Simulation Research on a Compact High Power Microwave Source Based on Gyromagnetic Nonlinear Transmission Lines
-
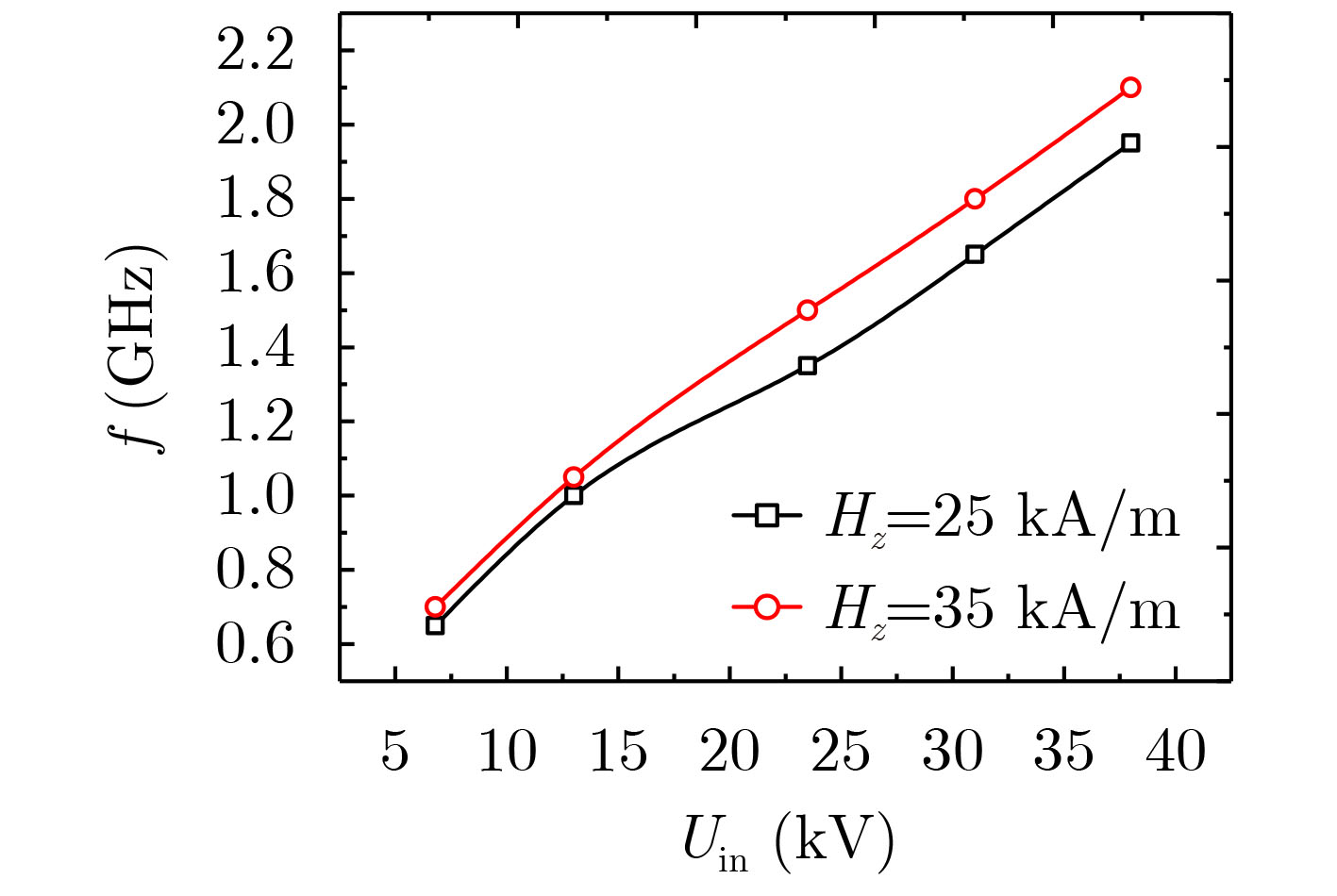
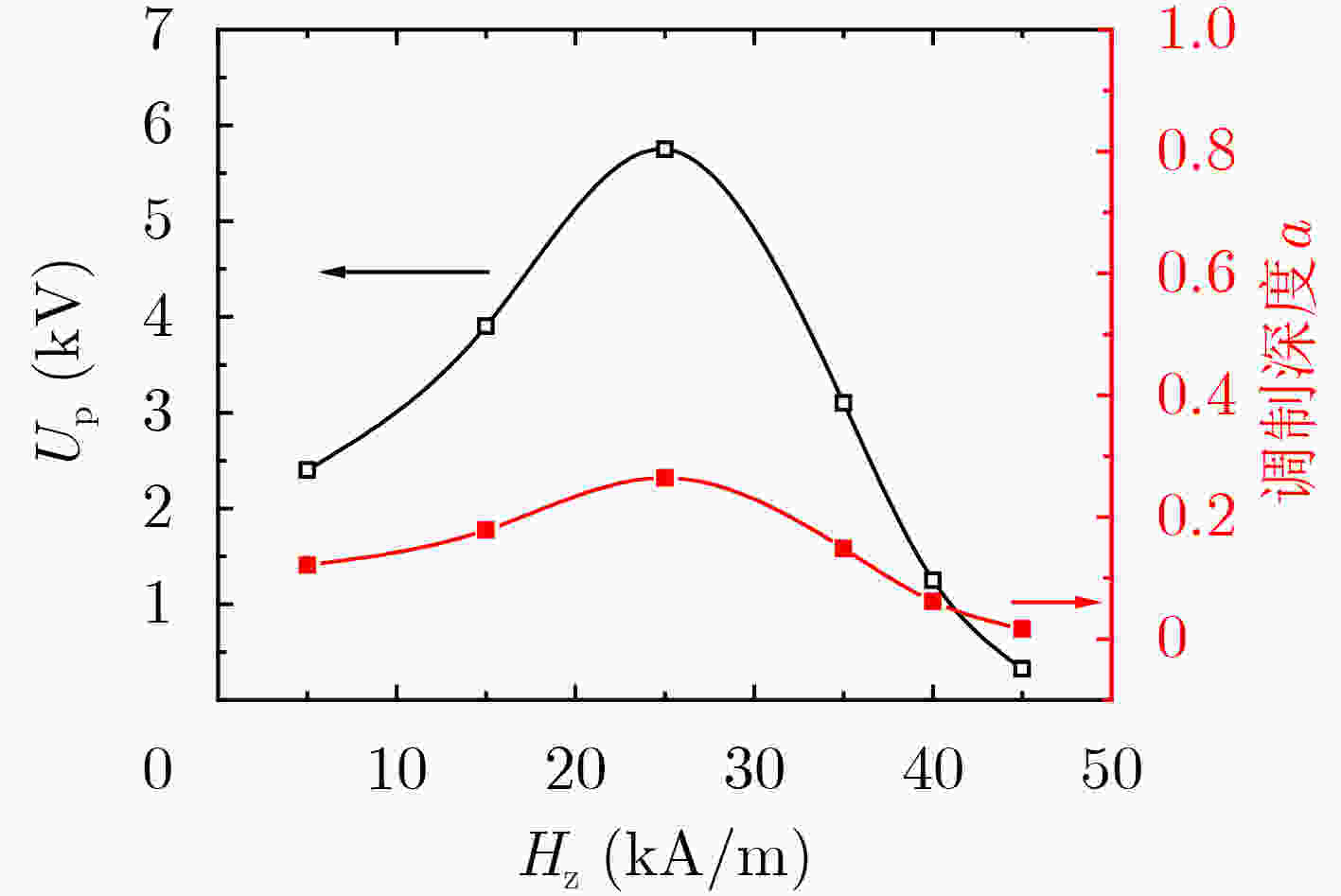
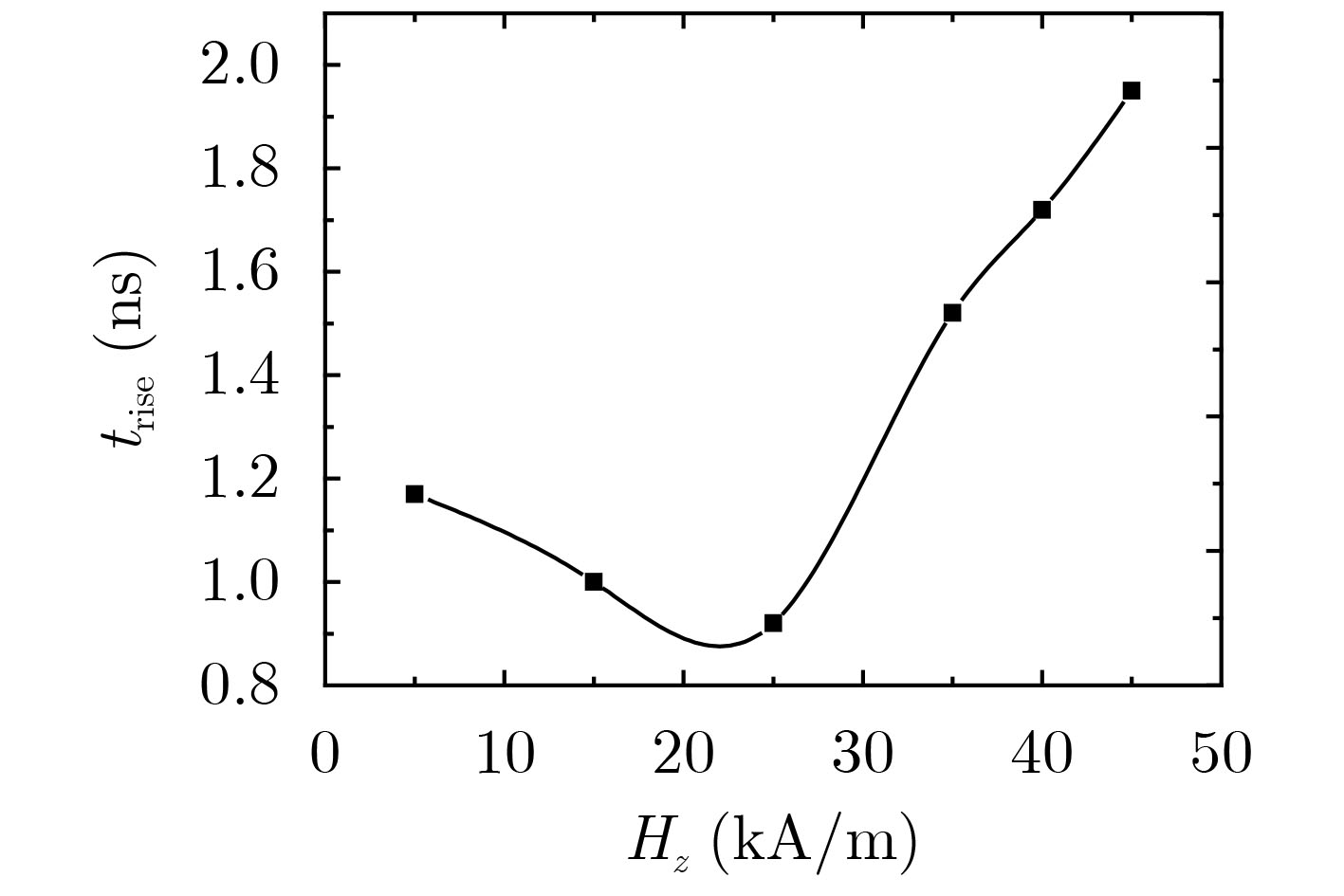
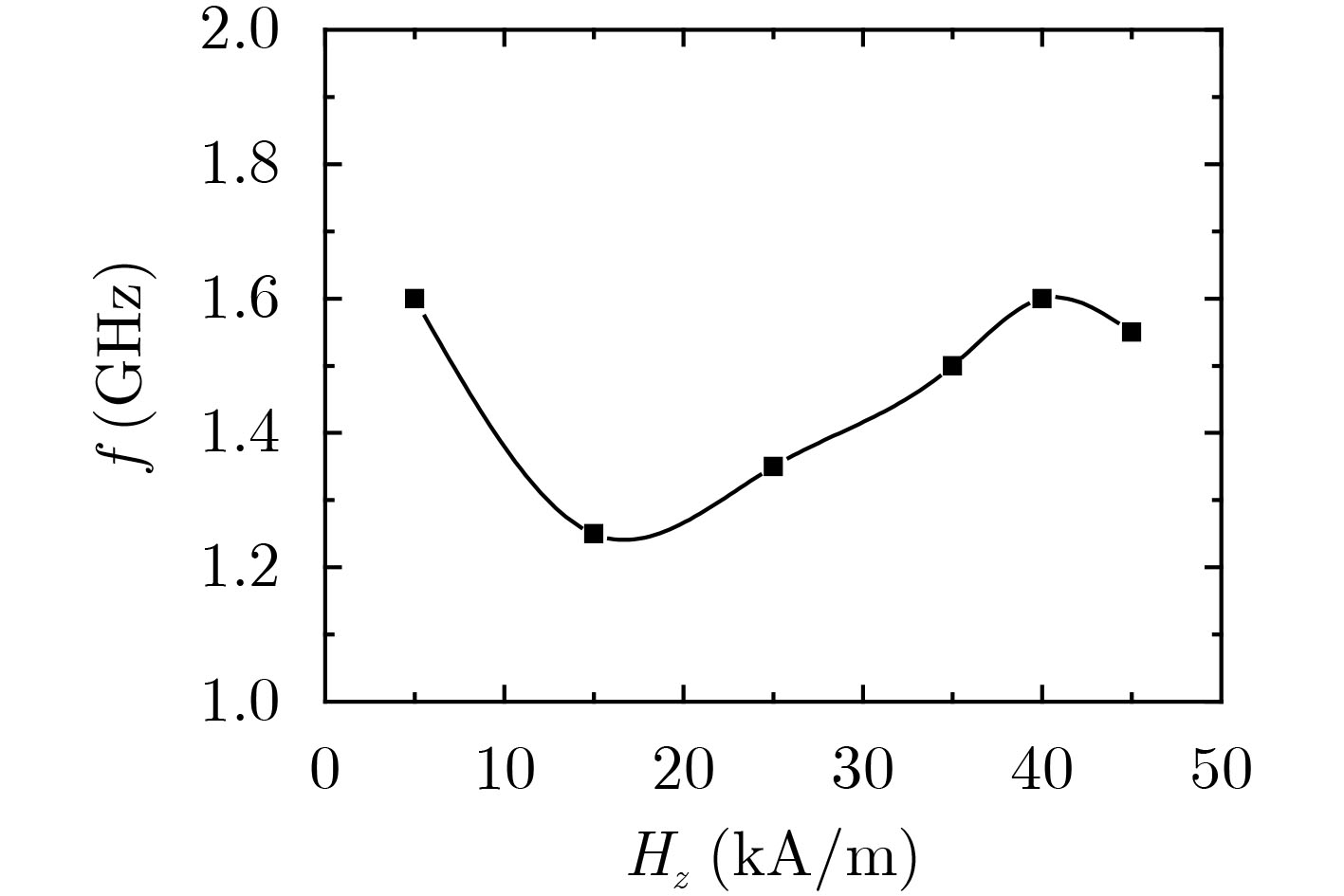
摘要: 与传统基于电真空器件的窄谱高功率微波源相比,基于旋磁非线性传输线(GNLTL)的宽谱强电磁脉冲源无须驱动电子束、导引磁场和真空条件,具有能量效率高、工作频率可调以及可重频运行等优势,是一种结构简单、适合小型化和固态化的技术方案。该文通过理论分析其产生射频振荡和脉冲陡化的工作机制,并利用商业软件建立一套可视化的2-D GNLTL仿真模型进行验证。通过仿真分别研究不同注入电压和不同轴向偏置磁场下的旋磁输出脉冲的时域和频域特性。模拟结果表明:随着注入电压增大,经调制的振荡电压峰值升高,而调制深度则是先增加后减小到几乎不变,输出电压上升沿减小后趋于稳定,而中心频率则随着注入电压增大而增加;随着偏置磁场增加,输出振荡峰值电压和调制深度均是先增大后减小,输出电压上升沿先减小后增大,而中心频率先减小后增大。Abstract: Compared with the traditional high power microwave sources based on the electronic vacuum tube, the wide-band high power microwave sources based on the Gyromagnetic NonLinear Transmission Line (GNLTL) does not need the electron beam, the confining magnetic field and the vacuum system. It is a simple, compact and solid-state scheme. It has the advantages of adjustable frequency and repetitive operation. It can not only improve the energy utilization rate, but also break through the limitation of single operation of electromagnetic pulse projectile. In this paper, the RF pulse formation dynamics and sharpening characteristics of the gyromagnetic nonlinear transmission line are analyzed in theory. The visible two-dimensional model is composed for numerical analysis of the modulated pulse waveforms in time domain and frequency domain under a varied incident voltage or a varied axial biasing magnetic field. The simulation results show that when the incident voltage increases, the modulated peak voltage grows, the modulated depth rises and then declines to some constant value, the rise time of the modulated pulse reduces and then ceases, and the central frequency augments. When the axial biasing magnetic field increases, the modulated peak voltage and the modulated depth both rises and then declines, the rise time of the modulated pulse and the central frequency both reduces and then increases.
-
表 1 同轴GNLTL射频源的研究现状
表 2 不同电压下对应的角向磁场强度
编号 1 2 3 4 5 Uin(kV) 6.80 13.00 23.50 31.00 38.00 Hϕ(kA/m) 9.69 18.52 33.48 44.17 54.14 -
[1] BRAGG J W B, DICKENS J C, and NEUBER A A. Ferrimagnetic nonlinear transmission lines as high-power microwave sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2013, 41(1): 232–237. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2012.2226169 [2] ROMANCHENKO I V and ROSTOV V V. Energy levels of oscillations in a nonlinear transmission line filled with saturated ferrite[J]. Technical Physics, 2010, 55(7): 1024–1027. doi: 10.1134/S1063784210070170 [3] ROMANCHENKO I V, ROSTOV V V, GUNIN A V, et al. High power microwave beam steering based on gyromagnetic nonlinear transmission lines[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(21): 214907. doi: 10.1063/1.4922280 [4] ROSTOV V V, EL'CHANINOV A A, KLIMOV A I, et al. Phase control in parallel channels of shock-excited microwave nanosecond oscillators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2013, 41(10): 2735–2741. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2013.2270571 [5] ROSTOV V V, BYKOV N M, BYKOV D N, et al. Generation of subgigawatt RF pulses in nonlinear transmission lines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2010, 38(10): 2681–2685. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2048722 [6] ROMANCHENKO I V, ROSTOV V V, GUBANOV V P, et al. Repetitive sub-gigawatt RF source based on gyromagnetic nonlinear transmission line[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83(7): 074705. doi: 10.1063/1.4738641 [7] GUSEV A I, PEDOS M S, RUKIN S N, et al. Solid-state repetitive generator with a gyromagnetic nonlinear transmission line operating as a peak power amplifier[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88(7): 074703. doi: 10.1063/1.4993732 [8] ULMASKULOV M R, PEDOS M S, RUKIN S N, et al. High repetition rate multi-channel source of high-power RF-modulated pulses[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2015, 86(7): 074702. doi: 10.1063/1.4926458 [9] PRATHER W D, BAUM C E, TORRES R J, et al. Survey of worldwide high-power wideband capabilities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2004, 46(3): 335–344. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2004.831826 [10] REALE D V, PARSON J M, NEUBER A A, et al. Investigation of a stripline transmission line structure for gyromagnetic nonlinear transmission line high power microwave sources[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(3): 034706. doi: 10.1063/1.4942246 [11] GUBANOV V P, GUNIN A V, KOVAL’CHUK O B, et al. Effective transformation of the energy of high-voltage pulses into high-frequency oscillations using a saturated-ferrite-loaded transmission line[J]. Technical Physics Letters, 2009, 35(7): 626–628. doi: 10.1134/S1063785009070116 [12] CHADWICK S J F, SEDDON N, and RUKIN S. A novel solid-state HPM source based on a gyromagnetic NLTL and SOS-based pulse generator[C]. 2011 IEEE Pulsed Power Conference, Chicago, America, 2011: 178–181. [13] BRAGG J W B, SULLIVAN III W W, MAUCH D, et al. All solid-state high power microwave source with high repetition frequency[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2013, 84(5): 054703. doi: 10.1063/1.4804196 [14] ROMANCHENKO I V, PRIPUTNEV P V, and ROSTOV V V. RF pulse formation dynamics in gyromagnetic nonlinear transmission lines[C]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 5th International Congress on Energy Fluxes and Radiation Effects, Tomsk, Russia, 2017: 012034. [15] 廖勇, 徐刚, 谢平, 等. 非线性传输线数值模拟方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27(8): 083001. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.083001LIAO Yong, XU Gang, XIE Ping, et al. Numerical simulation of non-linear transmission line[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27(8): 083001. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.083001 [16] 谢平, 徐刚, 廖勇, 等. 非线性传输线产生射频脉冲原理研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26(4): 043002. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.043002XIE Ping, XU Gang, LIAO Yong, et al. Research on nonlinear transmission line generating radio-frequency pulses[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26(4): 043002. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.043002 [17] 廖勇, 张现福, 徐刚, 等. 非线性传输线高功率实验[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28(5): 053007. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.053007LIAO Yong, ZHANG Xianfu, XU Gang, et al. High Power experiment of nonlinear transmission lines system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28(5): 053007. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.053007 [18] TIE Weihao, MENG Cui, ZHAO Chengguang, et al. Optimized analysis of sharpening characteristics of a compact RF pulse source based on a gyro-magnetic nonlinear transmission line for ultrawideband electromagnetic pulse application[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2019, 21(9): 095503. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/ab2626 [19] 铁维昊, 赵程光, 孟萃, 等. 旋磁型非线性传输线调制脉冲特性数值分析[J]. 高电压技术, 2019, 45(1): 301–309. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20181229028TIE Weihao, ZHAO Chengguang, MENG Cui, et al. Numerical analysis on modulated RF pulse characteristics of gyro-magnetic nonlinear transmission line[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2019, 45(1): 301–309. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20181229028 [20] REALE D V, BRAGG J W B, GONSALVES N R, et al. Bias-field controlled phasing and power combination of gyromagnetic nonlinear transmission lines[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2014, 85(5): 054706. doi: 10.1063/1.4878339 [21] REALE D V. Coaxial ferrimagnetic based gyromagnetic nonlinear transmission lines as compact high power microwave sources[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Texas Tech University, 2013. [22] KARELIN S Y, KRASOVITSKY V B, MAGDA I I, et al. RF Oscillations in a coaxial transmission line with a saturated ferrite: 2-D simulation and experiment[C]. 2016 8th International Conference on Ultrawideband and Ultrashort Impulse Signals (UWBUSIS), Odessa, Ukraine, 2016: 60–63. [23] WEINER M and SILBER L. Pulse sharpening effects in ferrites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 1981, 17(4): 1472–1477. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.1981.1061243 [24] BRAGG J W B, DICKENS J C, and NEUBER A A. Material selection considerations for coaxial, ferrimagnetic-based nonlinear transmission lines[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(6): 064904. doi: 10.1063/1.4792214 [25] DOLAN J E and BOLTON H R. Shock front development in ferrite-loaded coaxial lines with axial bias[J]. IEE Proceedings - Science, Measurement and Technology, 2000, 147(5): 237–242. doi: 10.1049/ip-smt:20000447 [26] ROSSI J O, YAMASAKI F S, SCHAMILOGLU E, et al. Operation analysis of a novel concept of RF source known as gyromagnetic line[C]. 2017 SBMO/IEEE MTT-S International Microwave and Optoelectronics Conference (IMOC), Aguas de Lindoia, Brazil, 2017: 1–4. [27] ROMANCHENKO I V, ROSTOV V V, GUNIN A V, et al. Gyromagnetic RF source for interdisciplinary research[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88(2): 024703. doi: 10.1063/1.4975182 -





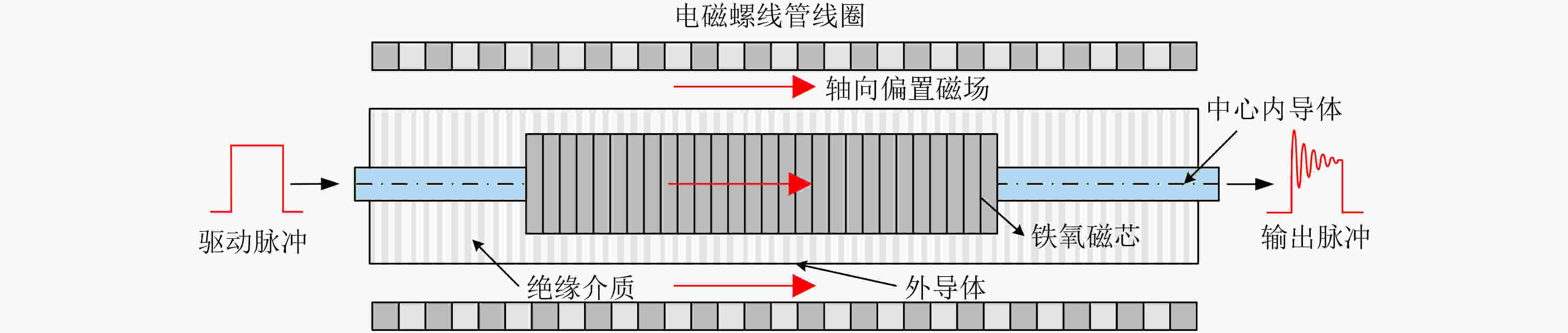
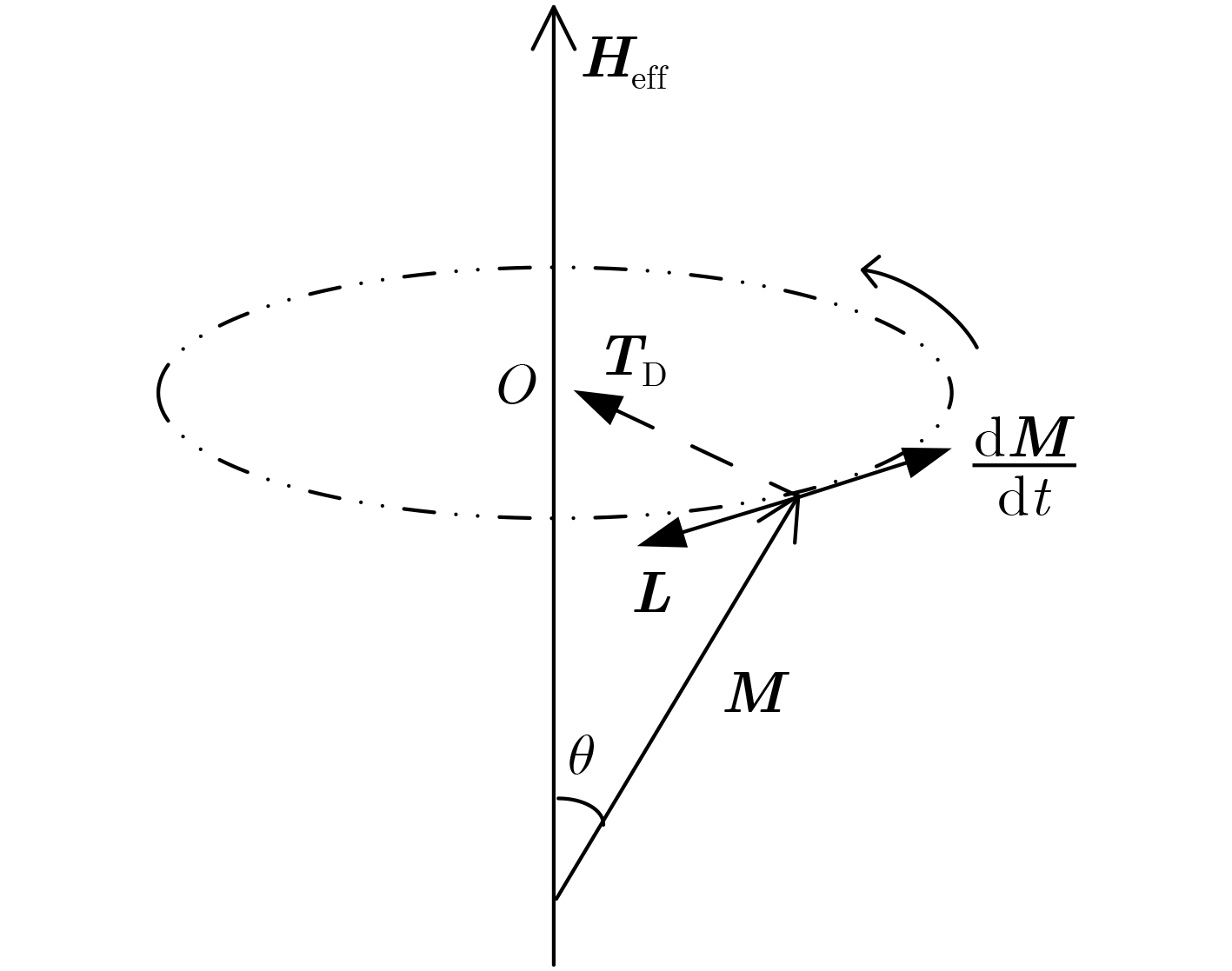
 下载:
下载:
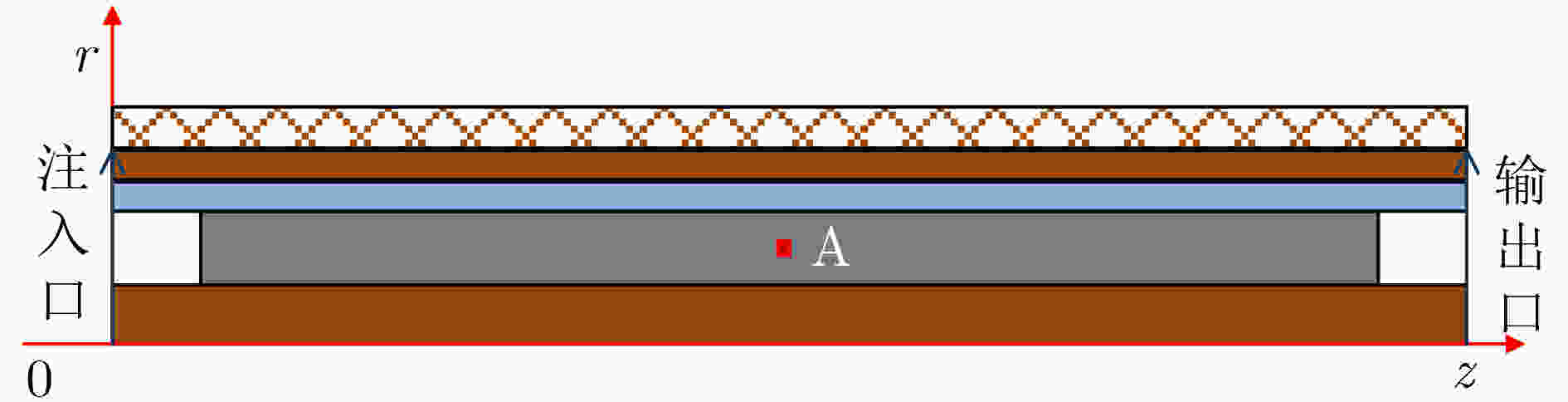
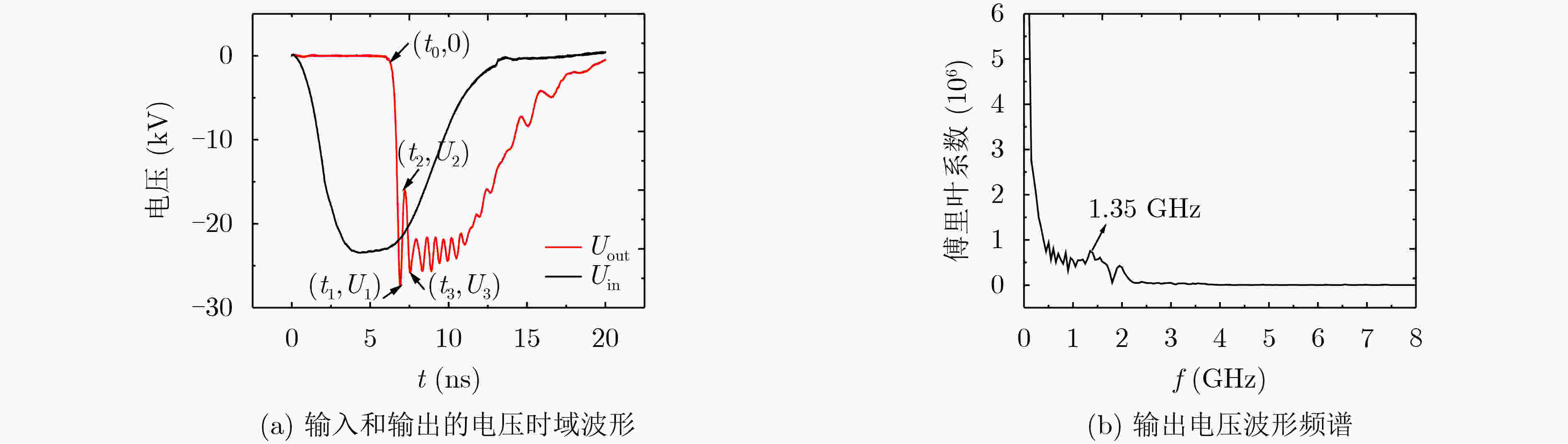
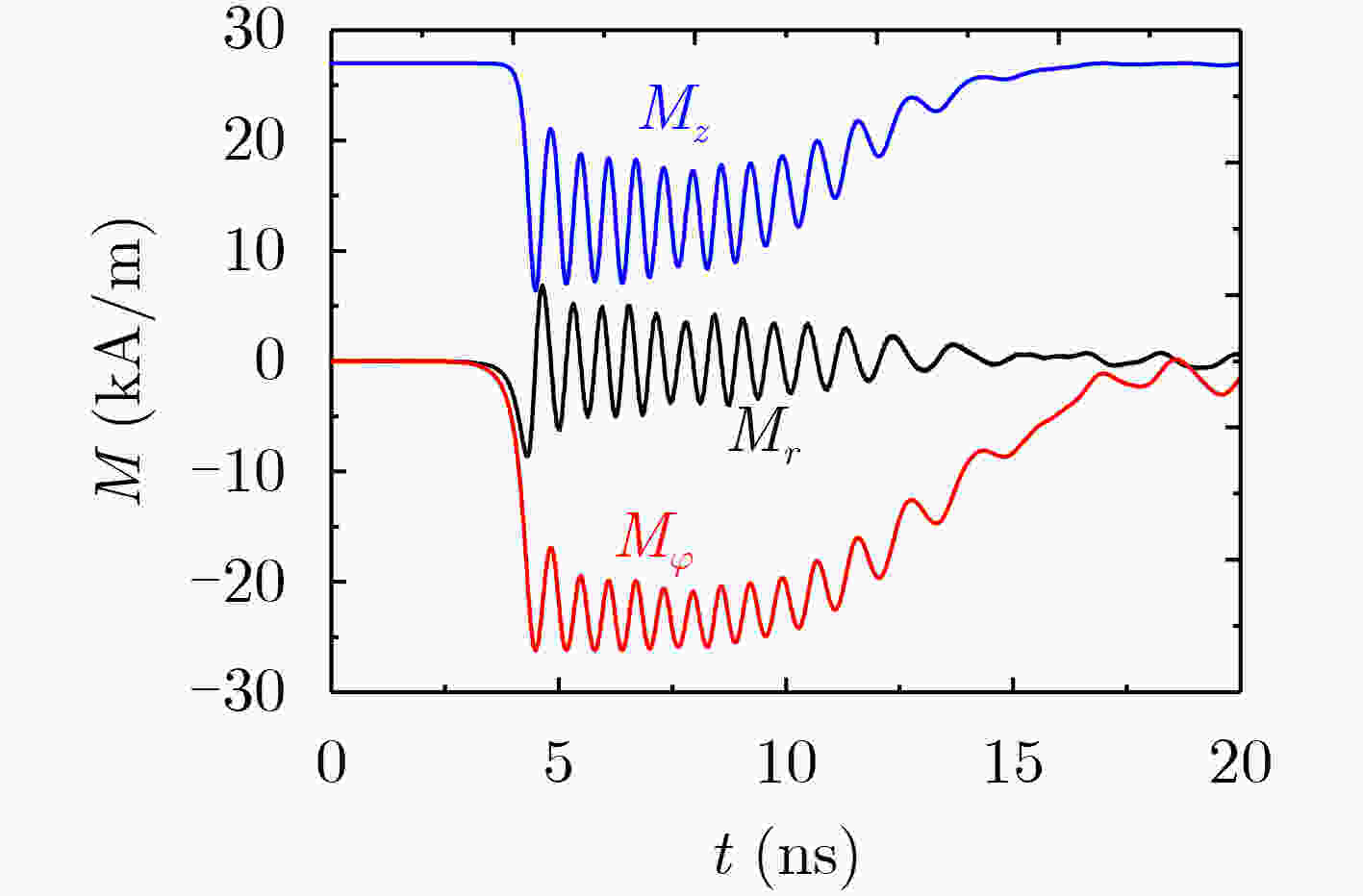
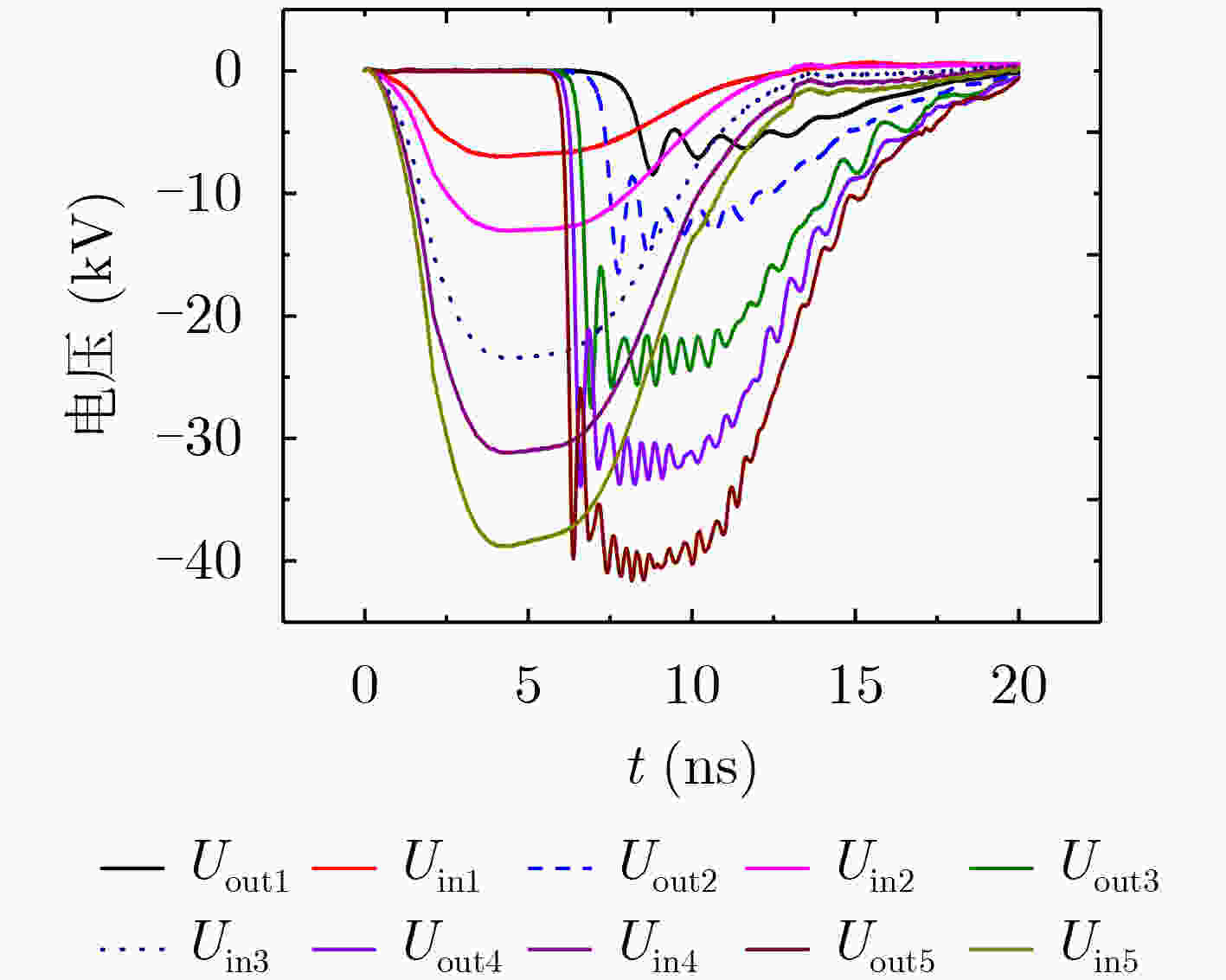
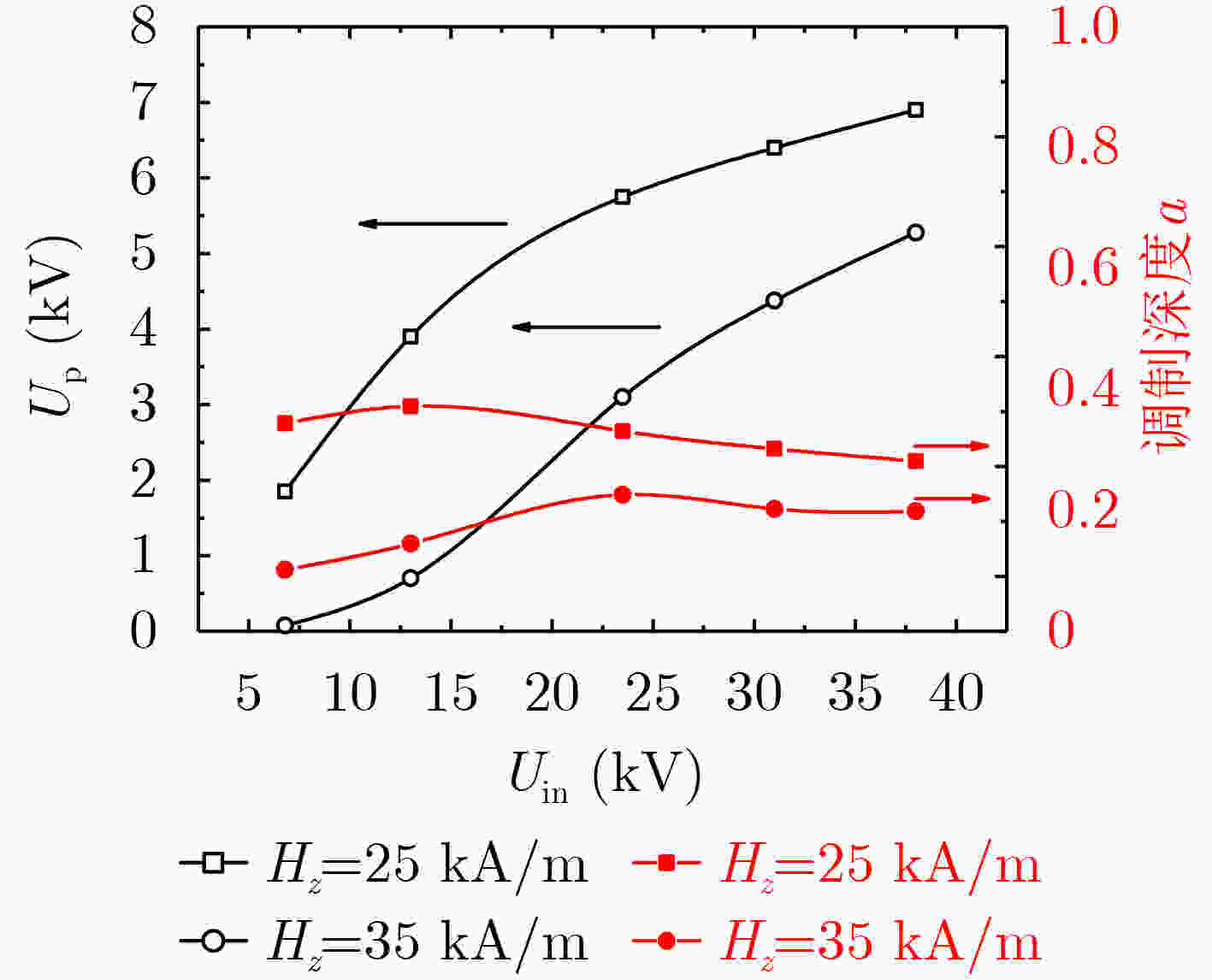
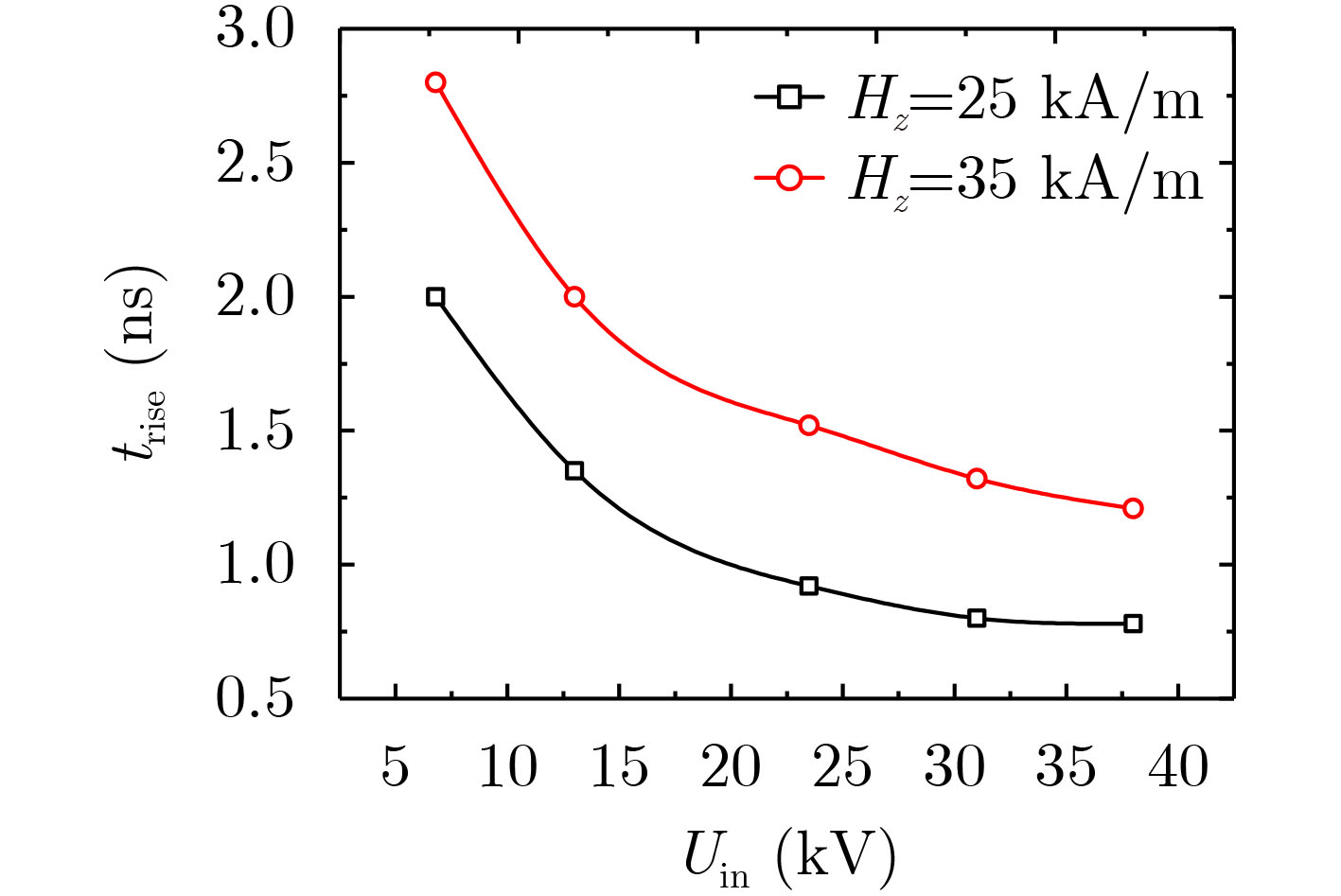


 下载:
下载:
