Target Capacity Based Power Allocation Scheme in Radar Network
-
摘要: 针对现有网络化雷达功率资源利用率低的问题,该文提出一种基于目标容量的功率分配(TC-PA)方案以提升保精度跟踪目标个数。TC-PA方案首先将网络化雷达功率分配模型制定为非光滑非凸优化问题;而后引入Sigmoid函数将原问题松弛为光滑非凸优化问题;最后运用近端非精确增广拉格朗日乘子法(PI-ALMM)对松弛后的非凸问题进行求解。仿真结果表明,PI-ALMM对于求解线性约束非凸优化问题可以较快地收敛到一个稳态点。另外,相比传统功率均分方法和遗传算法,所提TC-PA方案可以最大限度地提升目标容量。Abstract: In view of the fact that low power resource utilization rate exists in radar network, a Target Capacity based Power Allocation (TC-PA) scheme is proposed to increase the number of the targets that satisfy tracking accuracy requirements. Firstly, this scheme formulates the power allocation model of radar network as a non-smooth and non-convex optimization problem. Then the original problem is relaxed into a smooth and non-convex problem through introducing Sigmoid function. Finally, the relaxed non-convex problem is solved by utilizing the Proximal Inexact Augmented Lagrangian Multiplier Method (PI-ALMM). Simulation results show that the PI-ALMM can quickly converge to a stationary point for solving the non-convex optimization problem with linear constraints. Moreover, the proposed TC-PA scheme outperforms the traditional uniform power allocation method and genetic algorithm, in terms of target capacity.
-
Key words:
- Radar network /
- Multiple target tracking /
- Resource allocation /
- Non-convex optimization
-
表 1 PI-ALMM求解流程
(1) 初始化参数$\rho > 0$,$\alpha > 0$, $0 < c \le {1 / {\bar L}}$, $\ell > - \tau $, $0 < \beta \le 1$,及迭代下标$j = 0$; (2) 初始化变量${\boldsymbol{p}}_{q,k}^j{\rm{ = }}{\left( {{{{{p}}_{{\rm{total}}}^1} / {Q{{,{{p}}_{{\rm{total}}}^2} / Q}{{, ··· ,{{p}}_{{\rm{total}}}^N} / Q}}}} \right)^{\rm{T}}}$, 令${\boldsymbol{p}}_k^j = \left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{1,k}^j;{\boldsymbol{p}}_{2,k}^j; ··· ;{\boldsymbol{p}}_{Q,k}^j} \right)$, ${\boldsymbol{b}}_k^j{\rm{ = }}{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^j$及${\boldsymbol{a} }_k^j{\rm{ = } }{ {{{\textit{0}}} }_{N \times 1} }$; (3) 计算$L\left( {{{\boldsymbol{p}}_k},{{\boldsymbol{b}}_k};{{\boldsymbol{a}}_k}} \right)$关于${{\boldsymbol{p}}_k}$的梯度 $\begin{array}{l} { {\text{∇} }_{ { {\boldsymbol{p} }_k} } }L\left( { { {\boldsymbol{p} }_k},{ {\boldsymbol{b} }_k};{ {\boldsymbol{a} }_k} } \right) = { {\nabla }_{ { {\boldsymbol{p} }_k} } }f\left( { { {\boldsymbol{p} }_k} } \right) + { {\boldsymbol{A} }^{\rm{T} } }{ {\boldsymbol{a} }_k} + \rho { {\boldsymbol{A} }^{\rm{T} } } \\ \begin{array}{*{20}{c} } {}&{}&{} \end{array}\left( { {\boldsymbol{A} }{ {\boldsymbol{p} }_k} - { {\boldsymbol{p} }_{ {\rm{total} } } } } \right) + \ell \left( { { {\boldsymbol{p} }_k} - { {\boldsymbol{b} }_k} } \right) \end{array}d{array}$; (4) 循环 (a) ${\boldsymbol{a}}_k^{j + 1} = {\boldsymbol{a}}_k^j + \alpha \left( {A{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^j - {{\boldsymbol{p}}_{{\rm{total}}}}} \right)$; (b) ${\boldsymbol{p} }_k^{j + 1} = {\left[ { {\boldsymbol{p} }_k^j - c \cdot { \nabla_{ {\boldsymbol{p} }_k^j} }L\left( { {\boldsymbol{p} }_k^j,{\boldsymbol{b} }_k^j;{\boldsymbol{a} }_k^{j + 1} } \right)} \right]_ + }$; (c) ${\boldsymbol{b}}_k^{j + 1} = {\boldsymbol{b}}_k^j + \beta \left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^{j + 1} - {\boldsymbol{b}}_k^j} \right)$; (d) $j = j + 1$; (5) 直到$\left| {f\left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^j} \right) - f\left( {{\boldsymbol{p}}_k^{j - 1}} \right)} \right| \le \varepsilon $($\varepsilon $为给定算法终止门限),退
出循环,令功率分配结果${\boldsymbol{p}}_k^{{\rm{opt}}} = {\boldsymbol{p}}_k^j$。 -
[1] GRECO M S, GINI F, STINCO P, et al. Cognitive radars: On the road to reality: Progress thus far and possibilities for the future[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2018, 35(4): 112–125. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2018.2822847 [2] 王祥丽, 易伟, 孔令讲. 基于多目标跟踪的相控阵雷达波束和驻留时间联合分配方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 602–610. doi: 10.12000/JR17045WANG Xiangli, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Joint beam selection and dwell time allocation for multi-target tracking in phased array radar system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 602–610. doi: 10.12000/JR17045 [3] 严俊坤, 刘宏伟, 戴奉周, 等. 基于非线性机会约束规划的多基雷达系统稳健功率分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(3): 509–515. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00656YAN Junkun, LIU Hongwei, DAI Fengzhou, et al. Nonlinear chance constrained programming based robust power allocation algorithm for multistatic radar systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(3): 509–515. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00656 [4] SHI Chenguang, DING Lintao, WANG Fei, et al. Low probability of intercept-based collaborative power and bandwidth allocation strategy for multi-target tracking in distributed radar network system[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(12): 6367–6377. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2977328 [5] YAN Junkun, DAI Jinhui, PU Wenqiang, et al. Quality of service constrained-resource allocation scheme for multiple target tracking in radar sensor network[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(1): 771–779. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2990409 [6] YAN Junkun, PU Wenqiang, ZHOU Shenghua, et al. Optimal resource allocation for asynchronous multiple targets tracking in heterogeneous radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4055–4068. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3007313 [7] XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, KONG Lingjiang, et al. Receive-beam resource allocation for multiple target tracking with distributed MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(5): 2421–2436. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2818579 [8] XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Joint node selection and power allocation strategy for multitarget tracking in decentralized radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(3): 729–743. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2777394 [9] YI Wei, YUAN Ye, HOSEINNEZHAD H, et al. Resource scheduling for distributed multi-target tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1602–1617. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2976587 [10] ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, XIE Junwei, et al. Joint subarray selection and power allocation for cognitive target tracking in large-scale MIMO radar networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(2): 2569–2580. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2960401 [11] 严俊坤, 纠博, 刘宏伟, 等. 一种针对多目标跟踪的多基雷达系统聚类与功率联合分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(8): 1875–1881. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01470YAN Junkun, JIU Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Joint cluster and power allocation algorithm for multiple targets tracking in multistatic radar systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(8): 1875–1881. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01470 [12] YAN Junkun, PU Wenqiang, ZHOU Shenghua, et al. Collaborative detection and power allocation framework for target tracking in multiple radar system[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 55: 173–183. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.08.010 [13] 秦童, 戴奉周, 刘宏伟, 等. 火控相控阵雷达的时间资源管理算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2016, 38(3): 545–550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.03.11QING Tong, DAI Fengzhou, LIU Hongwei, et al. Time resource management algorithm for the fire control phased-array radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(3): 545–550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.03.11 [14] YAN Junkun, ZHANG Peng, DAI Jinhui, et al. Target capacity based simultaneous multibeam power allocation scheme for multiple target tracking application[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 178: 107794. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107794 [15] GURBUZ A C, MDRAFI R, and CETINER B A. Cognitive radar target detection and tracking with multifunctional reconfigurable antennas[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2020, 35(6): 64–76. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2020.2990589 [16] NEITZ O and EIBERT T F. A plane-wave synthesis approach for 3D monostatic RCS prediction from near-field measurements[C]. 2018 15th European Radar Conference, Madrid, Spain, 2018: 99–102. doi: 10.23919/EuRAD.2018.8546622. [17] SONG Wanjun and ZHANG Hou. RCS prediction of objects coated by magnetized plasma via scale model with FDTD[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(6): 1939–1945. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2645567 [18] TICHAVSKY P, MURAVCHIK C H, and NEHORAI A. Posterior Cramer-Rao bounds for discrete-time nonlinear filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1998, 46(5): 1386–1396. doi: 10.1109/78.668800 [19] ILIEV A, KYURKCHIEV N, MARKOV S. On the approximation of the step function by some sigmoid functions[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2017, 133: 223–234. doi: 10.1016/j.matcom.2015.11.005 [20] GARULLI A and VICINO A. Convex relaxations in circuits, systems, and control[J]. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 2009, 9(2): 46–56. doi: 10.1109/MCAS.2008.931737 [21] ZHANG Jiawei and LUO Zhiquan. A proximal alternating direction method of multiplier for linearly constrained nonconvex minimization[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2020, 30(3): 2272–2302. doi: 10.1137/19M1242276 [22] ZHANG Jiawei and LUO Zhiquan. A global dual error bound and its application to the analysis of linearly constrained nonconvex optimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2006.16440, 2020. [23] GREFENSTETTE J J. Optimization of control parameters for genetic algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1986, 16(1): 122–128. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1986.289288 -





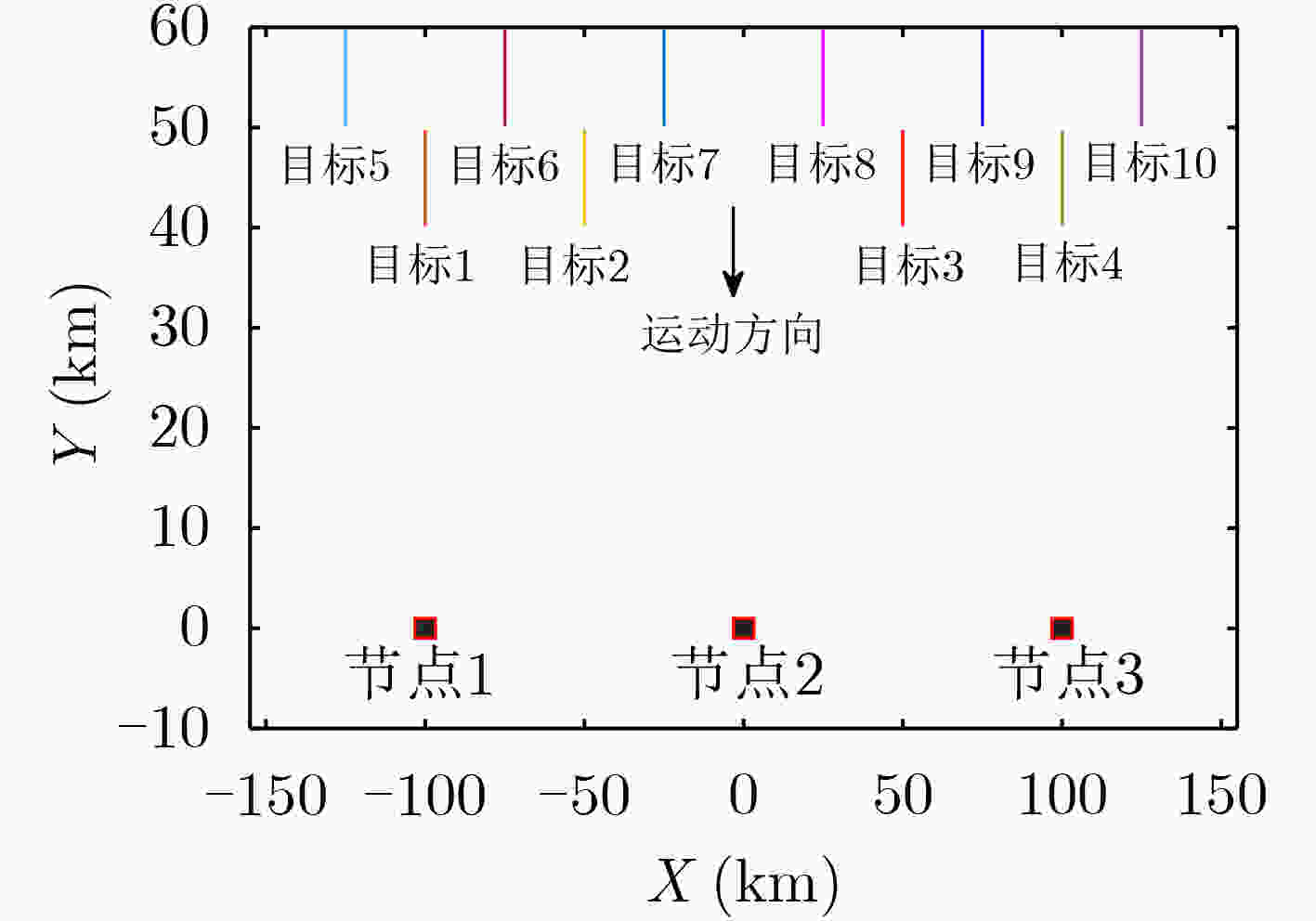
 下载:
下载:
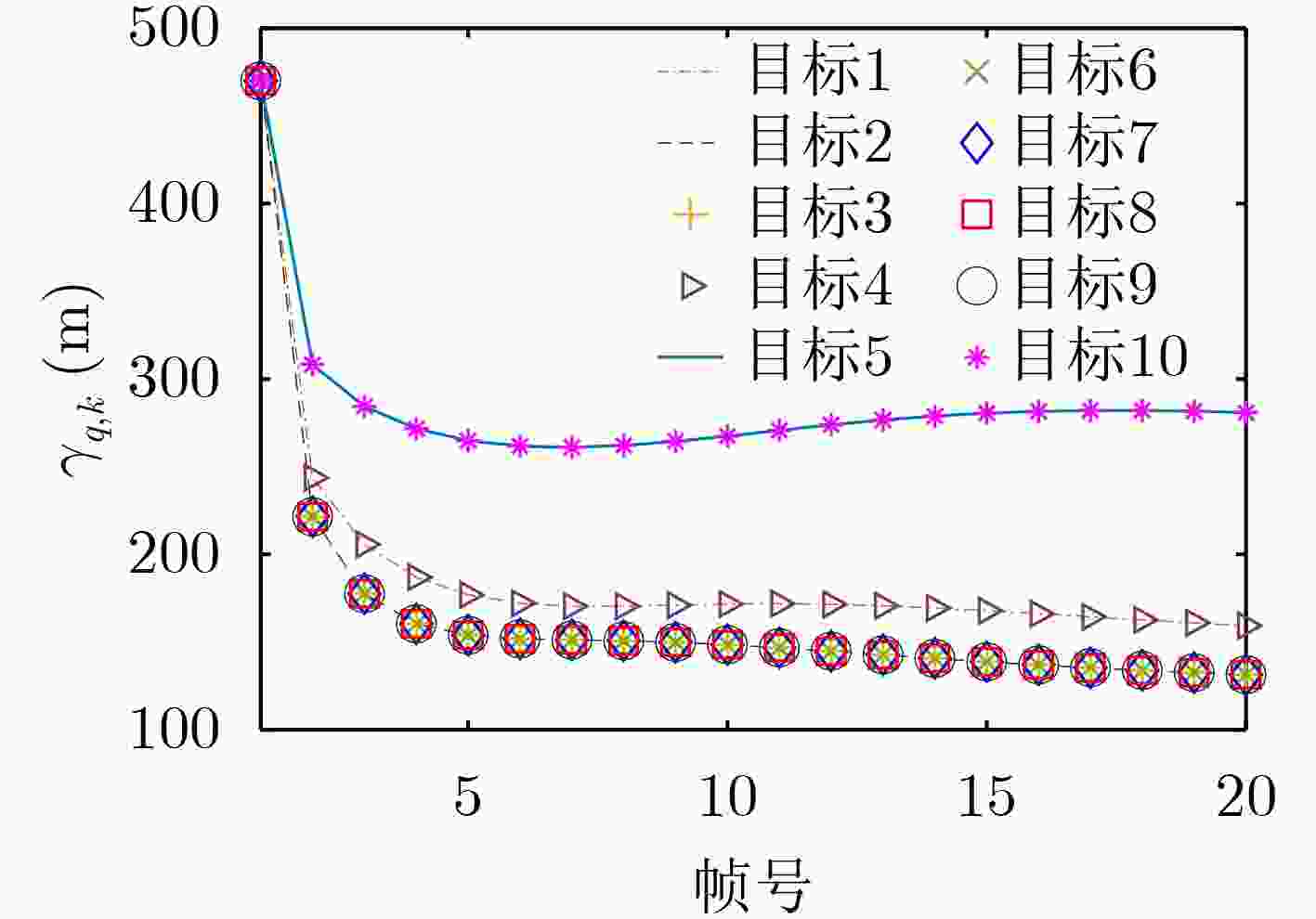
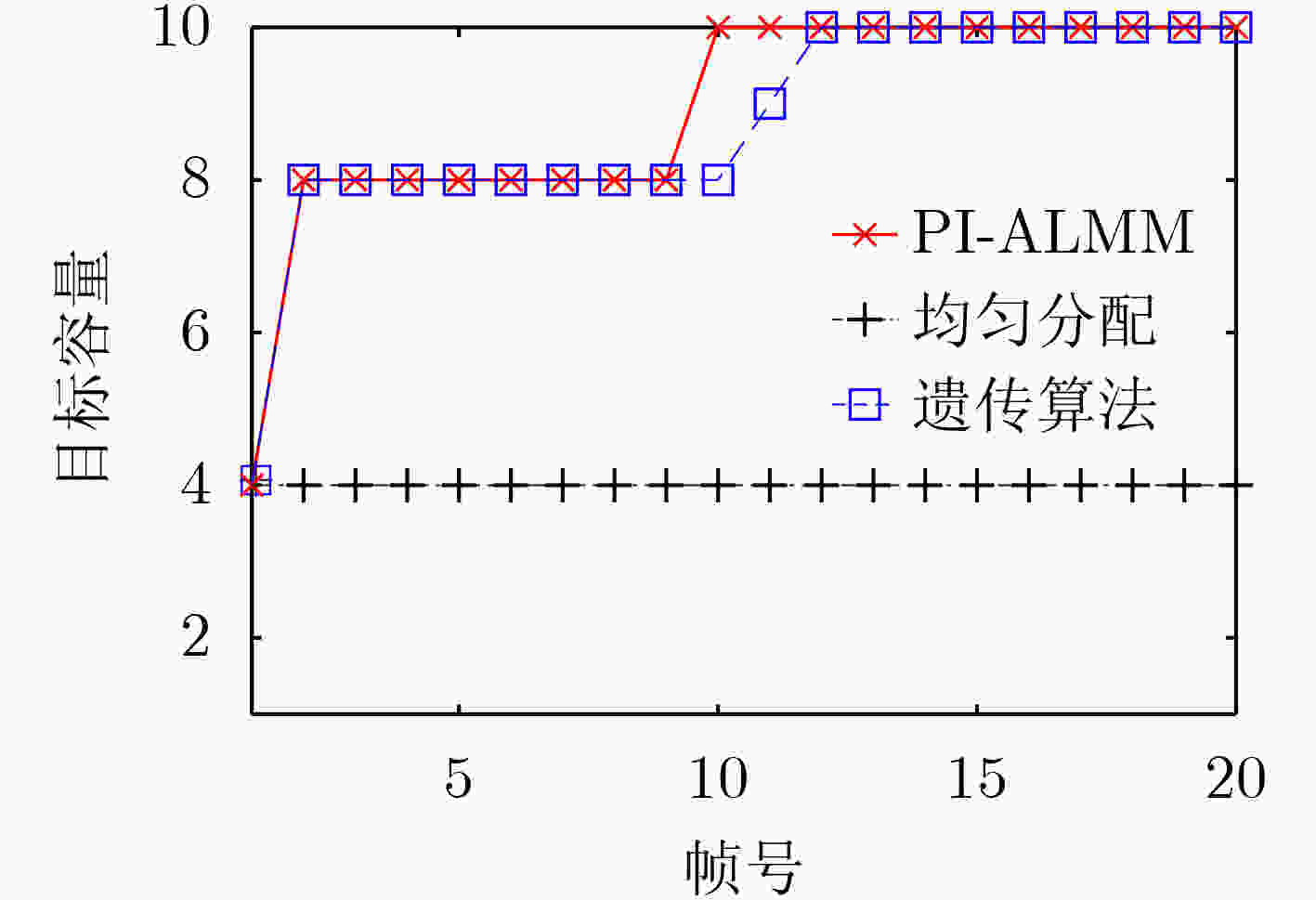
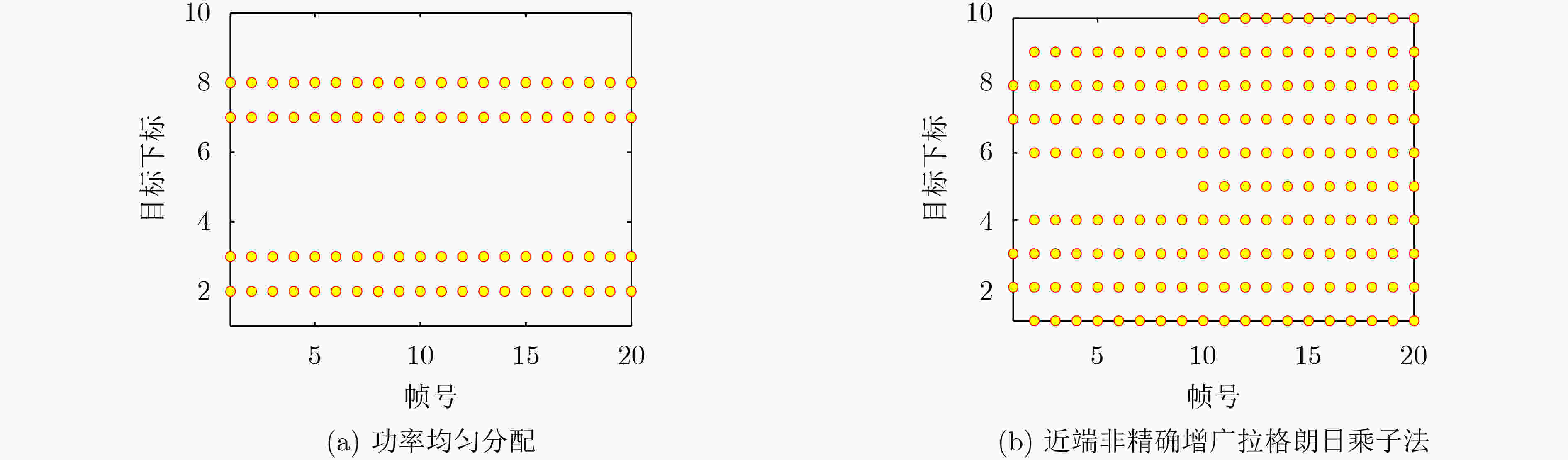
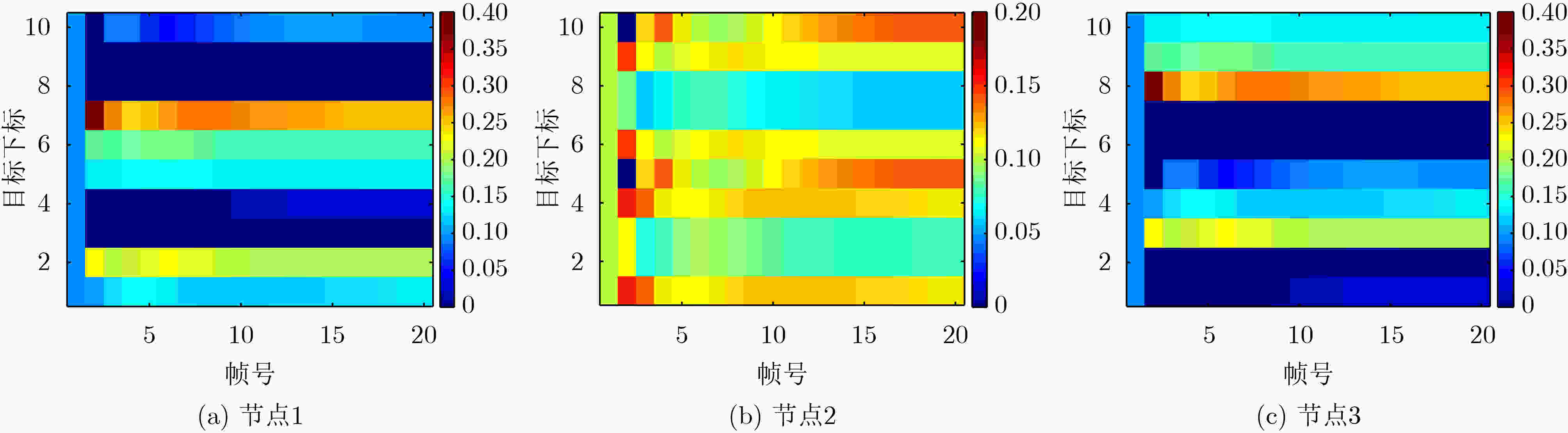
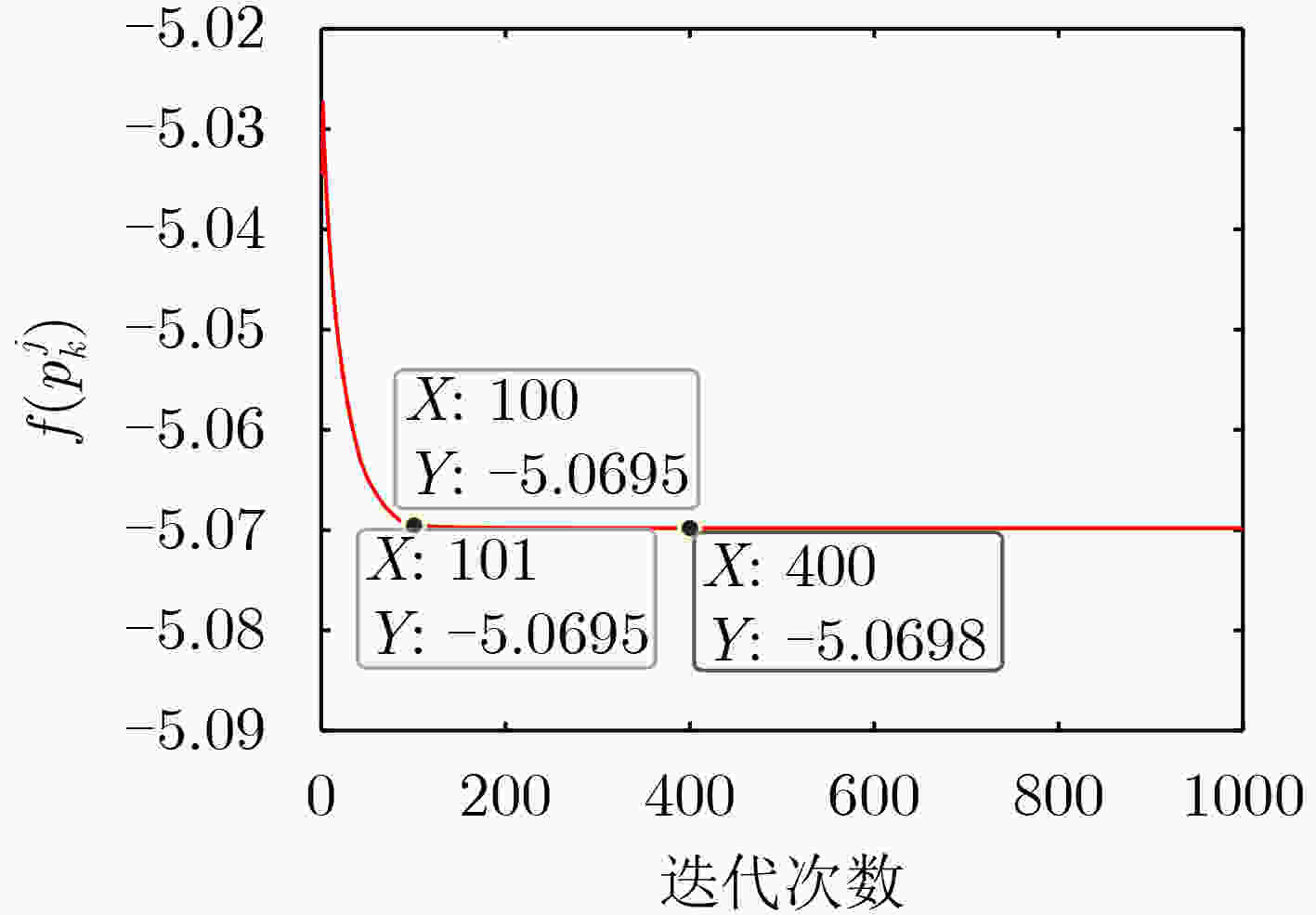
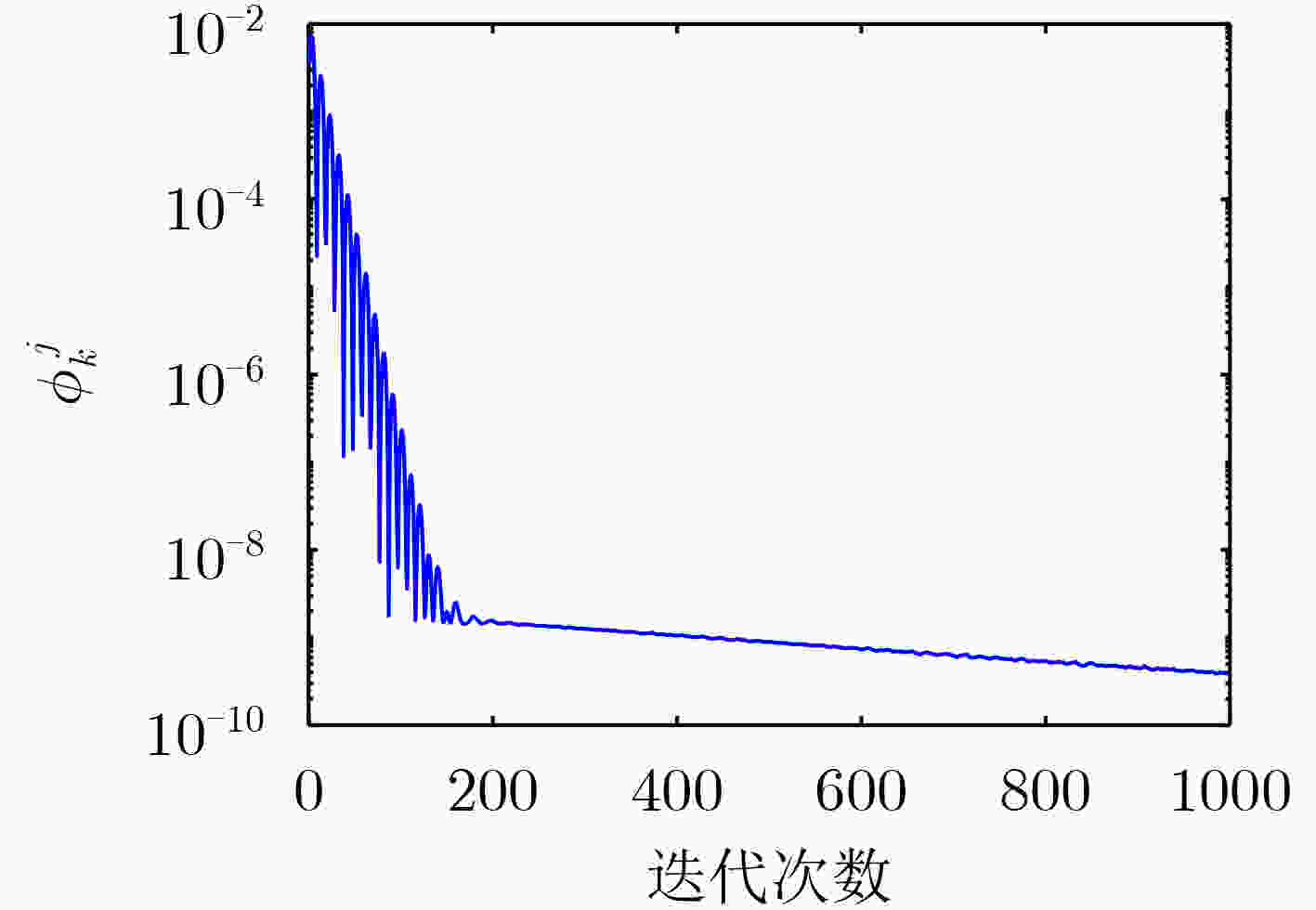



 下载:
下载:
