Research on Single-channel Blind Deconvolution Algorithm for Multi-source Signals
-
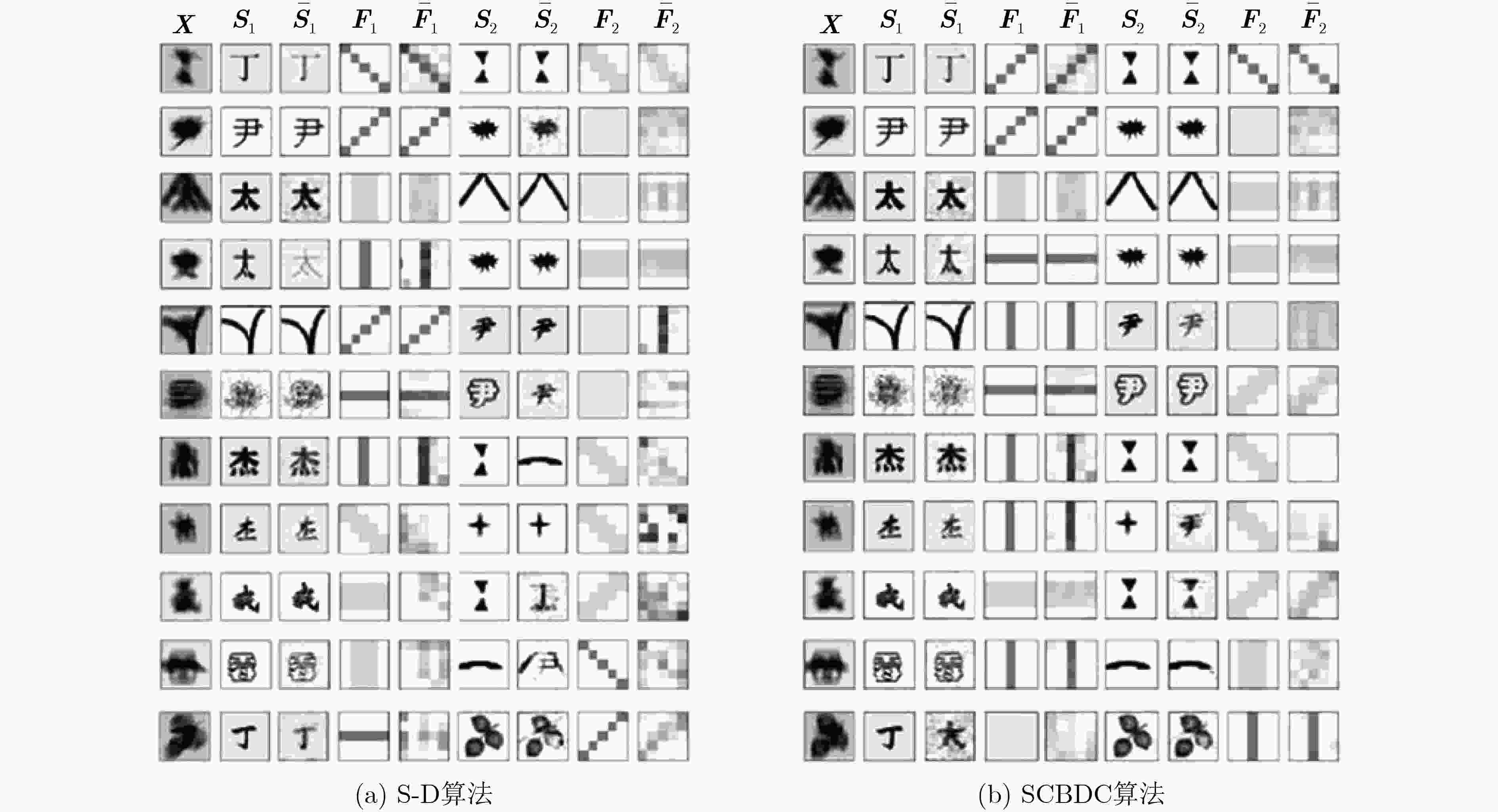
摘要: 传统的单通道盲去卷积的方法存在仅能从混合信号中分离出2路源信号的局限,考虑到以上问题,该文提出一种基于优化的深度卷积生成对抗网络的单通道盲去卷积算法(SCBDC),能从1路混合信号中分离和解卷积出3路以上的独立源信号和混合矩阵。该文实验在汉字和遮挡图像数据集上进行,随机选择4路信号与混合矩阵进行卷积混合,实验结合峰值信噪比(PSNR)和信号相关性指标来评价分离的效果,结果显示,该算法能够有效地分离出多路源信号并去卷积。Abstract: Traditional single-channel blind deconvolution method has the limitation that it can only separate two sources from a mixture. Considering this problem, a Single-Channel Blind Deconvolution algorithm based on optimized deep Convolutional generative adversarial networks (SCBDC) is proposed to separate and deconvolve more than three independent sources and mixing matrix only from a mixture. The experiments are carried on the occlusion Chinese character image datasets, four sources are randomly selected to be mixed with mixing matrix. Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and signal correlation index are combined to evaluate the separation effect. The result shows that the multiple sources can be effectively separated and deconvolved.
-
表 1 SCBDC算法
输出:源信号$ \bar s $和混合矩阵${\bar {\boldsymbol{F}}_{} }$ 1: 选择满足高斯分布N(0,1)的m个100维噪声样本z1, z2, ···, zm; 2: 来自实际数据的m个样本s1, s2, ···, sm; 3: 训练 ODCGAN 一定程度地增加判别器的梯度来更新D: $\nabla {\theta _d}\dfrac{1}{m}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\left[ {\lg D\left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_i} } \right) + \lg\left( {1 - D\left( {G\left( { {{\boldsymbol{z}}_i} } \right)} \right)} \right)} \right]}$ 一定程度地降低生成器的梯度来更新G: $\nabla {\theta _g}\dfrac{1}{m}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\lg\left( {1 - D\left( {G\left( { {{\boldsymbol{z}}_i} } \right)} \right)} \right)}$ 4: 选择来自高斯分布N(0,1)的随机m个样本z1, z2, ···, zm和混合
矩阵F1, F2, ···, Fm;5: 迭代 计算$\bar {\boldsymbol{X}}$: $\bar {\boldsymbol{X}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\left( { {{\boldsymbol{F}}_m} * G\left( { {{\boldsymbol{z}}_m} } \right)} \right)}$ 按照式(12)计算梯度$\nabla {\boldsymbol{\varPhi}}$ 使用adam优化器更新${\boldsymbol{\varPhi}}$ 表 2 不同初始化的PSNR值(dB)
初始化 PSNR 1 5.4 15 8.6 40 10.4 50 10.4 表 4 目标信号与源信号的互相关性值
${{\boldsymbol{S}}_1}$和$ {\bar {\boldsymbol{S}}_1} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{S}}_2} $和$ {\bar {\boldsymbol{S}}_2} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{S}}_3} $和$ {\bar {\boldsymbol{S}}_3} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{S}}_4} $和$ {\bar {\boldsymbol{S}}_4} $ 平均值 第1行 0.9245 0.9613 0.9523 0.7286 0.8917 第2行 0.7599 0.9698 0.8020 0.9154 0.8618 第3行 0.5835 0.9972 0.9119 0.0470 0.6349 第4行 0.7714 0.9444 0.3641 0.9488 0.7412 第5行 0.3824 0.9456 0.9367 0.7104 0.7437 第6行 0.9254 0.9006 0.9684 0.8249 0.9048 -
[1] 付卫红, 周新彪, 农斌. 单通道盲源分离的研究现状与展望[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2017, 40(5): 1–11. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2017-001FU Weihong, ZHOU Xinbiao, and NONG Bin. The research of SCBSS technology: Survey and prospect[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017, 40(5): 1–11. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2017-001 [2] LEE D D and SEUNG H S. Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization[J]. Nature, 1999, 401(6755): 788–791. doi: 10.1038/44565 [3] KITAMURA D, SARUWATARI H, SHIKANO K, et al. Music signal separation by supervised nonnegative matrix factorization with basis deformation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Fira, Greece, 2013: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICDSP.2013.6622812. [4] 赵志强, 颜学龙. 基于EMD和ICA的单通道语音盲源分离算法[J]. 电子科技, 2012, 25(7): 66–68,75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7820.2012.07.020ZHAO Zhiqiang and YAN Xuelong. Algorithm for EMD and ICA-based single-channel voice blind source separation[J]. Electronic Science and Technology, 2012, 25(7): 66–68,75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7820.2012.07.020 [5] SEGARS W P, TSUI B M W, CAI Jing, et al. Application of the 4-D XCAT Phantoms in Biomedical Imaging and Beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(3): 680–692. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2017.2738448 [6] KRISHNA P K M and RAMASWAMY K. Single channel speech separation based on empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert transform[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2017, 11(5): 579–586. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0450 [7] 贾花萍. 盲去卷积算法在图像恢复中的应用研究[J]. 信息技术, 2011(5): 38–39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2552.2011.05.013JIA Huaping. Blind deconvolution algorithm in application of image restoration[J]. Information Technology, 2011(5): 38–39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2552.2011.05.013 [8] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C, DE VLEESCHOUWER C, et al. Color balance and fusion for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(1): 379–393. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2759252 [9] SATO Y. A method of self-recovering equalization for multilevel amplitude-modulation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1975, 23(6): 679–682. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1975.1092854 [10] GODARD D. Self-recovering equalization and carrier tracking in two-dimensional data communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1980, 28(11): 1867–1875. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1980.1094608 [11] YELLIN D and WEINSTEIN E. Criteria for multichannel signal separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(8): 2158–2168. doi: 10.1109/78.301850 [12] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, CHEN Yunjin, et al. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142–3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 [13] GRAIS E M, ROMA G, SIMPSON A J R, et al. Two-stage single-channel audio source separation using deep neural networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2017, 25(9): 1773–1783. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2017.2716443 [14] 郑昌艳, 张雄伟, 曹铁勇, 等. 一种基于LSTM-RNN的喉振传声器语音盲增强算法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2019, 34(4): 615–624. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2019.04.005ZHENG Changyan, ZHANG Xiongwei, CAO Tieyong, et al. Blind enhancement algorithm for throat microphone speech based on LSTM re-current neural networks[J]. Data Collection &Processing, 2019, 34(4): 615–624. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2019.04.005 [15] 王恬, 仇春春, 俞婧, 等. 基于改进SAE网络的自然图像分类[J]. 信息技术, 2016(8): 1–4,8. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2016.08.001WANG Tian, QIU Chunchun, YU Jing, et al. Natural image classification with improved SAE network[J]. Information Technology, 2016(8): 1–4,8. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2016.08.001 [16] SUBAKAN Y C and SMARAGDIS P. Generative adversarial source separation[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018: 26–30. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8461671. [17] KONG Qiuqiang, XU Yong, JACKSON P J B, et al. Single-channel signal separation and deconvolution with generative adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial, Macao, China, 2019: 2747–2753. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2019/381. [18] CICHOCKI A, ZDUNEK R, PHAN A H, et al. Nonnegative Matrix and Tensor Factorizations: Applications to Exploratory Multi-way Data Analysis and Blind Source Separation[M]. Chichester: John Wiley, 2009: 132–138, 197. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
