An Identity Recognition Method Based on ElectroCardioGraph and PhotoPlethysmoGraph Feature Fusion
-
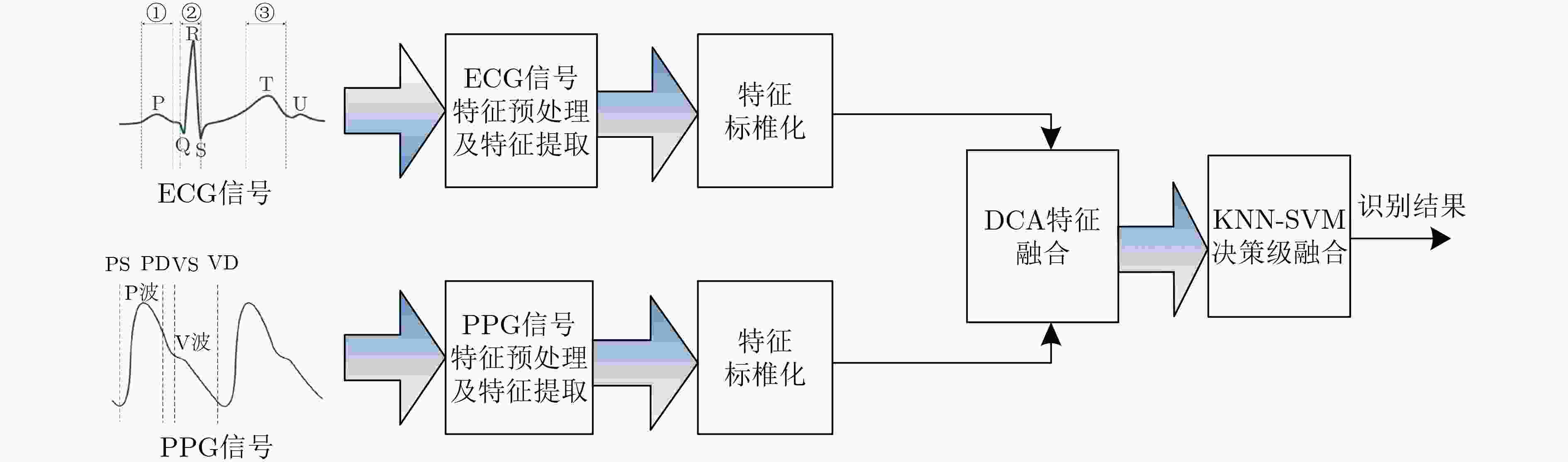
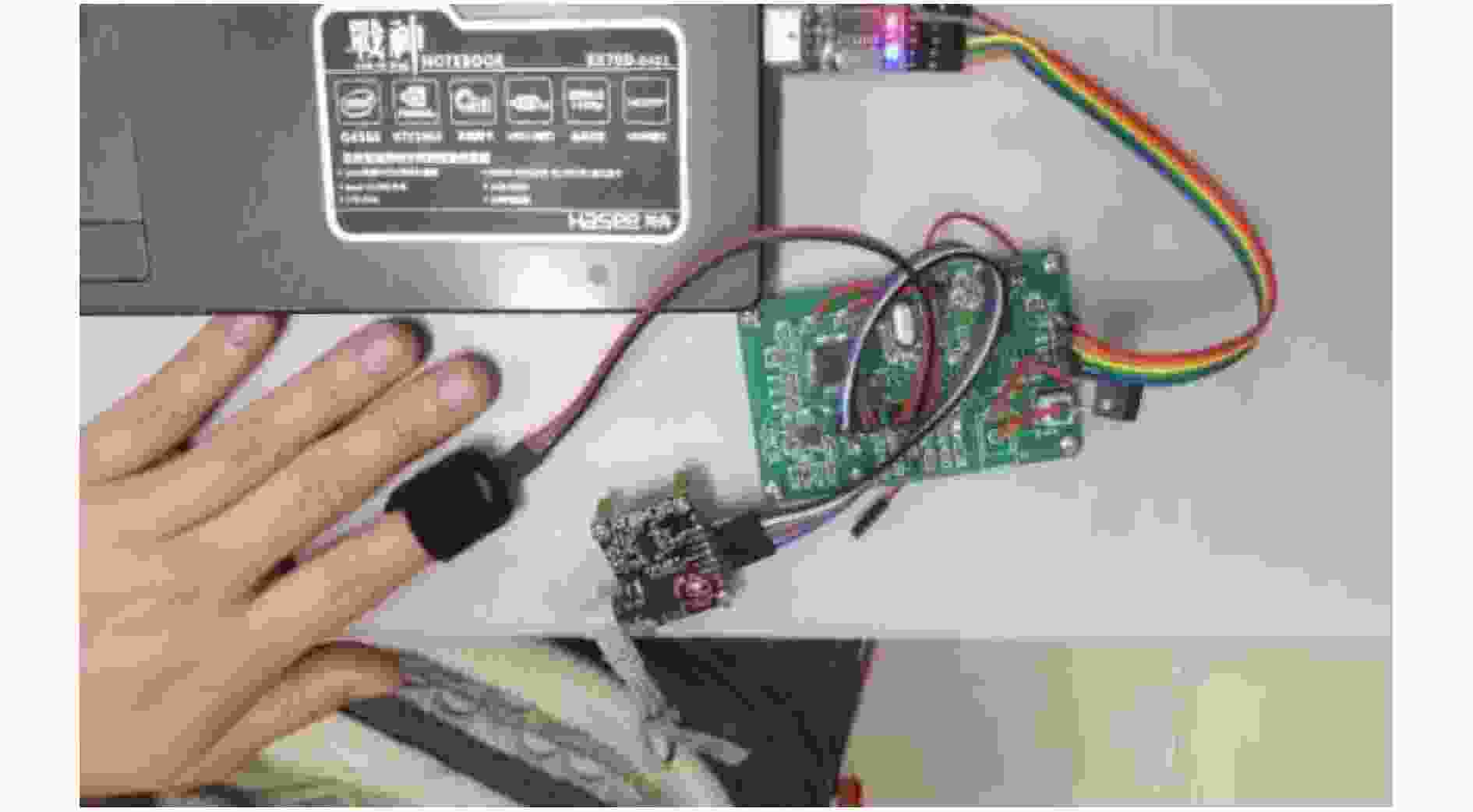
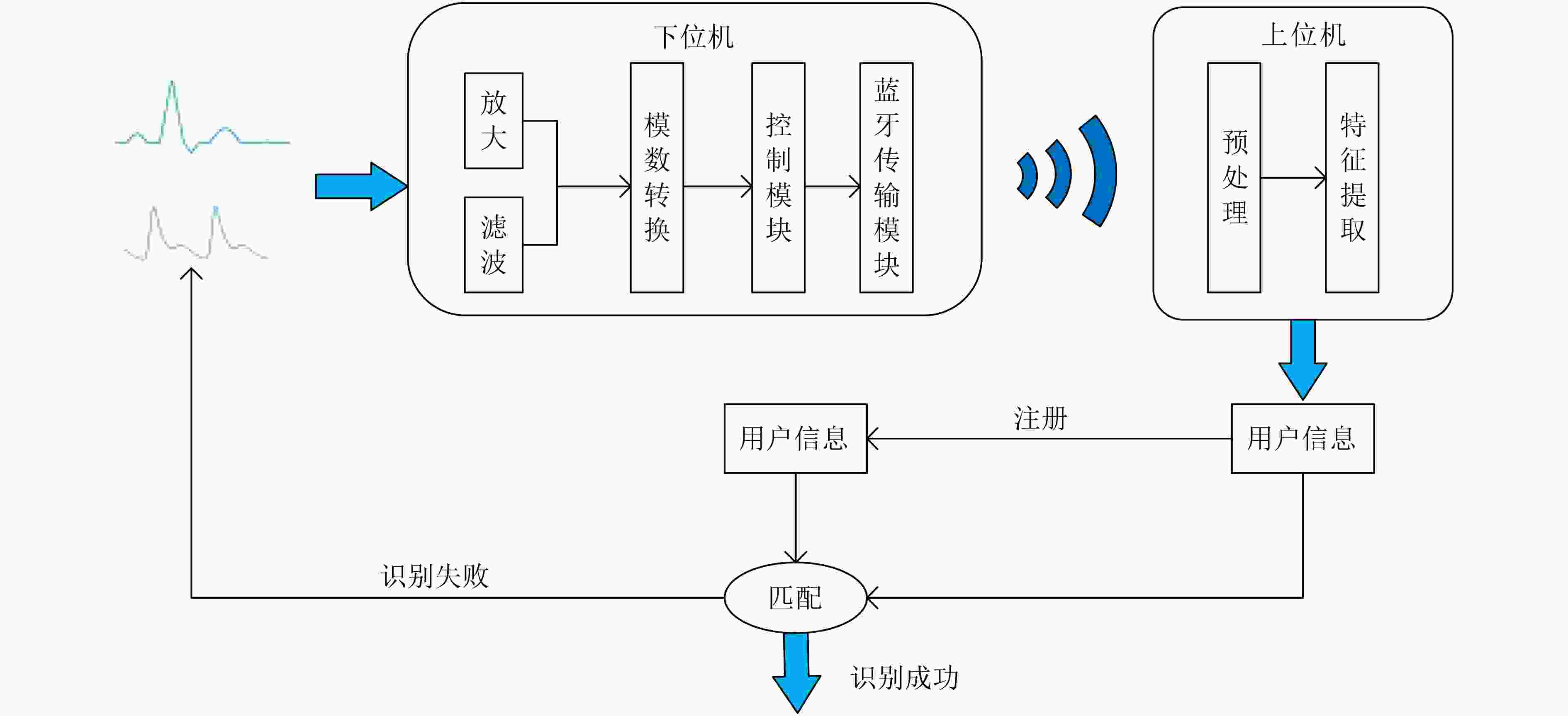
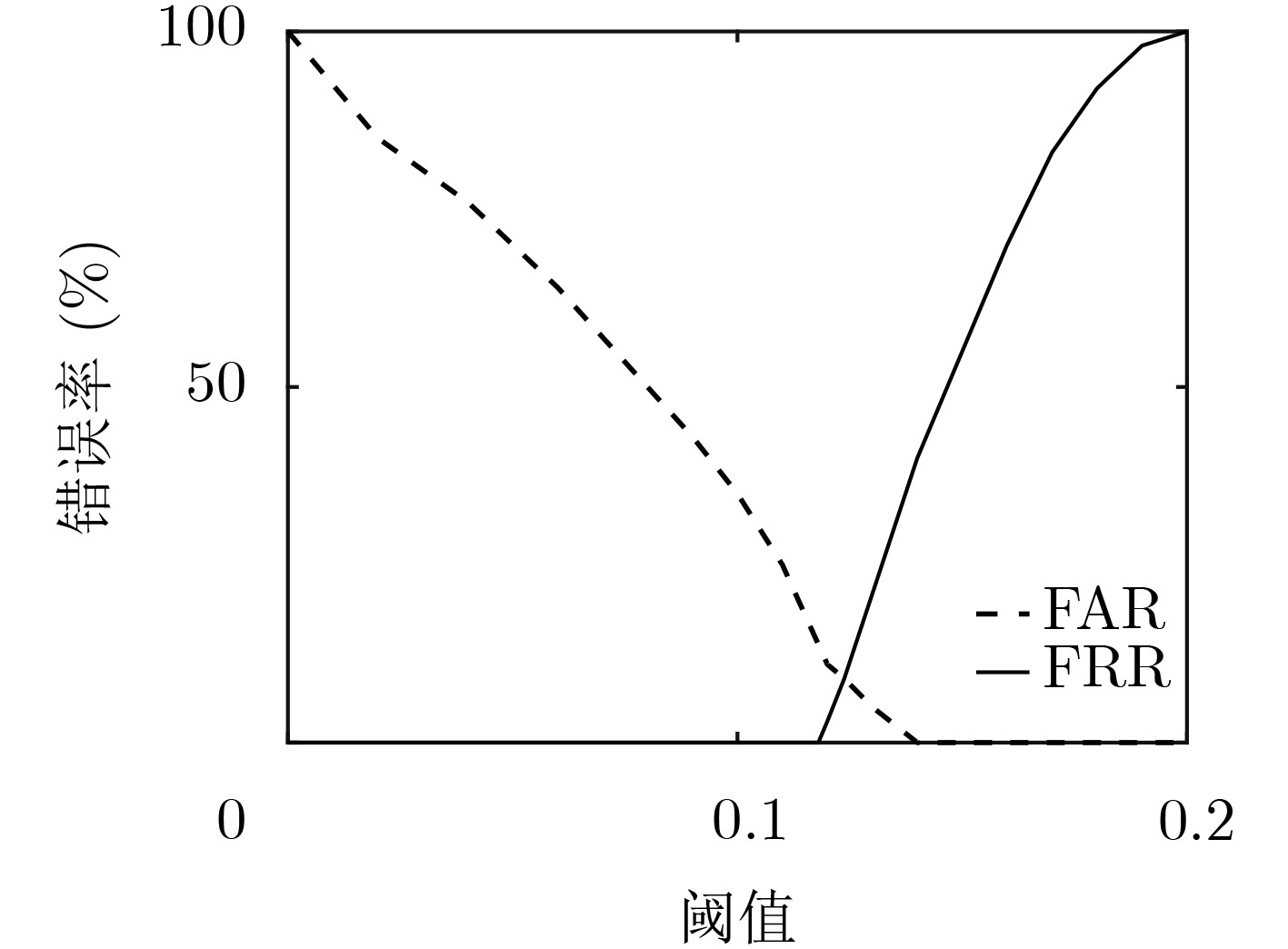
摘要: 针对单模态的心电信号(ECG)或光电容积脉搏波信号(PPG)识别技术中存在的精度不高,未考虑类内相关性等问题,该文提出基于判别相关分析法(DCA)对ECG与PPG组合特征矩阵进行特征层融合以及对K-最近邻(KNN)和支持向量机(SVM)分类器在决策层融合的识别方法。实验结果表明,使用融合特征(ECG-PPG)与融合分类器(KNN-SVM)的方法对23名受试者进行分类识别的准确率可以达到98.2%,识别精度在常规环境下优于单模态识别。为多模生物特征身份识别提供了一种有效模型。Abstract: Because single mode ElectroCardioGraph (ECG) and PhotoPlethysmoGraph(PPG) existed problem with the low recognition accuracy, not considering intra-class correlation, this paper proposes a recognition method based on the Discriminant Correlation Analysis (DCA) for the feature layer fusion of the ECG and PPG combined feature matrix and the fusion of the K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifiers at the decision layer. The experimental results show that the use of fusion features (ECG-PPG) and fusion the classifier (KNN-SVM) method can classify and recognize 23 subjects with an accuracy of 98.2%, and the recognition accuracy is better than single-modal recognition in the conventional environment. It provides an effective model for multimodal biometric identification.
-
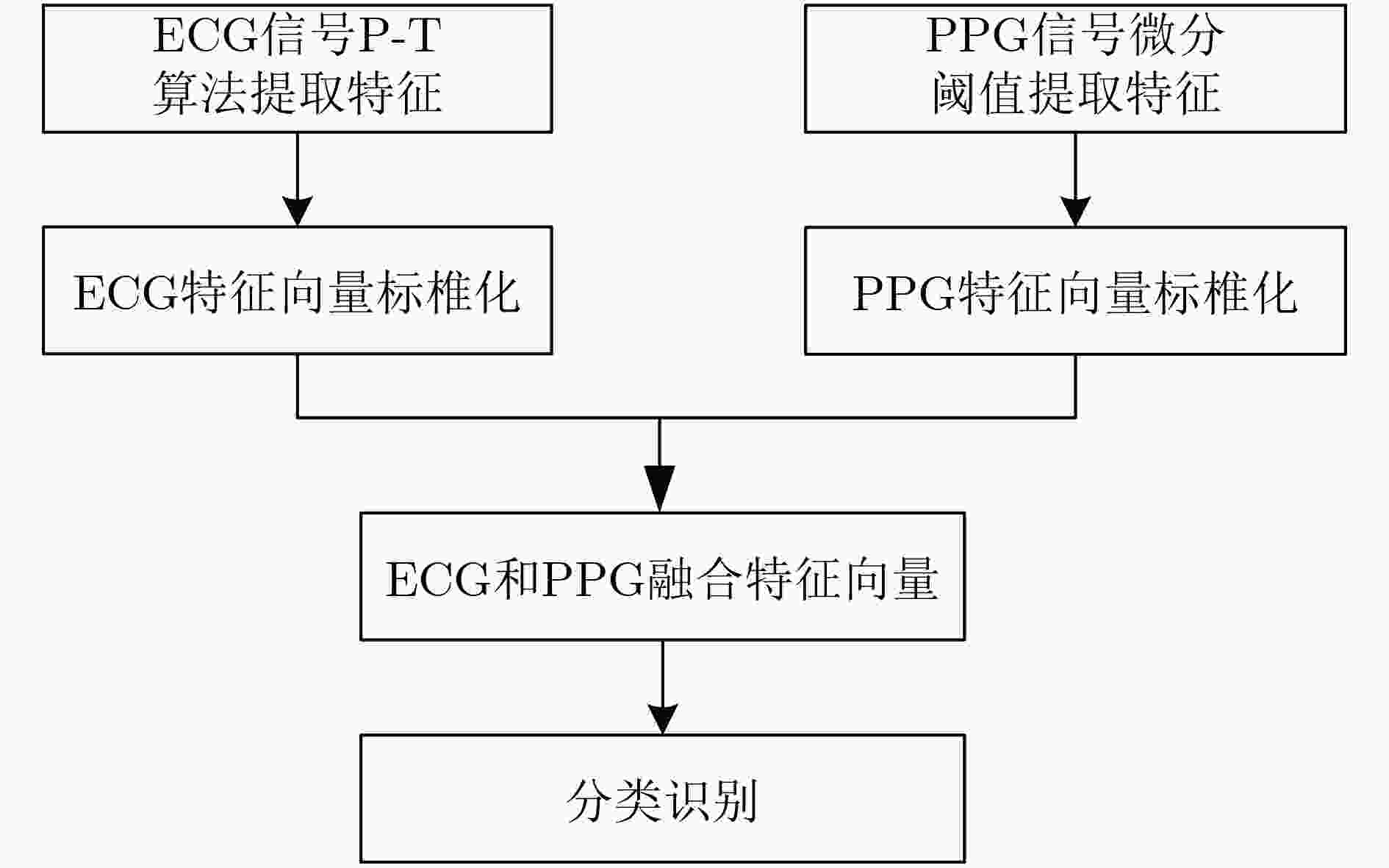
表 1 小波变换提取到的信号特征
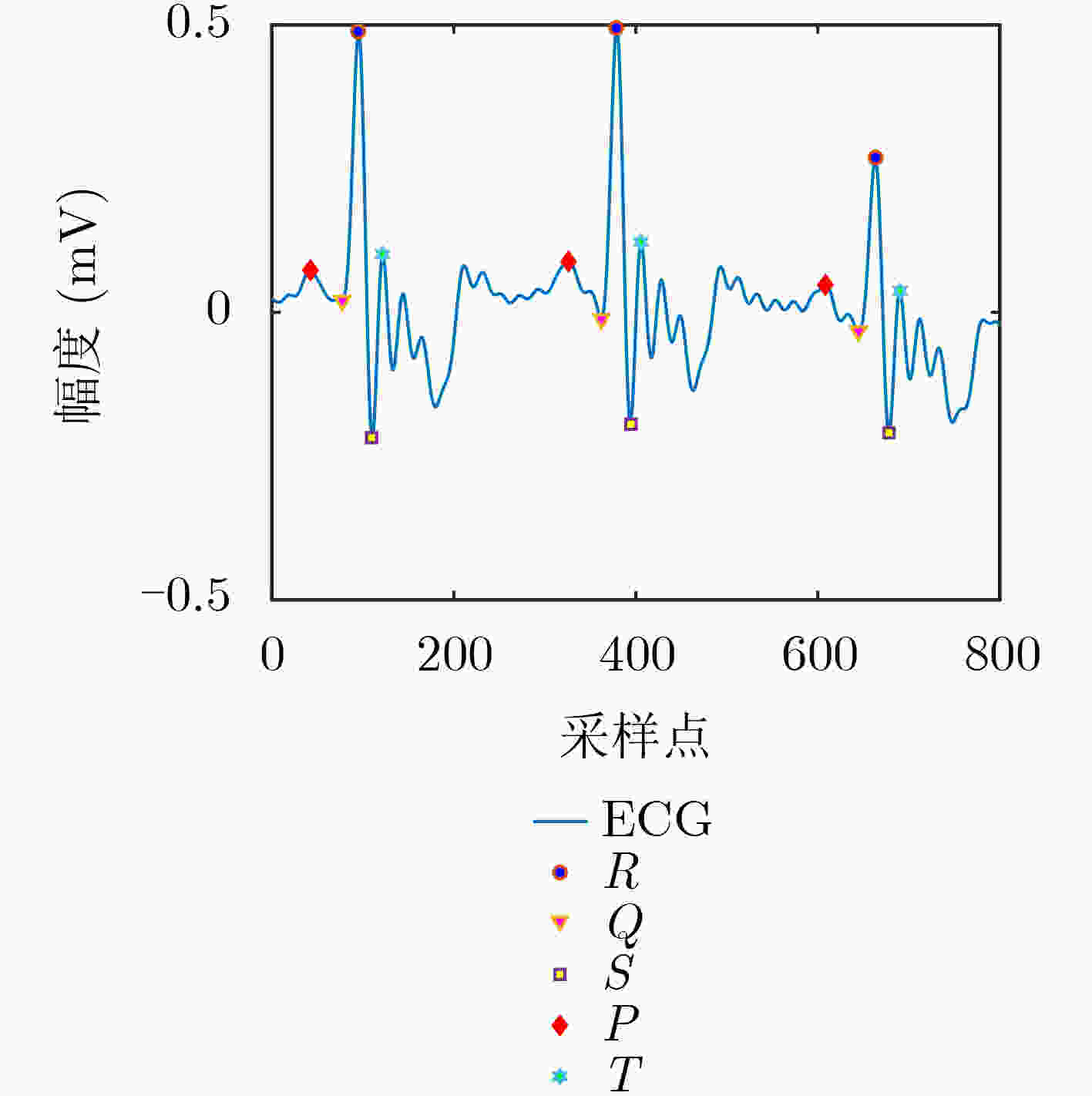
编号 特征 具体描述 1 PQ_T PQ波持续时间(ms) 2 ST_T ST波持续时间(ms) 3 QR_T QR波持续时间(ms) 4 RS_T RS波持续时间(ms) 5 R_A R波幅值(μV) 6 PT_A PT波振幅差 7 SQ_A SQ波振幅差 8 PR_A PR波振幅差 表 2 PPG信号的特征与描述
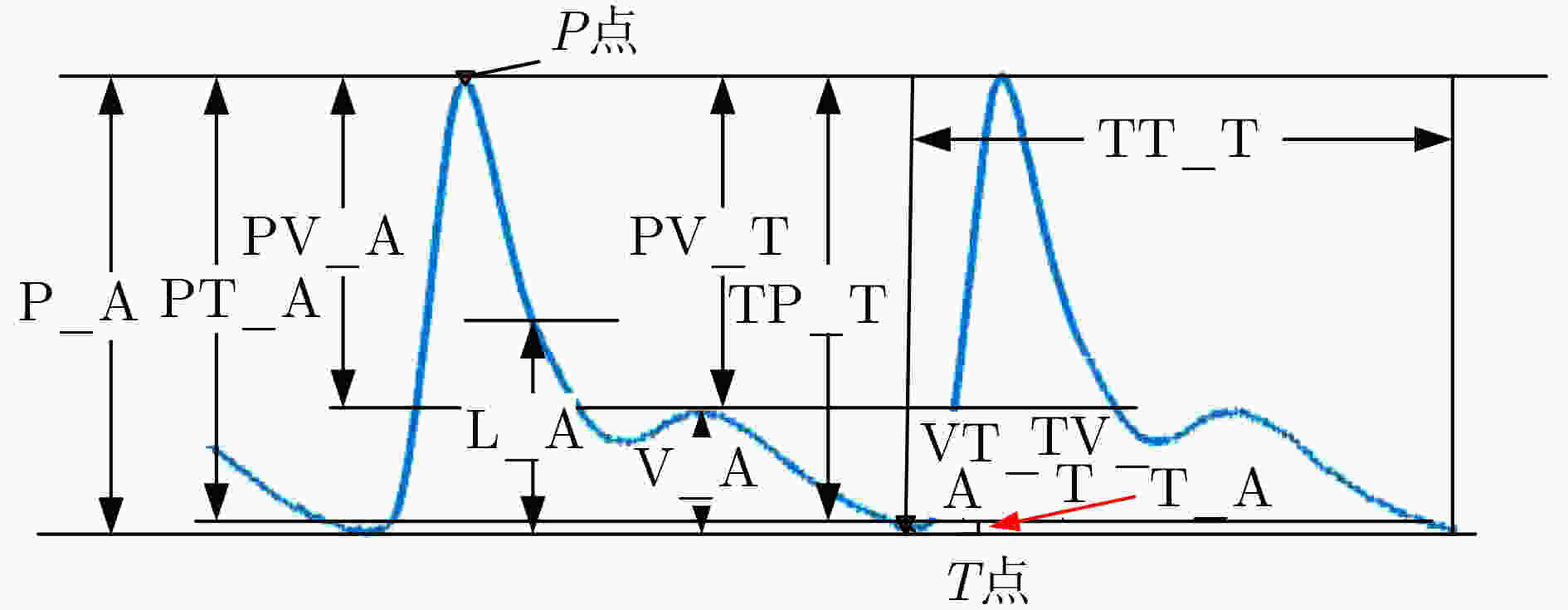
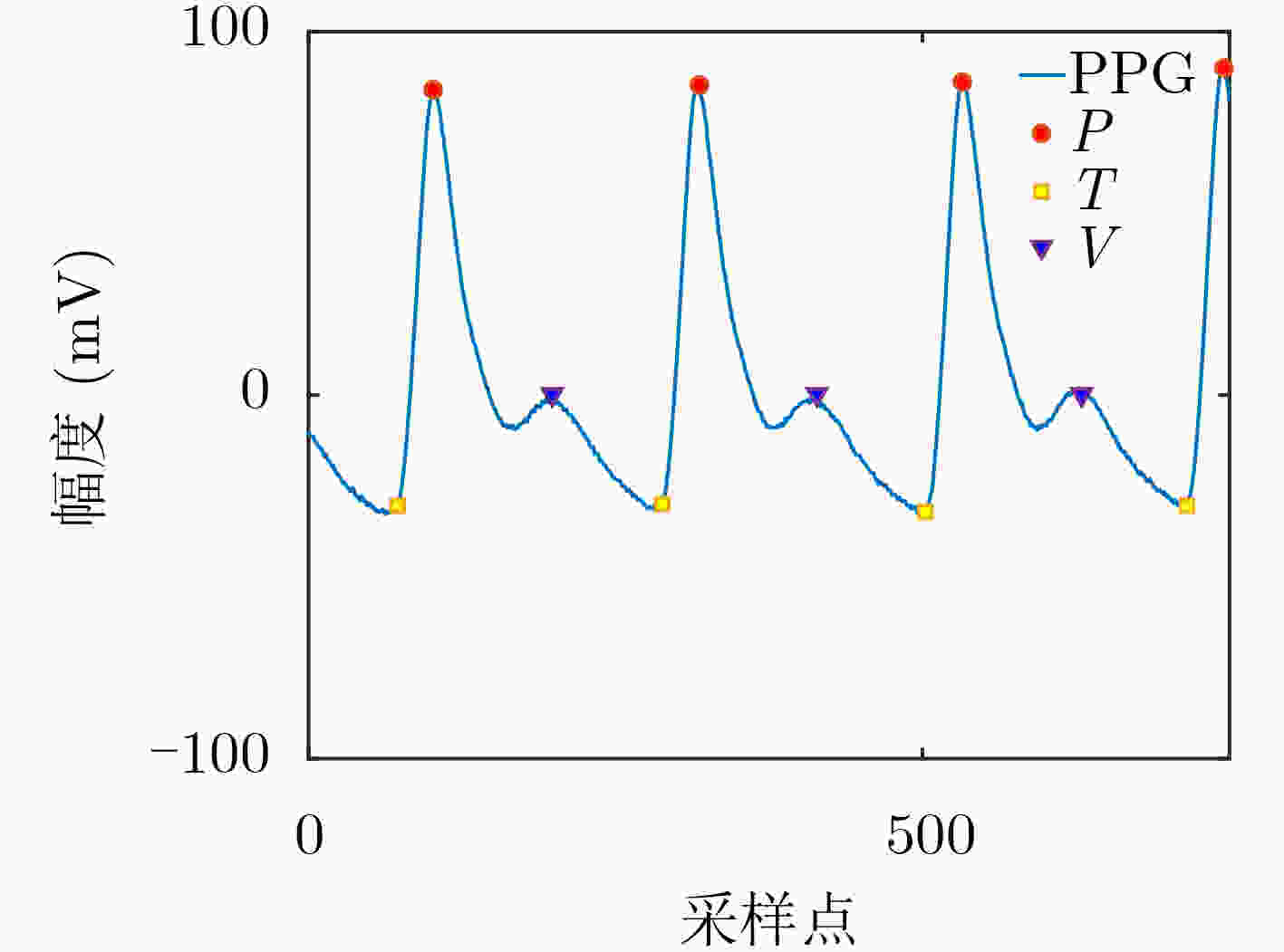
编号 特征 具体描述 1 P_A 收缩波峰幅值(μV) 2 V_A 舒张波幅值(μV) 3 L_A 降中峡幅值(μV) 4 T_A 波谷幅值(μV) 5 PT_A 波谷到收缩波幅值差(μV) 6 VT_A 波谷到舒张波距离幅值差(μV) 7 PV_A 收缩波峰到舒张波幅值差(μV) 8 TT_T 波谷到波谷持续时间(ms) 9 TP_T 波谷到收缩波峰持续时间(ms) 10 PV_T 收缩波峰到舒张波时间(ms) 11 TV_T 波谷到舒张波时间(ms) 表 3 不同模式下识别准确率
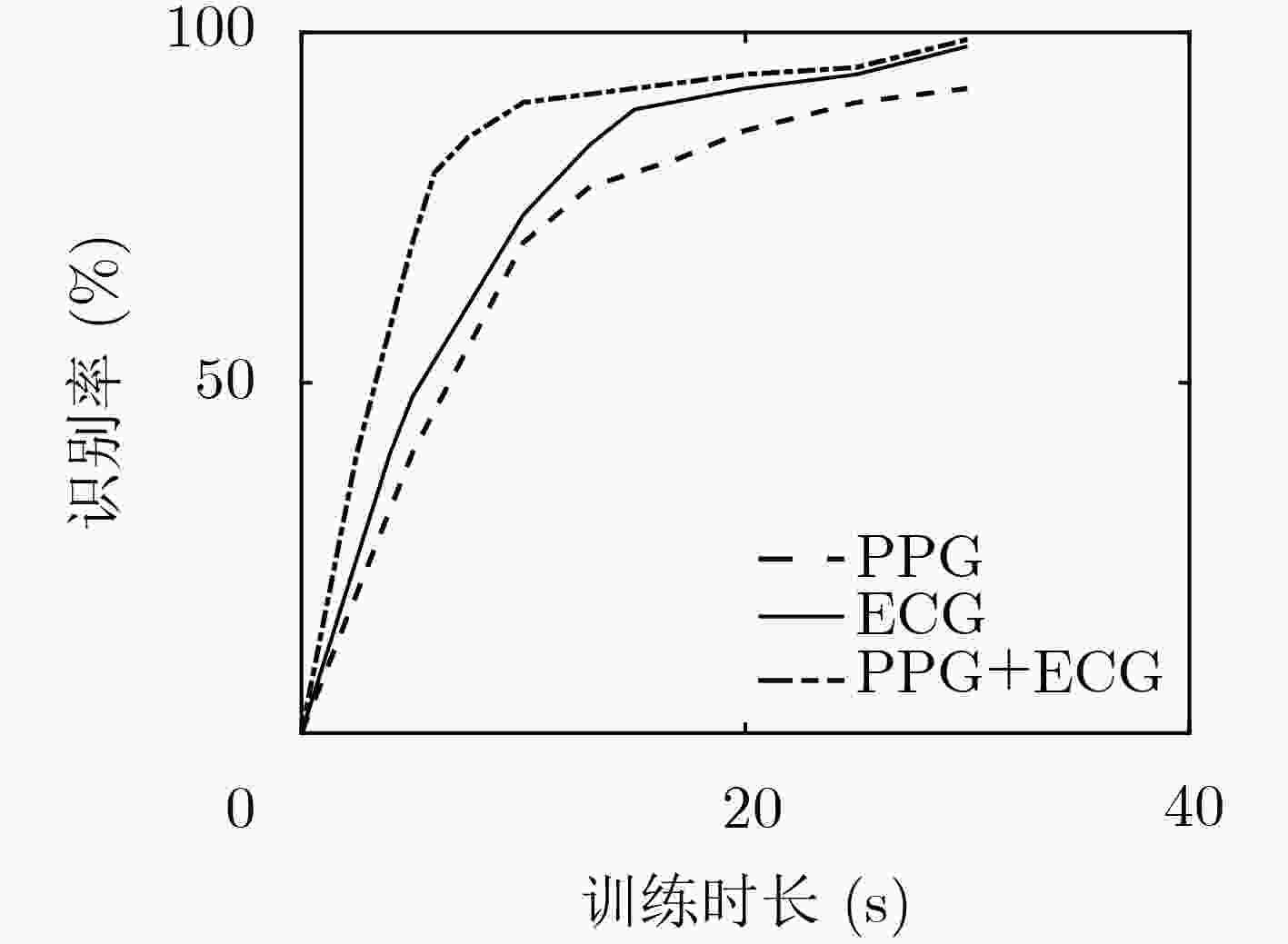
ECG PPG ECG-PPG SVM 0.880 0.810 0.961 KNN 0.845 0.745 0.915 KNN-SVM 0.910 0.824 0.982 -
[1] KAUR G, SINGH G, and KUMAR V. A review on biometric recognition[J]. International Journal of Bio-Science and Bio-Technology, 2014, 6(4): 69–76. doi: 10.14257/ijbsbt.2014.6.4.07 [2] ROSS A A, NANDAKUMAR K J, and JAIN A K. Handbook of Multibiometrics[M]. New York: Springer, 2006: 37–58. [3] ROSS A and JAIN A. Information fusion in biometrics[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2003, 24(13): 2115–2125. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8655(03)00079-5 [4] 张敏贵, 潘泉, 张洪才, 等. 多生物特征识别[J]. 信息与控制, 2002, 31(6): 524–528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0411.2002.06.010ZHANG Mingui, PAN Quan, ZHANG Hongcai, et al. Multibiometrics identification techniques[J]. Information and Control, 2002, 31(6): 524–528. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0411.2002.06.010 [5] CHAA M, BOUKEZZOULA N E, and MERAOUMIA A. Features-level fusion of reflectance and illumination images in finger-knuckle-print identification system[J]. International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools, 2018, 27(3): 1850007. doi: 10.1142/S0218213018500070 [6] CHEN Junkai, CHEN Zenghai, CHI Zheru, et al. Facial expression recognition in video with multiple feature fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2018, 9(1): 38–50. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2016.2593719 [7] GUPTA P. Multibiometric authentication system using slap fingerprints, palm dorsal vein, and hand geometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(12): 9777–9784. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2823686 [8] HAMMAD M and WANG Kuanquan. Parallel score fusion of ECG and fingerprint for human authentication based on convolution neural network[J]. Computers & Security, 2019, 81: 107–122. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2018.11.003 [9] ARTEAGA-FALCONI J S, AL OSMAN H, and EL SADDIK A. ECG and fingerprint bimodal authentication[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2018, 40: 274–283. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2017.12.023 [10] BASHAR K. ECG and EEG based multimodal biometrics for human identification[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Miyazaki, Japan, 2018: 4345–4350. [11] 杨宜蒙. 基于ECG和PPG信号身份识别算法的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.YANG Yimeng. A study of ECG & PPG-based biometrics technology[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016. [12] SUN Quansen, ZENG Shenggen, LIU Yan, et al. A new method of feature fusion and its application in image recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2005, 38(12): 2437–2448. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2004.12.013 [13] CORREA N M, ADALI T, LI Yiou, et al. Canonical correlation analysis for data fusion and group inferences[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(4): 39–50. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936725 [14] HAGHIGHAT M, ABDEL-MOTTALEB M, and ALHALABI W. Fully automatic face normalization and single sample face recognition in unconstrained environments[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 47: 23–34. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.047 [15] GAO Xizhan, SUN Quansen, and YANG Jing. MRCCA: A novel CCA based method and its application in feature extraction and fusion for matrix data[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 62: 45–56. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.10.008 [16] 胡敏, 滕文娣, 王晓华, 等. 融合局部纹理和形状特征的人脸表情识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(6): 1338–1344. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170799HU Min, TENG Wendi, WANG Xiaohua, et al. Facial expression recognition based on local texture and shape features[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1338–1344. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170799 [17] GUO Manshan, YANG Xu, ZHANG Feng, et al. Supervised dictionary learning supported classifier with feature fusion scheme to noninvasively detect TRISO-particle defects[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2019, 523: 43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2019.05.040 [18] SCHOTT J R. Principles of multivariate analysis: A user’s perspective[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2002, 97(458): 657–658. doi: 10.1198/jasa.2002.s479 [19] HAGHIGHAT M, ABDEL-MOTTALEB M, and ALHALABI W. Discriminant correlation analysis: Real-time feature level fusion for multimodal biometric recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(9): 1984–1996. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2569061 [20] TURK M and PENTLAND A. Eigenfaces for recognition[J]. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 1991, 3(1): 71–86. doi: 10.1162/jocn.1991.3.1.71 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
