A Multi-domain Text Classification Method Based on Recurrent Convolution Multi-task Learning
-
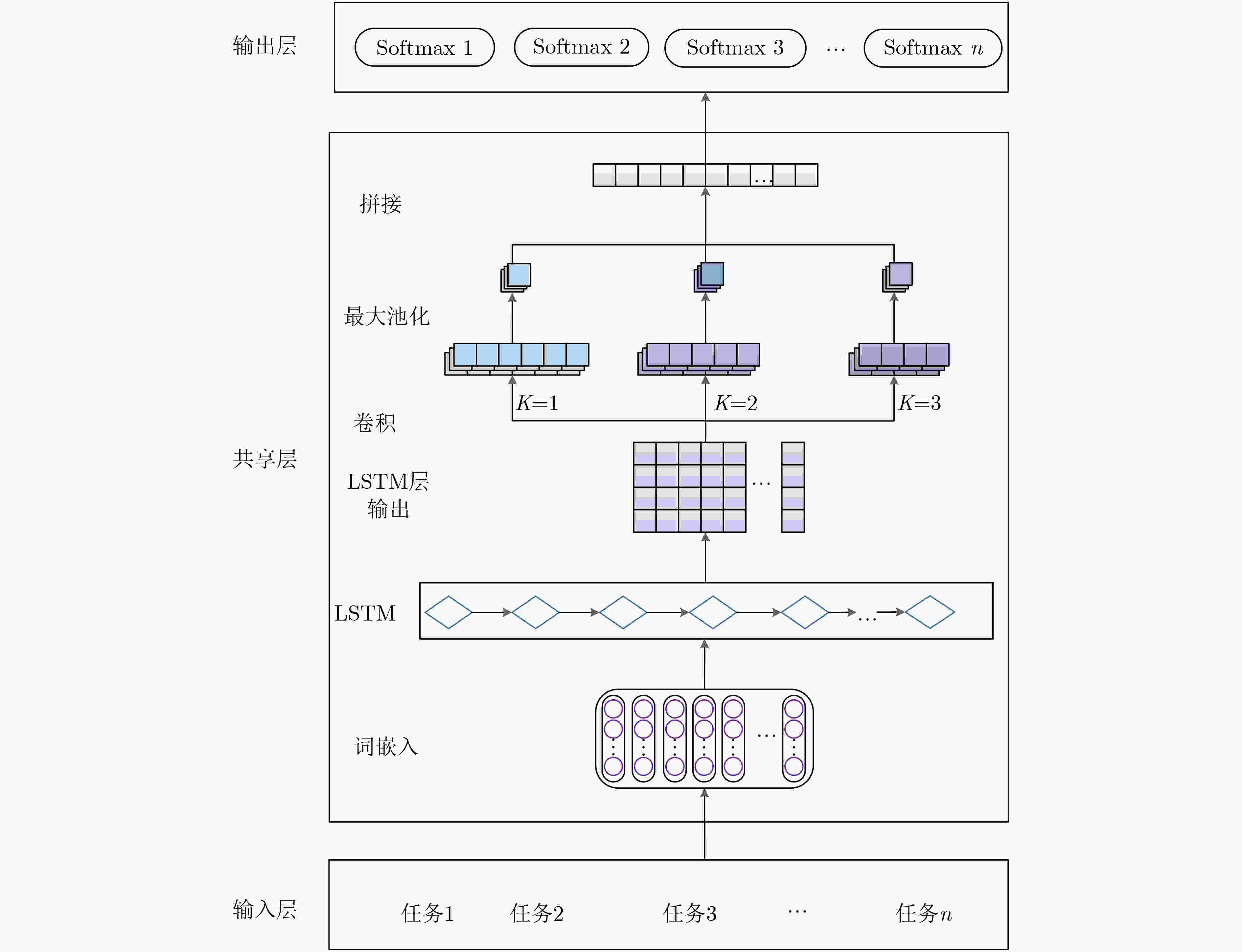
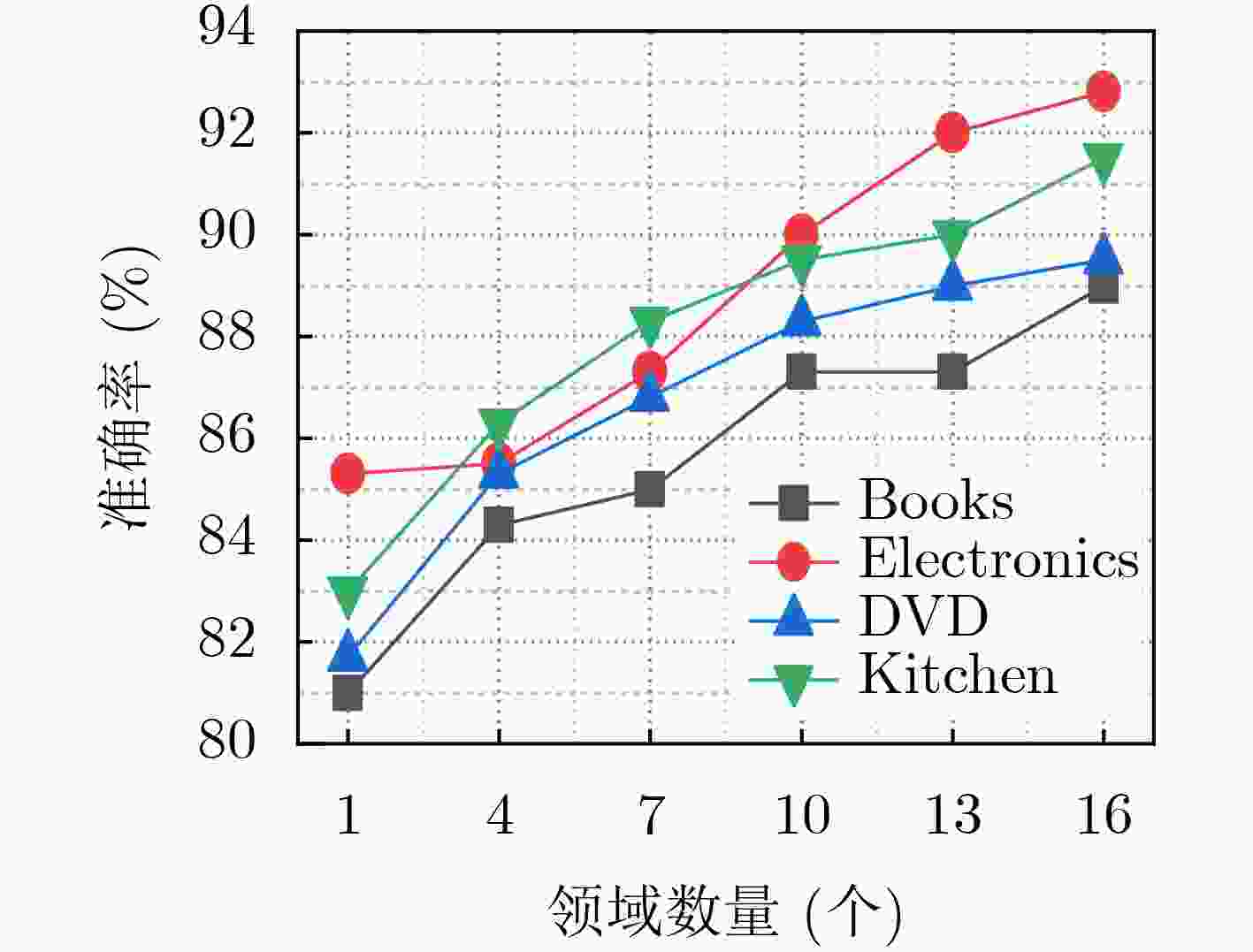
摘要: 文本分类任务中,不同领域的文本很多表达相似,具有相关性的特点,可以解决有标签训练数据不足的问题。采用多任务学习的方法联合学习能够将不同领域的文本利用起来,提升模型的训练准确率和速度。该文提出循环卷积多任务学习(MTL-RC)模型用于文本多分类,将多个任务的文本共同建模,分别利用多任务学习、循环神经网络(RNN)和卷积神经网络(CNN)模型的优势获取多领域文本间的相关性、文本长期依赖关系、提取文本的局部特征。基于多领域文本分类数据集进行丰富的实验,该文提出的循环卷积多任务学习模型(MTL-LC)不同领域的文本分类平均准确率达到90.1%,比单任务学习模型循环卷积单任务学习模型(STL-LC)提升了6.5%,与当前热门的多任务学习模型完全共享多任务学习模型(FS-MTL)、对抗多任务学习模型(ASP-MTL)、间接交流多任务学习框架(IC-MTL)相比分别提升了5.4%, 4%和2.8%。Abstract: In the text classification task, many texts in different domains are similarly expressed and have the characteristics of correlation, which can solve the problem of insufficient training data with labels. The text of different fields can be combined with the multi-task learning method, and the training accuracy and speed of the model can be improved. A Recurrent Convolution Multi-Task Learning (MTL-RC) model for text multi-classification is proposed, jointly modeling the text of multiple tasks, and taking advantage of multi-task learning, Recurrent Neural Network(RNN) and Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) models to obtain the correlation between multi-domain texts, long-term dependence of text. Local features of text are extracted. Rich experiments are carried out based on multi-domain text classification datasets, the Recurrent Convolution Multi-Task Learning(MTL-LC) proposed in this paper has an average accuracy of 90.1% for text classification in different fields, which is 6.5% higher than the single-task learning model STL-LC. Compared with mainstream multi-tasking learning models Full Shared Multi-Task Learning(FS-MTL), Adversarial Multi-Task Learninng(ASP-MTL), and Indirect Communciation for Multi-Task Learning(IC-MTL) have increased by 5.4%, 4%, and 2.8%, respectively.
-
表 1 参数设置
超参数 取值 选择 隐藏层状态维数 50/100/128 100 卷积核大小 1/2/3/4/5 1/2/3 过滤器个数 50/64/100/128/256 100 dropout 0.3/0.4/0.5/0.6/0.7/0.8 0.7 训练次数 10/20/30/40/50 40 批次 8/16/32 16 学习率 0.1/0.01/0.001/0.0005 0.0005 表 2 与其它模型准确率对比(%)
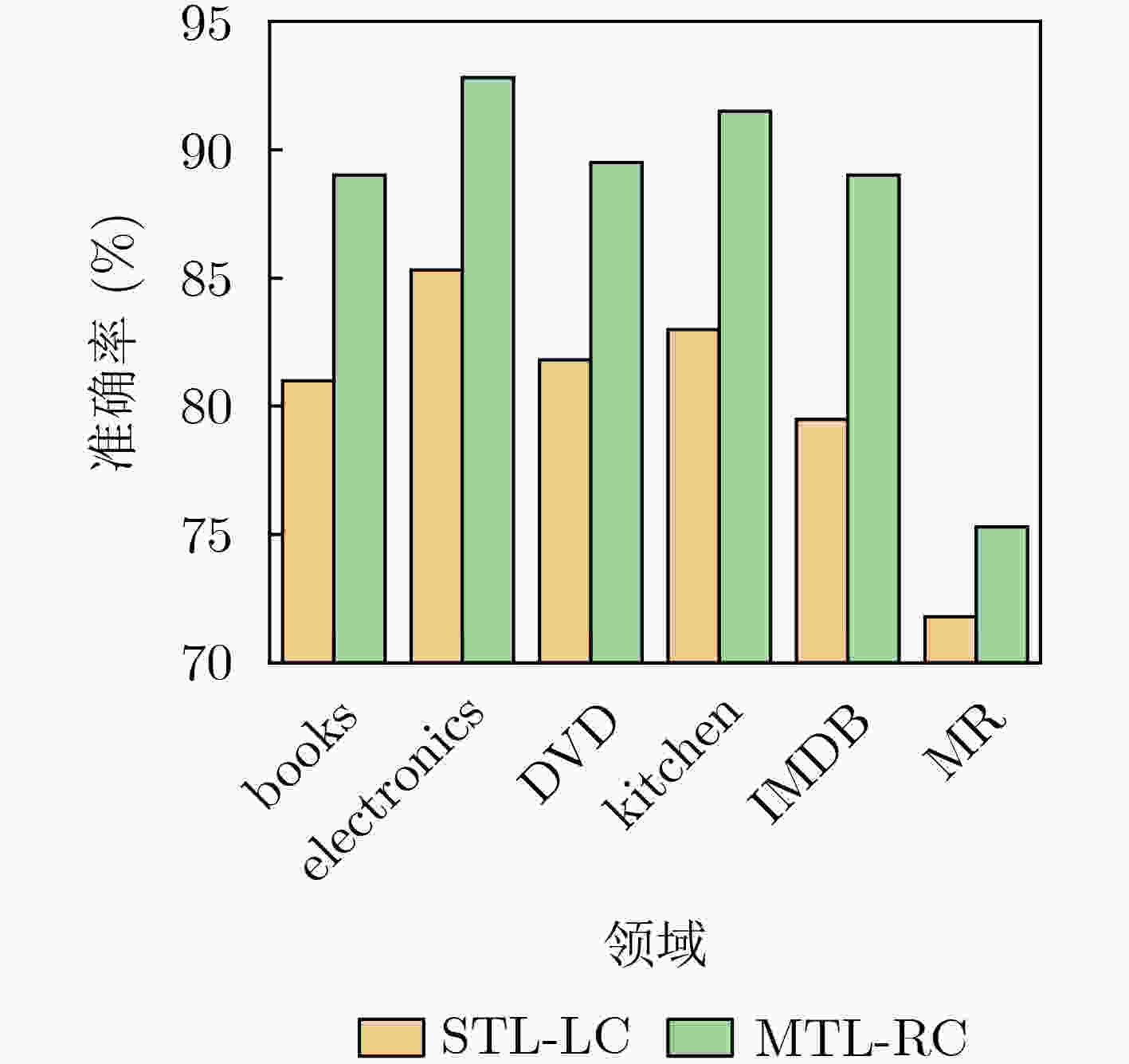
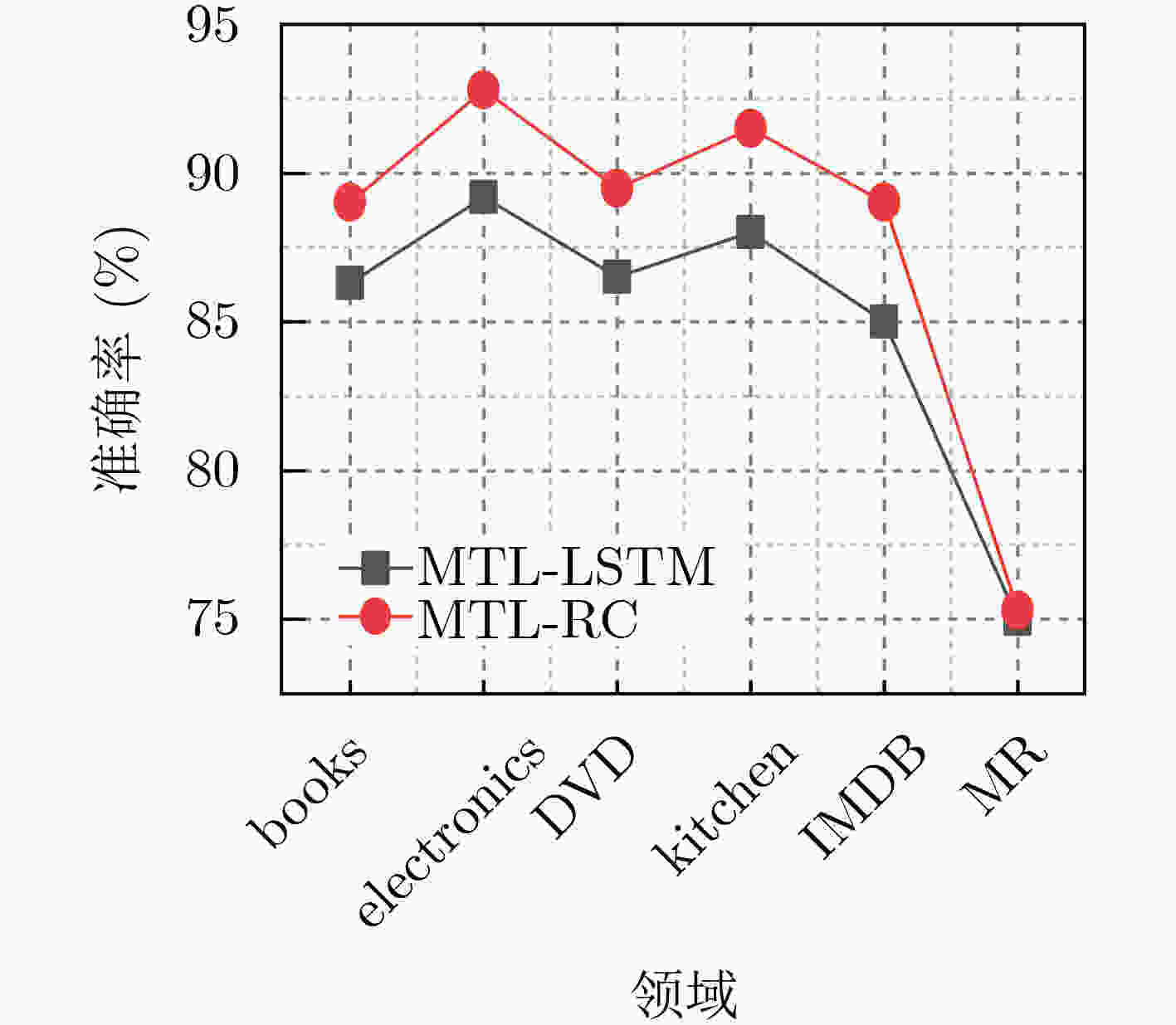
任务 LSTM CNN MTL-DNN MTL-CNN FS-MTL ASP-MTL IC-MTL MTL-RC books 77.8 79.8 82.2 84.5 82.5 84.0 86.2 89.0 electronics 79.8 80.3 81.7 83.2 85.7 86.8 88.5 92.8 DVD 78.0 77.8 84.2 84.0 83.5 85.5 88.0 89.5 kitchen 81.8 78.5 80.7 83.2 86.0 86.2 88.2 91.5 apparel 82.8 82.0 85.0 83.7 84.5 87.0 87.5 89.8 camera 82.5 83.0 86.2 86.0 86.5 89.2 89.0 93.0 health 83.3 84.3 85.7 87.2 88.0 88.2 89.5 92.0 music 77.0 77.8 84.7 83.7 81.2 82.5 85.7 88.0 toys 82.8 80.5 87.7 89.2 84.5 88.0 89.2 91.3 video 85.5 81.8 85.0 81.5 83.7 84.5 86.0 91.0 baby 84.8 81.0 88.0 87.7 88.0 88.2 88.7 91.8 magazines 90.5 86.5 89.5 87.7 92.5 92.2 92.2 93.3 software 84.0 81.5 85.7 86.5 86.2 87.2 87.2 93.3 sports 80.8 81.8 83.2 84.0 85.5 85.7 76.7 91.5 IMDB 76.3 77.5 83.2 86.2 82.5 85.5 86.5 89.0 MR 70.8 67.0 75.5 74.5 74.7 76.7 78.0 75.3 平均数 81.2 80.1 84.3 84.5 84.7 86.1 87.3 90.1 表 3 MTL-LC与STL-LC模型准确率与时间比较
方法 STL-LC MTL-RC 平均准确率(%) 83.6 90.1 平均1次训练的时间(s) 483.4 270.3 表 4 MTL-RC模型使用不同卷积核的准确率对比
卷积核 1 2 3 4 5 (3, 4, 5) (2, 3, 4) (1, 2, 3) 准确率(%) 88.6 89.5 89.2 89.2 89.4 89.3 89.5 90.1 -
[1] 谢金宝, 侯永进, 康守强, 等. 基于语义理解注意力神经网络的多元特征融合中文文本分类[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1258–1265. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170815XIE Jinbao, HOU Yongjin, KANG Shouqiang, et al. Multi-feature fusion based on semantic understanding attention neural network for Chinese text categorization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1258–1265. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170815 [2] KIM Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification[C]. 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 2014: 1746–1751. doi: 10.3115/v1/D14-1181. [3] BLITZER J, DREDZE M, and PEREIRA F. Biographies, Bollywood, boom-boxes and blenders: Domain adaptation for sentiment classification[C]. The 45th Annual Meeting of the Association of Computational Linguistics (ACL), Prague, Czech Republic, 2007: 440–447. [4] CARUANA R. Multitask learning[J]. Machine Learning, 1997, 28(1): 41–75. doi: 10.1023/A:1007379606734 [5] LIU Xiaodong, GAO Jianfeng, HE Xiaodong, et al. Representation learning using multi-task deep neural networks for semantic classification and information retrieval[C]. The 2015 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL), Denver, USA, 2015: 912–921. [6] LIU Pengfei, QIU Xipeng, and HUANG Xuanjing. Recurrent neural network for text classification with multi-task learning[C]. The Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), New York, USA, 2016: 2873–2879. [7] LIU Pengfei, QIU Xipeng, and HUANG Xuanjing. Adversarial multi-task learning for text classification[C]. The 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 1–10. [8] HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [9] 王鑫, 李可, 宁晨, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络和多核学习的遥感图像分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1098–1105. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180628WANG Xin, LI Ke, NING Chen, et al. Remote sensing image classification method based on deep convolution neural network and multi-kernel learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1098–1105. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180628 [10] KALCHBRENNER N, GREFENSTETTE E, and BLUNSOM P. A convolutional neural network for modelling sentences[C]. The 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), Baltimore, USA, 2014: 655–665. [11] 刘宗林, 张梅山, 甄冉冉, 等. 融入罪名关键词的法律判决预测多任务学习模型[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 59(7): 497–504. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2019.21.020LIU Zonglin, ZHANG Meishan, ZHEN Ranran, et al. Multi-task learning model for legal judgment predictions with charge keywords[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University:Science and Technology, 2019, 59(7): 497–504. doi: 10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2019.21.020 [12] COLLOBERT R and WESTON J. A unified architecture for natural language processing: Deep neural networks with multitask learning[C]. The 25th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Helsinki, Finland, 2008: 160–167. [13] LI Shoushan, HUANG Churen, and ZONG Chengqing. Multi-domain sentiment classification with classifier combination[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2011, 26(1): 25–33. doi: 10.1007/s11390-011-9412-y [14] LIU Pengfei, QIU Xipeng, and HUANG Xuanjing. Deep multi-task learning with shared memory for text classification[C]. 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Austin, USA, 2016: 118–127. [15] LIU Pengfei, FU Jie, DONG Yue, et al. Learning multi-task communication with message passing for sequence learning[C]. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Palo Alto, USA, 2019: 4360–4367. [16] YUAN Zhigang, WU Sixing, WU Fangzhao, et al. Domain attention model for multi-domain sentiment classification[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 155: 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.05.004 [17] MAAS A L, DALY R E, PHAM P T, et al. Learning word vectors for sentiment analysis[C]. The 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (ACL), Portland, USA, 2011: 142–150. [18] PANG Bo and LEE L. Seeing stars: Exploiting class relationships for sentiment categorization with respect to rating scales[C]. The 43rd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), Ann Arbor, USA, 2005: 115–124. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
