A Puncturing Algorithm of Polar Code Based on Gaussian Approximation
-
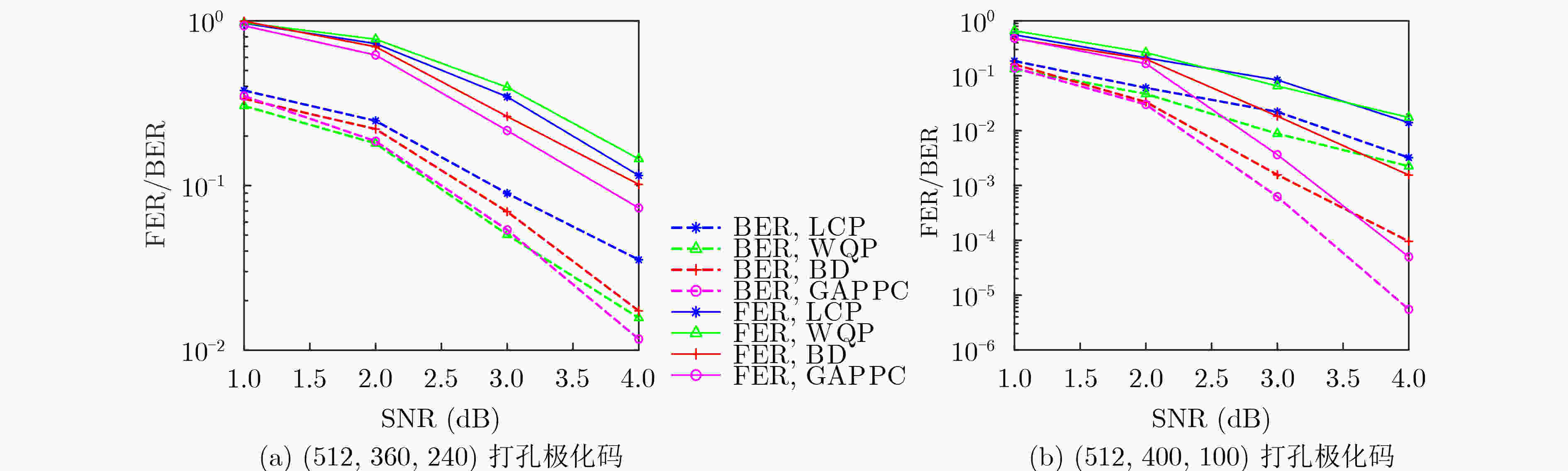
摘要: 现有的极化码打孔算法均未考虑信道构造过程对算法性能的影响,针对这一问题,该文提出一种基于高斯近似的极化码打孔算法(GAPPC)。首先将高斯近似作为极化码构造算法,分析高斯近似与打孔算法的关系,以降低信道构造输出值为目标,引入高斯修正因子,推导出改进的高斯近似函数。然后将改进的高斯近似函数引入信道构造,对极化子信道进行排序获得信道可靠性排序集合。最后依据信道容量关系确定映射规则,选出打孔比特集合和冻结比特集合,完成打孔极化码的构建。实验结果显示,在不同的码长和码率下,误帧率和误码率均获得显著降低。Abstract: The influence of channel construction process on the algorithm performance is not considered in the existing polar code puncturing algorithms. To solve this problem, a Puncturing algorithm of Polar Code based on Gaussian Approximation (GAPPC) is proposed. Firstly, using Gaussian approximation for channel construction of polar code and analyzing the relationship between Gaussian approximation and puncturing algorithm, the modified Gaussian approximation function is derived to reduce the output value of channel construction with introduced Gaussian correction factors. Then the ordered channel reliability set is obtained by ordering the polarization subchannels under the channel construction with the modified Gaussian approximation function. Finally, the mapping rule is determined according to the relationship of channel capacity, and the puncturing bit set and frozen bit set are selected so that the puncturing polar code is completed. Experimental results show that the frame error rate and bit error rate are significantly reduced under different code lengths and bit rates.
-
Key words:
- Polar code /
- Rate-compatible /
- Puncturing /
- Gaussian Approximation(GA)
-
表 1 GAPPC算法
输入:极化码的码长$N$,打孔后码长$M$,信息比特长度$K$,打孔比特长度$P = N - M$ (1) 使用对N长的极化码进行MGA构造,获得子信道可靠性升序集合${R_{\rm{MGA}}}$ (2) 选出无能力比特位置集合$\mathcal{Q} = \left\{ {1,2,\cdots,P} \right\}$,应用改进信道映射在编码结构中找出打孔比特位置集合$\mathcal{P}$ (3) 在${R_{\rm{MGA}}}$中除去无能力比特位置找出可靠性最低的$M - K$比特,设为剩余冻结比特集合${\mathcal{Q}^C}$ (4) 依据${\mathcal{Q}^C}$和$\mathcal{Q}$得出冻结比特集合${A^C}$和信息比特集合$A$ 表 2 4种算法的计算复杂度对比
打孔算法 (256, 186, 93) (512, 400, 100) (1024, 860, 512) (2048,1900,1024) LCP 2049 4609 10241 22529 WQP 2118 4720 10404 22676 BD 2049 4609 10241 22529 GAPPC 2608 5616 11880 24156 -
[1] ARIKAN E. Channel polarization: A method for constructing capacity-achieving codes for symmetric binary-input memoryless channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(7): 3051–3073. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2021379 [2] 刘建航, 何怡静, 李世宝, 等. 基于预译码的极化码最大似然简化连续消除译码算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 959–966. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180324LIU Jianhang, HE Yijing, LI Shibao, et al. Pre-decoding based maximum-likelihood simplified successive-cancellation decoding of polar codes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 959–966. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180324 [3] 王琼, 罗亚洁, 李思舫. 基于分段循环冗余校验的极化码自适应连续取消列表译码算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1572–1578. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180716WANG Qiong, LUO Yajie, and LI Sifang. Polar adaptive successive cancellation list decoding based on segmentation cyclic redundancy check[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1572–1578. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180716 [4] ESLAMI A and PISHRO-NIK H. A practical approach to polar codes[C]. 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory Proceedings (ISIT), St. Petersburg, Russia, 2011: 16–20. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2011.6033837. [5] SHIN D M, LIM S C, and YANG K. Design of length-compatible polar codes based on the reduction of polarizing matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(7): 2593–2599. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.052013.120543 [6] NIU Kai, CHEN Kai, and LIN Jiaru. Beyond turbo codes: Rate-compatible punctured polar codes[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Budapest, Hungary, 2013: 3423–3427. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2013.6655078. [7] NIU Kai, DAI Jincheng, CHEN Kai, et al. Rate-compatible punctured polar codes: Optimal construction based on polar spectra[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.01352, 2016. [8] LIU Wei, WANG Yue, LI Ao, et al. An improved puncturing scheme for polar codes[C]. 2020 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Limassol, Cyprus, 2020: 154–158. doi: 10.1109/IWCMC48107.2020.9148522. [9] HANIF M A and VAFI S. A modified approach to punctured product polar codes[J]. Journal of Telecommunications and Information Technology, 2019, 3: 63–69. doi: 10.26636/jtit.2019.132219 [10] JANG M, AHN S K, JEONG H, et al. Rate matching for polar codes based on binary domination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(10): 6668–6681. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2930502 [11] HONG S N and JEONG M O. An efficient construction of rate-compatible punctured polar (RCPP) codes using hierarchical puncturing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(11): 5041–5052. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2854183 [12] ZHAO Jianhan, ZHANG Wei, LIU Yanyan, et al. A rate-matching concatenation scheme of polar codes with outer reed-Solomon codes[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(3): 459–463. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3033850 [13] ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Zhaoyang, WANG Xianbin, et al. On the puncturing patterns for punctured polar codes[C]. 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Honolulu, USA, 2014: 121–125. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2014.6874807. [14] BIOGLIO V, GABRY F, and LAND I. Low-complexity puncturing and shortening of polar codes[C]. 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops (WCNCW), San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNCW.2017.7919040. [15] LI Liping, SONG Wei, and NIU Kai. Optimal puncturing of polar codes with a fixed information set[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 65965–65972. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2918346 [16] WU Daolong, LI Ying, and SUN Yue. Construction and block error rate analysis of polar codes over AWGN channel based on Gaussian approximation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(7): 1099–1102. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2325811 [17] TAL I and VARDY A. How to construct polar codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(10): 6562–6582. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2272694 [18] CHUNG S Y, RICHARDSON T J, and URBANKE R L. Analysis of sum-product decoding of low-density parity-check codes using a Gaussian approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2001, 47(2): 657–670. doi: 10.1109/18.910580 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
