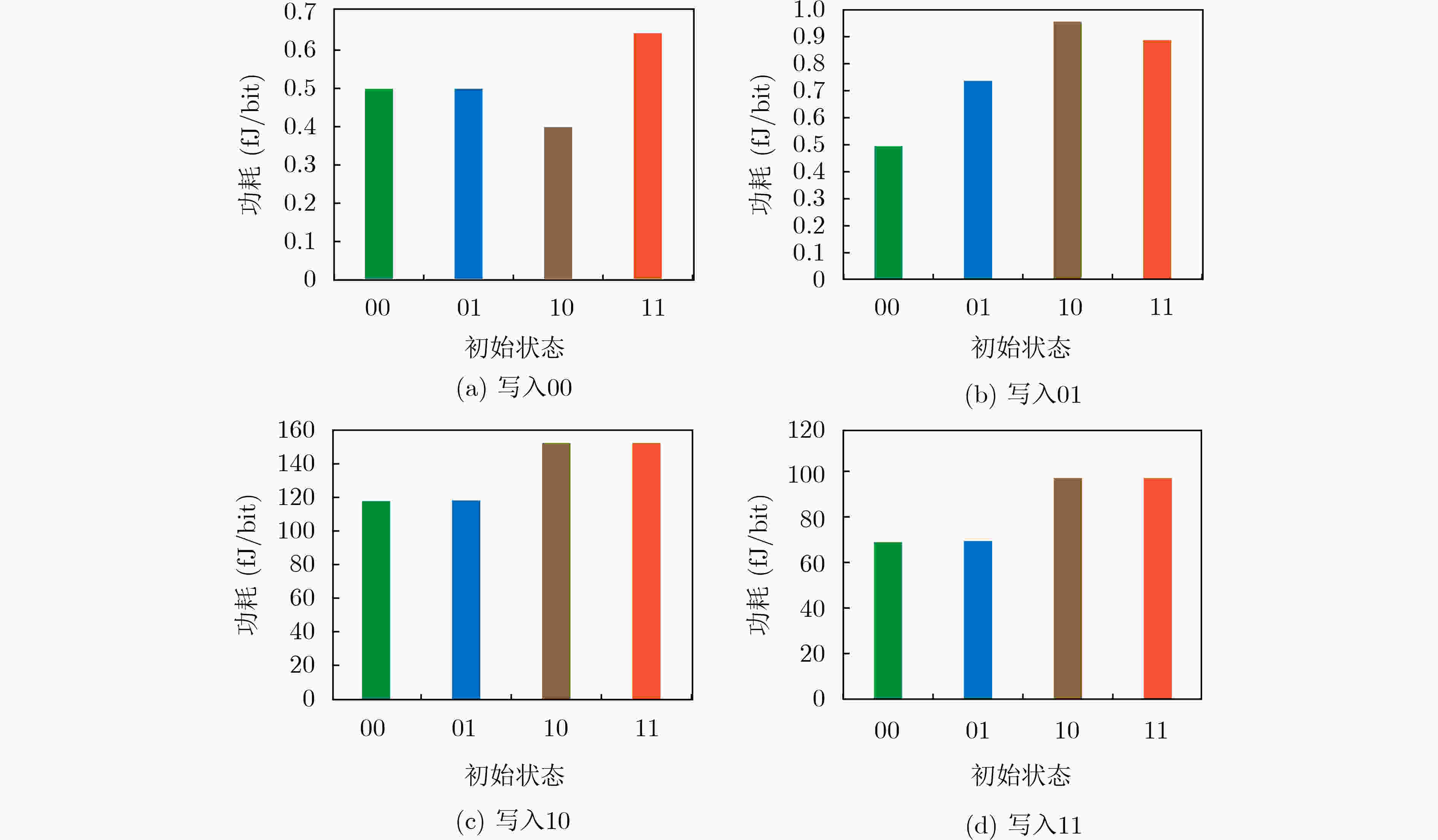


 下载:
下载:
