Evaporation Characteristics of Oxygen Free Copper for Microwave Vacuum Electron Devices
-
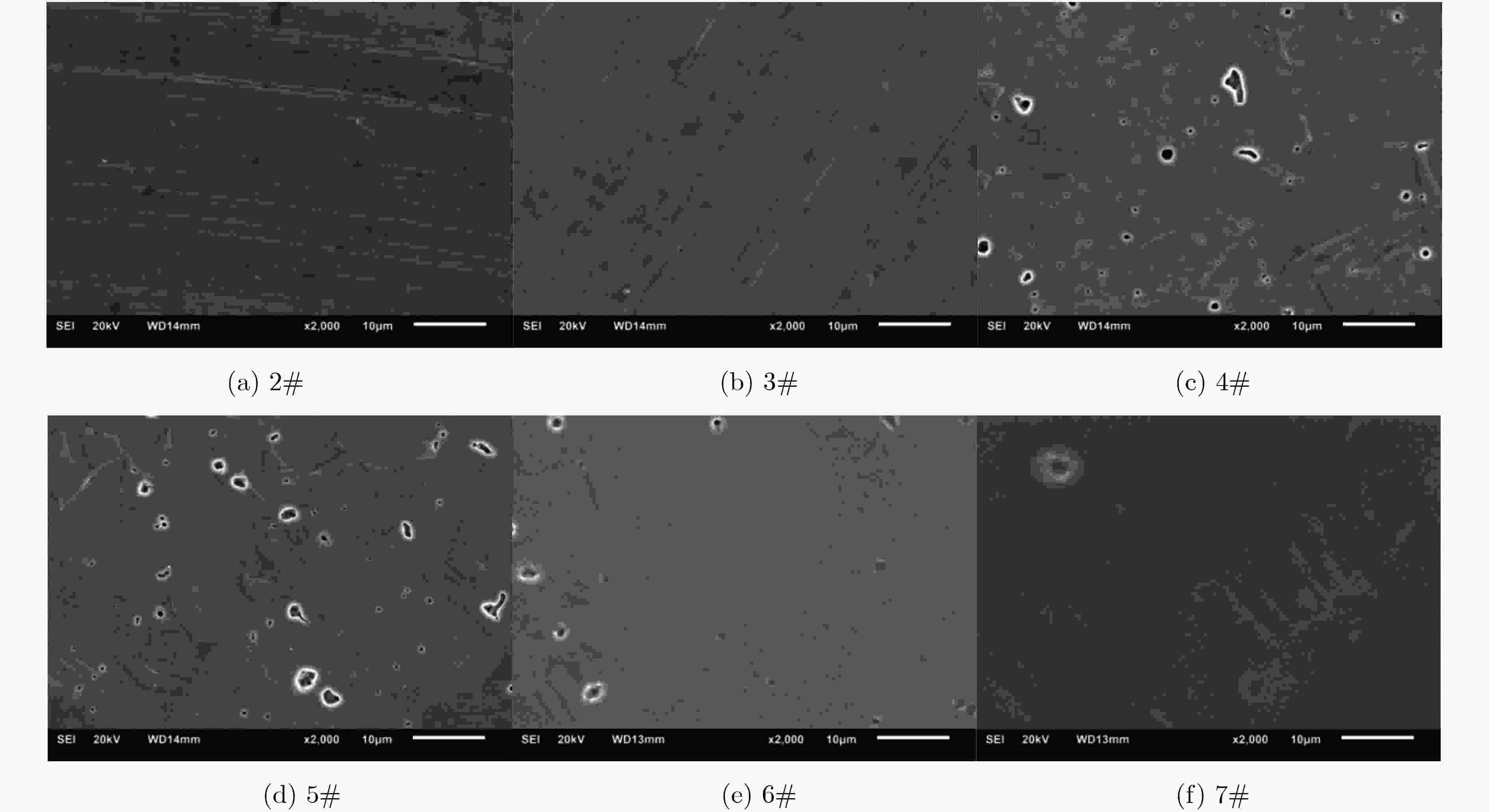
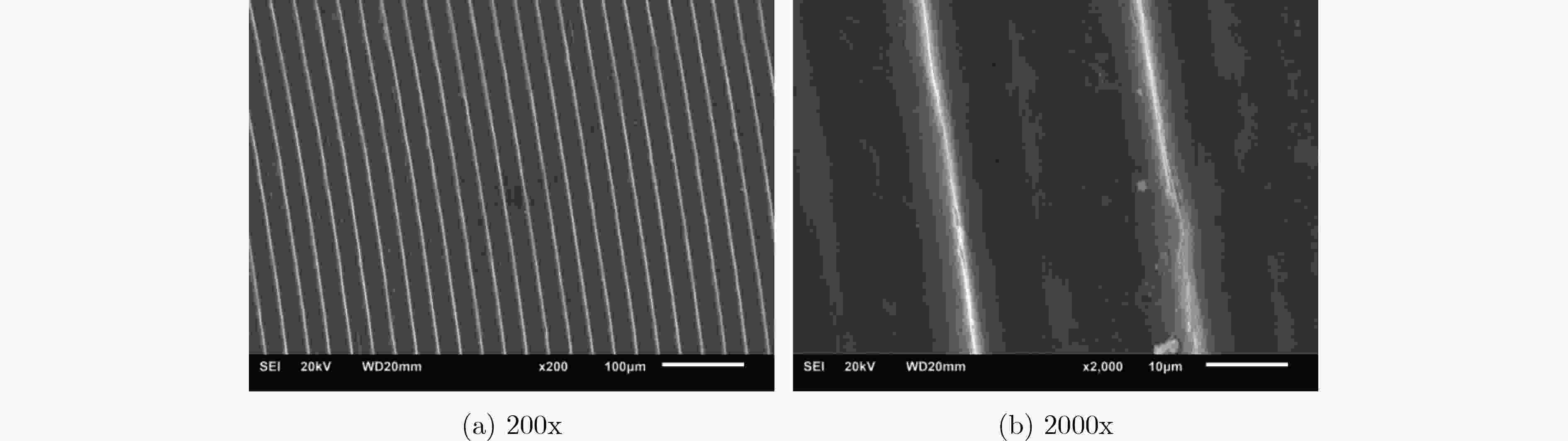
摘要: 作为微波真空电子器件的常用材料之一,无氧铜材料的蒸发特性会对微波真空电子器件的电性能产生影响。该文利用超高真空测试设备,研究了处理工艺对无氧铜材料的蒸发性能的影响,采用X射线测厚仪测试了蒸发的铜膜厚度,用扫描电镜(SEM)观测了无氧铜材料的表面形貌。结果表明表面宏观形貌粗糙度对无氧铜材料的蒸发性能影响不大,但处理工艺对蒸发性能影响很大;无氧铜材料经过酸洗后,会大大增加蒸发量;无氧铜材料经过烧氢处理,可降低蒸发量,而经过去油清洗并烧氢处理的无氧铜的蒸发量极低。对无氧铜材料进行了表面分析,发现无氧铜材料的真空蒸发性能与材料的表面形貌状态有关,当表面微观形貌比较光滑、无孔洞等缺陷时,无氧铜材料的真空蒸发量就少。Abstract: As one of the commonly used materials for microwave vacuum electronic devices, the evaporation characteristics of oxygen free copper materials will affect the electrical properties of microwave vacuum electronic devices. In this paper, the effect of treatment process on the evaporation performance of oxygen free copper is studied by using ultra-high vacuum testing equipment. The thickness of evaporated copper film is measured by X-ray thickness gauge. And the surface morphology of oxygen free copper is observed by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). The results show that the macro-appearance surface roughness has little effect on the evaporation performance of oxygen free copper materials, but the treatment process has a great influence on the evaporation performance. The evaporation capacity of oxygen free copper will be increased after acid pickling and the evaporation capacity of oxygen free copper materials can be reduced by calcination in hydrogen. The evaporation capacity of oxygen free copper treated by deoiling cleaning and calcination in hydrogen is very low. The surface of oxygen free copper is analyzed. It is found that the vacuum evaporation performance of oxygen free copper material is related to the surface morphology of the material. The microscopic surface is smooth without oxidation and holes, and the vacuum evaporation of oxygen free copper material is less.
-
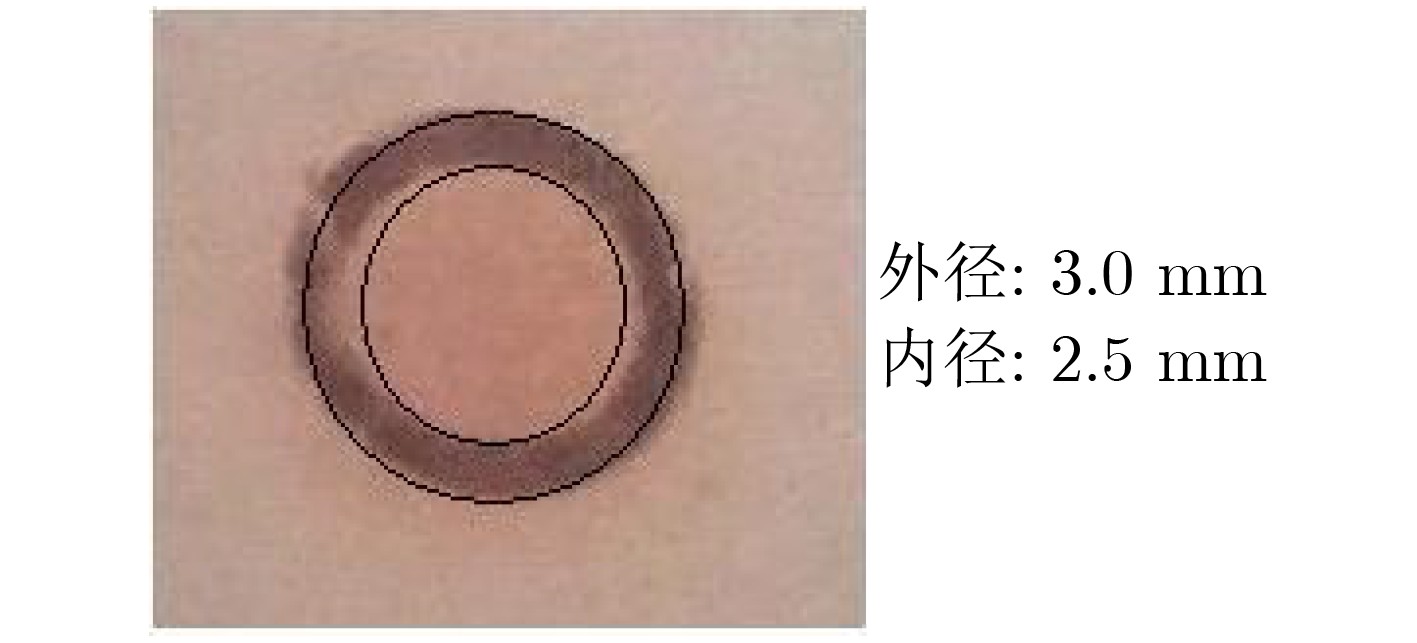
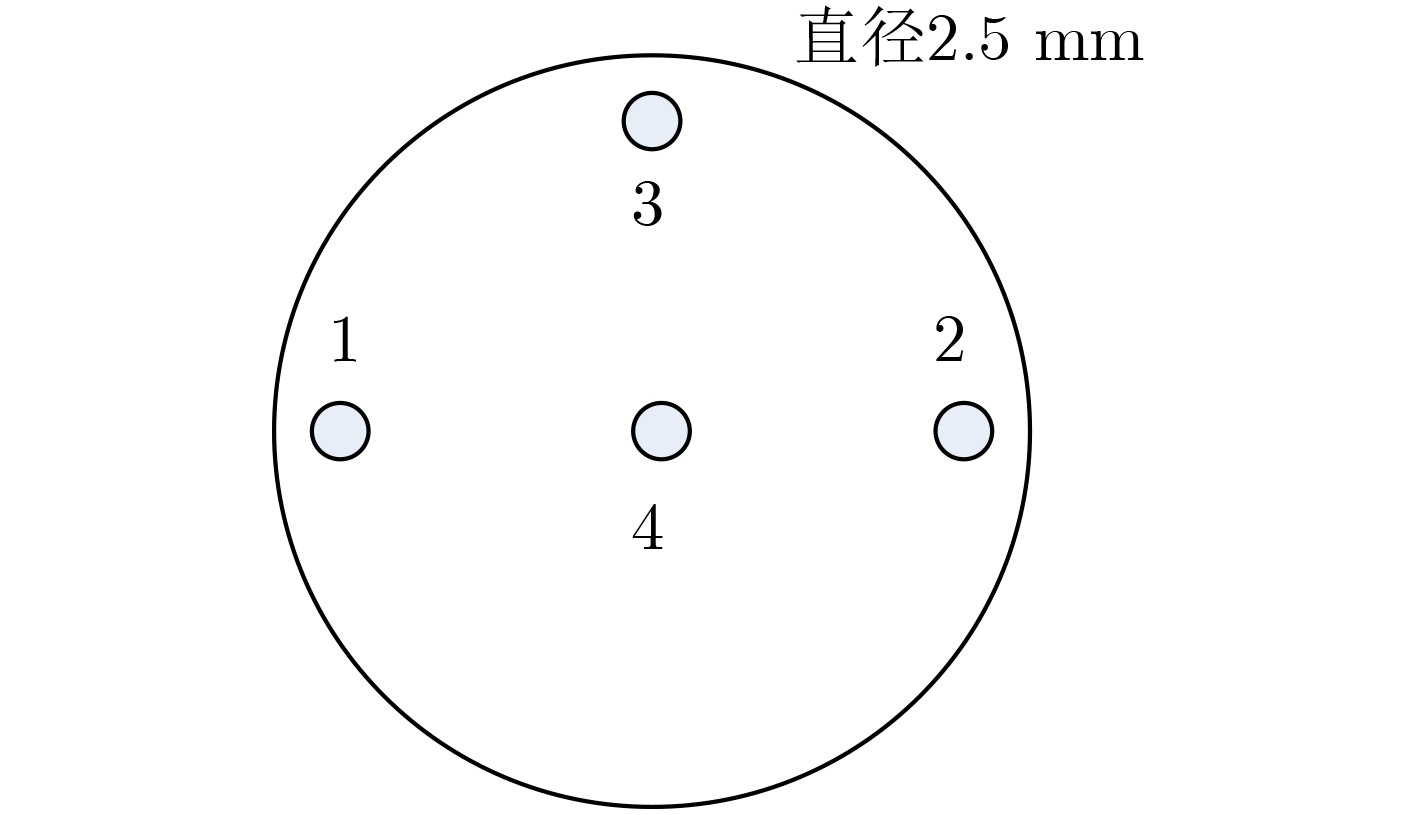
表 1 无氧铜的状态、处理过程及对应的钼片上沉积的铜膜厚度
样品编号 样品处理过程及状态 铜膜厚度(μm) 粗糙度 清洗方式 烧氢温度及时间 位置1 位置2 位置3 位置4 平均厚度 1# Ra0.8 去油 / 0.50 0.46 0.48 0.54 0.495 2# Ra1.6 去油 / 0.52 0.49 0.55 0.56 0.530 3# Ra1.6 去油 600 ℃, 10 min 0 0 0 0 0 4# Ra1.6 去油并酸洗 / 0.94 0.87 0.94 0.98 0.933 5# Ra1.6 去油并酸洗 600 ℃, 10 min 0.22 0.21 0.20 0.24 0.218 6# Ra1.6 去油并酸洗 800 ℃, 10 min 0.12 0.13 0.11 0.16 0.130 7# Ra1.6 去油并酸洗 920 ℃, 10 min 0.06 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.060 -
[1] LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, LU Yuxin, et al. Influences of diamond material on heat dissipation capabilities of helical slow wave structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2019, 66(12): 5321–5326. doi: 10.1109/TED.2019.2945969 [2] LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, HAN Yong, et al. Temperature variation of a thermionic cathode during electron emission[J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2008, 51(9): 1497–1501. doi: 10.1007/s11431-008-0161-2 [3] 刘燕文, 王小霞, 田宏, 等. 纳米粒子薄膜热电子发射性能[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2015, 45(1): 145–156. doi: 10.1360/N112013-00201LIU Yanwen, WANG Xiaoxia, TIAN Hong, et al. Study on emission properties of the nanopatical films[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2015, 45(1): 145–156. doi: 10.1360/N112013-00201 [4] SHIN Y M, BARNETT L R, GAMZINA D, et al. Terahertz vacuum electronic circuits fabricated by UV lithographic molding and deep reactive ion etching[J]. Applied Physics Letter, 2009, 95(18): 181505. doi: 10.1063/1.3259823 [5] 刘燕文, 田宏, 陆玉新, 等. 用于浸渍阴极的钨海绵基体的净化[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2018, 38(2): 144–149. doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2018.02.12LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, LU Yuxin, et al. Purificationand cleaning of spongy tungsten disc used as impregnated dispenser-cathode in vacuum[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2018, 38(2): 144–149. doi: 10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2018.02.12 [6] DAYTON J A, MEARINI G T, CHEN H, et al. Diamond-studded helical traveling wave tube[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2005, 52(5): 695–701. doi: 10.1109/TED.2005.845863 [7] SENGELE S, JIANG Hongrui, BOOSKE J H, et al. Microfabrication and characterization of a selectively metallized W-band meander-line TWT circuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2009, 56(5): 730–737. doi: 10.1109/TED.2009.2015416 [8] 刘燕文, 田宏, 韩勇, 等. 支取发射电流过程对热阴极温度影响的研究[J]. 中国科学E辑: 技术科学, 2008, 38(9): 1515–1520.LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, HAN Yong, et al. Study on the influence of discharge current on hot cathode temperature[J]. China Science E, 2008, 38(9): 1515–1520. [9] WANG Jinshu, ZHANG Xizhu, LIU Wei, et al. High current density Sc2O3-W matrix dispenser cathode[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2012, 55(1): 98–105. doi: 10.1007/s11432-011-4518-y [10] WANG Xiaoxia, LIAO Xianheng, LUO Jirun, et al. Study on the Ni-Re-Ir sponge oxide cathode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2012, 59(2): 492–495. [11] 刘燕文, 田宏, 韩勇, 等. 新型的覆纳米粒子薄膜阴极的研究[J]. 物理学报, 2009, 58(12): 8635–8642. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2009.12.081LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, HAN Yong, et al. Emission properties of impregnated cathode with nanoparticle films[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2009, 58(12): 8635–8642. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2009.12.081 [12] LI Ji, YU Zhiqiang, SHAO Wensheng, et al. High current density M-type cathodes for vacuum electron devices[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2005, 251(1/4): 151–158. [13] WANG Xiaoxia, LIAO Xianheng, LUO Qinglan, et al. Performance of an oxide cathode prepared from submicrometer carbonates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2011, 58(9): 3195–3199. doi: 10.1109/TED.2011.2158648 [14] 电子工业生产技术手册编委会. 电子工业生产技术手册(4)[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1990: 317.Editorial Board of Production Technical Manual for Electronic Industry. Technical Manual for Electronic Industry (4)[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1990: 317. [15] 刘燕文, 田宏, 韩勇, 等. 利用飞行时间质谱研究热阴极蒸发特性[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2007, 27(5): 437–441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7126.2007.05.017LIU Yanwen, TIAN Hong, HAN Yong, et al. Time of flight mass spectroscopy study of thermonic cathode evaporation[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2007, 27(5): 437–441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7126.2007.05.017 [16] 刘燕文, 王小霞, 陆玉新, 等. 用于电真空器件的金属材料蒸发特性[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(6): 068502. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.068502LIU Yanwen, WANG Xiaoxia, LU Yuxin, et al. Study on evaporation from alloys used in microwave vacuum electron devices[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(6): 068502. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.068502 [17] 周安林, 刘建伟, 李建峰, 等. 超导材料用无氧铜表面洁净化清洗工艺研究[J]. 低温物理学报, 2010, 32(2): 91–95.ZHOU Anlin, LIU Jianwei, LI Jianfeng, et al. Cleaning progress research of the oxygen-free copperfor superconducting materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2010, 32(2): 91–95. [18] 周安林, 陈江, 刘建伟, 等. 超导材料用无氧铜过硫酸钠溶液清洗工艺研究[J]. 低温物理学报, 2013, 35(4): 282–287.ZHOU Anlin, CHEN Jiang, LIU Jianfei, et al. Sodium persulfate solution cleaning progress research of the oxygen-free copper for superconducting materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2013, 35(4): 282–287. [19] 周安林. 无氧铜表面特定清洗液的腐蚀机制及溶液特性[J]. 表面技术, 2017, 46(1): 229–233. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2017.01.037ZHOU Anlin. Corrosion mechanism and solution properties of specific cleaning solution for oxygen-free copper surface[J]. Surface Technology, 2017, 46(1): 229–233. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2017.01.037 -





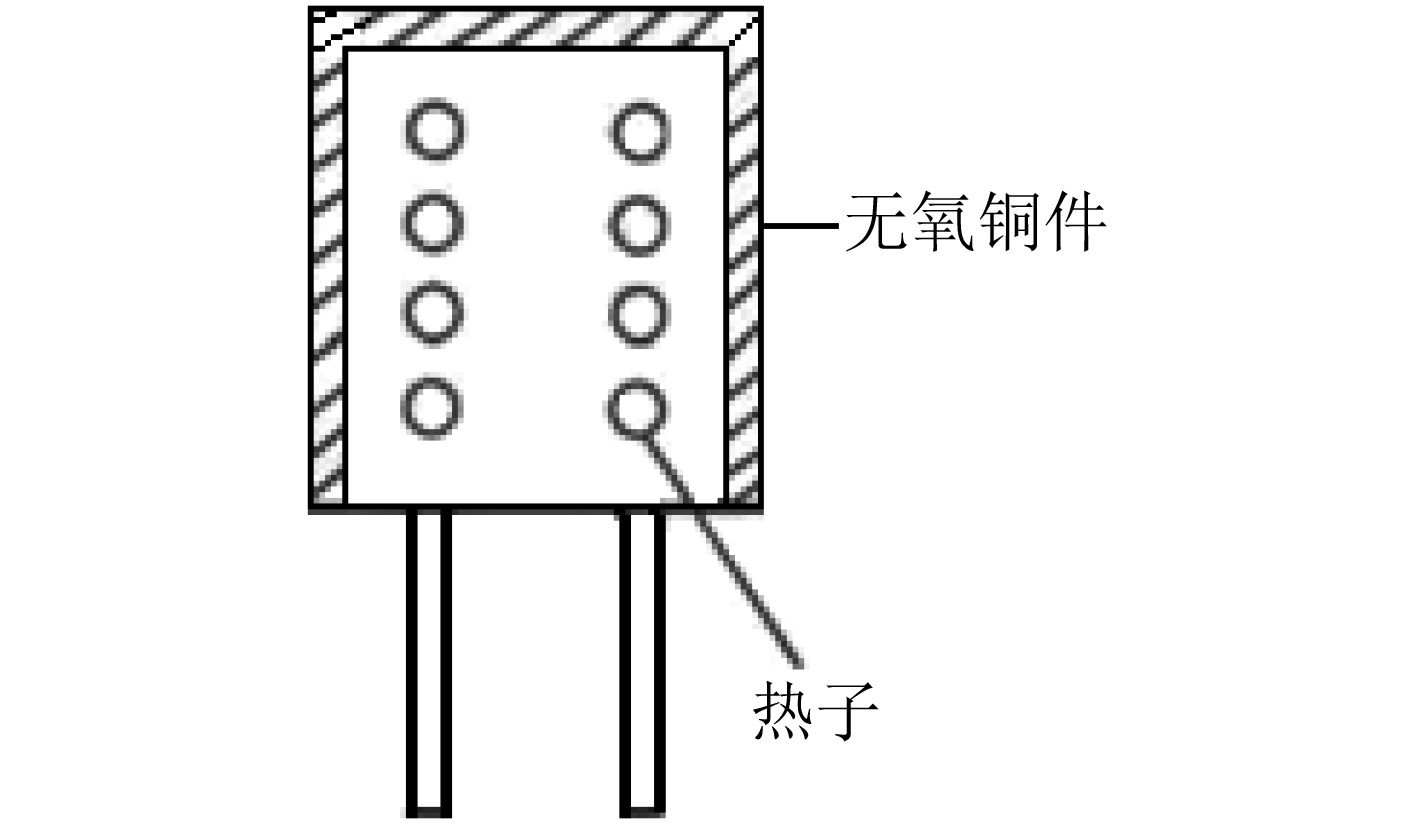
 下载:
下载:
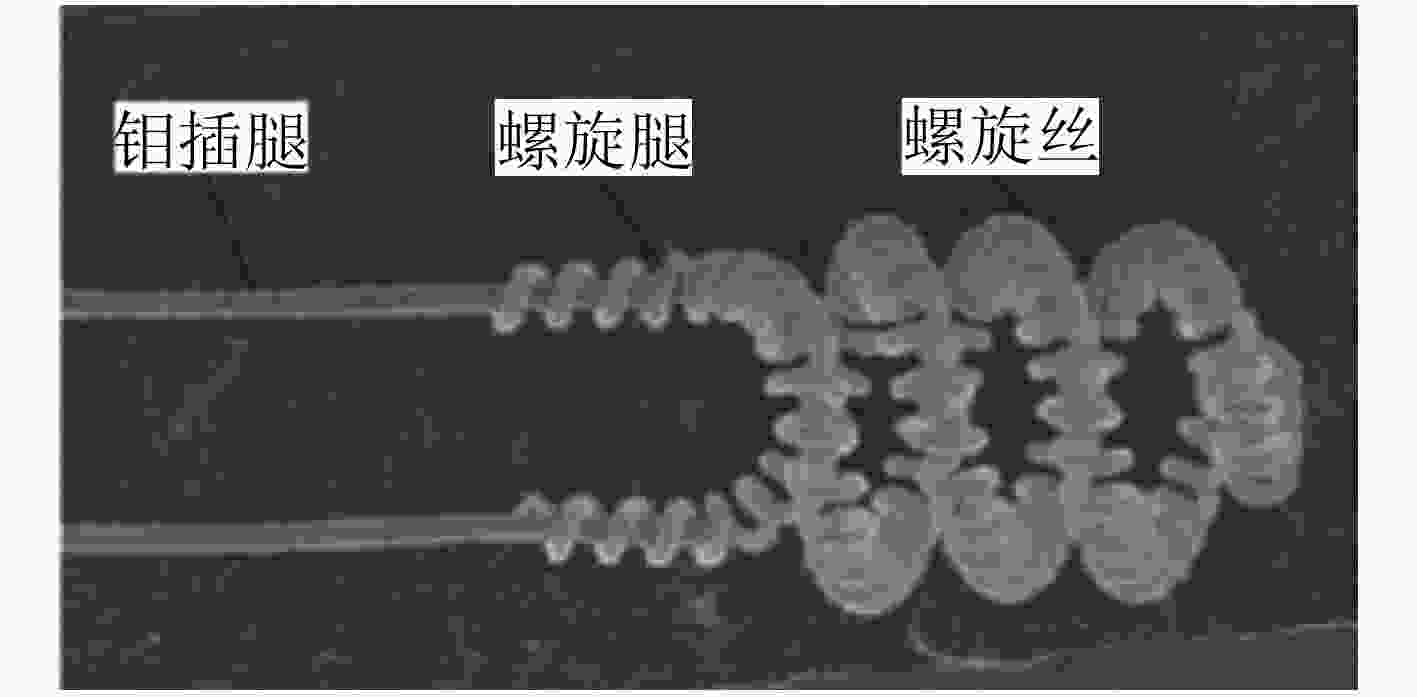
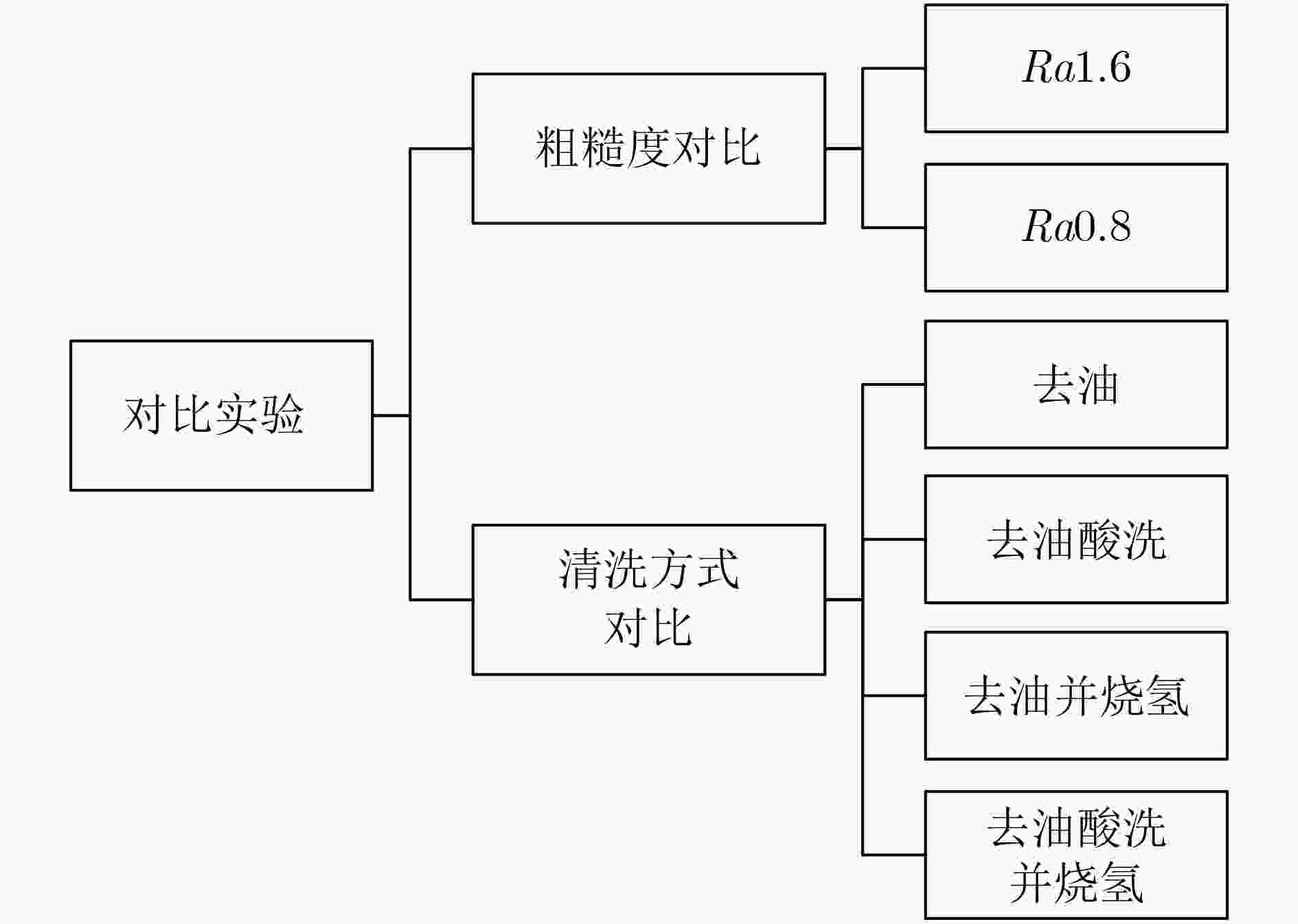
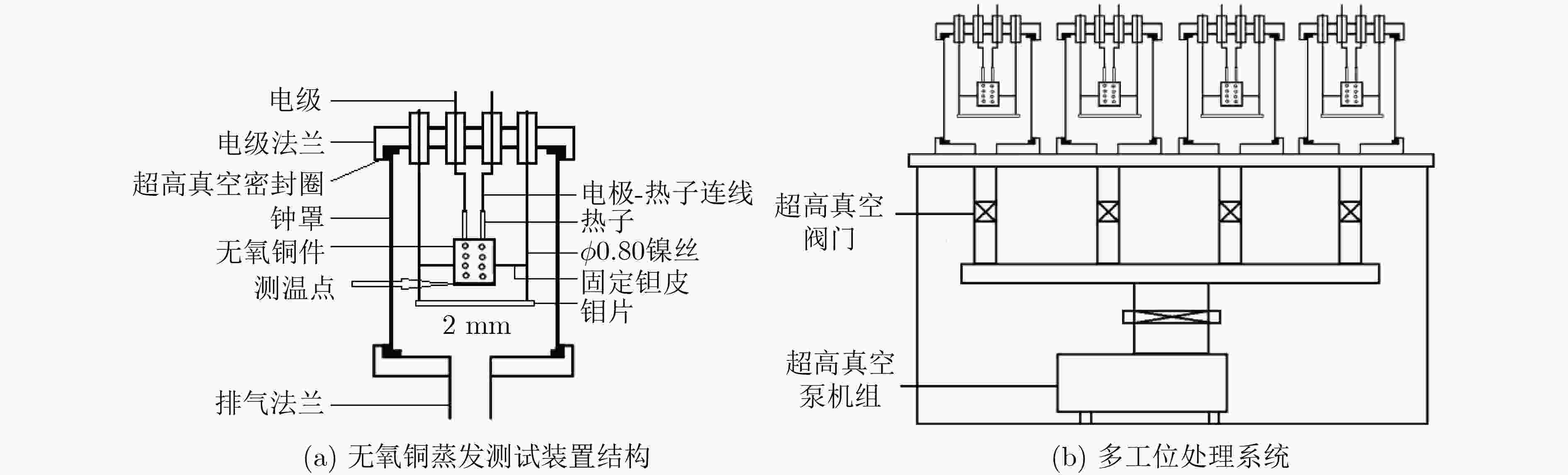


 下载:
下载:
