Mixed Noise Suppression Algorithm Based on Developable Local Surface of Image
-
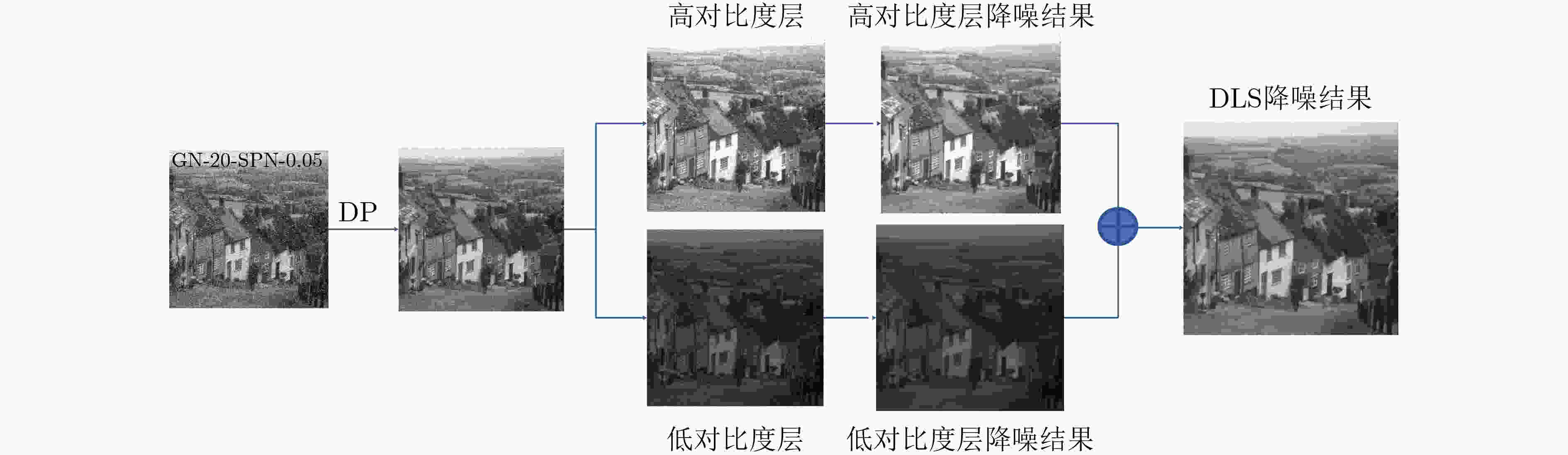
摘要: 为满足基于旋翼无人机(UAV)载具的室外目标检测所需的低资源开销混合噪声抑制,该文提出一种基于图像局部曲面可展化的混合噪声抑制算法(DLS),该算法实现了局部曲面可展化算法和分层降噪算法优势互补,达到了两算法各自无法企及的降噪效果。首先,对图像进行局部可展化处理,抑制图像的椒盐噪声和低密度高斯噪声,得到初步降噪图像;接着,在空间域和傅里叶域分层降噪,在去除高斯噪声残余的同时,最大限度地保留图像边缘、纹理等细节;最后,迭代局部曲面可展化和分层降噪,进一步去除混合噪声残余成分,达到抑制目标检测图像混合噪声的目的。实验结果表明,在去除图像混合噪声时,相比于其他7种降噪算法,本文算法具有一定的优势,其降噪图像的主观视觉指标和客观数据指标统计优于其他7种算法。Abstract: In order to meet the requirement of low resource cost and mixed noise suppression for outdoor target detection based on rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), a mixed noise suppression algorithm based on Developable Local Surface (DLS) is proposed. This algorithm realizes the complementary advantages of the developable local surface algorithm and the layered noise reduction algorithm, and achieves the noise reduction effect that the neither algorithm can reach. Firstly, the developable local surface of image is used to suppress salt & pepper noise and low-density Gaussian noise in the image to obtain a preliminary denoised image. Then, the layered noise reduction in the spatial domain and the Fourier domain is carried, removing Gaussian noise and maximize the preservation of image edges, textures and other details. Finally, iteratively developable local surface and layered noise reduction to remove further residual components of mixed noise to achieve the purpose of suppressing mixed noise in target detection images. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has certain advantages over the other seven algorithms in removing mixed noise, and its subjective visual index and objective data index statistics are superior to those of the other seven algorithms.
-
表 1 DLS算法在BSD68和Set12的数据集的综合性能
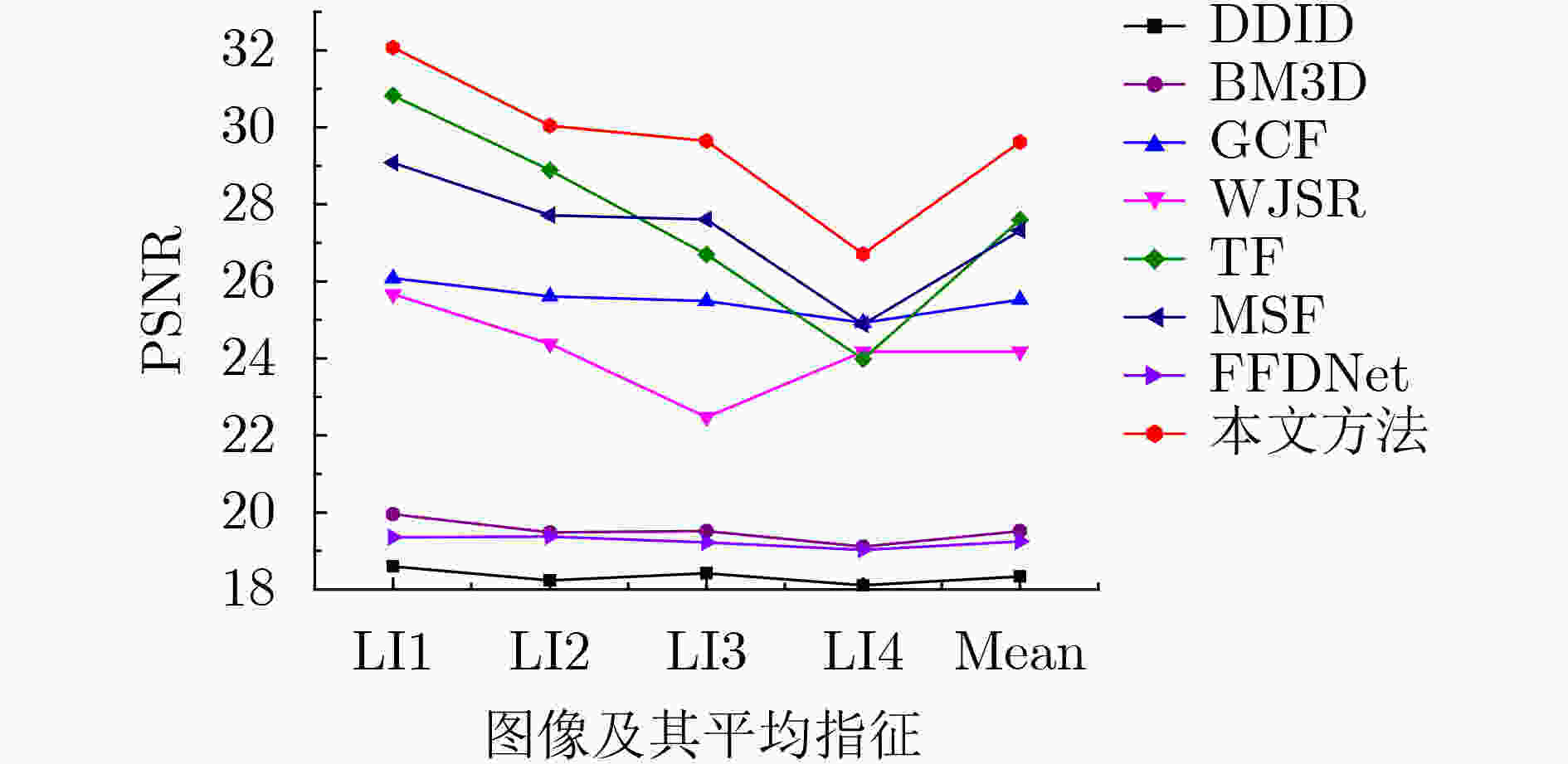
数据集 指标数据 PSNR MSE SSIM Set12 29.8146 18.2188 0.8630 BSD68 28.9350 24.1347 0.8266 表 2 8种算法降噪图像的MSE统计
GN+SPN DDID BM3D GCF WJSR TF MSF FFDNet 本文方法 5+0.03 7.58 10.27 9.58 38.75 13.33 8.37 10.56 7.74 10+0.02 10.34 13.16 24.11 37.81 14.84 17.08 15.81 11.38 LI1 15+0.05 22.82 34.08 43.34 48.57 17.93 24.95 38.59 14.76 20+0.05 31.31 34.58 58.09 52.46 22.67 31.31 46.23 18.80 30+0.1 66.45 63.86 80.99 78.52 38.64 43.36 76.62 27.33 40+0.15 88.56 80.35 93.71 106.95 63.63 55.36 88.58 40.67 5+0.03 11.99 13.49 19.03 53.03 51.80 28.15 12.19 25.69 10+0.02 23.25 25.97 33.94 52.56 52.18 39.42 24.45 33.10 LI2 15+0.05 40.29 47.39 50.79 58.33 53.63 49.09 46.01 41.83 20+0.05 52.72 52.55 63.70 60.47 56.59 53.79 55.63 47.22 30+0.1 84.11 72.29 83.03 73.15 68.97 61.86 75.99 55.43 40+0.15 103.17 76.79 94.36 85.15 93.54 69.17 87.52 60.42 表 3 8种算法降噪图像的SSIM统计
GN+SPN DDID BM3D GCF WJSR TF MSF FFDNet 本文方法 5+0.03 0.448 0.464 0.850 0.791 0.860 0.889 0.462 0.894 10+0.02 0.549 0.599 0.728 0.773 0.849 0.816 0.576 0.874 LI1 15+0.05 0.319 0.371 0.544 0.733 0.827 0.754 0.345 0.851 20+0.05 0.328 0.429 0.446 0.694 0.796 0.712 0.343 0.823 30+0.1 0.191 0.273 0.280 0.591 0.694 0.633 0.191 0.757 40+0.15 0.135 0.186 0.187 0.484 0.561 0.522 0.134 0.650 5+0.03 0.597 0.608 0.882 0.552 0.495 0.820 0.625 0.843 10+0.02 0.656 0.689 0.814 0.535 0.489 0.733 0.685 0.800 LI2 15+0.05 0.421 0.468 0.676 0.520 0.477 0.601 0.464 0.701 20+0.05 0.434 0.497 0.584 0.497 0.459 0.532 0.453 0.651 30+0.1 0.243 0.318 0.394 0.454 0.416 0.436 0.282 0.528 40+0.15 0.173 0.243 0.273 0.409 0.363 0.386 0.197 0.456 -
[1] 张强. 基于BM3D的彩色图像混合噪声滤波算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 吉林大学, 2019.ZHANG Qiang. Mixed noise filtering algorithm for color images based on BM3D[D]. [Master dissertation], Jilin University, 2019. [2] YIN Xiangrui, ZHAO Qianlong, LIU Jin, et al. Domain progressive 3D residual convolution network to improve low-dose CT imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(12): 2903–2913. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2917258 [3] LIU Jin, HU Yining, YANG Jian, et al. 3D feature constrained reconstruction for low-dose CT imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 28(5): 1232–1247. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2643009 [4] CHEN Yang, SHI Luyao, FENG Qianjing, et al. Artifact suppressed dictionary learning for low-dose CT image processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2014, 33(12): 2271–2292. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2336860 [5] FAN Haiyan, LI Chang, GUO Yulan, et al. Spatial–spectral total variation regularized low-rank tensor decomposition for hyperspectral image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 6196–6213. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2833473 [6] ABAZARI R and LAKESTANI M. A hybrid denoising algorithm based on shearlet transform method and yaroslavsky’s filter[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(14): 17829–17851. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-5648-7 [7] SHAHDOOSTI H R and KHAYAT O. Image denoising using sparse representation classification and non-subsampled shearlet transform[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2016, 10(6): 1081–1087. doi: 10.1007/s11760-016-0862-0 [8] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. FFDNet: Toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4608–4622. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2839891 [9] ZHANG Jing, SANG Liu, WAN Zekang, et al. Deep convolutional neural network based on multi-scale feature extraction for image denoising[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Macau, China, 2020: 213–216. doi: 10.1109/VCIP49819.2020.9301843. [10] RAFIQUE H. Simulation of harmonic analysis, synthesis and Gibbs effect of periodic signals[C]. The 16th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Istanbul, Turkey, 2019: 282–287. doi: 10.1109/SSD.2019.8893281. [11] LI Wenhao, JIA Tong, CHEN Qiusheng, et al. Omnidirectional ring structured light noise filtering based on DCGAN network and autoencode[C]. The International Conference on Culture-oriented Science & Technology (ICCST), Beijing, China, 2020: 452–456. doi: 10.1109/ICCST50977.2020.00093. [12] GONG Yuanhao and SBALZARINI I F. Curvature filters efficiently reduce certain variational energies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4): 1786–1798. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2658954 [13] 王满利, 田子建, 桂伟峰, 等. 基于高斯曲率优化和非下采样剪切波变换的高密度混合噪声去除算法[J]. 光子学报, 2019, 48(9): 0910003. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194809.0910003WANG Manli, TIAN Zijian, GUI Weifeng, et al. High density mixed noise removal algorithm based on gaussian curvature optimization and non-subsampled shearlet transform[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2019, 48(9): 0910003. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194809.0910003 [14] 王满利, 田子建, 张元刚. 曲率差分驱动的极小曲面滤波器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 764–771. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190216WANG Manli, TIAN Zijian, and ZHANG Yuangang. Minimal surface filter driven by curvature difference[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 764–771. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190216 [15] 汤成, 许建龙, 周志光. 改进的曲率滤波强噪声图像去噪方法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 24(3): 346–356. doi: 10.11834/jig.180302TANG Cheng, XU Jianlong, and ZHOU Zhiguang. Strong noise image-denoising algorithm based on improved curvature filters[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(3): 346–356. doi: 10.11834/jig.180302 [16] XU Zhiya, DAI Tao, NIU Li, et al. Sure-based dual domain image denoising[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, Canada, 2018: 1418–1422. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8461324. [17] KNAUS C and ZWICKER M. Dual-domain image denoising[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 440–444. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2013.6738091. [18] DABOV K, FOI A, KATKOVNIK V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080–2095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238 [19] LIU Licheng, CHEN Long, CHEN C L P, et al. Weighted joint sparse representation for removing mixed noise in image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(3): 600–611. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2521428 [20] LIU Yinghui, GAO Kun, and NI Guoqiang. An improved trilateral filter for Gaussian and impulse noise removal[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Industrial Mechatronics and Automation, Wuhan, China, 2010: 385–388. doi: 10.1109/ICINDMA.2010.5538290. -





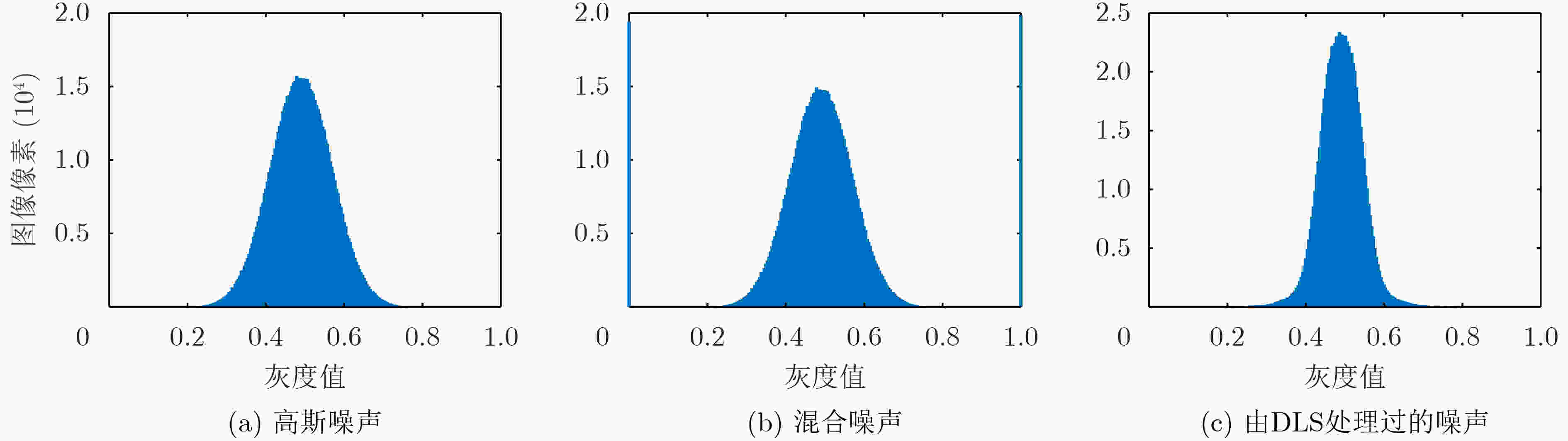
 下载:
下载:


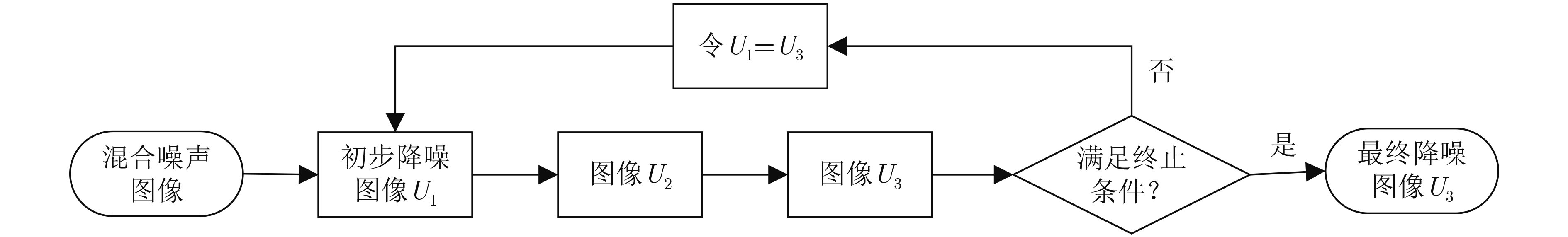

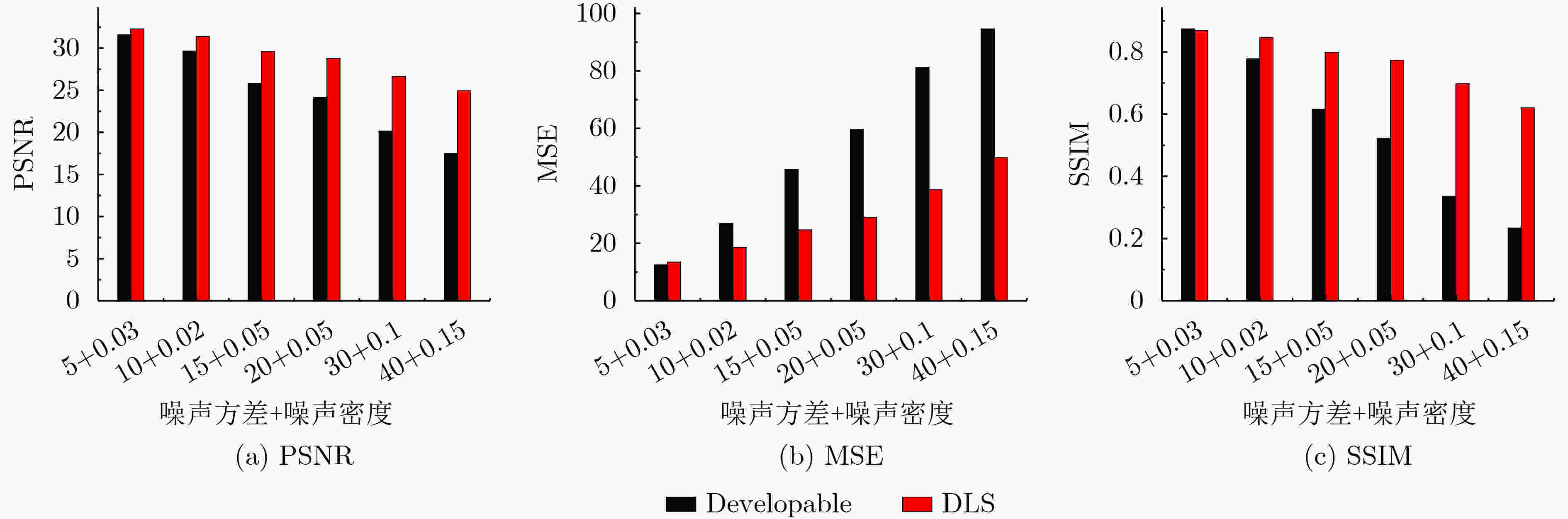
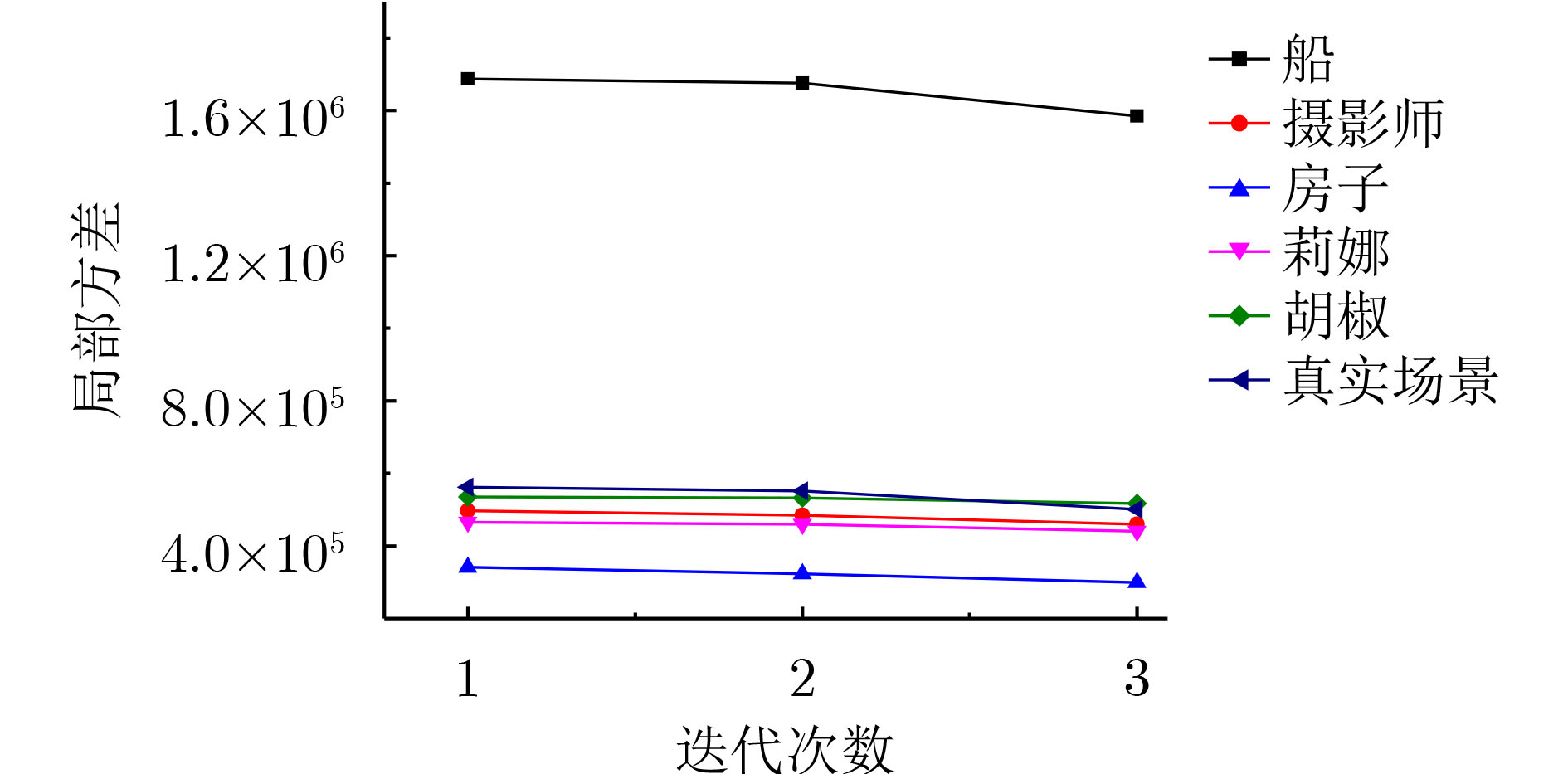



 下载:
下载:
