An Anchor-free Method Based on Context Information Fusion and Interacting Branch for Ship Detection in SAR Images
-
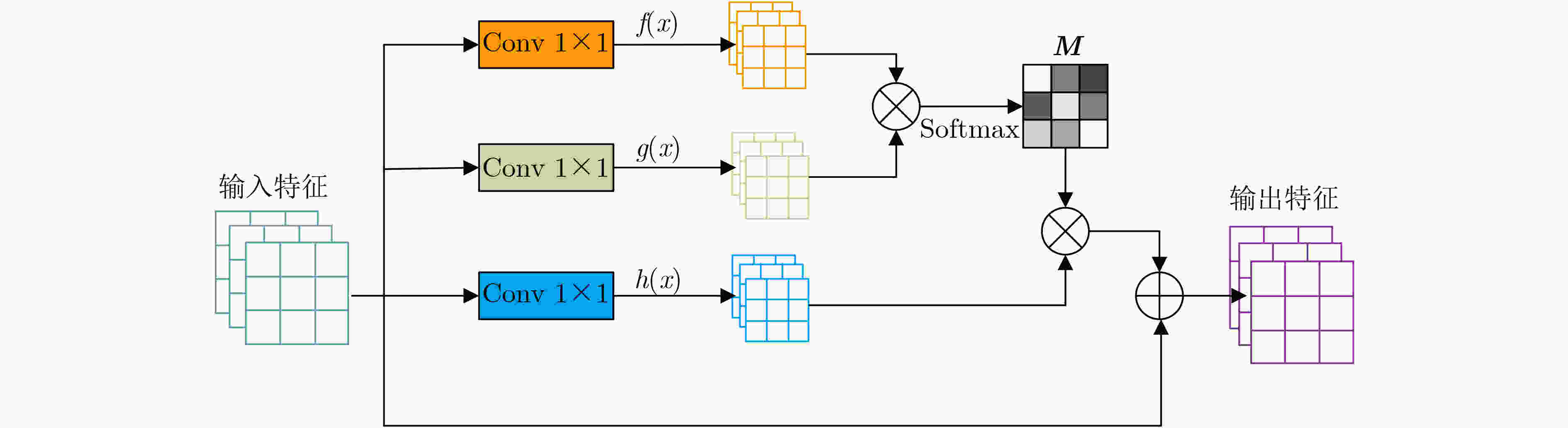
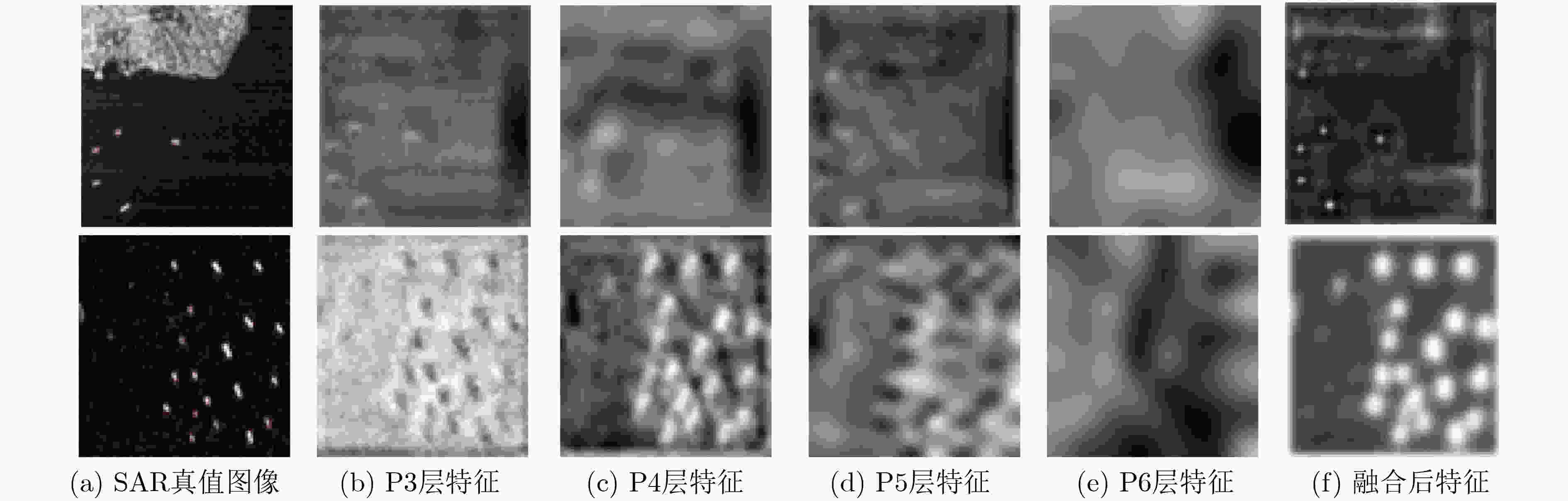
摘要: SAR图像中舰船目标稀疏分布、锚框的设计,对现有基于锚框的SAR图像目标检测方法的精度和泛化性有较大影响,因此该文提出一种上下文信息融合与分支交互的SAR图像舰船目标无锚框检测方法,命名为CI-Net。考虑到SAR图中舰船尺度的多样性,在特征提取阶段设计上下文融合模块,以自底向上的方式融合高低层信息,结合目标上下文信息,细化提取到的待检测特征;其次,针对复杂场景中目标定位准确性不足的问题,提出分支交互模块,在检测阶段利用分类分支优化回归分支的检测框,改善目标定位框的精准性,同时将新增的IOU分支作用于分类分支,提高检测网络分类置信度,抑制低质量的检测框。实验结果表明:在公开的SSDD和SAR-Ship-Dataset数据集上,该文方法均取得了较好的检测效果,平均精度(AP)分别达到92.56%和88.32%,与其他SAR图舰船检测方法相比,该文方法不仅在精度上表现优异,在摒弃了与锚框有关的复杂计算后,较快的检测速度,对SAR图像实时目标检测也有一定的现实意义。Abstract: Ship targets are sparsely distributed in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images, and the design of anchor frame has a great impact on the accuracy and generalization of existing SAR image target detection method based on anchor. Therefore, an anchor-free method based on context information fusion and interacting branch for ship detection in SAR images (named as CI-Net) is proposed. Considering the diversity of ship scale in SAR images, a context fusion module is designed in the feature extraction stage, integrate high and low levels of information in a bottom-up manner and refine the extracted features to be detected by combining with the target context information. Secondly, aiming at the problem of complex targets in the scene is not accurate, interacting branch module is put forward. In the detection phase, use classification branches optimization regression testing box is used, to improve the target frame’s precision. At the same time, the new Intersection over Union (IOU) is used on branches of the classification to improve detection network classification confidence, to inhibit detection box of low quality. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves good detection results on both SSDD and SAR-Ship-Dataset, with Average Precision (AP) reaching 92.56% and 88.32%, respectively. Compared with other ship detection methods in SAR image, the proposed method not only has excellent performance in accuracy, but also has a faster detection speed after abandoning the complex calculation related to anchor frame. It also has a certain practical significance for real-time target detection in SAR image.
-
Key words:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) /
- Ship detection /
- Anchor-free /
- Context information /
- Self-attention
-
表 1 舰船数据集的基本信息
数据集 传感器来源 空间分辨率(m) 极化方式 输入图像大小 场景 SSDD RadarSat-2, TerraSAR-X, Sentinel-1 1~15 VV, HH, VH, HV 500×500 近海、近岸区域 SAR-Ship Dataset GF-3, Sentinel-1 3, 5, 8, 10等 VV, HH, VH, HV 256×256 远海区域 表 2 模型实验结果
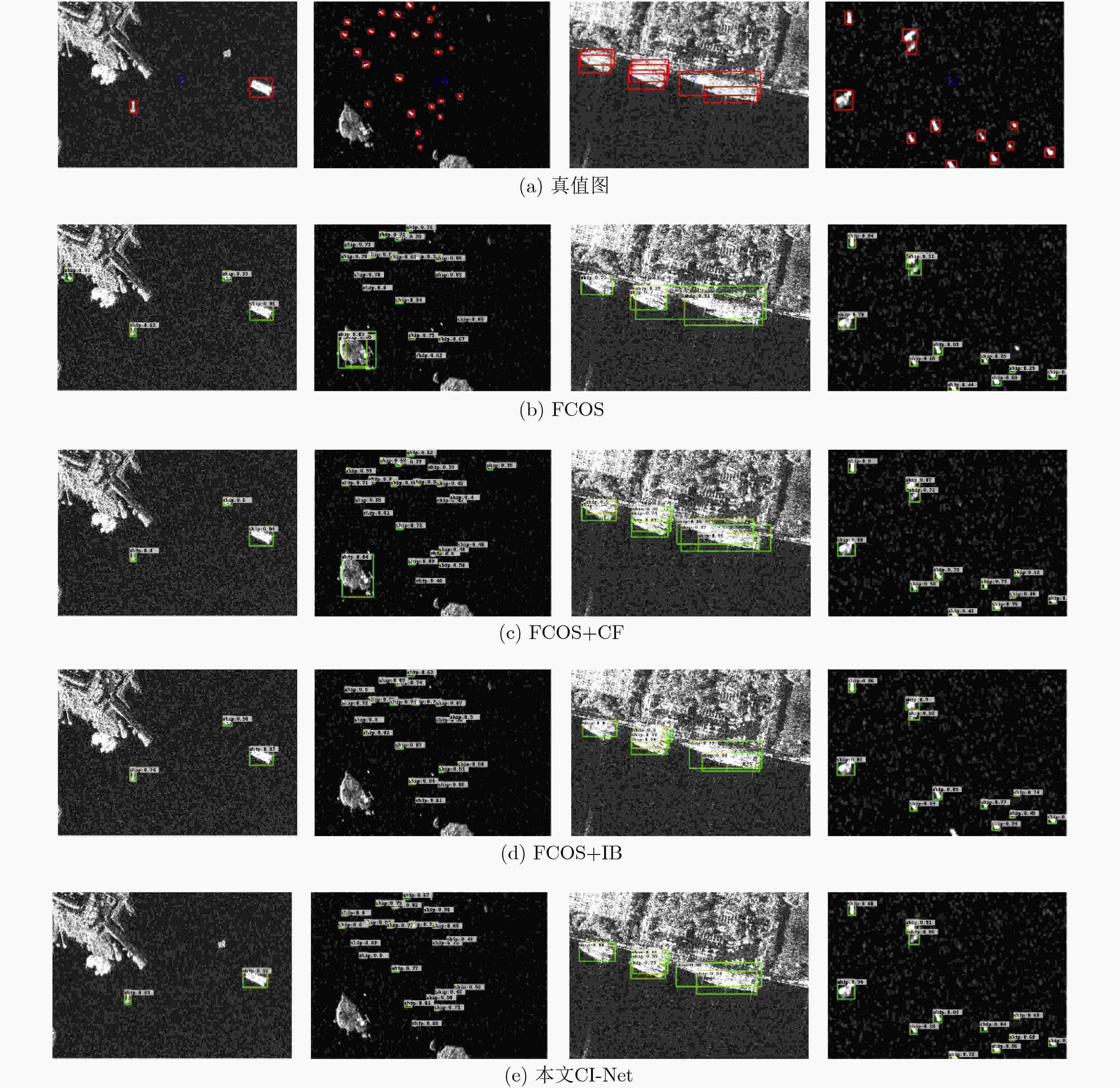
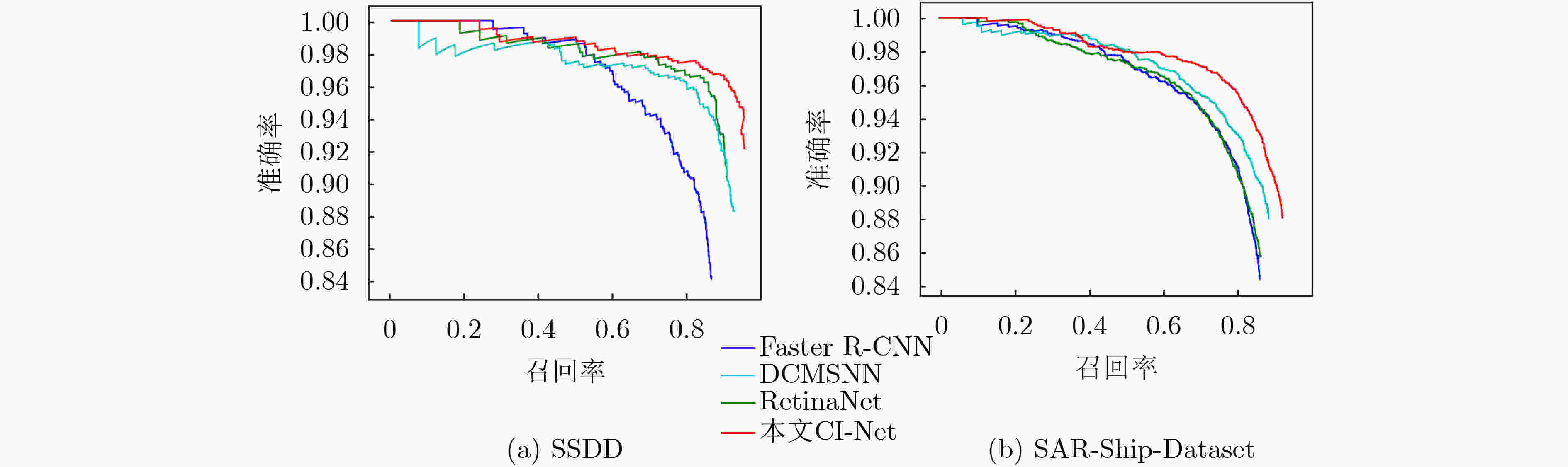
表 3 不同方法在SSDD数据集上检测性能对比
方法 单阶段 无锚框 召回率(%) 准确率(%) 平均精度(%) F1(%) fps Faster R-CNN × × 85.39 84.18 83.07 84.78 11 RetinaNet √ × 89.40 90.43 87.94 89.91 16 DCMSNN × × 91.59 88.33 89.34 89.93 8 本文CI-Net √ √ 94.27 92.04 92.56 93.14 28 表 4 不同方法在SAR-Ship-Dataset上检测性能对比
方法 单阶段 无锚框 召回率(%) 准确率(%) 平均精度(%) F1(%) fps Faster R-CNN × × 84.30 84.47 81.77 84.39 13 RetinaNet √ × 84.60 85.83 82.02 85.21 21 DCMSNN × × 86.64 88.07 84.36 87.35 9 本文CI-Net √ √ 90.28 88.14 88.32 89.20 34 -
[1] 杨国铮, 禹晶, 肖创柏, 等. 基于形态字典学习的复杂背景SAR图像舰船尾迹检测[J]. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(10): 1713–1725. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160274YANG Guozheng, YU Jing, XIAO Chuangbai, et al. Ship Wake detection in SAR images with complex background using morphological dictionary learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(10): 1713–1725. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160274 [2] 李健伟, 曲长文, 彭书娟, 等. 基于生成对抗网络和线上难例挖掘的SAR图像舰船目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 143–149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180050LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, PENG Shujuan, et al. Ship detection in SAR images based on generative adversarial network and online hard examples mining[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 143–149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180050 [3] HOU Biao, CHEN Xingzhong, and JIAO Licheng. Multilayer CFAR detection of ship targets in very high resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 811–815. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2362955 [4] LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and SHAO Jiaqi. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications, Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA.2017.8124934. [5] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [6] JIAO Jiao, ZHANG Yue, SUN Hao, et al. A densely connected end-to-end neural network for multiscale and multiscene SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 20881–20892. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2825376 [7] 胡昌华, 陈辰, 何川, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的SAR图像舰船小目标检测[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2019, 27(3): 397–405, 414. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2019.03.018HU Changhua, CHEN Chen, HE Chuan, et al. SAR detection for small target ship based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2019, 27(3): 397–405, 414. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2019.03.018 [8] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.106. [9] CUI Zongyong, LI Qi, CAO Zongjie, et al. Dense attention pyramid networks for multi-scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8983–8997. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923988 [10] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. [11] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [12] SHRIVASTAVA A, GUPTA A, and GIRSHICK R. Training region-based object detectors with online hard example mining[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 761–769. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.89. [13] DUAN Kaiwen, BAI Song, XIE Lingxi, et al. CenterNet: Keypoint triplets for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 6568–6577. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00667. [14] TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, CHEN Hao, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 9626–9635. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00972. [15] PANG Jiangmiao, CHEN Kai, SHI Jianping, et al. Libra R-CNN: Towards balanced learning for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 821–830. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00091. [16] CAO Yue, XU Jiarui, LIN S, et al. GCNet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, South Korea,2019: 1971–1980. doi: 10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00246. [17] WANG Xiaolong, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7794–7803. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00813. [18] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [19] LI Huan and TANG Jinglei. Dairy goat image generation based on improved-self-attention generative adversarial networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 62448–62457. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2981496 [20] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318–327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 [21] WANG Yuanyuan, WANG Chao, ZHANG Hong, et al. A SAR dataset of ship detection for deep learning under complex backgrounds[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(7): 765. doi: 10.3390/rs11070765 [22] HUANG Lanqing, LIU Bin, LI Boying, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to Sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195–208. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755672 [23] KANG Miao, JI Kefeng, LENG Xiangguang, et al. Contextual region-based convolutional neural network with multilayer fusion for SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8): 860. doi: 10.3390/rs9080860 -





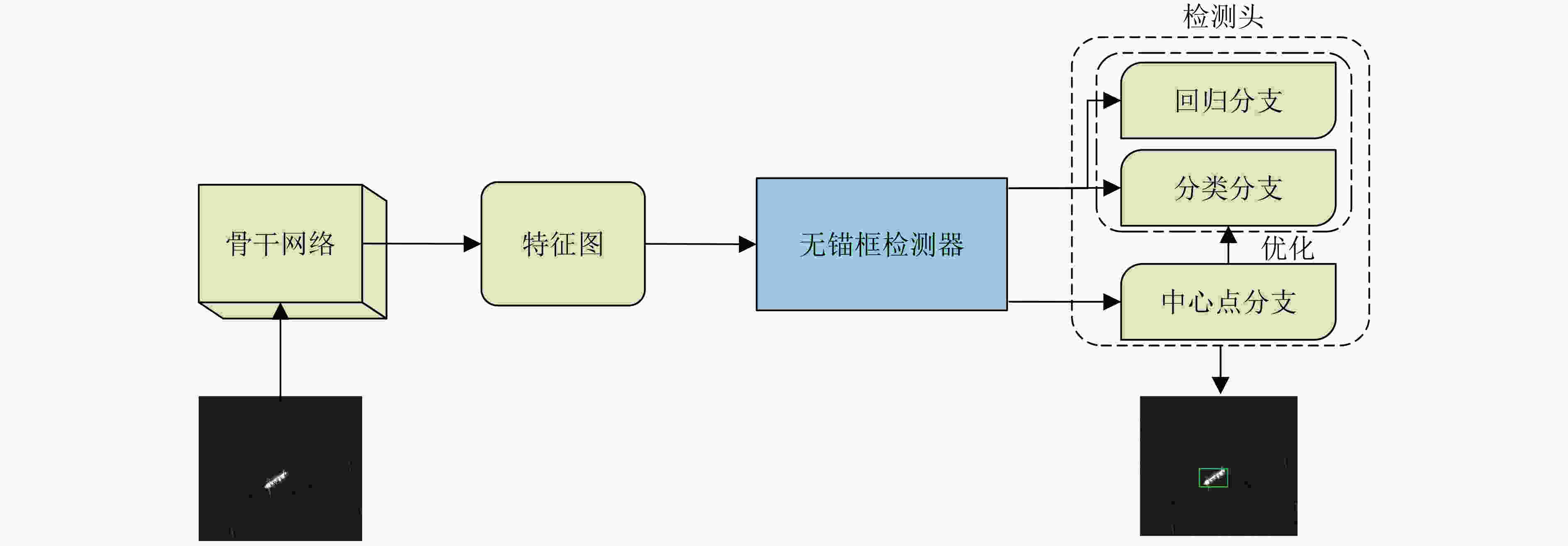
 下载:
下载:
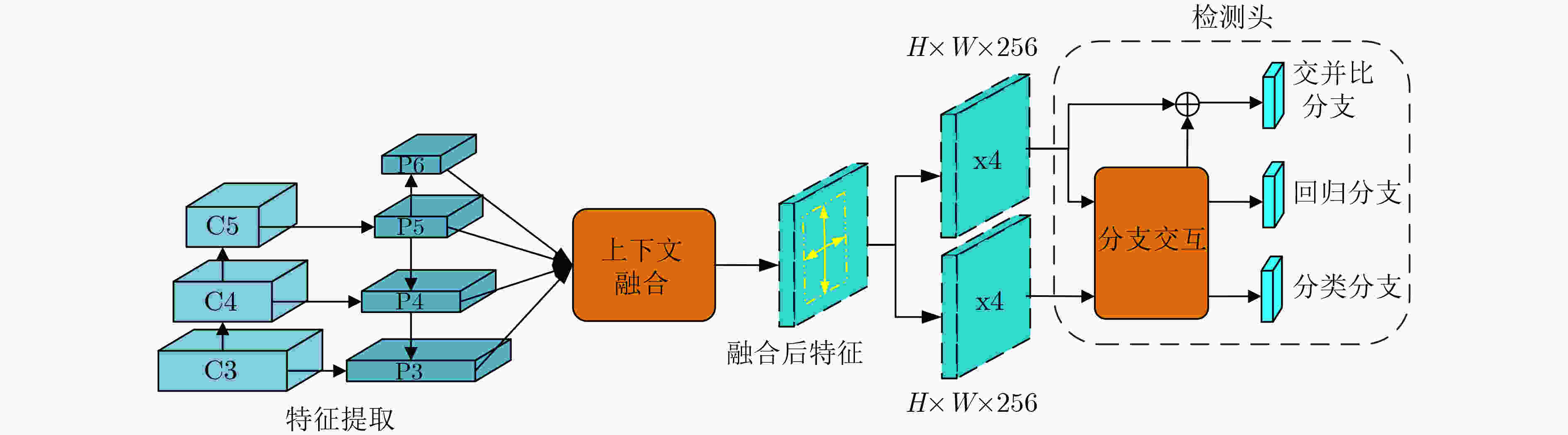
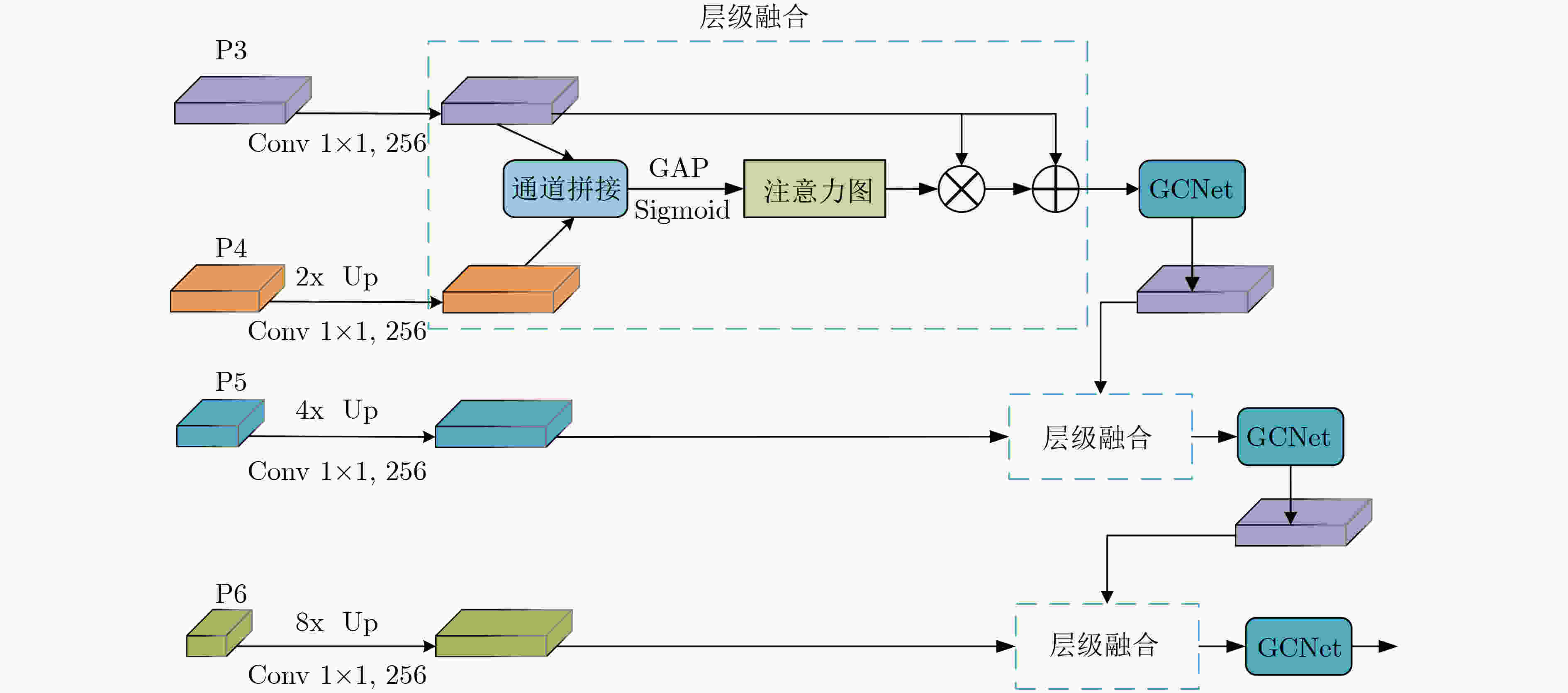
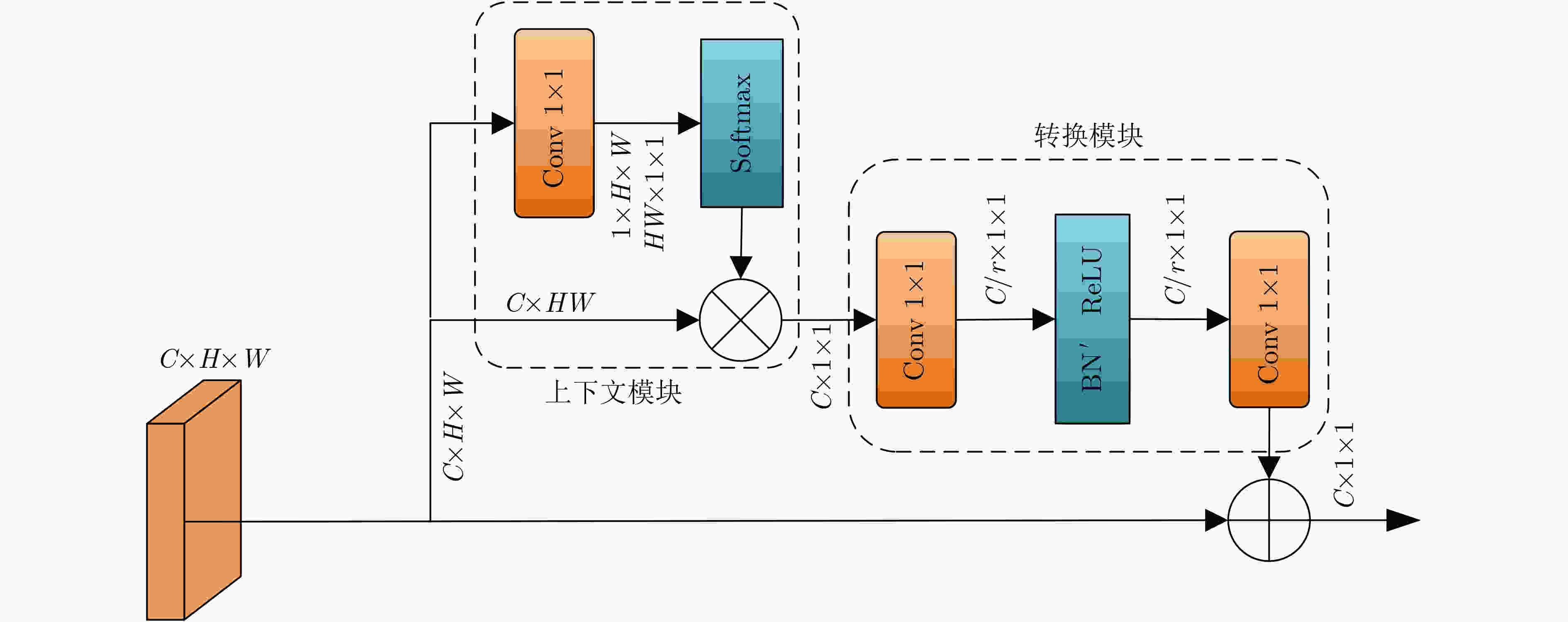


 下载:
下载:
