Secure Energy-efficient Resource Allocation in Mobile Edge Computing Based on Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access
-
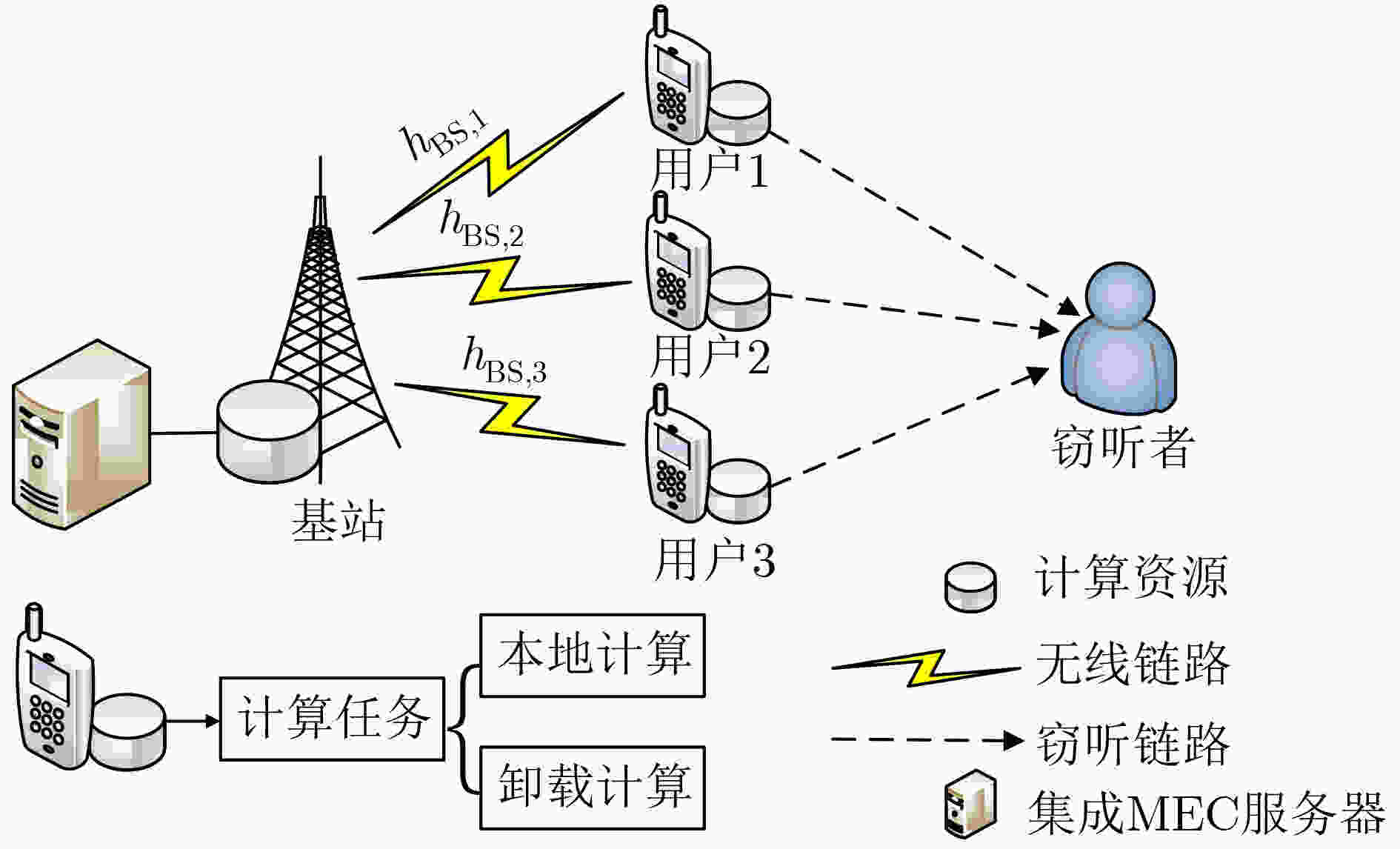
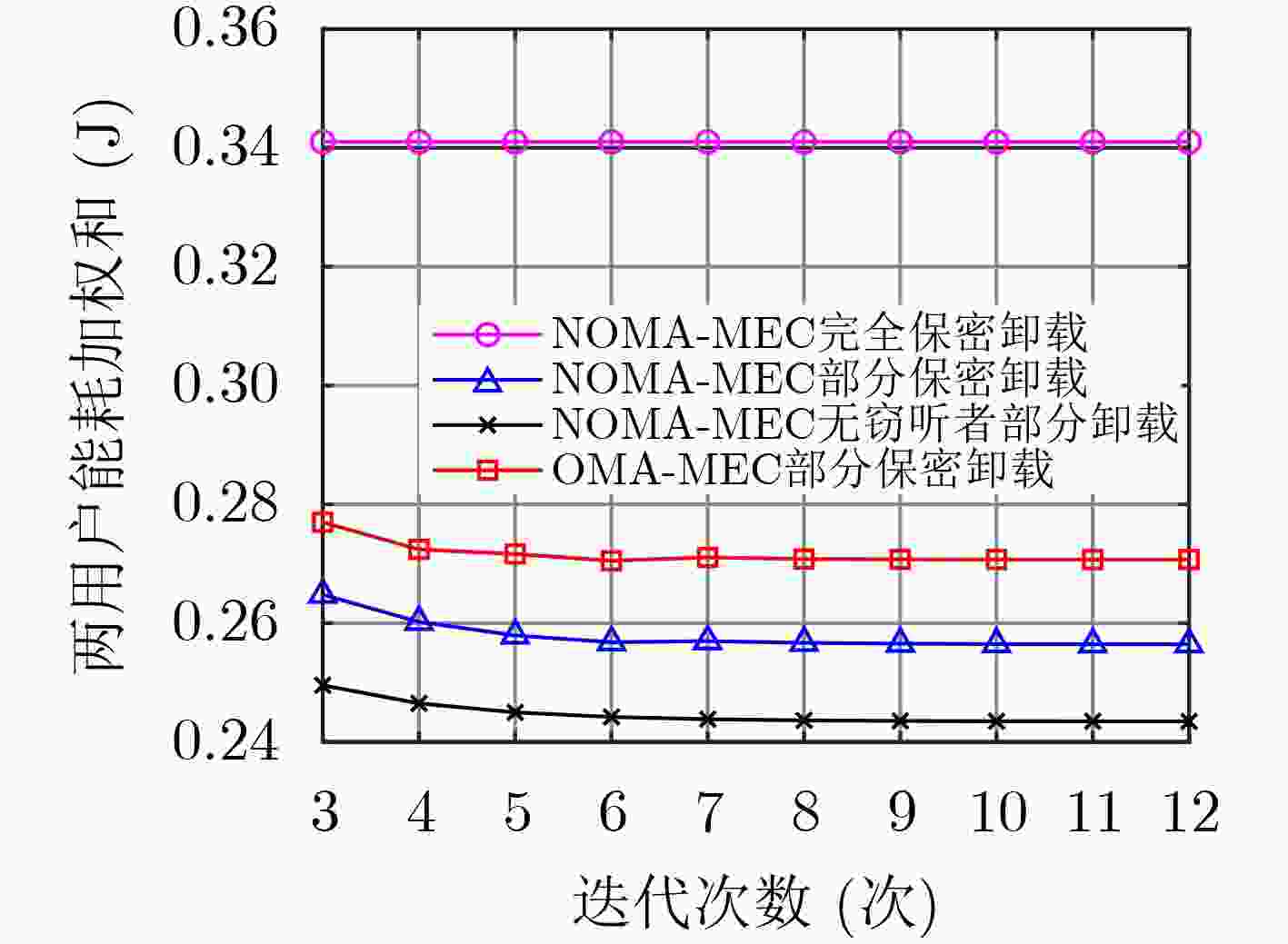
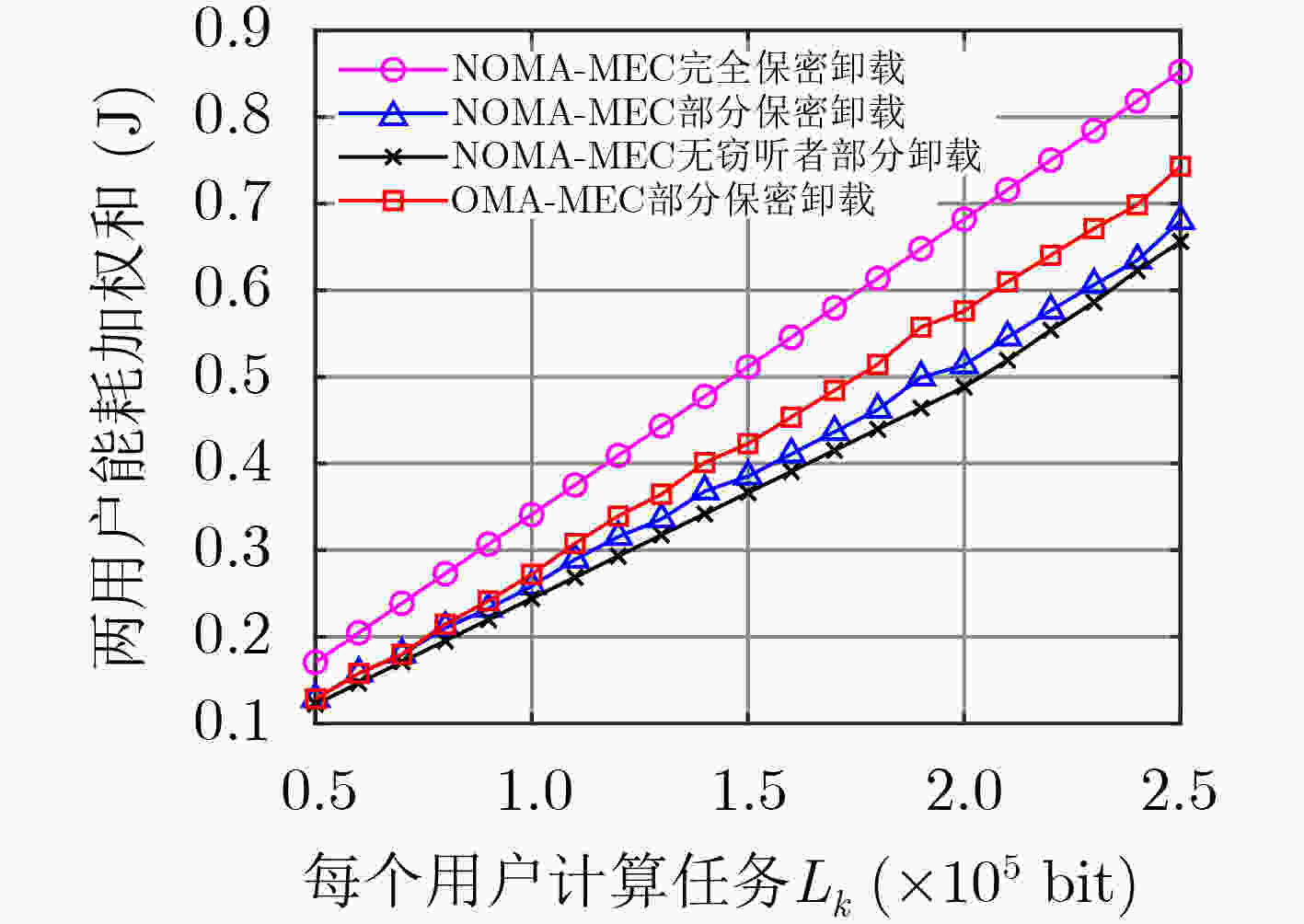
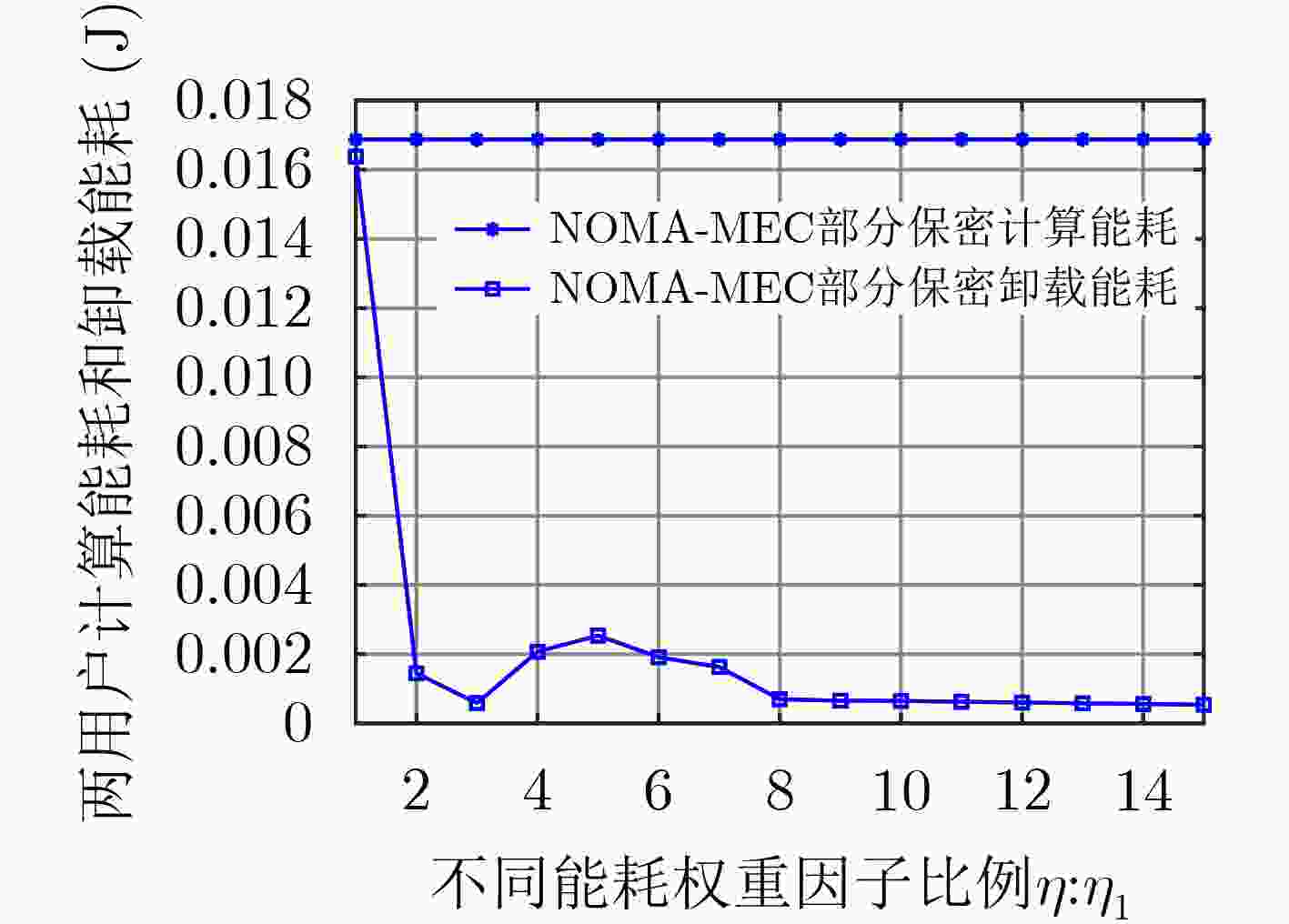
摘要: 为提高基于非正交多址接入(NOMA)的移动边缘计算(MEC)系统中计算任务部分卸载时的安全性,该文在存在窃听者情况下研究MEC网络的物理层安全,采用保密中断概率来衡量计算卸载的保密性能,考虑发射功率约束、本地任务计算约束和保密中断概率约束,同时引入能耗权重因子以平衡传输能耗和计算能耗,最终实现系统能耗加权和最小。在满足两个用户优先级情况下,为降低系统开销,提出一种联合任务卸载和资源分配机制,通过基于二分搜索的迭代优化算法寻求问题变换后的最优解,并获得最优的任务卸载和功率分配。仿真结果表明,所提算法可有效降低系统能耗。Abstract: In order to improve the security of Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) based Mobile Edge Computation (MEC) system when computation tasks are partially offloading, the physical layer security of MEC network in the presence of eavesdroppers is considered, and the security interruption probability is used to measure the security performance of computation offloading. Considering the transmit power constraint, local task calculation constraint and secret outage probability constraint, and then, the energy consumption weight factor is introduced to balance the transmission energy consumption and the calculated energy consumption. After that, the sum of system weighted energy consumption is finally achieved. In the case of satisfying two user priorities, to reduce the system overhead, a joint task offloading and resource allocation mechanism is proposed to archive the optimal solution of the transformed problem through an iterative optimization algorithm based on bisection search, and the optimal computing task offloading and power allocation are obtained. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively reduce the energy consumption of the system.
-
表 1 问题P2的二等分迭代优化算法
初始化:$C_k^{{\rm{loc}}},C_k^{{\rm{ser}}},f_k^{{\rm{loc}}},f_k^{{\rm{ser}}},{\delta ^{{\rm{loc}}}},{\delta ^{{\rm{ser}}}},$ $B,T,\alpha ,\varepsilon ,{\gamma _{{\rm{BS}},k}}$, 迭代次 数$x$, ${ {{X} }_{\max } }$, $l_k^{{\rm{MIN}}} = 0$, $l_k^{{\rm{MAX}}} = 0.7{L_k}$, 精度$\tau $ (1) while $l_k^{ {\rm{max} } } - l_k^{ {\rm{min} } } \ge \tau$do 定义${l_1}{\rm{ = } }\dfrac{ {l_1^{ {\rm{min} } } + l_1^{ {\rm{max} } } }}{2}$ 根据式(21)计算${R^*_{ {\rm{s} },1} }$ 根据式(22a)计算${p^*_1}$ 根据式(17a)计算${P_{{\rm{so}},1}}$ if ${P_{ {\rm{so} },1} } \le \varepsilon$ $l_1^{{\rm{MIN}}}{\rm{ = }}{l_1}$ else $l_1^{{\rm{MAX}}}{\rm{ = }}{l_1}$ (2) until ${l_1}$满足式(7)和$x$=${ {{X} }_{\max } }$ (3) $x$=$x + 1$ (4) while $l_k^{ {\rm{max} } } - l_k^{ {\rm{min} } } \ge \tau$ do 定义${l_2}{\rm{ = } }\dfrac{ {l_2^{ {\rm{min} } } + l_2^{ {\rm{max} } } }}{2}$ 根据式(21)计算${R^*_{ {\rm{s} },2} }$ 根据式(22b)计算${p^*_2}$ 根据式(17b)计算${P_{{\rm{so}},2}}$ if $\dfrac{{C_2^{{\rm{loc}}}{l_2}}}{{f_2^{{\rm{loc}}}}} \le T$ $l_2^{ {\rm{min} } }{\rm{ = } }{l_2}$ else $l_2^{ {\rm{max} } }{\rm{ = } }{l_2}$ (5) until ${l_2}$满足式(7)和$x$=${{{X}}_{\max }}$ (6) $x$=$x + 1$ (7) end while 表 2 仿真参数
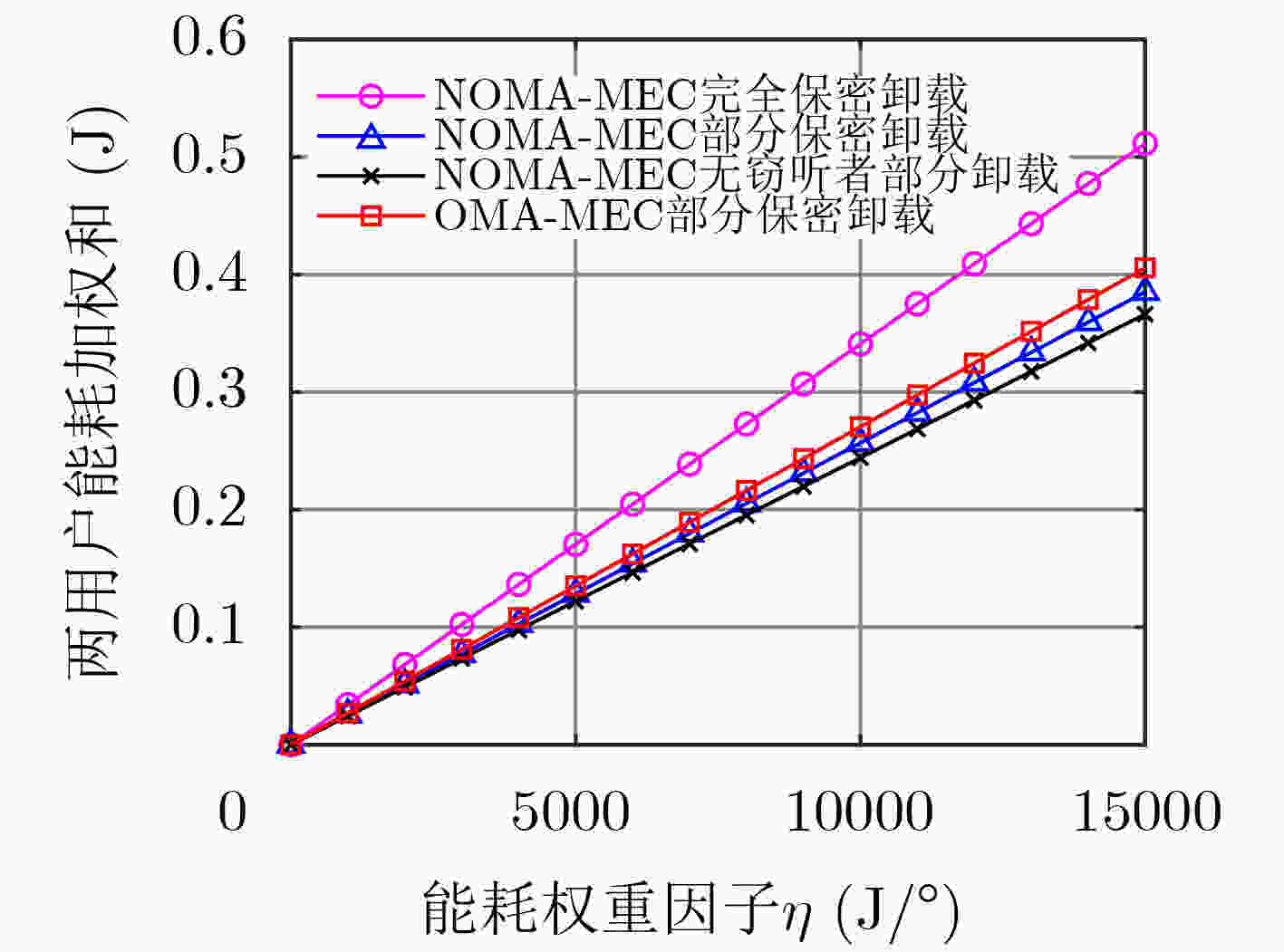
参数 数值 任务计算比特${L_k}$ 0.5~2.5$ \times $105 bit 计算任务所需CPU周期$C_k^{{\rm{loc}}},C_k^{{\rm{ser}}}$ 1000 cycles/bit 移动终端计算能力$f_k^{{\rm{loc}}}$ 1.415 GHz MEC服务器计算能力$f_k^{{\rm{ser}}}$ 3.3 GHz 移动终端CPU每周期能耗${\delta ^{{\rm{loc}}}}$ 1.4265$ \times $10–4 W MEC服务器CPU每周期能耗${\delta ^{{\rm{ser}}}}$ 5.6265$ \times $10–4 W 路径损耗指数$\alpha $ 4 系统最大发射功率$p_k^{\max }$ 0.1 W 能耗权重因子$\eta $ 10000 J/s 最大保密中断概率$\varepsilon $ 5% 用户$k$到基站的距离${d_{{\rm{BS}},k}}$ 60 m 用户$k$到窃听者的距离${d_{{\rm{e}},k}}$ 100 m 噪声方差$\sigma _{{\rm{BS}}}^2,\sigma _{\rm{e}}^2$ –105 dBm/Hz 系统带宽$B$ 1 MHz 时延预算$T$ 0.1 s -
[1] ZENG Ming, HAO Wanming, DOBRE O A, et al. Delay minimization for massive MIMO assisted mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(6): 6788–6792. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2979434 [2] NING Bing, HAO Wanming, ZHANG Aihua, et al. Energy efficiency–delay tradeoff for a cooperative NOMA system[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(4): 732–735. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2900320 [3] WANG Xinxin, WU Wei, LÜ Bin, et al. Delay minimization for secure NOMA mobile-edge computing[C]. 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Xi’an, China, 2019: 1529–1534. doi: 10.1109/ICCT46805.2019.8947270. [4] 唐伦, 肖娇, 赵国繁, 等. 基于能效的NOMA蜂窝车联网动态资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 526–533. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190006TANG Lun, XIAO Jiao, ZHAO Guofan, et al. Energy efficiency based dynamic resource allocation algorithm for cellular vehicular based on non-orthogonal multiple access[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 526–533. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190006 [5] DING Zhiguo, LEI Xianfu, KARAGIANNIDIS G K, et al. A survey on non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G networks: Research challenges and future trends[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(10): 2181–2195. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2725519 [6] DING Zhiguo, FAN Pingzhi, and VINCENT POOR H. Impact of non-orthogonal multiple access on the offloading of mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(1): 375–390. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2870894 [7] MAO Yuyi, YOU Changsheng, ZHANG Jun, et al. A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2322–2358. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2745201 [8] XIAO Zhu, DAI Xingxia, JIANG Hongbo et al. Vehicular task offloading via heat-aware MEC cooperation using game-theoretic method[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(3): 2038–2052. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2960631 [9] FANG Sangsha, CHEN Hongyang, KHAN Z, et al. On the content delivery efficiency of NOMA assisted vehicular communication networks with delay constraints[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(6): 847–850. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2973138 [10] WANG Feng, XU Jie, and DING Zhiguo. Multi-antenna NOMA for computation offloading in multiuser mobile edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(3): 2450–2463. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2881725 [11] HUA Meihui, TIAN Hui, NI Wanli, et al. Energy efficient task offloading in NOMA-based mobile edge computing system[C]. 2019 IEEE 30th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Istanbul, Turkey, 2019: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2019.8904347. [12] DING Zhiguo, XU Jie, DOBRE O A, et al. Joint power and time allocation for NOMA–MEC offloading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 6207–6211. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2907253 [13] YE Yinghui, HU R Q, LU Guangyue, et al. Enhance latency-constrained computation in MEC networks using uplink NOMA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(4): 2409–2425. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2969666 [14] KIANI A and ANSARI N. Edge computing aware NOMA for 5G networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(2): 1299–1306. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2796542 [15] WU Wei, ZHOU Fuhui, HU R Q, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation for secure NOMA-enabled mobile edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(1): 493–505. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2949994 [16] HE Biao, LIU An, YANG Nan, et al. On the design of secure non-orthogonal multiple access systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(10): 2196–2206. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2725698 [17] ZHENG Tongxing, WANG Huiming, and DENG Hao. Improving anti-eavesdropping ability without eavesdropper’s CSI: A practical secure transmission design perspective[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(6): 946–949. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2840152 [18] DING Zhiguo, YANG Zheng, FAN Pingzhi, et al. On the performance of non-orthogonal multiple access in 5G systems with randomly deployed users[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(12): 1501–1505. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2343971 [19] 3rd Generation Partnership Project. Study on downlink multiuser superposition transmission for LTE[R]. 3GPP TSG RAN #67. RP-150496, 2015. [20] LI Linfeng, KUANG Zhufang, and LIU Anfeng. Energy efficient and low delay partial offloading scheduling and power allocation for MEC[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2019.8761160. [21] SUN Yan, NG D W K, ZHU Jun, et al. Robust and secure resource allocation for full-duplex MISO multicarrier NOMA systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(9): 4119–4137. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2830325 [22] ZHOU Xiangyun, MCKAY M R, MAHAM B, et al. Rethinking the secrecy outage formulation: A secure transmission design perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2011, 15(3): 302–304. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2011.011811.102433 [23] MAO Yuyi, ZHANG Jun, and LETAIEF K B. Joint task offloading scheduling and transmit power allocation for mobile-edge computing systems[C]. 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2017.7925615. [24] LIU Yuanwei, QIN Zhijin, ELKASHLAN M, et al. Enhancing the physical layer security of non-orthogonal multiple access in large-scale networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(3): 1656–1672. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2650987 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
