Floating Small Target Detection Based on Graph Connected Density in Sea Surface
-
摘要: 海面漂浮小目标由于其能量弱,一直是海面目标检测的重难点。传统基于统计模型的漂浮小目标检测算法借助回波能量进行检测,没有利用数据频域幅度间的关联性,导致检测性能受损。该文借助图的处理方式,首先利用回波数据脉冲间频域幅度的关联性计算连通密度,生成邻接矩阵,接着将邻接矩阵转换为拉普拉斯矩阵,提取拉普拉斯矩阵的最大特征值作为检测特征,提出了一种基于图的连通密度的海面漂浮小目标检测算法。通过对实测的全相参的X波段 (IPIX)雷达数据进行连通密度的分析,发现海杂波构成的图比较稠密,而海面漂浮小目标构成的图比较稀疏,故通过连通密度构成的图可以有效地检测海杂波中的漂浮小目标。进一步地,通过与对比算法实验分析发现,该文所提基于图的连通密度的检测算法检测性能明显优越。Abstract: Due to the weak energy of the floating small targets, it is hard to be detected in sea surface. Relying on the energy, the traditional detectors based on statistical model inevitable loss the detection performance, regardless of the correlation between the frequency domain amplitudes. Therefore, in the paper, the correlation between the frequency domain amplitudes is considered by using the graph. Firstly, the connected density is calculated by the correlation between the frequency domain amplitudes of the echo pulses. Secondly, an adjacency matrix is generated based on the correlation. Thirdly, the adjacency matrix is converted to a Laplacian matrix. Lastly, the maximum eigenvalue of the Laplacian matrix is extracted as the detection feature. Thus, the detector based on the connected density of the graph is proposed for the floating small targets in sea surface. The analysis of the connected density of the measured Ice multiParameter Imaging X-band(IPIX) radar data shows that the graph composed by the sea clutter is relatively dense, whereas the graph composed by the floating small targets is relatively sparse. Thus, the connected density can effectively distinguish the floating small targets between the sea clutter. Furthermore, the experimental results show that, compared with other algorithms, the detection performance of the proposed connected density of the graph algorithm is obviously superior.
-
表 1 IPIX雷达数据说明
数据
编号数据
名称风速
(km/h)浪高
(m)角度
(°)目标
单元受影响
单元1 #17 9 2.2 9 9 8, 10, 11 2 #26 9 1.1 97 7 6, 8 3 #30 19 0.9 98 7 6, 8 4 #31 19 0.9 98 7 6, 8, 9 5 #40 9 1.0 88 7 5, 6, 8 6 #54 20 0.7 8 8 7, 9, 10 7 #280 10 1.6 130 8 7, 9, 10 8 #310 33 0.9 30 7 6, 8, 9 9 #311 33 0.9 40 7 6, 8, 9 10 #320 28 0.9 30 7 6, 8, 9 -
[1] 丁昊, 刘宁波, 董云龙, 等. 雷达海杂波测量试验回顾与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006DING Hao, LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, et al. Overview and prospects of radar sea clutter measurement experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006 [2] 张坤, 水鹏朗, 王光辉. 相参雷达K分布海杂波背景下非相干积累恒虚警检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1627–1635. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190441ZHANG Kun, SHUI Penglang, and WANG Guanghui. Non-coherent integration constant false alarm rate detectors against K-distributed sea clutter for coherent radar systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1627–1635. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190441 [3] ZHOU Wei, XIE Junhao, LI Gaopeng, et al. Robust CFAR detector with weighted amplitude iteration in nonhomogeneous sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1520–1535. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2671798 [4] SHI Yanling. Three GLRT detectors for range distributed target in grouped partially homogeneous radar environment[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 135: 121–131. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.12.030 [5] ROBEY F C, FUHRMANN D R, KELLY E J, et al. A CFAR adaptive matched filter detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1992, 28(1): 208–216. doi: 10.1109/7.135446 [6] LI Dongchen and SHUI Penglang. Floating small target detection in sea clutter via normalised Hurst exponent[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(17): 1240–1242. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.1569 [7] SHI Yanling, ZHANG Xueliang, and LIU Zipeng. Floating small target detection in sea clutter based on jointed features in FRFT domain[C]. The 3rd EAI International Conference on Advanced Hybrid Information Processing, Nanjing, China, 2019: 128–139. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-36405-2_14. [8] 陈小龙, 关键, 于晓涵, 等. 基于短时稀疏时频分布的雷达目标微动特征提取及检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1017–1023. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161040CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, YU Xiaohan, et al. Radar Micro-Doppler signature extraction and detection via short-time sparse time-frequency distribution[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1017–1023. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161040 [9] SHI Yanling, XIE Xiaoyan, and LI Dongchen. Range distributed floating target detection in sea clutter via feature-based detector[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1847–1850. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2614750 [10] 时艳玲, 杜宇翔, 蒋锐, 等. 部分均匀海杂波中基于分组加权的协方差矩阵估计算法[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(7): 1170–1179. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.07.006SHI Yanling, DU Yuxiang, JIANG Rui, et al. A grouped weighted covariance matrix estimator in partially homogeneous sea clutter[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(7): 1170–1179. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.07.006 [11] XU Shuwen, ZHENG Jibin, PU Jia, et al. Sea-surface floating small target detection based on polarization features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(10): 1505–1509. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2852560 [12] 陈世超, 高鹤婷, 罗丰. 基于极化联合特征的海面目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 664–673. doi: 10.12000/JR20072CHEN Shichao, GAO Heting, and LUO Feng. Target detection in sea clutter based on combined characteristics of polarization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 664–673. doi: 10.12000/JR20072 [13] CHEN Shichao, LUO Feng, and LUO Xianxian. Multiview feature-based sea surface small target detection in short observation time[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020(99): 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2994341 [14] SANDRYHAILA A and MOURA J M F. Discrete signal processing on graphs: Frequency analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(12): 3042–3054. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2014.2321121 [15] 姜琦, 王锐, 周超, 等. 基于代数图论的修正贝叶斯群目标航迹起始算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 531–538. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200449JIANG Qi, WANG Rui, ZHOU Chao, et al. Modified Bayesian group target track initiation algorithm based on algebraic graph theory[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 531–538. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200449 [16] YAN Kun, WU H C, XIAO Hailin, et al. Novel robust band-limited signal detection approach using graphs[J]. IEEE Communications Letter, 2017, 21(1): 20–23. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2618871 [17] YAN Kun, BAI Yu, WU H C, et al. Robust target detection within sea clutter based on graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 7093–7103. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2911451 [18] 李炯生, 张晓东, 潘永亮. 图的Laplace特征值[J]. 数学进展, 2003, 32(2): 157–165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0917.2003.02.003LI Jiongsheng, ZHANG Xiaodong, and PAN Yongliang. Laplacian eigenvalues of graphs[J]. Advances in Mathematics, 2003, 32(2): 157–165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0917.2003.02.003 [19] DE ABREU N M M. Old and new results on algebraic connectivity of graphs[J]. Linear Algebra and its Applications, 2007, 423(1): 53–73. doi: 10.1016/j.laa.2006.08.017 [20] LI Ying, YANG Yonghu, and ZHU Xueyuan. Target detection in sea clutter based on multifractal characteristics after empirical mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1547–1551. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2721463 [21] HAYKIN S. The mcmaster IPIX radar sea clutter database in 1993[EB/OL]. http://soma.ece.mcmaster.ca/ipix/dartmouth, 2016. [22] SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120657 -





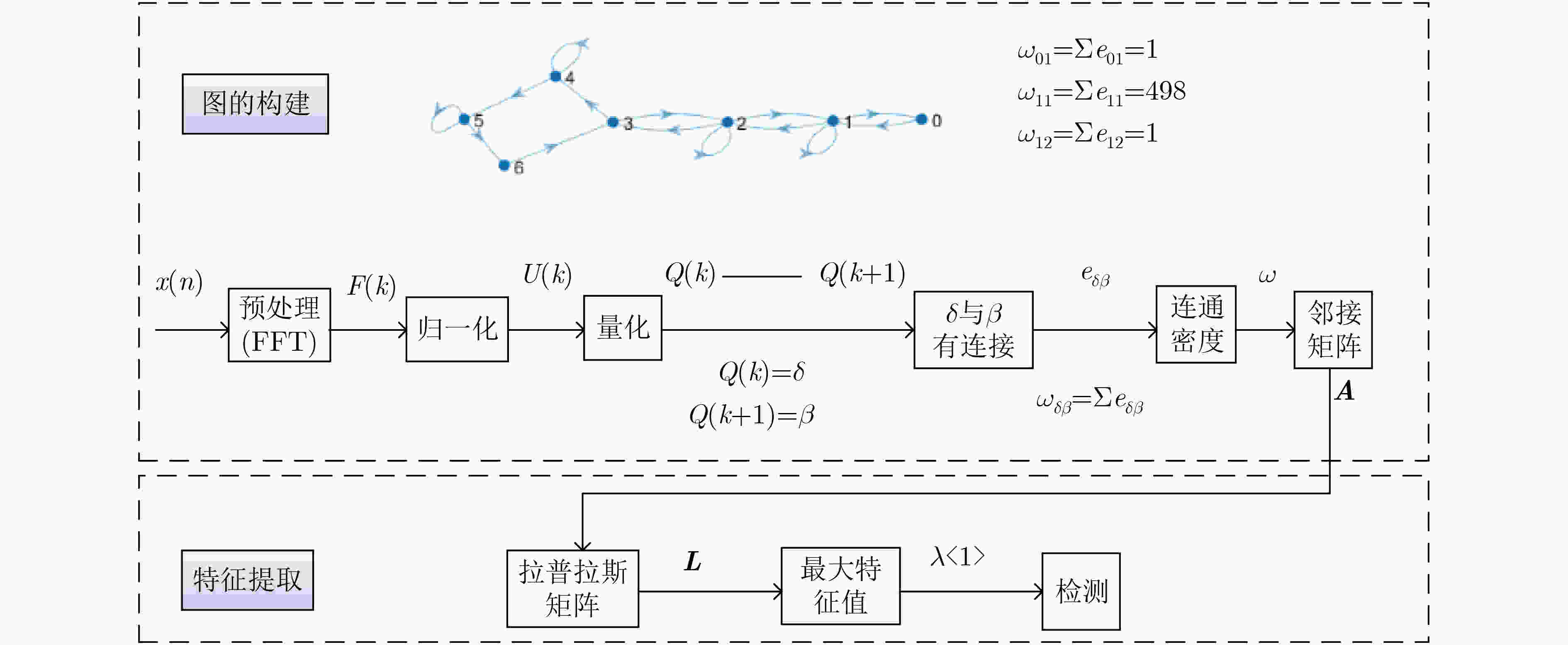
 下载:
下载:
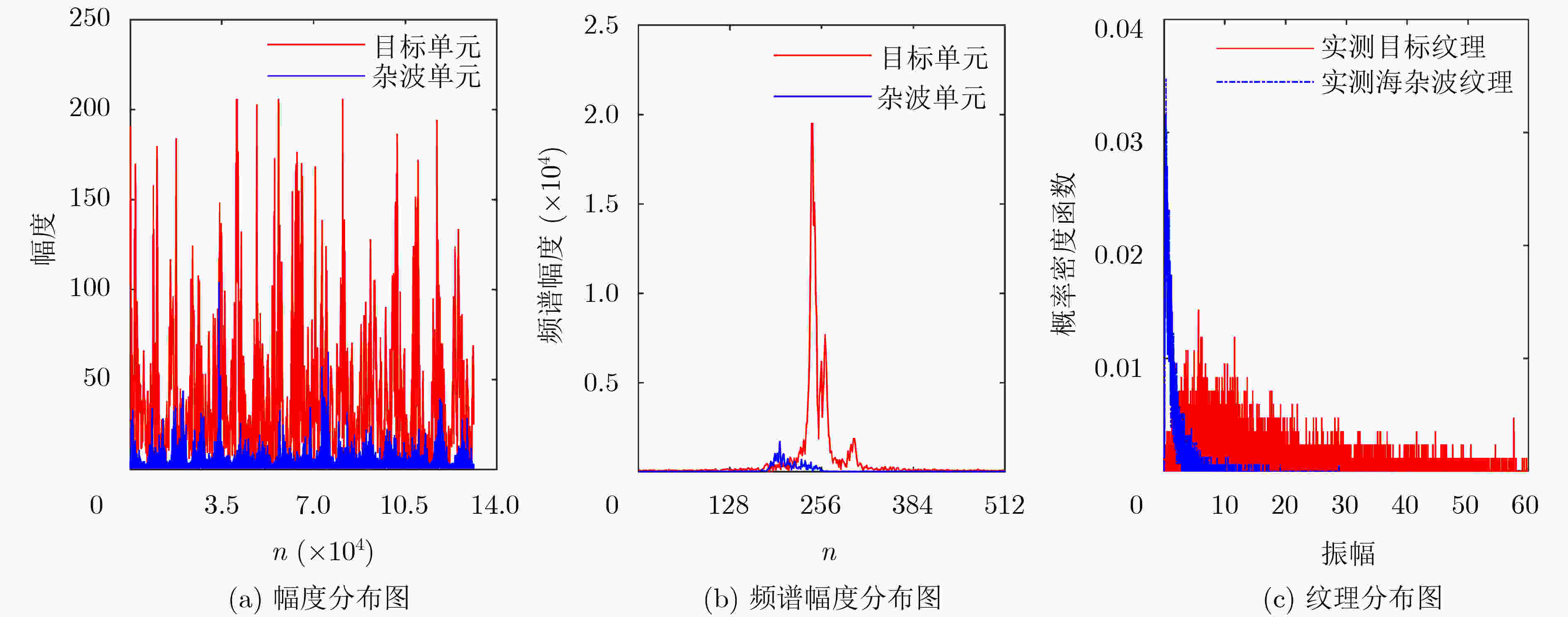

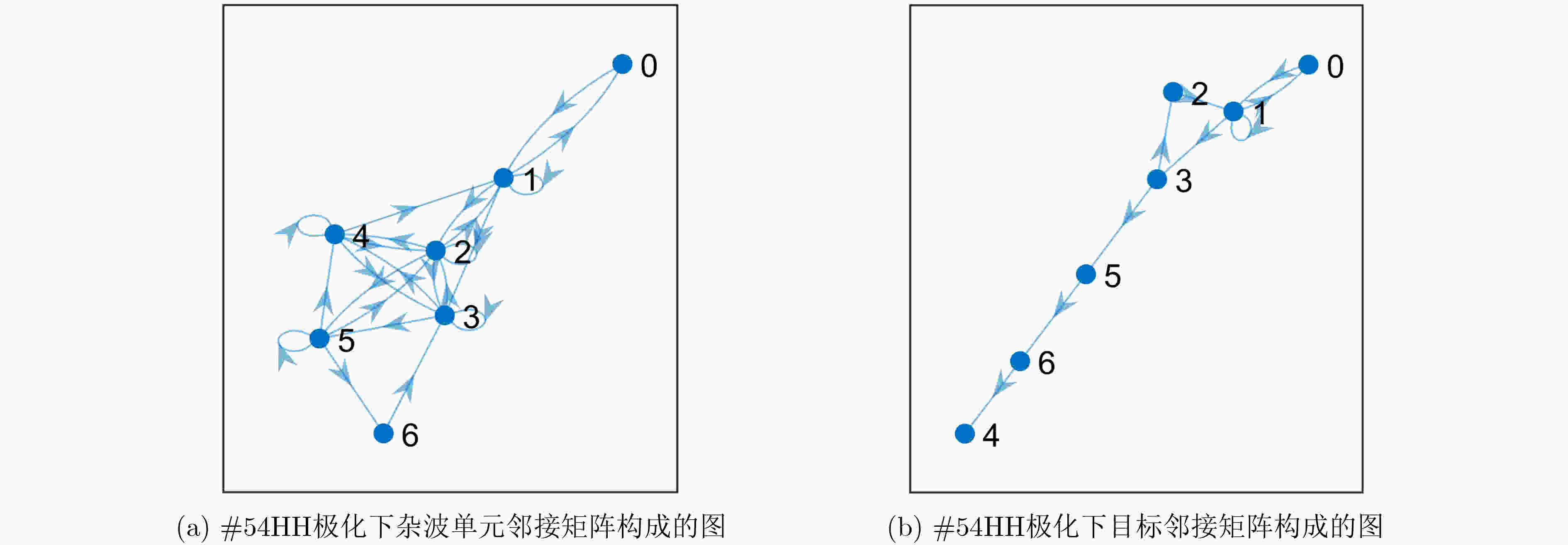




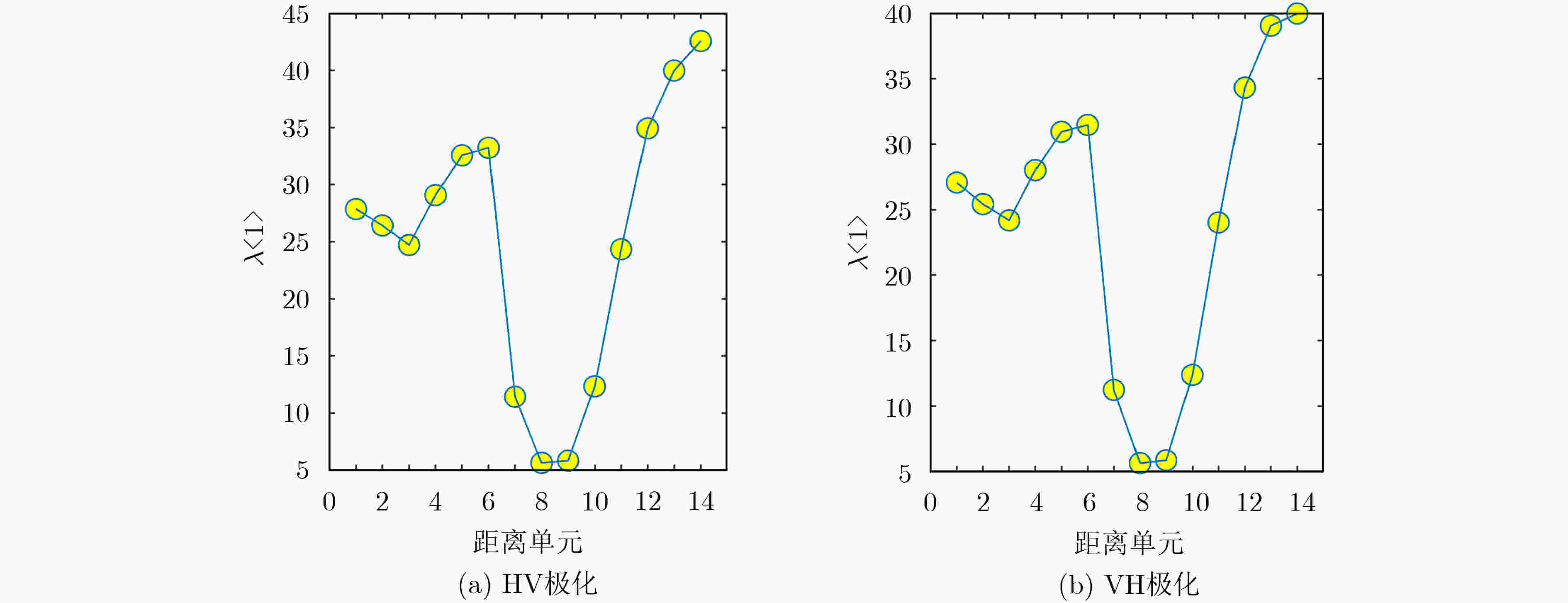




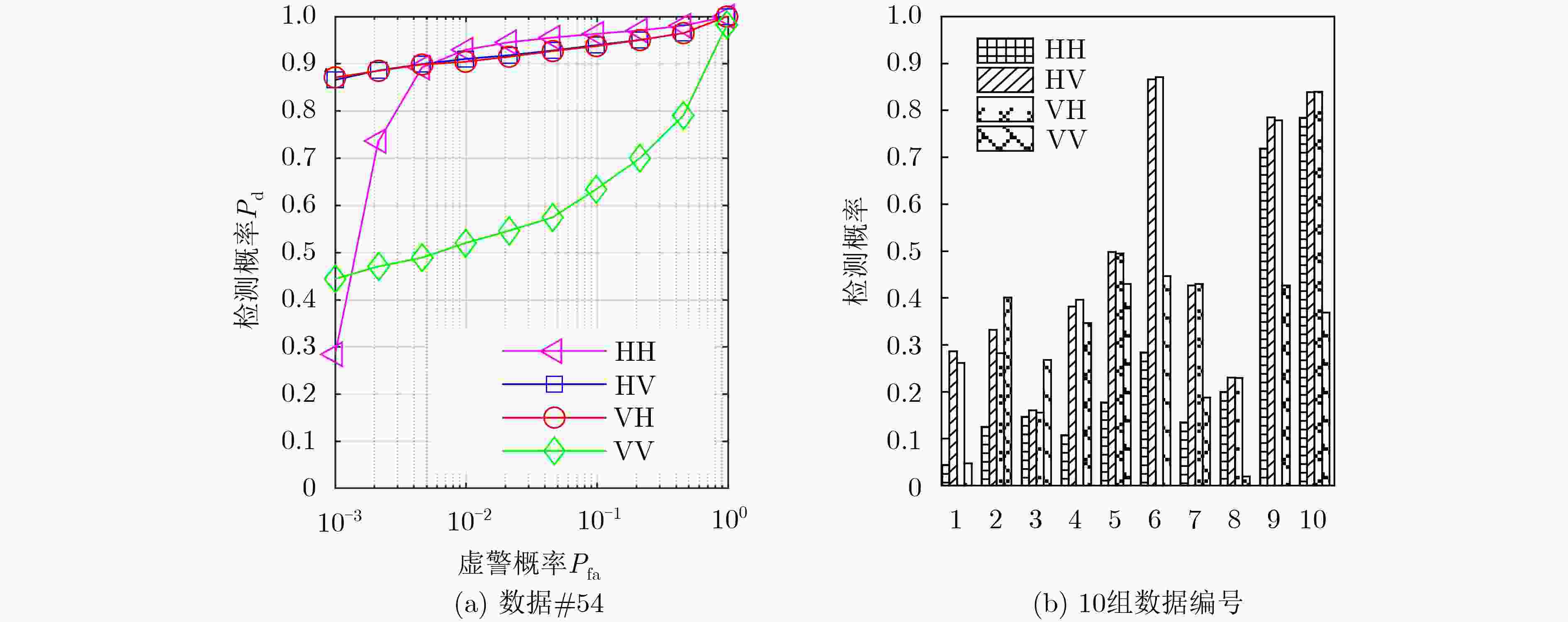




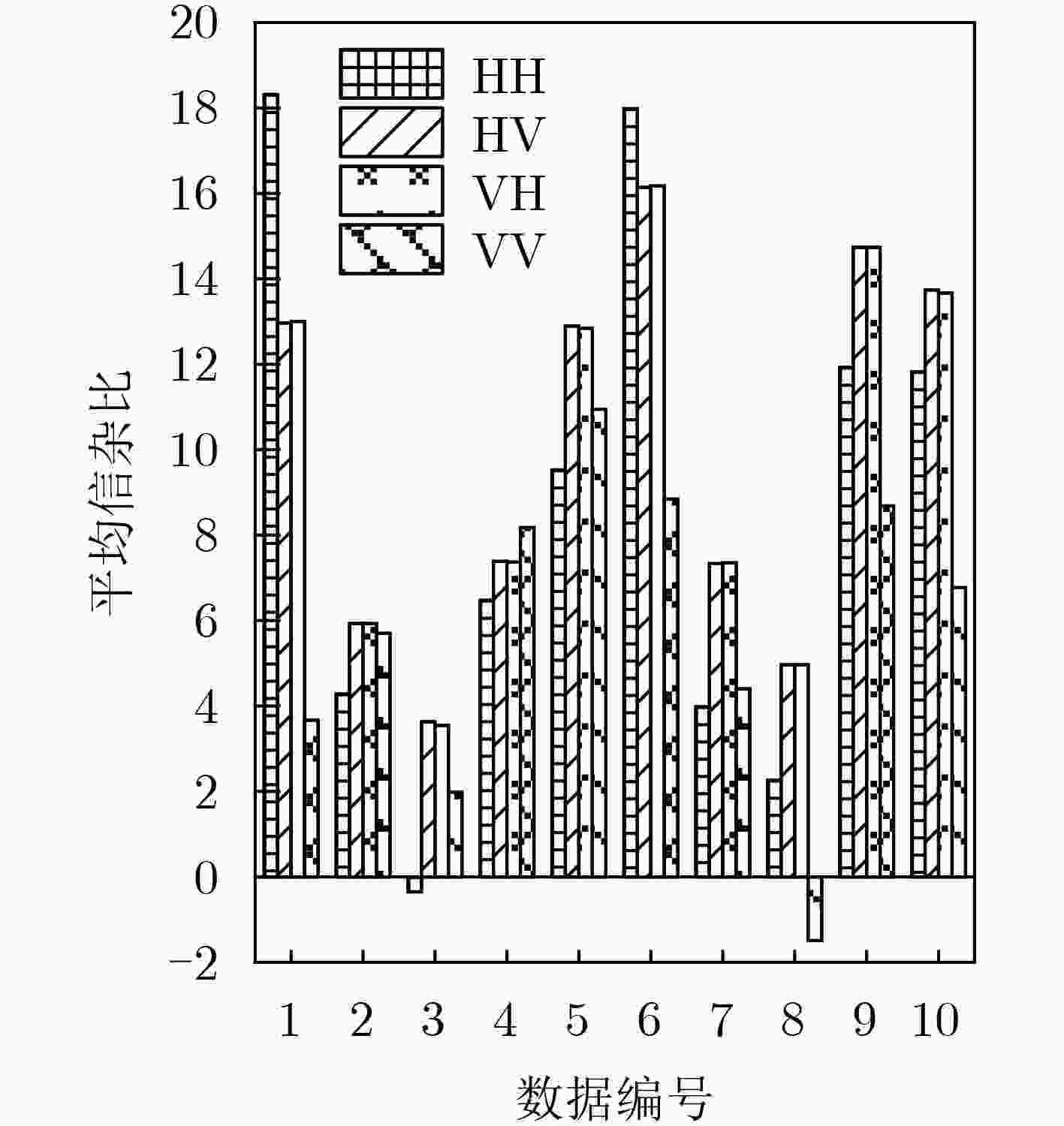
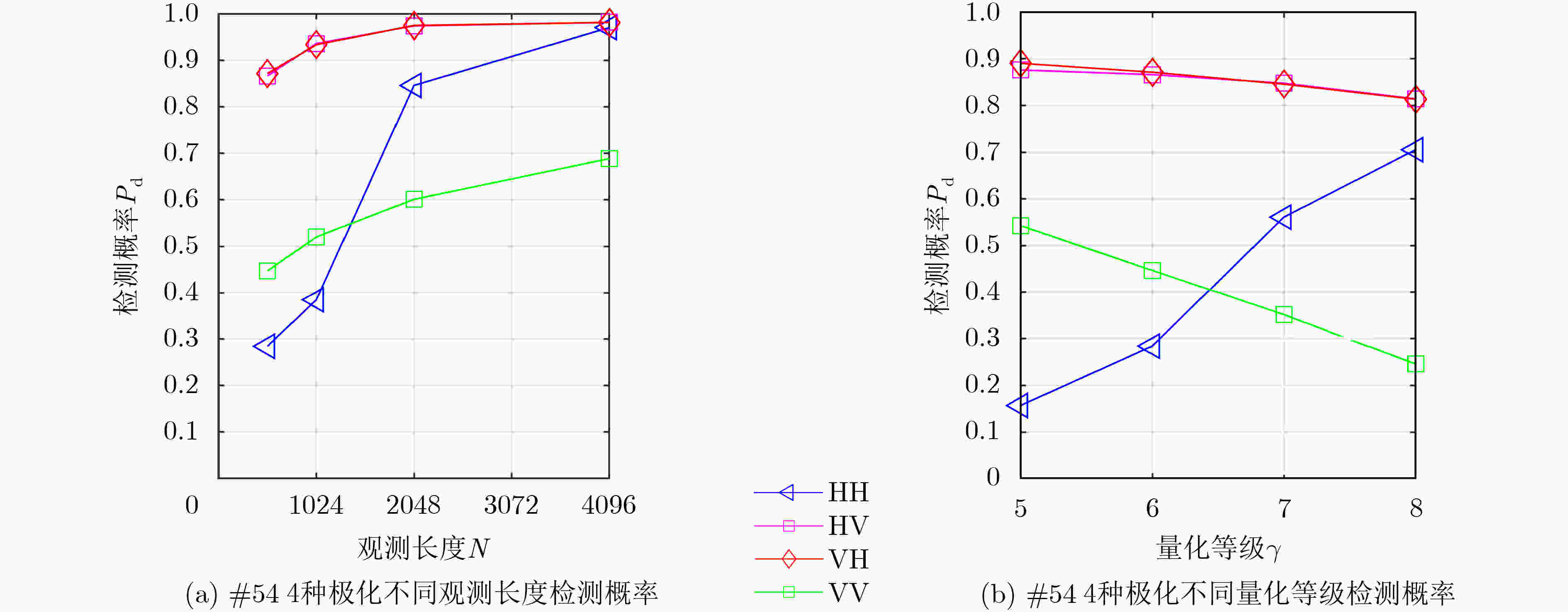

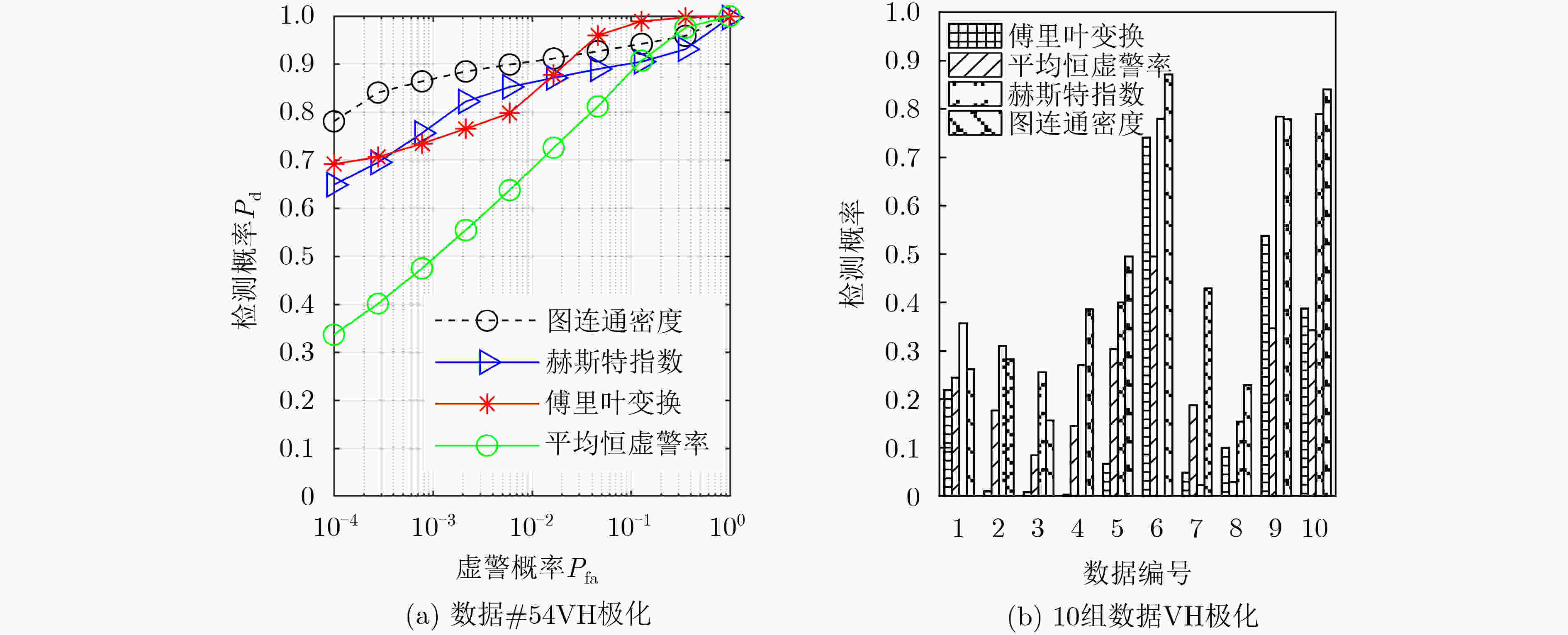






 下载:
下载:
