Hybrid Multi-level Hardware Trojan Detection Method for Gate-level Netlists Based on XGBoost
-
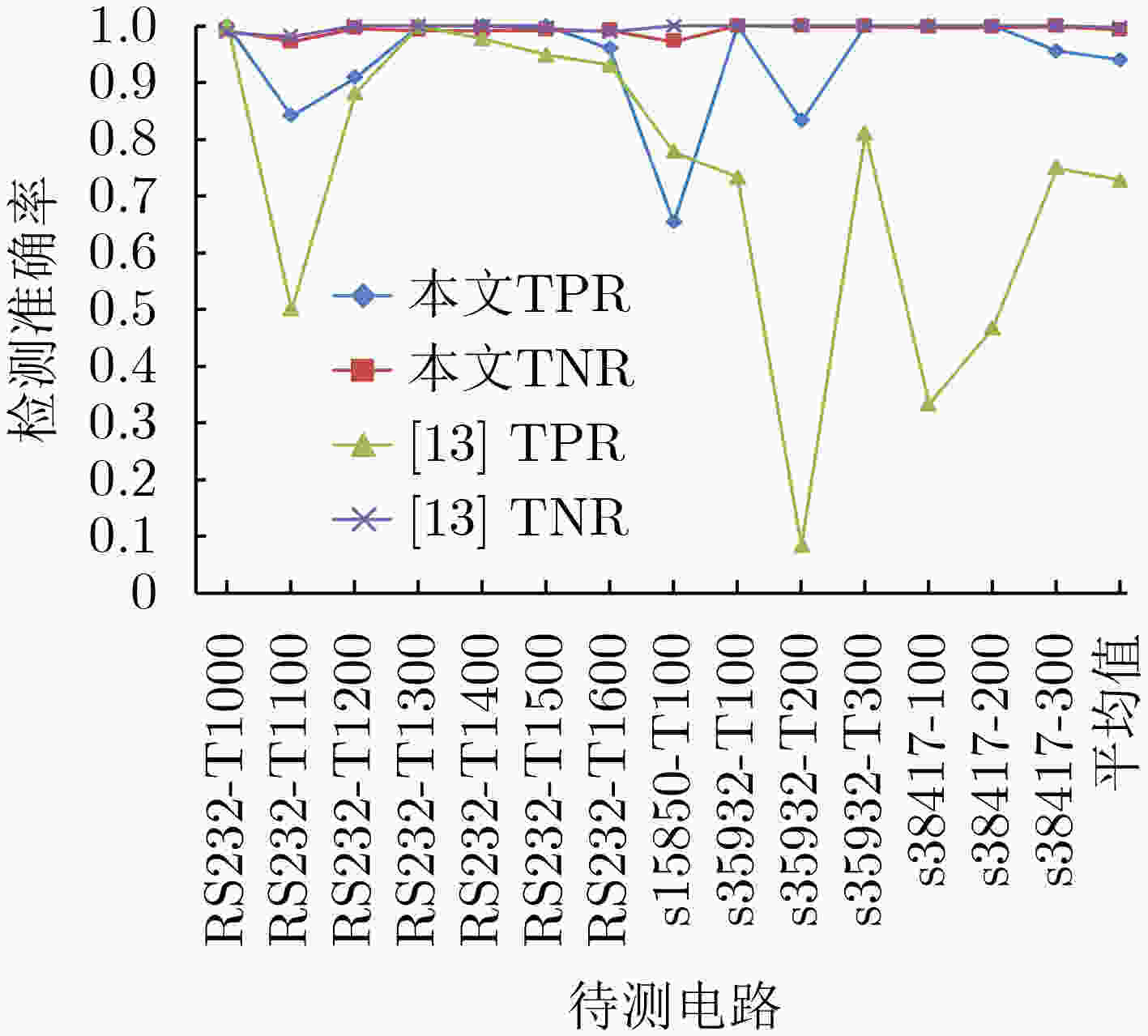
摘要: 针对恶意的第三方厂商在电路设计阶段中植入硬件木马的问题,该文提出一种基于XGBoost的混合模式门级硬件木马检测方法。该检测方法将电路的每个线网类型作为节点,采用混合模式3层级的检测方式。首先,基于提取的电路静态特征,利用XGBoost算法实现第1层级的检测。继而,通过分析扫描链的结构特征,对第1层级分离得到的正常电路继续进行第2层级的面向扫描链中存在木马电路的静态检测。最后,在第3层级采用动态检测方法进一步提升检测的准确性。Trust-Hub基准测试集的实测结果表明,该方法与现有的其他检测方法相比具有较优的木马检测率,可达到94.0%的平均真阳率(TPR)和99.3%的平均真阴率(TNR)。Abstract: A hybrid multi-level hardware Trojan detection method based on XGBoost algorithm is proposed for the problem of hardware Trojans implanted by malicious third-party manufacturers. The detection method treats each wire in gate-level netlist as a node and detects Trojans in three levels. Firstly, the effective static features of the circuit are extracted and the XGBoost algorithm is applied to detect the suspicious Trojan circuits. Common circuits distinguished at the first level continued to be detected at the second level by analyzing scan chain structural features. Finally, dynamic detection is used to increase further the accuracy of Trojans detection. Experimental results on Trust-hub benchmark show that this method has a higher accuracy compared with other existing detection methods. This detection method can finally achieve 94.0% average True Positive Rate (TPR) and 99.3% average True Negative Rate (TNR).
-
Key words:
- Hardware Trojan detection /
- XGBoost /
- Gate-level netlists /
- Static detection /
- Dynamic detection
-
表 1 各层级检测结果详细参数
层级
电路第1层级 第2层级 第3层级 测试电路 TN FP FN TP TPR TNR TN FP FN TP TPR TNR TN FP FN TP TPR TNR Trust-Hub s38417-T100 5461 10 4 7 0.636 0.998 5461 10 4 7 0.636 0.998 5461 10 0 11 1 0.998 s38417-T200 5462 9 0 11 1 0.998 5462 9 0 11 1 0.998 5462 9 0 11 1 0.998 s38417-T300 5467 1 4 43 0.915 0.999 5467 1 3 44 0.936 0.999 5467 1 2 43 0.956 0.999 s35932-T100 5867 0 0 17 1 1.000 5867 0 0 17 1 1 5867 0 0 17 1 1 s35932-T200 5857 9 4 8 0.667 0.999 5857 9 2 10 0.833 0.999 5857 9 2 10 0.833 0.999 s35932-T300 5862 4 2 34 0.944 0.999 5862 4 0 36 1 0.999 5862 4 0 36 1 0.999 s15850-T100 2122 58 11 15 0.577 0.973 2122 58 9 17 0.654 0.973 2122 58 9 17 0.654 0.973 RS232-T1000 238 2 0 37 1 0.992 238 2 0 37 1 0.992 238 2 0 37 1 0.992 RS232-T1100 242 7 6 32 0.842 0.972 242 7 6 32 0.842 0.972 242 7 6 32 0.842 0.972 RS232-T1200 252 1 3 30 0.909 0.996 252 1 3 30 0.909 0.996 252 1 3 30 0.909 0.996 RS232-T1300 251 2 0 27 1 0.992 251 2 0 27 1 0.992 251 2 0 27 1 0.992 RS232-T1400 237 2 0 44 1 0.992 237 2 0 44 1 0.992 237 2 0 44 1 0.992 RS232-T1500 245 2 0 38 1 0.992 245 2 0 38 1 0.992 245 2 0 38 1 0.992 RS232-T1600 250 2 3 22 0.880 0.992 250 2 3 22 0.880 0.992 250 2 1 24 0.960 0.992 平均值 TPR:88.4% TNR:99.3% TPR:90.6% TNR:99.3% TPR:94.0% TNR:99.3% DeTrust DT-1 575 53 4 17 0.810 0.916 575 53 4 17 0.810 0.916 575 40 4 19 0.826 0.920 DT-2 570 49 5 18 0.783 0.921 570 49 5 18 0.783 0.921 570 47 4 18 0.818 0.924 DT-3 552 51 4 15 0.789 0.915 552 51 4 15 0.789 0.915 552 46 4 17 0.810 0.923 DT-4 582 55 5 19 0.792 0.914 582 55 5 19 0.792 0.914 582 52 5 21 0.808 0.918 DT-5 563 49 3 15 0.833 0.920 563 49 3 15 0.833 0.920 563 46 3 16 0.842 0.924 平均值 TPR:80.1% TNR:91.7% TPR:80.1% TNR:91.7% TPR:82.1% TNR:92.2% 平均值 TPR:84.2% TNR:95.5% TPR:85.3% TNR:95.5% TPR:88.1% TNR:95.8% -
[1] ELNAGGAR R, CHAKRABARTY K, and TAHOORI M B. Hardware Trojan detection using changepoint-based anomaly detection techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2019, 27(12): 2706–2719. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2925807 [2] CHEN Jinghui, DONG Chen, ZHANG Fan, et al. A Hardware-Trojans detection approach based on eXtreme Gradient Boosting[C]. 2019 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Computer and Communication Engineering Technology (CCET), Beijing, China, 2019: 69–73. [3] 张毅军, 张晓, 林少锋, 等. 基于功耗特征的硬件木马检测方法[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2019, 15(31): 15–16, 26.ZHANG Yijun, ZHANG Xiao, LIN Shaofeng, et al. Hardware Trojan detection method based on power consumption features[J]. Computer Knowledge and Technology, 2019, 15(31): 15–16, 26. [4] SAAD W, SANJAB A, WANG Yunpeng, et al. Hardware Trojan detection game: A prospect-theoretic approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(9): 7697–7710. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2686853 [5] 佟鑫, 李莹, 陈岚. SVM算法在硬件木马旁路分析检测中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1643–1651. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190532TONG Xin, LI Ying, and CHEN Lan. Application of SVM machine learning to hardware Trojan detection using side-channel analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1643–1651. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190532 [6] 王晓晗, 王韬, 李雄伟, 等. 基于人工蜂群的硬件木马测试向量生成方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2019, 53(10): 1218–1224.WANG Xiaohan, WANG Tao, LI Xiongwei, et al. Test pattern generation method for hardware Trojan detection based on artificial bee colony[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2019, 53(10): 1218–1224. [7] LIU Yanjiang, ZHAO Yiqiang, HE Jiaji, et al. A statistical test generation based on mutation analysis for improving the Hardware Trojan detection[J]. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 2020, 29(3): 2050049. doi: 10.1142/S0218126620500498 [8] SALMANI H. COTD: Reference-free hardware Trojan detection and recovery based on controllability and observability in gate-level netlist[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(2): 338–350. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2613842 [9] CUI Xiaotong, KOOPAHI E, WU Kaijie, et al. Hardware Trojan detection using the order of path delay[J]. ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems, 2018, 14(3): 33. [10] WAKSMAN A, SUOZZO M, and SETHUMADHAVAN S. FANCI: Identification of stealthy malicious logic using Boolean functional analysis[C]. The 2013 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer & Communications Security (ACM-CCS), Berlin, Germany, 2013: 697–708. [11] HASEGAWA K, OYA M, YANAGISAWA M, et al. Hardware Trojans classification for gate-level netlists based on machine learning[C]. 2016 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on On-Line Testing and Robust System Design (IOLTS), Sant Feliu de Guixols, Spain, 2016: 203–206. [12] HASEGAWA K, YANAGISAWA M, and TOGAWA N. Hardware Trojans classification for gate-level netlists using multi-layer neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on On-line Testing and Robust System Design, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2017: 227–232. [13] HASEGAWA K, YANAGISAWA M, and TOGAWA N. Trojan-feature extraction at gate-level netlists and its application to hardware-Trojan detection using random forest classifier[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS 2017), Baltimore, USA, 2017: 1–4. [14] HASEGAWA K, YANAGISAWA M, and TOGAWA N. A hardware-Trojan classification method utilizing boundary net structures[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, USA, 2018: 1–4. [15] Trust-Hub [EB/OL]. http://www.trust-hub.org, 2021. [16] ZHANG Jie, YUAN Feng, and XU Qiang. DeTrust: Defeating hardware trust verification with stealthy implicitly-triggered hardware Trojans[C]. The 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Scottsdale, USA, 2014: 153–166. [17] HUANG Zhao, WANG Quan, CHEN Yin, et al. A survey on machine learning against hardware Trojan attacks: Recent advances and challenges[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 10796–10826. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2965016 [18] BHUNIA S, HSIAO M S, BANGA M, et al. Hardware Trojan attacks: Threat analysis and countermeasures[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2014, 102(8): 1229–1247. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2014.2334493 [19] HU Wei, CHANG C H, SENGUPTA A, et al. An overview of hardware security and trust: Threats, countermeasures, and design tools[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2021, 40(6): 1010–1038. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2020.3047976 [20] CHEN Tianqi and GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system[C]. The 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 785–794. -





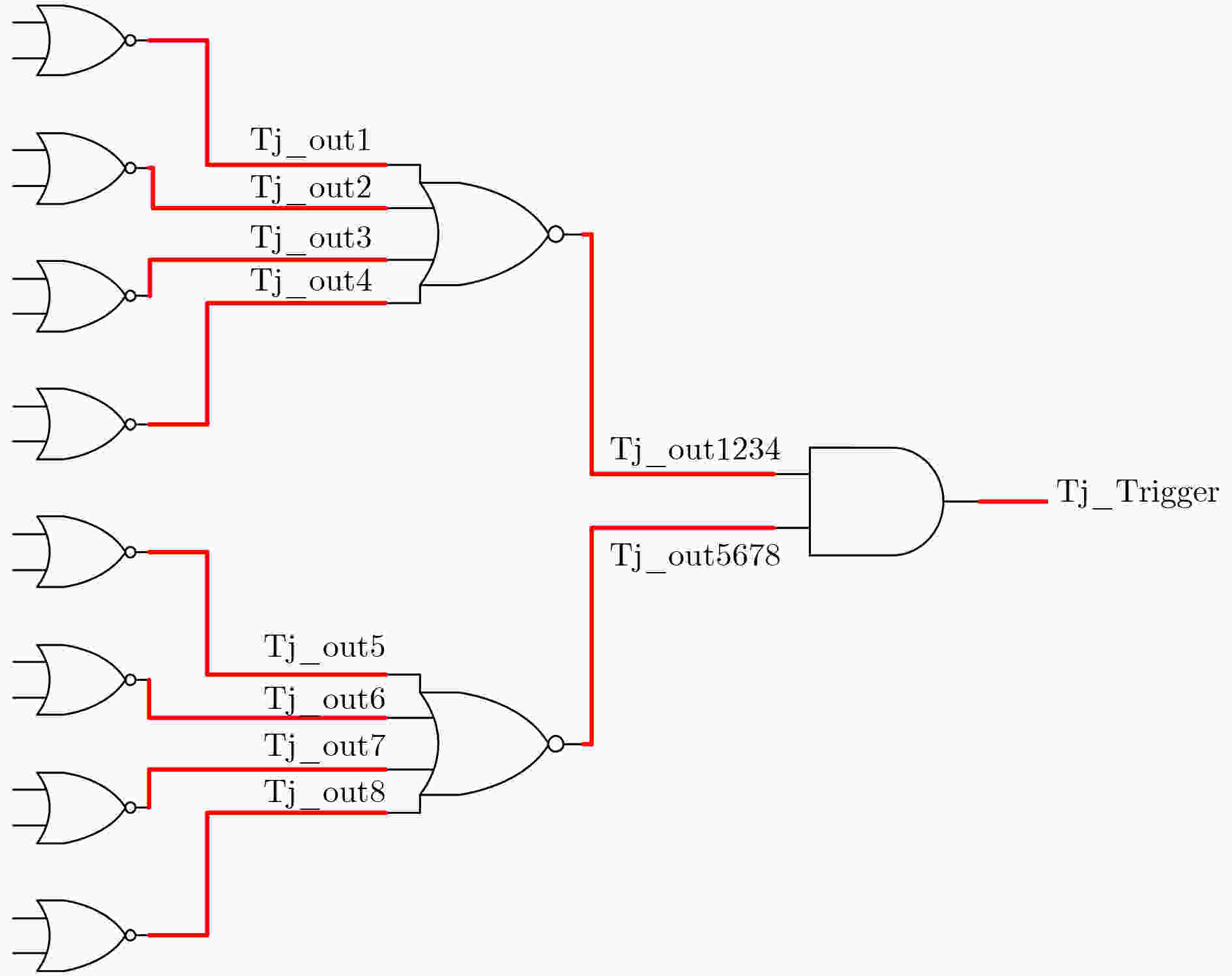
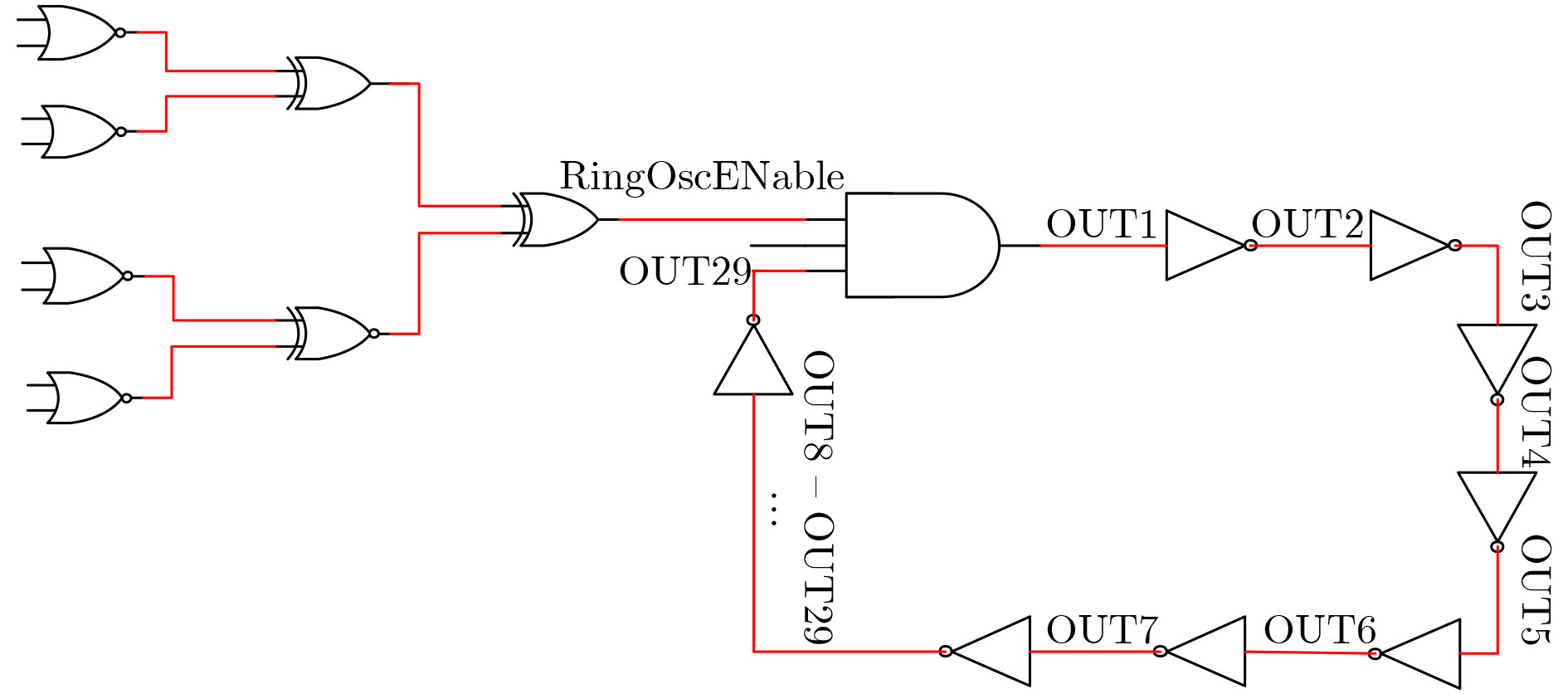
 下载:
下载:
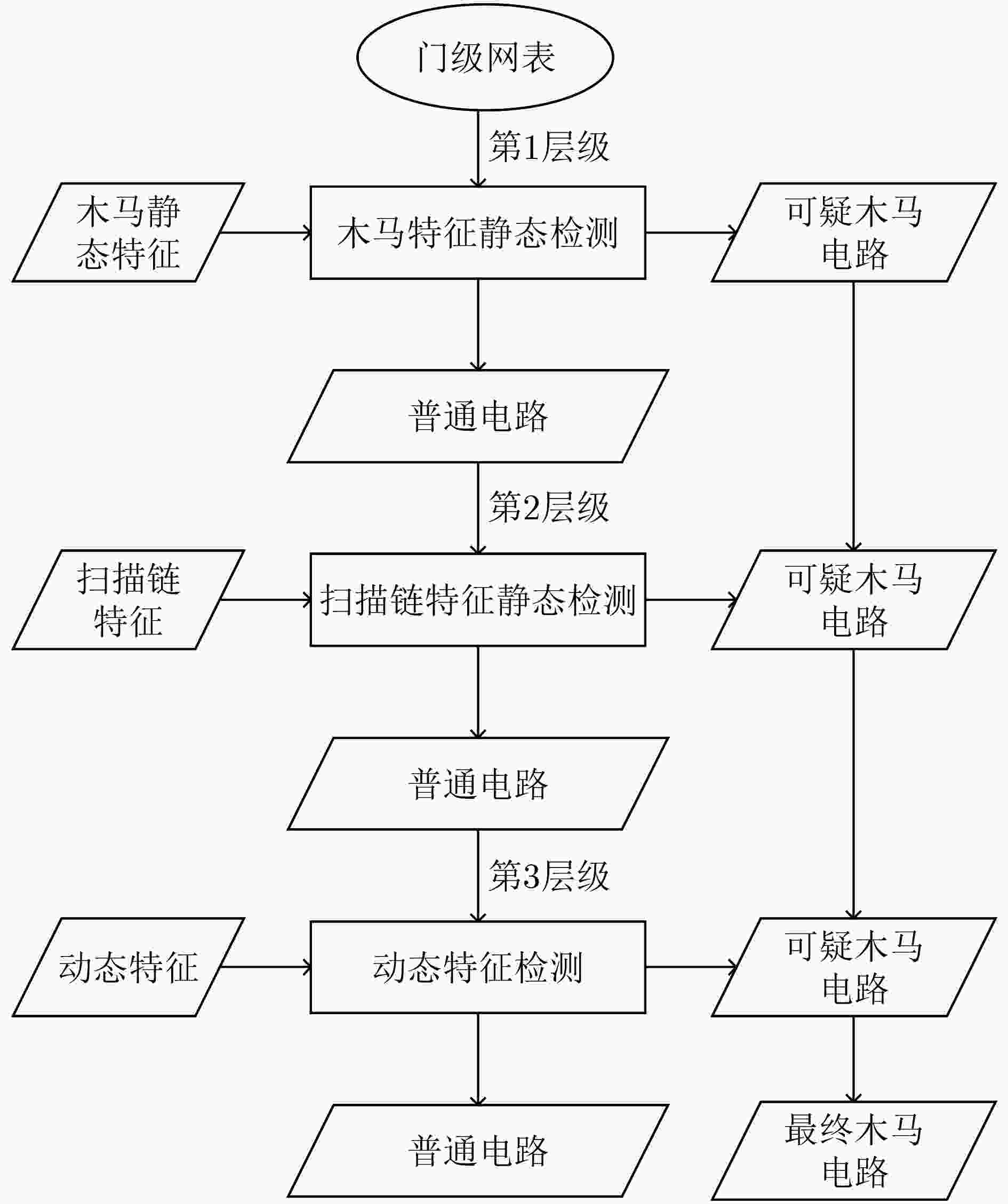
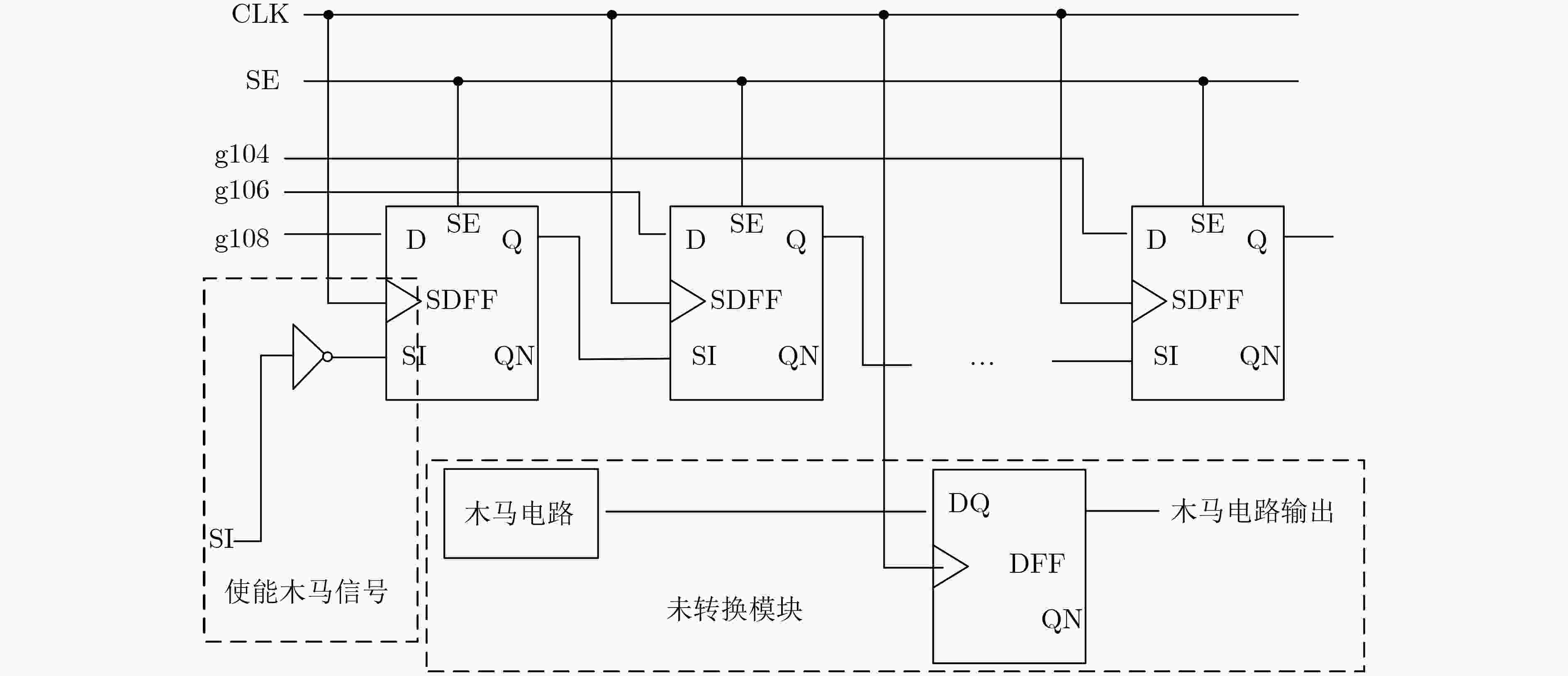



 下载:
下载:
