Efficient Consistency Consensus Algorithm of Blockchain for Heterogeneous Nodes in the Internet of Vehicles
-
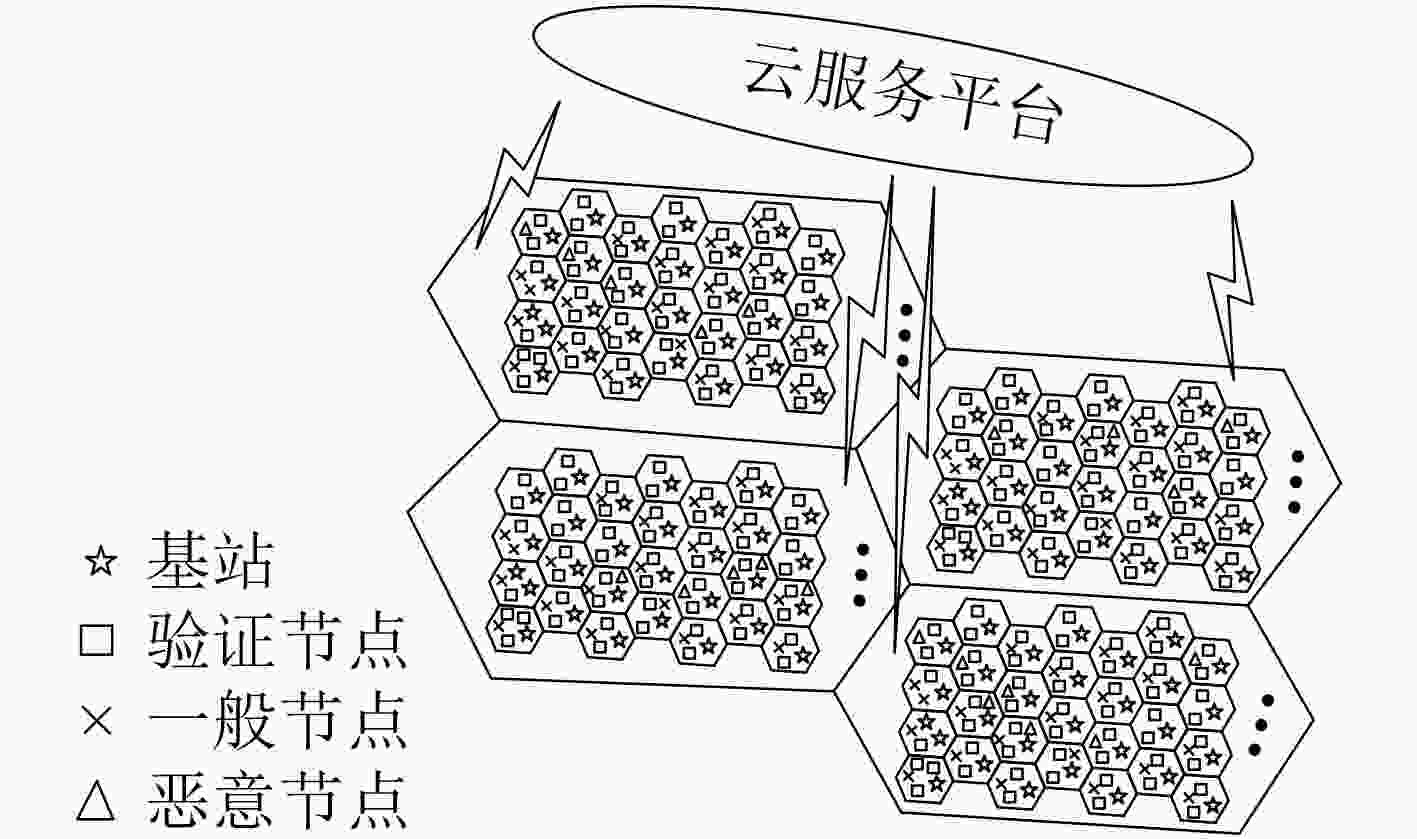
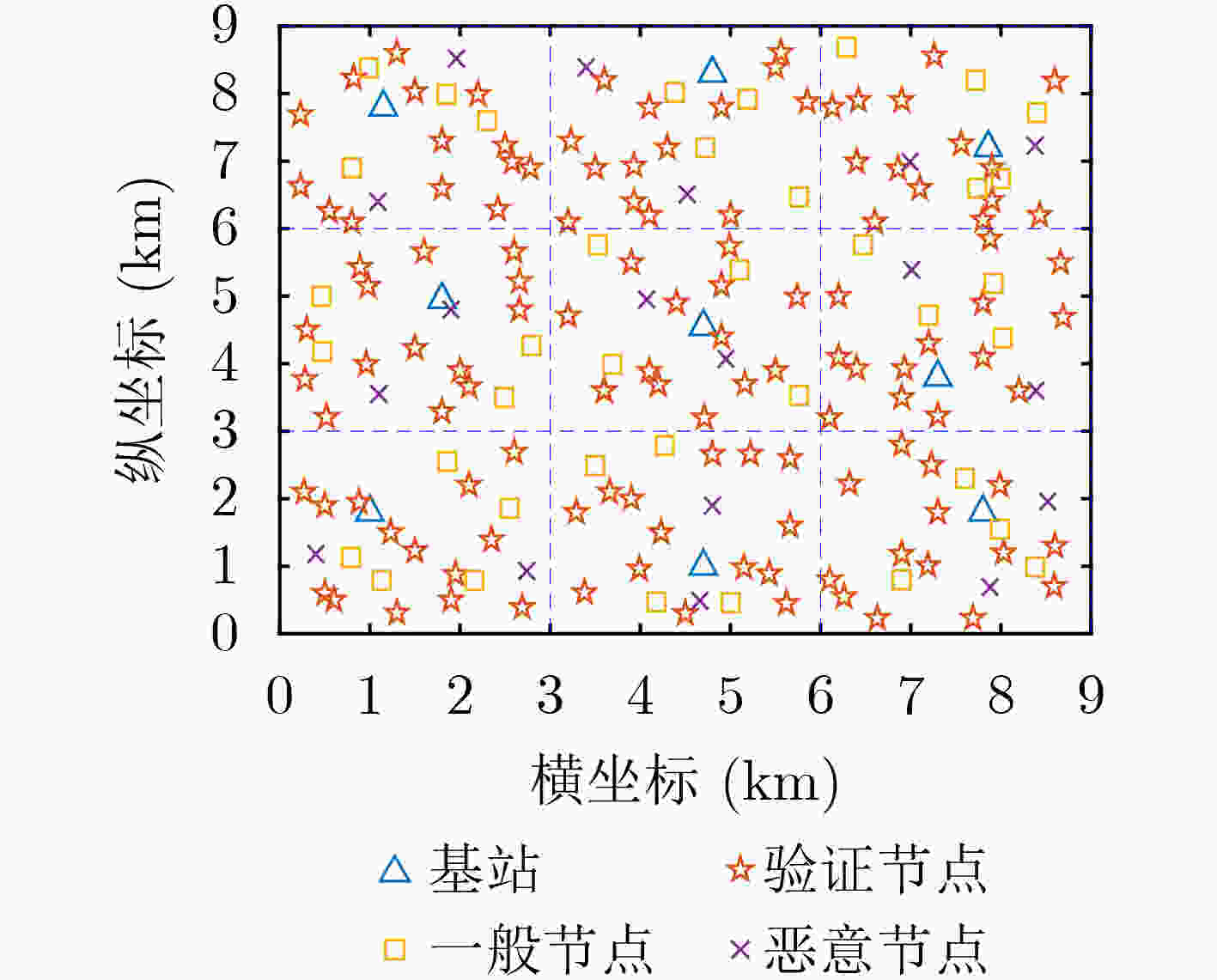
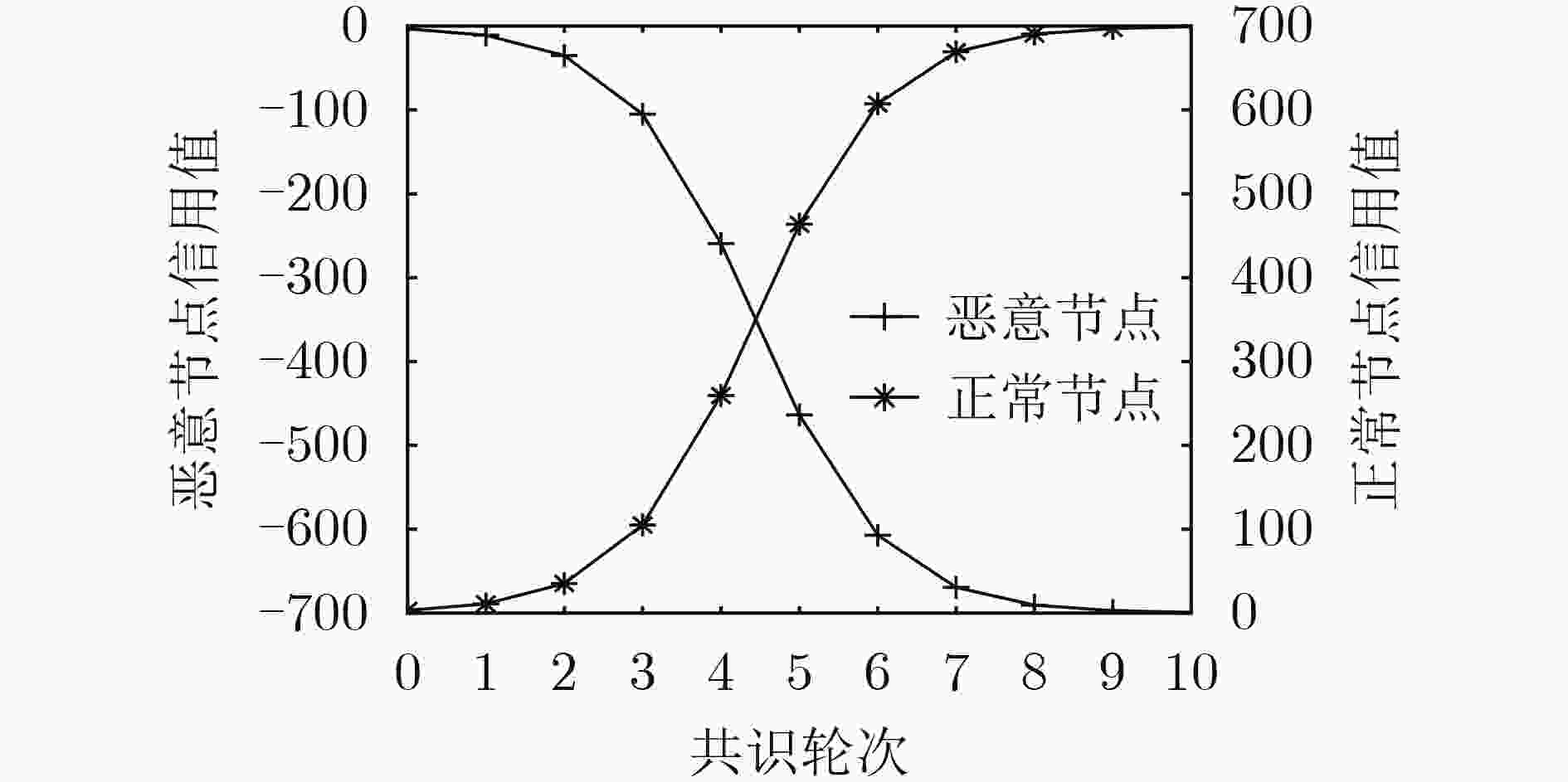
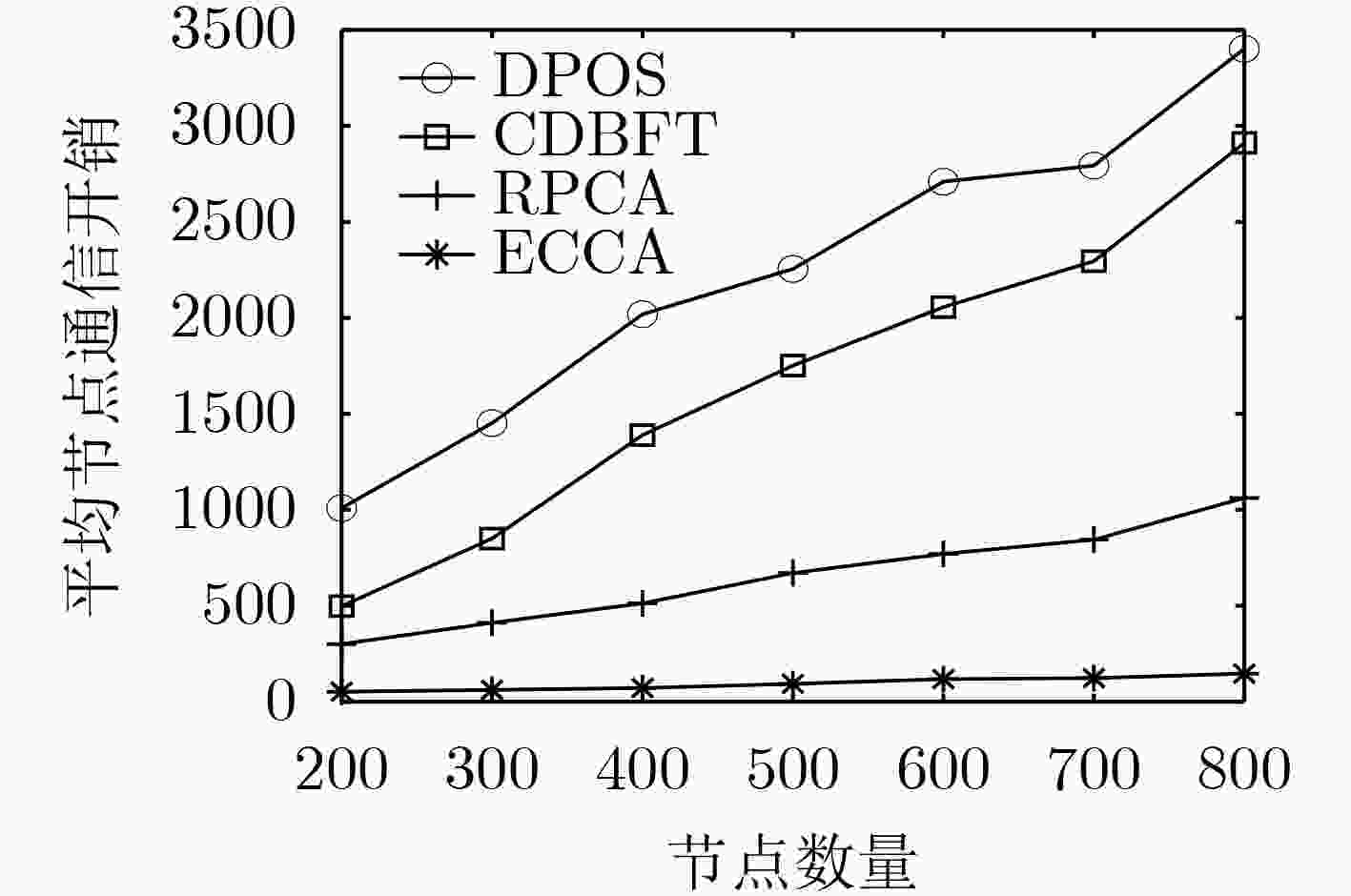
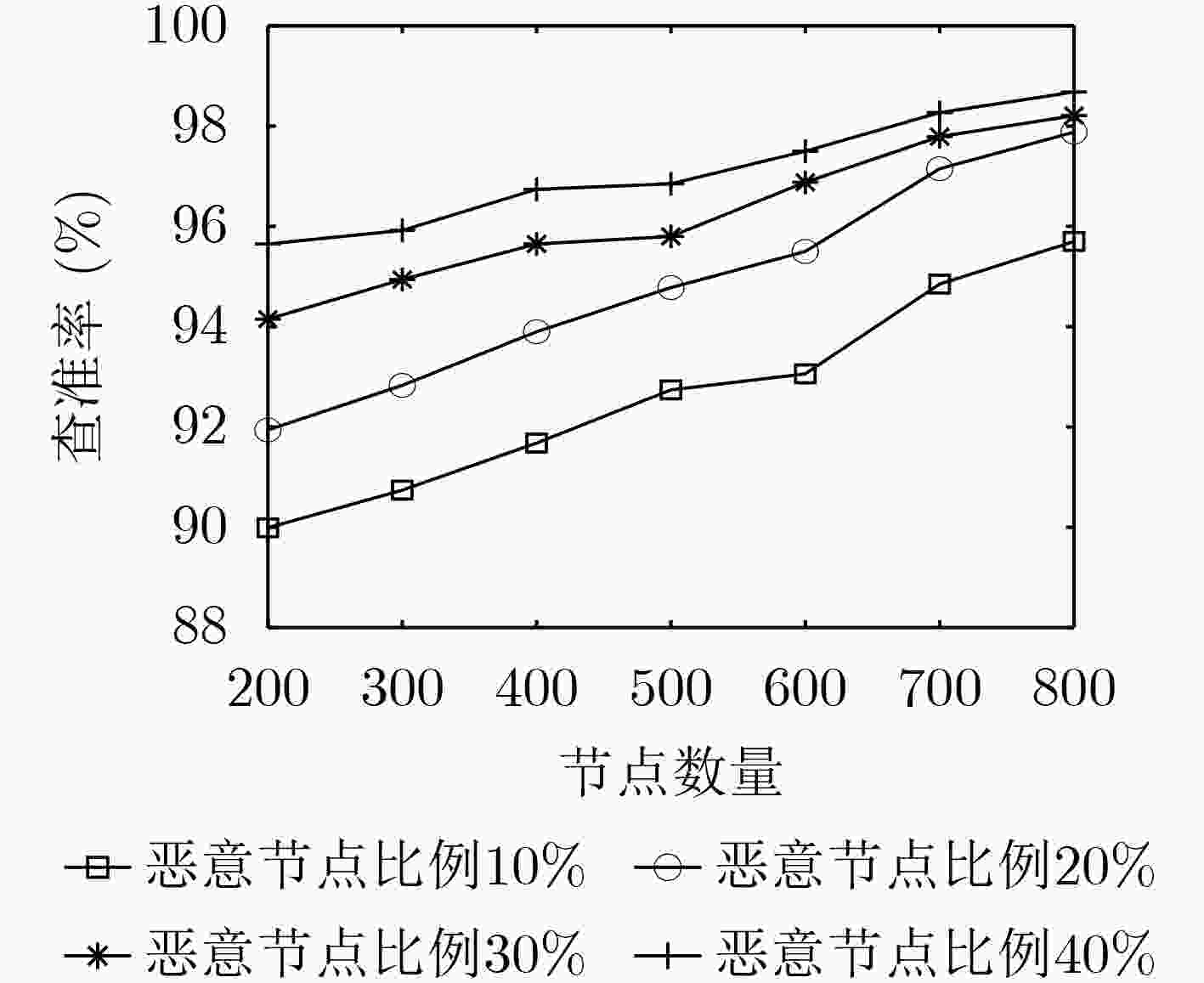
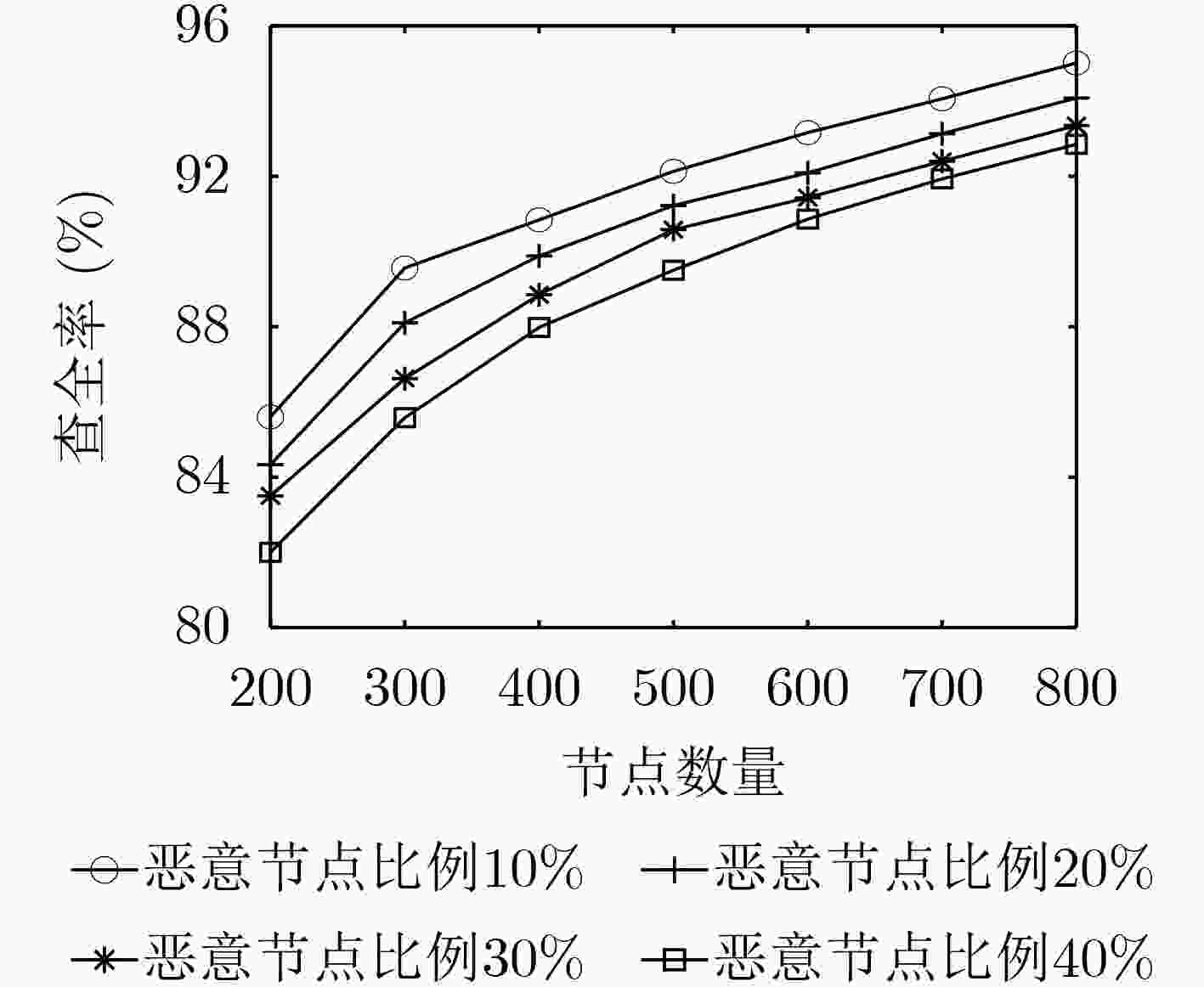
摘要: 车联网异构节点由于其性能差异大、具有移动性等原因会造成区块链共识算法交易吞吐率低、交易时延较大等问题,该文提出面向车联网异构节点的区块链高效一致性共识算法(ECCA)。首先,在ECCA中,考虑由验证节点、一般节点和恶意节点组成的车联网异构节点,提出一种信用等级机制,实现信用等级划分和3类异构节点的划分。其次,提出一种跨区下的节点身份变更机制,及时调整当前区域内的节点身份。最后,提出一种改进的一致性共识算法,满足车联网的时效性需求。仿真结果表明:ECCA算法降低性能较差的一般节点和恶意节点对区块共识效率的影响,提高交易吞吐量,降低平均交易时延和平均节点通信开销。Abstract: Because heterogeneous nodes of internet of vehicles have big performance difference and mobility, it leads that blockchain consensus algorithm has many problems, such as low transaction throughput and large transaction delay. Therefore, an Efficient Consistency Consensus Algorithm (ECCA) of blockchain for heterogeneous nodes in the internet of vehicles is proposed. In ECCA, the heterogeneous nodes of internet of vehicles which consists of verification nodes, general nodes and malicious nodes are considered. The credit rating mechanism is proposed to realize the classification of credit rating and division of three types of heterogeneous nodes. Then, a cross-region node identity change mechanism is proposed to adjust timely the node identity in the current region is proposed. Finally, an improved consensus algorithm is proposed to meet the timeliness requirement of the internet of vehicles. The simulation results show that the ECCA algorithm can reduce the impact of poorly performing general nodes and malicious nodes on the efficiency of block consensus, and increase transaction throughput and reduces average transaction delay and average node communication overhead.
-
Key words:
- Internet of vehicles /
- Heterogeneous nodes /
- Blockchain /
- Consistency consensus /
- Credit rating
-
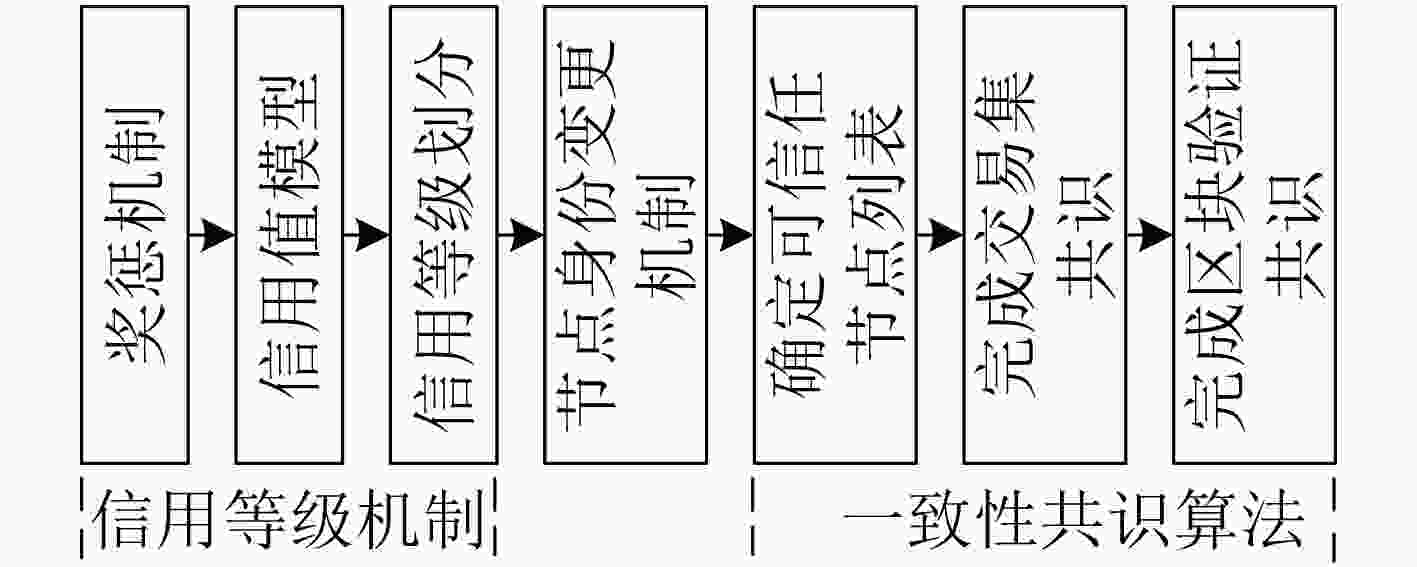
表 1 面向车联网异构节点的区块链高效一致性共识算法(ECCA)算法流程
输入: 网络中节点的基本信息 输出: 网络对车联网数据的区块共识结果 (1) $\gamma $=60; $\kappa $=60; $\theta $=180; $\upsilon $=0.01; $\sigma $=2; ···; (2) while 1 (3) if 当前不是第一次区块共识 then (4) 各区域根据前一次区块共识结果执行奖惩机制; (5) end (6) 各区域将各节点的累积表现分转换为累积信用值,并通过
FCM聚类方法进行信用等级划分;(7) if各区域中验证节点数量小于下限阈值${\vartheta _{1}}$或各区域中验证节
点数量大于上限阈值${\vartheta _{2}}$ then(8) 该区域执行节点身份变更机制,及时调整区域内节点身份; (9) end (10) if 事务范围只在单个区域内部 then (11) 该区域内部的全部验证节点选为参与区块共识的节点; (12) else (13) 多区域内的全部验证节点选为参与区块共识的节点; (14) end (15) 参与区块共识的验证节点通过可通信列表与节点信任等
级,确定其可信任节点列表;(16) 参与区块共识的验证节点结合节点的信用等级权重交易,
统计投票结果,确定交易集共识结果;(17) 参与区块共识的验证节点进行区块验证共识; (18) if 事务范围只在单个区域内部 then (19) 将区块写入到该区域从链; (20) else (21) 将区块写入全局主链; (22) end (23) end -
[1] KANG Jiawen, XIONG Zehui, NIYATO D, et al. Toward secure blockchain-enabled internet of vehicles: Optimizing consensus management using reputation and contract theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(3): 2906–2920. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2894944 [2] LAI Chengzhe, LU Rongxing, ZHENG Dong, et al. Security and privacy challenges in 5G-enabled vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(2): 37–45. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.1900220 [3] DWORK C and NAOR M. Pricing via processing or combatting junk mail[C]. 12th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 1992: 139–147. doi: 10.1007/3-540-48071-4_10. [4] 王缵, 田有亮, 李秋贤, 等. 基于信用模型的工作量证明算法[J]. 通信学报, 2018, 39(8): 185–198. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018138WANG Zuan, TIAN Youliang, LI Qiuxian, et al. Proof of work algorithm based on credit model[J]. Journal on Communications, 2018, 39(8): 185–198. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2018138 [5] LIU Yinqiu, WANG Kun, LIN Yun, et al. LightChain: A lightweight blockchain system for industrial internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(6): 3571–3581. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2904049 [6] LI Xinyu, XU Jing, FAN Xiong, et al. Puncturable signatures and applications in proof-of-stake blockchain protocols[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 3872–3885. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.3001738 [7] FAN Xinxin and CHAI Qi. Roll-DPoS: A randomized delegated proof of stake scheme for scalable blockchain-based internet of things systems[C]. The 15th EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services, New York, USA, 2018: 482–484. doi: 10.1145/3286978.3287023. [8] 谈森鹏, 杨超. 区块链DPoS共识机制的研究与改进[J]. 现代计算机, 2019(6): 11–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2019.06.003TAN Senpeng and YANG Chao. Research and improvement of blockchain’s DPoS consensus mechanism[J]. Modern Computer, 2019(6): 11–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2019.06.003 [9] 黄嘉成, 许新华, 王世纯. 委托权益证明共识机制的改进方案[J]. 计算机应用, 2019, 39(7): 2162–2167. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018122527HUANG Jiacheng, XU Xinhua, and WANG Shichun. Improved scheme of delegated proof of stake consensus mechanism[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(7): 2162–2167. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018122527 [10] CASTRO M and LISKOV B. Practical byzantine fault tolerance[C]. The 3rd Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, New Orleans, USA, 1999: 173–186. doi: 10.1145/571637.571640. [11] 闵新平, 李庆忠, 孔兰菊, 等. 许可链多中心动态共识机制[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(5): 1005–1020. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.01005MIN Xinping, LI Qiangzhong, KONG Lanju, et al. Permissioned blockchain dynamic consensus mechanism based multi-centers[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(5): 1005–1020. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.01005 [12] HAN Runchao, SHAPIRO G, GRAMOLI V, et al. On the performance of distributed ledgers for internet of things[J]. Internet of Things, 2020, 10: 100087. doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2019.100087 [13] D’AGOSTINO S F and TIMPANARO J P. Ripple protocol performance improvement: Small world theory applied to cross border payments[C]. XIX Simposio Argentino de Ingeniería de Software (ASSE)-JAIIO 47 (CABA, 2018), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2018: 143–154. doi: 10915/70884. [14] WANG Miao, WANG Guiling, ZHANG Yujun, et al. A high-reliability multi-faceted reputation evaluation mechanism for online services[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2019, 12(6): 836–850. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2016.2638812 [15] KANG Jiawen, YU Rong, HUANG Xumin, et al. Blockchain for secure and efficient data sharing in vehicular edge computing and networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 4660–4670. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875542 [16] ZHAO Pincan, FU Yuchuan, LI Fan, et al. Blockchain-enabled targeted information dissemination framework in vehicular networks[C]. 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Victoria, USA, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTC2020-Fall49728.2020.9348576. [17] WANG Mingfu and KU H. Utilizing historical data for corporate credit rating assessment[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 165: 113925. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113925 [18] ZHANG Xiaoyan, ZHU Shanying, HE Jianping, et al. Credit rating based real-time energy trading in microgrids[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 236: 985–996. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.12.013 [19] ARUNKUMAR N, MOHAMMED M A, GHANI M K A, et al. K-means clustering and neural network for object detecting and identifying abnormality of brain tumor[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(19): 9083–9096. doi: 10.1007/s00500-018-3618-7 [20] LEI Tao, JIA Xiaohong, ZHANG Yanning, et al. Significantly fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm based on morphological reconstruction and membership filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(5): 3027–3041. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2796074 [21] WANG Yuhao, CAI Shanbin, LIN Changlong, et al. Study of blockchains’s consensus mechanism based on credit[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 10224–10231. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2891065 -





 下载:
下载:
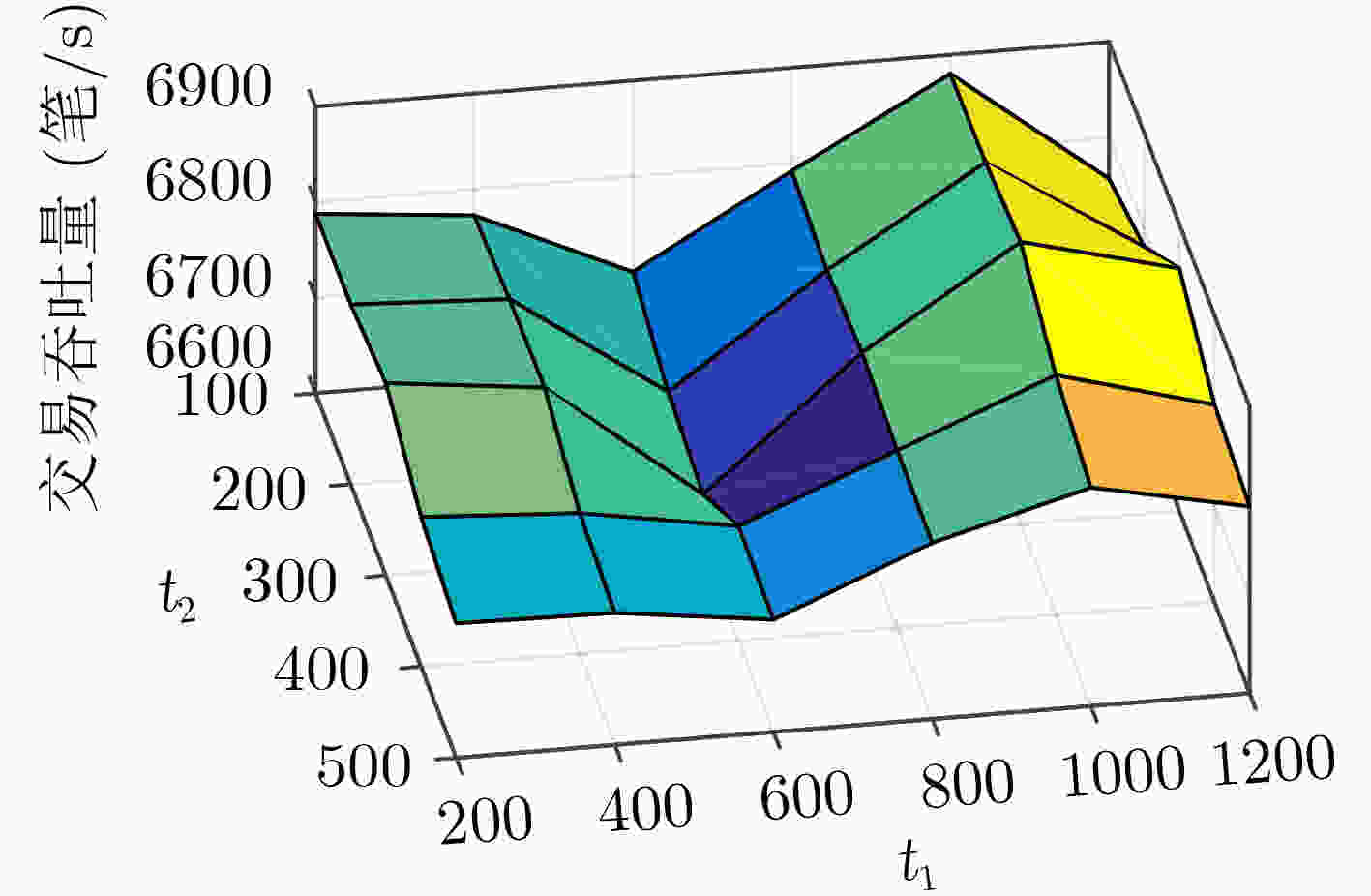
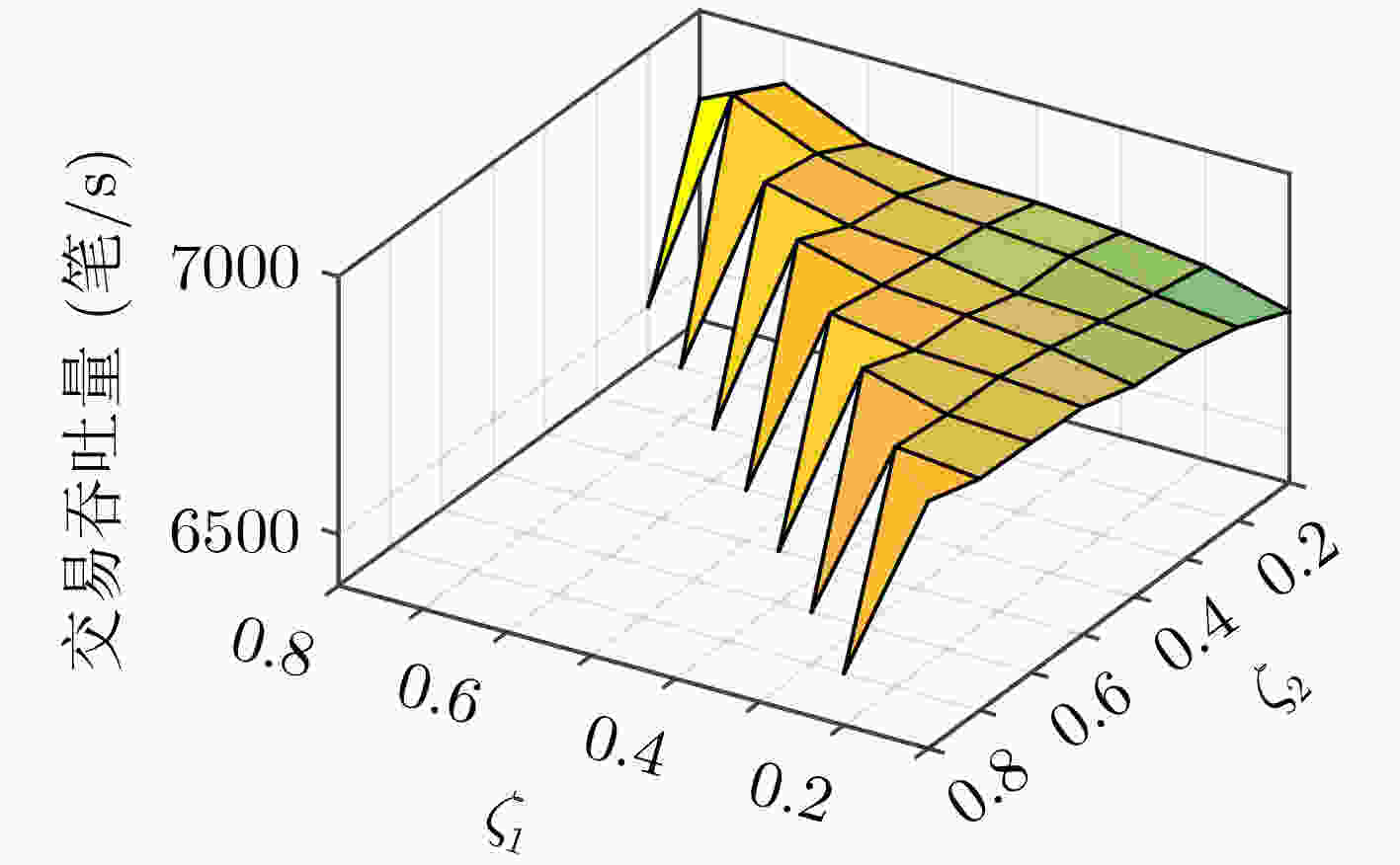
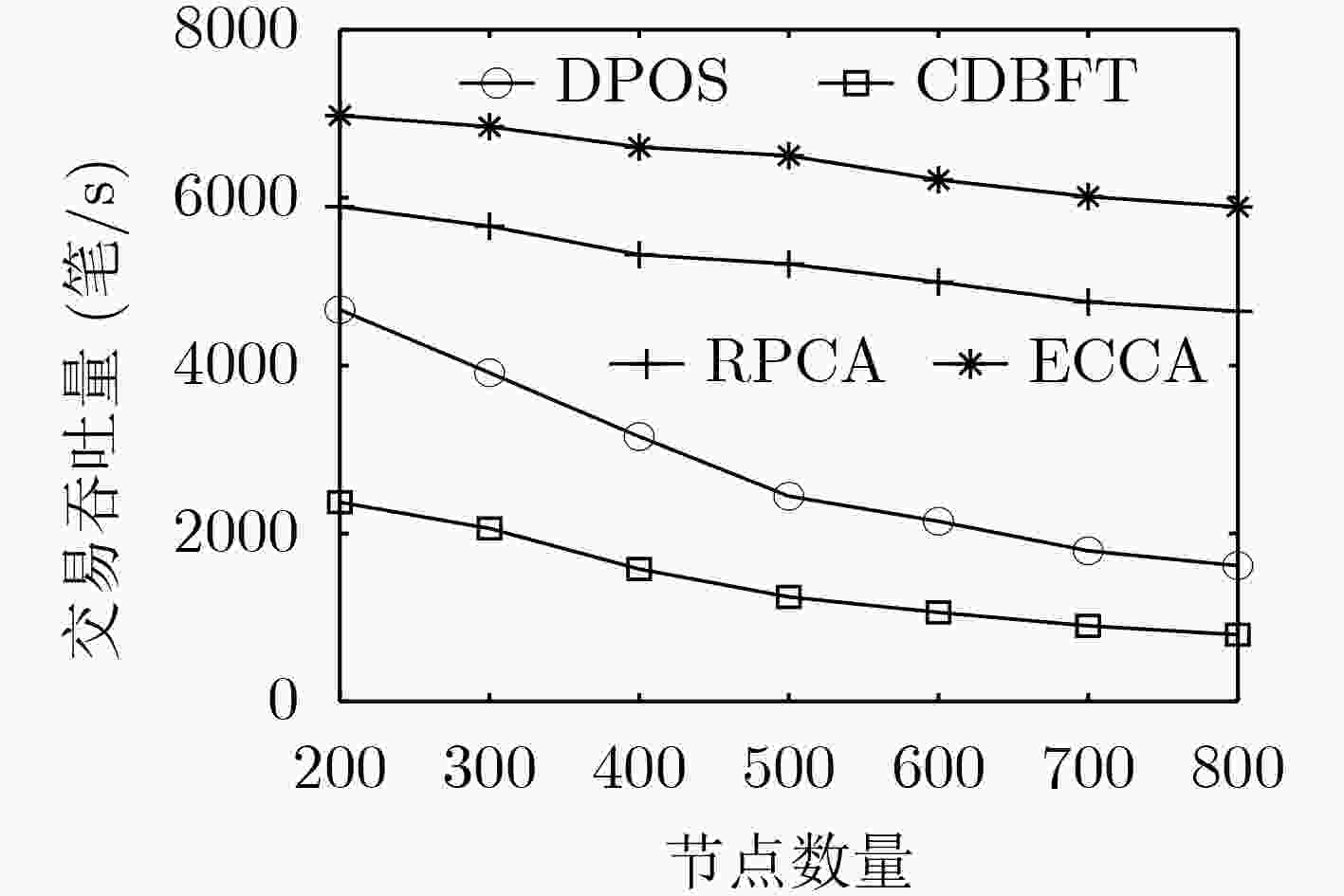
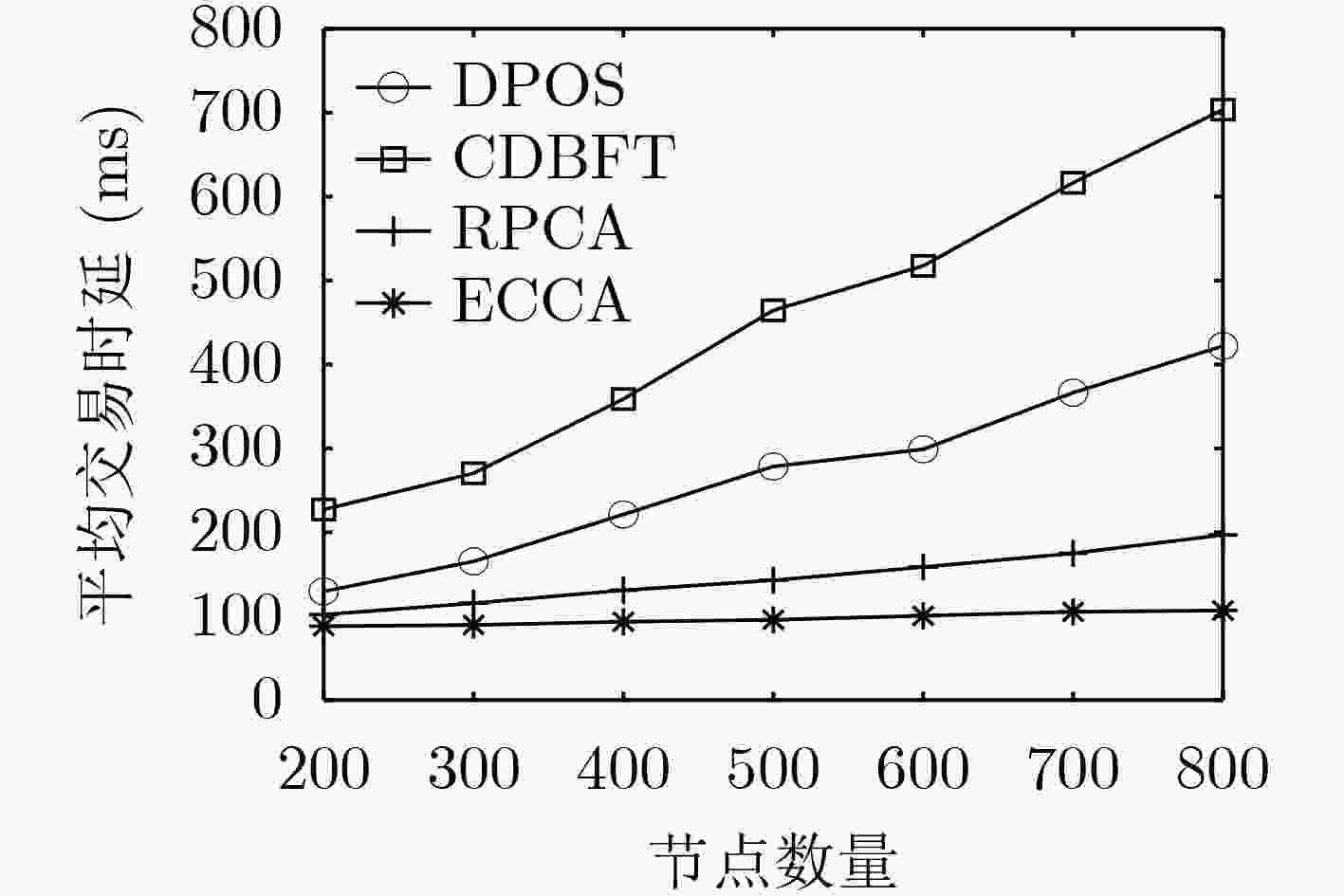


 下载:
下载:
