Research Status of Vortex Electromagnetic Wave Wireless Communication Technologies
-
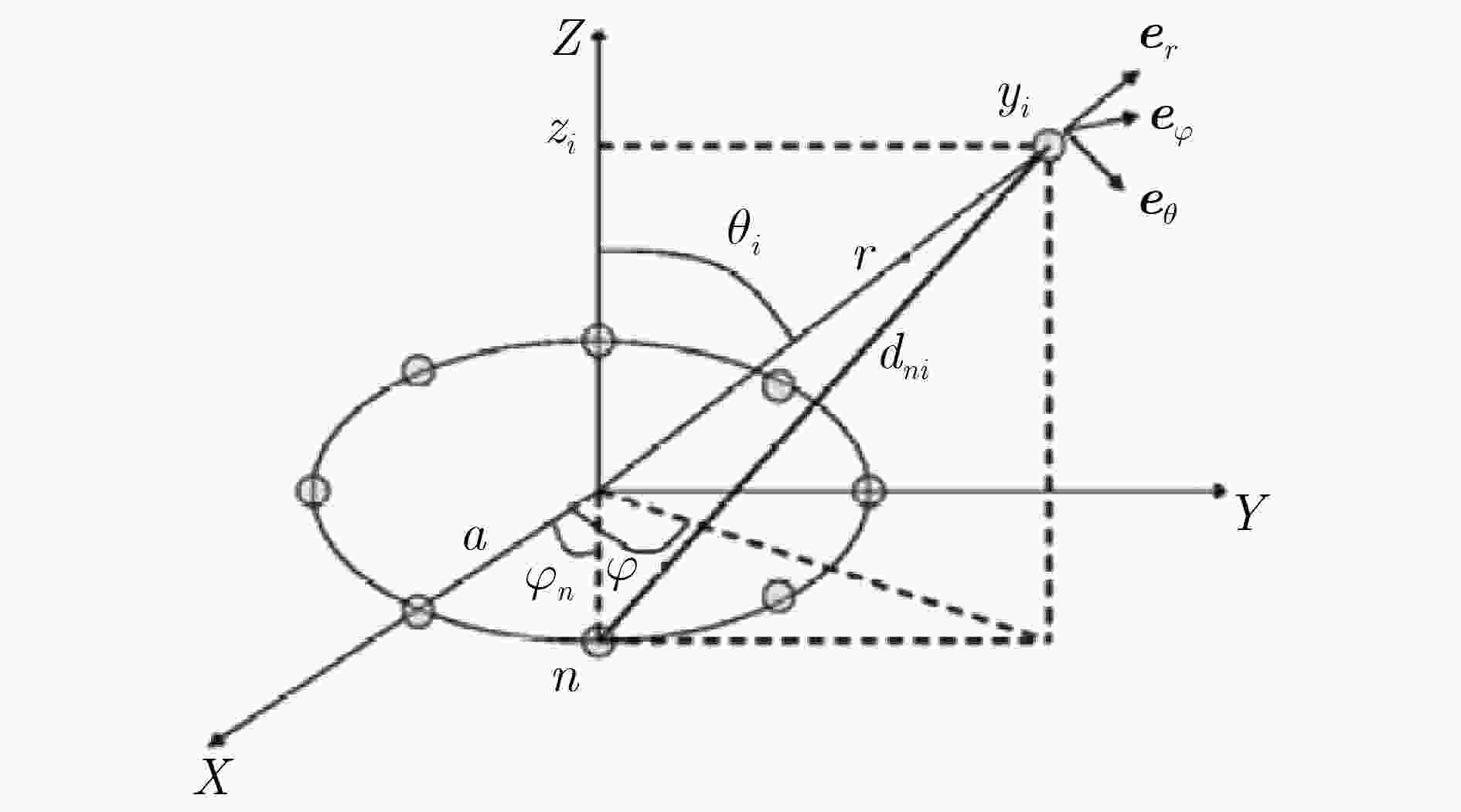
摘要: 由电磁动力学可知,电磁波可携带与极化方式相关的自旋角动量(Spin Angular Momentum, SAM) 和与坡印廷矢量运动方式相关的轨道角动量(Orbital Angular Momentum, OAM)。当OAM不为零时,电磁波的波前电场分布呈漩涡状且具有沿轴向传播的特性,人们形象地将这类电磁波称为涡旋电磁波。学界在平面电磁波场强数学模型的基础上引入了一个以OAM 的拓扑荷
$ \ell $ (又称模态)为参数的傅里叶旋转因子描述涡旋电磁波的波前场,因此,涡旋电磁波波前具有与拓扑荷$ \ell $ 相关联的“极化”图案,利用不同模态的涡旋电磁波的极化图案可进一步提升无线通信系统信道容量。研究表明,在开放环境下由均匀圆阵列(Uniform Circular Array, UCA)阵列产生“平面”涡旋电磁波波束尽管可行,但要获得模态复用增益,需要探索基于复平面内单位圆周上分布的正交相位序列的涡旋电磁波波束产生与信息传输方法。文中也调研了无线射频领域OAM与MIMO体制相兼容的研究现状。Abstract: It is known from electromagnetic momentum that electromagnetic waves can carry Spin Angular Momentum (SAM) related to polarization and Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM) related to the trajectory of the Poynting vector. When OAM is not zero, the wave-front electric field distribution of the electromagnetic wave is vortex-like and has the characteristic of propagating along the axial direction. Therefore, this electromagnetic wave is aptly named vortex electromagnetic wave. Based on the mathematical model of the plane electromagnetic wave field, the researchers introduce a Fourier factor that uses the topological charge (also called mode) of the OAM as a parameter to describe the field of the vortex electromagnetic wave. Therefore, the wave-front of the vortex electromagnetic wave with a “polarization” pattern associated with topological charge, the use of polarization patterns of vortex electromagnetic waves in different modes can further increase the spectrum effect of the wireless communication system. Studies show that although it is feasible to generate "planar" vortex electromagnetic wave beams from Uniform Circular Array (UCA) arrays in an open environment, to obtain modal multiplexing gain, and it is necessary to explore vortex electromagnetic wave beams based on orthogonal phase sequences distributed on a unit circle in the complex plane. At the same time, the paper also investigates the current research status of compatibility between OAM and Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) systems in the field of radio frequency. -
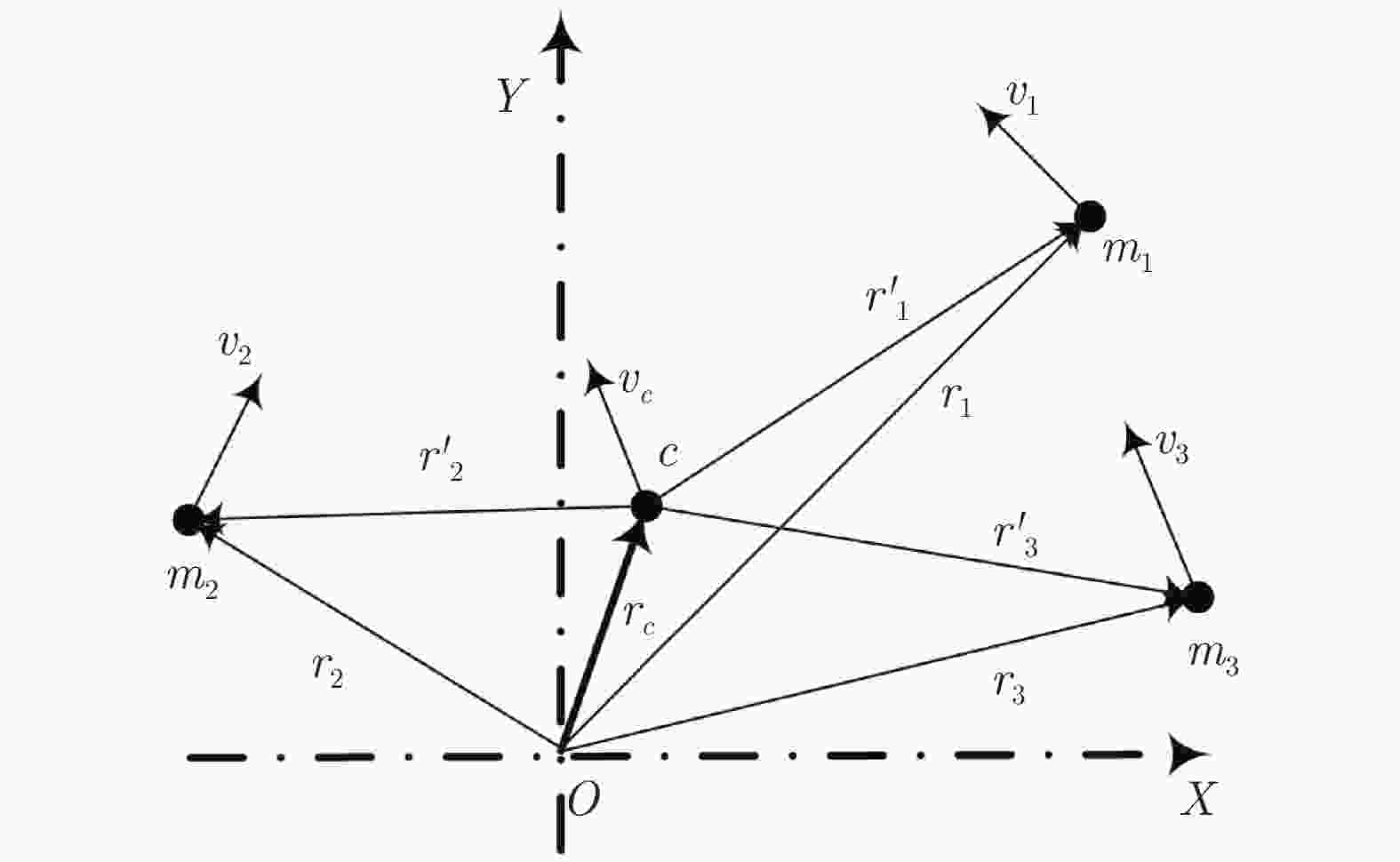
图 1 携带角动量的质点系[21]
图 2 电基本阵子角动量密度矢量示意图[21]
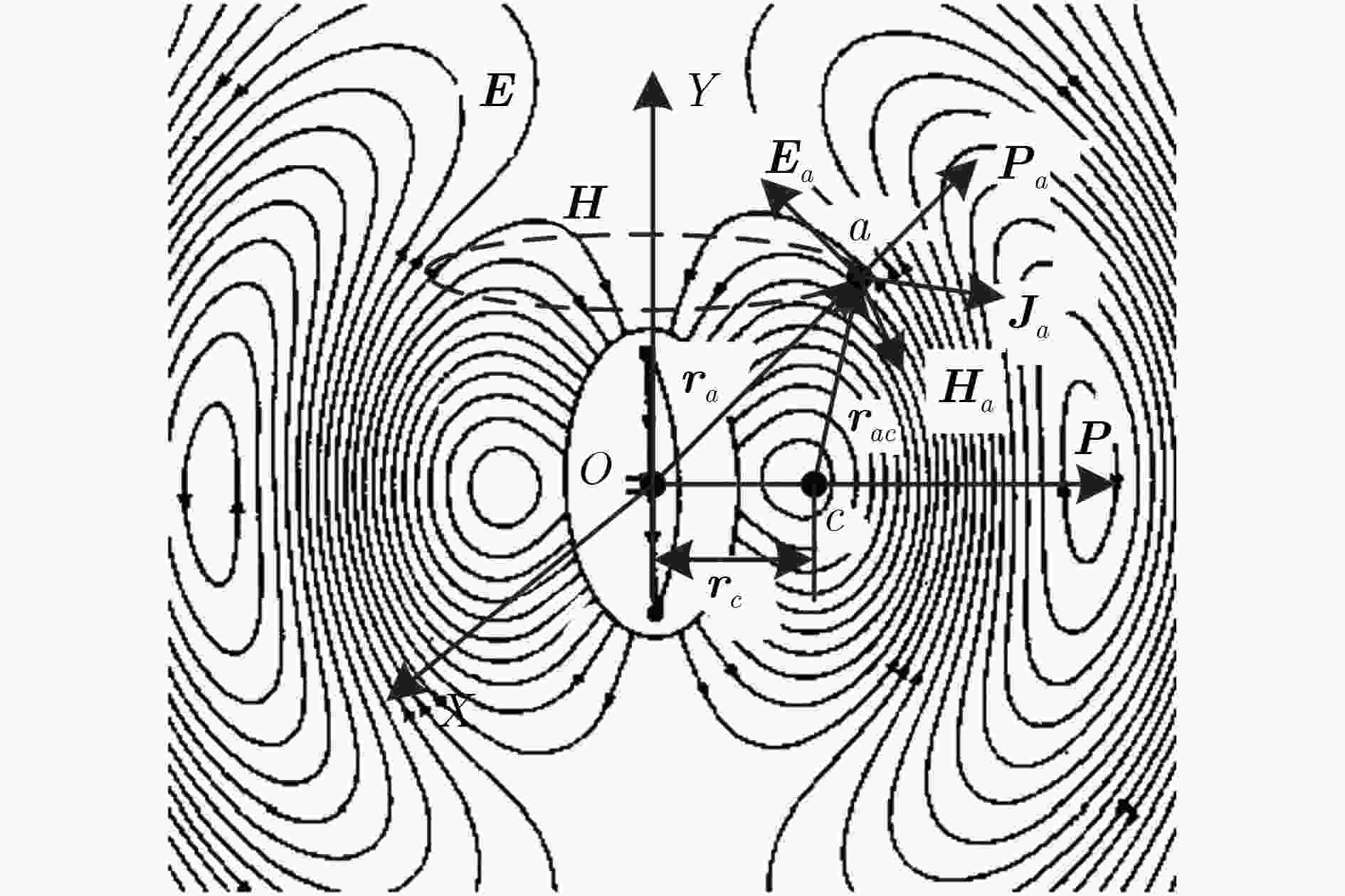
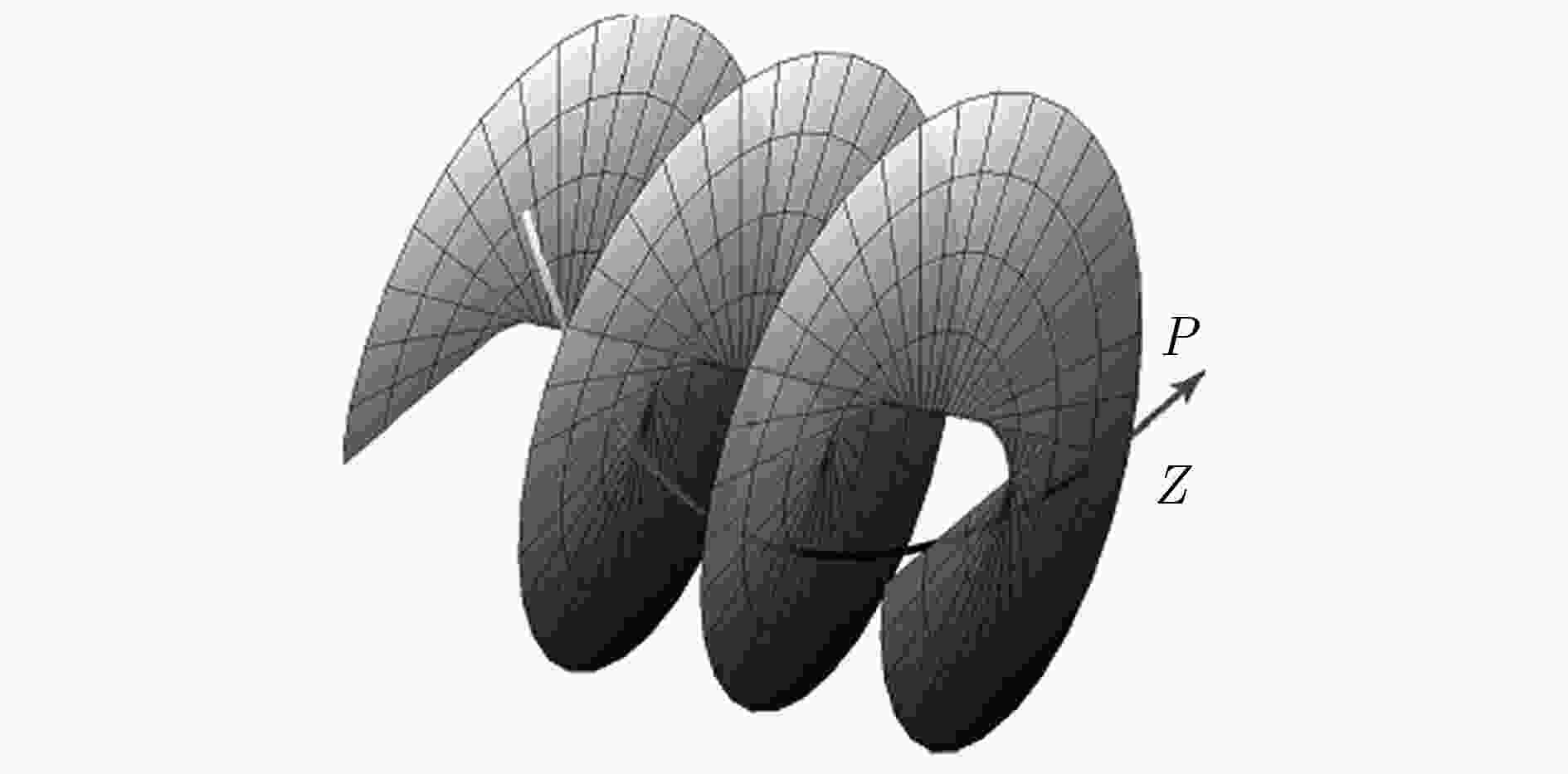
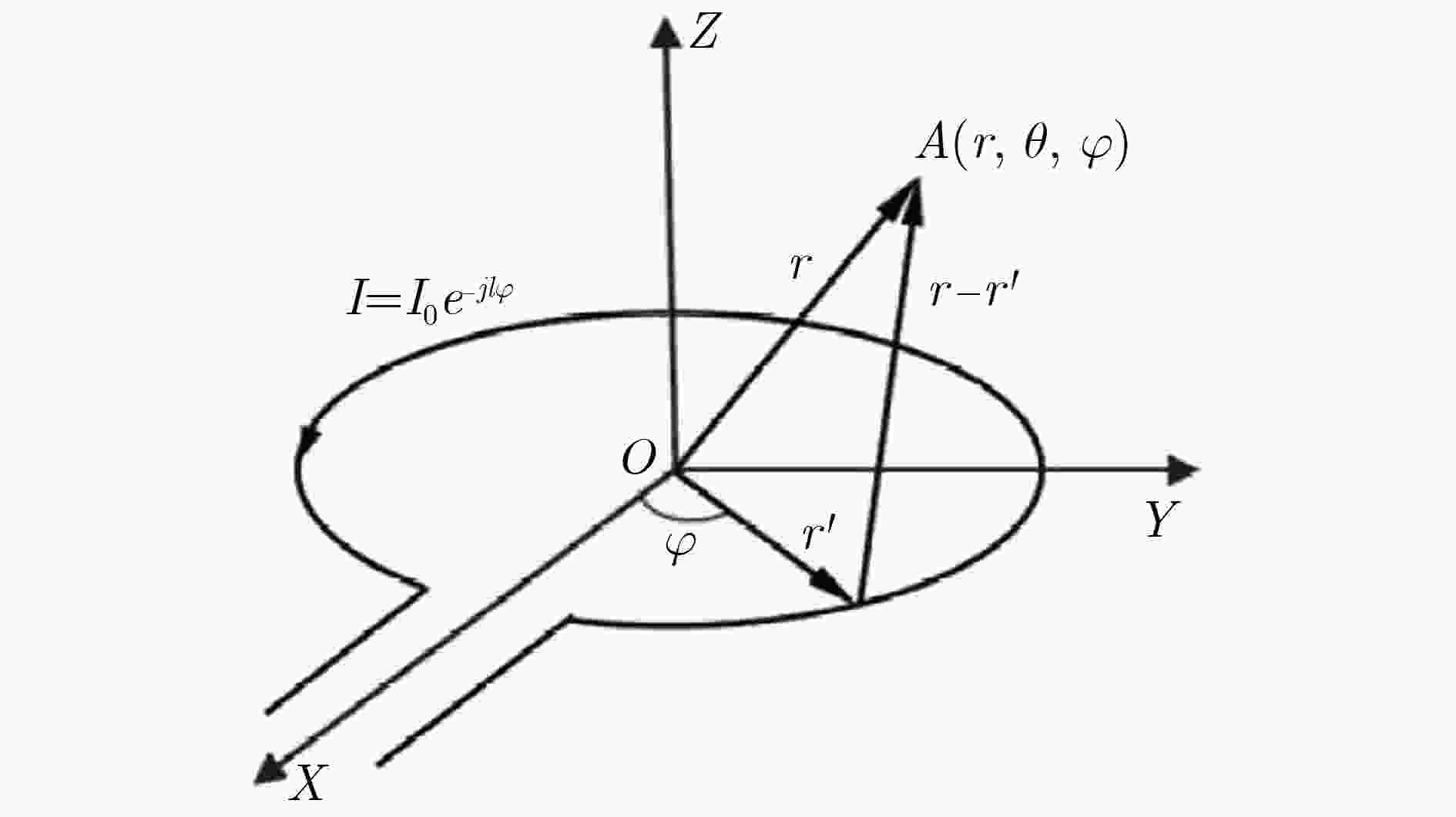
图 3 携有OAM电磁波坡印廷矢量轨迹及其波前结构示意[24]
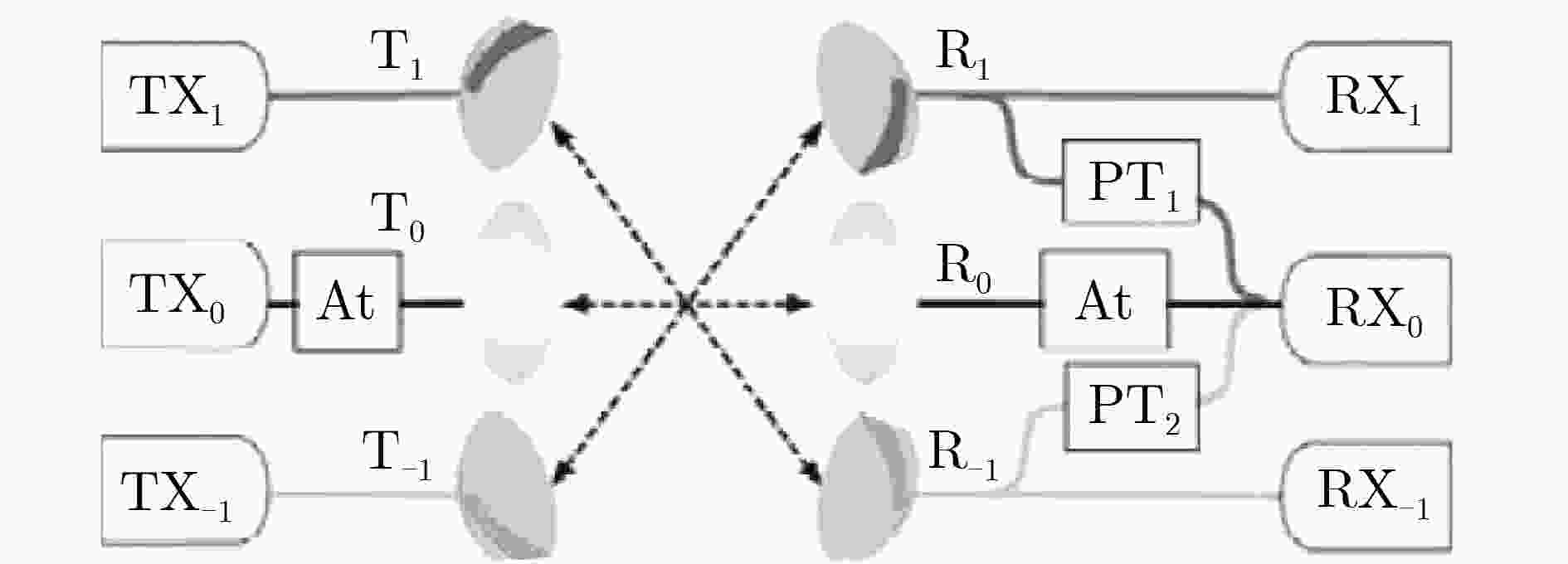
图 7 射频域信号移相馈电网络示意图[52]
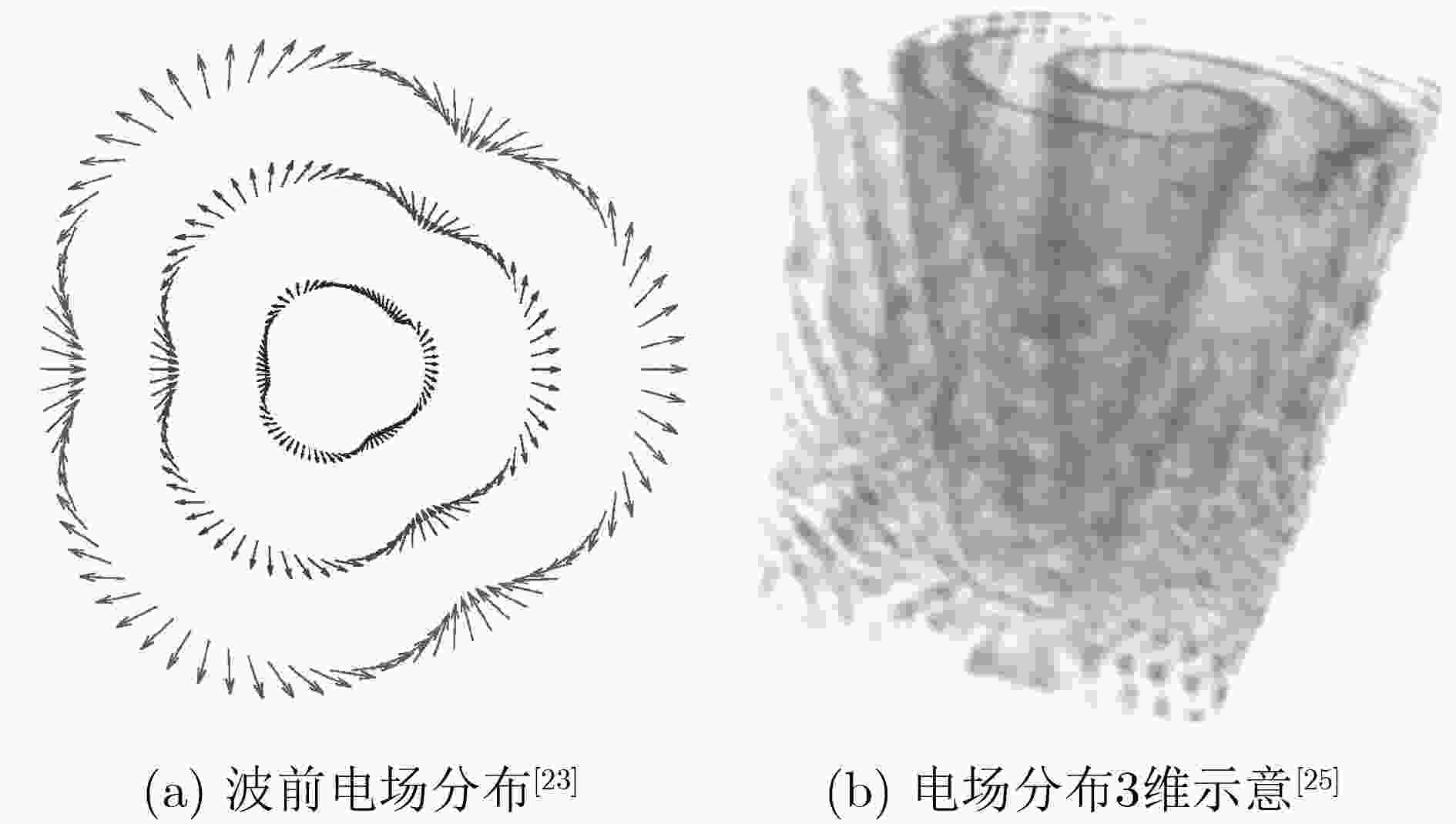
图 8 相位梯度检测方法示意[25]
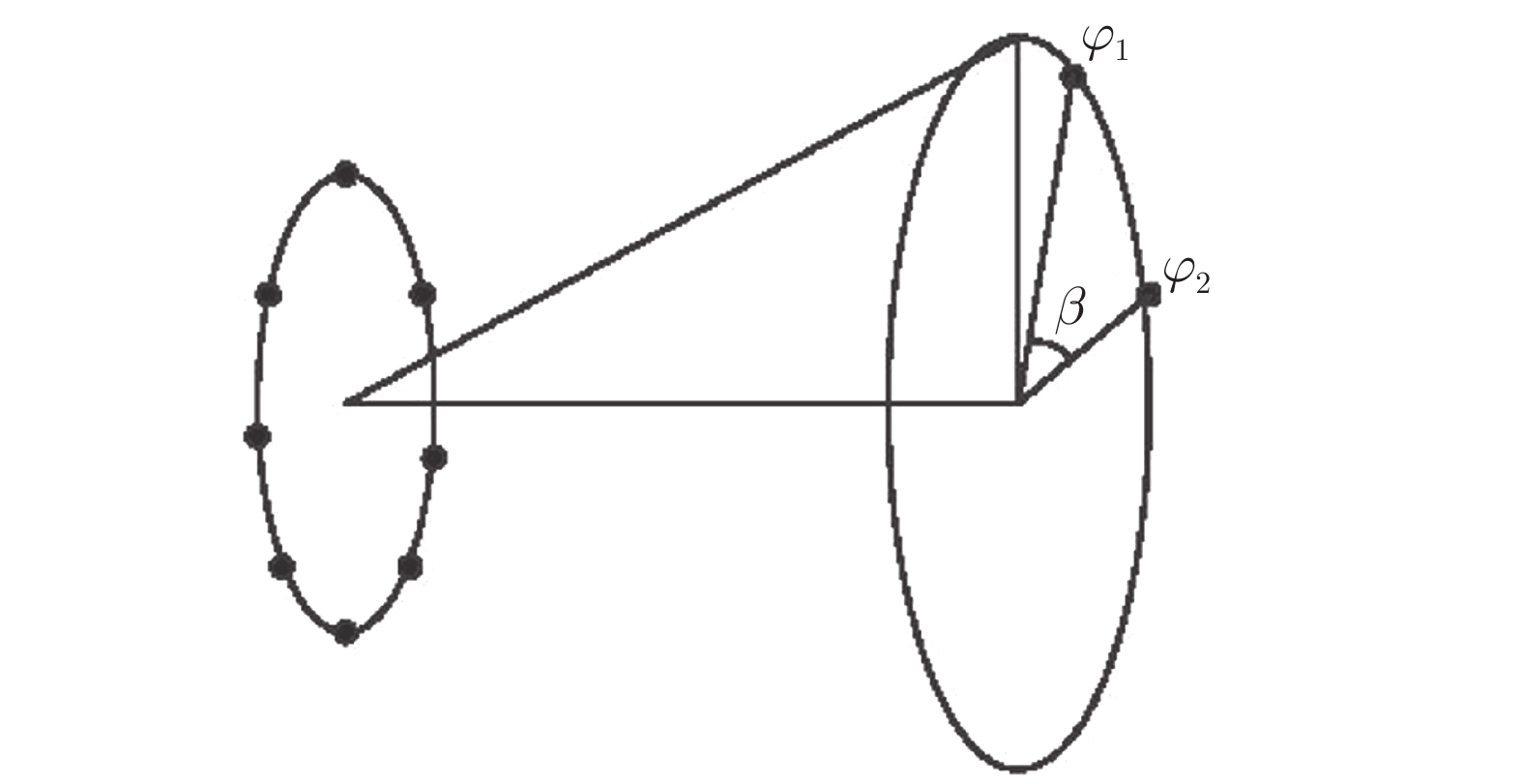
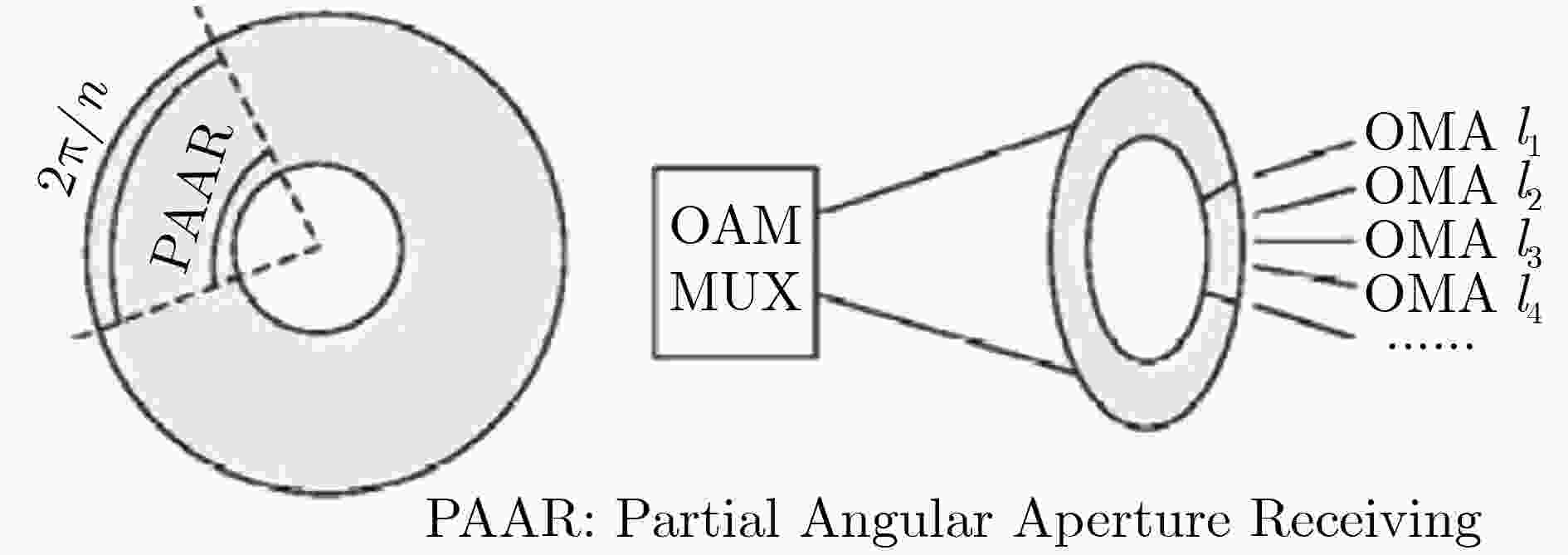
图 9 部分方位角接收示意图[53]
图 10 全方位角采样接收方法示意图[54]
图 11 3个OAM复用的MIMO链路示意图[62]
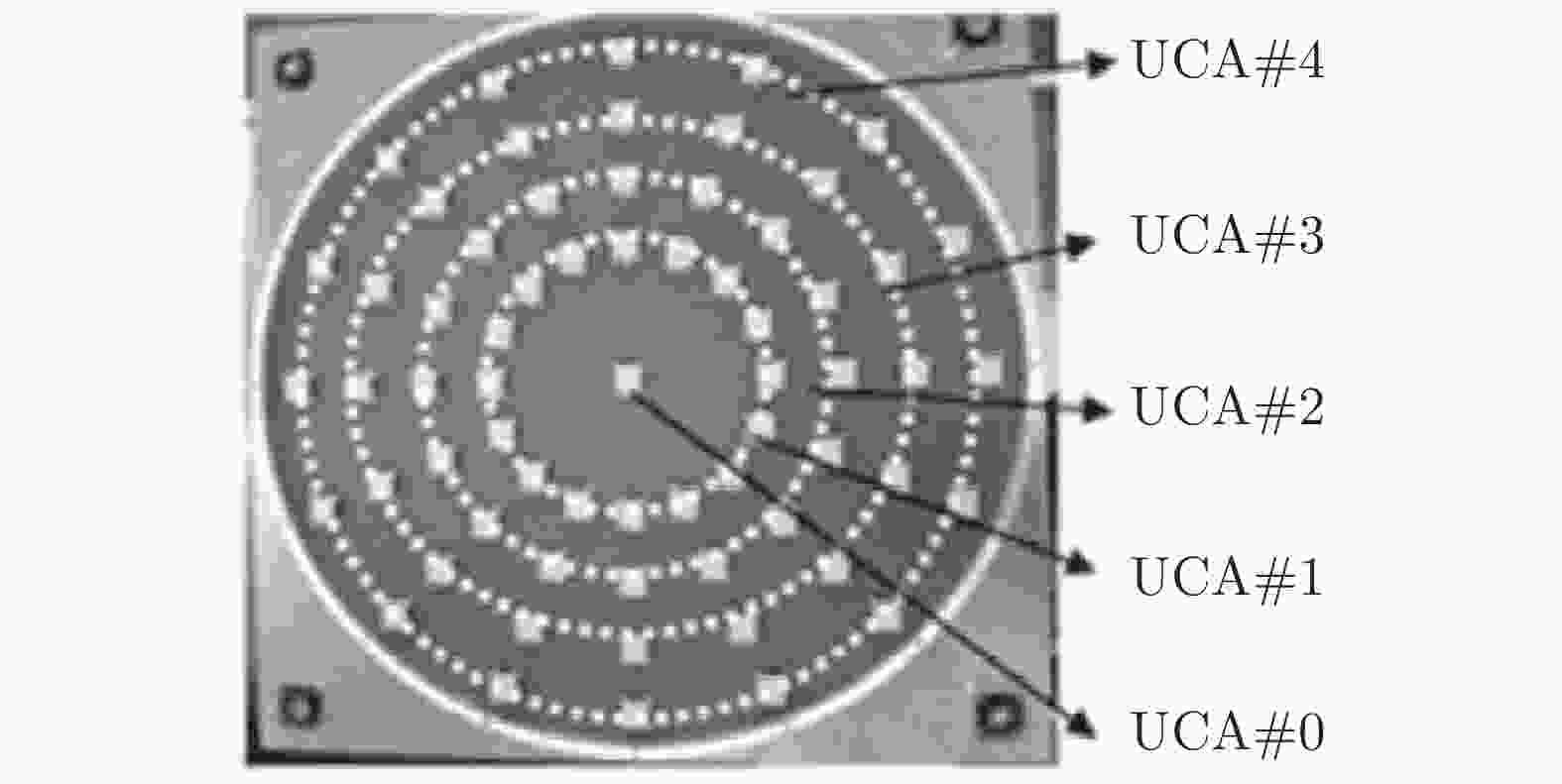
图 12 同心圆嵌套时的模态复用OAM MIMO系统示意图[65]
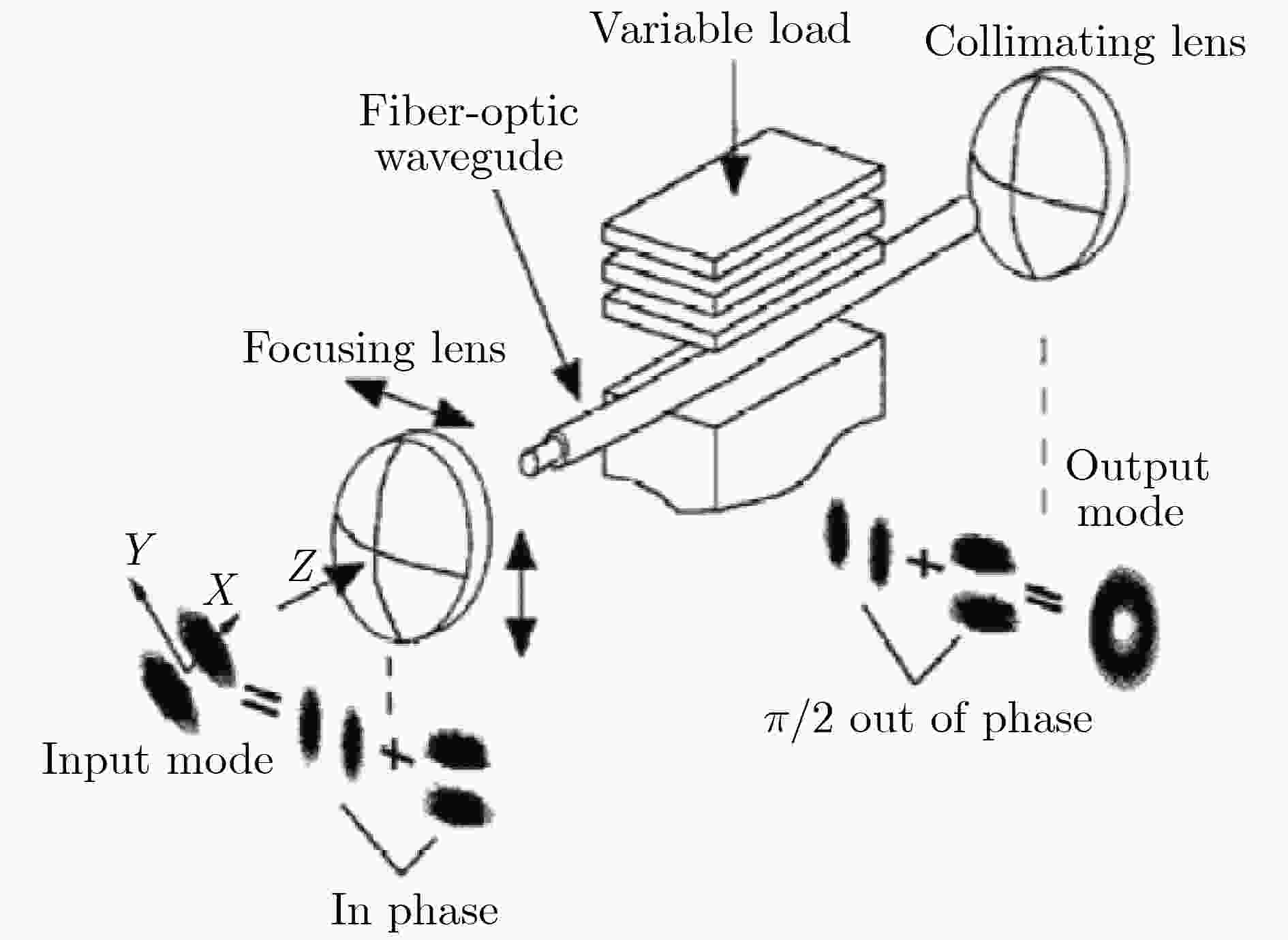
图 13 OAM光通信方案示意图[66]
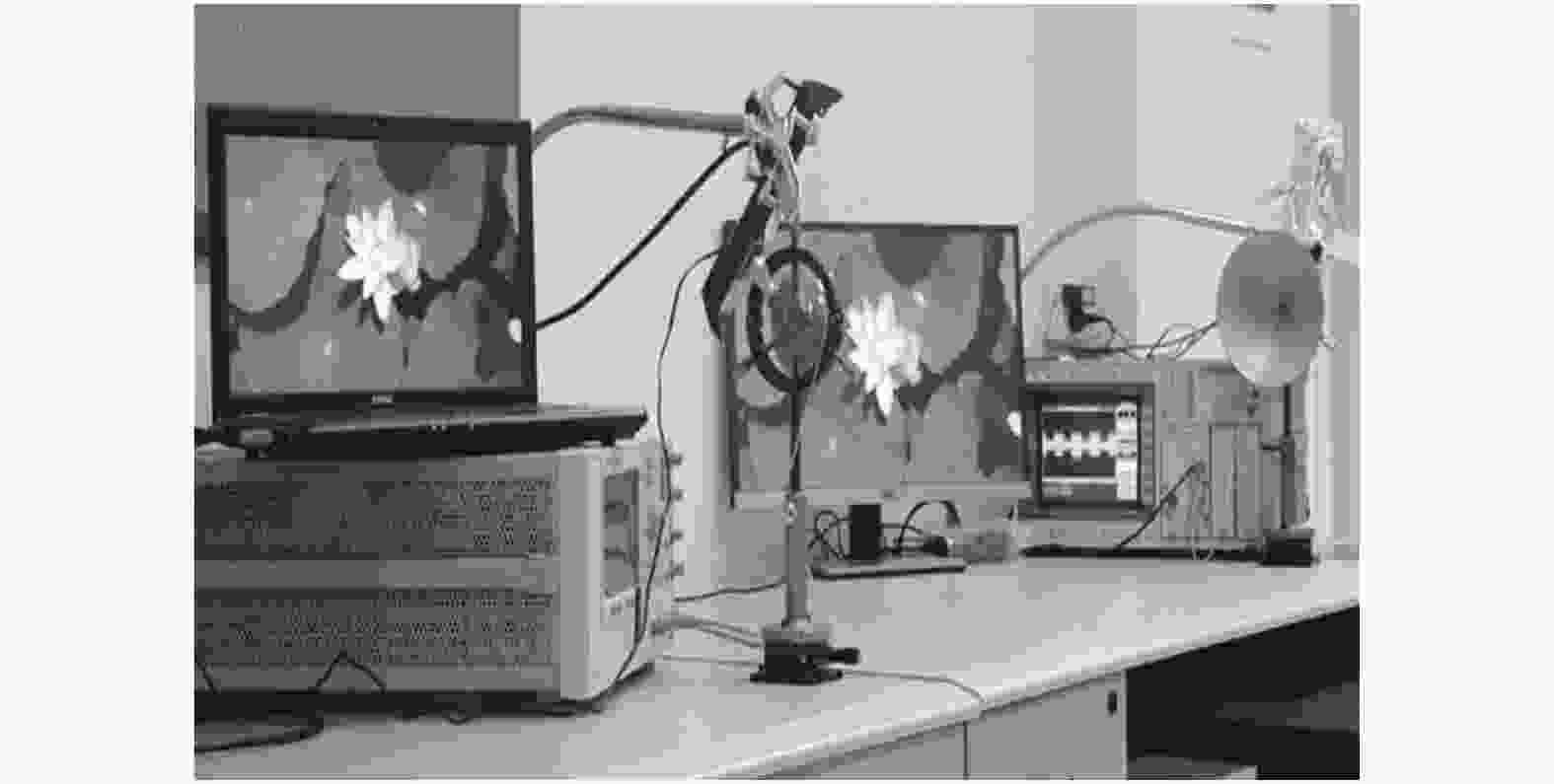
图 14 双模态无线室内演示系统示意图[75]
-
[1] SHANNON C E. A mathematical theory of communication[J]. Bell System Technical Journal, 1948, 27(3): 379–423. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x [2] GOLDSMITH A, JAFAR S A, JINDAL N, et al. Capacity limits of MIMO channels[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2003, 21(5): 684–702. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2003.810294 [3] WANG Linlin, WANG Shuxun, SUN Xiaoying, et al. Combined beamforming and space-time block coding for wireless communications[C]. 14th IEEE Proceedings on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, 2003. PIMRC 2003, Beijing, 2003: 607–611. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2003.1264344. [4] 刘盛纲, 钟任斌. 太赫兹科学技术及其应用的新发展[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2009, 38(5): 481–486. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2009.05.001LIU Shenggang and ZHONG Renbin. Recent development of terahertz science and technology and it's applications[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2009, 38(5): 481–486. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2009.05.001 [5] 胡海翔, 李光伟. 电磁辐射的生物学效应[M]. 胡海翔, 李光伟. 电磁辐射对人体的影响及防护. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2015: 56–141. [6] 袁明文. 太赫兹波的几个基本问题[J]. 微纳电子技术, 2009, 46(5): 257–262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4776.2009.05.001YUAN Mingwen. Several key problems of Terahertz[J]. Micronanoelectronic Technology, 2009, 46(5): 257–262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4776.2009.05.001 [7] ROSE M E. Physical sciences: Elementary theory of angular momentum[J]. Science, 1958: 127. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3304.976 [8] 李书民. 电磁波的能量、动量与角动量[M]. 李书民. 电动力学概论. 合肥: 中国科技大学出版社, 2010: 124–125. [9] ALLEN L, BEIJERSBERGEN M W, SPREEUW R J C, et al. Orbital angular momentum of light and the transformation of Laguerre-gaussian laser modes[J]. Physical Review A, 1992, 45(11): 8185–8189. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.45.8185 [10] THIDÉ B, THEN H, SJÖHOLM J, et al. Utilization of photon orbital angular momentum in the low-frequency radio domain[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(8): 087701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.087701 [11] MAXWELL J C A. A treatise on electricity and magnetism[J]. Nature, 7(182): 478–480. doi: 10.1038/007478a0. [12] BURROWS C R. The history of radio wave propagation up to the end of world war I[J]. Proceedings of the IRE, 1962, 50(5): 682–684. doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1962.288097 [13] ANDERSEN J B. History of communications/radio wave propagation from Marconi to MIMO[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(2): 6–10. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.7841460 [14] BETH R A. Mechanical detection and measurement of the angular momentum of light[J]. Physical Review Journals Archive, 1936, 50(2): 115–125. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.50.115 [15] PADGETT M J. Orbital angular momentum 25 years on [invited][J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(10): 11265–11274. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.011265 [16] PLAAT O. Separation of variables[J]. American Mathematical Monthly, 1968, 75(8): 844–847. doi: 10.2307/2314333 [17] WILCOX C H. Scattering Theory for the D’Alembert Equation in Exterior Domains[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1975: 14–38. doi: 10.1007/BFb0070581. [18] 竺子民. 电磁场的动量守恒定律[M]. 竺子民. 物理光学. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2009: 18–21. [19] LEBEDEW P. Untersuchungen über die druckkräfte des lichtes[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1901, 311(11): 433–458. doi: 10.1002/andp.19013111102 [20] FORD K W, 高航, 译. 第9章角动量[M]. FORD K W, 高航, 译. 经典和近代物理学 第2册. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1982: 147–160. [21] KRAUS J D and MARHEFKA R J. Antennas for All Applications[M]. 2nd ed. Boston: McGraw Hill, 1998: 50–60. [22] VAN ENK S J and NIENHUIS G. Eigenfunction description of laser beams and orbital angular momentum of light[J]. Optics Communications, 1992, 94(1/3): 147–158. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(92)90424-P [23] SJÖHOLM J and PALMER K. Angular momentum of electromagnetic radiation. Fundamental physics applied to the radio domain for innovative studies of space and development of new concepts in wireless communications[J]. Physics, 2009, 48(1): 15–21. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.48.1.15 [24] ALLEN L and PADGETT M. The orbital angular momentum of light: An introduction[M]. TORRES J P and TORNER L. Twisted Photons: Applications of Light with Orbital Angular Momentum. Weinheim: Wiley, 2011: 1–12. doi: 10.1002/9783527635368.ch1. [25] MOHAMMADI S M, DALDORFF L K S, BERGMAN J E S, et al. Orbital angular momentum in radio—a system study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(2): 565–572. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2037701 [26] SIMPSON B N, DHOLAKIA K, ALLEN L, et al. Mechanical equivalence of spin and orbital angular momentum of light: An optical spanner[J]. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(1): 52–54. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.000052 [27] YAO A M and PADGETT M J. Orbital angular momentum: Origins, behavior and applications[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2011, 3(2): 161–204. doi: 10.1364/AOP.3.000161 [28] O’NEIL A T, MACVICAR I, ALLEN L, et al. Intrinsic and extrinsic nature of the orbital angular momentum of a light beam[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 88(5): 053601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.053601 [29] LITVIN I A, DUDLEY A, and FORBES A. Poynting vector and orbital angular momentum density of superpositions of Bessel beams[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(18): 16760–16771. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.016760 [30] VAN ENK S J and NIENHUIS G. Commutation rules and eigenvalues of spin and orbital angular momentum of radiation fields[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 1994, 41(5): 963–977. doi: 10.1080/09500349414550911 [31] SHAO Zengkai, ZHU Jiangbo, CHEN Yujie, et al. Spin-orbit interaction of light induced by transverse spin angular momentum engineering[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 926. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03237-5 [32] BALANIS C A. Advanced Engineering Electromagnetics[M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken, America: Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2012: 924–927. [33] LIU Aiping, XIONG Xiao, REN Xifeng, et al. Detecting orbital angular momentum through division-of-amplitude interference with a circular plasmonic lens[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3(1): 2402. doi: 10.1038/srep02402 [34] PATERSON C. Atmospheric turbulence and orbital angular momentum of single photons for optical communication[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 94(15): 153901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.153901 [35] JIANG Yuesong, HE Yuntao, and LI Fang. Wireless communications using millimeter-wave beams carrying orbital angular momentum[C]. 2009 WRI International Conference on Communications and Mobile Computing, Kunming, China, 2009: 495–500. doi: 10.1109/CMC.2009.315. [36] 中国科学院大气物理研究所微波遥感组. 中国晴空和云雨大气的微波辐射和传播特性[M]. 北京: 中防工业出版社, 1982. [37] LI Yaqing, WANG Liguo, and WU Zhensen. Study on intensities, phases and orbital angular momentum of vortex beams in atmospheric turbulence using numerical simulation method[J]. Optik, 2018, 158: 1349–1360. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.01.029 [38] FU Shiyao and GAO Chunqing. Influences of atmospheric turbulence effects on the orbital angular momentum spectra of vortex beams[J]. Photonics Research, 2016, 4(5): B1–B4. doi: 10.1364/prj.4.0000b1 [39] BOZINOVIC N, YANG Yue, REN Yongxiong, et al. Terabit-scale orbital angular momentum mode division multiplexing in fibers[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6140): 1545–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.1237861 [40] ZHANG Zhaoyang, YUAN Yuqing, CANG Ji, et al. An orbital angular momentum-based in-band full-duplex communication system and its mode selection[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(5): 1183–1186. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2660478 [41] CHENG Wenchi, ZHANG Wei, JING Haiyue, et al. Orbital angular momentum for wireless communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(1): 100–107. doi: 10.1109/mwc.2017.1700370 [42] TAMBURINI F, THIDÉ B, BOAGA V, et al. Experimental demonstration of free-space information transfer using phase modulated orbital angular momentum radio[J]. Physics, 2013: 1–7. [43] BEIJERSBERGEN M W, COERWINKEL R P C, KRISTENSEN M, et al. Helical-wavefront laser beams produced with a spiral phaseplate[J]. Optics Communications, 1994, 112(5/6): 321–327. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(94)90638-6 [44] YU Shixing, LI Long, SHI Guangming, et al. Design, fabrication, and measurement of reflective metasurface for orbital angular momentum vortex wave in radio frequency domain[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 108(12): 121903. doi: 10.1063/1.4944789 [45] ZHANG Kuang, YUAN Yueyi, ZHANG Dawei, et al. Phase-engineered metalenses to generate converging and non-diffractive vortex beam carrying orbital angular momentum in microwave region[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(2): 1351–1360. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.001351 [46] PALACIN B, SHARSHAVINA K, NGUYEN K, et al. An 8×8 butler matrix for generation of waves carrying orbital angular momentum (OAM)[C]. The 8th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2014), The Hague, 2014: 2814–2818. doi: 10.1109/EuCAP.2014.6902412. [47] XU Chen, ZHENG Shilie, ZHANG Weite, et al. Free-space radio communication employing OAM multiplexing based on Rotman lens[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2016, 26(9): 738–740. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2016.2597262 [48] STEIDL G and TASCHE M. A polynomial approach to fast algorithms for discrete Fourier-cosine and Fourier-sine transforms[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1991, 56(193): 281–296. doi: 10.1090/s0025-5718-1991-1052103-1 [49] ZHANG Zhuofan, ZHENG Shilie, ZHANG Weite, et al. Experimental demonstration of the capacity gain of plane spiral OAM-based MIMO system[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2017, 27(8): 757–759. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2017.2723719 [50] BEYME S and LEUNG C. Efficient computation of DFT of Zadoff-Chu sequences[J]. Electronics Letters, 2009, 45(9): 461–463. doi: 10.1049/el.2009.3330 [51] ZHENG Shilie, HUI Xiaonan, JIN Xiaofeng, et al. Transmission characteristics of a twisted radio wave based on circular traveling-wave antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(4): 1530–1536. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2393885 [52] ZHANG Weite, ZHENG Shilie, HUI Xiaonan, et al. Four-OAM-mode antenna with traveling-wave ring-slot structure[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2016, 16: 194–197. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2569540 [53] ZHENG Shilie, HUI Xiaonan, ZHU Jiangbo, et al. Orbital angular momentum mode-demultiplexing scheme with partial angular receiving aperture[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(9): 12251–12257. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.012251 [54] XIE Mutong, GAO Xinlu, ZHAO Mingyang, et al. Mode measurement of a dual-mode radio frequency orbital angular momentum beam by circular phase gradient method[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 1143–1146. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2624737 [55] YAO E, FRANKE-ARNOLD S, COURTIAL J, et al. Fourier relationship between angular position and optical orbital angular momentum[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(20): 9071–9076. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.009071 [56] EDFORS O and JOHANSSON A J. Is orbital angular momentum (OAM) based radio communication an unexploited area?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 60(2): 1126–1131. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2011.2173142 [57] MAHMOULI F E and WALKER S. Orbital angular momentum generation in a 60GHz wireless radio channel[C]. 2012 20th Telecommunications forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 2012: 315–318. doi: 10.1109/TELFOR.2012.6419210. [58] WANG Xinguang, YANG Zhen, and ZHAO Shengmei. Influence of oceanic turbulence on propagation of Airy vortex beam carrying orbital angular momentum[J]. Optik, 2019, 176: 49–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.09.028 [59] 柯熙政, 胥俊宇. 涡旋光束轨道角动量干涉及检测的研究[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(9): 0905003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0905003KE Xizheng and XU Junyu. Interference and detection of vortex beams with orbital angular momentum[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(9): 0905003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0905003 [60] SHIN D, PARK E, KANG J, et al. Identification of non-ideal receiver condition for orbital angular momentum transmission[C]. 2014 IEEE 79th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Seoul, South Korea, 2014: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTCSpring.2014.7022936. [61] TAMAGNONE M, SILVA J S, CAPDEVILA S, et al. The orbital angular momentum (OAM) multiplexing controversy: OAM as a subset of MIMO[C]. 2015 9th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Lisbon, Portugal, 2015: 1–5. [62] OLDONI M, SPINELLO F, MARI E, et al. Space-division demultiplexing in orbital-angular-momentum-based MIMO radio systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(10): 4582–4587. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2456953 [63] ZHU Qibiao, JIANG Tao, QU Daiming, et al. Radio vortex–multiple-input multiple-output communication systems with high capacity[J]. IEEE Access, 2015, 3: 2456–2464. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2015.2503293 [64] ZHAO Linjun, ZHANG Hailin, and CHENG Wenchi. Fractal uniform circular arrays based multi-orbital-angular-momentum-mode multiplexing vortex radio MIMO[J]. China Communications, 2018, 15(9): 118–135. doi: 10.1109/CC.2018.8456457 [65] LEE D, SASAKI H, FUKUMOTO H, et al. An evaluation of orbital angular momentum multiplexing technology[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(9): 1729. doi: 10.3390/app9091729 [66] MCGLOIN D, SIMPSON N B, and PADGETT M J. Transfer of orbital angular momentum from a stressed fiber-optic waveguide to a light beam[J]. Applied Optics, 1998, 37(3): 469–472. doi: 10.1364/AO.37.000469 [67] GIBSON G, COURTIAL J, PADGETT M J, et al. Free-space information transfer using light beams carrying orbital angular momentum[J]. Optics Express, 2004, 12(22): 5448–5456. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.12.005448 [68] LIN Jiawei, YUAN X C, TAO Shaohua, et al. Multiplexing free-space optical signals using superimposed collinear orbital angular momentum states[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(21): 4680–4685. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.004680 [69] YAN Yan, XIE Guodong, LAVERY M P J, et al. High-capacity millimetre-wave communications with orbital angular momentum multiplexing[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 4876. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5876 [70] REN Yongxiong, WANG Zhe, LIAO Peicheng, et al. Experimental characterization of a 400 Gbit/s orbital angular momentum multiplexed free-space optical link over 120 m[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(3): 622–625. doi: 10.1364/ol.41.000622 [71] BAGHDADY J, MILLER K, MORGAN K, et al. Multi-gigabit/s underwater optical communication link using orbital angular momentum multiplexing[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(9): 9794–9805. doi: 10.1364/oe.24.009794 [72] YAN Yan, XIE Guodong, HUANG Hao, et al. Demonstration of 8-mode 32-Gbit/s millimeter-wave free-space communication link using 4 orbital-angular-momentum modes on 2 polarizations[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Sydney, Australia, 2014: 4850–4855. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2014.6884088. [73] YAN Yan, LI Long, ZHAO Zhe, et al. 32-Gbit/s 60-GHz millimeter-wave wireless communication using orbital angular momentum and polarization multiplexing[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2016.7511277. [74] NYQUIST H. Certain factors affecting telegraph speed[J]. Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers, 1924, 43(2): 412–422. doi: 10.1109/T-AIEE.1924.5060996 [75] HUI Xiaonan, ZHENG Shilie, CHEN Yiling, et al. Multiplexed millimeter wave communication with dual orbital angular momentum (OAM) mode antennas[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 10148. doi: 10.1038/srep10148 [76] LEI X Y and CHENG Y J. Ka-band orbital angular momentum folded reflectarray antenna[C]. 2015 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Nanjing, China, 2015: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/APMC.2015.7413306. [77] ÉMILE O, BROUSSEAU C, ÉMILE J, et al. Energy and angular momentum transfers from an electromagnetic wave to a copper ring in the UHF band[J]. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2017, 18(2): 137–143. doi: 10.1016/j.crhy.2016.12.003 [78] BASAR E. Orbital angular momentum with index modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(3): 2029–2037. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2787992 -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
