Research on Cyclic Generation Countermeasure Network Based Super-resolution Image Reconstruction Algorithm
-
摘要: 为了提高图像超分辨率重建的效果,该文将注意力机制引入多级残差网络(Multi-level Residual Attention Network, MRAN)作为CycleGAN的重建网络,提出了基于循环生成对抗网络(CycleGAN)的超分辨率重建模型MRA-GAN。MRA-GAN模型中重建网络负责将低分辨率(LR)图像重建为高分辨率(HR)图像,退化网络负责将HR图像降采样为LR图像,LR判别器负责鉴别真实LR图像和通过退化网络降采样得到的LR图像,HR判别器负责鉴别真实HR图像和通过重建网络重建得到的HR图像,并且改进了CycleGAN原有的判别器判别方式和损失函数。实验结果验证了MRA-GAN模型与现有算法相比,在峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性(SSIM)等指标上都有所改进。Abstract: In order to improve the effect of image super-resolution reconstruction, the attention mechanism is introduced into Multi-level Residual Attention Network (MRAN) as the improved reconstruction network of Cycle Generation Countermeasure Network (CycleGAN) in this paper. A super-resolution reconstruction model MRA-GAN based on CycleGAN is proposed. The designed reconstruction network in MRA-GAN model is responsible for mapping from Low Resolution (LR) image to High Resolution (HR) image and the designed degradation network is responsible for reconstructing HR image to LR image. The LR discriminator is used to identify the real LR image which is obtained through the degraded network. The HR discriminator is used to identify the real HR image which is reconstructed by the reconstructed network. Moreover, the original discriminator and loss function of CycleGAN is improved. Experimental results verify that MRA-GAN model can obtain better Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) than the existing deep learning based super-resolution algorithms.
-
表 1 测试参数设置
测试参数 参数值 图像输入类型 RGB 图像输入大小 48×48 每批次图像数量 16 Adam指数衰减率${\beta _{\text{1}}}$ 0.9 Adam指数衰减率${\beta _2}$ 0.999 Adam参数$\varepsilon $ 10–8 学习率 10–4 预训练轮数 10 表 2 不同残差组数量实验结果
残差组数量 参数量 PSNR (×4 Set5) SSIM (×4 Set5) 8 1760325 32.44 0.8892 16 3207877 32.72 0.8913 32 6102981 32.95 0.8920 48 8998085 32.97 0.8914 64 11893189 32.94 0.8921 表 3 实验结果对比
方法 倍率 Set5 Set14 BSD100 Urban100 Manga109 PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM Bicubic ×2 33.66 0.9299 30.24 0.8688 29.56 0.8431 26.88 0.8403 30.80 0.9339 SRCNN 36.66 0.9542 32.45 0.9067 31.36 0.8879 29.50 0.8946 35.60 0.9663 VDSR 37.53 0.9590 33.05 0.9130 31.90 0.8960 30.77 0.9140 37.22 0.9750 EDSR 38.11 0.9602 33.92 0.9195 32.32 0.9013 32.93 0.9351 39.10 0.9773 MRA-GAN 38.59 0.9589 34.16 0.9256 33.99 0.9158 34.25 0.9329 39.05 0.9781 Bicubic ×3 30.39 27.55 27.55 0.7742 27.21 0.7385 24.46 0.7349 26.95 0.8556 SRCNN 32.75 0.9090 29.30 0.8215 28.41 0.7863 26.24 0.7989 30.48 0.9117 VDSR 33.67 0.9210 29.78 0.8320 28.83 0.7990 27.14 0.8290 32.01 0.9340 EDSR 34.65 0.9280 30.52 0.8462 29.25 0.8093 28.80 0.8653 34.17 0.9476 MRA-GAN 34.98 0.9265 31.22 0.8686 30.70 0.8350 30.54 0.8676 34.45 0.9531 Bicubic ×4 26.70 0.7803 23.87 0.6577 24.26 0.6399 21.17 0.6193 20.5 0.6986 SRCNN 29.01 0.8504 26.85 0.7513 26.90 0.7101 24.52 0.7221 27.45 0.8412 VDSR 31.13 0.8830 27.95 0.7680 27.29 0.7260 25.18 0.7540 28.83 0.8707 EDSR 32.35 0.8909 28.44 0.8016 27.71 0.7420 26.64 0.8033 30.76 0.9064 MRA-GAN 32.97 0.8904 29.01 0.8198 28.22 0.7776 28.31 0.8089 32.13 0.9164 Bicubic ×8 24.40 0.6580 23.10 0.5660 23.67 0.5480 20.74 0.5160 21.47 0.6500 SRCNN 25.33 0.6900 23.76 0.5910 24.13 0.5660 21.29 0.5440 22.46 0.6950 VDSR 25.93 0.7240 24.26 0.6140 24.49 0.5830 21.70 0.5710 23.16 0.7250 EDSR 26.96 0.7762 24.91 0.6420 24.81 0.5985 22.51 0.6221 24.69 0.7841 MRA-GAN 27.56 0.7798 25.46 0.6656 25.54 0.6094 23.32 0.6493 25.85 0.7986 -
[1] 陈嘉琪, 刘祥梅, 李宁, 等. 一种超分辨SAR图像水域分割算法及其应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 700–707. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200366CHEN Jiaqi, LIU Xiangmei, LI Ning, et al. A high-precision water segmentation algorithm for SAR image and its application[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 700–707. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200366 [2] TAO Huanjie and LU Xiaobo. Contour-based smoky vehicle detection from surveillance video for alarm systems[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2019, 13(2): 217–225. doi: 10.1007/s11760-018-1348-z [3] 王钢, 周若飞, 邹昳琨. 基于压缩感知理论的图像优化技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 222–233. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190669WANG Gang, ZHOU Ruofei, and ZOU Yikun. Research on image optimization technology based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 222–233. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190669 [4] 陈书贞, 曹世鹏, 崔美玥, 等. 基于深度多级小波变换的图像盲去模糊算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 154–161. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190947CHEN Shuzhen, CAO Shipeng, CUI Meiyue, et al. Image blind deblurring algorithm based on deep multi-level wavelet transform[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 154–161. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190947 [5] YANG Chenxue, YE Mao, TANG Song, et al. Semi-supervised low-rank representation for image classification[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2017, 11(1): 73–80. doi: 10.1007/s11760-016-0895-4 [6] DING Chunhui, BAO Tianlong, KARMOSHI S, et al. Single sample per person face recognition with KPCANet and a weighted voting scheme[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2017, 11(7): 1213–1220. doi: 10.1007/s11760-017-1077-8 [7] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3262–3271. [8] HE Chao, CHEN Zhenxue, and LIU Chengyun. Salient object detection via images frequency domain analyzing[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2016, 10(7): 1295–1302. doi: 10.1007/s11760-016-0954-x [9] HOU H and ANDREWS H. Cubic splines for image interpolation and digital filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1978, 26(6): 508–517. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1978.1163154 [10] SCHULTZ R R and STEVENSON R L. A Bayesian approach to image expansion for improved definition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1994, 3(3): 233–242. doi: 10.1109/83.287017 [11] LI Xin and ORCHARD M T. New edge-directed interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(10): 1521–1527. doi: 10.1109/83.951537 [12] IRANI M and PELEG S. Improving resolution by image registration[J]. CVGIP:Graphical Models and Image Processing, 1991, 53(3): 231–239. doi: 10.1016/1049-9652(91)90045-L [13] STARK H and OSKOUI P. High-resolution image recovery from image-plane arrays, using convex projections[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1989, 6(11): 1715–1726. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.6.001715 [14] SCHULTZ R R and STEVENSON R L. Extraction of high-resolution frames from video sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1996, 5(6): 996–1011. doi: 10.1109/83.503915 [15] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 184–199. [16] DONG Chao, LOY C C, and TANG Xiaoou. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 391–407. [17] KIM J, LEE J K, and LEE K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1646–1654. [18] SHI Wenzhe, CABALLERO J, HUSZÁR F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1874–1883. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.207. [19] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. [20] LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZÁR F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 105–114. [21] LIM B, SON S, KIM H, et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1132–1140. [22] ZHANG Yulun, LI Kunpeng, LI Kai, et al. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 294–310. [23] SHOCHER A, COHEN N, and IRANI M. Zero-Shot super-resolution using deep internal learning[C]. 2017 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3118–3126. [24] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [25] RADFORD A, METZ L, and CHINTALA S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.06434.pdf, 2016. -





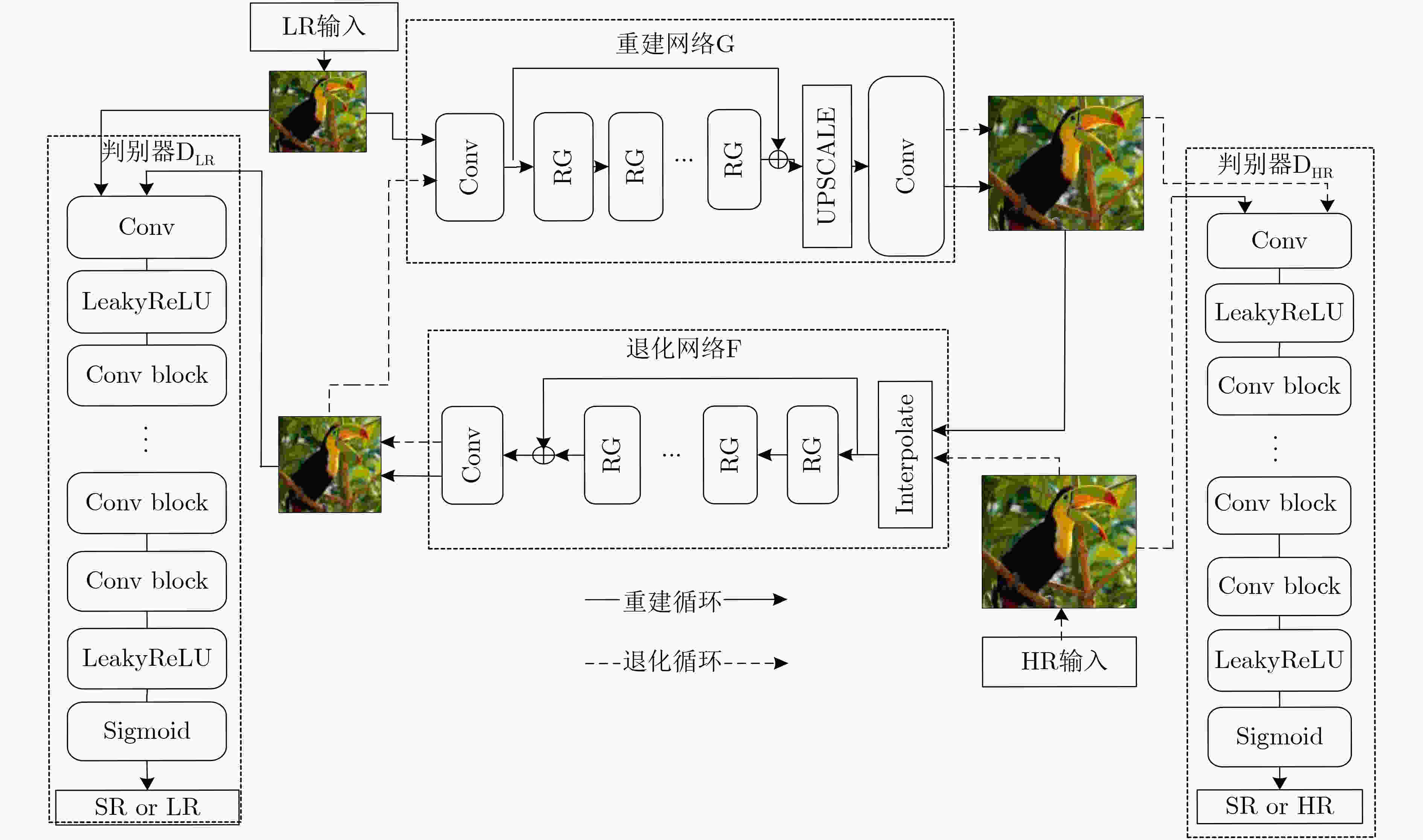
 下载:
下载:
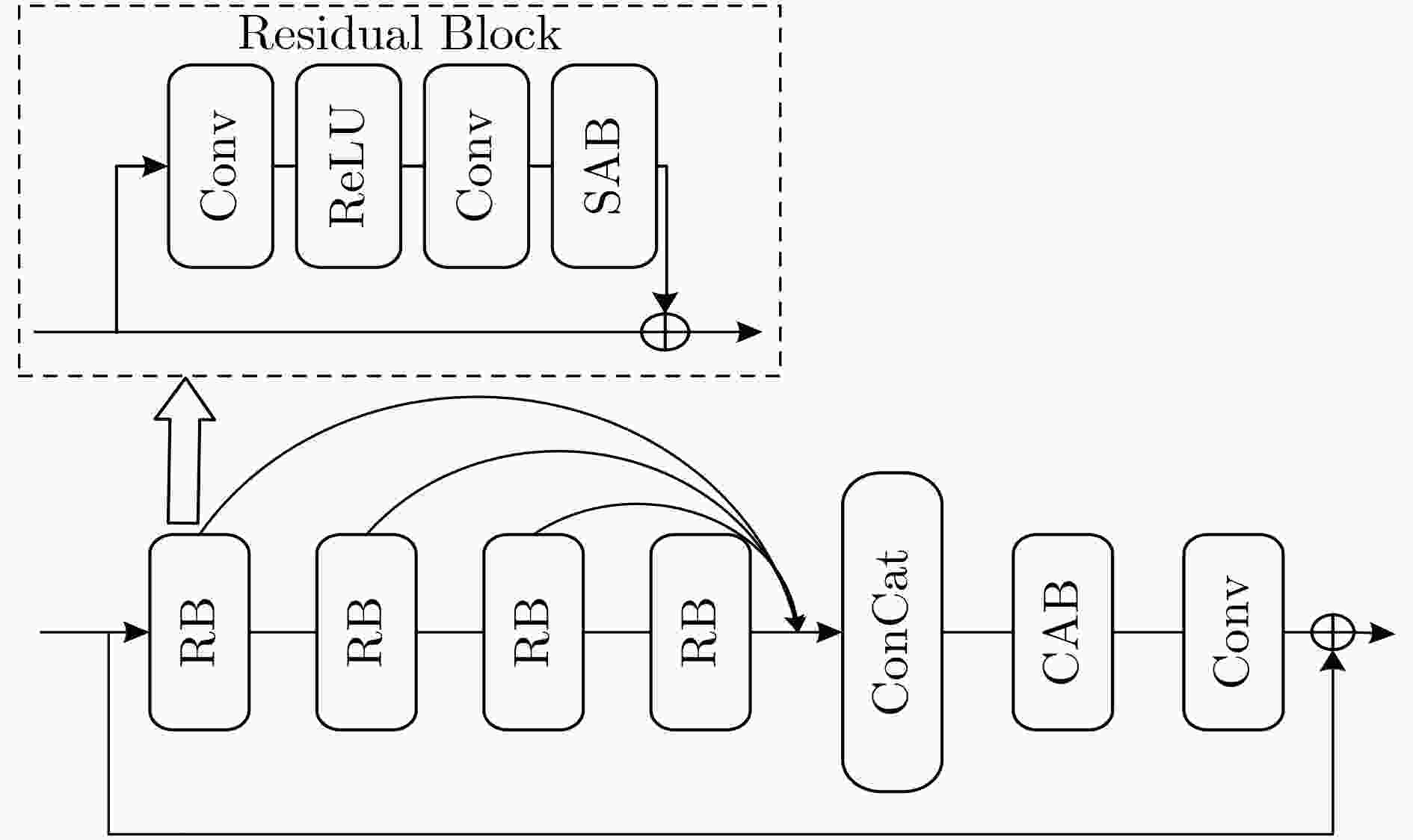
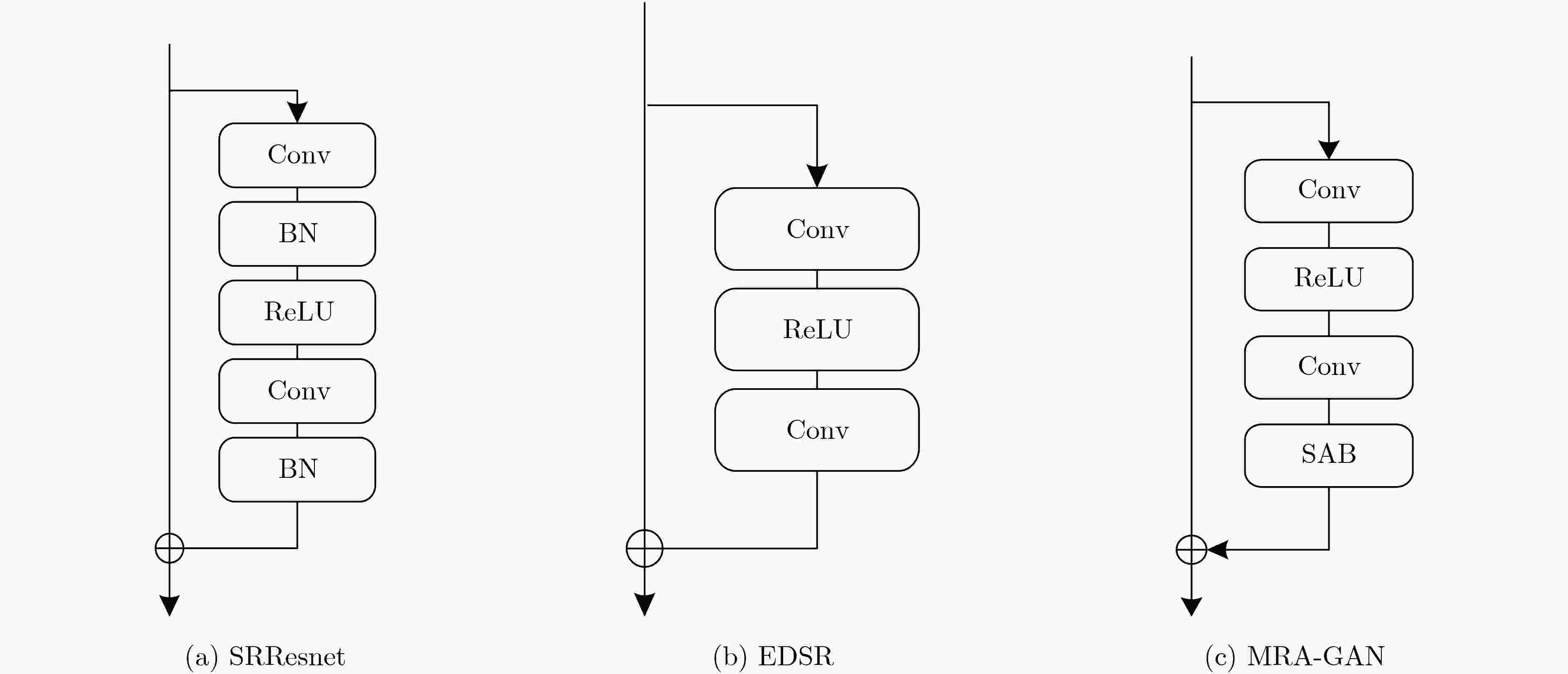
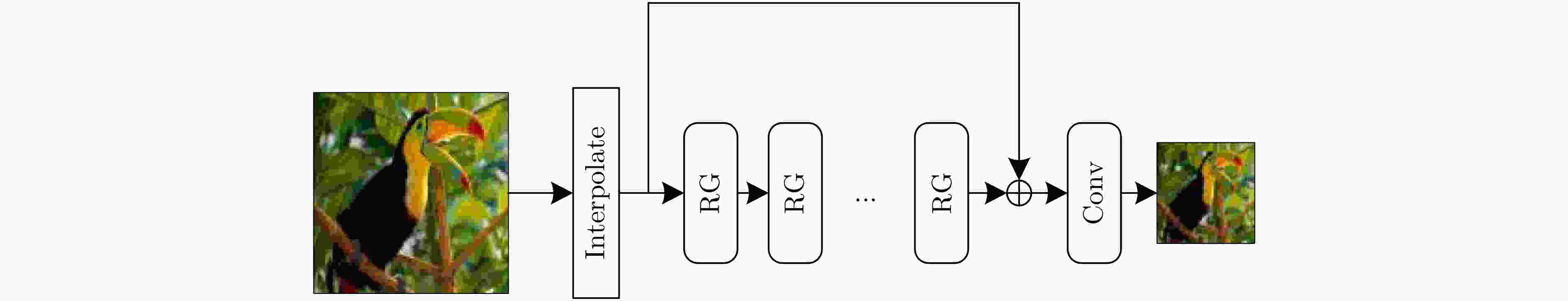
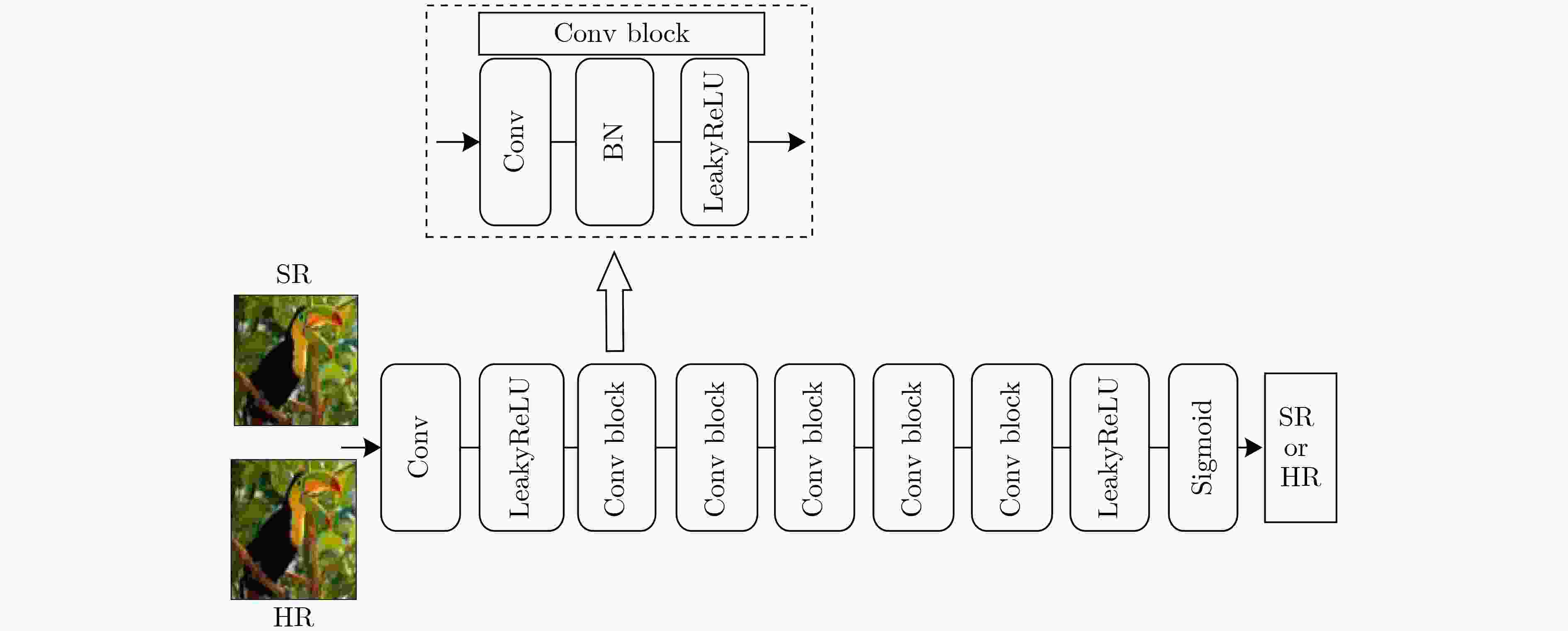
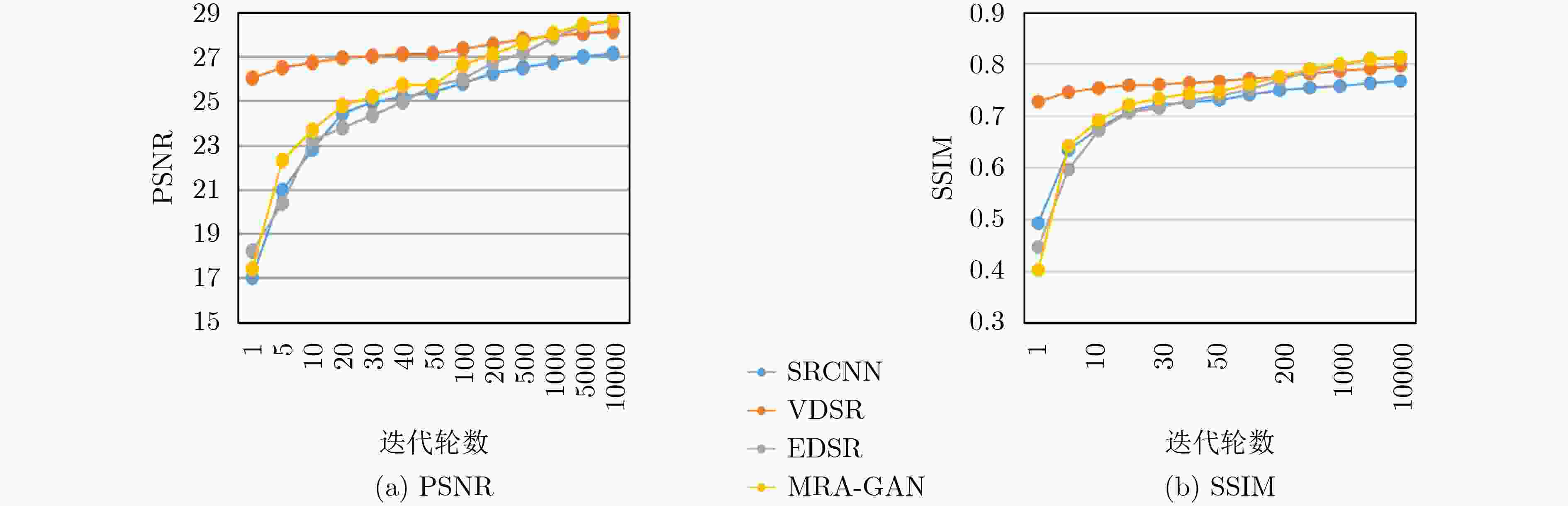



 下载:
下载:
