Synthetic Aperture Sonar Underwater Multi-scale Target Efficient Detection Model Based on Improved Single Shot Detector
-
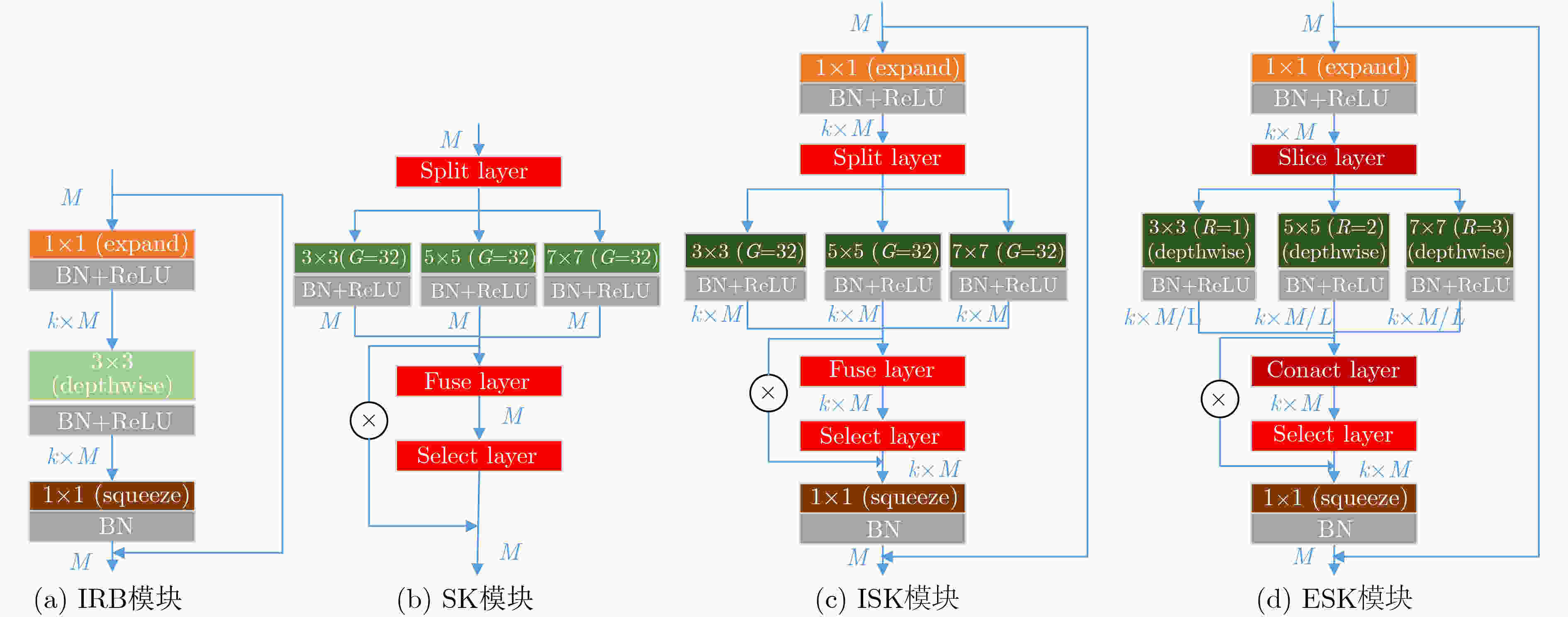
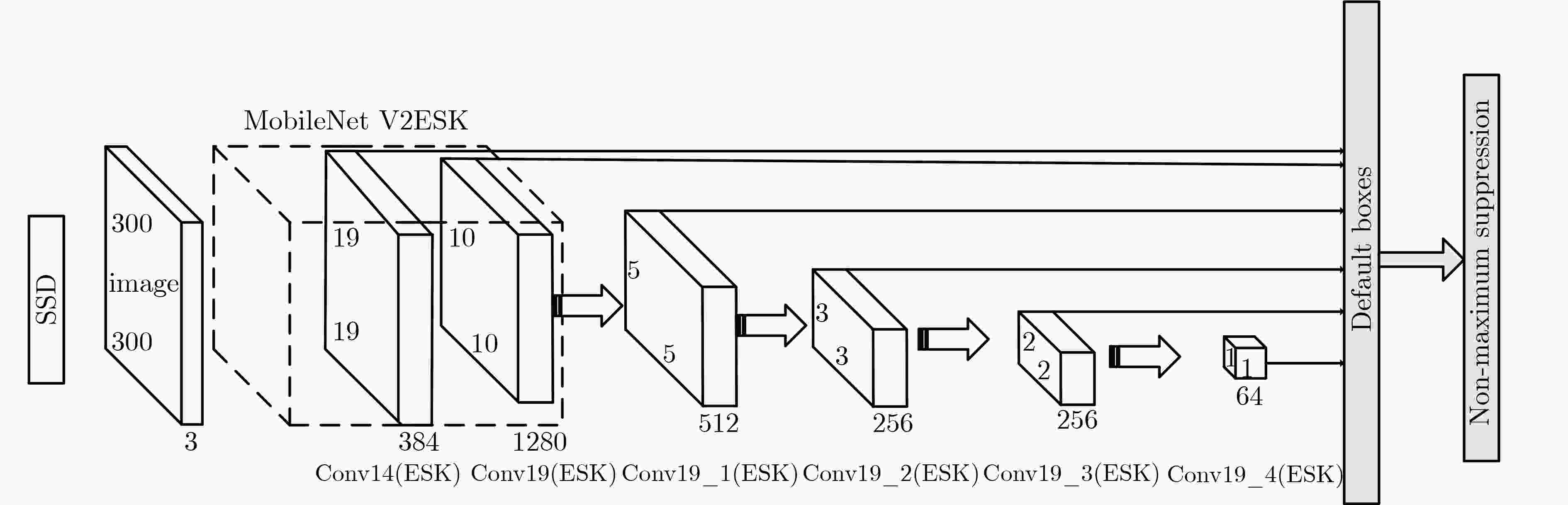
摘要: 针对轻量化目标检测模型SSD-MV2对合成孔径声呐(SAS)图像水下多尺度目标检测精度低的问题,该文提出一种新的卷积核模块-可扩张可选择模块(ESK),ESK具有通道可扩张、通道可选择和模型参数少的优点。与此同时,利用ESK模块重新设计了SSD的基础网络和附加特征提取网络,记作SSD-MV2ESK,并为其选择了合理的扩张系数和多尺度系数。在合成孔径声呐图像水下多尺度目标检测数据集SST-DET上,SSD-MV2ESK在模型参数基本相等的条件下,检测精度比SSD-MV2提升4.71%。实验结果表明,SSD-MV2ESK适用于合成孔径声呐图像水下多尺度目标检测任务。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径声呐 /
- 图像水下多尺度目标检测 /
- SSD /
- MobileNet V2 /
- 多通道可选择 /
- 深度可分离空洞卷积
Abstract: In view of the problem that the efficient detection model SSD-MV2 (Single Shot Detector MobileNet V2) has low detection accuracy to underwater multi-scale targets in Synthetic Aperture Sonar (SAS) images, a novel feature extraction module Extended Selective Kernel (ESK) is proposed in this paper. ESK has the advantages of channel scalability, channel selection and few model parameters. At the same time, the basic network and additional feature extraction network of SSD are redesigned by using ESK module, which is named SSD-MV2ESK, and a set of reasonable expansion coefficient and multi-scale coefficient are selected for SSD-MV2ESK. On SST-DET, the mAP of SSD-MV2ESK is 4.71% higher than that of SSD-MV2 when the model parameters are basically the same. The experimental results show that SSD-MV2ESK is suitable for SAR underwater multi-scale target detection task in embedded platform. -
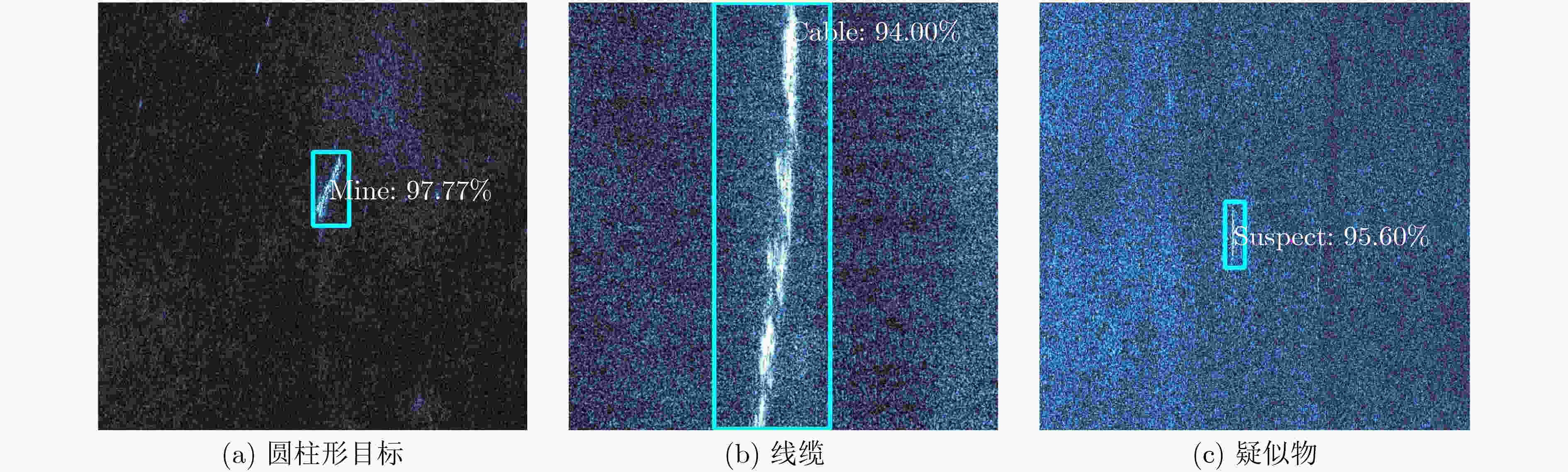
表 1 合成孔径声呐水下多尺度目标检测数据集组成
目标 训练(幅) 测试(幅) 圆柱形目标 103 8 线缆 275 30 疑似物 255 33 总计 633 71 表 2 目标检测模型性能比较
表 3 基础网络扩张系数对SSD-MV2ESK性能的影响
扩张系数 mAP(%) 模型参数(MB) 检测时间(ms) 1 66.27 6.4 28.20 5 74.39 14.9 31.34 10 74.72 30.5 31.36 15 78.32 52.4 31.77 20 81.67 80.6 32.28 40 85.29 256.0 32.92 表 4 基础网络多尺度系数对SSD-MV2ESK性能的影响
多尺度系数 mAP(%) 模型参数(MB) 检测时间(ms) 1 70.46 12.5 30.89 2 71.81 12.5 36.29 4 75.08 12.6 46.46 表 5 模型分类准确率(%)
分类网络 MobileNet V2_4_1 MobileNet V2_4_2 MobileNet V2_4_4 准确率 72.72 77.27 78.78 -
[1] HAYES M P and GOUGH P T. Synthetic aperture sonar: A review of current status[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2009, 34(3): 207–224. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2009.2020853 [2] 吴浩然, 张非也, 唐劲松, 等. 基于参考距离史的多子阵SAS成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 650–656. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200620WU Haoran, ZHANG Feiye, TANG Jinsong, et al. A imaging algorithm based on the reference range history for the multiple receivers synthetic aperture sonar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 650–656. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200620 [3] WANG Peng, CHI Cheng, ZHANG Yu, et al. Fast imaging algorithm for downward-looking 3D synthetic aperture sonars[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(3): 459–467. [4] SUN Sibo, CHEN Yingchun, QIU Longhao, et al. Inverse synthetic aperture sonar imaging of underwater vehicles utilizing 3-D rotations[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2020, 45(2): 563–576. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2891281 [5] HINTON G. Where do features come from?[J]. Cognitive Science, 2014, 38(6): 1078–1101. doi: 10.1111/cogs.12049 [6] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [7] SCHMIDHUBER J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview[J]. Neural Networks, 2015, 61: 85–117. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003 [8] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [9] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [10] XIE Saining, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5987–5995. [11] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Washington, USA, 2014: 580–587. [12] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, USA, 2015: 1440–1448. [13] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [14] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [15] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [16] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Kingdom of the Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [17] IANDOLA F N, HAN Song, MOSKEWICZ M W, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size[C]. The 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. [18] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. [19] HOWARD A G, ZHU Menglong, CHEN Bo, et al. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, 2017. [20] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU Menglong, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4510–4520. [21] HU Jie, SHEN Li, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011–2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [22] LI Xiang, WANG Xiang, HU Xiaolin, et al. Selective kernel networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 510–519. [23] WILLIAMS D P. Underwater target classification in synthetic aperture sonar imagery using deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexican, 2016: 2497–2502. [24] MCKAY J, GERG I, MONGA V, et al. What’s mine is yours: Pretrained CNNs for limited training sonar ATR[C]. OCEANS 2017 - Anchorage, Anchorage, USA, 2017: 1–7. [25] WILLIAMS D P. On the use of tiny convolutional neural networks for human-expert-level classification performance in sonar imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2021, 46(1): 236–260. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2963041 [26] 李宝奇, 贺昱曜, 强伟, 等. 基于并行附加特征提取网络的SSD地面小目标检测模型[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(1): 84–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.01.010LI Baoqi, HE Yuyao, QIANG Wei, et al. SSD with parallel additional feature extraction network for ground small target detection[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(1): 84–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.01.010 [27] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [28] WANG Panqu, CHEN Pengfei, YUAN Ye, et al. Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, USA, 2018: 1451–1460. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
