High Performance Crypto Module with Array of Hardware Engines
-
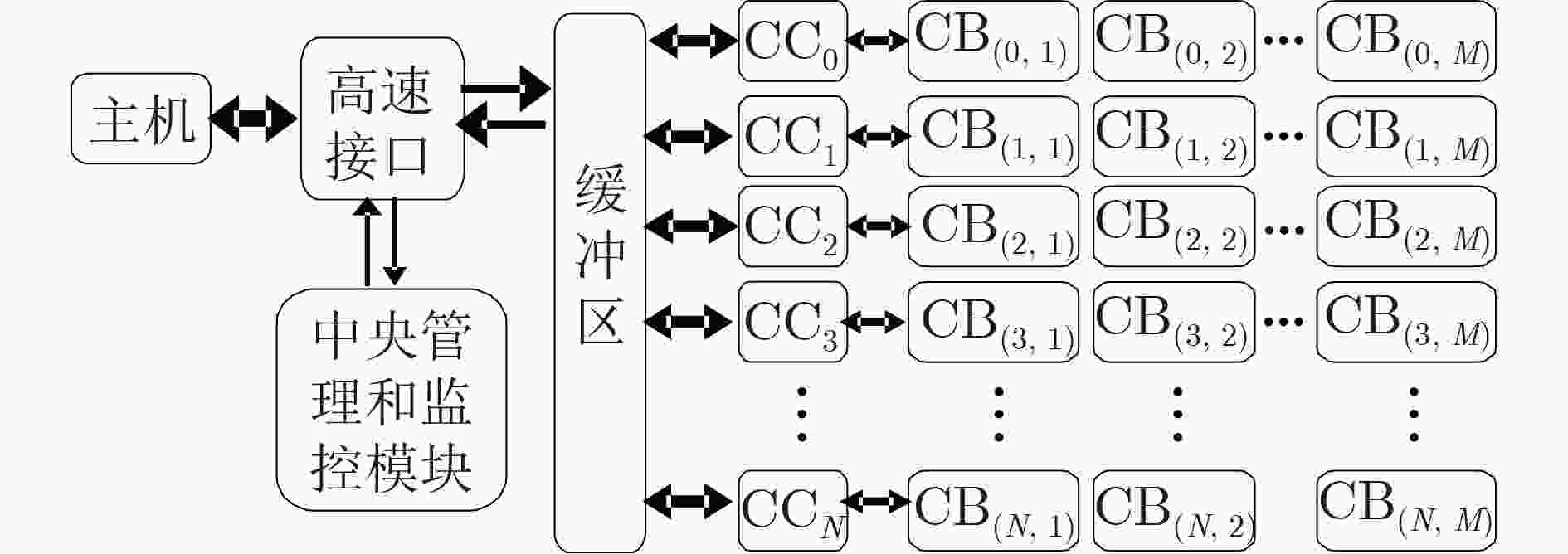
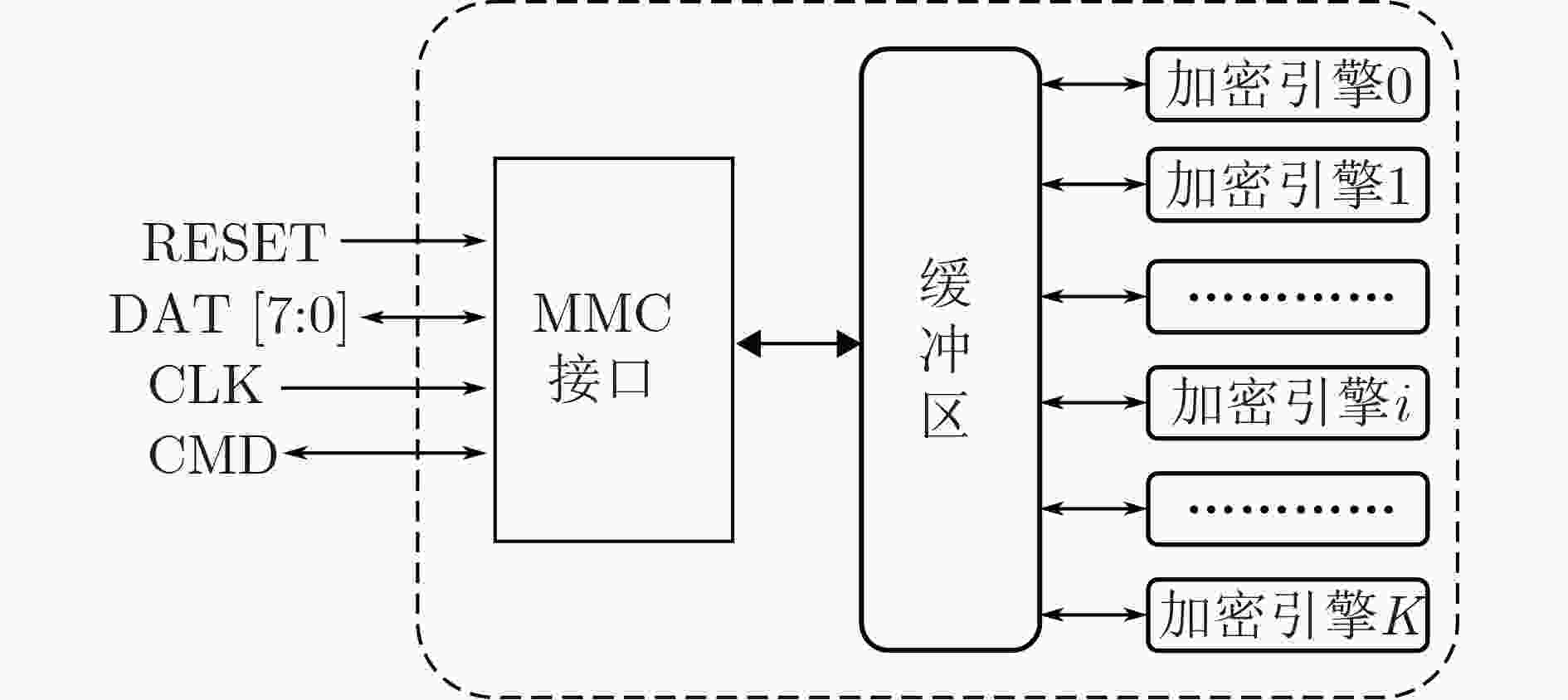
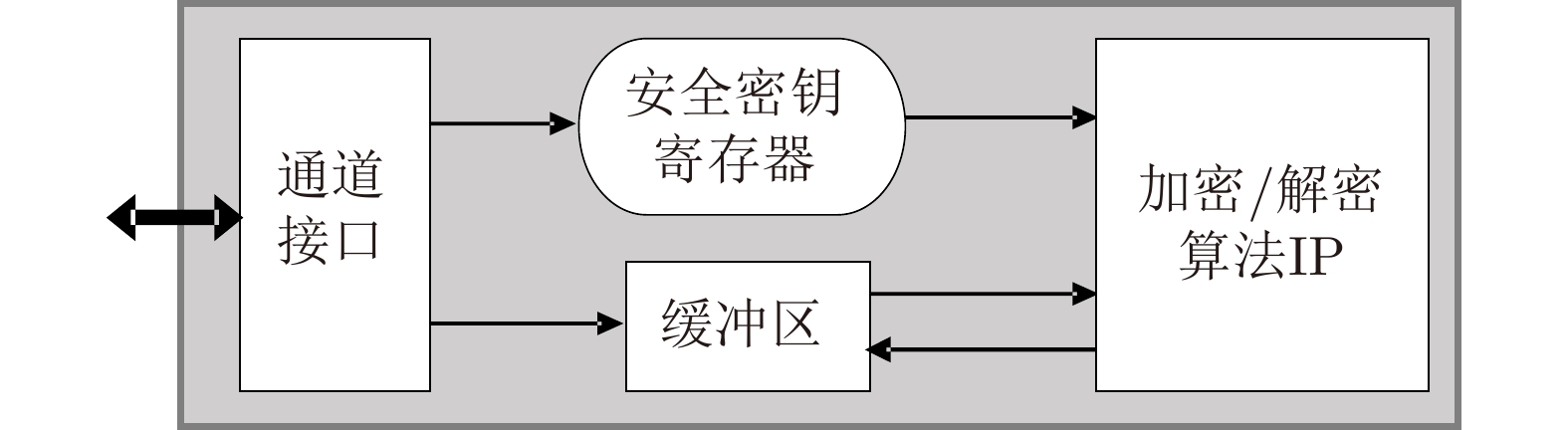
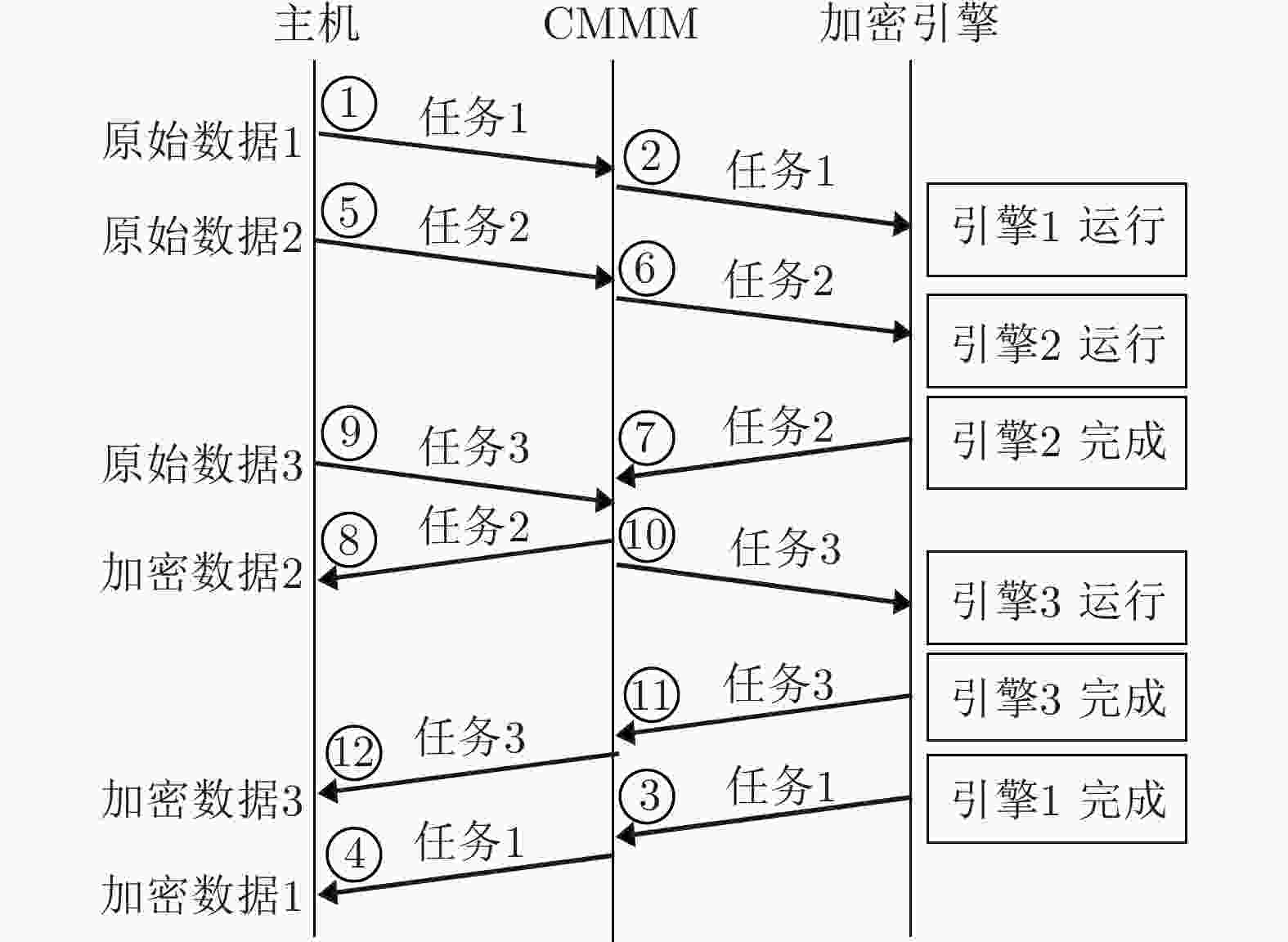
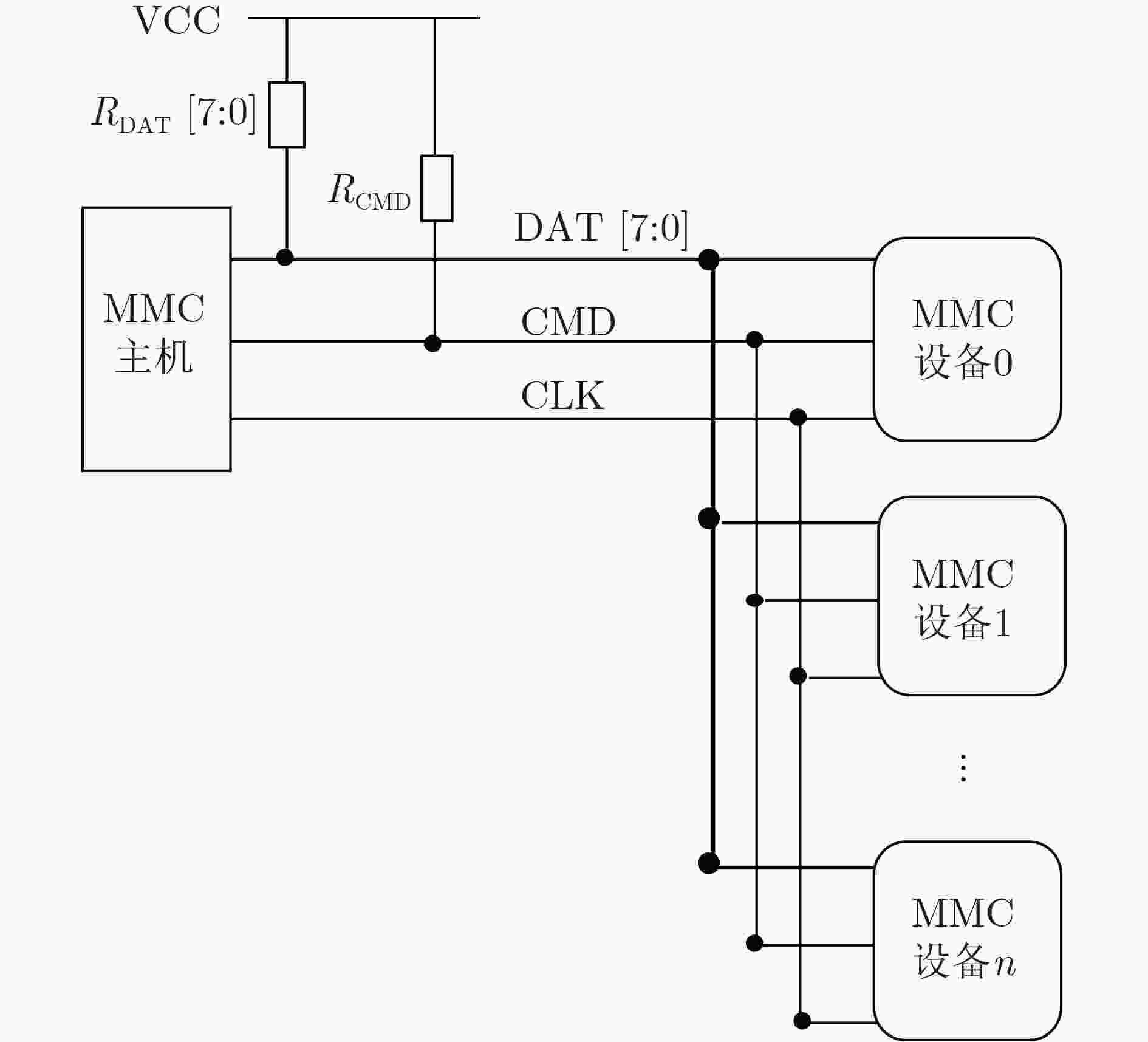
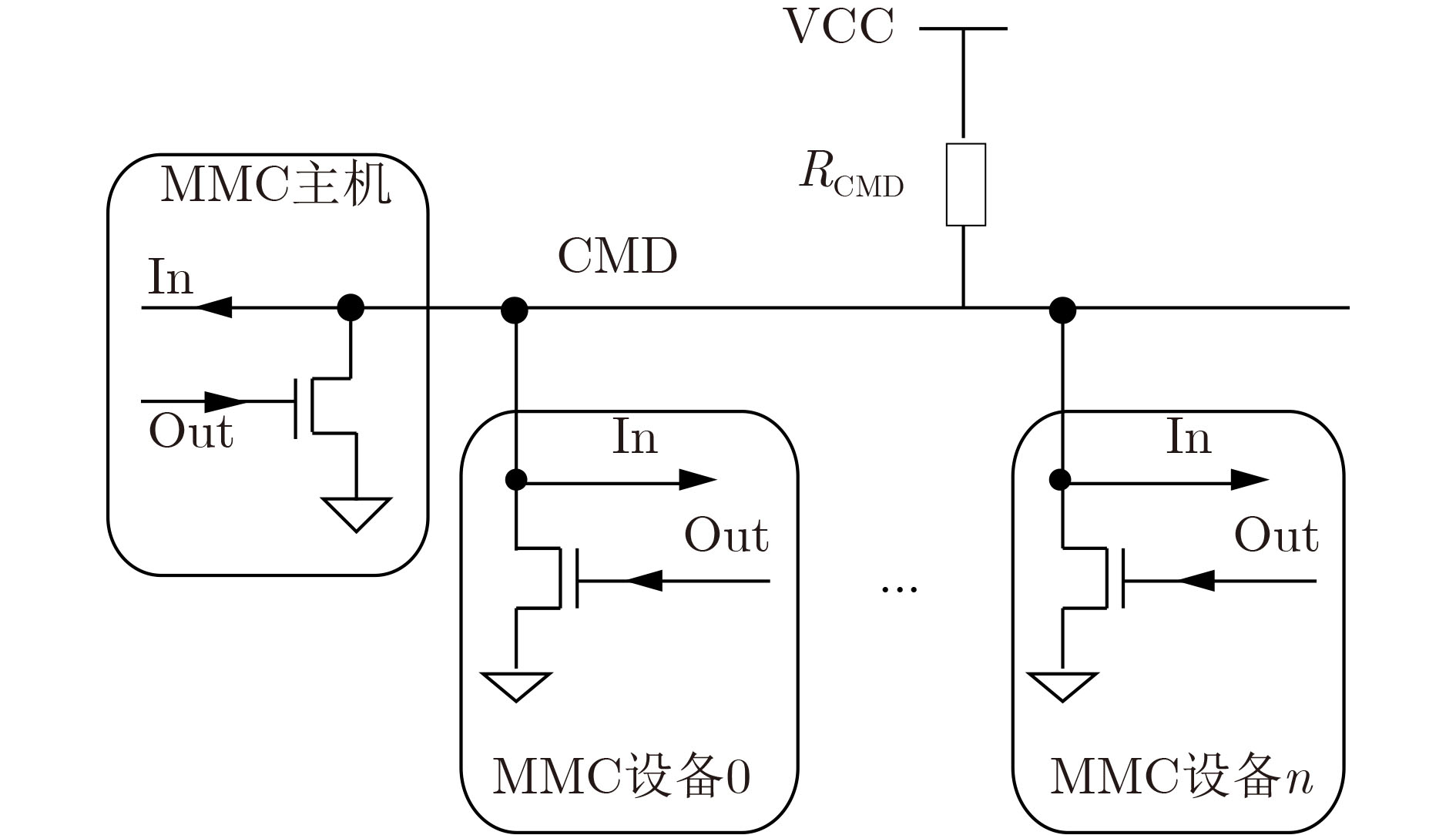
摘要: 该文提出一种高性能硬件加密引擎阵列架构,为大数据应用提供了先进的安全解决方案。该模块架构包括一个高速接口、一个中央管理和监视模块(CMMM)、一组多通道驱动加密引擎阵列,其中CMMM将任务分配给加密引擎,经由专用算法处理后再将数据传回主机。由于接口吞吐量和加密引擎阵列规模会限制模块性能,针对PCIe高速接口,采用MMC/eMMC总线连接构建阵列,发现更多加密引擎集成到系统后,模块性能将会得到提升。为验证该架构,使用55 nm制程工艺完成了一个PCIe Gen2×4接口的ASIC加密卡,测试结果显示其平均吞吐量高达419.23 MB。Abstract: A high-performance crypto module prescribed in this paper offers advanced security solutions in big data applications. A module architecture, which consists of a high throughput interface, Central Manage & Monitor Module (CMMM) and multiple channels driving a group of crypto engines, is discussed here. CMMM distributes the tasks to the crypto engines and guides the data back to the host after processing by the dedicated algorithm. Since the module's performance is limited by the interface throughput and the scale of the crypto engines, an array with MMC/eMMC bus connections is built for PCIe high-speed interfaces. The more crypto engines are integrated into a system, the higher performance of this system can reach. To verify this architecture, an ASIC encryption card with PCIe Gen2×4 interface is made under semiconductor manufacturing process technology of 55 nm, and tested. The average throughput of this card can achieve up to 419.23 MB.
-
表 1 不同情况下的最大总时延(ms)
N=1 N=2 N=4 N=8 M=1 24007 12008 6010 3014 M=8 3014 1522 788 445 表 2 性能测试
#1 #2 #3 #4 连续读(MB/s) 1105.00 1102.00 1103.00 1103.00 连续写(MB/s) 912.60 912.10 912.00 912.20 随机读(k-IOPS) 50.85 84.98 82.83 85.23 随机写(k-IOPS) 105.00 104.75 104.75 104.73 吞吐率(MB/s) 420.00 419.00 419.00 428.92 表 3 随机读写的时延(μs)
平均时延 最大时延 随机读(4 kB) 53 1894 随机写(4 kB) 24 1039 -
[1] SEZER S. T1C: IoT Security: -Threats, security challenges and IoT security research and technology trends[C]. Proceedings of 2018 31st IEEE International System-on-Chip Conference, Arlington, USA, 2018: 1–2. doi: 10.1109/SOCC.2018.8618571. [2] WAZID M, DAS A K, ODELU V, et al. Secure remote user authenticated key establishment protocol for smart home environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2020, 17(2): 391–406. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2017.2764083 [3] 闫宏强, 王琳杰. 物联网中认证技术研究[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(7): 213–222. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020131YAN Hongqiang and WANG Linjie. Research of authentication techniques for the Internet of things[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(7): 213–222. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020131 [4] 纪兆轩, 杨秩, 孙瑜, 等. 大数据环境下SHA1的GPU高速实现[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(2): 75–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2020.02.010JI Zhaoxuan, YANG Zhi, SUN Yu, et al. GPU high speed implementation of SHA1 in big data environment[J]. Netinfo Security, 2020, 20(2): 75–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2020.02.010 [5] 孙婷婷, 黄皓, 王嘉伦, 等. 面向CPU-GPU异构系统的数据分析负载均衡策略[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2019, 41(3): 417–423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2019.03.005SUN Tingting, HUANG Hao, WANG Jialun, et al. A load balancing strategy on heterogeneous CPU-GPU data analytic systems[J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2019, 41(3): 417–423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2019.03.005 [6] MENEZES A J, VAN OORSCHOT P C, and VANSTONE S A. Handbook of Applied Cryptography[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1996: 433–446. [7] HANKERSON D, MENEZES A J, and VANSTONE S. Guide to Elliptic Curve Cryptography[M]. New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2004: 6–14. [8] Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 197. Advanced encryption standard (AES)[S]. 2001. [9] BUDRUK R, ANDERSON D, and SHANLEY T. PCI Express System Architecture[M]. Boston: Addison-Wesley Professional, 2004: 9–11. [10] 刘金峒, 梁科, 王锦, 等. SM4加密算法可裁剪式结构设计与硬件实现[J]. 南开大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 52(4): 41–45.LIU Jintong, LIANG Ke, WANG Jin, et al. Cuttable structure design and hardware implementation of SM4 encryption algorithm[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 52(4): 41–45. [11] SUHAILI S B and WATANABE T. Design of high-throughput SHA-256 hash function based on FPGA[C]. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Langkawi, Malaysia, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICEEI.2017.8312449. [12] 赵军, 曾学文, 郭志川. 支持国产密码算法的高速PCIe密码卡的设计与实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(10): 2402–2408. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190003ZHAO Jun, ZENG Xuewen, and GUO Zhichuan. Design and implementation of high speed PCIe cipher card supporting GM algorithms[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(10): 2402–2408. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190003 [13] JEDEC. JESD 84-B50 Embedded multi-media card (e·MMC) electrical standard (5.0)[S]. Arlington: JEDEC Solid State Technology Association, 2013. [14] Motorola, Inc. SPI block guide V03.06[S]. Motorola Inc. , 2001. [15] Serial ATA International Organization. Serial ATA revision 3.0[S]. Serial ATA International Organization, 2009. [16] PATTERSON D A, GIBSON G, and KATZ R H. A case for redundant arrays of inexpensive disks (RAID)[C]. Proceedings of the 1988 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Chicago, USA, 1988: 109–116. doi: 10.1145/50202.50214. [17] CHANG Lipin and KUO T W. An adaptive striping architecture for flash memory storage systems of embedded systems[C]. Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium, San Jose, USA, 2002: 187–196. doi: 10.1109/RTTAS.2002.1137393. [18] REDDY A K, PARAMASIVAM P, and VEMULA P B. Mobile secure data protection using eMMC RPMB partition[C]. Proceedings of 2015 International Conference on Computing and Network Communications, Trivandrum, India, 2015: 946–950. doi: 10.1109/CoCoNet.2015.7411305. [19] GREMBOWSKI T, LIEN R, GAJ K, et al. Comparative analysis of the hardware implementations of hash functions SHA-1 and SHA-512[C]. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Security, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2002: 75–89. doi: 10.1007/3-540-45811-5_6. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
