A Low-complexity Decoding Algorithm Based on Parity-Check-Concatenated Polar Codes
-
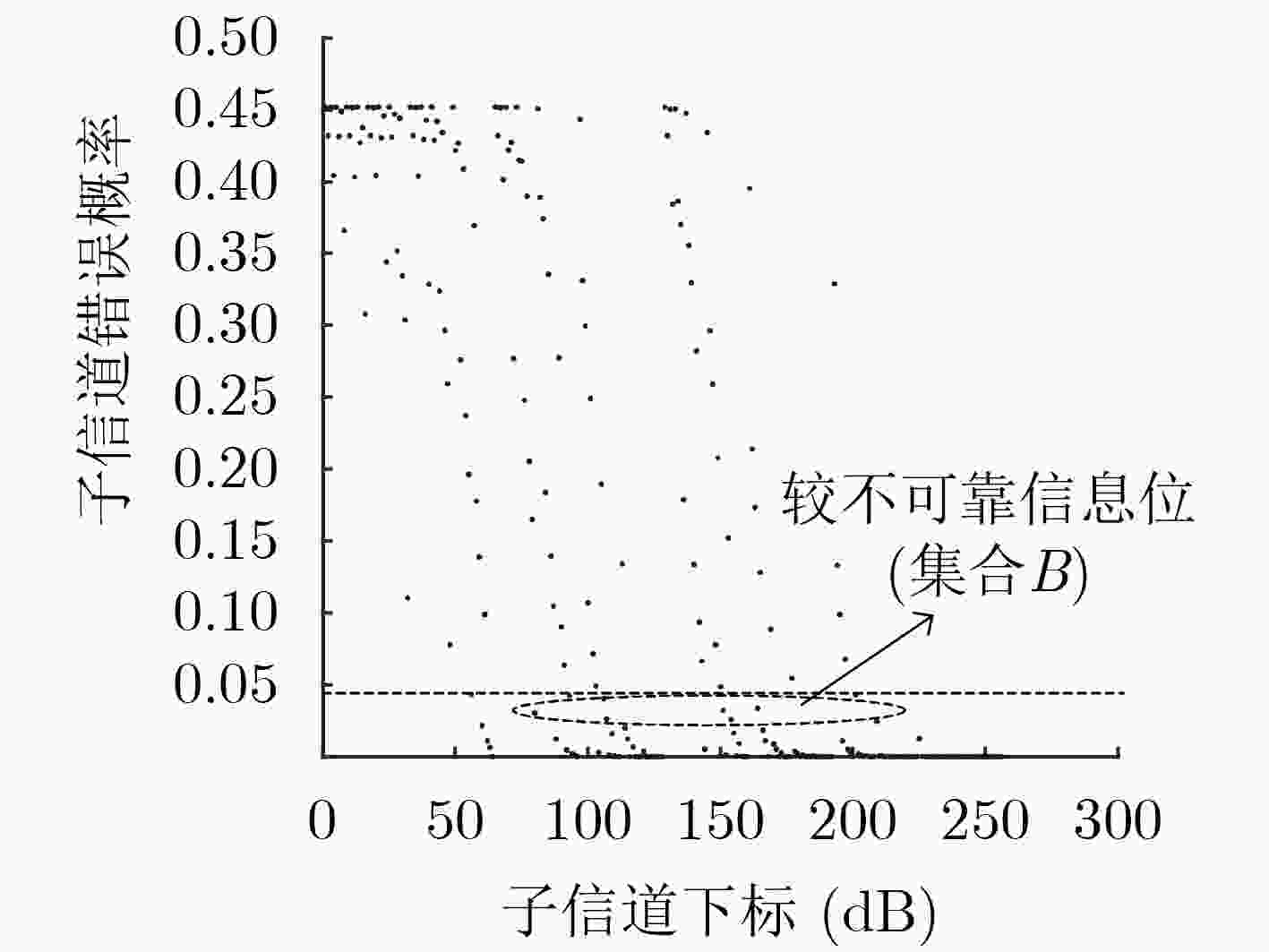
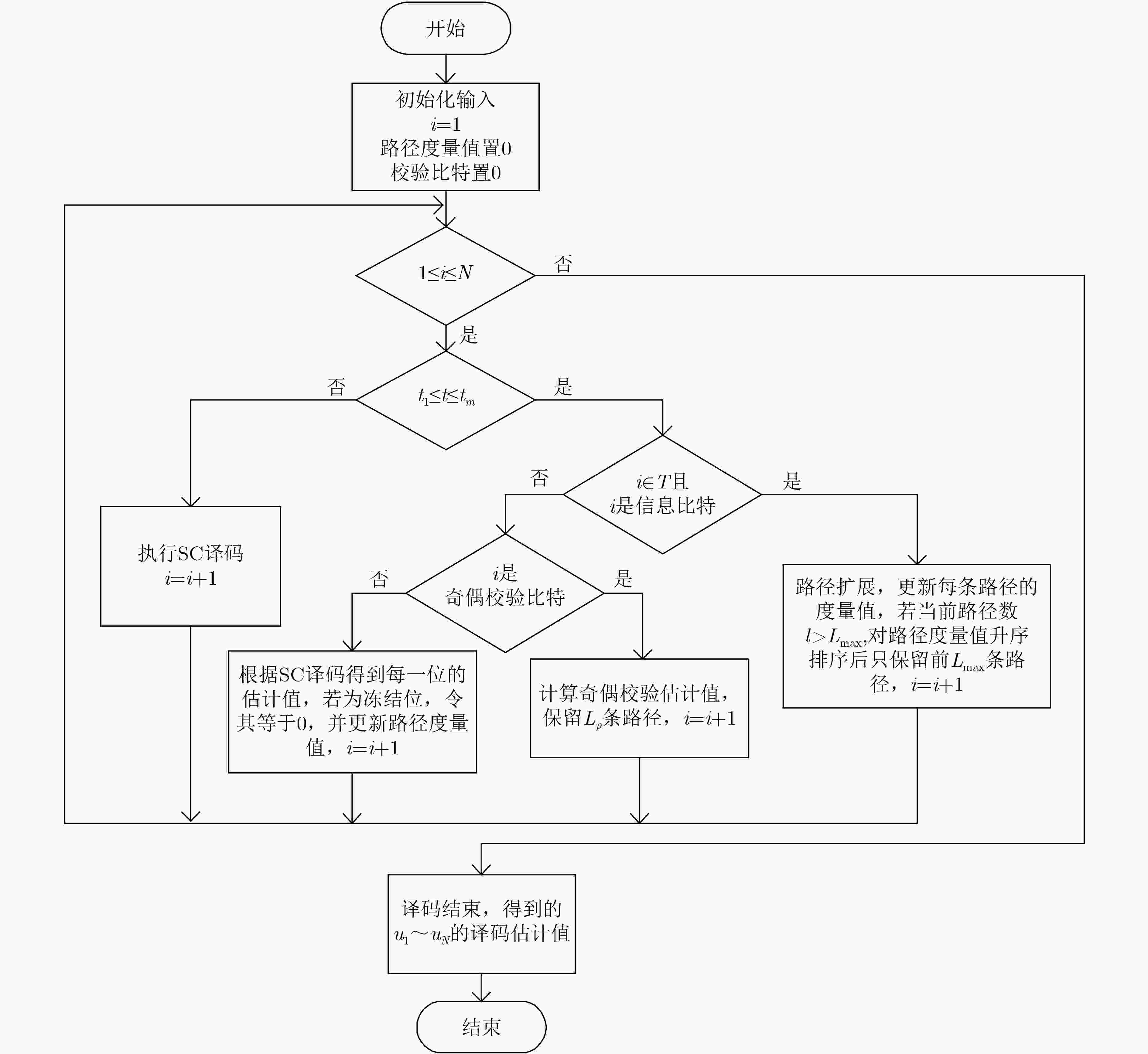
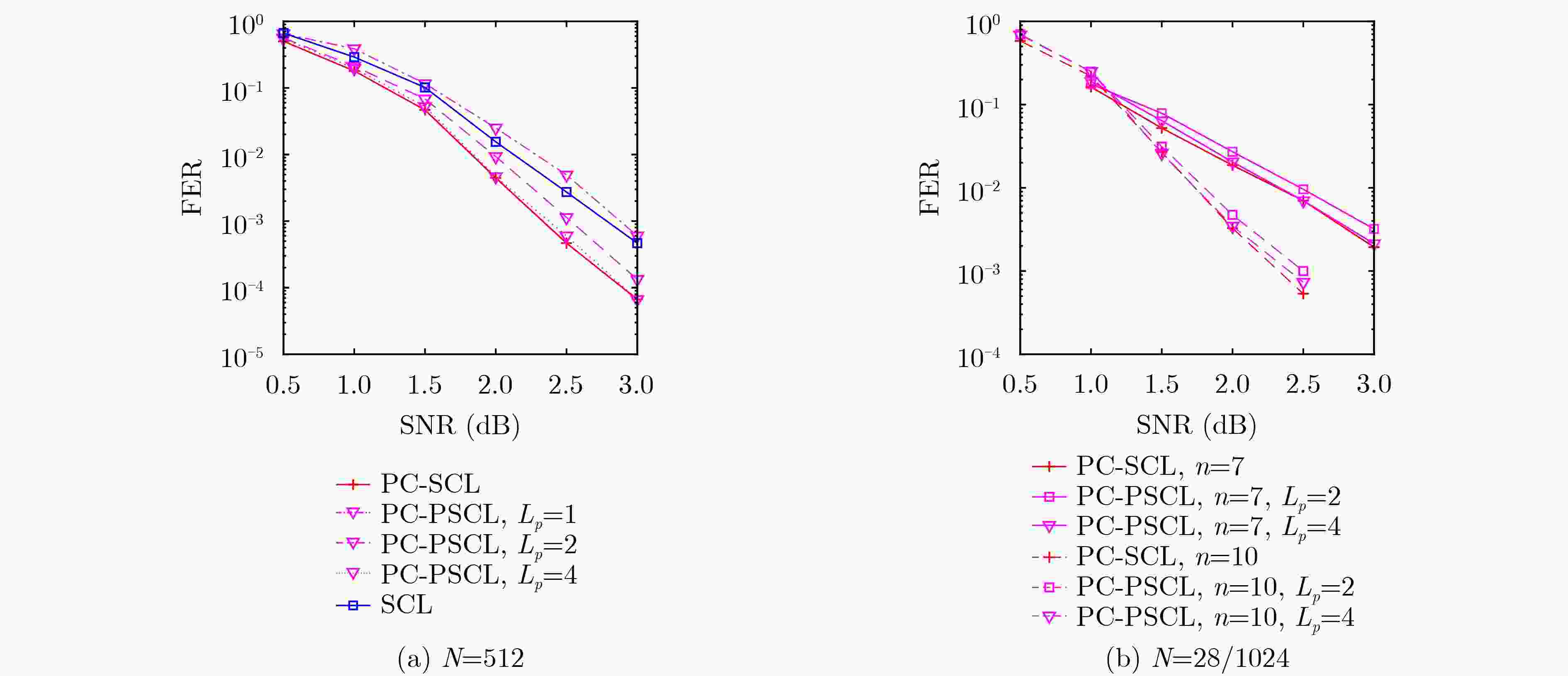
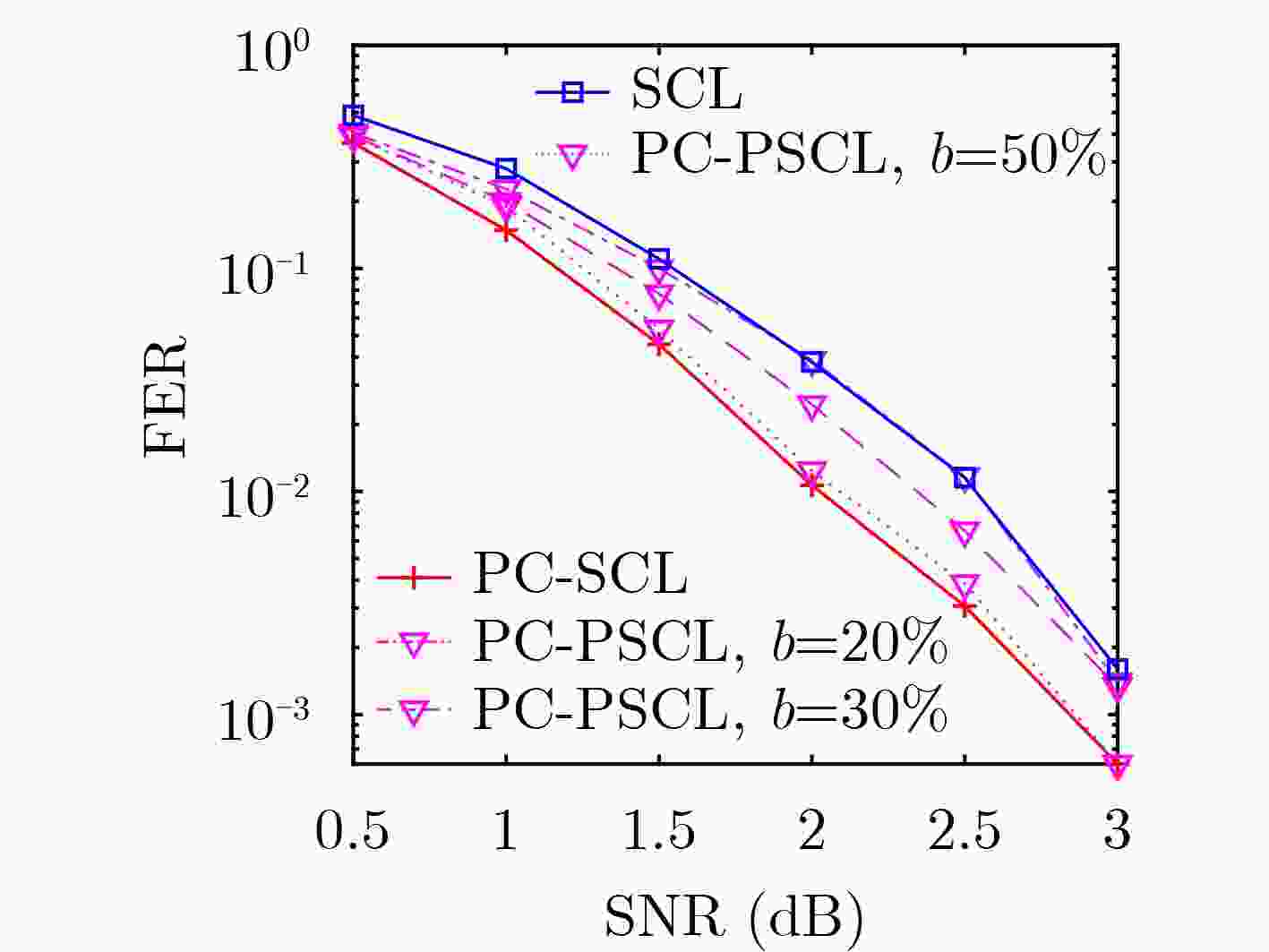
摘要: 极化码作为一种纠错码,具有较好的编译码性能,已成为 5G 短码控制信道的标准编码方案。但在码长较短时,其性能不够优异。作为一种新型级联极化码,奇偶校验码与极化码的级联方案提高了有限码长的性能,但是其译码算法有着较高的复杂度。该文针对这一问题,提出一种基于奇偶校验码级联极化码的串行抵消局部列表译码(PC-PSCL)算法,该算法在编码前进行外码构造,通过高斯近似(GA)得到的子信道错误概率选取较不可靠的信息位,对选取的较不可靠的信息位进行串行抵消列表(SCL)译码和奇偶校验,其余信息比特仅进行串行抵消(SC)译码。仿真结果表明,在高斯信道下,当码长为512,码率为1/2,误帧率为10–3,最大列表长度为8时,该文提出的低复杂度译码算法比SCL译码算法获得了0.5 dB的增益;与基于奇偶校验的SCL译码算法性能相近,但是空间复杂度和时间复杂度分别降低了38.09%, 15.63%。Abstract: Polar codes have perfect coding and decoding performance as a kind of error correction code, which have become a standard coding scheme for 5G short code control channel. While the length of polar codes is short, its performance is not good enough. A novel concatenating scheme, parity check codes concatenating polar codes, has improved the performance of the limited length of polar codes. However, its decoding algorithm has high complexity. In order to solve the problem, a Parity Check aided Partial Successive Cancellation List(PC-PSCL) algorithm based on parity-check-concatenated polar codes is proposed. In this algorithm, outer codes are constructed before encoding and the information bits with not enough reliability are selected through sub-channel error probability obtained by Gaussian Approximation (GA), which perform Successive Cancellation List (SCL) decoding with the help of parity check codes, while the remaining bits just perform Successive Cancellation (SC) decoding. The simulations in additive white Gaussian noise channel reveal that when the codes length is 512, the codes rate is 1/2, the frame error rate is
$ {10}^{-3} $ and the maximum list length is 8, the proposed low-complexity decoding algorithm achieves a gain of about 0.5 dB over the SCL decoding algorithm, keeps the similar performance compared with the original decoding algorithm, and the space complexity and time complexity of the decoding algorithm are reduced by 38.09% and 15.63% respectively.-
Key words:
- Polar codes /
- Parity Check (PC) code /
- Successive Cancellation List (SCL) /
- Complexity
-
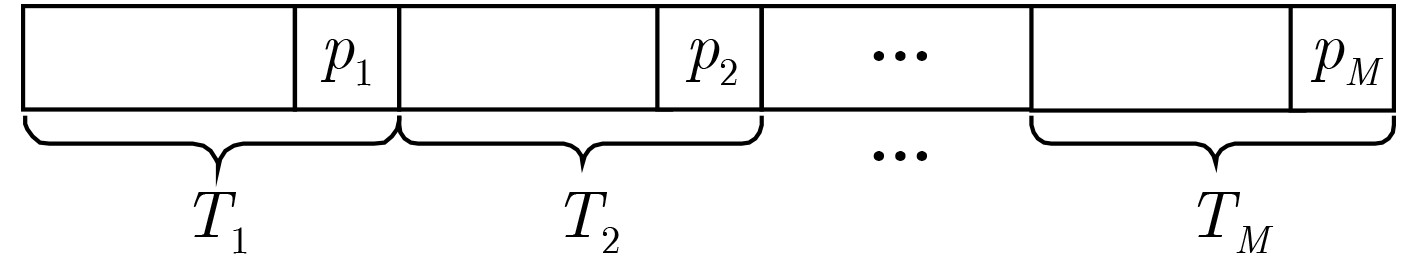
表 1 外码块T的取值
外码块 取值 ${{\boldsymbol{T}}_1}$ $\left\{ {56,60,62,63,64} \right\}$ ${{\boldsymbol{T}}_2}$ $\left\{ {80,88,92,93,94,95,103,104,106,107,108,109,110,111,114,115,116,117,118,119} \right\}$ ${{\boldsymbol{T}}_3}$ $\left\{ {121,144,150,151,152,154,155,156,157,158,159} \right\}$ ${{\boldsymbol{T}}_4}$ $\{ 164,166,167,168,170,171,173,178,179,181,185,196,198,$
$199,201,202,203,205,209,210,211,213,217\} $${{\boldsymbol{T}}_5}$ $\left\{ {225,226,227,229,233} \right\}$ 表 2 3种译码算法复杂度对比
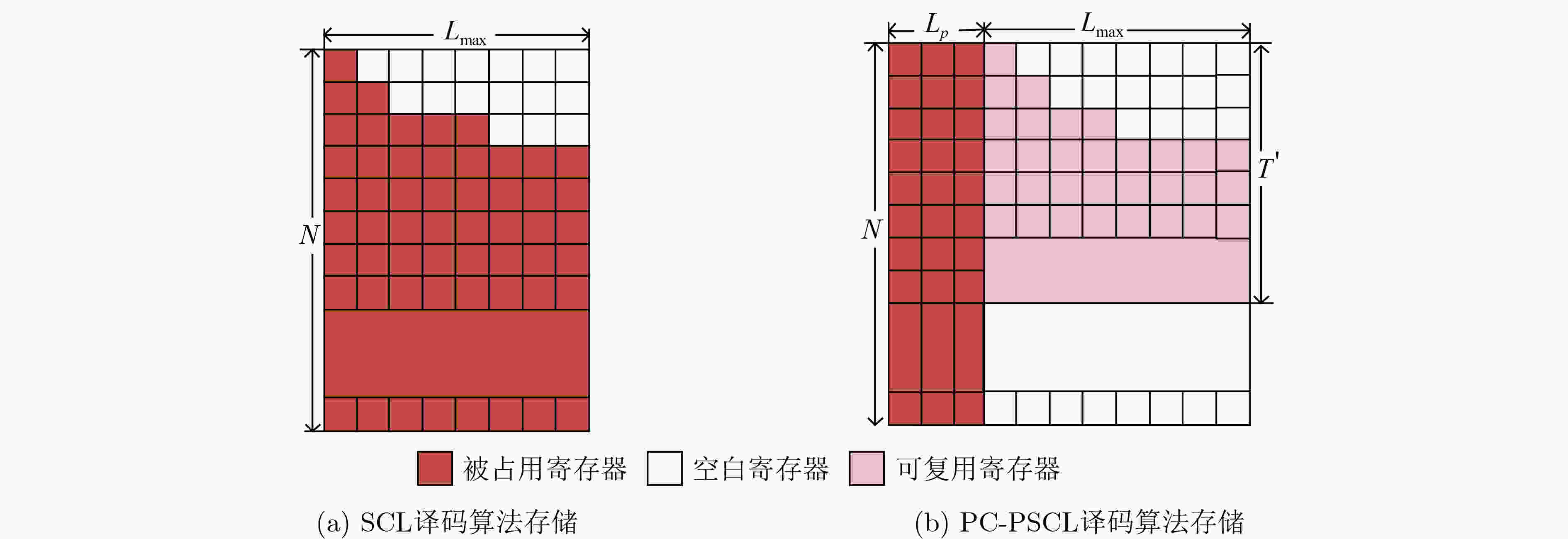
译码算法 空间复杂度 时间复杂度 SC译码 $O(N)$ $O(N{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_2}N)$ PC-SCL译码 $O({L_{{\text{max}}}}N)$ $O({L_{{\text{max}}}}N{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_2}N)$ PC-PSCL译码 $O({L_{ {\text{max} } } }T_{i\max }^{'} + N{L_p})$ $O(({L_{{\text{max}}}}T' + {L_p}(N - T')){\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_2}N)$ 表 3 N = 512时两种译码算法复杂度对比
译码算法 ${L_p}$ 时间复杂度 空间复杂度 PC-PSCL 1 26784 (27.34%) 1000(75.59%) 2 28224(23.44%) 1512(63.09%) 4 31104(15.63%) 2536 (38.09%) PC-SCL – 36864 4096 表 4 N = 256时两种译码算法复杂度对比
译码算法 $ b $ 时间复杂度 空间复杂度 PC-PSCL 20% 11968(26.95%) 1136(44.53%) 30% 13024(20.51%) 1176(42.58%) 50% 13152(19.73%) 1240(39.45%) PC-SCL – 16384 2048 -
[1] ARIKAN E. Channel polarization: A method for constructing capacity-achieving codes for symmetric binary-input memoryless channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(7): 3051–3073. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2021379 [2] HONG S N, HUI D, and MARIĆ I. Capacity-achieving rate-compatible polar codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2017, 63(12): 7620–7632. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2017.2756668 [3] BIOGLIO V and LAND I. Polar-code construction of Golay codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(3): 466–469. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2793273 [4] 张孝甜, 赵生妹, 郑宝玉. 无线信道中的Polar码协商[J]. 信号处理, 2018, 34(7): 793–798. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.07.005ZHANG Xiaotian, ZHAO Shengmei, and ZHENG Baoyu. Key reconciliation using Polar code in wireless channel[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(7): 793–798. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.07.005 [5] 3GPP. 3GPP TS 38.212 v15.0. 0-2017 Multiplexing and channel coding (Release 15)[S]. Valbonne: 3GPP, 2017. [6] TAL I and VARDY A. List decoding of polar codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2015, 61(5): 2213–2226. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2015.2410251 [7] CHEN Kai, NIU Kai, and LIN Jiaru. List successive cancellation decoding of polar codes[J]. Electronics Letters, 2012, 48(9): 500–501. doi: 10.1049/el.2011.3334 [8] ERCAN F, CONDO C, HASHEMI S A, et al. On error-correction performance and implementation of polar code list decoders for 5G[C]. 2017 55th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, USA, 2017: 443–449. [9] NIU Kai and CHEN Kai. CRC-aided decoding of polar codes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2012, 16(10): 1668–1671. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2012.090312.121501 [10] 江涛, 王涛, 屈代明, 等. 极化码与奇偶校验码的级联编码: 面向5G及未来移动通信的编码方案[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2017, 32(3): 463–468. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2017.03.004JIANG Tao, WANG Tao, QU Daiming, et al. Concatenated coding of polar codes and parity-check codes: Coding scheme for 5G and future mobile communications[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2017, 32(3): 463–468. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2017.03.004 [11] MORI R and TANAKA T. Performance of polar codes with the construction using density evolution[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2009, 13(7): 519–521. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2009.090428 [12] TRIFONOV P. Efficient design and decoding of polar codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2012, 60(11): 3221–3227. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2012.081512.110872 [13] SCHÜRCH C. A partial order for the synthesized channels of a polar code[C]. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 220–224. [14] HE Gaoning, BELFIORE J C, LAND I, et al. Beta-expansion: A theoretical framework for fast and recursive construction of polar codes[C]. 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 2017: 1–6. [15] BALATSOUKAS-STIMMING A, PARIZI M B, and BURG A. LLR-based successive cancellation list decoding of polar codes[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Florence, Italy, 2014: 3903–3907. [16] 王琼, 罗亚洁, 李思舫. 基于分段循环冗余校验的极化码自适应连续取消列表译码算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1572–1578. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180716WANG Qiong, LUO Yajie, and LI Sifang. Polar adaptive successive cancellation list decoding based on segmentation cyclic redundancy check[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1572–1578. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180716 [17] CHUNG S Y, RICHARDSON T J, and URBANKE R L. Analysis of sum-product decoding of low-density parity-check codes using a Gaussian approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2001, 47(2): 657–670. doi: 10.1109/18.910580 [18] CHEN Kai, NIU Kai, and LIN Jiaru. A reduced-complexity successive cancellation list decoding of polar codes[C]. 2013 IEEE 77th Vehicular Technology Conference, Dresden, Germany, 2013: 1–5. [19] ZHANG Zhaoyang, ZHANG Liang, WANG Xianbin, et al. A split-reduced successive cancellation list decoder for polar codes[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(2): 292–302. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2504321 -







 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
