Research on Prediction Based Emergency Resource Allocation in 5G Uplink
-
摘要: 作为5G uRLLC的典型应用场景,工业应用对于数据传输的延迟和可靠性要求越来越严苛,且多样化业务带来的多样性数据的融合传输是当前亟待解决的问题,其中高效的无线资源调度以保障各种数据共存互不干扰、稳定可靠地传输和系统安全稳定的运行是重要的挑战之一。为解决无线网络中周期性的监测数据与紧急数据的协同传输问题,该文针对工业多样化业务数据传输场景中的5G上行链路传输,提出一种基于预测的资源分配方案,该方案利用自回归滑动平均(ARMA)模型根据紧急数据的历史传输周期的激活率预测下一传输周期的紧急数据激活率,根据预测激活率动态地为周期数据和紧急数据预留资源,以在满足紧急数据传输条件的前提下最小化对周期数据传输的影响。仿真实验表明,与传统的资源分配方案相比所提方案能有效降低紧急数据传输对周期数据的影响,并能提升频谱资源的利用率。Abstract: As a typical application scenario of 5G uRLLC, the data transmission delay and reliability requirements of industrial applications are more and more stringent, and the convergent transmission of diversified data becomes an urgent problem to be solved. One of the important challenges is the efficient scheduling of wireless resources to ensure the coexistence of various data transmission without interfering with each other and stable operation of the system. In view of 5G uplink transmission in industrial transmission scenarios, a prediction-based resource allocation scheme is proposed, which uses Auto Regressive Moving Average (ARMA) model to predict the activation rates of the next transmission cycle based on the historical data. Then the resources are dynamically reserved for periodic and emergency data, so as to minimize the impact on periodic data transmission under the premise of meeting the emergency data transmission conditions. Experimental results show that, compared with the traditional resource allocation scheme, this scheme can effectively reduce the impact of emergency data transmission on periodic data and improve the utilization of spectrum resources.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
仿真参数 参数值 数据包大小$B$ 100 bit 紧急设备数量${N_{\rm{s}}}$ 30 周期设备数量${N_{\rm{p}}}$ 22 总带宽$W$ 15 MHz 子载波间隔$\varpi $ 15 kHz 最小传输时间间隔$\tau $ 0.144 ms(2个符号长度) ACK时间间隔${t_{{\rm{ack}}}}$ 0.288 ms 延迟限制$T$ 1 ms 丢失率限制${P_{\rm{f}}}$ 10–5 重传数据包数量$\beta $ 3 -
[1] ESSWIE A A and PEDERSEN K I. Multi-user preemptive scheduling for critical low latency communications in 5G networks[C]. 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, Natal, Brazil, 2018: 136–141. doi: 10.1109/ISCC.2018.8538471. [2] PARVEZ I, RAHMATI A, GUVENC I, et al. A survey on low latency towards 5G: RAN, core network and caching solutions[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(4): 3098–3130. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2841349 [3] VITTURI S, ZUNINO C, and SAUTER T. Industrial communication systems and their future challenges: Next-generation ethernet, IIoT, and 5G[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(6): 944–961. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2913443 [4] 刘瑞祥. 基于物联网的煤矿井下监测网络平台关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国矿业大学(北京), 2015.LIU Ruixiang. Research on the key technology of coal mine monitoring network platform based on internet of things[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], China University of Mining and Technology (Beijng), 2015. [5] SHEN Wei, ZHANG Tingting, BARAC F, et al. PriorityMAC: A priority-enhanced MAC protocol for critical traffic in industrial wireless sensor and actuator networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2014, 10(1): 824–835. doi: 10.1109/TII.2013.2280081 [6] FARAG H, GIDLUND M, and ÖSTERBERG P. A delay-bounded MAC protocol for mission- and time-critical applications in industrial wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(6): 2607–2616. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2793946 [7] ELAYOUBI S E, BROWN P, DEGHEL M, et al. Radio resource allocation and retransmission schemes for URLLC over 5G networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(4): 896–904. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2898783 [8] CONDOLUCI M, MAHMOODI T, STEINBACH E, et al. Soft resource reservation for low-delayed teleoperation over mobile networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 10445–10455. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2707319 [9] CHEN Hongyang, WU Jianming, and SHIMOMURA T. New reference signal design for URLLC and eMBB multiplexing in new radio wireless communications[C]. 2018 IEEE 29th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Bologna, Italy, 2018: 1220–1225. [10] ALSENWI M, TRAN N H, BENNIS M, et al. eMBB-URLLC resource slicing: A risk-sensitive approach[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(4): 740–743. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2900044 [11] LI Mingyan, GUAN Xinping, HUA Cunqing, et al. Predictive pre-allocation for low-latency uplink access in industrial wireless networks[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu, USA, 2018: 306–314. [12] BROWN J and KHAN J Y. A Predictive resource allocation algorithm in the LTE uplink for event based M2M applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2015, 14(12): 2433–2446. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2015.2398447 [13] 唐伦, 杨希希, 施颖洁, 等. 无线虚拟网络中基于自回归滑动平均预测的在线自适应虚拟资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 16–23. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180048TANG Lun, YANG Xixi, SHI Yingjie, et al. ARMA-prediction based online adaptive dynamic resource allocation in wireless virtualized networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 16–23. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180048 [14] 陈强. 基于ARMA模型预测的云计算资源调度策略研究[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆大学, 2016.CHEN Qiang. Cloud computing resource scheduling strategy based on ARMA model prediction[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing University, 2016. [15] LIU C R, DUAN H Y, CHEN P W, et al. Improve production efficiency and predict machine tool status using Markov chain and hidden markov model[C]. 2018 8th International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology, Amman, Jordan, 2018: 276–281. [16] 熊余, 杨娅娅, 张振振, 等. 软件定义时分波分复用无源光网络中基于带宽预测的资源分配策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1885–1892. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180837XIONG Yu, YANG Yaya, ZHANG Zhenzhen, et al. Resource allocation based on bandwidth prediction in software-defined time and wavelength division multiplexed passive optical network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1885–1892. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180837 [17] ZHANG Zhengming, CHEN Hongyang, HUA Meng, et al. Double coded caching in ultra dense networks: Caching and multicast scheduling via deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(2): 1071–1086. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2955490 [18] 师圣蔓. 基于机器学习的网络流量预测与应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2019.SHI Shengman. Research on network traffic prediction and application based on machine learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. -





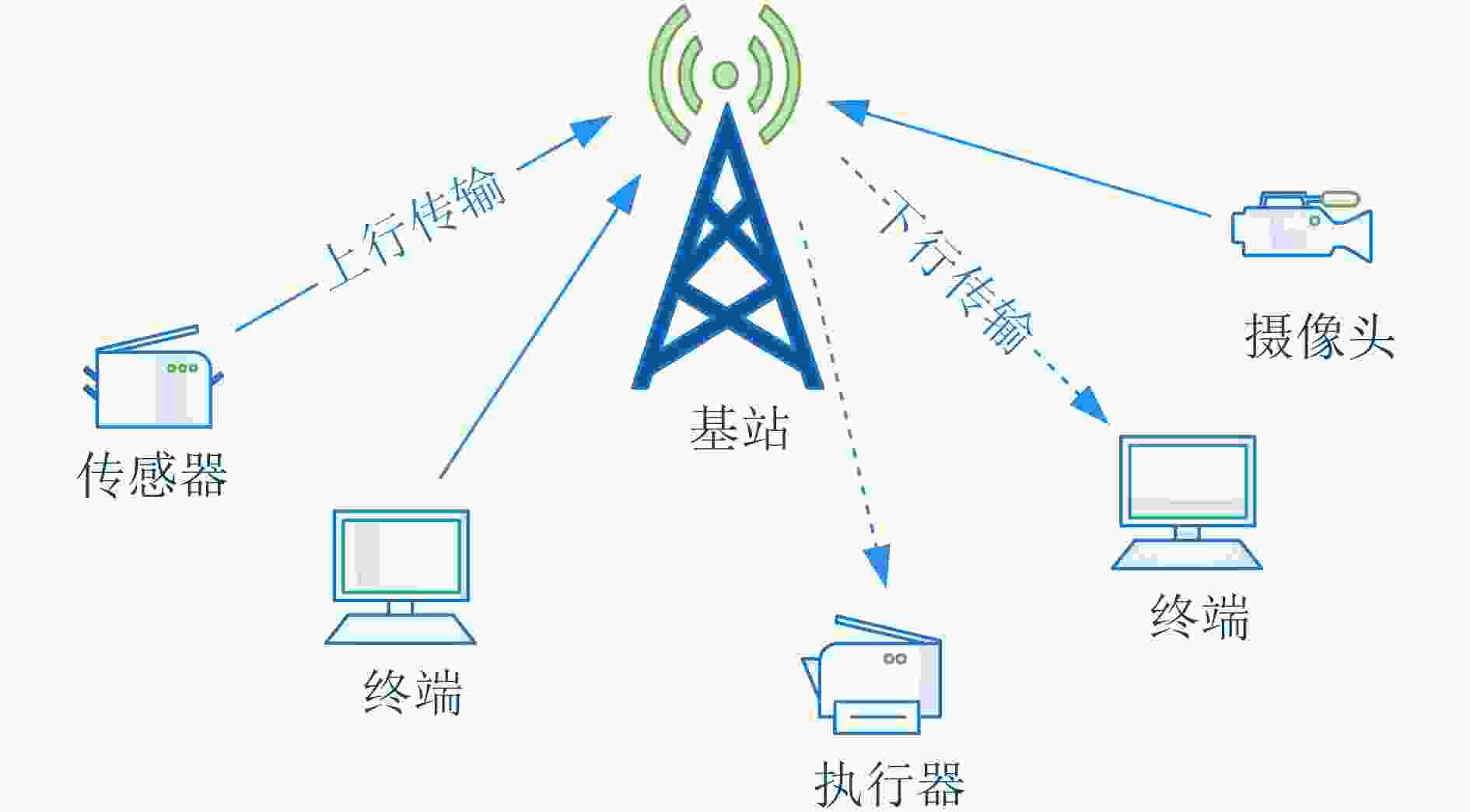
 下载:
下载:
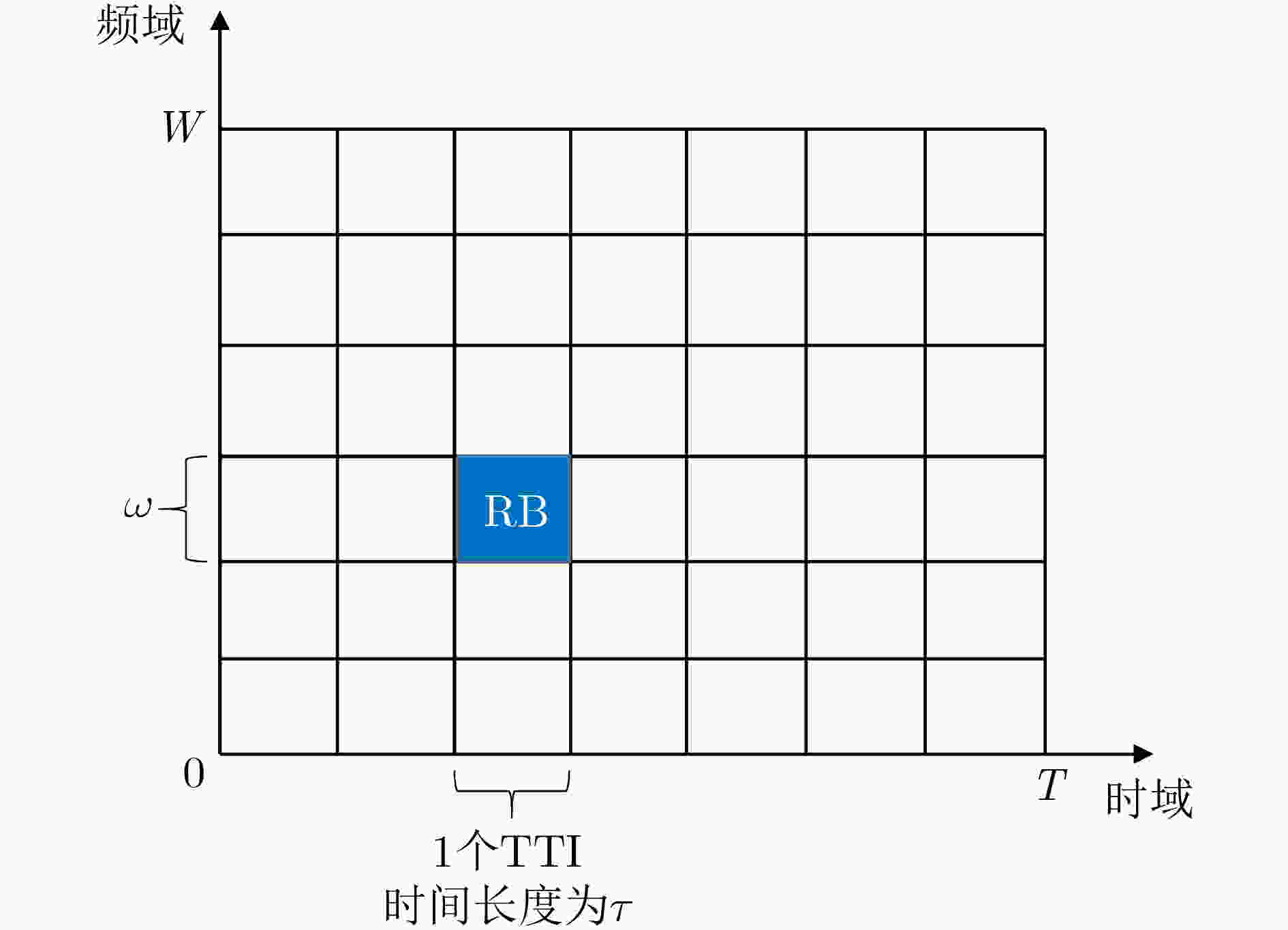
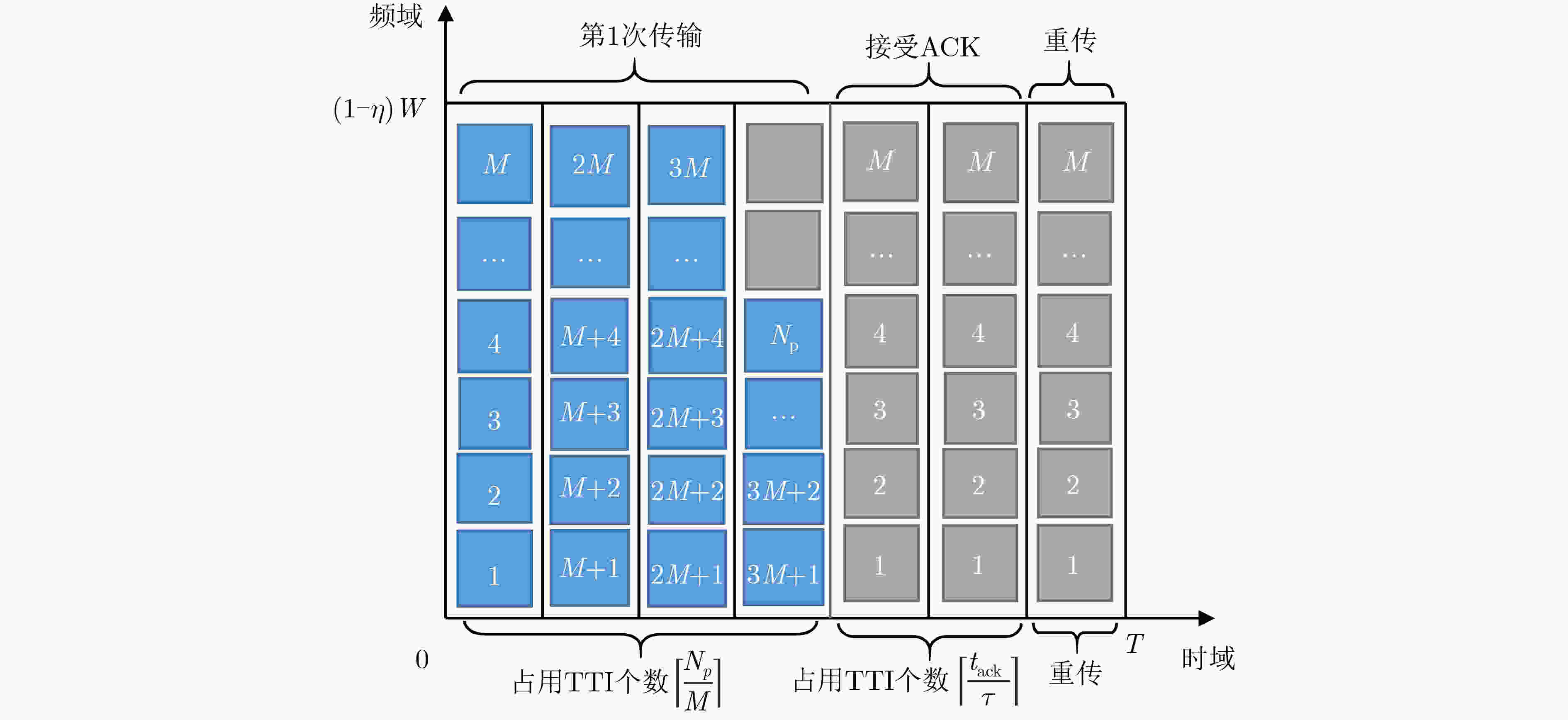
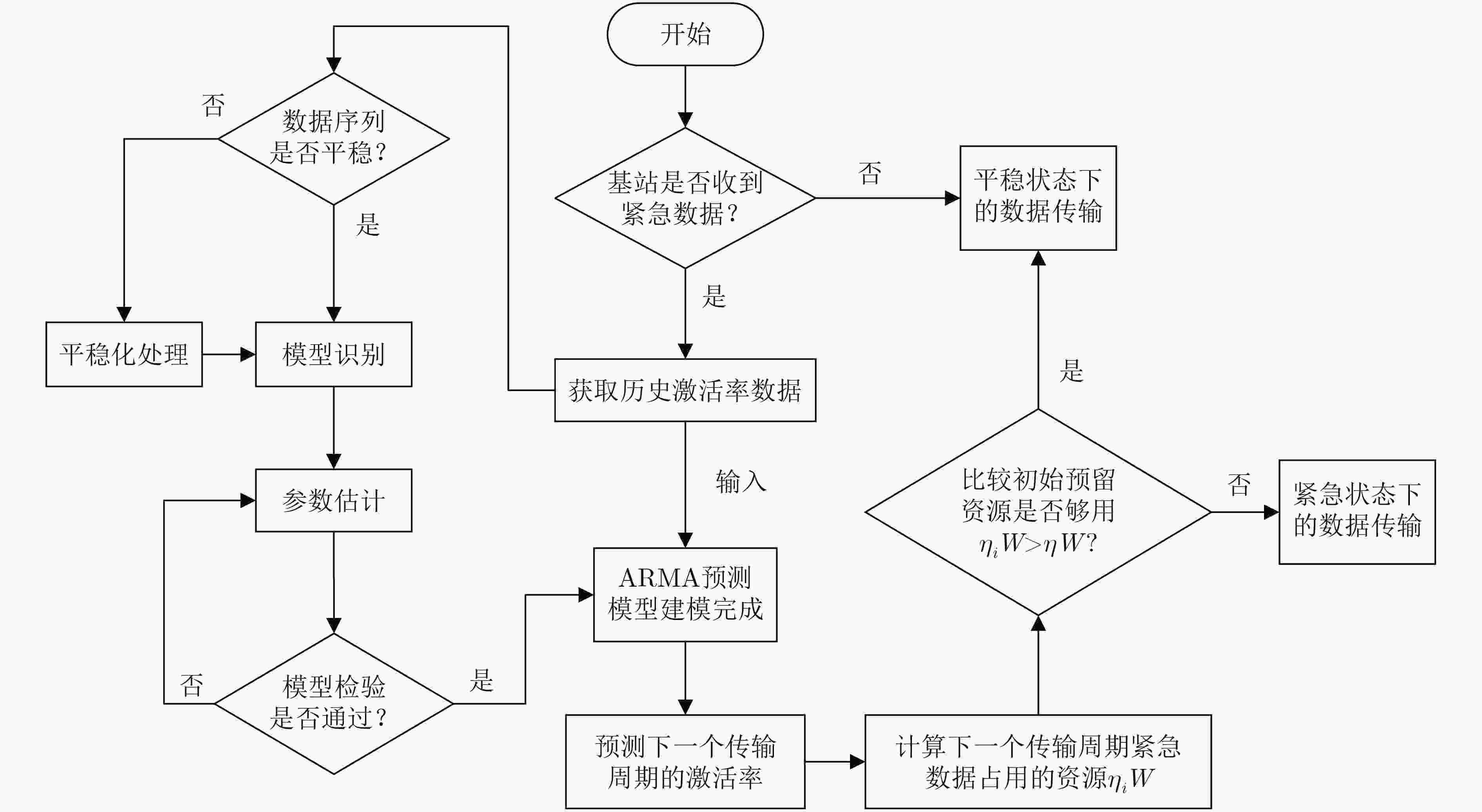
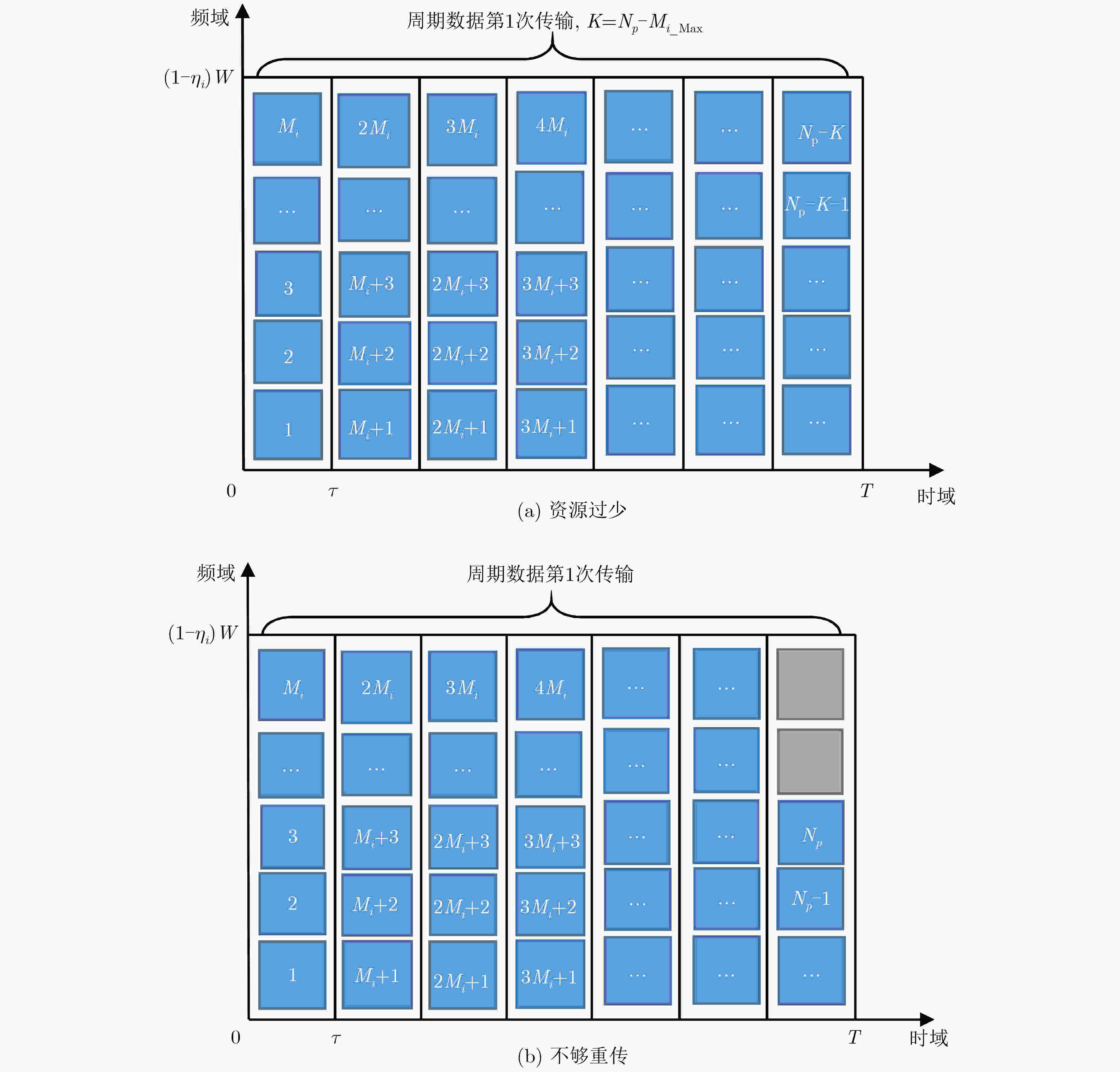
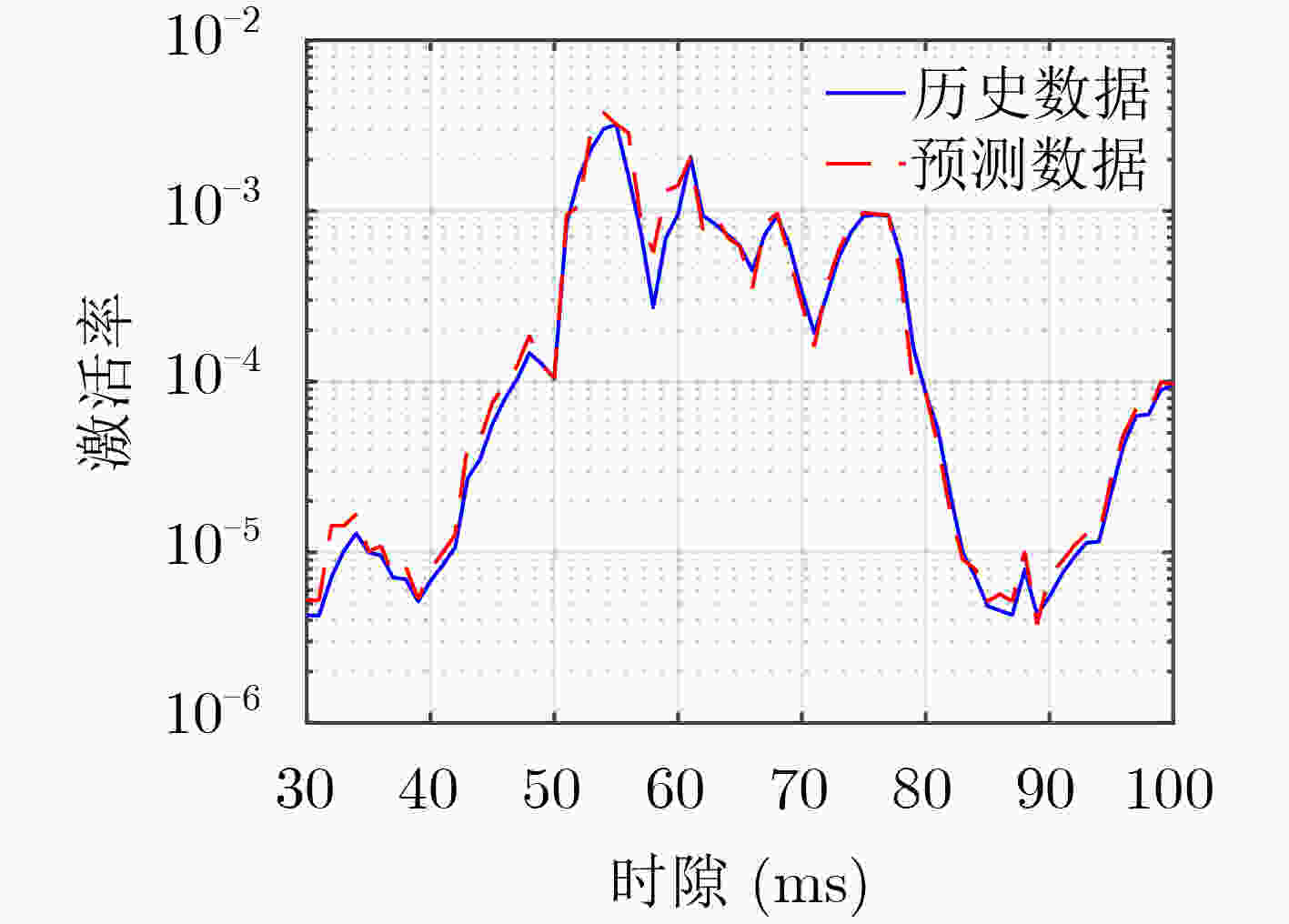
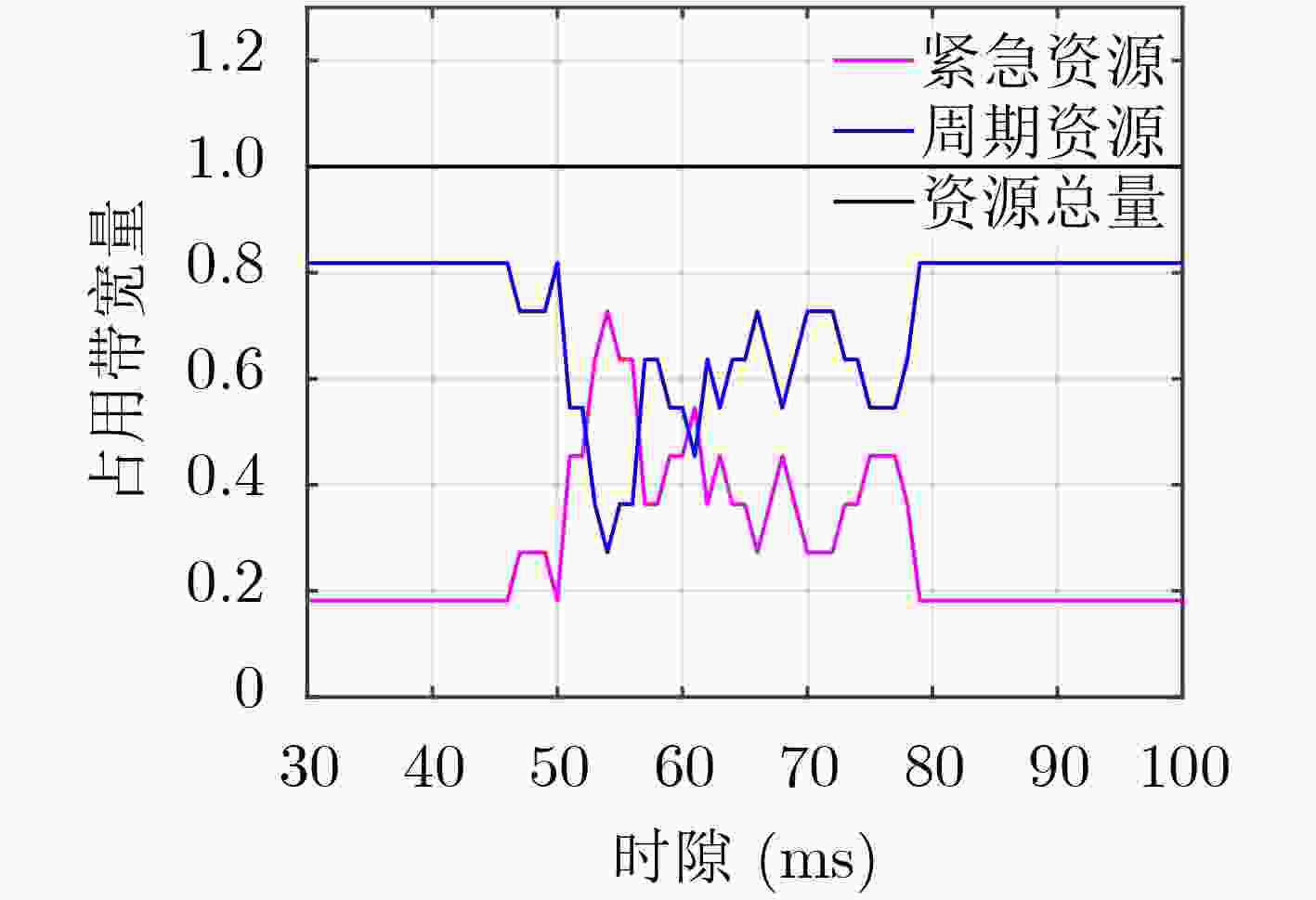
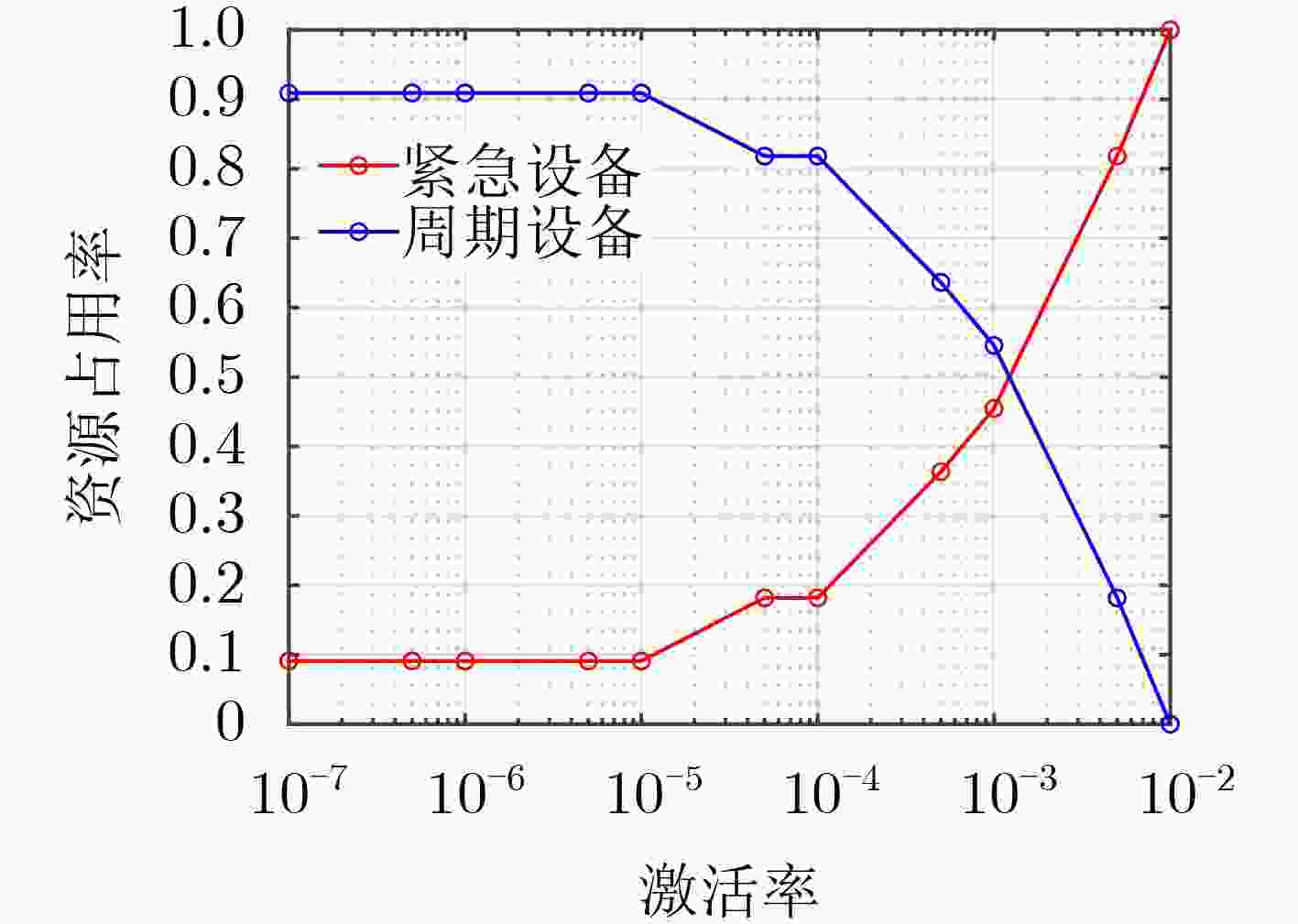
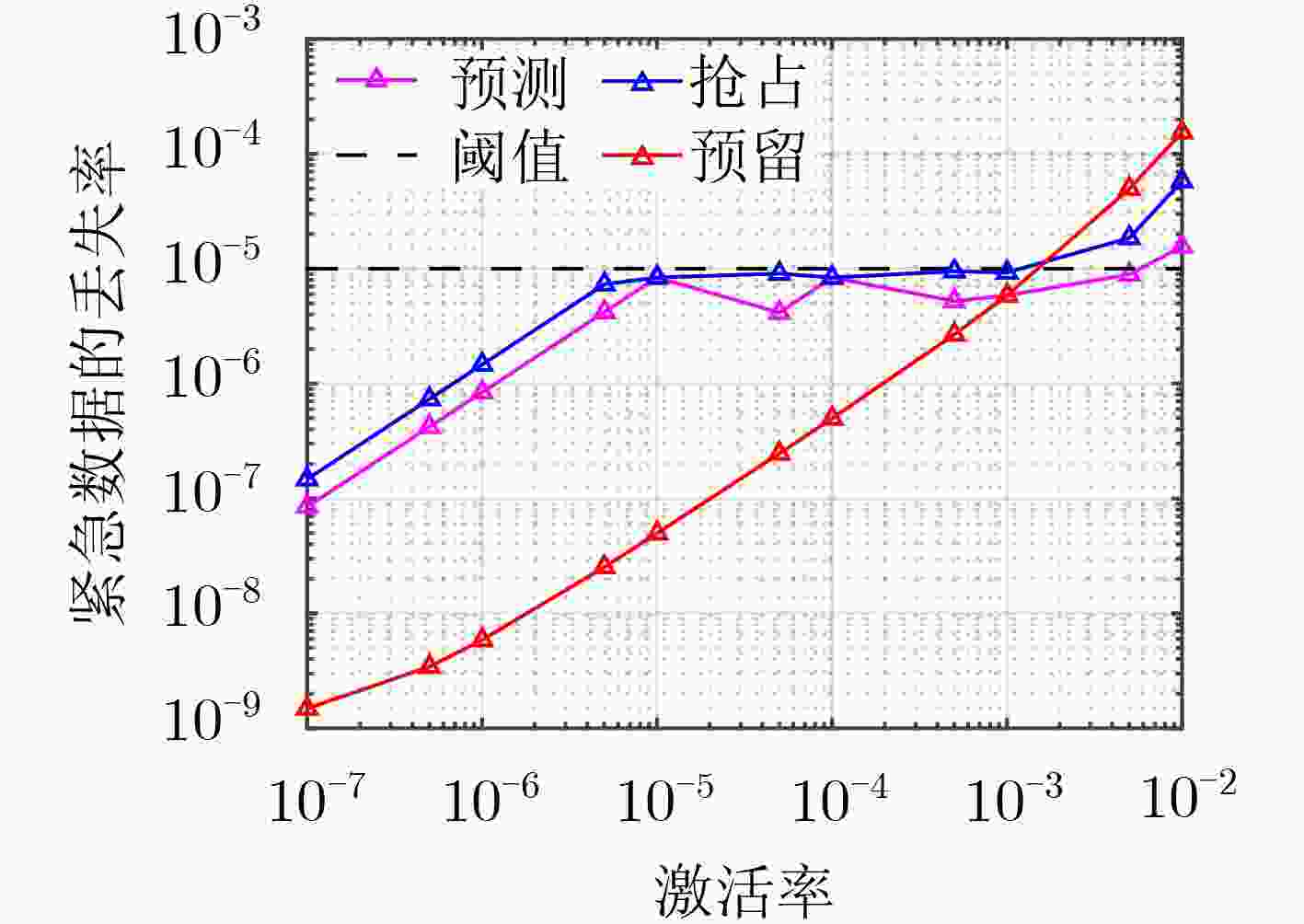
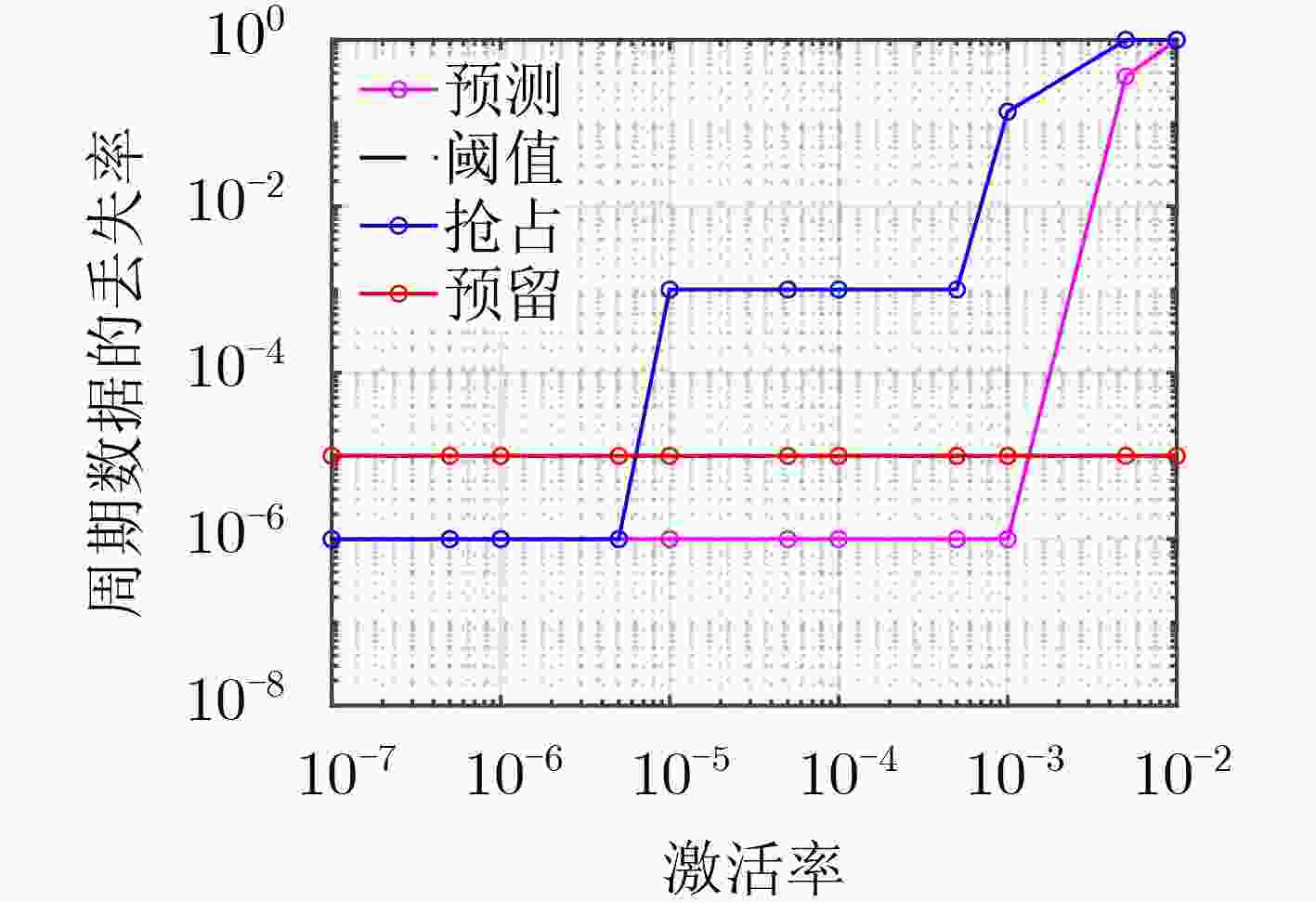

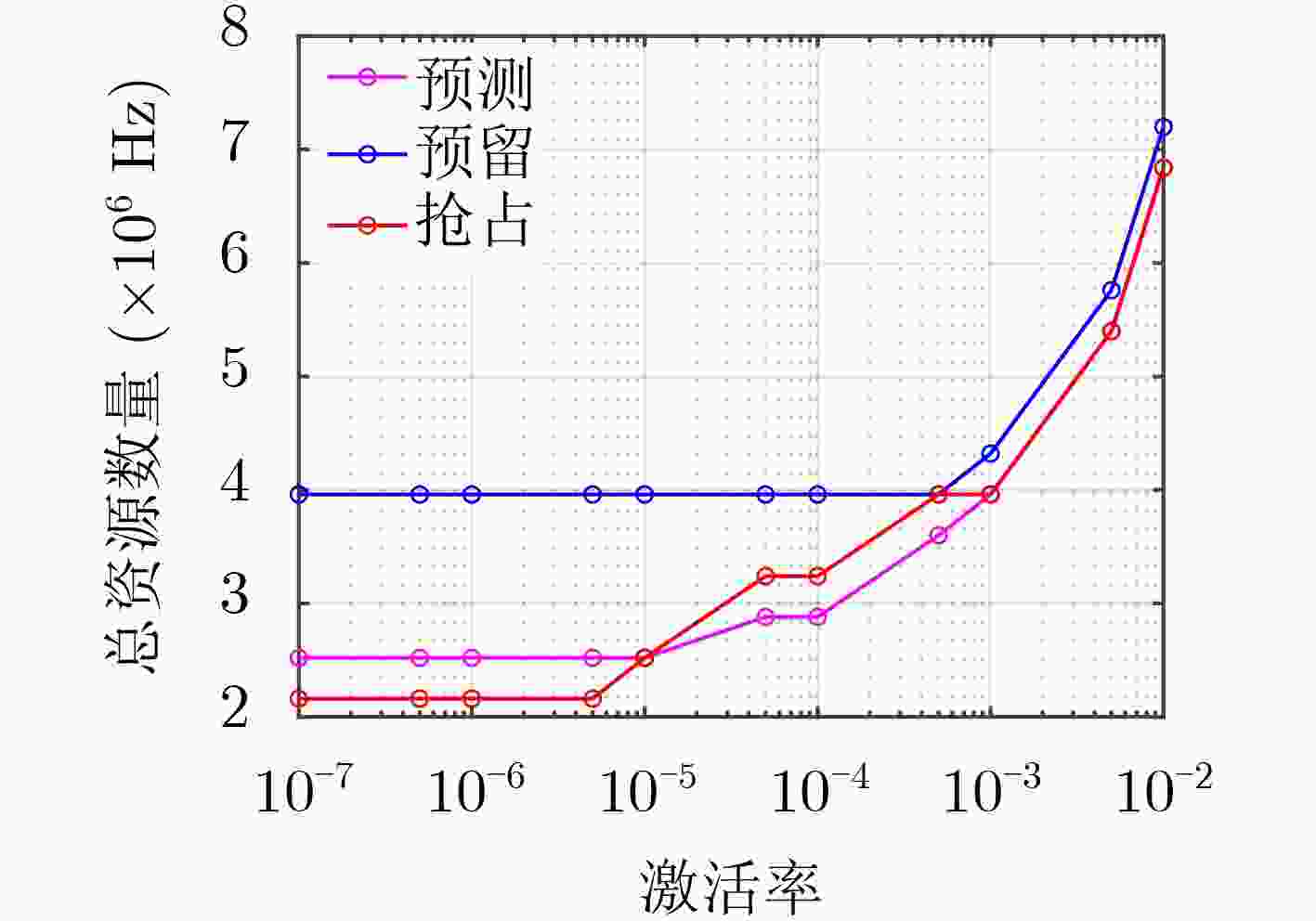


 下载:
下载:
