Dynamic Gesture Recognition Method Based on Millimeter-wave Radar by One-Dimensional Series Neural Network
-
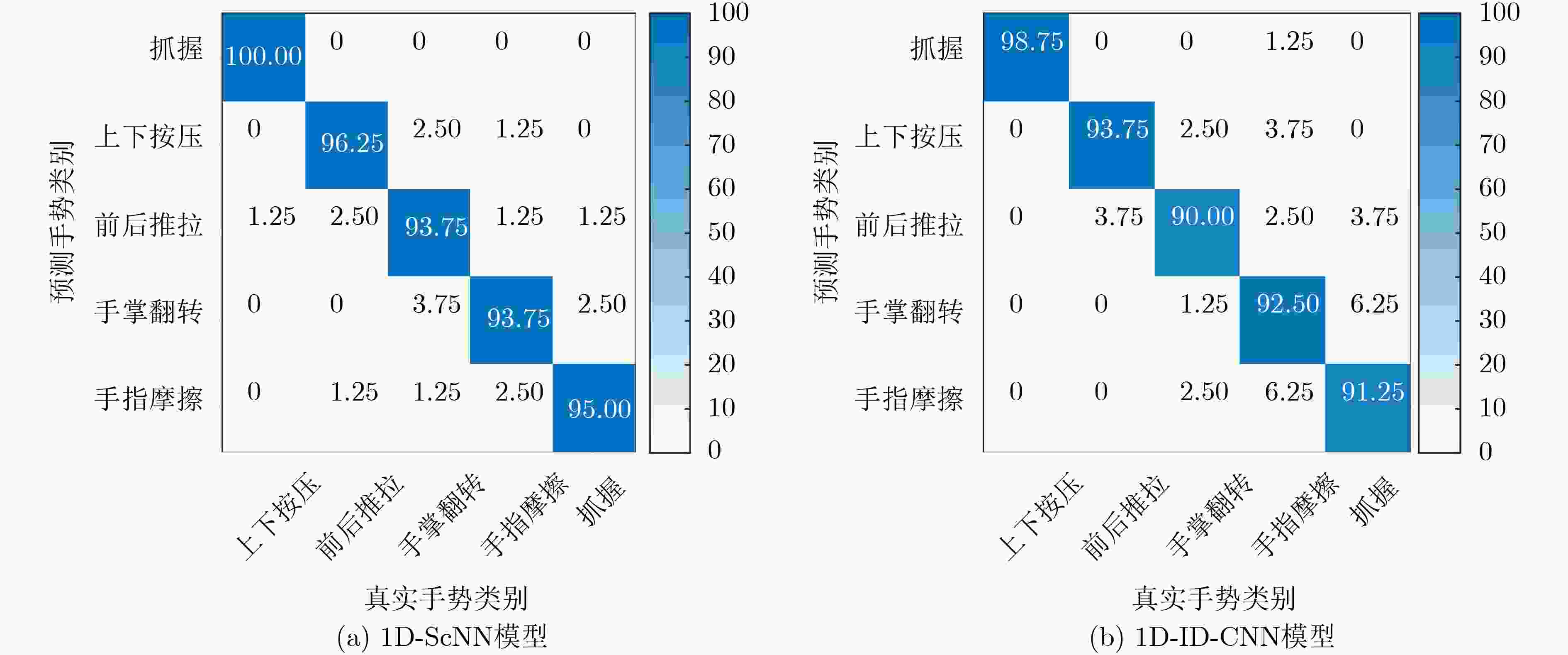
摘要: 现有的基于雷达传感器的手势识别方法,大多先利用雷达回波对手势的距离、多普勒和角度等信息进行参数估计,得到各种数据谱图,然后再利用卷积神经网络对这些谱图进行分类,实现过程较为复杂。该文提出一种基于串联式1维神经网络(1D-ScNN)的毫米波雷达动态手势识别方法。首先基于毫米波雷达获取动态手势的原始回波,然后利用1维卷积和池化操作对手势特征进行提取,并将这些特征信息输入1维Inception v3结构。最后在网络的末端接入长短期记忆(LSTM)网络来聚合1维特征,充分利用动态手势的帧间相关性,提高识别准确率和训练收敛速度。实验结果表明,该方法实现过程简单,收敛速度快,识别准确率可以达到96.0%以上,高于现有基于数据谱图的手势分类方法。Abstract: For the most of the existing gesture recognition methods based on the radar sensor, the parameters such as the distance, Doppler, and angle are estimated using the radar echo at first. And then the obtained data spectra are inputted into the convolutional neural networks to classify the gestures. The implementation process is complicated. A dynamic gesture recognition method is proposed based on the millimeter-wave radar using the One-Dimensional Series connection Neural Networks (1D-ScNN) in this paper. Firstly, the original echo of dynamic gesture is obtained by the millimeter-wave radar. The gesture features are extracted by the one-dimensional convolution and pooling operations, and then are inputted into the one-dimensional inception v3 structure. In order to aggregate the one-dimensional features, the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) modular is connected to the end of the network. The inter-frame correlation of dynamic gestures echo is fully utilized to improve the recognition accuracy and the convergence speed of training. The experimental results show that the proposed method is simple in implementation and has a fast convergence speed. The classification accuracy can reach more than 96.0%, which is higher than the traditional gesture classification methods.
-
表 1 雷达传感器参数
参数 数量 发射天线数量(个) 3 接收天线数量(个) 4 采集帧数 (帧) 32 帧时间(ms) 40 Chirp数(个) 32 带宽(MHz) 1798.92 采样点数 64 采样率(MHz) 10 表 2 1维卷积参数配置
类型 卷积核+步长 参数量 输出尺寸 时间复杂度(FLOPs) Input – 0 (8, 262144, 2) – Conv1D-1 64*48+8 6208 (8, 32768, 64) 2.01×108 Conv1D-2 128*9+8 73856 (8, 4095, 128) 3.02×108 MaxPool1D 1*4+4 0 (8, 1024, 128) – 1D-Inception(a) 64*4+1 7248 (8, 1024, 192) 1.43×104 MaxPool1D 1*4+4 0 (8, 256, 192) – 1D-Inception(b) 64*6+1 10448 (8, 256, 256) 2.05×104 MaxPool1D 1*4+4 0 (8, 64, 256) – 1D-Inception(c) 64*7+1 13584 (8, 64, 320) 2.36×104 MaxPool1D 1*4+2 0 (8, 32, 320) – -
[1] LIEN J, GILLIAN N, KARAGOZLER M E, et al. Soli: Ubiquitous gesture sensing with millimeter wave radar[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2016, 35(4): 142: 1–142: 19. doi: 10.1145/2897824.2925953 [2] KIM Y and LING H. Human activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures using a support vector machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1328–1337. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2012849 [3] 王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的手势动作雷达识别方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(6): 1117–1123. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0397WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Hand gesture recognition method by radar based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(6): 1117–1123. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0397 [4] 王勇, 王沙沙, 田增山, 等. 基于FMCW雷达的双流融合神经网络手势识别方法[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(7): 1408–1415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.07.003WANG Yong, WANG Shasha, TIAN Zengshan, et al. Two-stream fusion neural network approach for hand gesture recognition based on FMCW radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(7): 1408–1415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.07.003 [5] 夏朝阳, 周成龙, 介钧誉, 等. 基于多通道调频连续波毫米波雷达的微动手势识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 164–172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190797XIA Zhaoyang, ZHOU Chenglong, JIE Junyu, et al. Micro-motion gesture recognition based on multi-channel frequency modulated continuous wave millimeter wave radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 164–172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190797 [6] ZHANG Zhenyuan, TIAN Zengshan, and ZHOU Mu. Latern: Dynamic continuous hand gesture recognition using FMCW radar sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(8): 3278–3289. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2808688 [7] 王勇, 吴金君, 田增山, 等. 基于FMCW雷达的多维参数手势识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 822–829. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180485WANG Yong, WU Jinjun, TIAN Zengshan, et al. Gesture recognition with multi-dimensional parameter using FMCW radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 822–829. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180485 [8] LI Gang, ZHANG Rui, RITCHIE M, et al. Sparsity-driven micro-doppler feature extraction for dynamic hand gesture recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(2): 655–665. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2761229 [9] RYU S J, SUH J S, BAEK S H, et al. Feature-based hand gesture recognition using an FMCW radar and its temporal feature analysis[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(18): 7593–7602. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2859815 [10] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.308. [11] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594. [12] DUMOULIN V and VISIN F. A guide to convolution arithmetic for deep learning[J]. arXiv: 1603.07285, 2018. [13] CHEN Haiquan and YE Wenbin. Classification of human activity based on radar signal using 1-D convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(7): 1178–1182. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2942097 [14] KONSTANTINIDIS E and COTRONIS Y. A quantitative roofline model for GPU kernel performance estimation using micro-benchmarks and hardware metric profiling[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2017, 107: 37–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2017.04.002 [15] TRAN D, BOURDEV L, FERGUS R, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4489–4497. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.510. [16] LIN J, GAN Chuang, and HAN Song. TSM: Temporal shift module for efficient video understanding[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 7082–7092. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00718. [17] HAZRA S and SANTRA A. Robust gesture recognition using millimetric-wave radar system[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2018, 2(4): 7001804. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2018.2882642 -





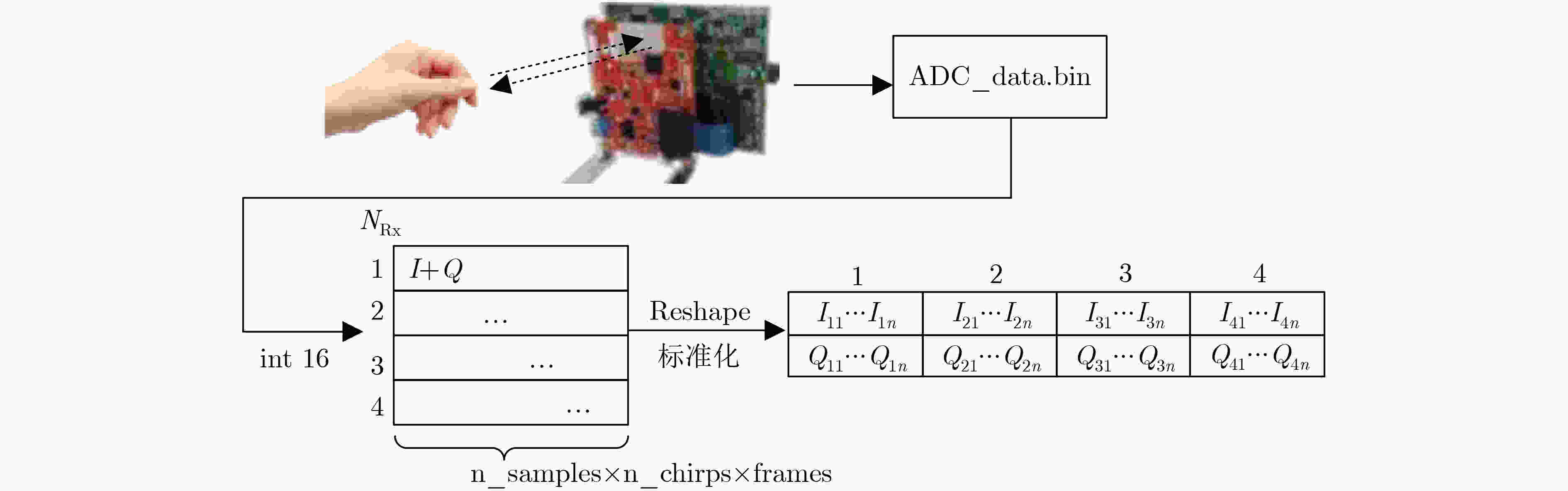
 下载:
下载:
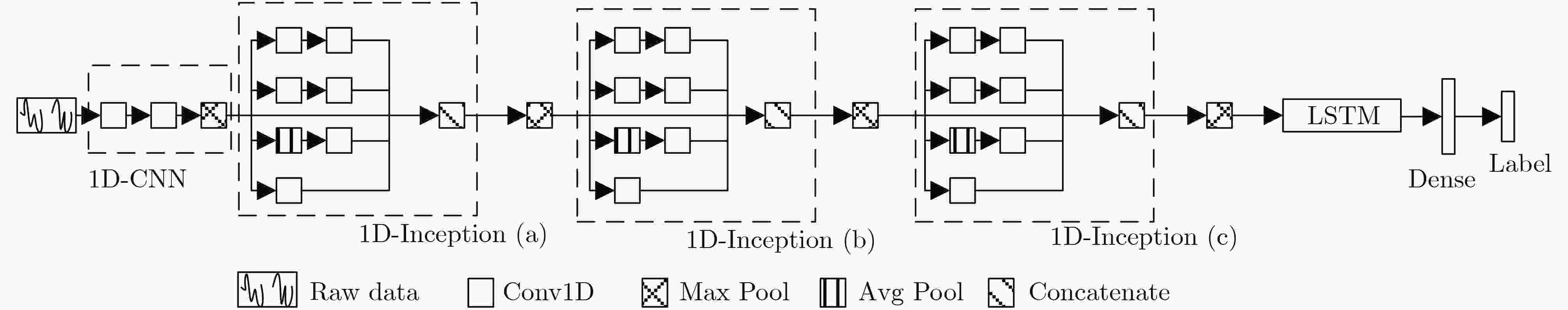
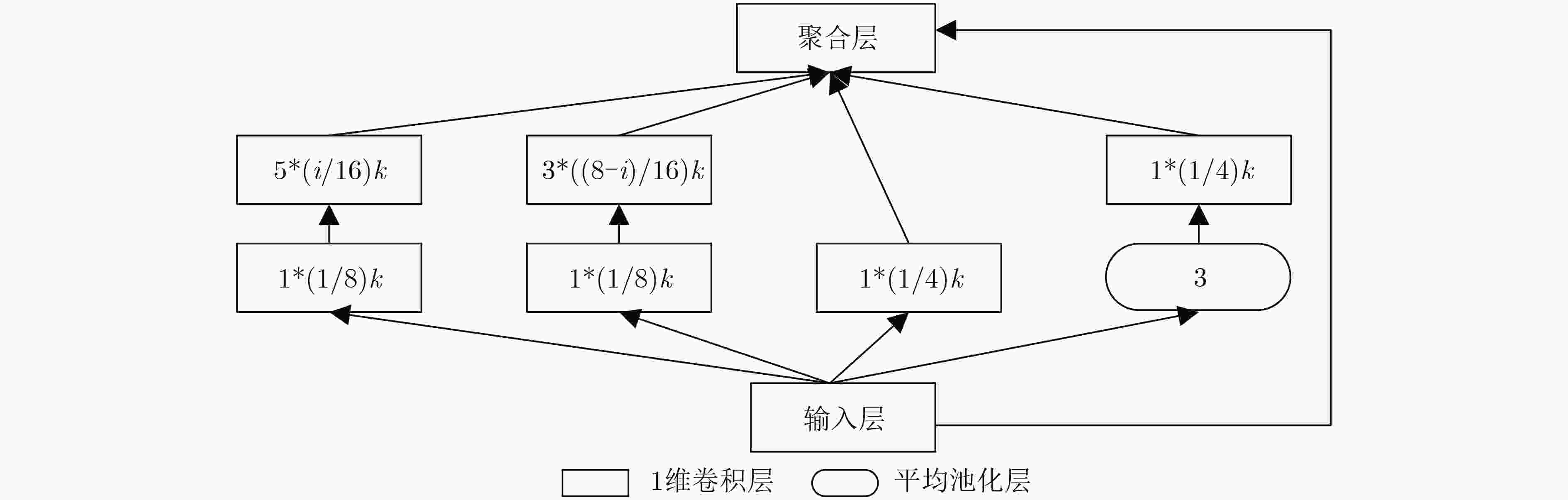
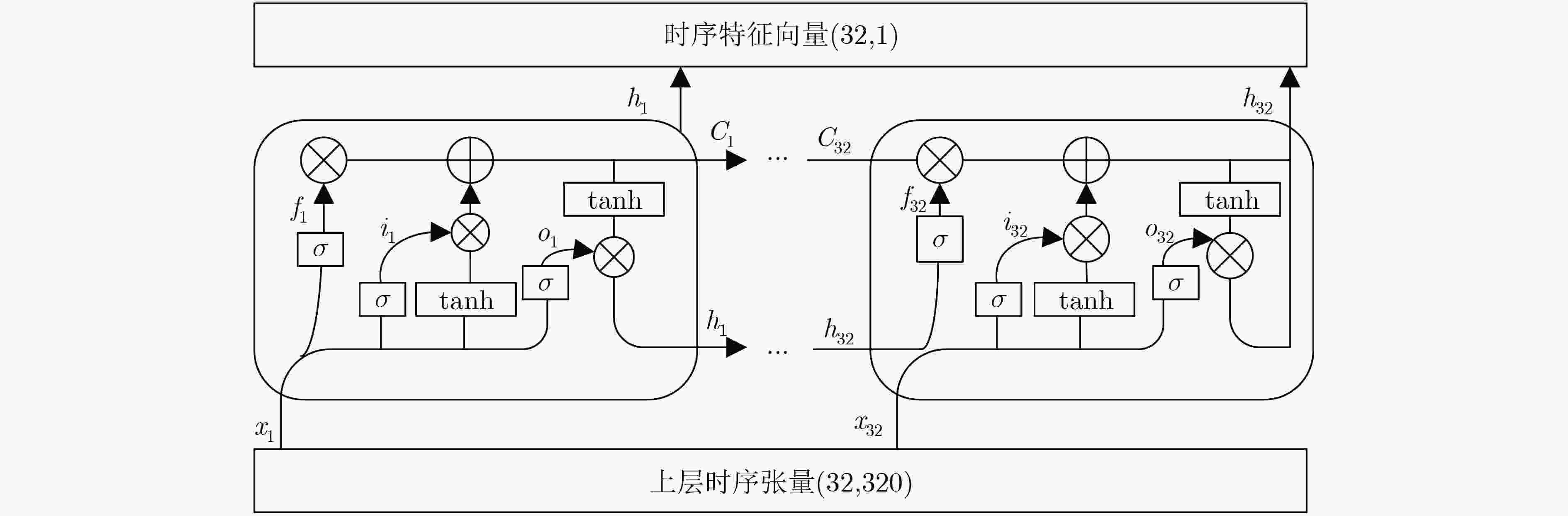
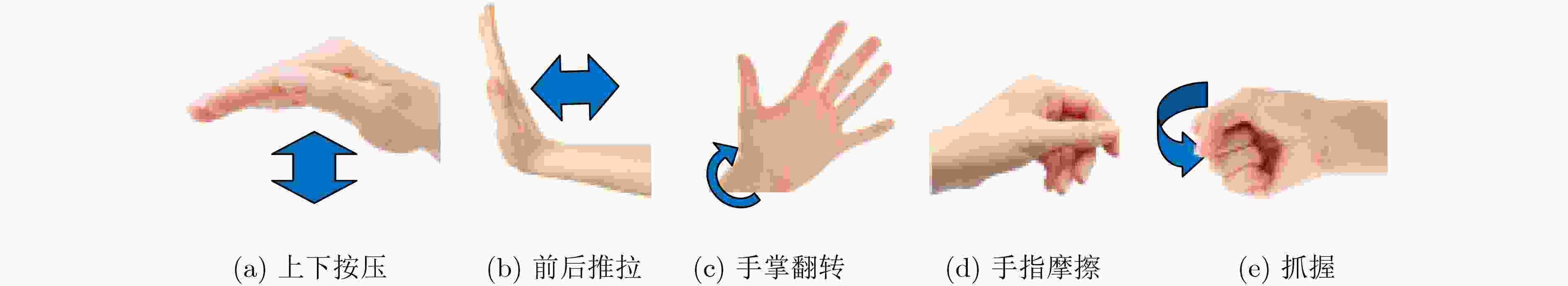
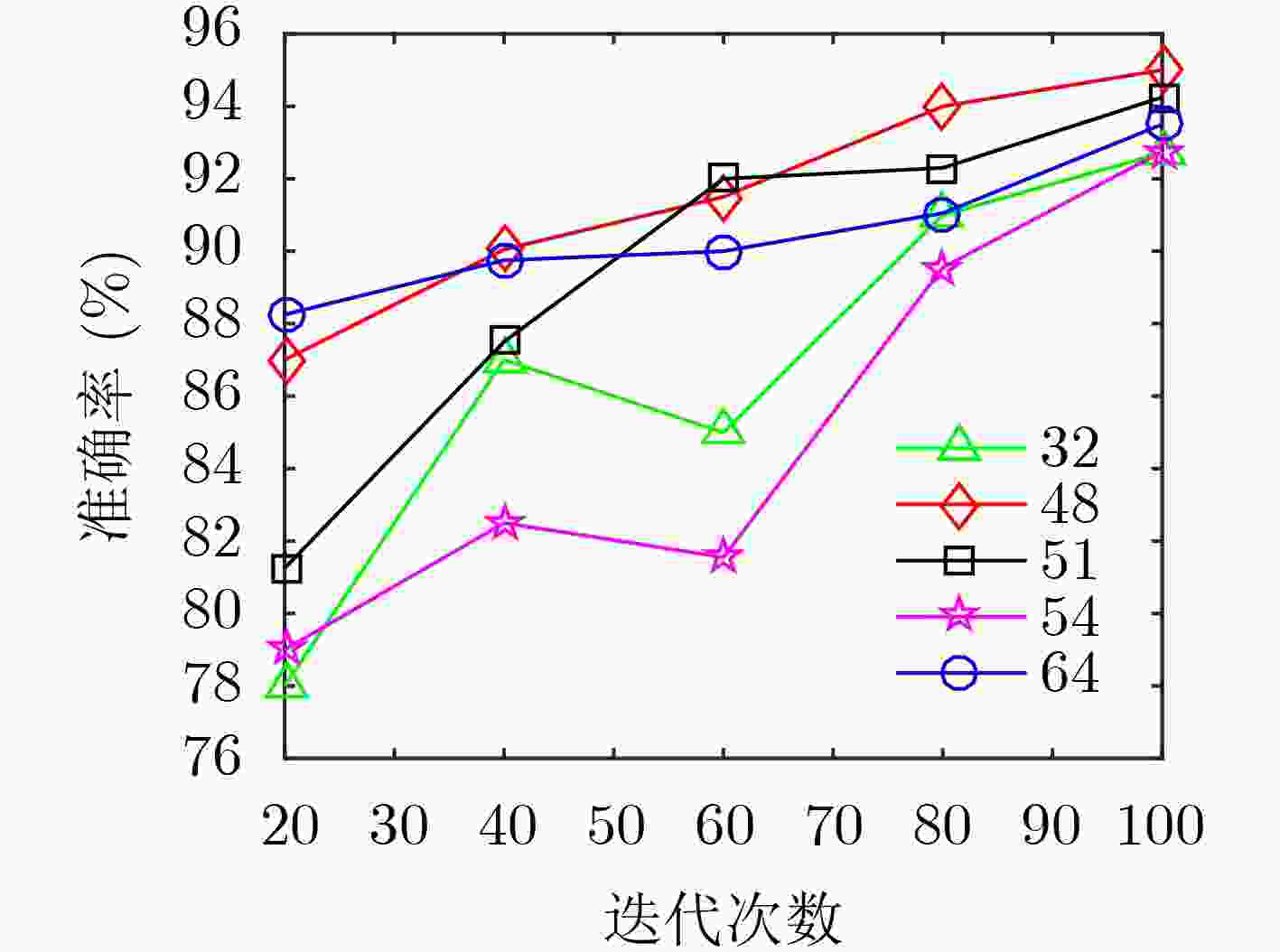
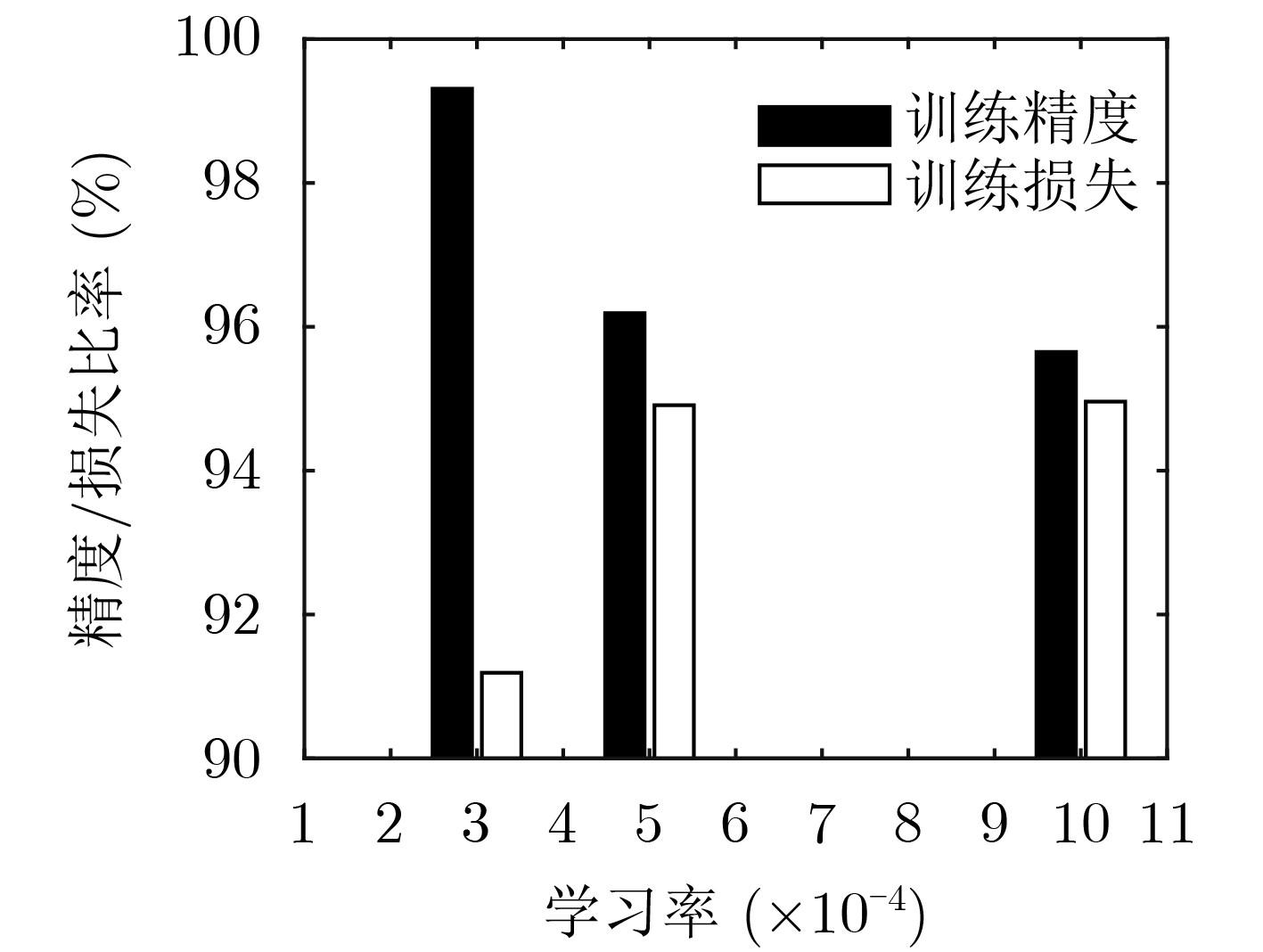
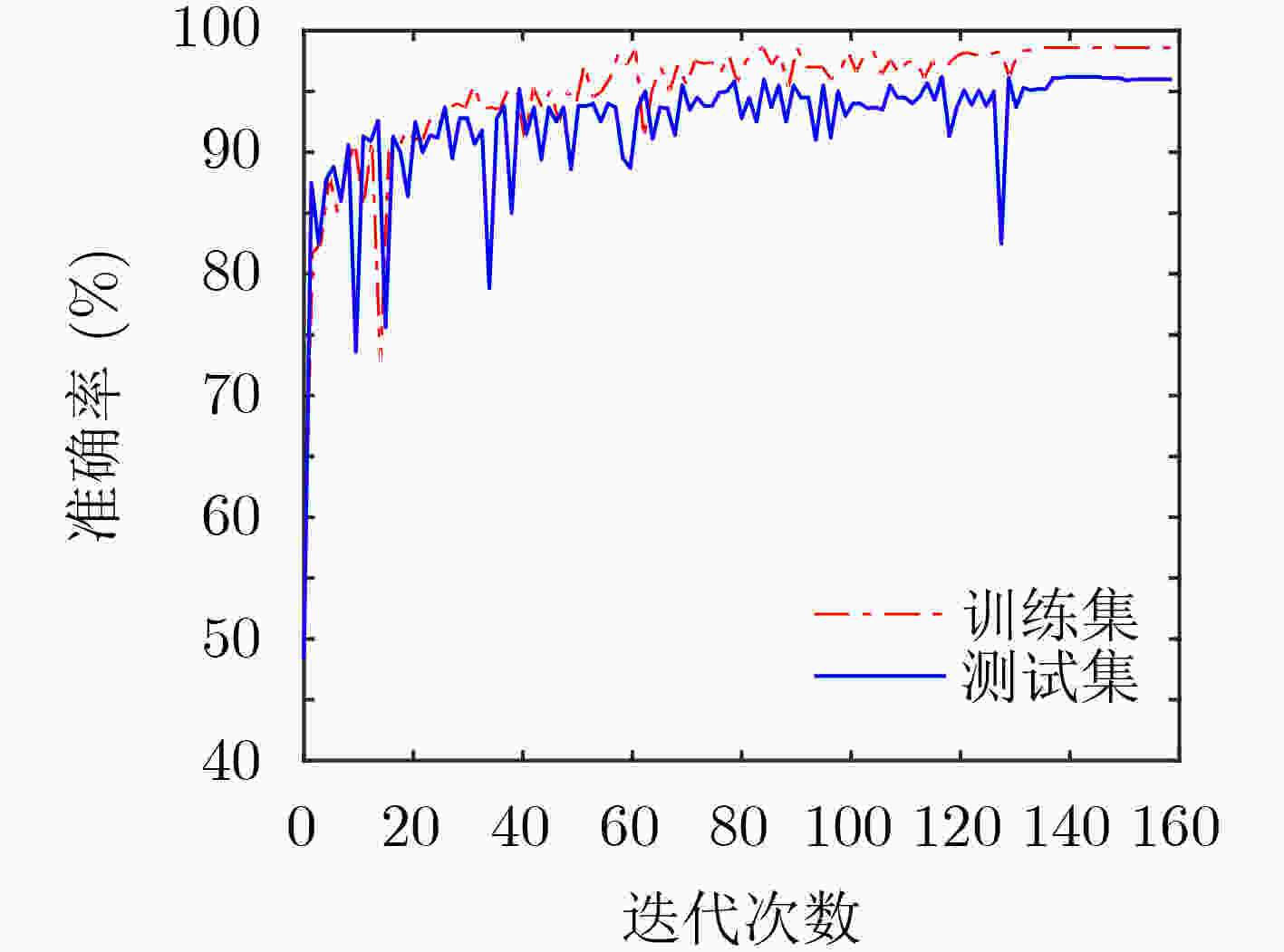


 下载:
下载:
