A Recommendation Method for Point-of-Interest Partition Based on Category Transfer Weighted Tensor Decomposition Model
-
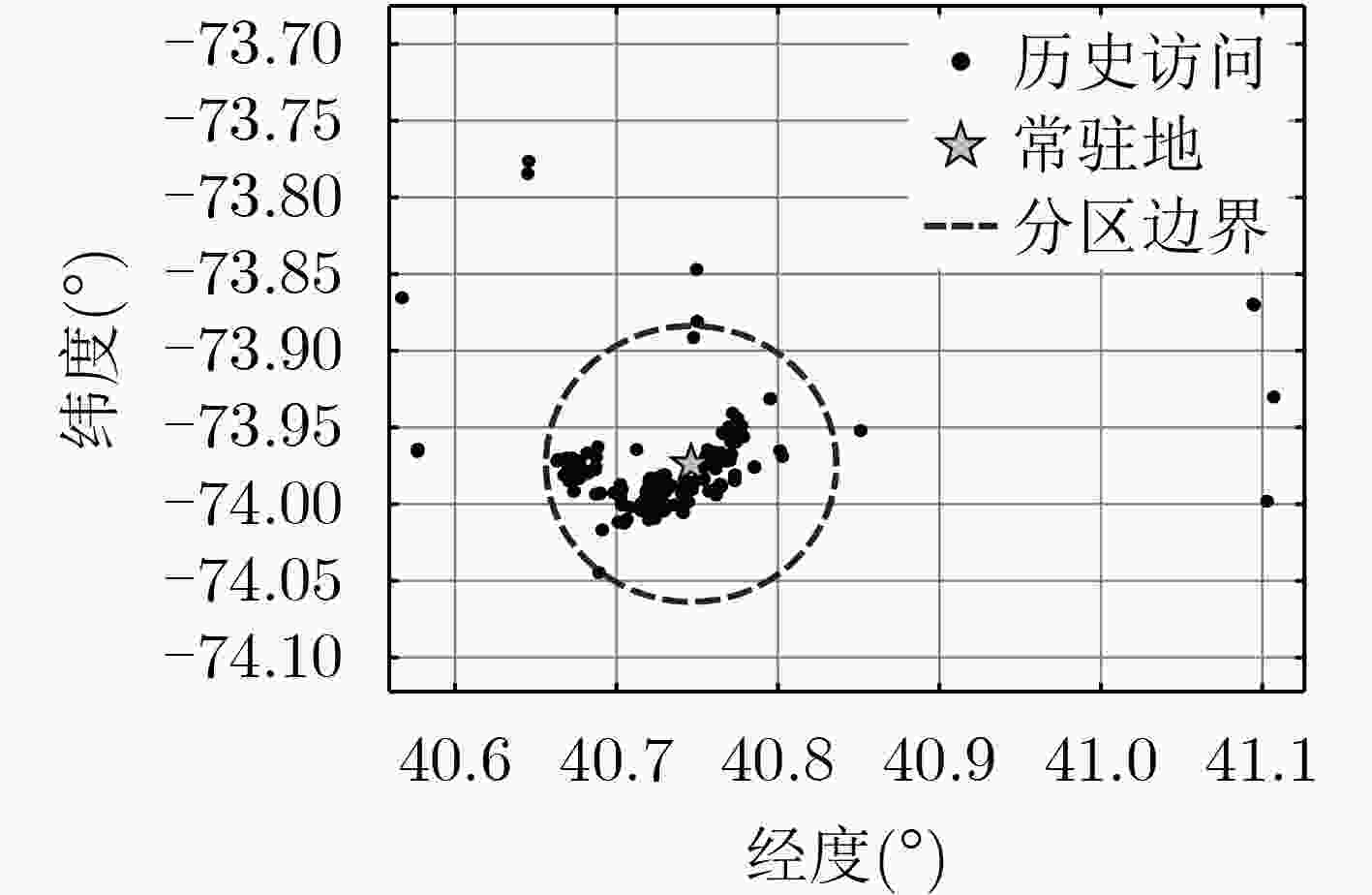
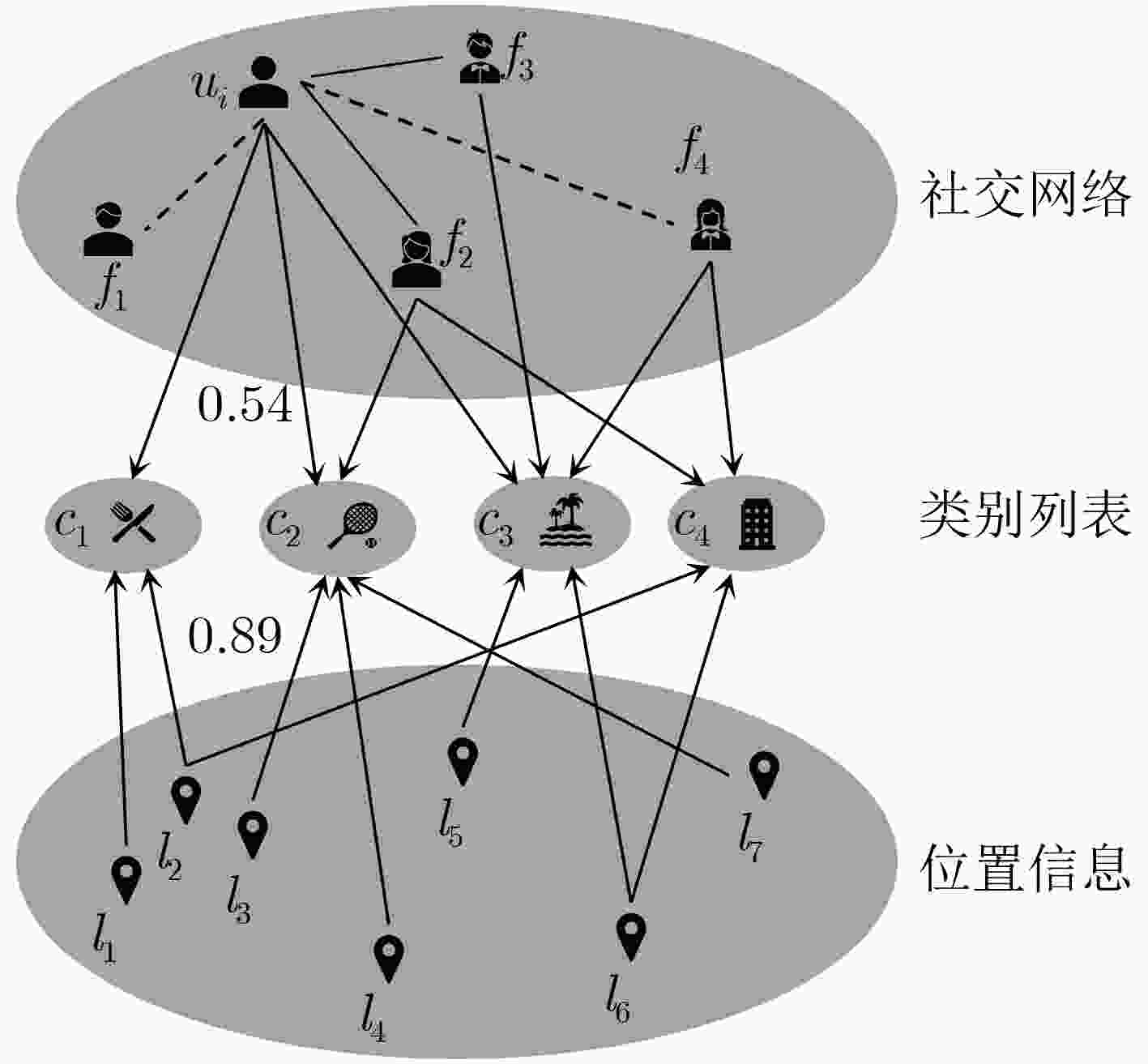
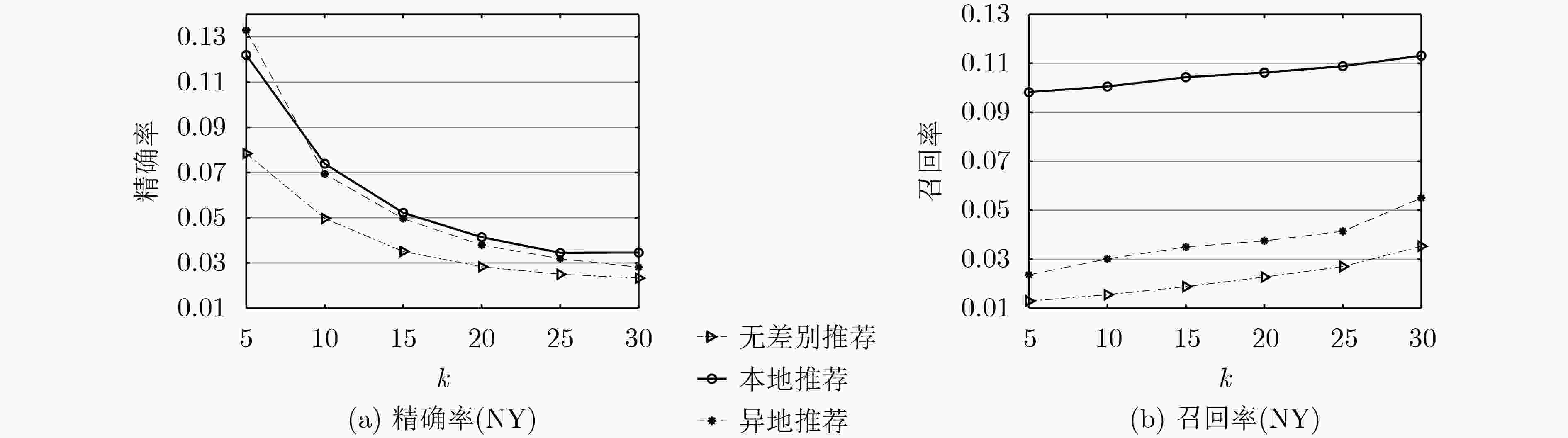
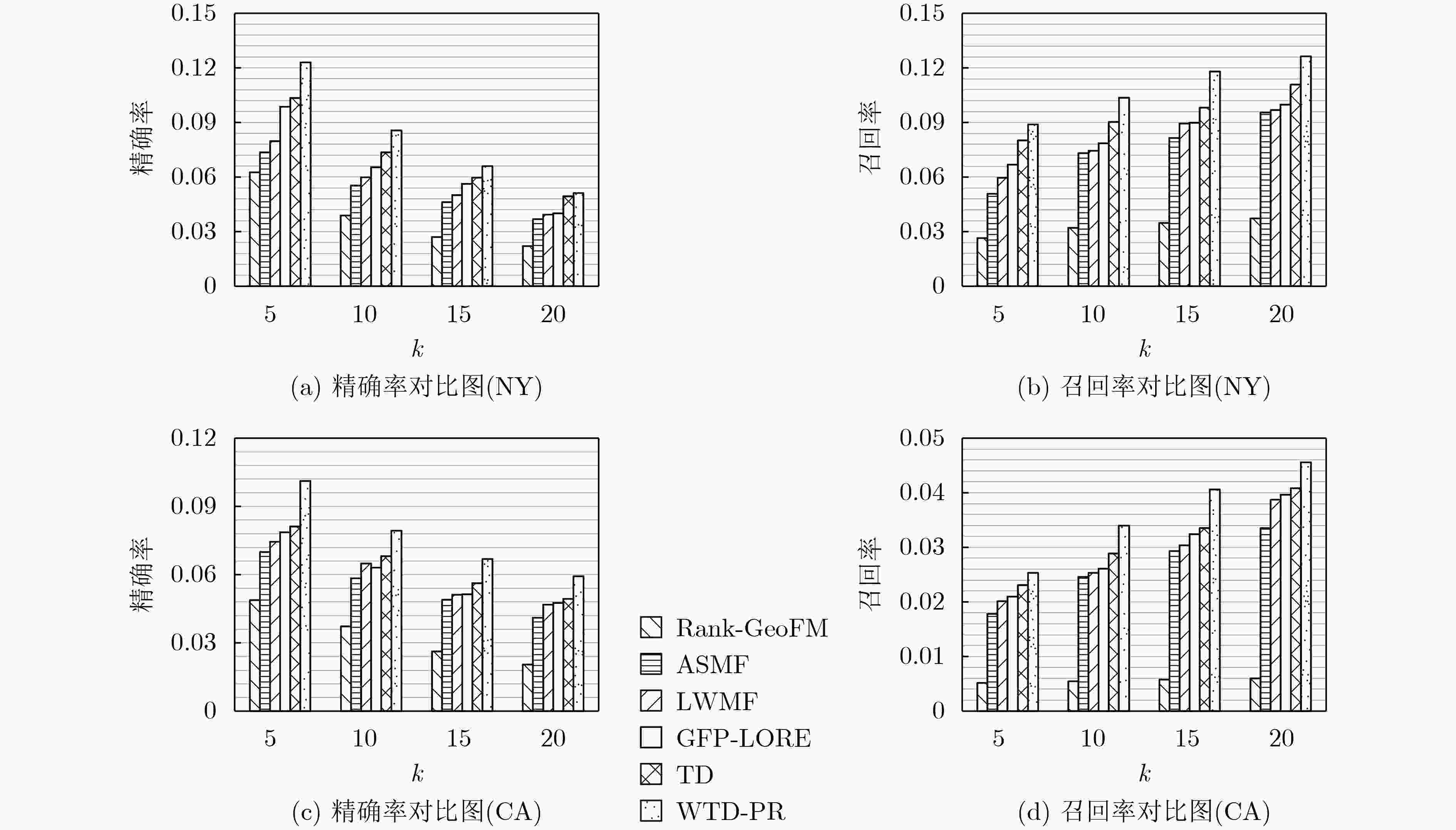
摘要: 基于位置社交网络的兴趣点(POI)推荐是人们发现有趣位置的重要途径,然而,现实中用户在不同区域的地点偏好侧重的差异,加之高维度的历史签到信息,使得精准而又个性化的POI推荐极富挑战性。对此,该文提出一种新型的基于类别转移加权张量分解模型的兴趣点分区推荐算法(WTD-PR)。通过结合用户连续行为和时间特征,来充分利用用户的历史访问信息,从而得到类别转移权重因子;接着改进用户-时间-类别张量模型,在此张量中加入类别转移权重,预测用户的喜好类别;最后,根据用户的历史访问区域划分出本地和异地,并基于用户的当前位置找出推荐区域范畴,进而引入位置因素和社交因素,结合候选类别作兴趣点分区推荐。通过在真实数据集上进行对比实验,实验结果表明,所提算法不仅具有通用性,而且在推荐性能上也优于其他对比算法。Abstract: Point-Of-Interest (POI) recommendation in location-based social networks is an important way for people to find interesting locations. However, in reality, both the various user preference of locations in different regions and the high-dimensional historical check-in information make accurate and personalized POI recommendations extremely challenging. In this regard, a new type of recommendation algorithm for point-of-interest Partition Recommendation based on a category transfer Weighted Tensor Decomposition (WTD-PR) model is proposed. The proposed algorithm makes full use of the user’s historical visit information by combining the user’s continuous behavior and time characteristics to obtain the category transfer weight factor; Then, by improving the user-time-category tensor model and adding the category transfer weight to the tensor to predict the user’s preference category; Finally, the local and remote locations are divided according to the user’s historical access area, and the recommended areas are found based on the user’s current location. After that, location and social factors are introduced and combined with the candidate categories to make the recommendation of points of interest. Through comparative experiments on real data sets, the proposed algorithm is proved not only to be universal, but also superior to other comparison algorithms in terms of recommendation performance.
-
表 1 类别预测算法
输入:张量${\boldsymbol{R}}$,权重${{\boldsymbol{W}}^{\rm{TC}}}$,误差阈值$\varepsilon $ 输出:因子矩阵${\boldsymbol{U}}$,${\boldsymbol{T}}$,${\boldsymbol{C}}$和核心张量${\boldsymbol{S}}$ (1) 通过HOSVD初始化张量${\boldsymbol{R}}$,得到${\boldsymbol{\hat R}}$; (2) 赋给${\boldsymbol{U}} \in {{\boldsymbol{R}}^{m \times {\tau _1}}}$, $\boldsymbol{T} \in {\boldsymbol{R}^{g \times {\tau _{\rm{2}}}}}$,${\boldsymbol{C}} \in {{\boldsymbol{R}}^{n \times {\tau _{\rm{3}}}}}$, ${\boldsymbol{S}} \in {{\boldsymbol{R}}^{{\tau _1} \times {\tau _2} \times {\tau _3}}}$随机数值,设置步长$\varphi $; (3) ${\rm{While}}\;\;{\rm{ }}{L_t} - {L_{t{\rm{ + }}1}} > \varepsilon :$ (4) ${\rm{For}}\;\;{\rm{ }}{{\boldsymbol{\hat R}}_{ijk}} \ne 0:$ (5) ${\hat {\boldsymbol{R}}_{ijk}} = {\boldsymbol{S}}{ \times _{\boldsymbol{U}}}{{\boldsymbol{U}}_{i * }}{ \times _{\boldsymbol{T}}}{{\boldsymbol{T}}_{j * }}{ \times _{\boldsymbol{C}}}{{\boldsymbol{C}}_{k * }}$ (6) $ {{\boldsymbol{U}}}_{i\ast }\leftarrow {{\boldsymbol{U}}}_{i\ast }-\phi \lambda {{\boldsymbol{U}}}_{i\ast }-\phi ({{\boldsymbol{Y}}}_{ijk}-{\boldsymbol{W}}^{{\rm{T}}{\rm{C}}}·{\widehat{{\boldsymbol{R}}}}_{i}{}_{jk}){\boldsymbol{S}}{\times }_{{\boldsymbol{T}}}{{\boldsymbol{T}}}_{j\ast }{\times }_{{\boldsymbol{C}}}{{\boldsymbol{C}}}_{k\ast }$ (7) $ {{\boldsymbol{T}}}_{j\ast }\leftarrow {{\boldsymbol{T}}}_{j\ast }-\phi \lambda {{\boldsymbol{T}}}_{j\ast }-\phi ({{\boldsymbol{Y}}}_{ijk}-{\boldsymbol{W}}^{{\rm{T}}{\rm{C}}}·{\widehat{{\boldsymbol{R}}}}_{i}{}_{jk}){\boldsymbol{S}}{\times }_{{\boldsymbol{U}}}{{\boldsymbol{U}}}_{i\ast }{\times }_{{\boldsymbol{C}}}{{\boldsymbol{C}}}_{k\ast }$ (8) $ {{\boldsymbol{C}}}_{k\ast }\leftarrow {{\boldsymbol{C}}}_{k\ast }-\phi \lambda {{\boldsymbol{C}}}_{k\ast }-\phi ({{\boldsymbol{Y}}}_{ijk}-{\boldsymbol{W}}^{{\rm{T}}{\rm{C}}}·{\widehat{{\boldsymbol{R}}}}_{i}{}_{jk}){\boldsymbol{S}}{\times }_{{\boldsymbol{U}}}{{\boldsymbol{U}}}_{i\ast }{\times }_{{\boldsymbol{T}}}{{\boldsymbol{T}}}_{j\ast }$ (9) $ {\boldsymbol{S}}\leftarrow {\boldsymbol{S}}-\phi \lambda {\boldsymbol{S}}-\phi ({{\boldsymbol{Y}}}_{ijk}-{\boldsymbol{W}}^{{\rm{T}}{\rm{C}}}·{\widehat{{\boldsymbol{R}}}}_{i}{}_{jk}){{\boldsymbol{U}}}_{i\ast }\otimes {{\boldsymbol{T}}}_{j\ast }\otimes {{\boldsymbol{C}}}_{k\ast }$ (10) $\rm{End}$ (11) 输出${\boldsymbol{U}}$, ${\boldsymbol{T}}$, ${\boldsymbol{C}}$, ${\boldsymbol{S}}$ 表 2 数据集统计分布表
数据集 用户数量 地点数量 地点类别 签到记录 NY 972 5880 368 13258 CA 4018 71422 396 401555 表 3 多维因素有效性验证
数据集 评价指标 WTD-T WTD-C WTD-LP WTD-FL WTD-FP WTD-PR NY $\rm{Pre}@10$ 0.0679 0.0685 0.0713 0.0739 0.0784 0.0810 $\rm{Rec}@10$ 0.0815 0.0862 0.0977 0.0961 0.1005 0.1035 CA $\rm{Pre}@10$ 0.0648 0.0653 0.0679 0.0685 0.0705 0.0794 $\rm{Rec}@10$ 0.0257 0.0261 0.0273 0.0286 0.0291 0.0340 -
[1] YU Fet, LI Zhijun, JIANG Shouxu, et al. Point-of-interest recommendation for location promotion in location-based social networks[C]. 2017 18th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management, Daejeon, South Korea, 2017: 344–347. doi: 10.1109/MDM.2017.57. [2] LI Xutao, CONG Gao, LI Xiaoli, et al. Rank-GeoFM: A ranking based geographical factorization method for point of interest recommendation[C]. The 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 433–442. doi: 10.1145/2766462.2767722. [3] LIAN Defu, ZHENG Kai, GE Yong, et al. GeoMF++: Scalable location recommendation via joint geographical modeling and matrix factorization[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2018, 36(3): 33. doi: 10.1145/3182166 [4] YAO Lina, SHENG Q Z, QIN Yongrui, et al. Context-aware point-of-interest recommendation using tensor factorization with social regularization[C]. The 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1007–1010. doi: 10.1145/2766462.2767794. [5] ZHANG Lu, SUN Zhu, ZHANG Jie, et al. Modeling hierarchical category transition for next POI recommendation with uncertain check-ins[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 515: 169–190. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.12.006 [6] LI Huayu, GE Yong, HONG Richang, et al. Point-of-Interest recommendations: Learning potential check-ins from friends[C]. The 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 975–984. doi: 10.1145/2939672.2939767. [7] GUO Lei, WEN Yufei, and LIU Fangai. Location perspective-based neighborhood-aware POI recommendation in location-based social networks[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(22): 11935–11945. doi: 10.1007/s00500-018-03748-9 [8] REN Yueqiang, WANG Ze, SUN Xiaona, et al. A multi-element hybrid location recommendation algorithm for location based social networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 100416–100427. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2929313 [9] YAO Lina, SHENG Q Z, WANG Xianzhi, et al. Collaborative location recommendation by integrating multi-dimensional contextual information[J]. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology, 2018, 18(3): 32. doi: 10.1145/3134438 [10] HE Jing, LI Xin, LIAO Lejian, et al. Inferring a personalized next point-of-interest recommendation model with latent behavior patterns[C]. The Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, USA, 2016: 137–143. doi: 10.5555/3015812.3015833. [11] DING Jingtao, YU Guanghui, LI Yong, et al. Learning from Hometown and current city: Cross-city POI recommendation via interest drift and transfer learning[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2019, 3(4): 131. doi: 10.1145/3369822 [12] YIN Hongzhi, ZHOU Xiaofeng, CUI Bin, et al. Adapting to user interest drift for POI recommendation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2016, 28(10): 2566–2581. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2016.2580511 [13] LIAN Defu, ZHANG Zhenyu, GE Yong, et al. Regularized content-aware tensor factorization meets temporal-aware location recommendation[C]. 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 1029–1034. doi: 10.1109/ICDM.2016.0131. [14] GAO Huiji, TANG Jiliang, HU Xia, et al. Exploring temporal effects for location recommendation on location-based social networks[C]. The 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Hong Kong, China, 2013: 93–100. doi: 10.1145/2507157.2507182. [15] 赵明, 闫寒, 曹高峰, 等. 融合用户信任度和相似度的基于核心用户抽取的鲁棒性推荐算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 180–186. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180142ZHAO Ming, YAN Han, CAO Gaofeng, et al. Robust recommendation algorithm based on core user extraction with user trust and similarity[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 180–186. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180142 [16] CHENG Chen, YANG Haiqin, KING I, et al. Fused matrix factorization with geographical and social influence in location-based social networks[C]. The Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, Canada, 2012: 17–23. doi: 10.5555/2900728.2900731. [17] 司亚利, 张付志, 刘文远. 基于签到活跃度和时空概率模型的自适应兴趣点推荐方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 678–686. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190287SI Yali, ZHANG Fuzhi, and LIU Wenyuan. An adaptive point-of-interest recommendation method based on check-in activity and temporal-spatial probabilistic models[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 678–686. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190287 [18] CHEN Jialiang, LI Xin, CHEUNG W K, et al. Effective successive POI recommendation inferred with individual behavior and group preference[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 210: 174–184. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.146 -





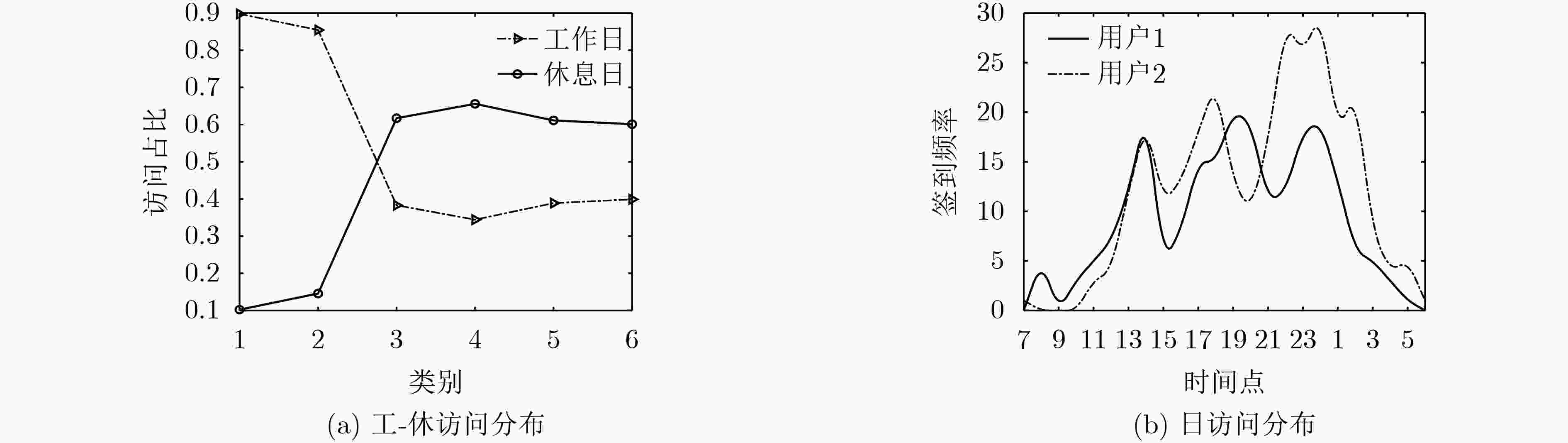
 下载:
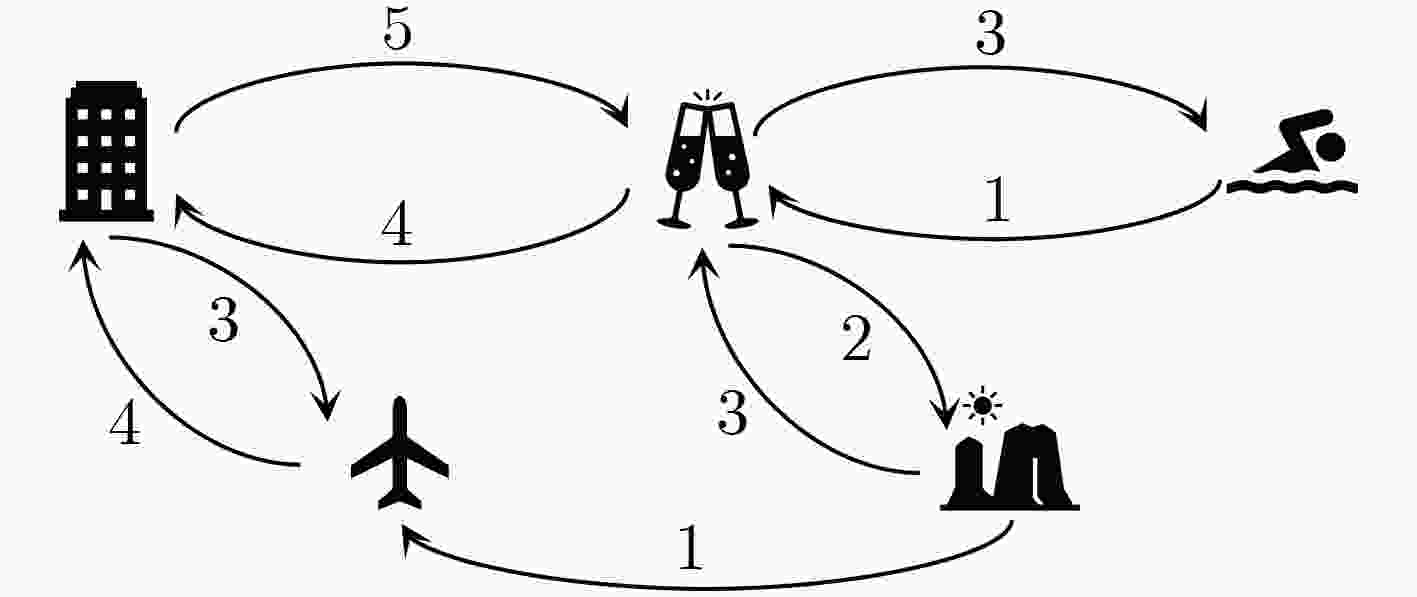
下载:
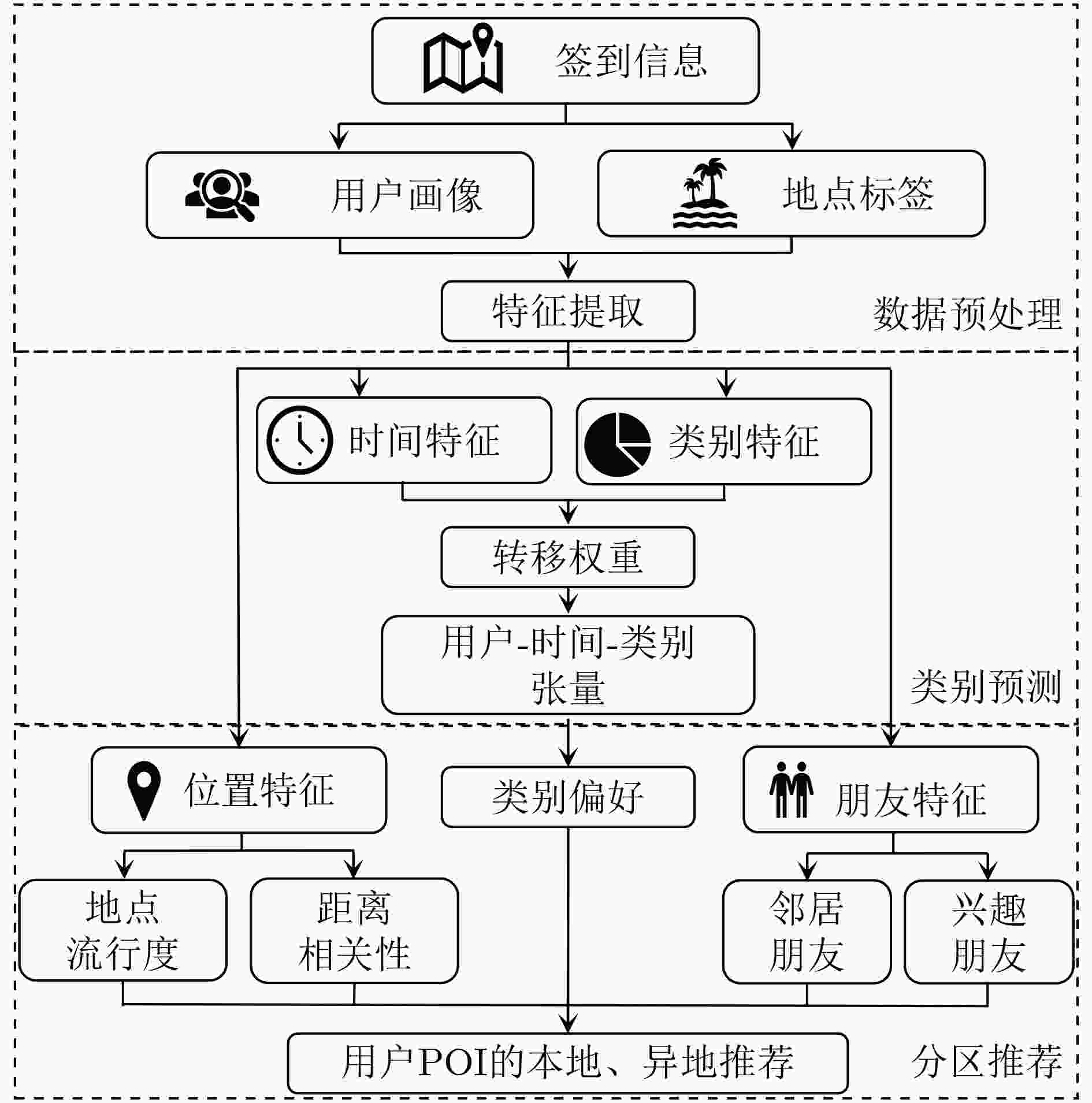



 下载:
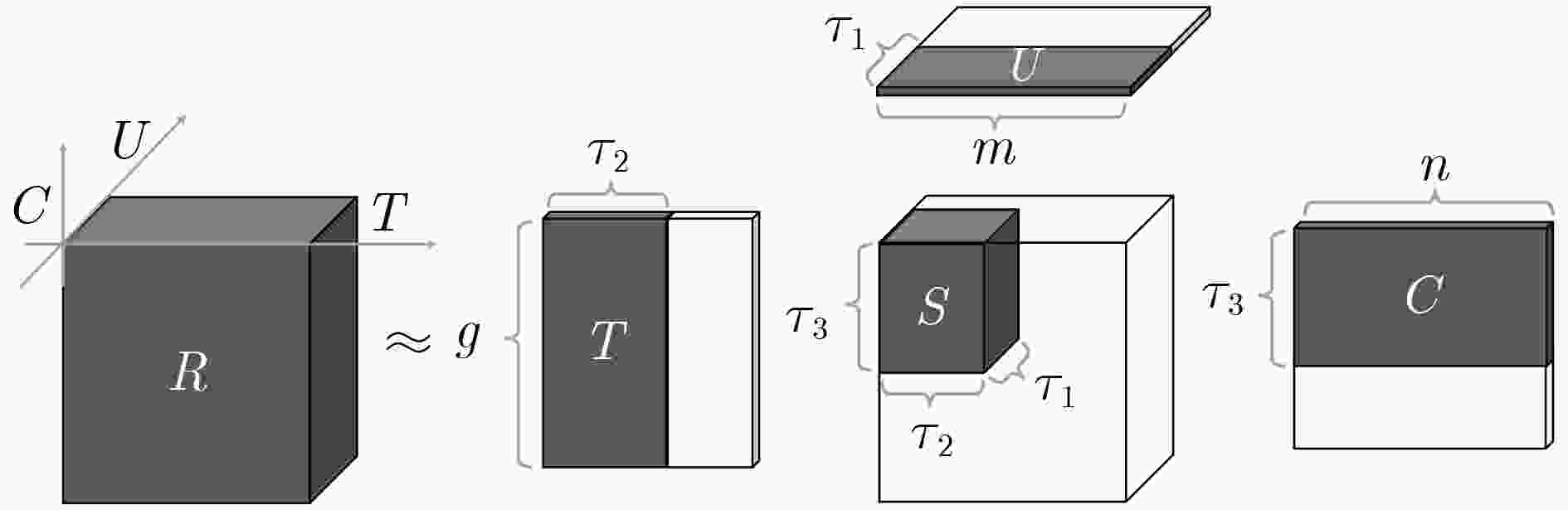
下载:
