Security Consensus Algorithm of Medical Data Based on Credit Rating
-
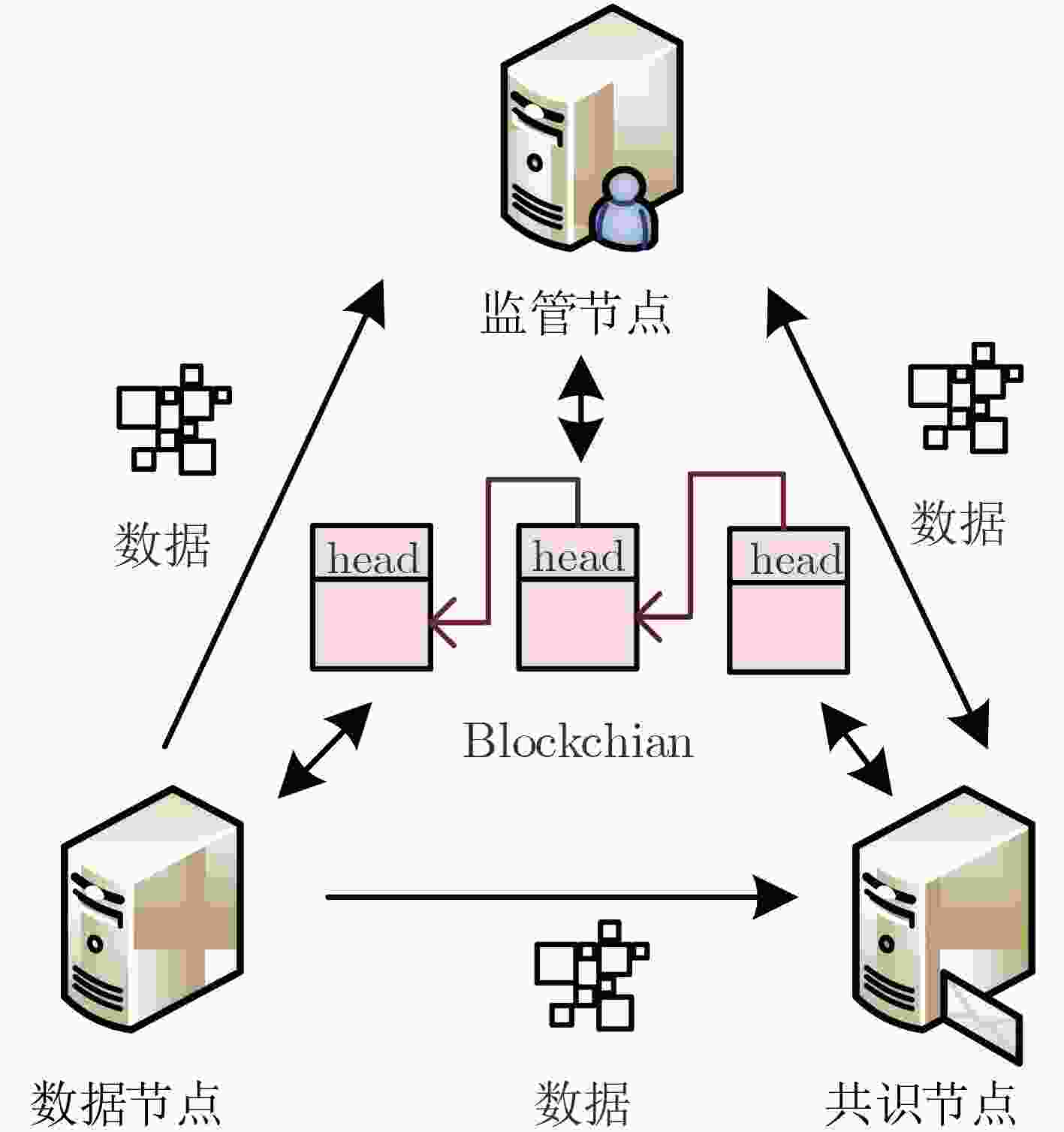
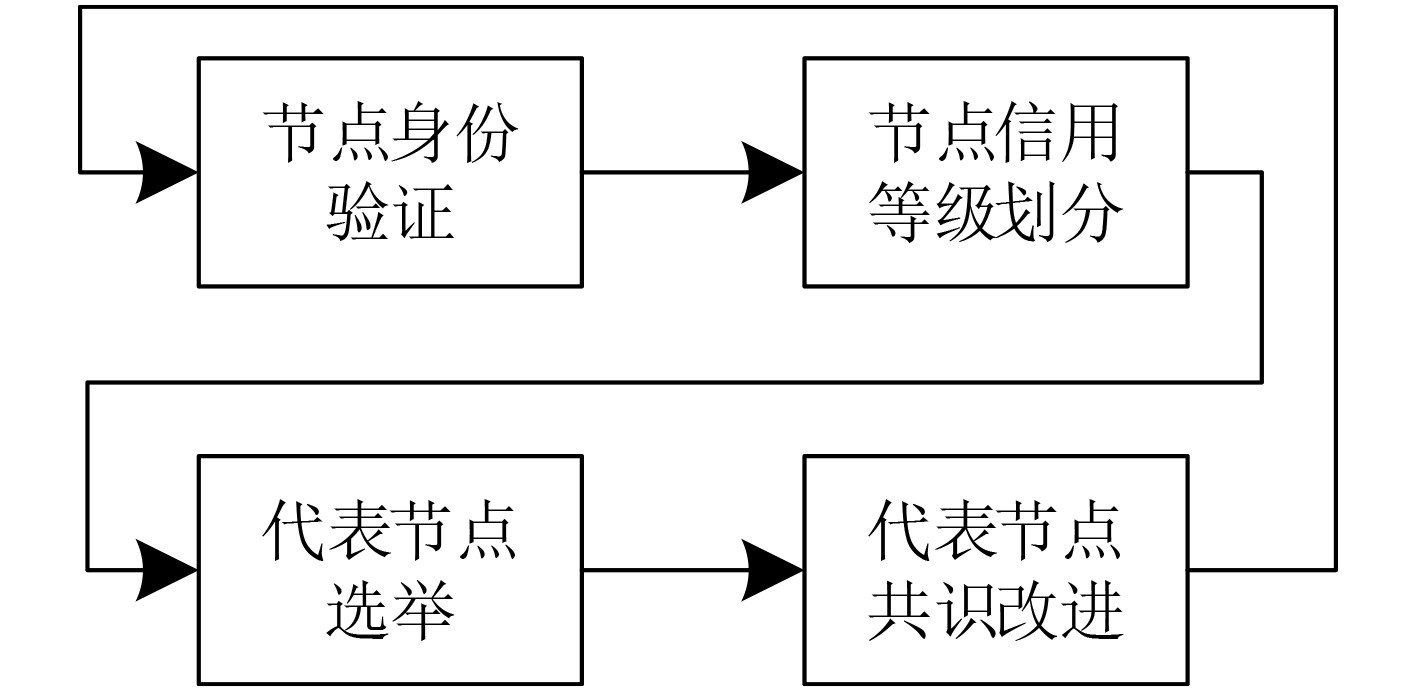
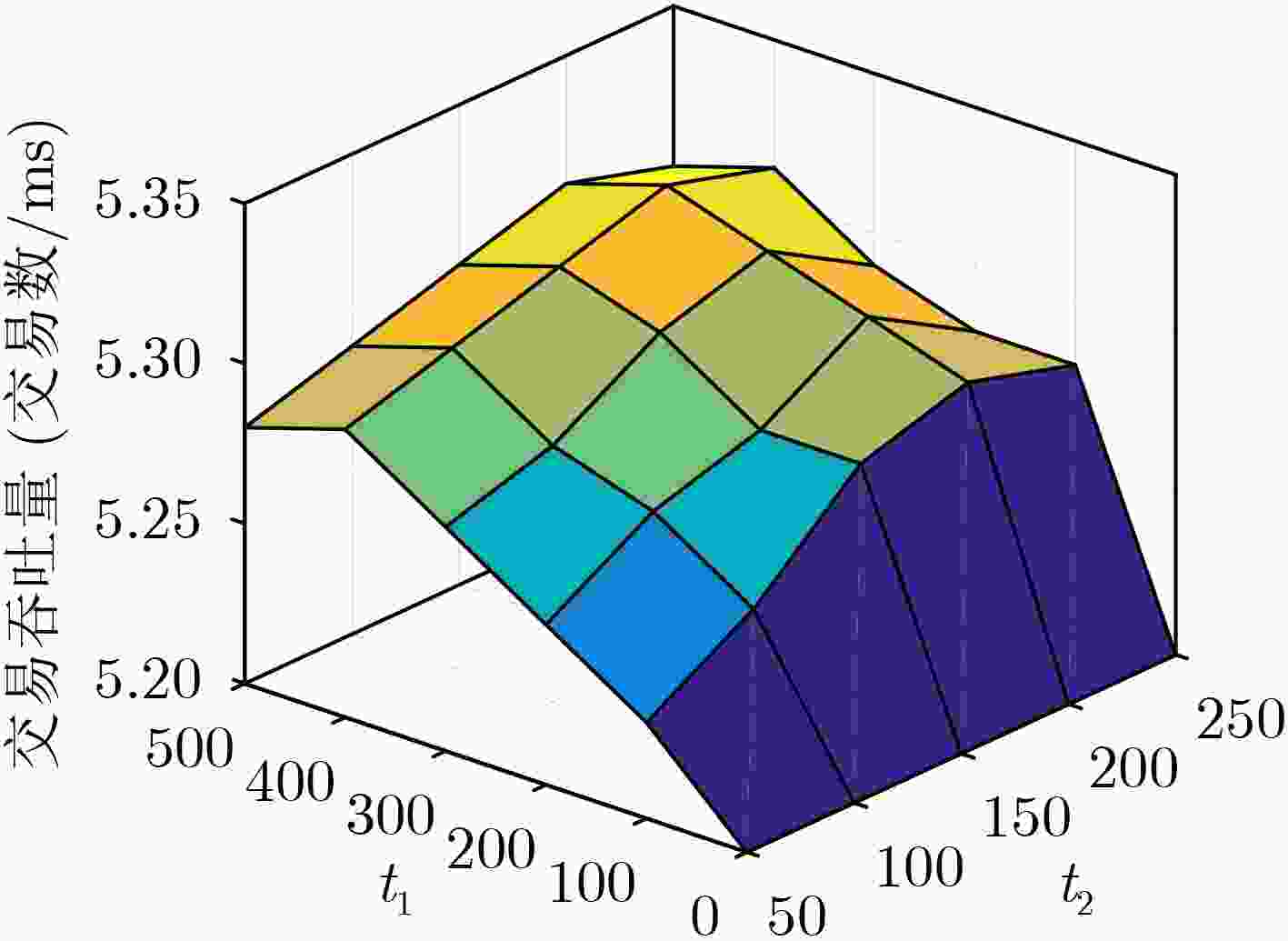
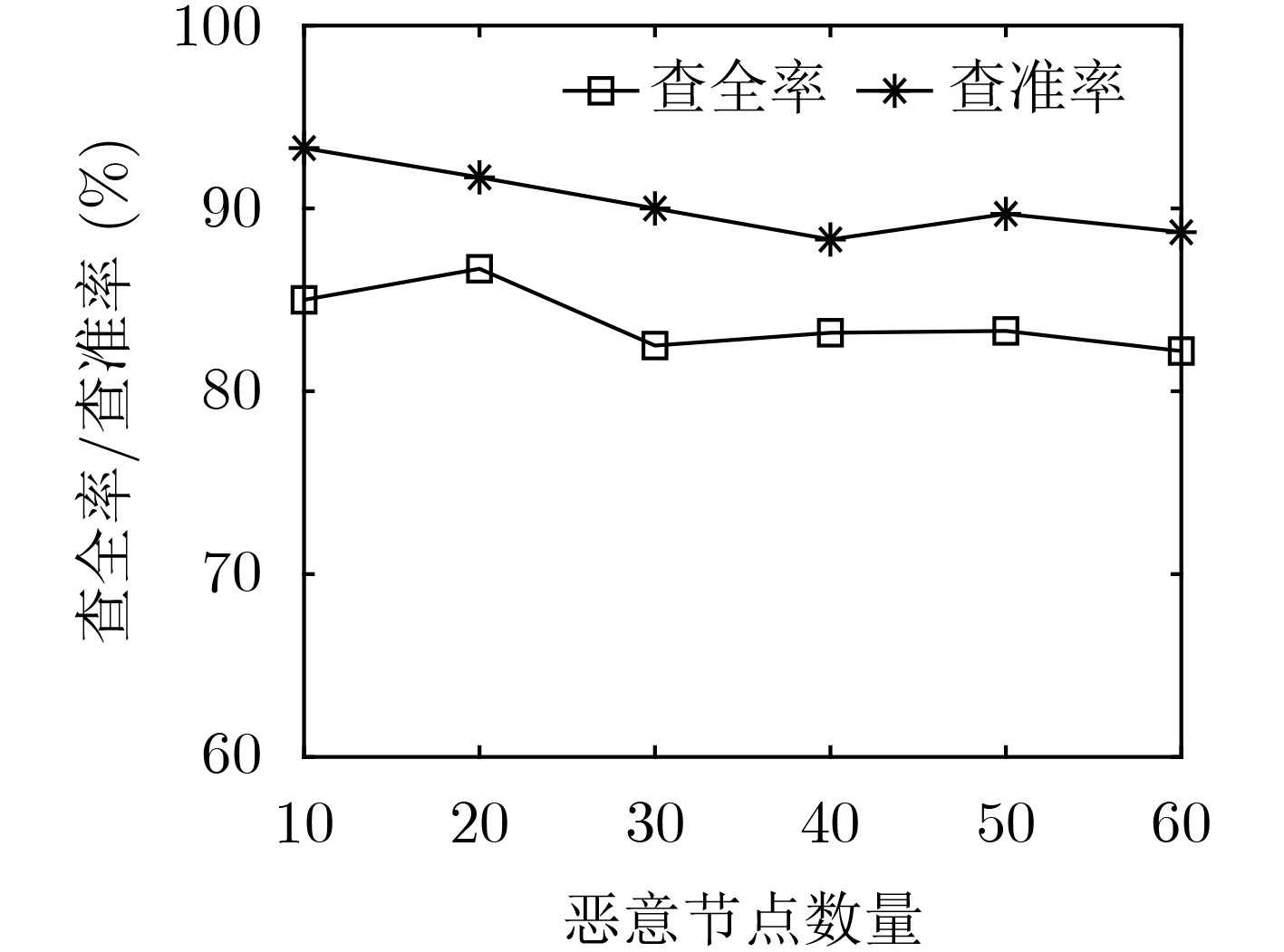
摘要: 在基于区块链的医疗数据共享系统中为防御恶意节点攻击并且提高共识效率,该文提出基于信用等级划分的医疗数据安全共识算法(SCA_MD)。首先,在SCA_MD中,考虑由数据节点、共识节点和监管节点组成的医疗区块共识模型,提出相应的节点身份验证机制,实现快速验证。其次,提出基于海洋掠食者的自我优化信用等级划分算法(SCRD),以限制恶意节点共识权力。最后改进代表节点选举机制和共识机制,提高共识的效率。实验结果表明:不管恶意节点数量如何变化,SCA_MD都能提高交易吞吐量,降低平均交易时延和平均节点通信开销。Abstract: In order to defend against malicious node attacks and improve consensus efficiency in the blockchain-based medical data sharing system, a Security Consensus Algorithm of Medical Data (SCA_MD) based on credit rating is proposed. In SCA_MD, the medical block consensus model which consists of data-based nodes, consensus nodes and supervisory nodes is considered. The corresponding node identity verification mechanism is proposed to achieve rapid verification. Then, a Self-optimizing Credit Rating Division (SCRD) algorithm based on marine predators is proposed to limit the consensus power of malicious nodes. Finally, the voting mechanism and consensus mechanism of representative nodes are proposed to improve the efficiency of consensus. The experimental results show that no matter how the number of malicious nodes changes, SCA_MD can increase transaction throughput, and reduce average transaction delay and average node communication overhead.
-
Key words:
- Bockchain /
- Medical data /
- Security consensus /
- Cedit grade
-
表 1 基于信用等级划分的医疗数据安全共识算法 (SCA_MD)
输入: 网络中节点的基本信息 输出: 网络对医疗数据的区块共识结果 (1) $\eta $=80; $\lambda $=80; $\mu $=20; $\gamma $=180; $\sigma $=180; $\theta $=350; ···; (2) 本节点将自身投票信息广播给其他节点; (3) 如果本节点收到全部节点的投票信息然后 (4) 本节点统计投票结果,选择${\rm{NAN}}$个代表节点,并广播其节
点信息;(5) end (6) while 1 (7) 如果本节点成为代表节点然后 (8) 本节点分别对$c$个节点执行节点身份验证机制; (9) 如果当前为第一次共识then (10) 本节点采用改进的PBFT共识算法完成区块共识; (11) 否则 (12) 本节点分别计算$\theta $个节点的累积信用值$y(t)$,并采集
其评估要素${y_l}$, ${\nu _l}$, ${\upsilon _l}$和${\chi _l}$;(13) 如果网络需要重新进行节点等级划分然后 (14) 本节点执行信用等级划分算法SCRD,并根据等级
结果给予每一个节点相应权力;(15) end (16) 如果网络需要重新进行代表节点选择然后 (17) 本节点根据公式(13)分别计算$b$个节点的得分,并
广播自身投票信息与候选节点信息;(18) end (19) 如果本节点收到全部节点的投票信息然后 (20) 本节点根据式(14)分别计算$e$个节点的投票结果,
选择${\rm{NAN}}$个代表节点,并广播;(21) end (22) 本节点采用改进一致性协议和视图切换协议完成区
块共识;(23) end (24) else (25) 本节点从网络中同步区块信息,并根据网络要求进行
投票;(26) end (27) end -
[1] ROEHRS A, DA COSTA C A, DA ROSA RIGHI R, et al. Toward a model for personal health record interoperability[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2019, 23(2): 867–873. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2836138 [2] STAN O P and MICLEA L. New Era for Technology in Healthcare Powered by GDPR and Blockchain[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2019: 311–317. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-6207-1_49. [3] XU Jie, XUE Kaiping, LI Shaohua, et al. Healthchain: A blockchain-based privacy preserving scheme for large-scale health data[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(5): 8770–8781. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2923525 [4] HYLOCK R H and ZENG Xiaoming. A blockchain framework for patient-centered health records and exchange (HealthChain): Evaluation and proof-of-concept study[J]. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 2019, 21(8): e13592. doi: 10.2196/13592 [5] 余荣威, 周博孝, 王丽娜, 等. 基于区块链的零知识位置证明方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2142–2149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191054YU Rongwei, ZHOU Boxiao, WANG Lina, et al. Zero-knowledge location proof based on blockchain[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2142–2149. doi: 10.11999/JEIT191054 [6] 李佩丽, 徐海霞. 区块链用户匿名与可追踪技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1061–1067. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190813LI Peili and XU Haixia. Blockchain user anonymity and traceability technology[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1061–1067. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190813 [7] AZARIA A, EKBLAW A, VIEIRA T, et al. MedRec: Using blockchain for medical data access and permission management[C]. 2016 2nd International Conference on Open and Big Data, Vienna, Austria, 2016: 25–30. doi: 10.1109/OBD.2016.11. [8] WANG Shuai, WANG Jing, WANG Xiao, et al. Blockchain-powered parallel healthcare systems based on the ACP approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2018, 5(4): 942–950. doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2018.2865526 [9] 张超, 李强, 陈子豪, 等. Medical Chain: 联盟式医疗区块链系统[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1495–1510. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180131ZHANG Chao, LI Qiang, CHEN Zihao, et al. Medical Chain: Alliance medical blockchain system[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1495–1510. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180131 [10] TOSH D, SHETTY S, FOYTIK P, et al. CloudPoS: A proof-of-stake consensus design for blockchain integrated cloud[C]. 2018 IEEE 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 302–309. doi: 10.1109/CLOUD.2018.00045. [11] MALAMAS V, DASAKLIS T, KOTZANIKOLAOU P, et al. A forensics-by-design management framework for medical devices based on blockchain[C]. 2019 IEEE World Congress on Services, Milan, Italy, 2019: 35–40. doi: 10.1109/SERVICES.2019.00021. [12] FAN Kai, WANG Shangyang, REN Yanhui, et al. MedBlock: Efficient and secure medical data sharing via blockchain[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2018, 42(8): 136. doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-0993-7 [13] HEO G, YANG Dana, DOH I, et al. Design of blockchain system for protection of personal information in digital content trading environment[C]. 2020 International Conference on Information Networking, Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 152–157. doi: 10.1109/ICOIN48656.2020.9016501. [14] TALUKDER A K, CHAITANYA M, ARNOLD D, et al. Proof of disease: A blockchain consensus protocol for accurate medical decisions and reducing the disease burden[C]. 2018 IEEE SmartWorld, Ubiquitous Intelligence & Computing, Advanced & Trusted Computing, Scalable Computing & Communications, Cloud & Big Data Computing, Internet of People and Smart City Innovation, Guangzhou, China, 2018: 257–262. doi: 0.1109/SmartWorld.2018.00079. [15] LEE H A, KUNG H H, UDAVANKARAN J G, et al. An architecture and management platform for blockchain-based personal health record exchange: Development and usability study[J]. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 2020, 22(6): e16748. doi: 10.2196/16748 [16] BOONCHOO T, AO Xiang, LIU Yang, et al. Grid-based DBSCAN: Indexing and inference[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 90: 271–284. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.01.034 [17] YUAN Sen, MAO Xia, and CHEN Lijiang. Multilinear spatial discriminant analysis for dimensionality reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(6): 2669–2681. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2685343 [18] FARAMARZI A, HEIDARINEJAD M, MIRJALILI S, et al. Marine predators algorithm: A nature-inspired metaheuristic[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 152: 113377. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113377 [19] XU Guangxia, LIU Yong, and KHAN P W. Improvement of the DPoS consensus mechanism in blockchain based on vague sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(6): 4252–4259. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2955719 [20] WANG Yuhao, CAI Shaobin, LIN Changlong, et al. Study of blockchains's consensus mechanism based on credit[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 10224–10231. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2891065 -





 下载:
下载:
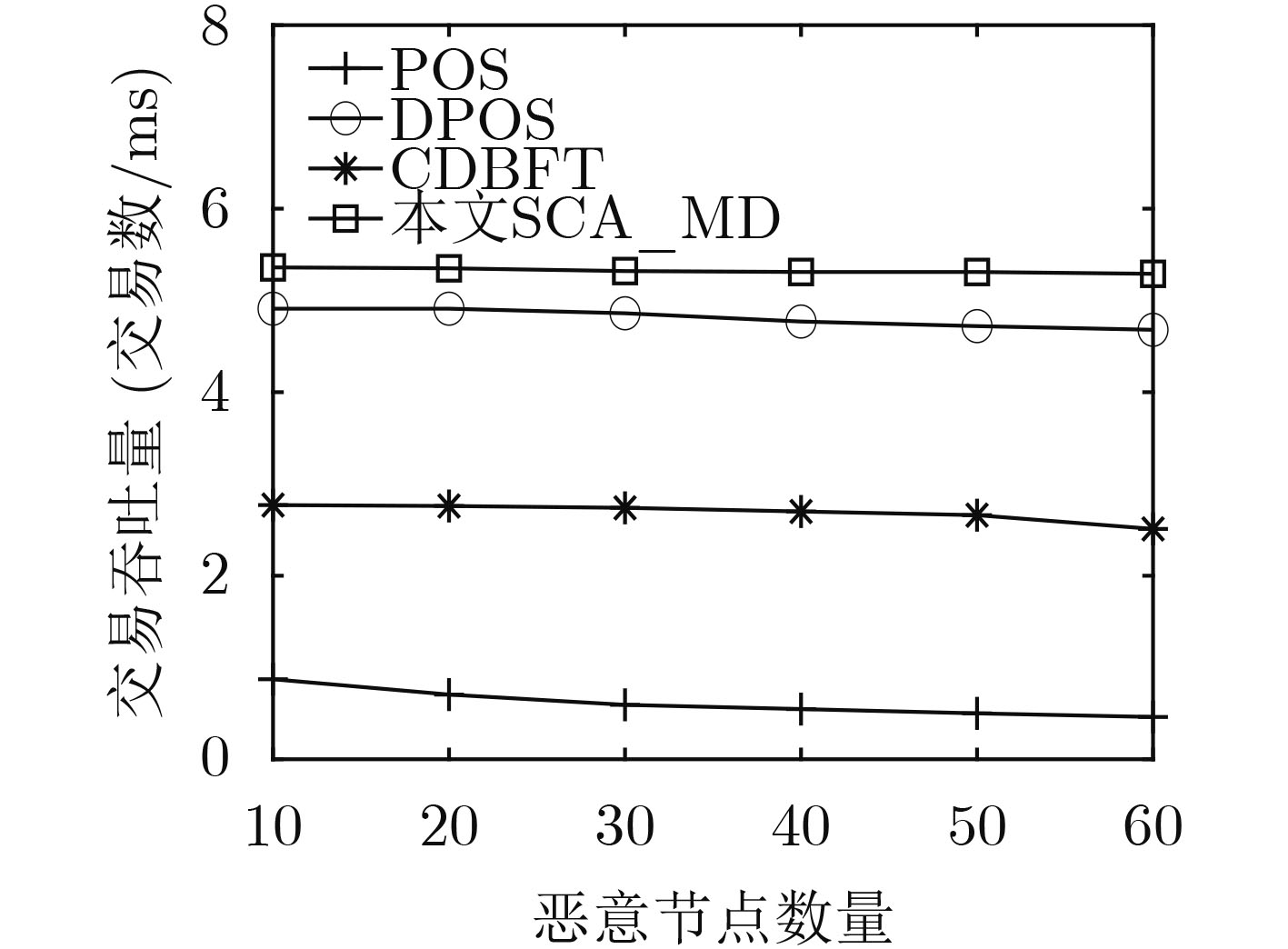
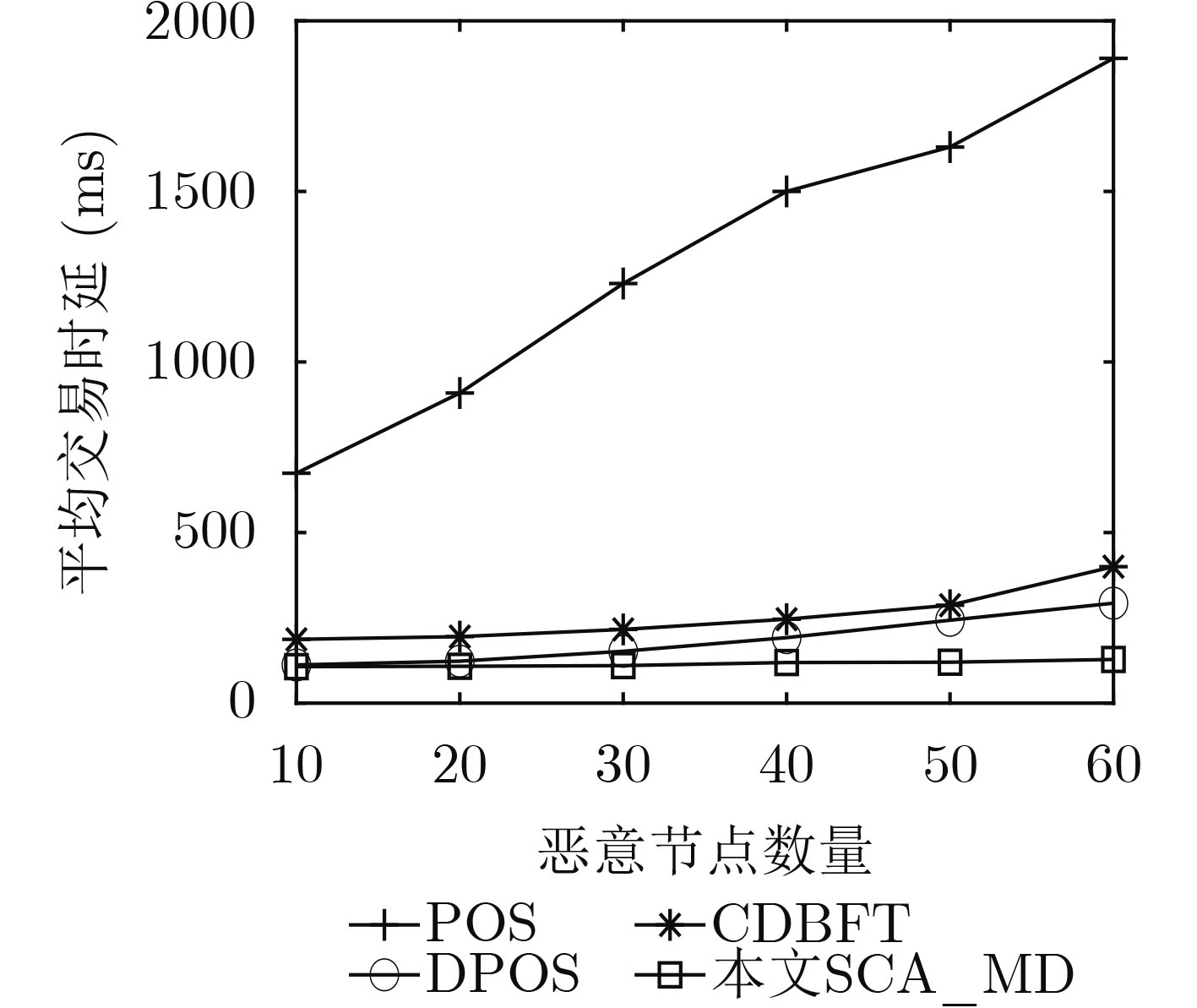



 下载:
下载:
