Adaptive Spatial and Anomaly Target Tracking
-
摘要: 为了解决判别式空间正则项的目标跟踪算法在遮挡、旋转等因素干扰下失跟率较高的问题,该文提出一种自适应空间异常的目标跟踪算法。首先,在目标函数中加入自适应空间正则项,既缓解了边界效应带来的影响,又提高了滤波器对目标和背景区域的分辨能力;其次,根据每一帧的响应值计算验证分数,分析跟踪结果的可信度和异常情况;最后为目标模型和响应图模型的更新速率实现动态取值。大量实验结果表明,自适应空间异常的目标跟踪算法能够较好地处理背景模糊、形状变化等多种异常情况,具有较高的跟踪性能。Abstract: In order to solve the problem that the target tracking algorithm based on the discriminant spatial regularization term has a high mistracking rate under the interference of occlusion, rotation and other factors, an adaptive spatial and anomaly target tracking is proposed. Firstly, an adaptive spatial regularization term is constructed in the objective function, which not only alleviates the influence of boundary effect, but also improves the resolution of the filter between the target and the background region. Secondly, the verification score is calculated according to the response value of each frame, and the reliability and abnormality of the tracking results are analyzed. Finally, the updating rate of target model and response model is dynamically evaluated. A large number of experimental results show that the target tracking algorithm based on adaptive spatial anomaly can deal with background blur, shape change and other abnormal situations well, and has robust tracking performance.
-
Key words:
- Target tracking /
- Adaptive space regular term /
- Anomaly analysis /
- Dynamic update
-
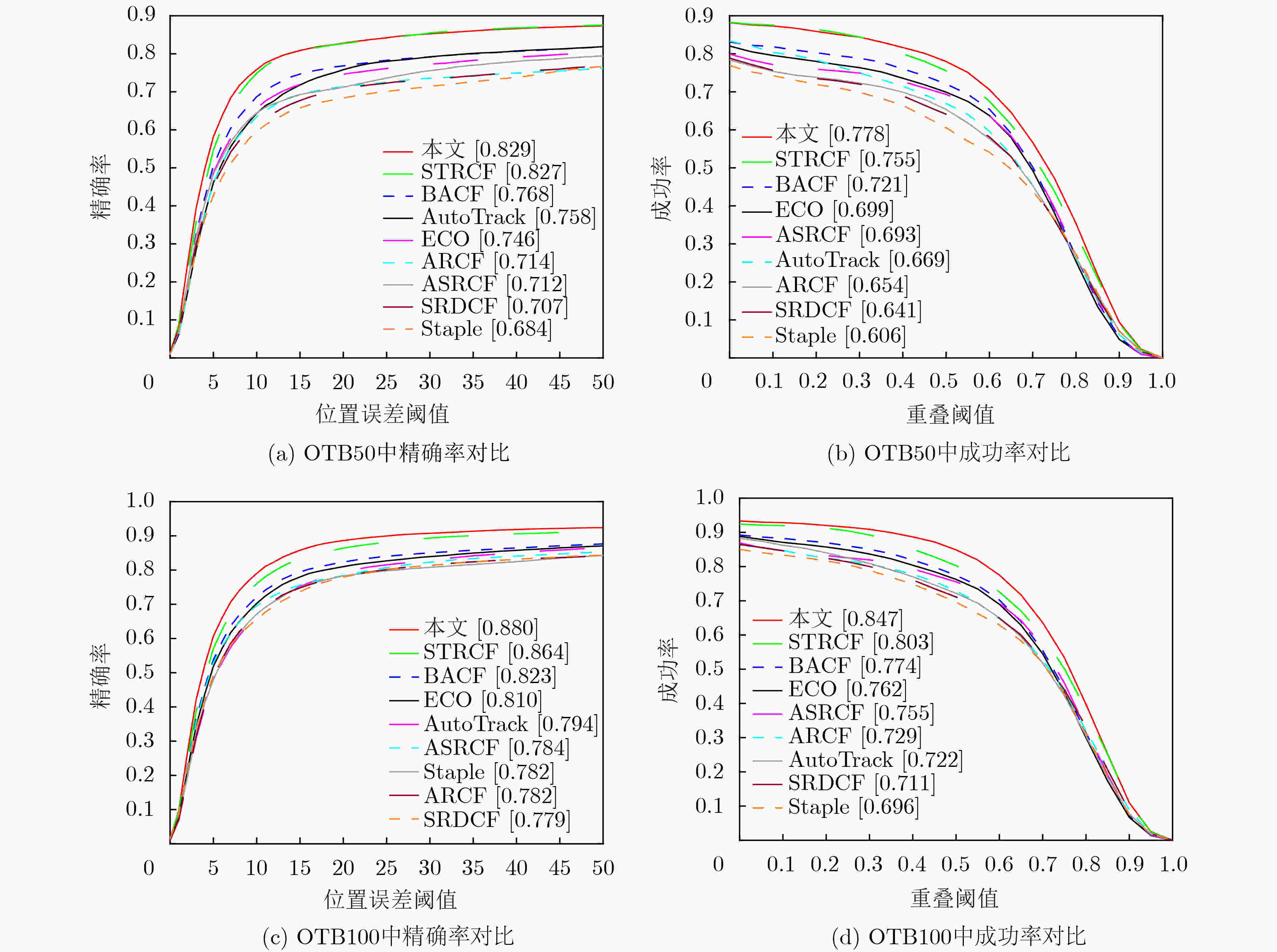
表 1 各种跟踪算法在数据集OTB100上各种属性的精确率得分
本文 STRCF SRDCF Staple BACF ECO ARCF ASRCF AutoTrack 光照变化 0.840 0.835 0.754 0.775 0.824 0.800 0.768 0.777 0.776 尺度变化 0.865 0.838 0.736 0.721 0.769 0.757 0.727 0.731 0.744 遮挡 0.858 0.812 0.726 0.724 0.740 0.720 0.683 0.691 0.713 形变 0.847 0.839 0.712 0.747 0.773 0.765 0.745 0.756 0.743 运动模糊 0.857 0.822 0.741 0.692 0.761 0.736 0.735 0.728 0.766 快速运动 0.843 0.803 0.763 0.710 0.807 0.789 0.745 0.733 0.770 平面内旋转 0.835 0.813 0.721 0.767 0.796 0.781 0.725 0.736 0.774 平面外旋转 0.878 0.848 0.725 0.736 0.785 0.767 0.723 0.755 0.751 超视野 0.832 0.771 0.621 0.668 0.765 0.748 0.671 0.677 0.723 复杂背景 0.854 0.875 0.738 0.748 0.830 0.800 0.787 0.761 0.758 低分辨率 0.810 0.746 0.631 0.610 0.739 0.741 0.707 0.582 0.764 表 2 各种跟踪算法在数据集OTB100上各种属性的成功率得分
本文 STRCF SRDCF Staple BACF ECO ARCF ASRCF AutoTrack 光照变化 0.802 0.797 0.697 0.708 0.797 0.776 0.749 0.749 0.746 尺度变化 0.815 0.750 0.650 0.596 0.695 0.689 0.646 0.689 0.648 遮挡 0.822 0.763 0.670 0.653 0.707 0.689 0.652 0.687 0.661 形变 0.788 0.744 0.640 0.656 0.705 0.693 0.694 0.715 0.686 运动模糊 0.840 0.784 0.708 0.639 0.734 0.727 0.711 0.711 0.731 快速运动 0.815 0.747 0.710 0.645 0.766 0.760 0.709 0.709 0.718 平面内旋转 0.792 0.730 0.630 0.668 0.714 0.704 0.651 0.686 0.667 平面外旋转 0.839 0.774 0.635 0.643 0.718 0.697 0.650 0.715 0.663 超视野 0.771 0.695 0.561 0.548 0.694 0.689 0.638 0.671 0.655 复杂背景 0.805 0.826 0.660 0.687 0.796 0.766 0.771 0.754 0.702 低分辨率 0.734 0.659 0.562 0.472 0.664 0.663 0.637 0.560 0.668 表 3 各种跟踪算法在数据集OTB100上平均跟踪速度(帧/s)
本文 STRCF SRDCF Staple BACF ECO ARCF ASRCF AutoTrack 14.9 13.3 3.9 61.4 16.9 27.9 12.6 19.8 16.2 -
[1] 卢湖川, 李佩霞, 王栋. 目标跟踪算法综述[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2018, 31(1): 61–67. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201801006LU Huchuan, LI Peixia, and WANG Dong. Visual object tracking: A survey[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 31(1): 61–67. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201801006 [2] 葛宝义, 左宪章, 胡永江. 视觉目标跟踪方法研究综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2018, 23(8): 1091–1107. doi: 10.11834/jig.170604GE Baoyi, ZUO Xianzhang, and HU Yongjiang. Review of visual object tracking technology[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2018, 23(8): 1091–1107. doi: 10.11834/jig.170604 [3] 孟琭, 杨旭. 目标跟踪算法综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1244–1260. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180277MENG Lu and YANG Xu. A survey of object tracking algorithms[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1244–1260. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180277 [4] 段建民, 马学峥, 柳新. 基于MFAPC的无人驾驶汽车路径跟踪方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2019, 45(6): 6–11, 20. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0052439DUAN Jianmin, MA Xuezheng, and LIU Xin. Path tracking method of unmanned vehicle based on MFAPC[J]. Computer Engineering, 2019, 45(6): 6–11, 20. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0052439 [5] 姜文涛, 刘万军, 袁姮. 基于软特征理论的目标跟踪研究[J]. 计算机学报, 2016, 39(7): 1334–1355. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2016.01334JIANG Wentao, LIU Wanjun, and YUAN Heng. Research of object tracking based on soft feature theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2016, 39(7): 1334–1355. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2016.01334 [6] 李娜, 吴玲风, 李大湘. 基于相关滤波的长期跟踪算法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2018, 31(10): 899–908. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201810004LI Na, WU Lingfeng, and LI Daxiang. Long-term tracking algorithm based on correlation filter[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 31(10): 899–908. doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201810004 [7] 刘万军, 孙虎, 姜文涛. 自适应特征选择的相关滤波跟踪算法[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(6): 0615004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0615004LIU Wanjun, SUN Hu, and JIANG Wentao. Correlation filter tracking algorithm for adaptive feature selection[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(6): 0615004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0615004 [8] 姜文涛, 涂潮, 刘万军. 背景与方向感知的相关滤波跟踪[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(3): 527–541. doi: 10.11834/jig.200139JIANG Wentao, TU Chao, and LIU Wanjun. Background and direction-aware correlation filter tracking[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(3): 527–541. doi: 10.11834/jig.200139 [9] BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2544–2550. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2010.5539960. [10] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]. The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 702–715. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33765-9_50. [11] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583–596. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390 [12] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F M, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4310–4318. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.490. [13] GALOOGAHI H K, SIM T, and LUCEY S. Correlation filters with limited boundaries[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 4630–4638. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299094. [14] GALOOGAHI H K, FAGG A, and LUCEY S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. Proceeding of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1144–1152. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.129. [15] LI Feng, TIAN Cheng, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4904–4913. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00515. [16] DAI Ke’nan, WANG Dong, LU Huchuan, et al. Visual tracking via adaptive spatially-regularized correlation filters[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4665–4674. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00480. [17] LI Yiming, FU Changhong, DING Fangqiang, et al. AutoTrack: Towards high-performance visual tracking for UAV with automatic spatio-temporal regularization[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11920–11929. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01194. [18] HUANG Ziyuan, FU Changhong, LI Yiming, et al. Learning aberrance repressed correlation filters for real-time UAV tracking[C]. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 2891–2900. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00298. [19] BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Machine Learning, 2010, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 [20] 马燕青. 求解约束优化问题的增广拉格朗日函数法[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆师范大学, 2013.MA Yanqing. Augmented lagrangian function methods for solving constrained optimization problems[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing Normal University, 2013. [21] BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, GOLODETZ S, et al. Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1401–1409. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.156. [22] DANELLJAN M, BHAT G, KHAN F S, et al. ECO: Efficient convolution operators for tracking[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6931–6939. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.733. -





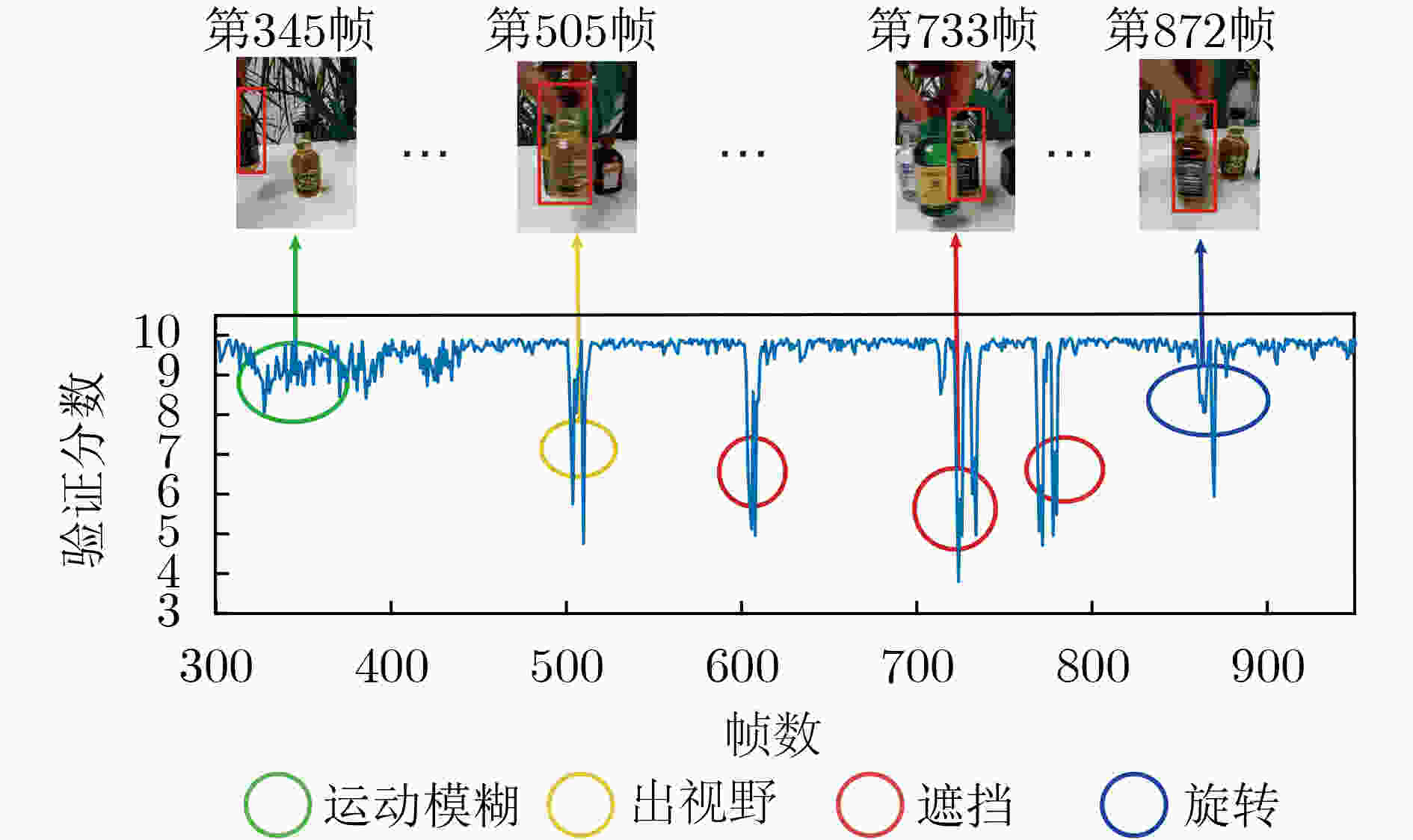
 下载:
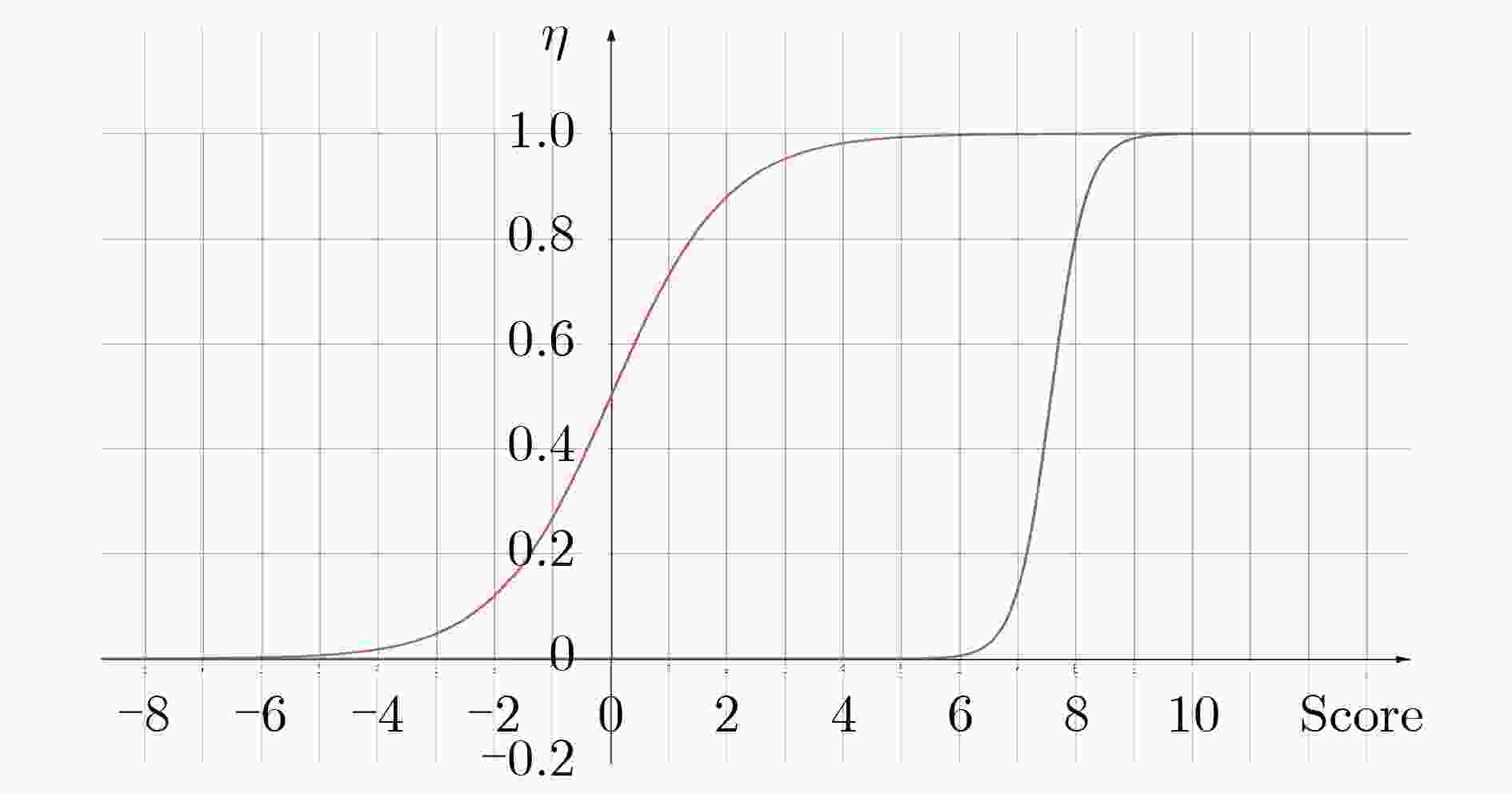
下载:
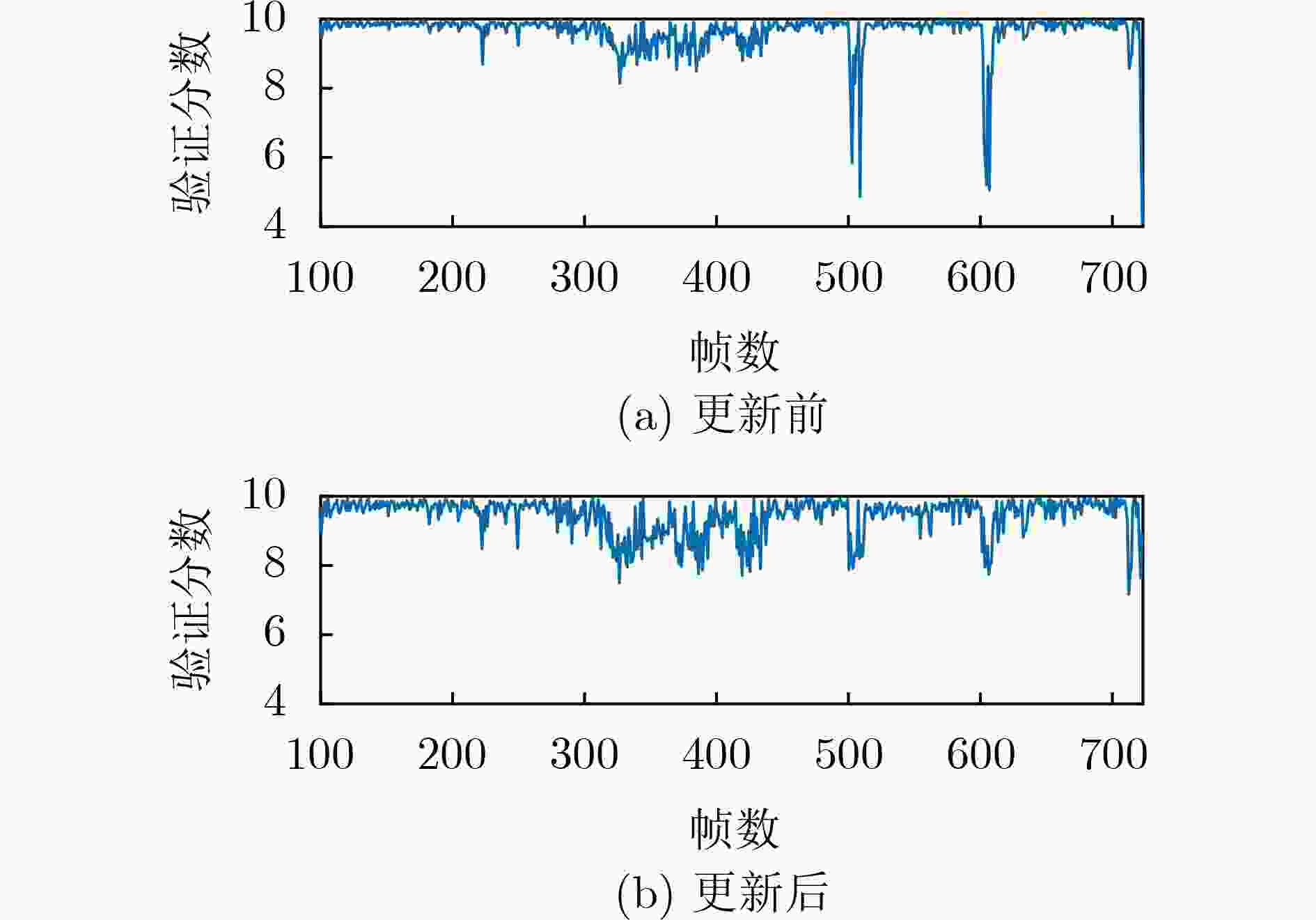



 下载:
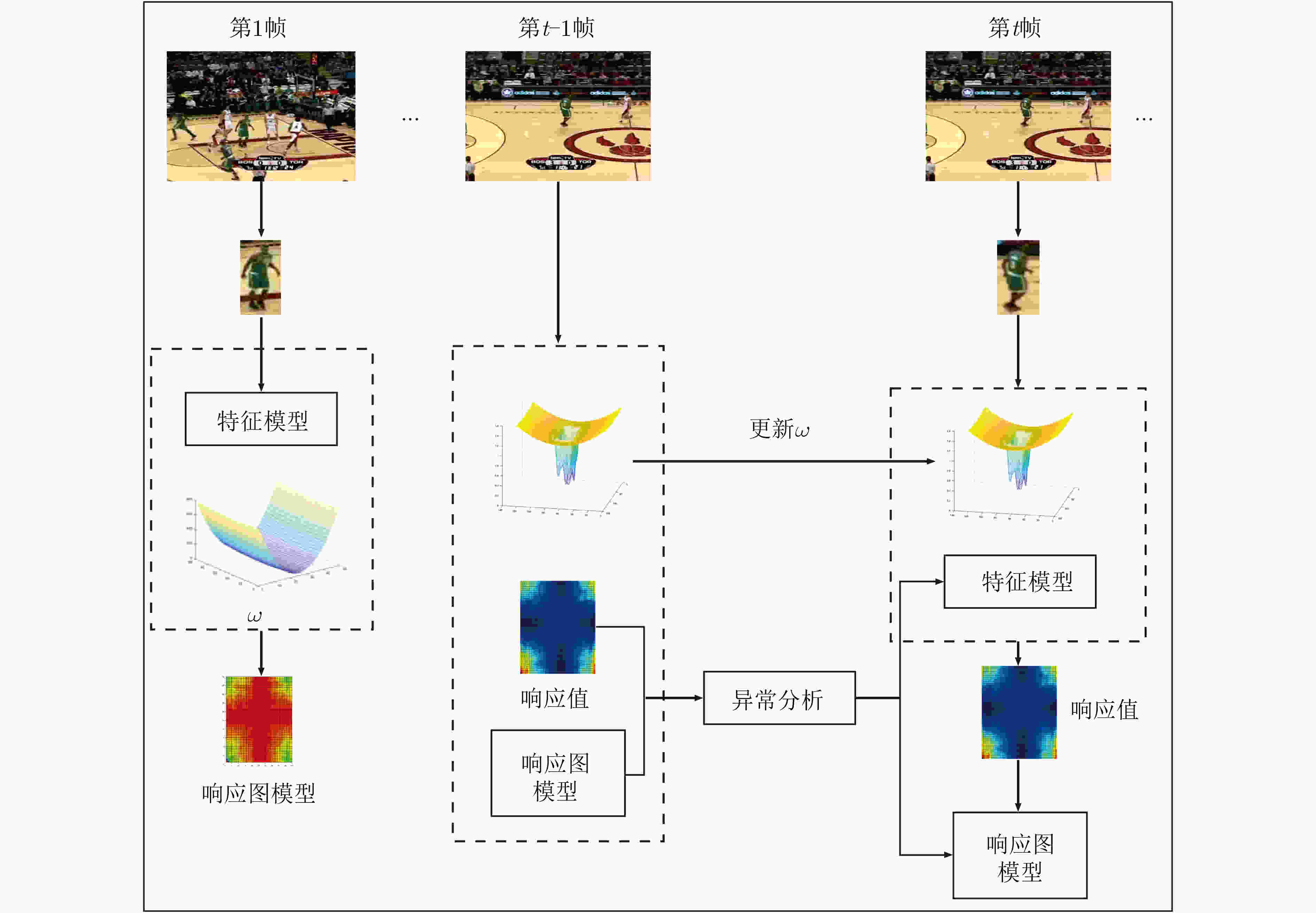
下载:
