Fair Energy Efficiency Scheduling in NOMA-Based Mobile Edge Computing
-
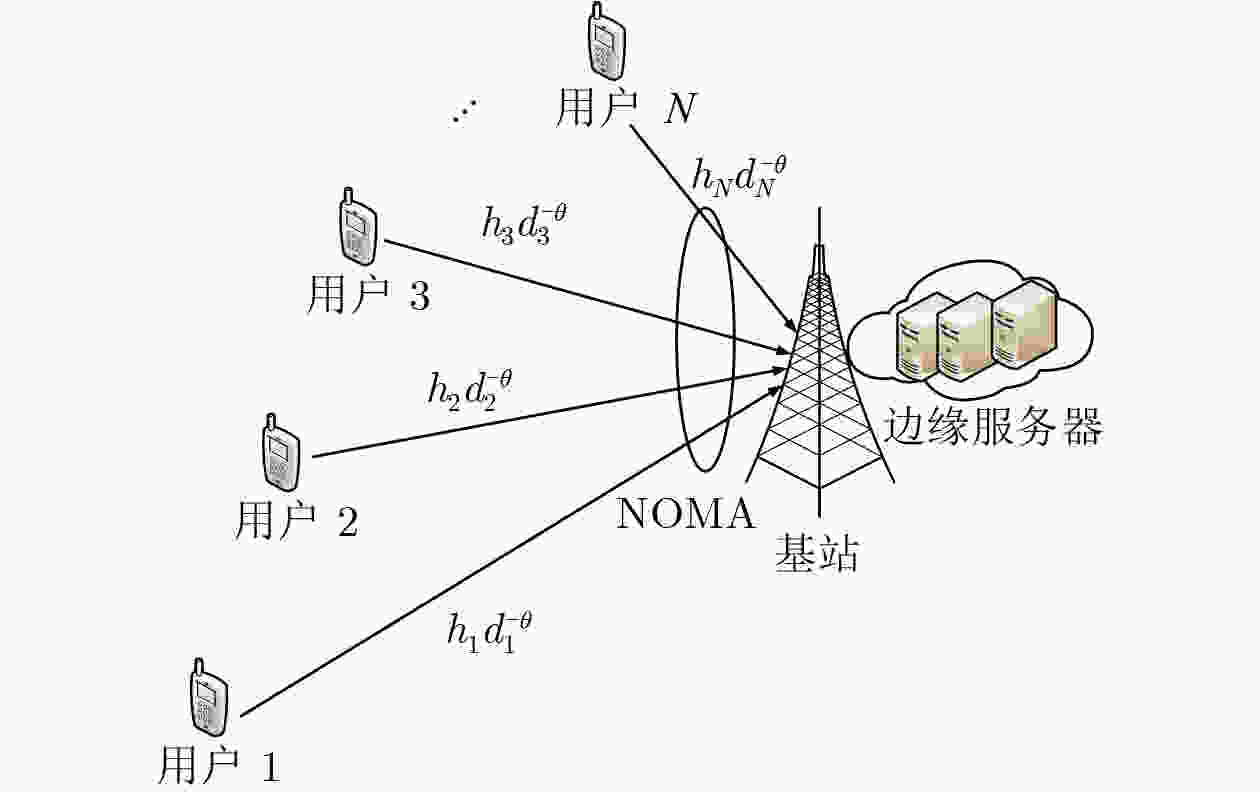
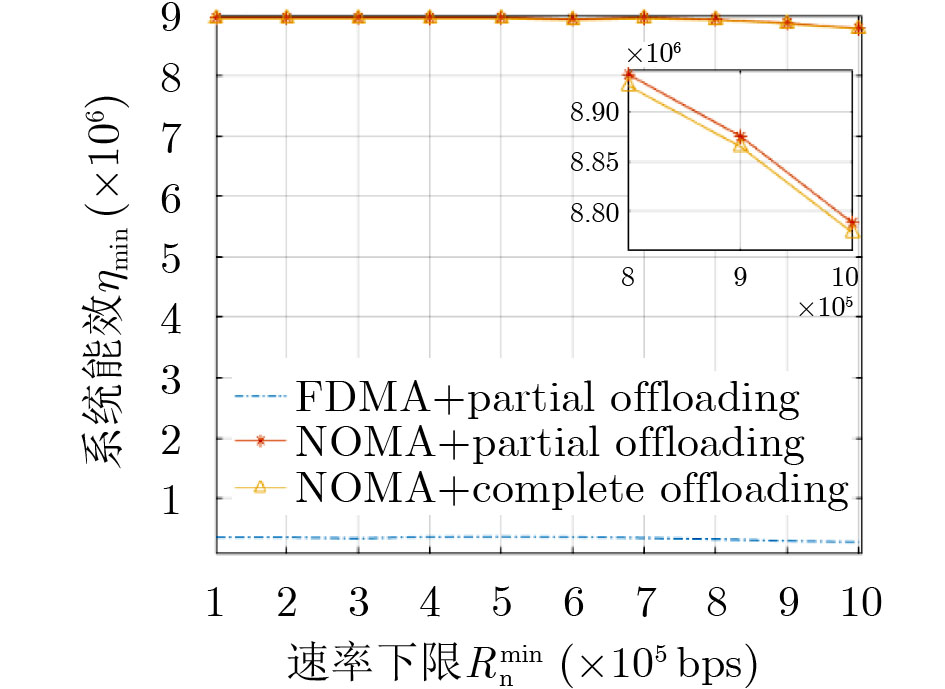
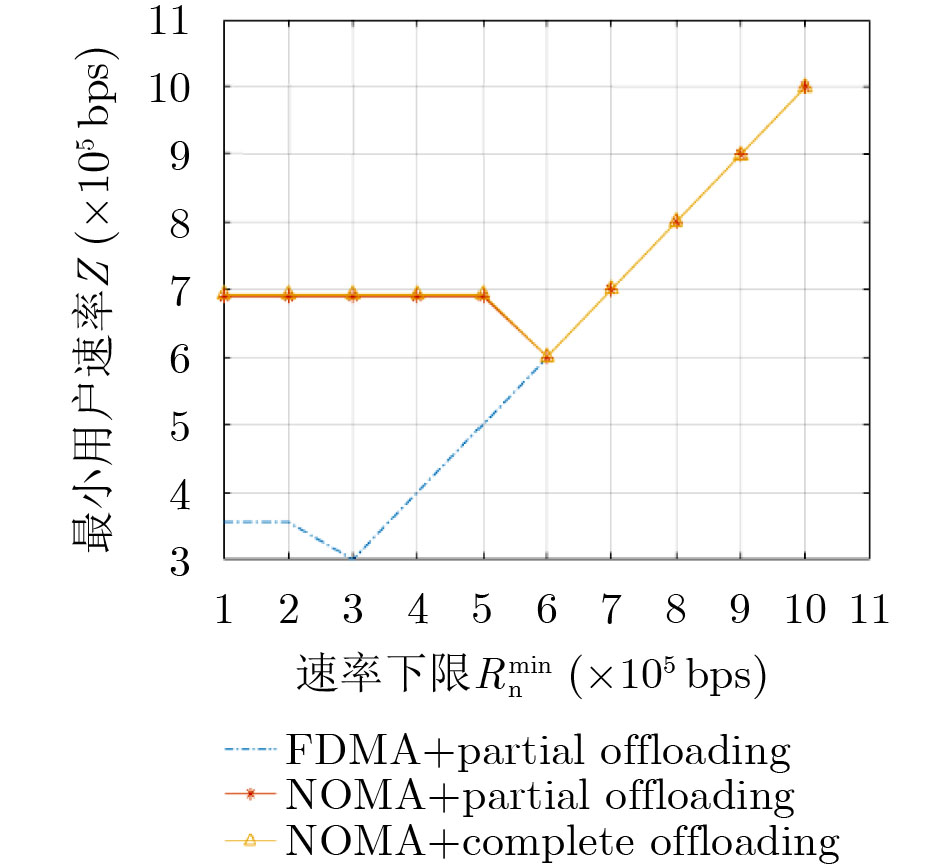
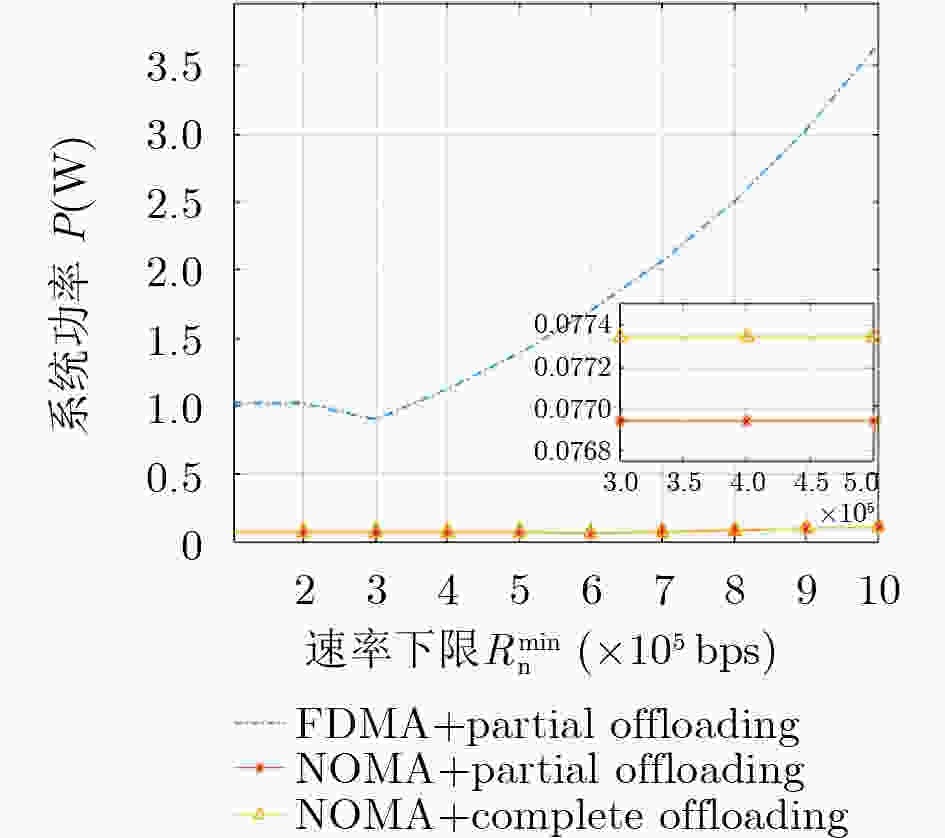
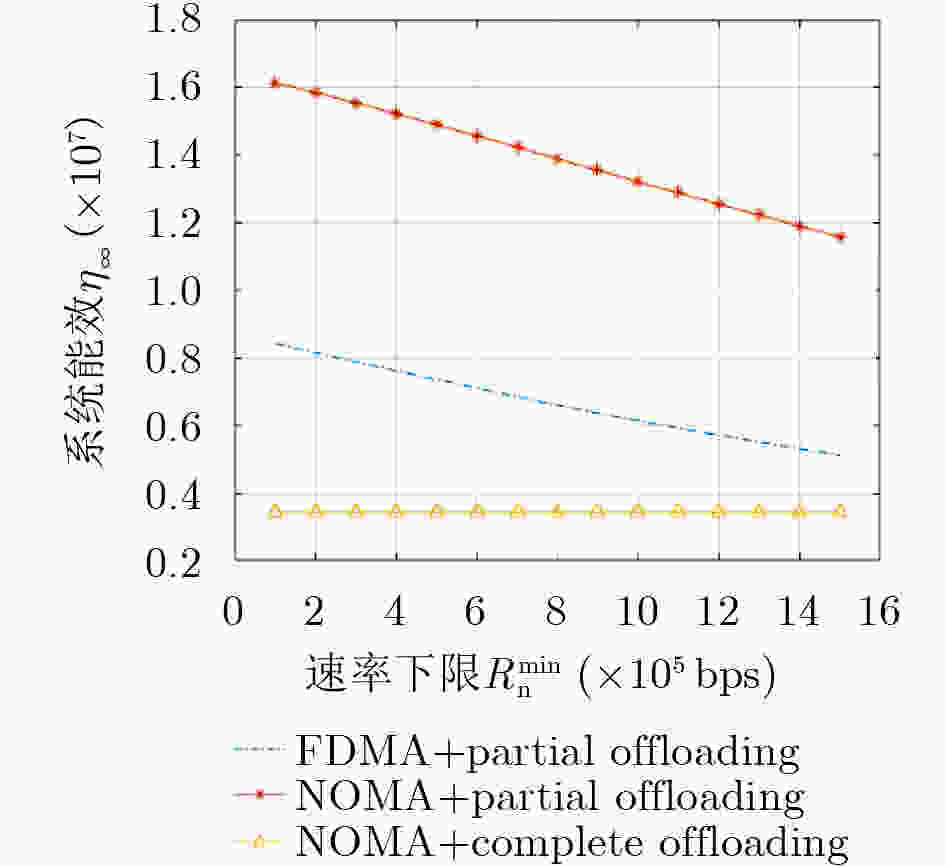
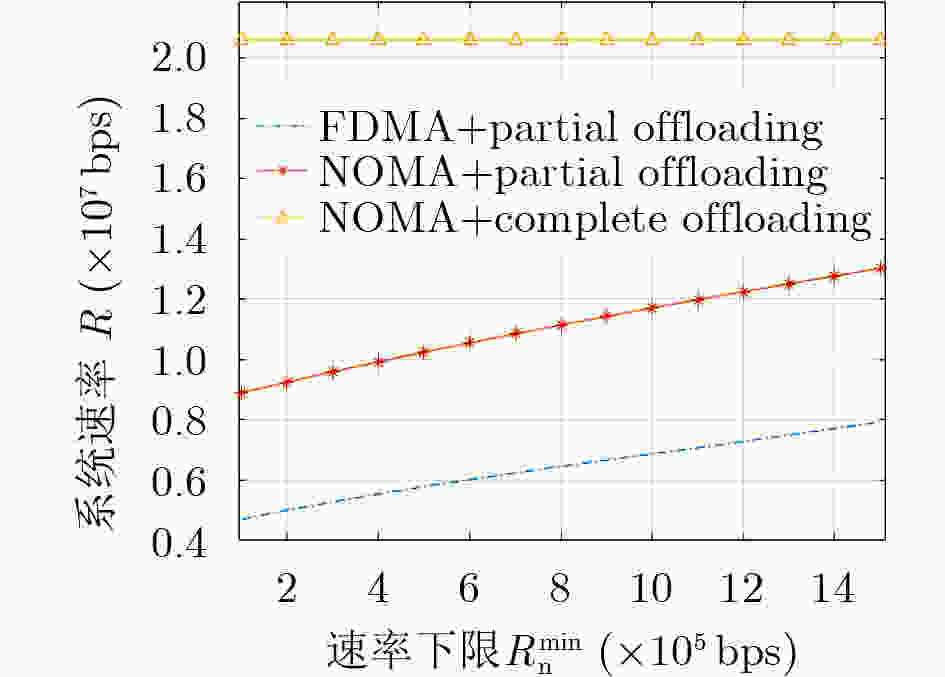
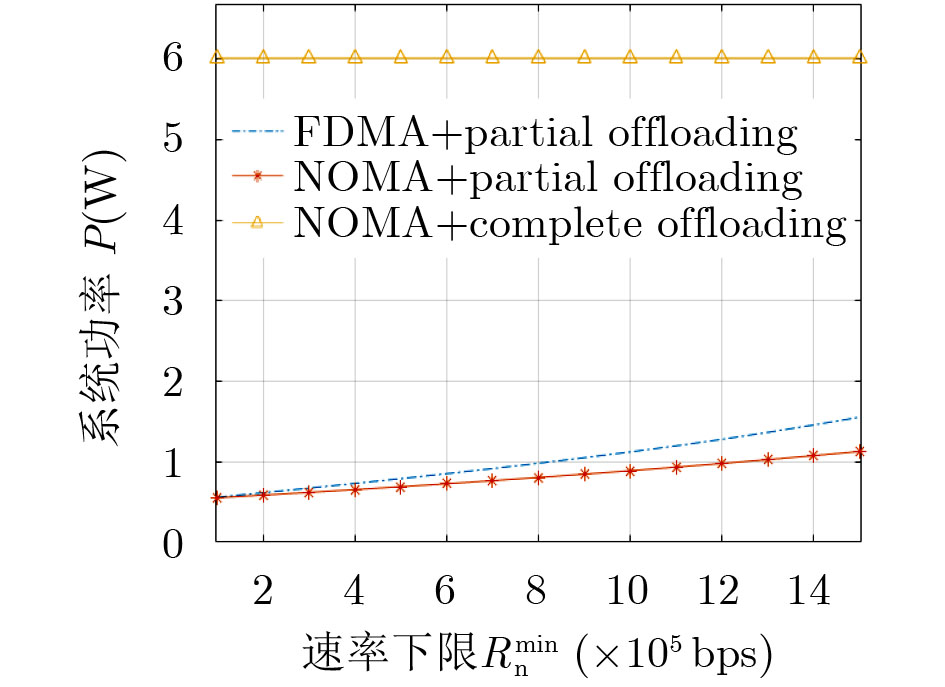
摘要: 将移动边缘计算技术(MEC)与非正交多址技术(NOMA)结合,同时考虑公平性,该文研究了采用NOMA上行部分卸载的MEC系统公平能效问题。首先将基于公平函数的用户速率与功耗比值定义为公平能效函数,随后提出了两种公平能效调度准则下的能效调度算法,即最大化最小速率准则下DK-SCA算法及最大化系统能效准则下DK-SCALE算法,通过算法实现分别得到两种公平能效调度准则下用户最佳本地CPU处理频率及最佳传输功率。最后通过仿真表明,与基准方案相比,所提基于NOMA的部分卸载方案能够有效地将本地计算和基于NOMA的边缘卸载结合,达到最佳的公平能效性能。Abstract: Combing Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) and Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) technologies while considering fairness, this paper studies the fair energy efficiency of the MEC system using NOMA partial offloading. First, the ratio of user rate to power consumption based on the fair function is defined as the fair energy efficiency function. Then, two energy efficiency scheduling algorithms under the fair energy efficiency scheduling criteria are proposed, namely the DK-SCA algorithm under the maximum-minimum rate criterion and the DK-SCALE algorithm under the maximum system energy efficiency criterion. The optimal CPU-frequency cycle and optimal transmit power under these two fair energy efficiency scheduling criteria are obtained, respectively. Finally, simulations show that compared with the benchmark schemes, the proposed NOMA -based partial offloading scheme can effectively combine local computing with edge offloading based on NOMA, which can achieve the best fair energy efficiency performance.
-
Key words:
- Edge computing /
- Computing offloading /
- Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) /
- Energy efficiency /
- Fair
-
表 1 DK-SCA迭代算法
步骤1:初始化本地计算速度$ f_n^{(0)} $和$ x_n^{{\text{u}}(0)} $,$ {Z^0} $,$ \eta _\infty ^0{\text{ = }}0 $,设置
停止阈值e,迭代次数I;步骤2: for i=1: I; 利用SCA迭代求解${{\text{P}}_{1.4}}$,得到结果
$ \left\{ {f_n^i,x_n^{{\text{u}},i},\eta _\infty ^i{\text{,z}}_n^{u,i}{\text{(k)}}} \right\} $,更新能效暂态值$\eta _\infty ^i{\text{ = } }\dfrac{ { {Z^i} } }{ {\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{n \in N} {\left( {\zeta {\text{exp} }\left( { {{x} }_n^{u,i} } \right) + {P_r} + \varepsilon f_n^{i3} } \right)} } }\qquad\qquad (19)$ 步骤3:if$||\eta _\infty ^i - \eta _\infty ^{ {\text{i - 1} } }|| \le e$ 获得最佳能效$ \eta _\infty ^*{\text{ = }}\eta _\infty ^i\; $; break; 步骤4:输出最佳能效$ \eta _\infty ^{\text{*}} $。 表 2 DK-SCALE迭代算法
步骤1:取$\zeta > 0,{R}_{n}^{\mathrm{min} } > 0,{P}_{n}^{\text{th} }> 0,{\eta }_{0}^{i}$;初始化${{\text{P}}_{2.3}}$,
$ Z(0) $,$ {f_n}(0) $,$ p_n^{\text{u}}(0) $,$ {a_n}(0) $,$ {b_n}(0) $迭代次数I;步骤2:for i =1: I 利用SCALE方法交替迭代求解${{\text{P}}_{2.3}}$,得到近似能效: $\eta _0^i = \frac{{\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{n \in N} {\left( {W{Z_n}(x_n^u,{a_n},{b_n}) + \frac{{{f_n}}}{{{\gamma _n}}}} \right)} }}{{\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{n \in N} {\left( {\zeta \exp \left( {x_n^u} \right) + {p_r} + \varepsilon f_n^3} \right)} }} \qquad (29)$ 步骤3:if$||\eta _0^i - \eta _0^{i - 1}|| \le e$ 获得最佳能效$ \eta _0^*{\text{ = }}\eta _0^i\; $; break; 步骤4:输出$( {}{f}_{n}^{*},{p}_{n}^{\text{u}*}\text{} )$和最佳能效$ \eta _0^{\text{*}} $。 -
[1] BARBERA M V, KOSTA S, MEI A, et al. To offload or not to offload? The bandwidth and energy costs of mobile cloud computing[C]. Proceedings - IEEE INFOCOM, Turin, Italy, 2013: 1285–1293. doi: 10.1109/INFCOM.2013.6566921. [2] TAN L T, HU R Q, and HANZO L. Twin-timescale artificial intelligence aided mobility-aware edge caching and computing in vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3086–3099. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2893898 [3] TAN L T and HU R Q. Mobility-aware edge caching and computing in vehicle networks: A deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(11): 10190–10203. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2867191 [4] HU Han, SONG Weiwei, WANG Qun, et al. Mobility-aware offloading and resource allocation in MEC-enabled IoT networks[C]. Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Mobility, Sensing and Networking (MSN), Tokyo, Japan, 2020: 554–560. doi: 10.1109/MSN50589.2020.00092. [5] ZHANG Yuan, DU Peng, WANG Jiang, et al. Resource scheduling for delay minimization in multi-server cellular edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7(99): 86265–86273. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2924032 [6] CHEN Ying, ZHANG Ning, ZHANG Yongchao, et al. Energy efficient dynamic offloading in mobile edge computing for internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2021, 9(3): 1050–1060. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2019.2898657 [7] TRAN T X and POMPILI D. Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-server mobile-edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 856–868. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2881191 [8] SUN Haijian, ZHOU Fuhui, and HU R Q. Joint offloading and computation energy efficiency maximization in a mobile edge computing system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 8,68(3): 3052–3056. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2893094 [9] YANG Zhaohui, PAN Cunhua, HOU Jiancao, et al. Efficient resource allocation for mobile-edge computing networks with NOMA: Completion time and energy minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(11): 7771–7784. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2935717 [10] ZENG Ming, NGUYEN N P, DOBRE O A, et al. Delay minimization for NOMA-assisted MEC under power and energy constraints[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(6): 1657–1661. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2934453 [11] PAN Yijin, CHEN Ming, YANG Zhaohui, et al. Energy-efficient NOMA-based mobile edge computing offloading[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(2): 310–313. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2882846 [12] PHAM Q V and HWANG W J. Fairness-aware spectral and energy efficiency in spectrum-sharing wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(11): 10207–10219. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2717926 [13] MO J and WALRAND J. Fair end-to-end window-based congestion control[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2000, 8(5): 556–567. doi: 10.1109/90.879343 [14] GUO Chongtao, ZHANG Yan, SHENG Min, et al. Alphaα-fair power allocation in spectrum-sharing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(5): 3771–3777. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2436068 [15] SCHWARZ S, MEHLFUHRER C, and RUPP M. Throughput maximizing multiuser scheduling with adjustable fairness[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kyoto, Japan, 2011: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/icc.2011.5963489. [16] YU Ye, BU Xiangyuan, YANG Kai, et al. Green large-scale fog computing resource allocation using joint benders decomposition, dinkelbach Algorithm, ADMM, and branch-and-bound[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(3): 4106–4117. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875587 [17] WEI Zhiqiang, ZHAO Lou, GUO Jiajia, et al. Multi-beam NOMA for hybrid mmWave systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(2): 1705–1719. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2879930 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
