Semi Supervised Learning of Metallographic Data Based on Self-organizing Incremental and Graph Convolution Neural Network
-
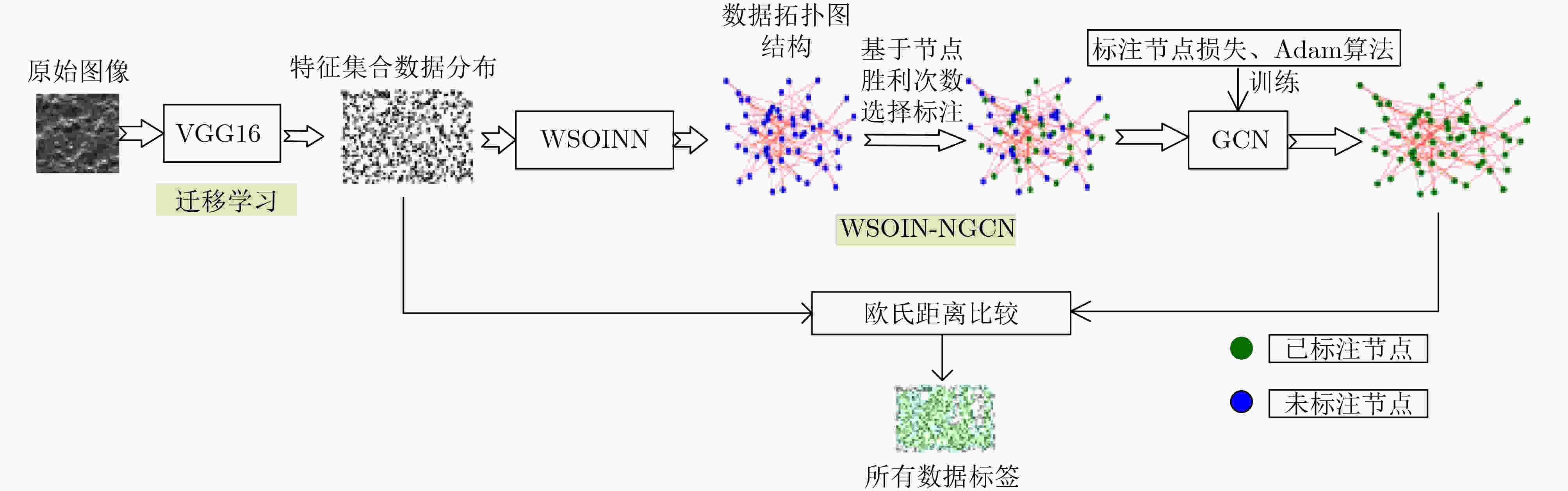
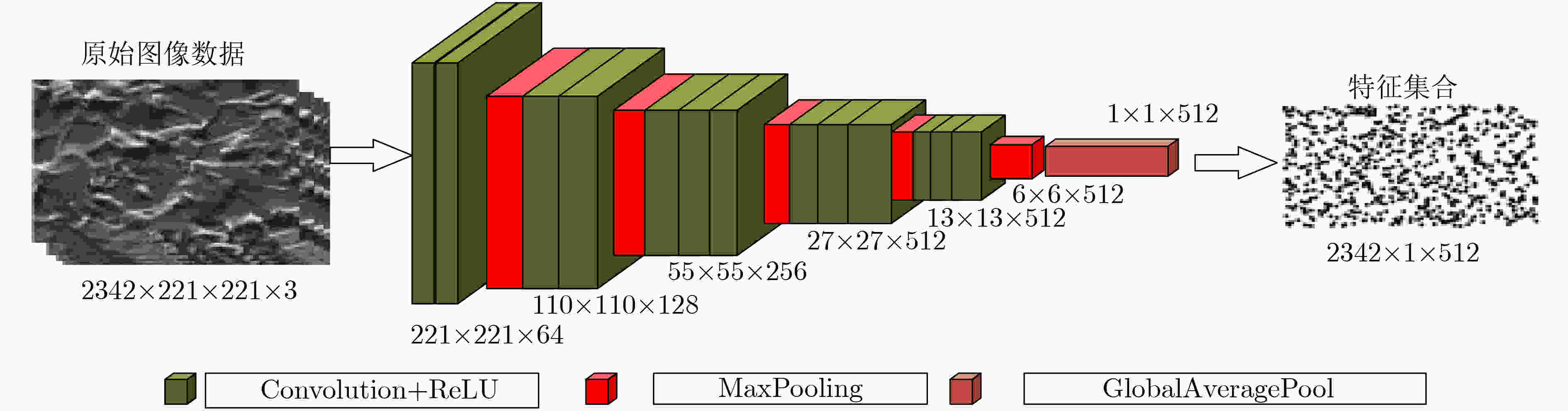
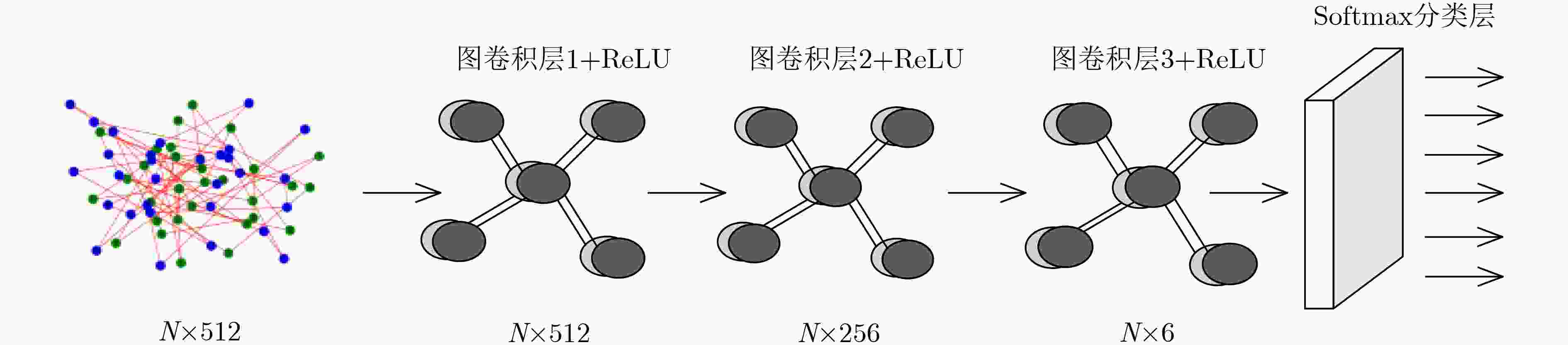
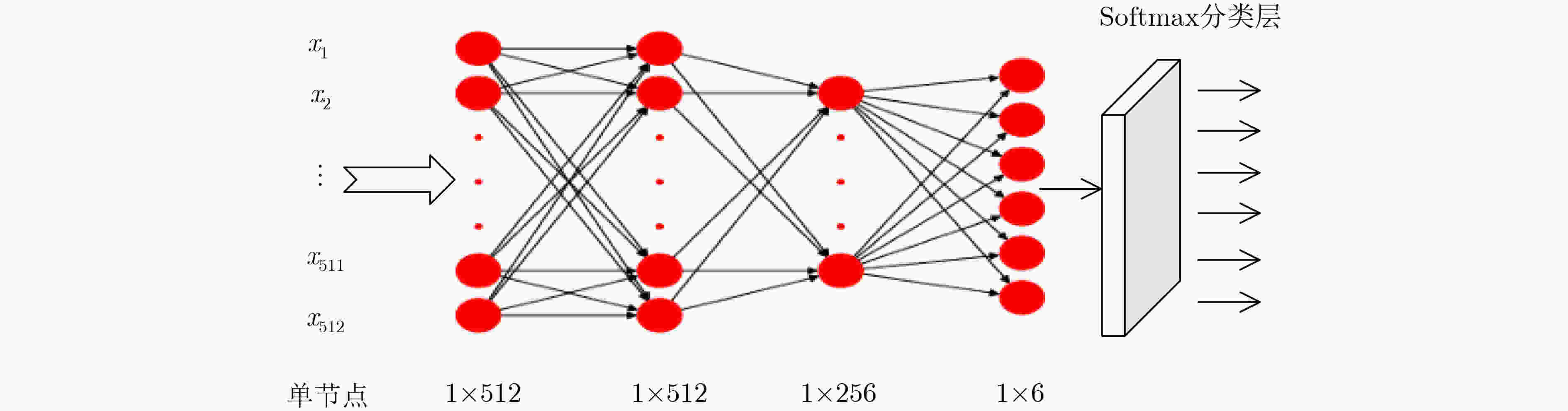
摘要: 采用深度学习对钢铁材料显微组织图像分类,需要大量带标注信息的训练集。针对训练集人工标注效率低下问题,该文提出一种新的融合自组织增量神经网络和图卷积神经网络的半监督学习方法。首先,采用迁移学习获取图像数据样本的特征向量集合;其次,通过引入连接权重策略的自组织增量神经网络(WSOINN)对特征数据进行学习,获得其拓扑图结构,并引入胜利次数进行少量人工节点标注;然后,搭建图卷积网络(GCN)挖掘图中节点的潜在联系,利用Dropout手段提高网络的泛化能力,对剩余节点进行自动标注进而获得所有金相图的分类结果。针对从某国家重点实验室收集到的金相图数据,比较了在不同人工标注比例下的自动分类精度,结果表明:在图片标注量仅为传统模型12%时,新模型的分类准确度可达到91%。Abstract: It needs a large number of training sets with annotation information to classify microstructure images of steel materials by deep learning. To solve the problem of low efficiency of manual image annotation, a new semi-supervised learning method combining self-organizing incremental neural network and graph convolutional neural network is proposed. Firstly, it uses transfer learning to obtain the feature vector set of images. Secondly, it obtains the topology structure by adopting the Weighted Self-Organizing Incremental Neural Network(WSOINN) based on connection weight strategy to learn feature data, and manually annotates a small number of nodes which are selected by the number of victories of node. Then, a Graph Convolution Network (GCN) is built to mine the potential connections of nodes in the graph, dropout is used to improve the generalization ability of the network, and the remaining nodes are automatically annotated to obtain the classification results of the metallograph. Experiment on the metallographic data collected from a state key laboratory, the accuracy of automatic classification under different manual annotation ratio is compared. The results show when the image annotation amount is only 12% of the traditional model, and the classification accuracy of the proposed model can reach up to 91%.
-
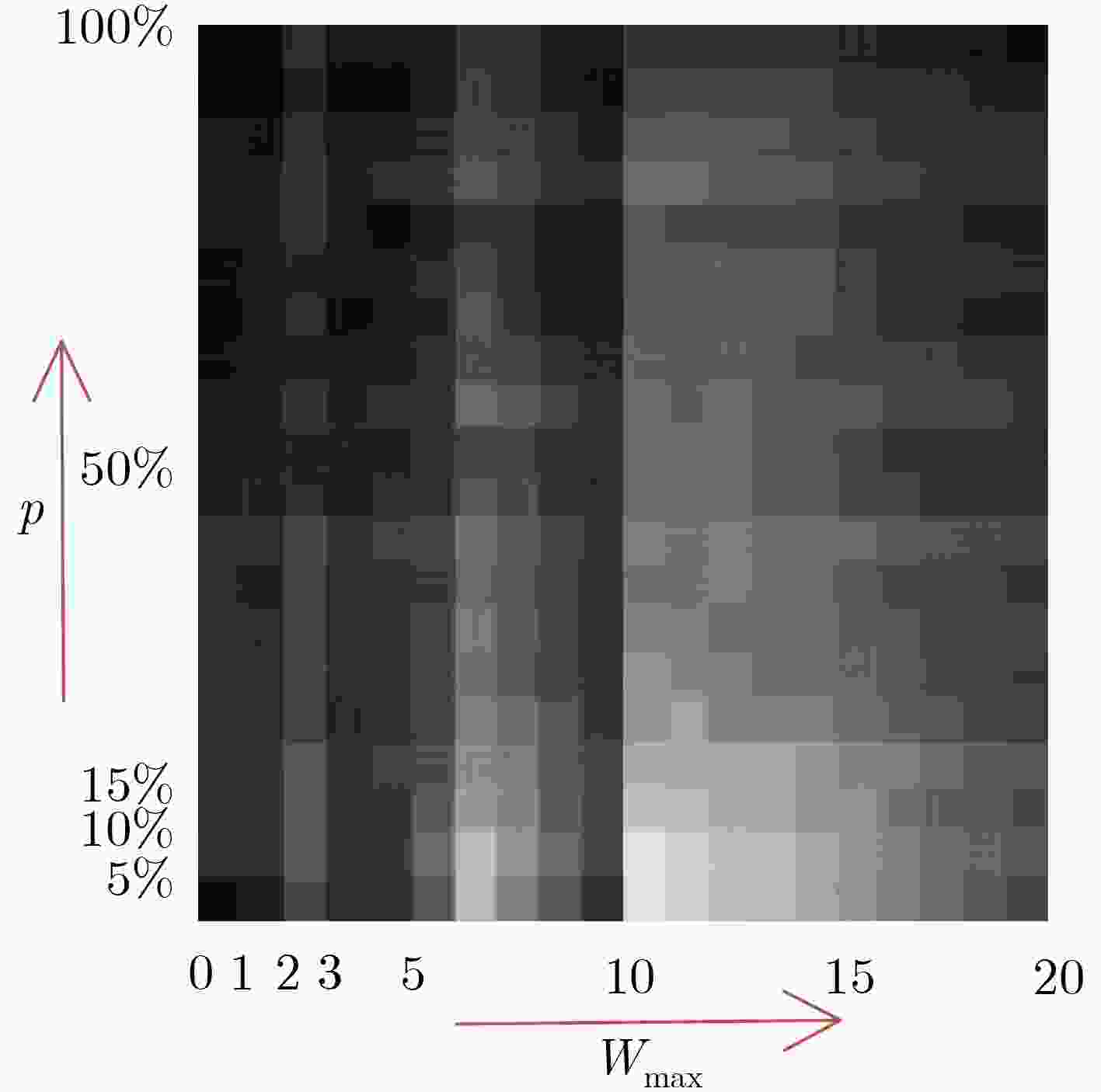
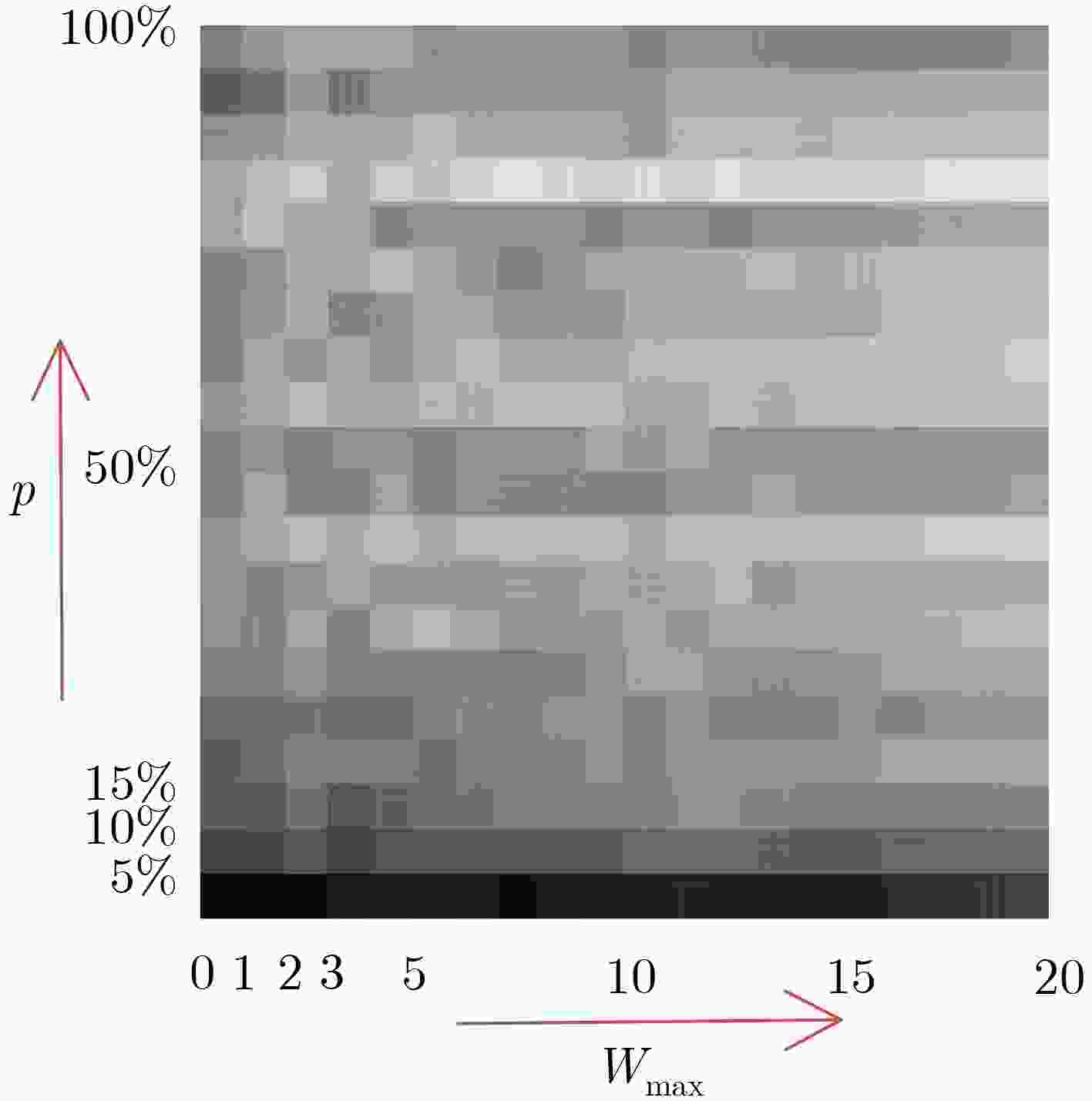
表 1 标注率为0.3时,不同p, Wmax值下剩余节点标注精度
${{{W}}_{{{\max}}}}$, ${{p}}$ 20, 100% 2, 10% 15, 45% 10, 5% 4, 30% 17, 70% $n$ 286 294 300 308 440 474 $a$ 720 324 734 688 640 946 Acc_w(%) 85 93 84 90 89 88 Acc_r(%) 70 81 80 75 88 85 表 2 不同节点标注率情况下剩余节点自动标注精度(%)
节点标注率(rate) WSOINN- GCN WSOINN- MLP 有Dropout 无Dropout 有Dropout 无Dropout 0.1 83 80 77 76 0.2 89 88 82 81 0.3 93 93 86 84 0.4 95 92 91 90 0.5 93 94 91 90 0.6 97 99 97 97 0.7 97 99 99 97 表 3 不同节点标注率情况下所有金相图分类精度(%)
节点标注率(rate) WSOINN-GCN WSOINN- MLP 有Dropout 无Dropout 有Dropout 无Dropout 0.1 81 81 74 79 0.2 88 87 81 80 0.3 91 91 82 81 0.4 92 91 89 85 0.5 92 92 88 92 0.6 90 94 90 92 0.7 90 94 89 92 表 4 节点标注率为0.3时,不同类别金相图的精确率与召回率(%)
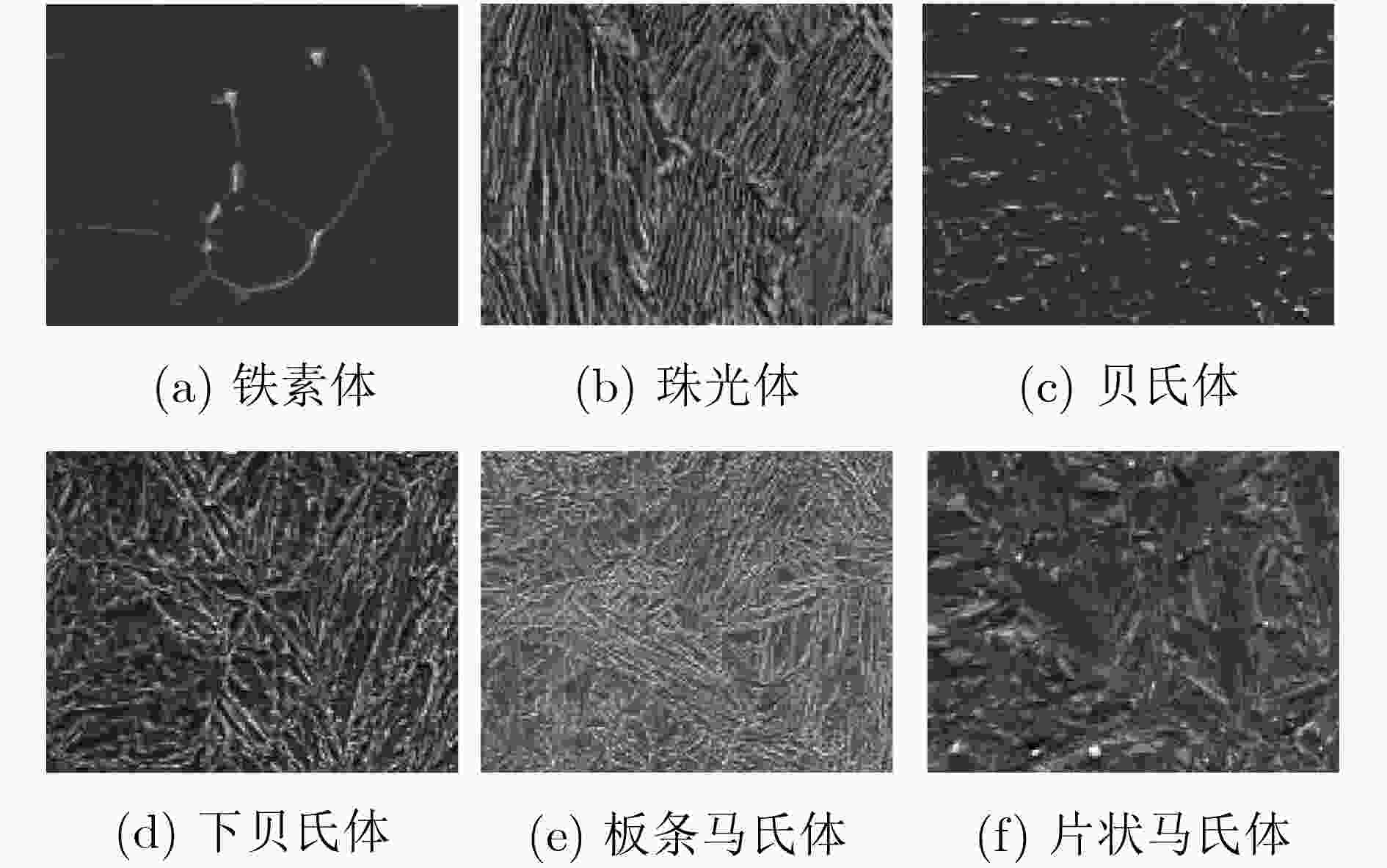
金相图类别 精确率 召回率 下贝氏体 90 92 低碳板条马氏体 93 93 珠光体 99 92 贝氏体 93 73 铁素体 100 100 高碳片状马氏体 74 97 表 5 选择30%标注,不同方法的所有图片自动分类效果
VGG-ICAM SOINN MLP WSOINN-GCN WSOINN-MLP 人工标注量(张) 730 730 730 88 88 训练时间(min) 240 1 1 2.5 2.5 分类精度(%) 74 39 51 91 82 表 6 分类精度达到90%,不同方法所需的标注量及训练时间
VGG-ICAM SOINN MLP WSOINN-GCN WSOINN-MLP 人工标注量(张) 1580 1702 1702 88 115 训练时间(min) 420 1.5 1.5 2.5 2.5 -
[1] ZHAO H, WYNNE B P, and PALMIERE E J. A phase quantification method based on EBSD data for a continuously cooled microalloyed steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2017, 123: 339–348. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2016.11.024 [2] YANG Youwen, HE Chongxian, E Dianyu, et al. Mg bone implant: Features, developments and perspectives[J]. Materials & Design, 2020, 185: 108259. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108259 [3] TERASAKI H, MIYAHARA Y, HAYASHI K, et al. Digital identification scheme for steel microstructures in low-carbon steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2017, 129: 305–312. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.05.021 [4] PANCHAL J H, KALIDINDI S R, and MCDOWELL D L. Key computational modeling issues in Integrated Computational Materials Engineering[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2013, 45(1): 4–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2012.06.006 [5] LU Xiaochong, ZHANG Xu, SHI Mingxing, et al. Dislocation mechanism based size-dependent crystal plasticity modeling and simulation of gradient nano-grained copper[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2019, 113: 52–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2018.09.007 [6] WANG Hongda, RIVENSON Y, JIN Yiyin, et al. Deep learning enables cross-modality super-resolution in fluorescence microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(1): 103–110. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0239-0 [7] DECOST B L, LEI Bo, FRANCIS T, et al. High throughput quantitative metallography for complex microstructures using deep learning: A case study in ultrahigh carbon steel[J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2019, 25(1): 21–29. doi: 10.1017/S1431927618015635 [8] PAULY J, BRITZ D, and MÜCKLICH F. Advanced microstructure classification using data mining methods[C]. In TMP - 5th International Conference on TermoMechanical Processing, Milan, Italy, 2016: 12–25. [9] CHOWDHURY A, KAUTZ E, YENER B, et al. Image driven machine learning methods for microstructure recognition[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2016, 123: 176–187. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2016.05.034 [10] AZIMI S M, BRITZ D, ENGSTLER M, et al. Advanced steel microstructural classification by deep learning methods[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 2128. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20037-5 [11] 李维刚, 谌竟成, 范丽霞, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的钢铁材料微观组织自动辨识[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2020, 32(1): 33–43. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20190147LI Weigang, SHEN Jingcheng, FAN Lixia, et al. Automatic identification of microstructure of iron and steel material based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2020, 32(1): 33–43. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.20190147 [12] LI Bentian and PI Dechang. Network representation learning: A systematic literature review[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(21): 16647–16679. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-04908-5 [13] 康世泽, 吉立新, 张建朋. 一种基于图注意力网络的异质信息网络表示学习框架[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(4): 915–922. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200034KANG Shize, JI Lixin, and ZHANG Jianpeng. Heterogeneous information network representation learning framework based on graph attention network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(4): 915–922. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200034 [14] 李世宝, 张益维, 刘建航, 等. 基于知识图谱共同邻居排序采样的推荐模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 待发表. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200735.LI Shibao, ZHANG Yiwei, LIU Jianhang, et al. Recommendation model based on public neighbor sorting and sampling of knowledge graph[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, To be published. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200735. [15] ORTEGA A, FROSSARD P, KOVAČEVIĆ J, et al. Graph signal processing: Overview, challenges, and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2018, 106(5): 808–828. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2820126 [16] HAMILTON W L, YING R, and LESKOVEC J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706.02216, 2017. [17] KIPF T N and WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1609.02907, 2016. [18] CHEN Jie, MA Tengfei, and XIAO Cao. FastGCN: Fast learning with graph convolutional networks via importance sampling[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.10247, 2018. [19] SHEN Furao and HASEGAWA O. An incremental network for on-line unsupervised classification and topology learning[J]. Neural Networks, 2006, 19(1): 90–106. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2005.04.006 -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
