High Steady-state Physical Unclonable Function Generator Based on Gas Sensors
-
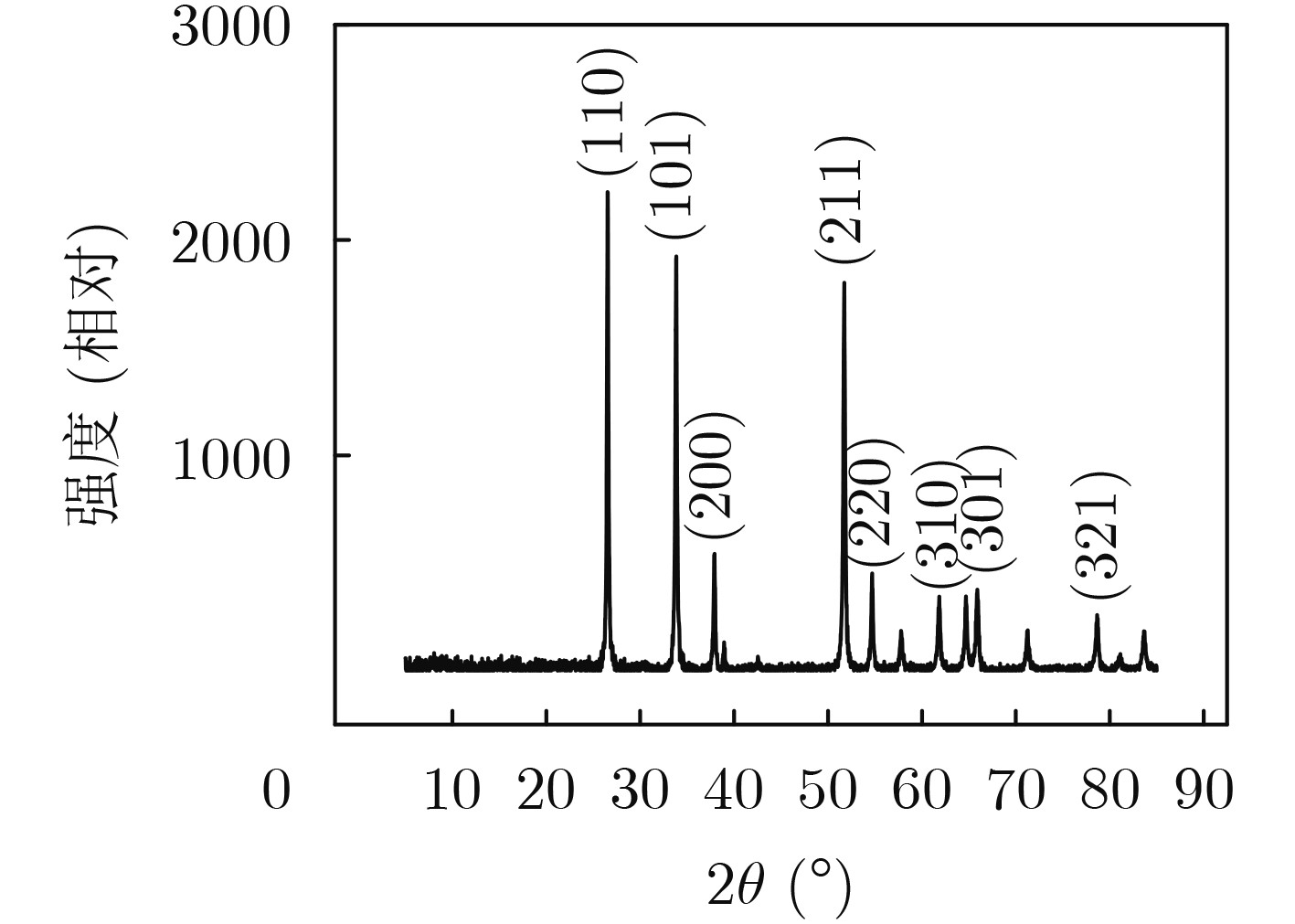
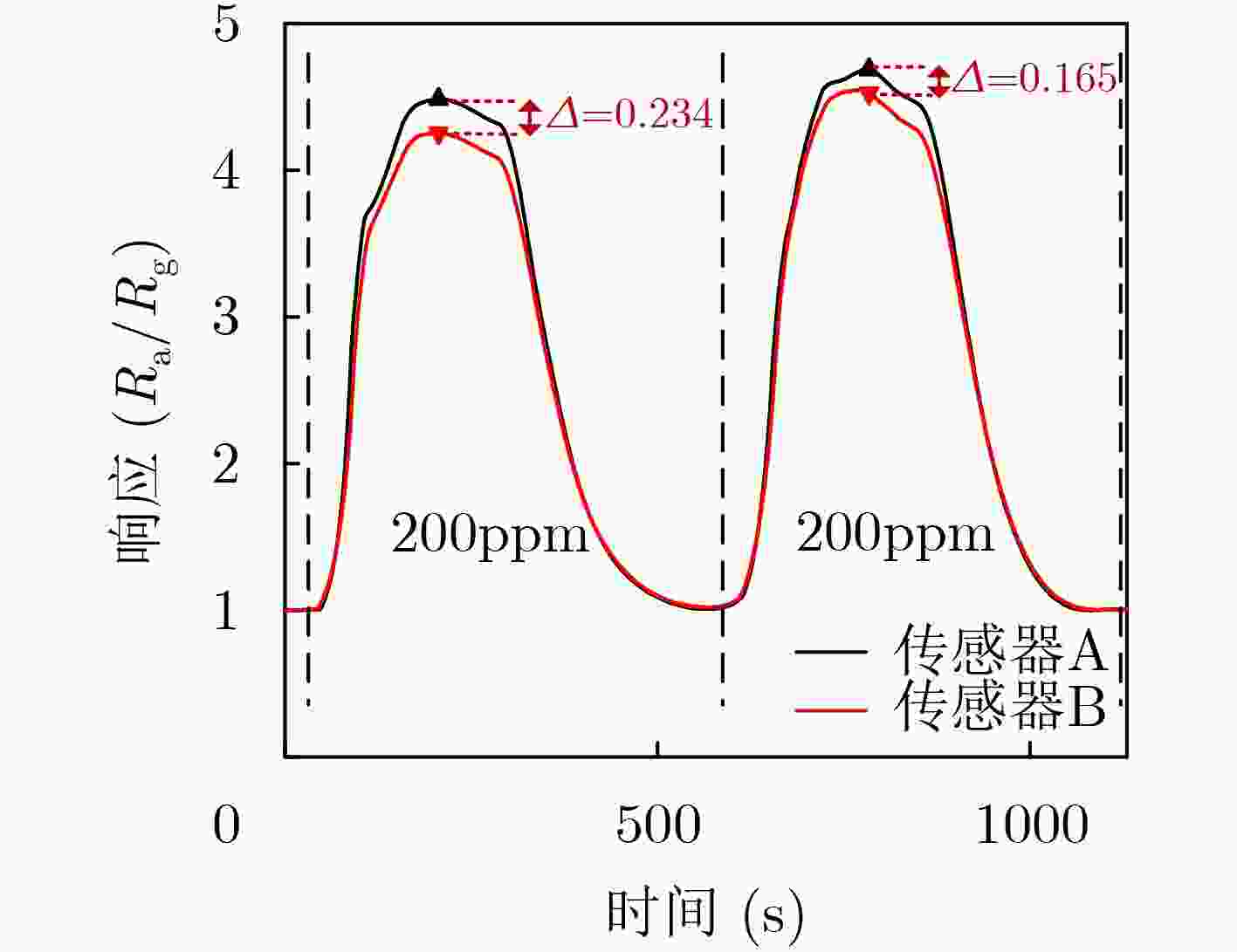
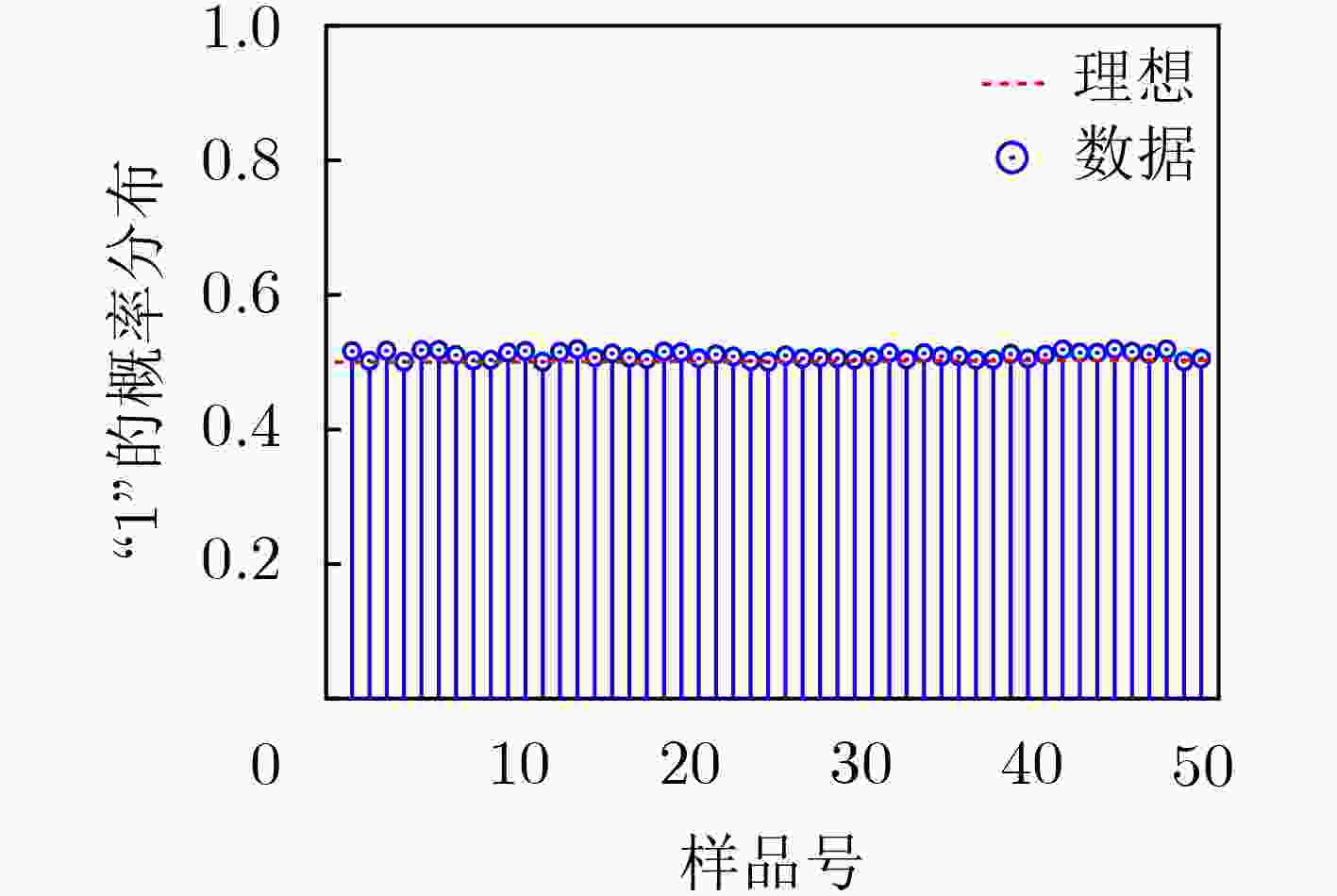
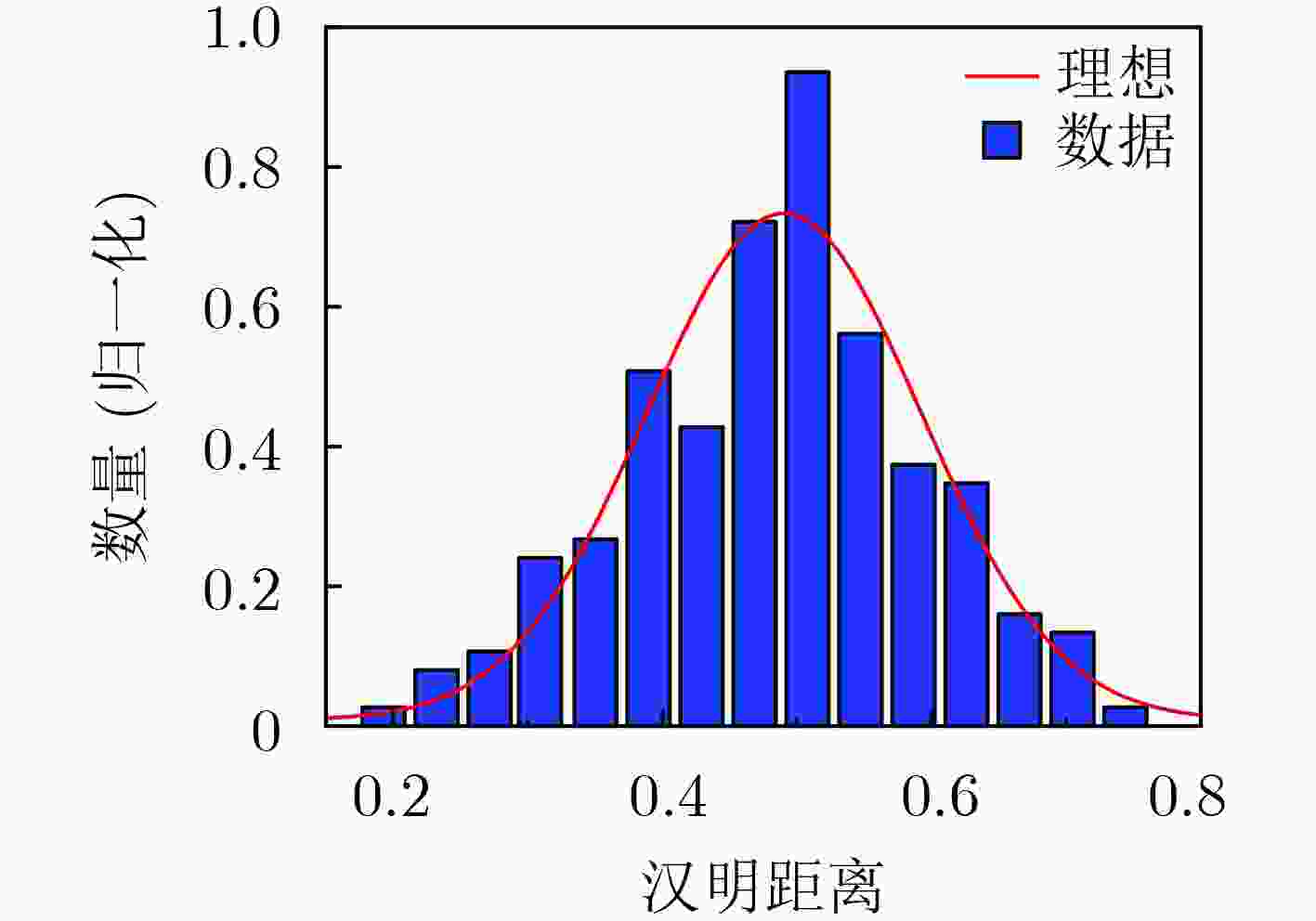
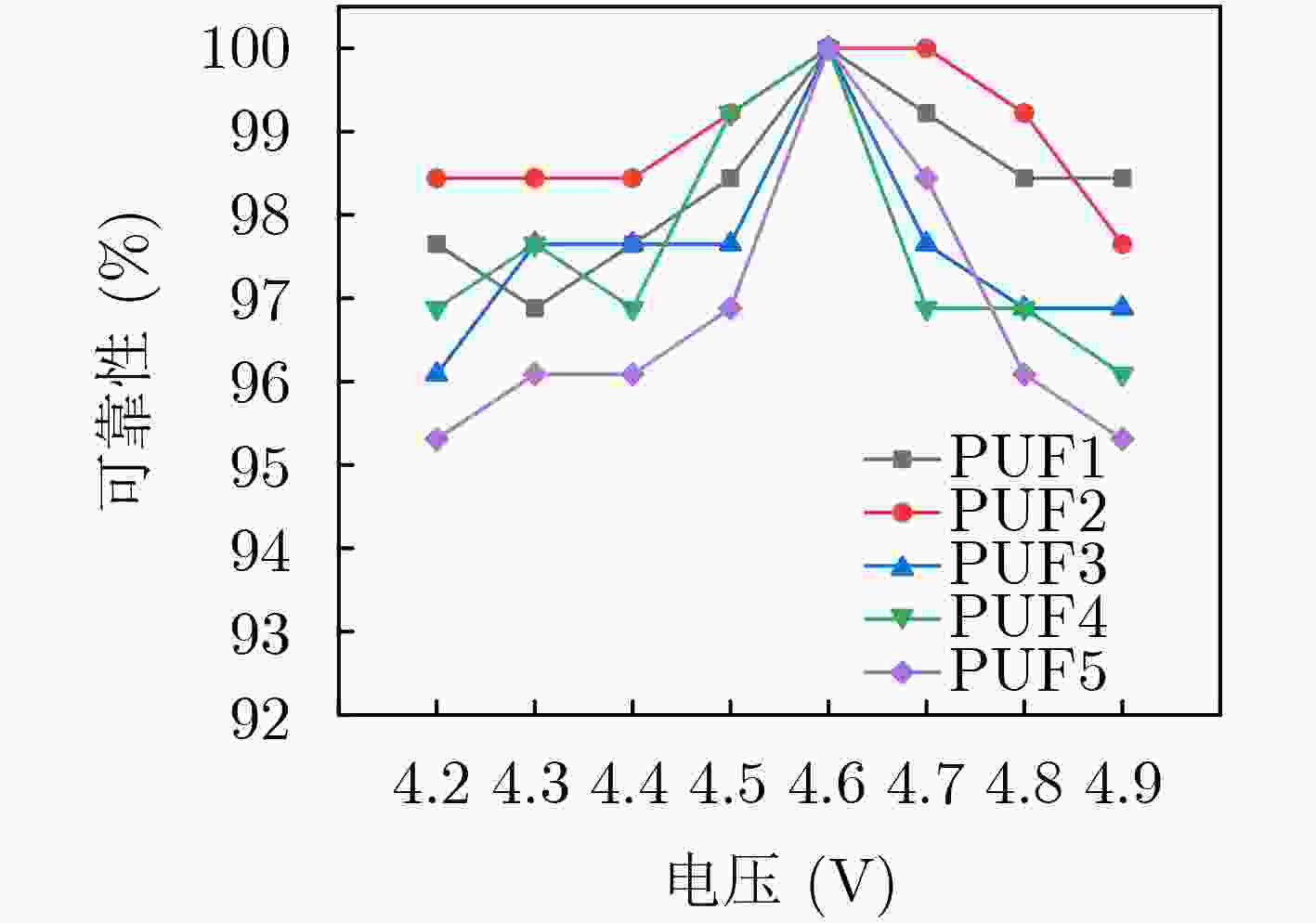
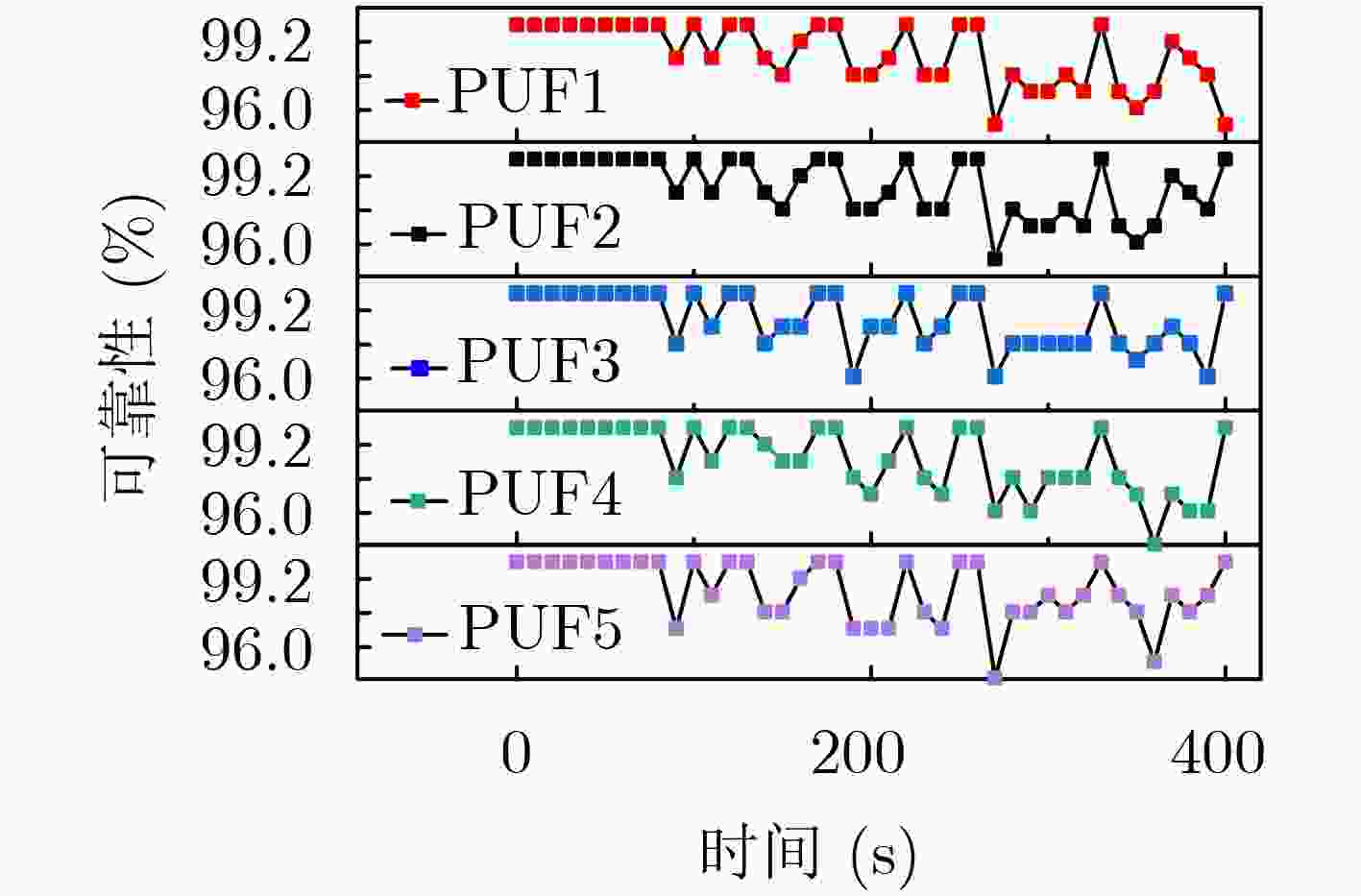
摘要: 物联网(IoT)作为战略性新兴产业已经上升为国家发展重点,但在实际应用中也面临各种安全威胁。确保资源受限物联网系统数据传输、处理和存储的安全已成为研究热点。该文通过对物理不可克隆函数(PUF)和传感器制备工艺偏差的研究,提出一种基于气敏传感器的高稳态物理不可克隆函数发生器设计方案。该方案首先采用静电喷雾沉积(ESD)方式生成具有高比表面积特性的纳米材料,结合高温煅烧技术制备Pd-SnO2气敏传感器;其次采集Pd-SnO2气敏传感器在不同气体浓度、环境温度、加热电压条件下对甲醛气体的响应数据;然后利用随机阻值多位平衡算法比较不同簇气敏传感器响应的阻值,进而产生多位高稳态PUF数据;最后对所设计PUF发生器的安全性和可靠性进行评估。实验结果表明,该PUF发生器的随机性为97.03%、可靠性为97.85%、唯一性为49.04%,可广泛应用于物联网安全领域。
-
关键词:
- 物理不可克隆函数 /
- 气敏传感器 /
- 物理不可克隆函数发生器 /
- 物联网安全
Abstract: As a strategic emerging industry, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become a national development focus, but it also faces various security threats in practical applications. Ensuring the security of data transmission, processing and storage of resource-constrained IoT systems has become a research hotspot. In this paper, a high steady-state Physical Unclonable Function(PUF) generator scheme is proposed by studying PUF and the deviation of the sensor preparation process. Firstly, the Electrostatic Spray Deposition (ESD) is used to generate nanofibers with high specific surface area characteristics and high-temperature calcination technology is combined to prepare Pd-SnO2 gas sensors. Secondly, the response data of gas sensors to formaldehyde gas is collected under different gas concentration, ambient temperature and heating voltage conditions. Then, a random resistance multi-bit balance algorithm is used to compare the response data of different clusters of gas sensors and then multiple high steady-state PUF data is generated. Finally, the safety and reliability of the designed PUF generator are evaluated. Experimental results show that the randomness of the PUF generator is 97.03%, the reliability is 97.85%, and the uniqueness is 49.04%, which can be widely used in IoT security field. -
表 1 8位随机阻值平衡算法伪代码
(1) int bit[place] (2) int lef[3] (3) int r[3] (4) double v[8] (5) i=0 (6) do {lsum=v[(i+lef[0])mod 8]+v[(i+lef[1])mod 8]+v[(i+lef[2]) mod 8] (7) rsum=v[(i+r[0]) mod 8]+v[(i+r[1]) mod 8]+v[(i+r[2])mod 8] (8) if lsum>rsum (9) then bits[palce]=1 (10) else bits[place]=0 (11) place=place+1} (12) while(i<8) (13) return -
[1] BUTUN I, OSTERBERG P, and SONG H. Security of the Internet of Things: Vulnerabilities, attacks, and countermeasures[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(1): 616–644. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2953364 [2] SAIRAM R, BHUNIA S, THANGAVELU V, et al. NETRA: Enhancing IoT security using NFV-based edge traffic analysis[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(22): 4660–4671. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2900097 [3] KOYUICEM D, BOUABDALLAH A, and LAKHLEF H. Internet of Things security: A top-down survey[J]. Computer Networks, 2018, 141(2018): 199–221. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2018.03.012 [4] PAPPU R, RECHT B, TAYLOR J, et al. Physical one-way functions[J]. Science, 2002, 297(5589): 2026–2030. doi: 10.1126/science.1074376 [5] 龚越, 叶靖, 胡瑜, 等. 内建自调整的仲裁器物理不可克隆函数[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2017, 29(9): 1734–1739. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2017.09.018GONG Yue, YE Jing, HU Yu, et al. Built-in self-adjusting arbiter PUF[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design &Computer Graphics, 2017, 29(9): 1734–1739. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2017.09.018 [6] 孙子文, 叶乔. 利用震荡环频率特性提取多位可靠信息熵的物理不可克隆函数研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 234–241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191013SUN Ziwen and YE Qiao. Study on the physical unclonable function of the reliable information entropy extracted by the frequency characteristic of oscillating ring[J]. Jounal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 234–241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191013 [7] LI Gang, WANG Pengjun, MA Xuejiao, et al. A 215-F2 bistable physically unclonable function with an ACF of < 0.005 and a native bit instability of 2.05% in 65-nm CMOS process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2020, 28(11): 2290–2299. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.3014892 [8] GOLANBARI M, KIAMEHR S, BISHNOI R, et al. Reliable memory PUF design for low-power applications[C]. The 19th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, Santa Clara, USA, 2018: 207−213. doi: 10.1109/ISQED.2018.8357289. [9] 张培勇, 袁晓东, 王雪洁, 等. 基于D触发器的物理不可克隆函数[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 2019, 46(1): 35–41. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2019.01.005ZHANG Peiyong, YUAN Xiaodong, WANG Xuejie, et al. D flip-flop based physical unclonable function[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition) , 2019, 46(1): 35–41. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2019.01.005 [10] FUKUSHIMA K, YOSHIMURA A, KIYOMOTO S, et al. Evaluation of software PUF based on gyroscope[C]. The 15th International Conference on Information Security Practice and Experience, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2019: 232-247. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34339-2_13. [11] KUMAR S, LABRADO C, BADHAN R, et al. Solar cell based physically unclonable function for cybersecurity in IoT devices[C]. 2018 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Hong Kong, China, 2018: 697–702. doi: 10.1109/ISVLSI.2018.00131. [12] ROSENFELD K, GAVAS E, and KARRI R. Sensor physical unclonable functions[C]. 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware-Oriented Security and Trust, Anaheim, USA, 2010: 112–117. doi: 10.1109/HST.2010.5513103. [13] DEY S, ROY N, XU Wenyuan, et al. AccelPrint: Imperfections of accelerometers make smartphones trackable[C]. Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2014: 1–16. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2014.23059. [14] AYSU A, GHALATY N, FRANKLIN Z, et al. Digital fingerprints for low-cost platforms using MEMS sensors[C]. Workshop on Embedded Systems Security, Montreal Quebec, Canada, 2013: 1-6. doi: 10.1145/2527317.2527319. [15] LABRADO C and THAPLIYAL H. Design of a piezoelectric-based physically unclonable function for IoT security[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 2770–2777. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2874626 [16] KANG D, KIM J, KIM I, et al. Experimental qualification of the process of electrostatic spray deposition[J]. Coatings, 2019, 9(5): 294–312. doi: 10.3390/coatings9050294 [17] 刘兆香, 刘勇, 王欣, 等. 静电纺丝过程中泰勒锥、射流鞭动和电晕现象分析[J]. 塑料, 2012, 41(3): 29–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9456.2012.03.010LIU Zhaoxiang, LIU Yong, WANG Xin, et al. Phenomena analysis of taylor cone, jet whipping and corona in process of electrospinning[J]. Plastic, 2012, 41(3): 29–34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9456.2012.03.010 [18] SHIN Y, HOHMAN M, BRENNER M, et al. Experimental characterization of electrospinning: The electrically forced jet and instabilities[J]. Polymer, 2001, 42(25): 9955–9967. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00540-7 [19] YI J, LEE J, and PARK W. Vertically aligned ZnO nanorods and graphene hybrid architectures for high-sensitive flexible gas sensors[J]. Sensors & Actuators, 2011, 155(1): 264–269. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2010.12.033 [20] 李刚, 汪鹏君, 张跃军, 等. 基于65 nm工艺的多端口可配置PUF电路设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(6): 1541–1546. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150968LI Gang, WANG Pengjun, ZHANG Yuejun, et al. Design of multi-port configurable PUF circuit based on 65 nm technology[J]. Jounal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1541–1546. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150968 -





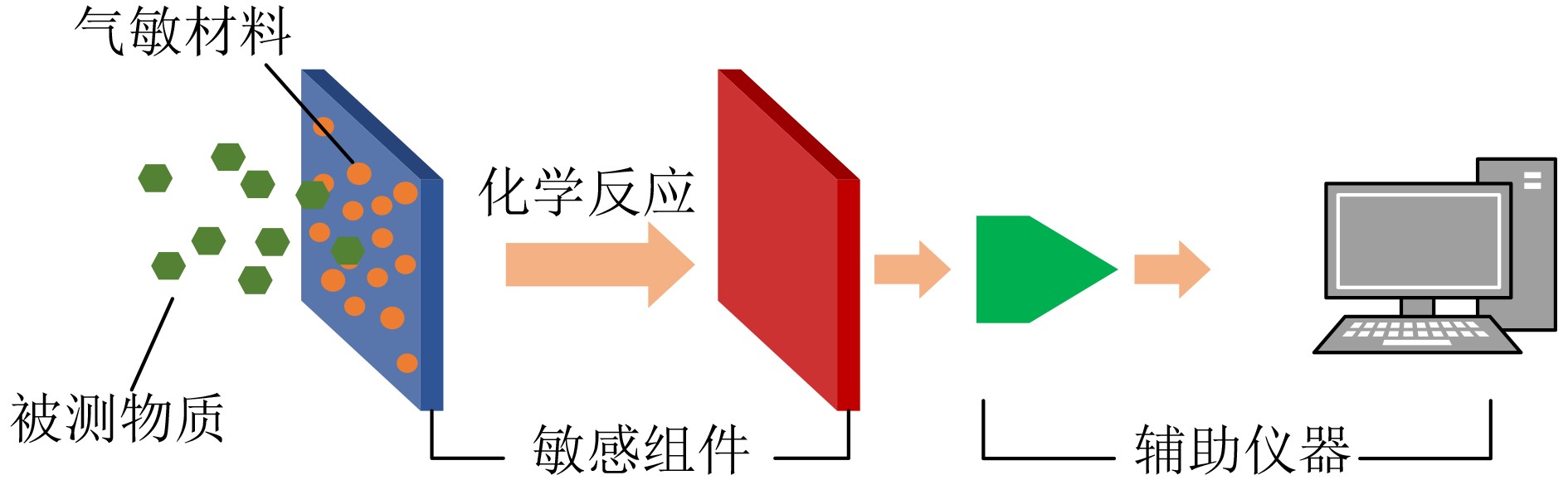
 下载:
下载:
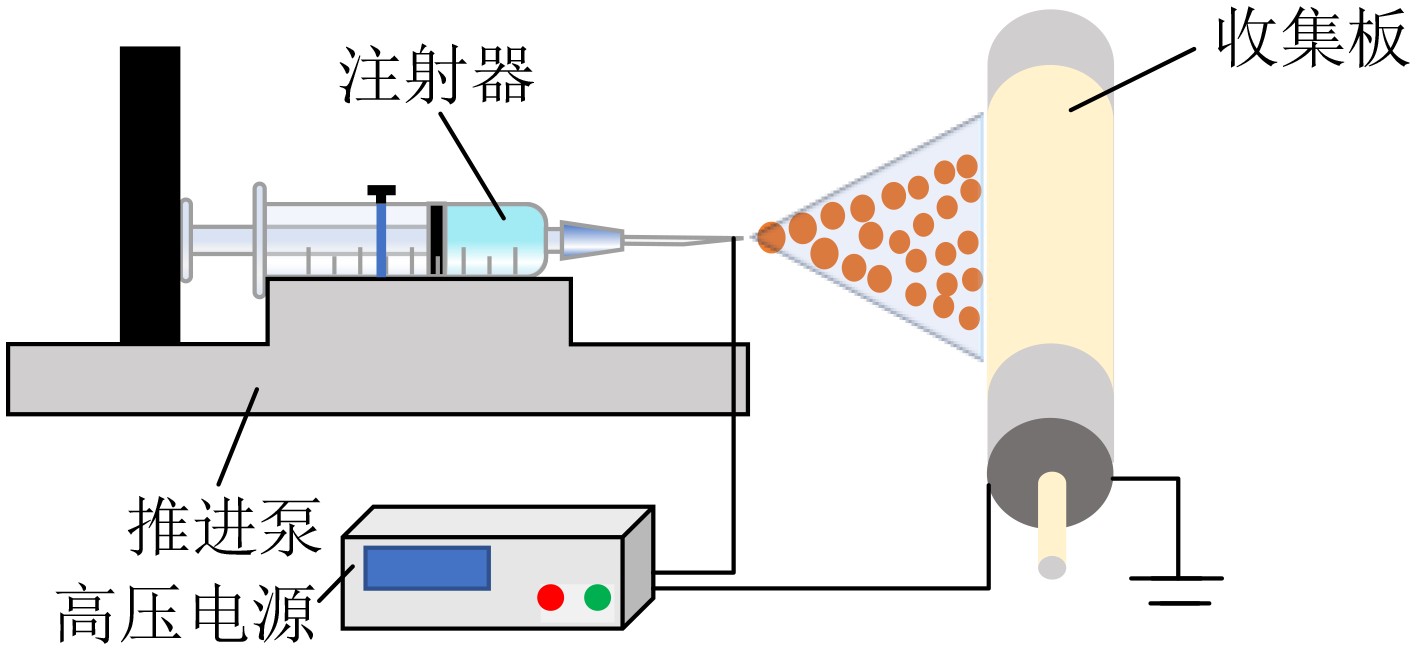
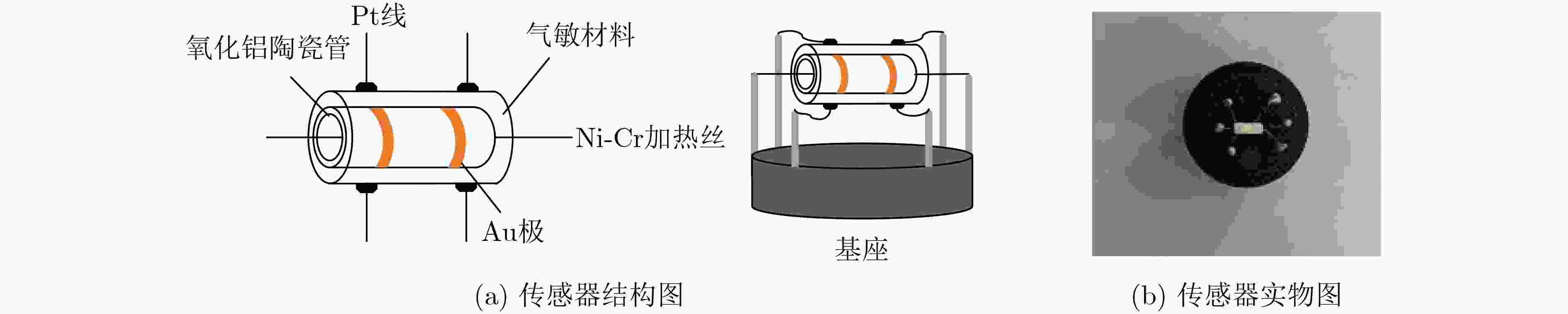

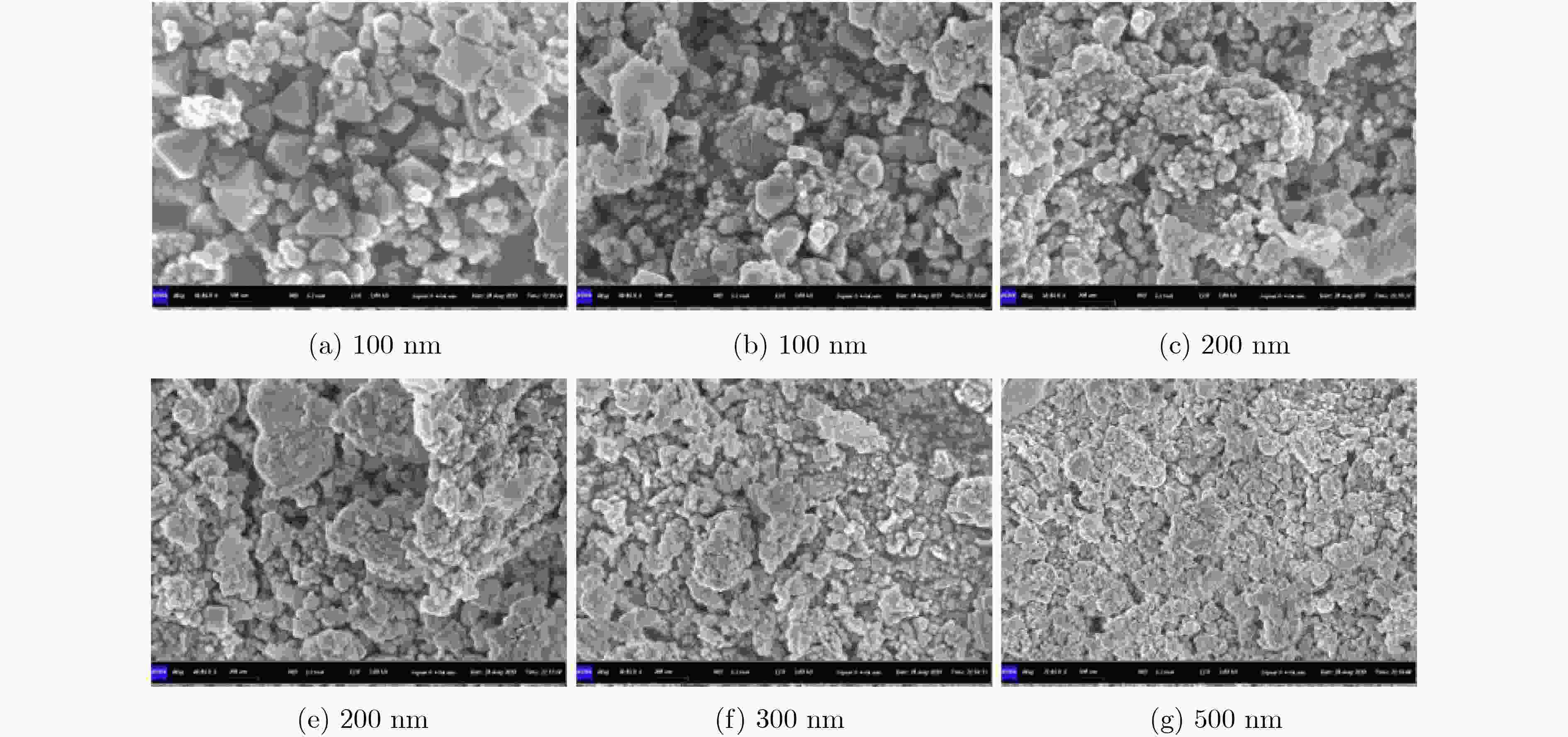


 下载:
下载:
