A User Association Algorithm for Maximizing Energy Efficiency with Human-to-Human and Machine-to-Machine Coexistence
-
摘要: 针对5G超密集异构蜂窝网络中人与人(H2H)和机器到机器(M2M)共存场景下有服务质量(QoS)保障和负载均衡的上行用户分配问题,该文提出一种基于匹配理论的用户分配算法。该算法在用户分配过程中同时考虑不同类型节点的接入控制策略,在最大化网络能效的同时,实现节点QoS保障。仿真结果表明,与其他算法相比,该算法不仅能够在能效、负载均衡以及QoS保障方面获得更好的性能,并且能获得与穷举法相近的性能。此外,所提算法的收敛速度很快且不受节点和基站数目变化的影响,适合解决H2H和M2M共存场景中的用户分配问题。
-
关键词:
- 超密集异构蜂窝网络 /
- 人与人和机器到机器共存 /
- 用户分配 /
- 能量有效 /
- 服务质量保障
Abstract: In this paper, a match theory based uplink user association algorithm is proposed for maximizing energy efficiency and guaranteeing Quality of Service (QoS) requirements in a ultra-dense heterogeneous cellular networks with Human-to-Human (H2H) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) coexistence. To maximize energy efficiency, balance load and guarantee QoS, simultaneously, the algorithm considers two access mechanisms for different types of node. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm not only outperforms existing schemes in terms of the overall energy efficiency, the load balance and QoS guarantees, but also achieves the same performance as exhaustive search. Furthermore, the convergence speed of the algorithm is very fast, and is not affected by the number of base stations and nodes. Thus, the algorithm is suitable to solve the problem of user association, while considering the networks with H2H and M2M coexistence. -
表 1 有QoS保障和负载均衡的能量有效用户分配(EEUAQL)算法
阶段1:基于偏好的分布式迭代准入(PDIA)子算法 初始化迭代次数${t_1} = 0$;每一个HTC用户根据式(7)定义的偏好关系对所有基站排序,然后向偏好程度最高的基站发送接入申请和传输速率需求; 在收到基站发送的申请后, For 基站j,$j = 1:N$ 基站j根据式(8)计算得到偏好列表$\mathcal{A}_j^{\rm{rank}}$,并根据式(9)计算${q_j}$; 如果${q_j} \ge \left| {{\mathcal{A}_j}} \right|$,基站j将所有的申请者都添加到接收列表中,否则,基站j只是将偏好列表$\mathcal{A}_j^{\rm{rank}}$中前${q_j}$个申请者添加到接收列表中,并拒绝其他申请者; End For Repeat 新一轮的申请开始:首先,被拒绝的HTC用户将申请接入偏好程度次好的基站; For基站j,$j = 1:N$ 基站j会获得一个基于新申请者和已经接收的HTC用户的新偏好列表,并且重新计算${q'_j}$; 如果${q'_j}$大于申请者和已经接收的HTC用户数目之和,基站j将所有的申请者都添加到接收列表中, 否则,基站j只是将新偏好列表中前${q'_j}$个申请者添加到接收列表中,拒绝其他申请者; End For ${t_1} = {t_1}{\rm{ + }}1$; Until 所有HTC用户都在基站的接收列表中,然后得到HTC用户的分割${{\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} '_{{\rm{HTC}}}}$。 阶段2:最大化能效的转移(TEEM)子算法 初始化迭代次数${t_2} = 0$;每一个MTC设备向距离自己最近的基站发送申请,此时形成一个初始MTC设备分割${\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} _{{\rm{MTC}}}^{\rm{initial}}$; 根据${\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} _{{\rm{MTC}}}^{\rm{initial}}$和HTC用户的分割${{\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} '_{{\rm{HTC}}}}$,基站两两之间进入如下MTC设备转移过程: Repeat For基站$a$, $b = a + 1:N,$ For 基站b, $b = a + 1:N,$ 基站a与基站b遍历两个集合的所有元素,若存在满足转移条件式(11)的MTC设备,执行转移; End For End For ${t_2} = {t_2}{\rm{ + }}1$; Until 没有基站进行转移,即可获得MTC设备分割${{\boldsymbol{\varOmega}} '_{{\rm{MTC}}}}$。 -
[1] XIA Nian, CHEN H H, and YANG C S. Radio resource management in Machine-to-Machine communications—a survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(1): 791–828. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2765344 [2] 谭晓衡, 谢朝臣, 郭坦. 基于区域感知贝叶斯决策的5G超密集异构网络联合垂直切换技术研究[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(3): 582–588. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.03.010TAN Xiaoheng, XIE Chaochen, and GUO Tan. Research of joint vertical handoff technology based on area sensing Bayesian decision in ultra-dense HetNet for 5G[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(3): 582–588. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.03.010 [3] 张剑, 邱玲, 陈正. 超密集网络中基于多连接的用户归属和功率控制联合优化[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2018, 35(1): 126–130. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2018.01.017ZHANG Jian, QIU Ling, and CHEN Zheng. Joint user-association and power-control algorithm based on multiple association in ultra-dense network[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 35(1): 126–130. doi: 10.7523/j.issn.2095-6134.2018.01.017 [4] 苏恭超, 陈彬, 林晓辉, 等. 异构蜂窝网络中一种基于匈牙利算法的用户关联方法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2017, 46(2): 346–351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.005SU Gongchao, CHEN Bin, LIN Xiaohui, et al. User association in heterogeneous cellular networks via the Hungarian method[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017, 46(2): 346–351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.02.005 [5] YE Qiaoyang, RONG Beiyu, CHEN Yudong, et al. User association for load balancing in heterogeneous cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(6): 2706–2716. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.040413.120676 [6] BOOSTANIMEHR H and BHARGAVA V K. Unified and distributed QoS-driven cell association algorithms in heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(3): 1650–1662. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2371465 [7] 陈剑, 吴建平, 李贺武. 基于用户分配和负载的频谱分配算法[J]. 软件学报, 2013, 24(7): 1638–1649. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2013.04312CHEN Jian, WU Jianping, and LI Hewu. Spectrum allocation algorithm based on user allocation and load[J]. Journal of Software, 2013, 24(7): 1638–1649. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2013.04312 [8] SAAD W, HAN Zhu, ZHENG Rong, et al. A college admissions game for uplink user association in wireless small cell networks[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM 2014), Toronto, Canada, 2014: 1096–1104. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2014.6848040. [9] BOOSTANIMEHR H and BHARGAVA V K. Joint downlink and uplink aware cell association in HetNets with QoS provisioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(10): 5388–5401. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2437878 [10] MESODIAKAKI A, ADELANTADO F, ALONSO L, et al. Joint uplink and downlink cell selection in cognitive small cell heterogeneous networks[C]. 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2014: 2643–2648. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2014.7037206. [11] LI G Y, NIU Jinping, LEE D, et al. Multi-cell coordinated scheduling and MIMO in LTE[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2014, 16(2): 761–775. doi: 10.1109/SURV.2014.022614.00186 [12] WANG Zehua and WONG V W S. Optimal access class barring for stationary machine type communication devices with timing advance information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(10): 5374–5387. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2437872 [13] GALE D and SHAPLEY L S. College admissions and the stability of marriage[J]. The American Mathematical Monthly, 1962, 69(1): 9–15. doi: 10.2307/2312726 [14] ROTH A E and SOTOMAYOR M A O. Two-Sided Matching: A Study in Game-Theoretic Modeling and Analysis[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1990: 150–161. [15] ANDREWS J G. Seven ways that HetNets are a cellular paradigm shift[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2013, 51(3): 136–144. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2013.6476878 [16] JAIN R K. The Art of Computer Systems Performance Analysis: Techniques for Experimental Design, Measurement, Simulation, and Modeling[M]. New York: Wiley, 1991: 141–153. -





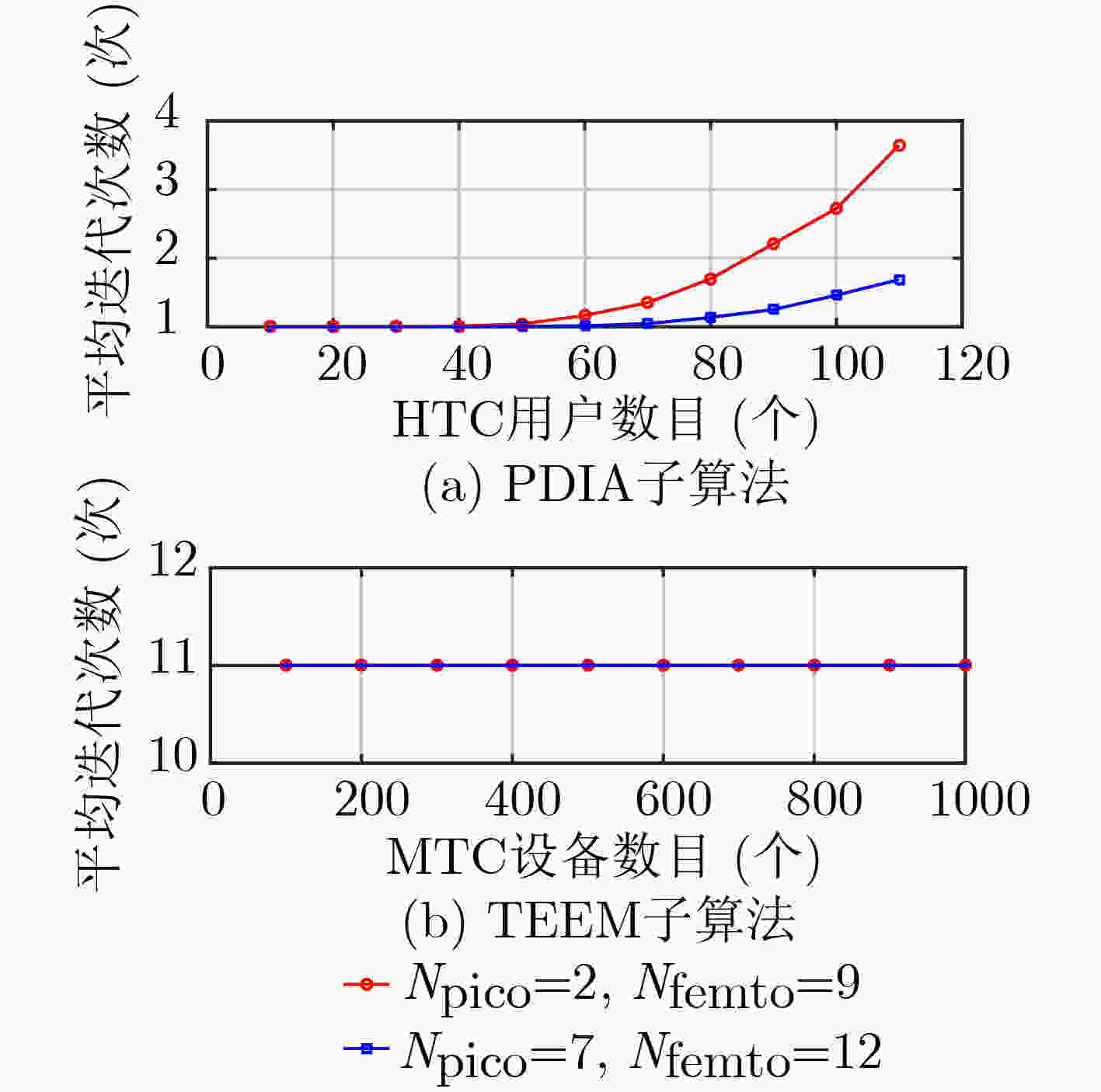
 下载:
下载:
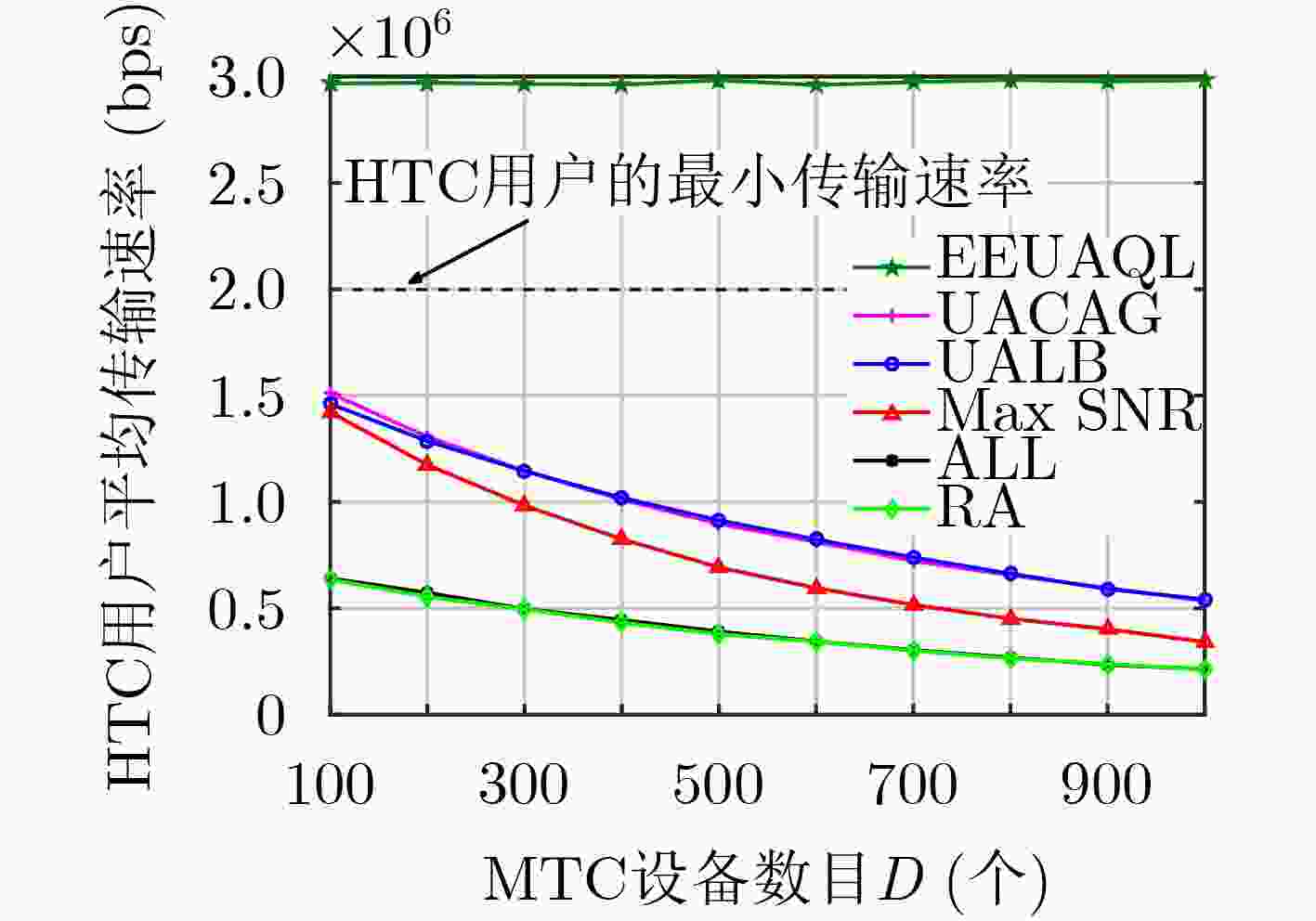
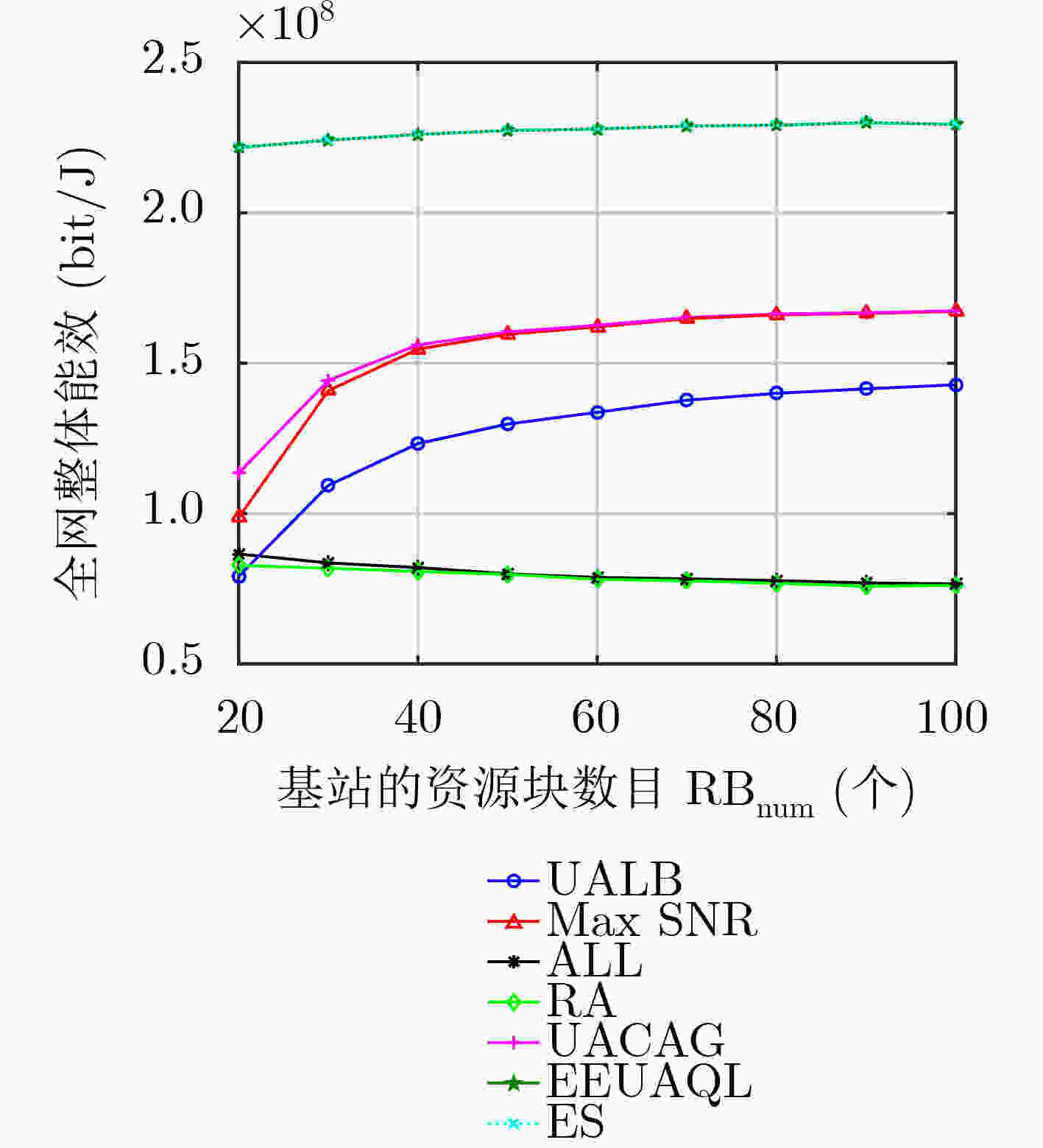
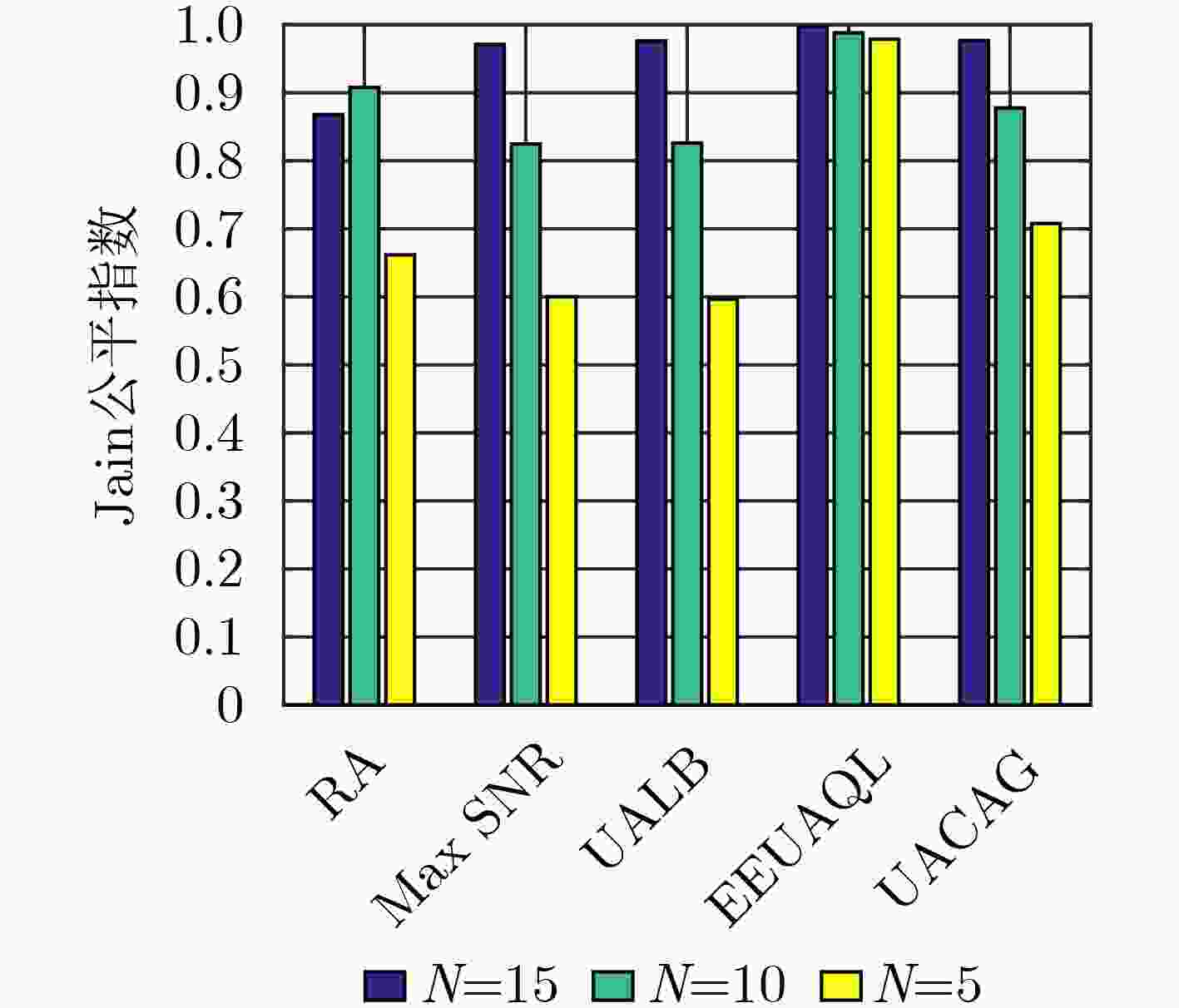


 下载:
下载:
